lec 11 synaptogenesis
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
after an outgrowing axon reaches its target are in the nervous system it must undergo a series of morphological changes in order to create a functional ________
synapse
synapses are classified by the modality in which ...
information is transmitted between cells
________________ ________ (____ ______) are structures formed between the membranes of two very closely-apposed neurons
electrical synapses (gap junctions)
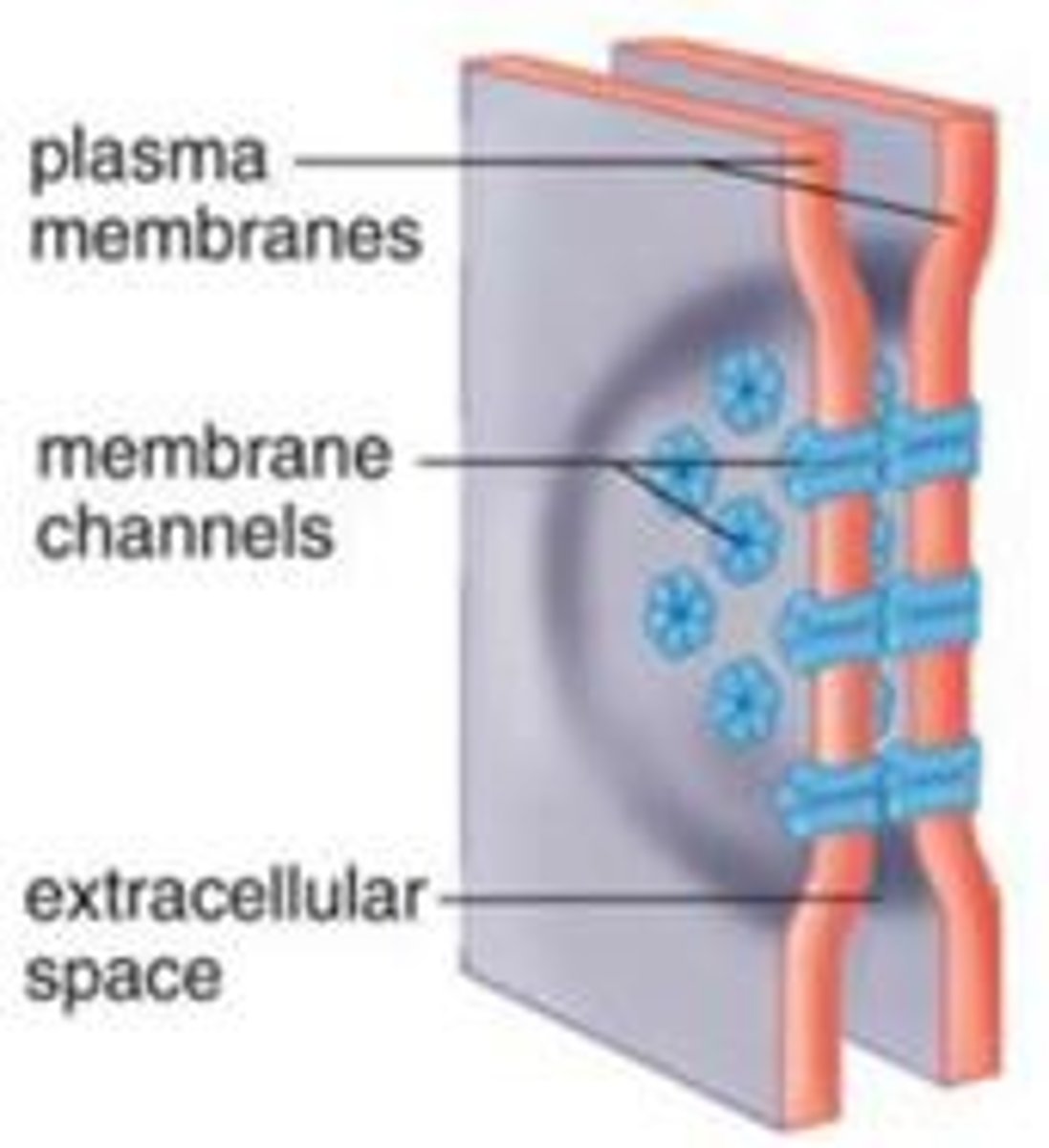
gap junctions are comprised of _________ which are channels that allow the direct transfer of ions.
this allows for very quick transfer of electrical activity
connexins
____________ ________ convert presynaptic action potentials to the release of chemical signals (neurotransmitters) onto the postsynaptic cell
chemical synapse
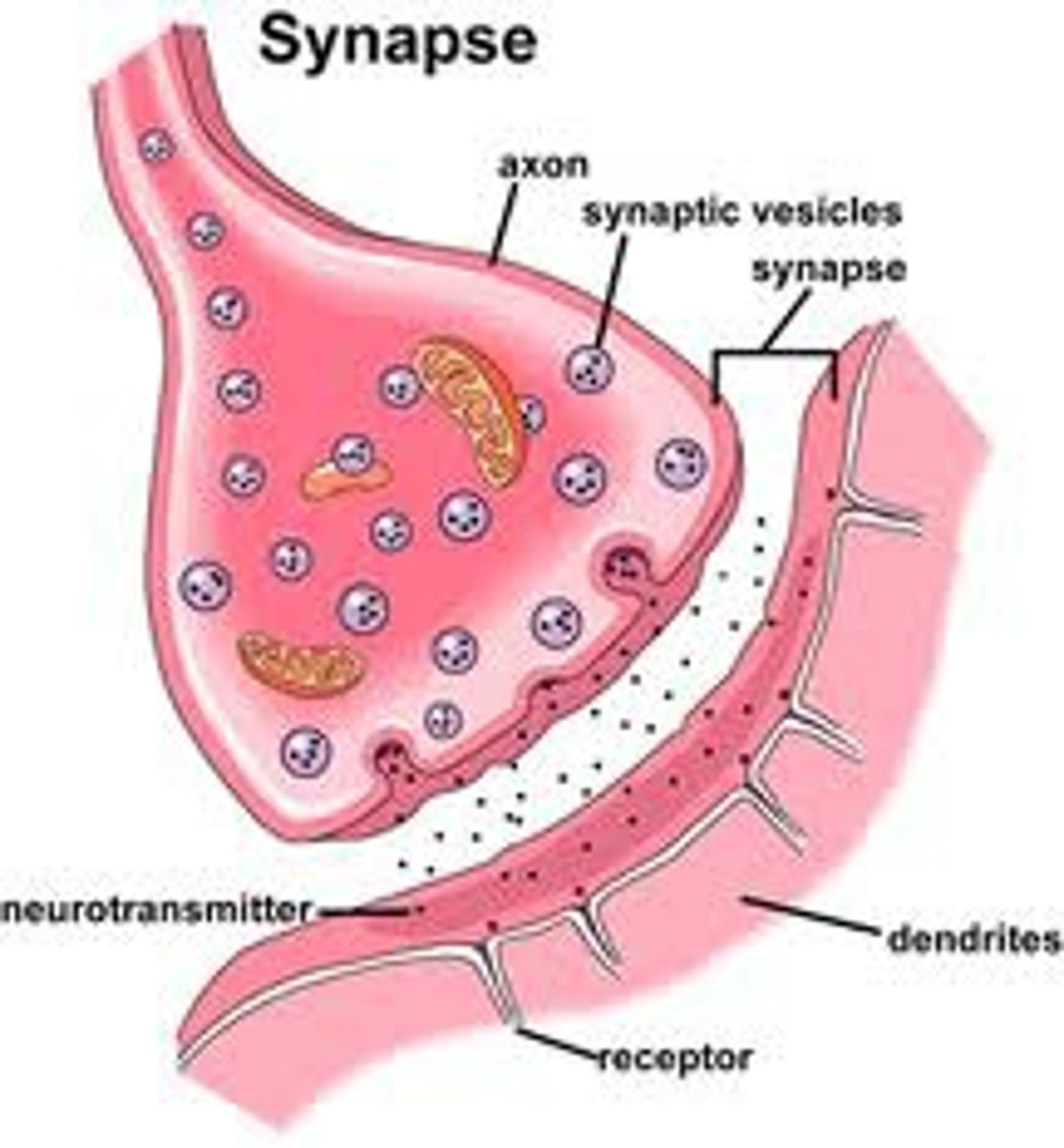
What is the difference between a chemical synapse and an electrical synapse?
the difference between chemical and electrical is that in chemical synapses rely on the release and diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules, where electrical synapses involve direct electrical coupling between neuron via gap junctions
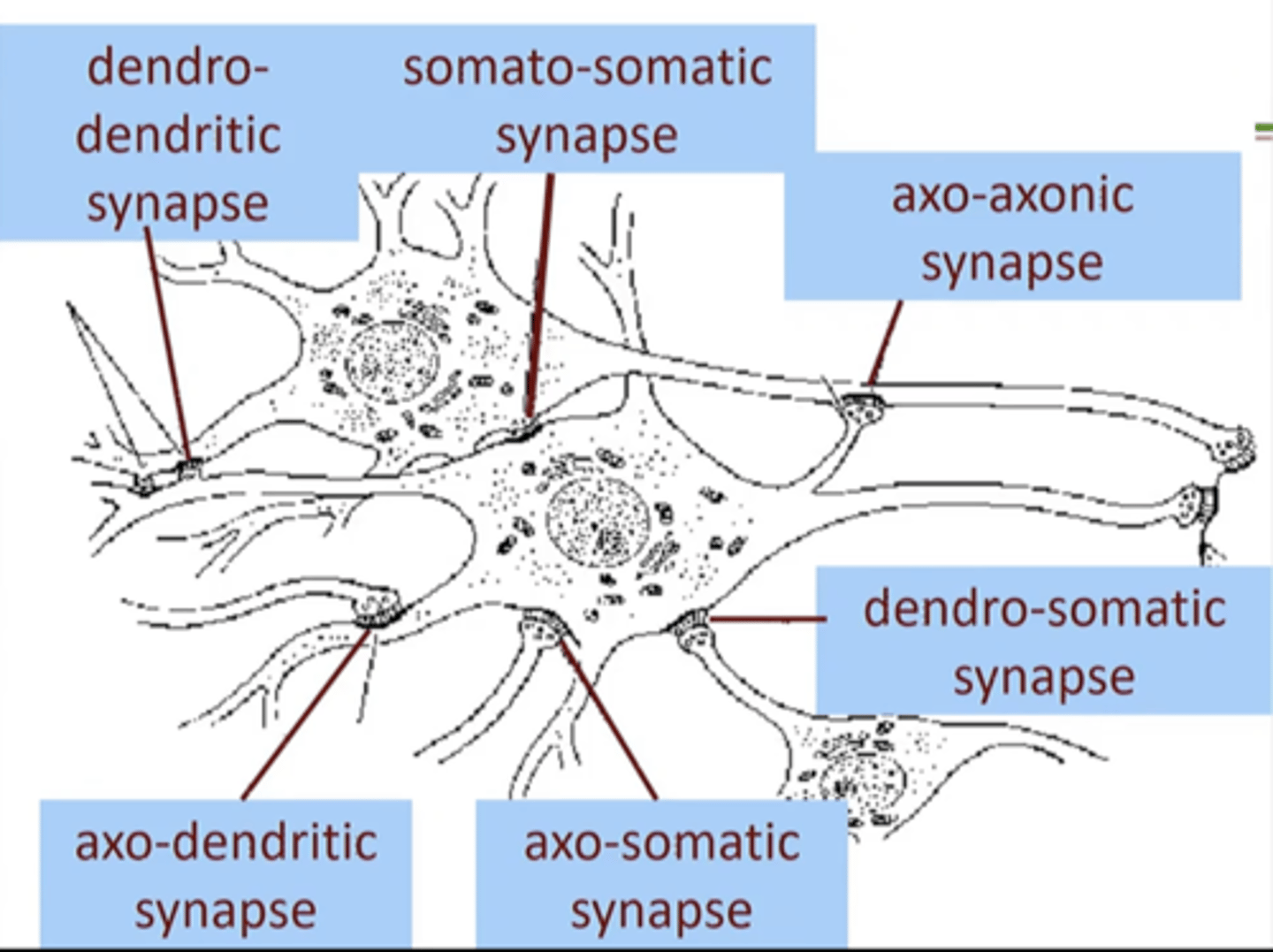
What are the different types of chemical synapses?
Theres 12 (6 axo, 2 dendro, 2 somato, and 2 other)
axo-dendritic, axo-somatic, axo-axonic, axo-synaptic, axo-secretory, axo-extracellular, dendro-dendritic, dendro-somatic, somato-dendritic, somato-somatic, autapse, neuromuscular junctions (NMJs)
The postsynaptic site at which a new synapse os formed influences its _______
function
Which synapse is the most common form of synapse in the nervous system. Where the axon terminal ends on a dendrite spine
axo-dendritic
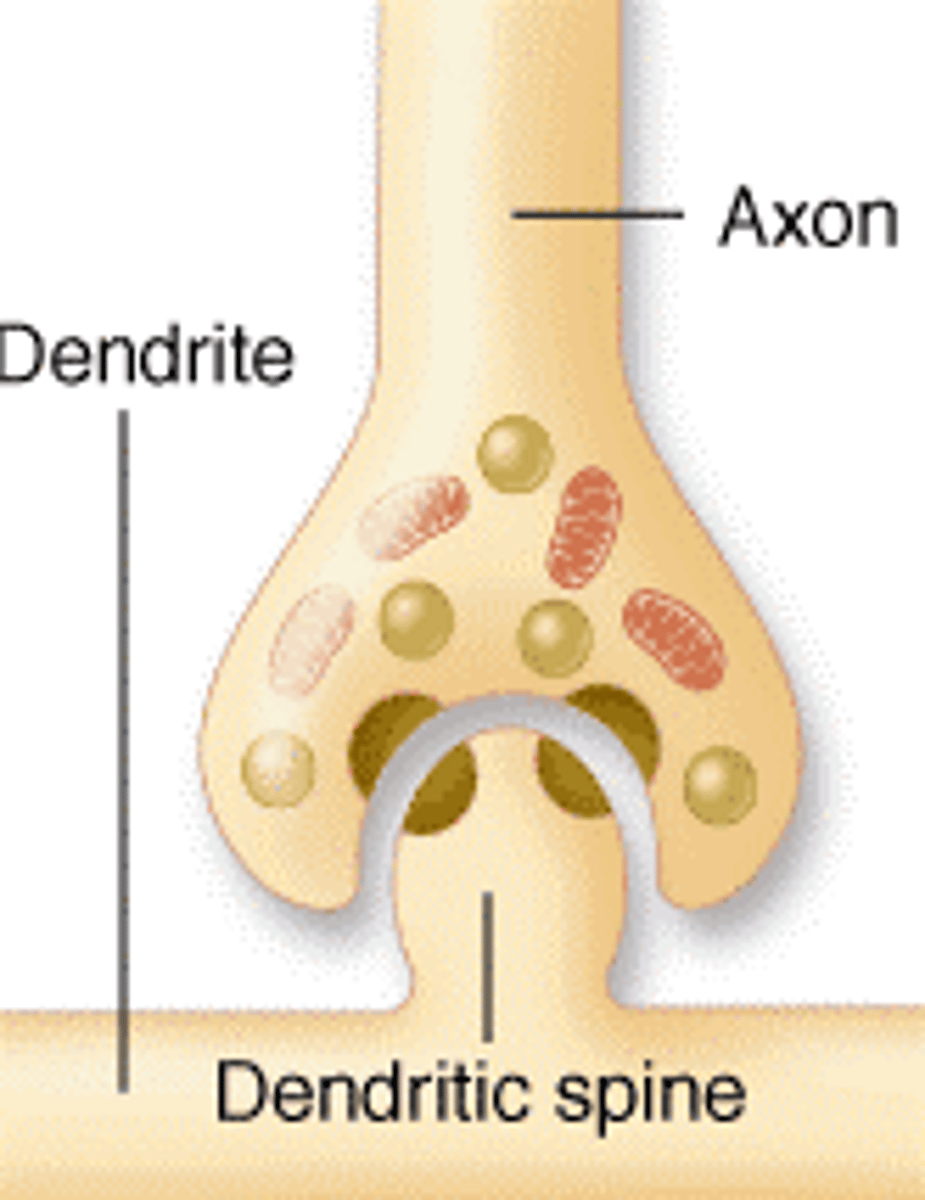
which synapse is it when an axon forms direct synapses on cell body? Axon terminal end on soma.
axo-somatic
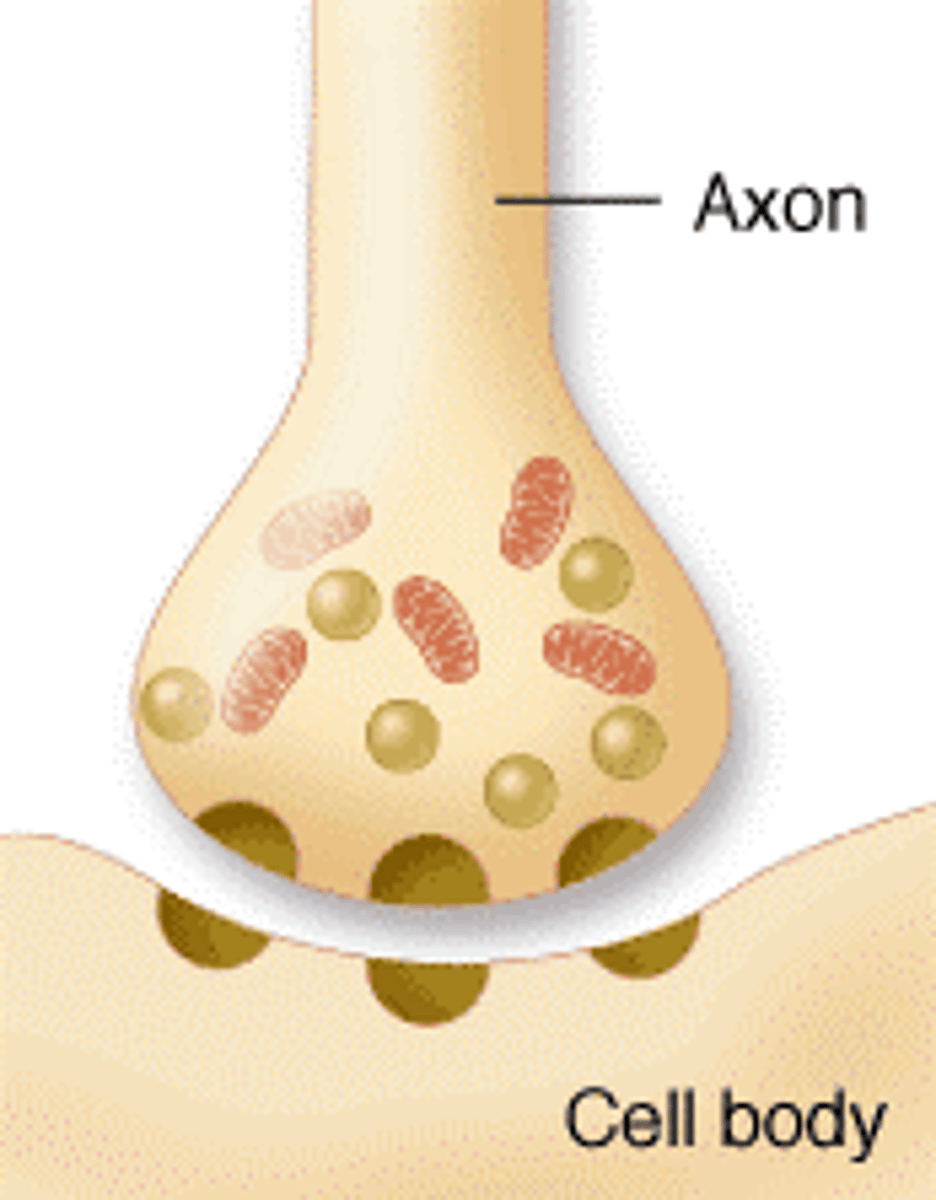
Which synapse is it when an axon forms direct synapse on another axon? axon terminal ends on another axon
axo-axonic
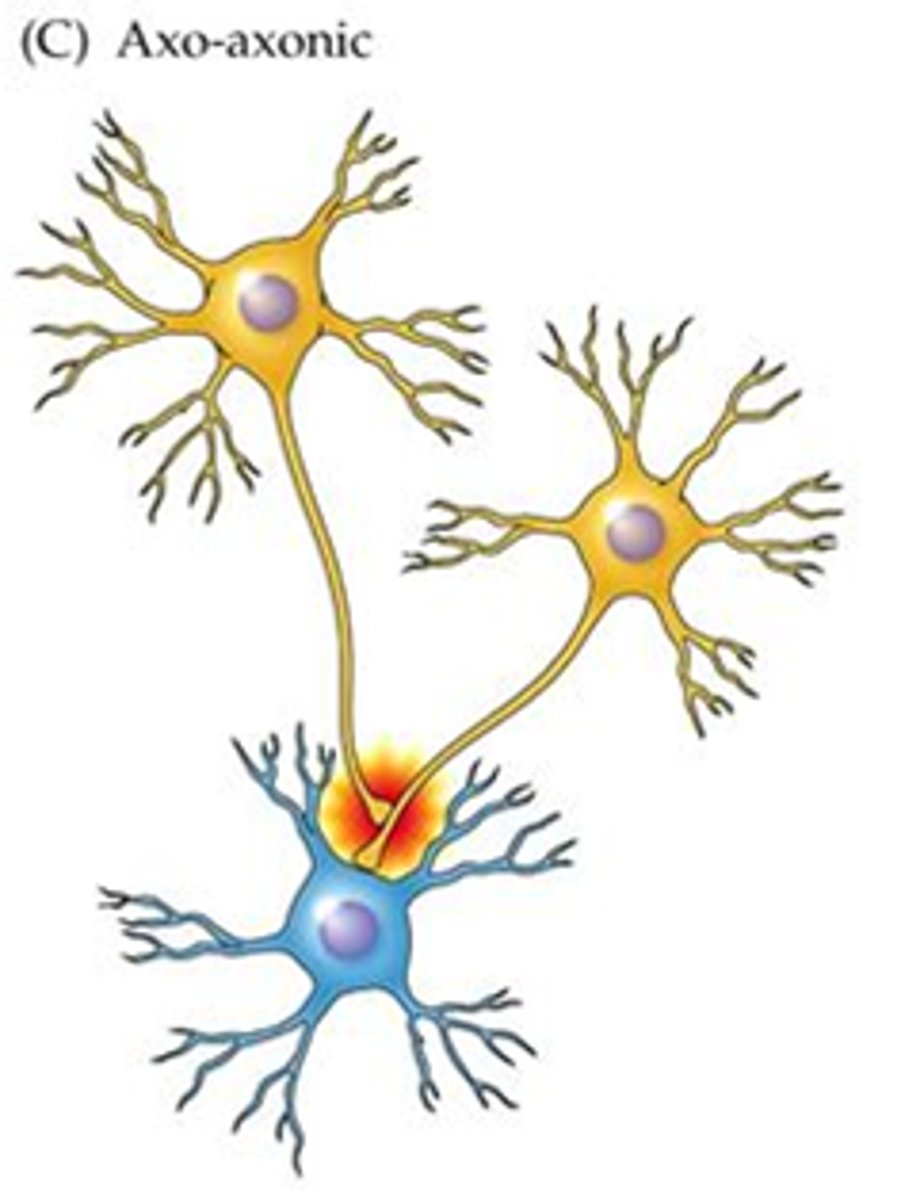
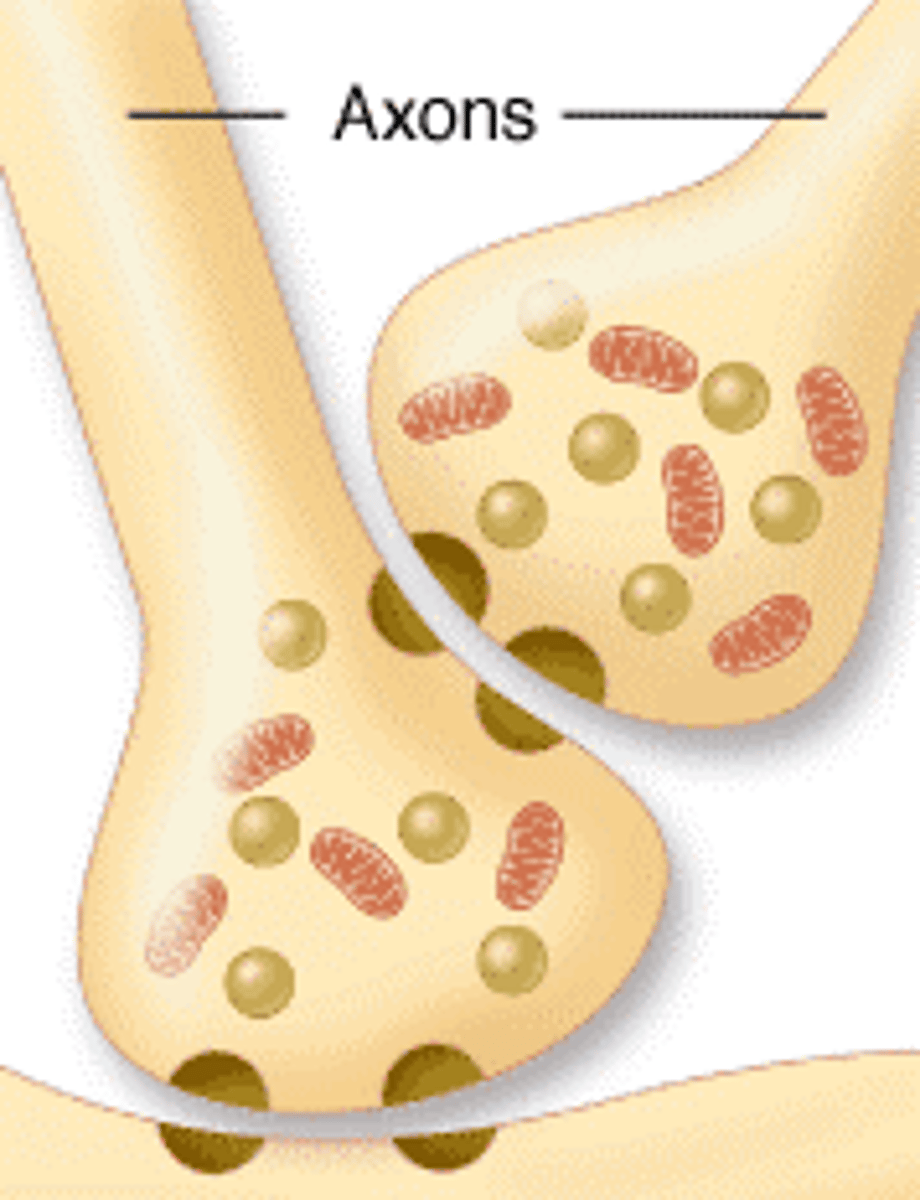
Which synapse is it when an axon forms direct synapse on axon terminals? axon terminal ends on another axon terminal.
axo-synaptic
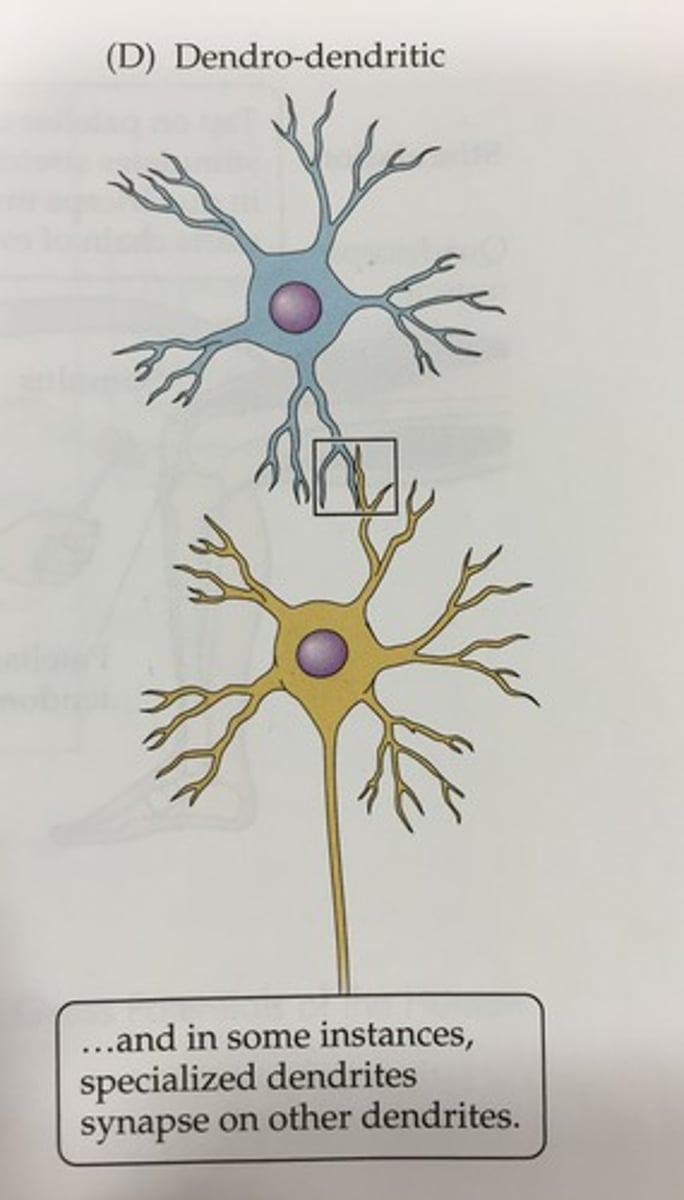
Which synapse is it when an dendrite synapses on another dendrite? This chemical synapse occurs between neurons of the olfactory bulb.
dendro-dendritic
which synapse is it when a dendrite synapses on cell body?
dendro-somatic
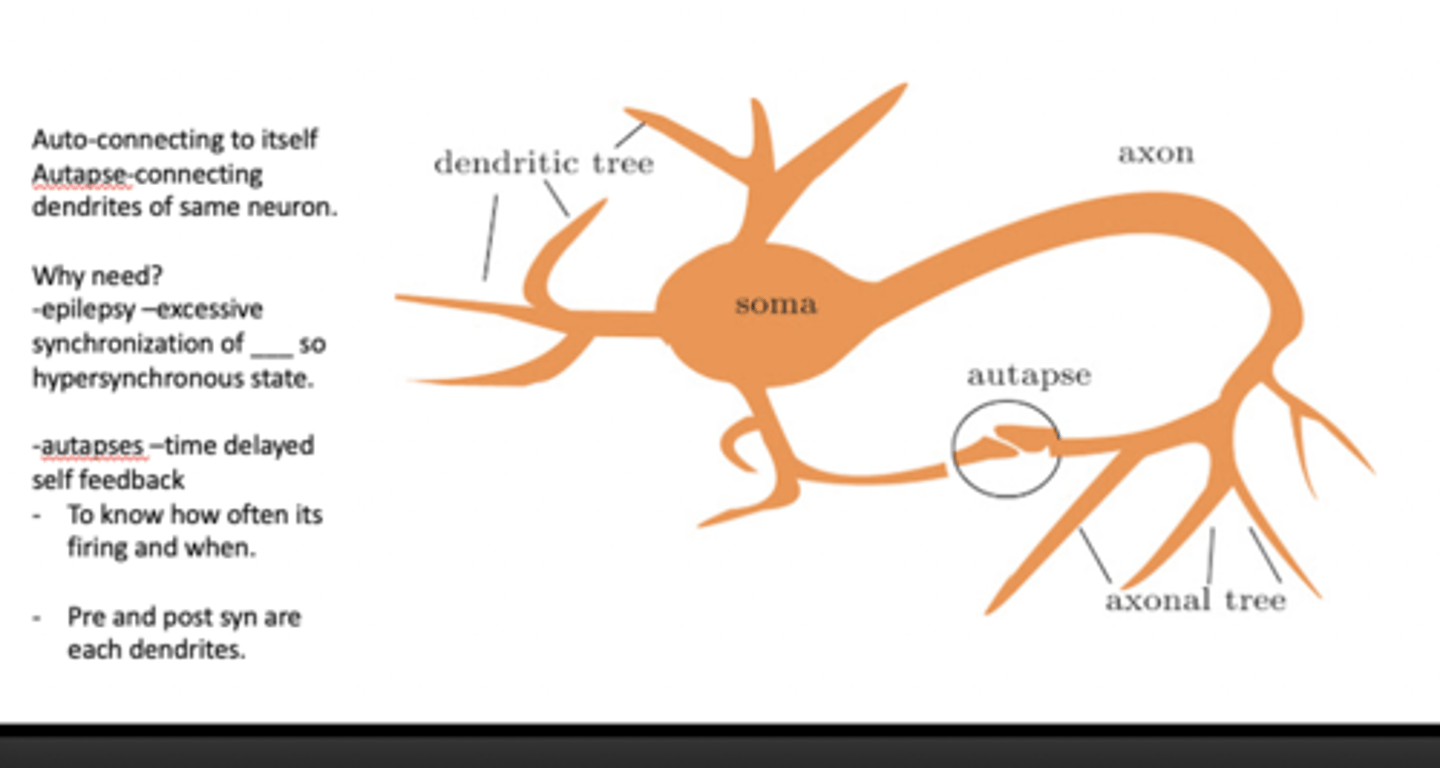
Which synapse is a synapse that a single neuron forms onto itself? connecting dendrites of the same neuron.
80% of the layer 5 pyramidal cortical neurons in the developing brain contain these connections
autapse
spinal cord motor axon terminals form direct synaptic connections onto skeletal muscle fibers at the ______________ ___________
neuromuscular junctions
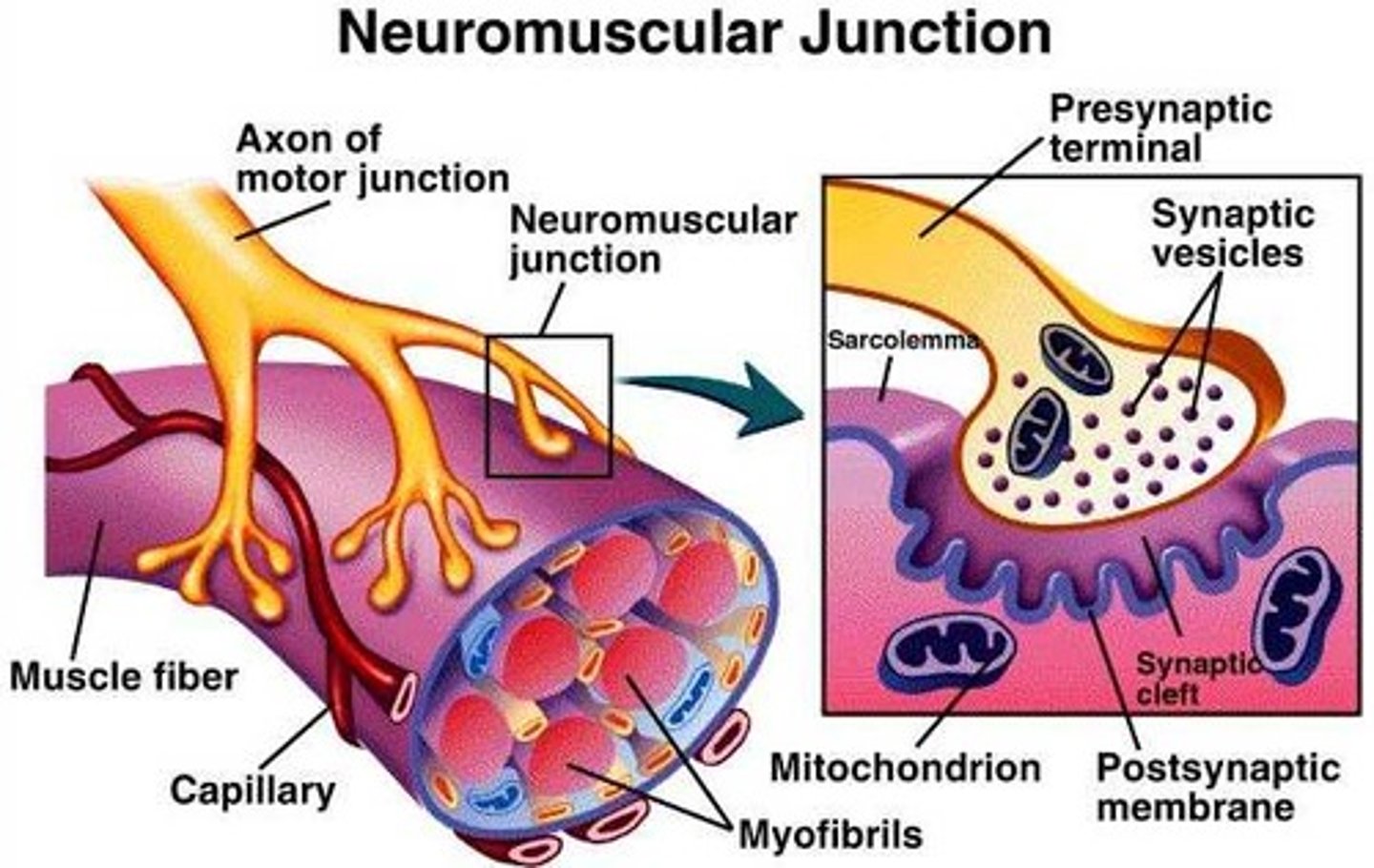
Name the anatomical components of a synapse.
accumulation of vesicles at the presynaptic membrane, synaptic cleft between the pre- and post-membranes, postsynaptic density
During early development of synapses, newly formed synapses do not posses all of the structural properties of the mature synapses.
What structures does an early/newly formed synapse have?
few vesicles, no synaptic cleft or postsynaptic density
The morphology of the developing nerve endbulb changes as development proceeds. The amount of surface area of contact between pre- and post- synaptic cells, and the shapes of the presynaptic nerve terminals ____ ______ _____. Do what over time
vary over time
What are the morphological changes that a growth cone must undergo during synapse formation?
1. chemotaxis guide growth cone toward target cells
2. filopodia extend and retract
3. recognition of target cells
4. adhesion of molecules stabilize contact b/w growth cone and target cell
5. synaptic contact forms through clustering of synaptic proteins and neurotransmitters.
Go into detail
Within hours of a presynaptic growth cone making contact with a target cell it begins to undergo structural changes.
the Filopodia retract and form very close, punctate contact with the postsynaptic membrane.
Protrusions on the presynaptic membrane become engulfed by the postsynaptic membrane
How does the rate of synaptogenesis change over time during development?
There is a gradual decline in the synaptic density of cortical regions throughout life.
In early development the synapse formation is quick and a lot
in maturation, synapse formation decreases
what is a "sniffer"?
also known as the outside out patch
a technique in which a small piece of postsynaptic membrane is attached to the end of a recording micropipette
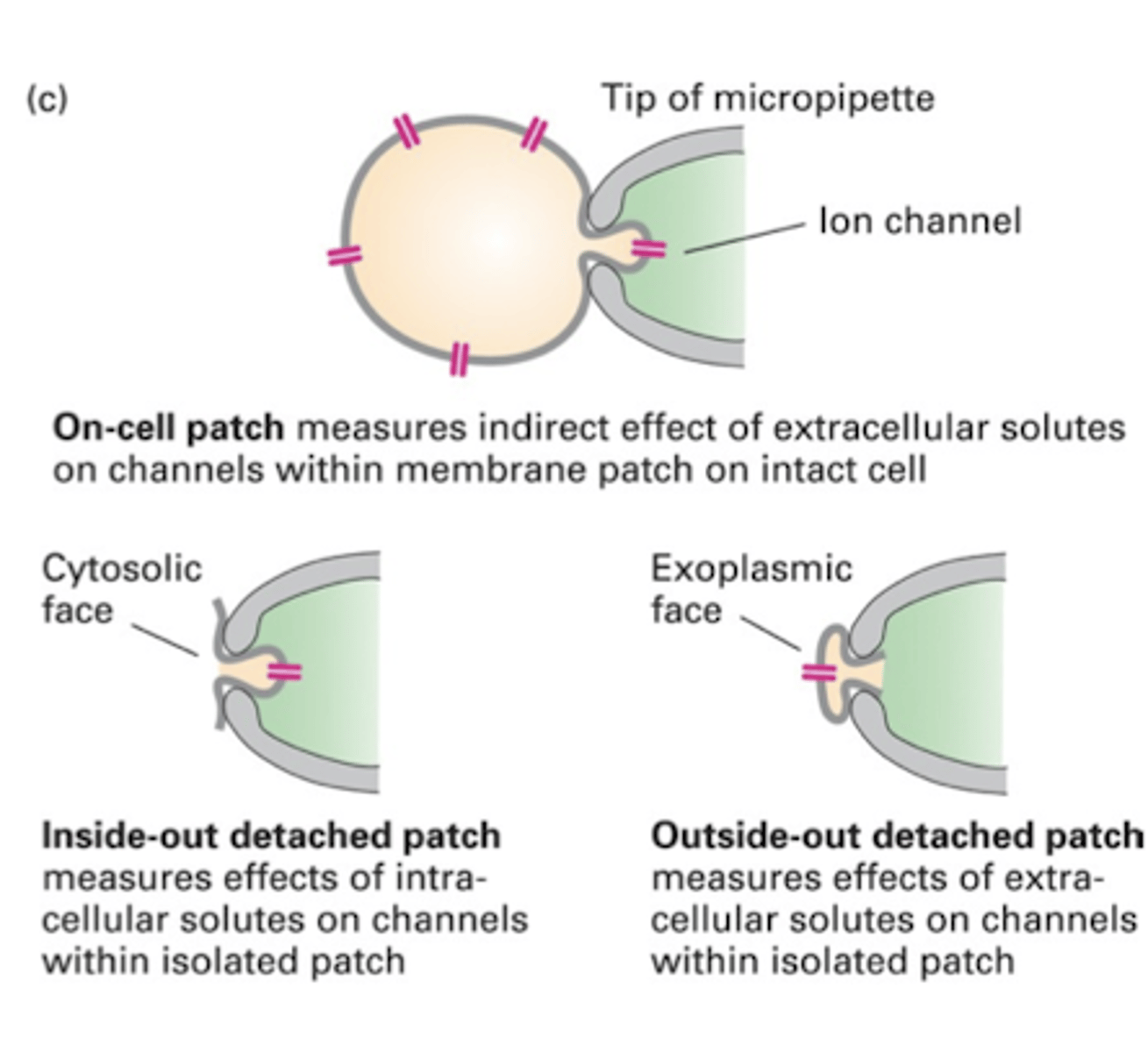
what does a sniffer demonstrate?
it demonstrates that neurotransmitters can be released from an outgrowing growth cone before mature presynaptic structure is formed
In human cortex, synaptic density increases to different extents in different cortical regions over the first few years of like.
There is a gradual decline in the synaptic density of these regions throughout life.
In humans this occurs on a _____ time scale than in other mammals
longer
Explain the intrinsic changes that occur in outgrowing axons that allow functional synapses to mature within hours after igniting cell-cell contact.
When an outgrowing growth cone encounters guidance cues in the environment its membrane potential can be modulated
For example: Growth cones exposed to chemoattractant netrin-1 exhibit depolarization while growth cones exposed to repulsive sema3A become hyperpolarized
intrinsic changes that occur prior to cell-cell contact include presynaptic expression of a neurotransmitter release mechanism and postsynaptic expression of neurotransmitter receptors
another example of intrinsic changes that occur in outgrowing axons that allow functional synapses to mature within hours after igniting cell-cell contact is
Neurons co-cultured with muscle cells illustrate the quick effect of cell-cell contact on presynaptic membrane potential
When growth cones contact a muscle cell in culture, growth cone calcium levels increase within seconds of contacting the muscle
This increase in intracellular calcium has depolarizing levels.
This change provides a signal for _____ _______ __________
growth cone differentiation
Based on the previous example if you increased calcium influx into an isolated growth cone it can slow the growth rate and change morphology to be rounder with reduced number of ________
filopodia
How do cell adhesion molecules influence synapse formation? Explain the experiments that revealed SynCAM1 is sufficient to induce synaptogenesis
The sudhof lab identified synCAM1 as protein localized in the brain.
The expression of synCAM1 on non-neuronal cells was sufficient to induce synapse formation onto cells by hippocampal neurons in co-culture and induce vesicular release.
This demonstrated that a single signal provided by SynCAM1 is sufficient to instruct the presynaptic terminal for differentiation and functional synapse formation
conclusion of experiments that revealed synCAM1 to be sufficient to induce synaptogenesis
showed that tightly adherent contacts were established in the first 15 min of cell-cell contact
What are synCAMs?
synaptic cell adhesion molecules that re specifically expressed in the nervous system and are important for synaptogenesis
SynCAM1 has a powerful role in synaptogenesis and its expression can be sufficient to induce ___________ _____________________
presynaptic differentiation
what is another molecule that is expressed at developing synapses?
cadherins and nectin
cadherins bring pre- and postsynaptic membranes in close apposition by interacting with
catenins
Nectin bring pre and postsynaptic membranes in close apposition by interacting with
afadin
the presynaptic release site on the nerve terminal is called the
active zone
the active zone is preassembled and trafficked down the axon in a
large protein complex
The large protein complex is referred to as
presynaptic transport packets
the presynaptic packets contain multiple other presynaptic proteins including cytoskeletal associated protein, vesicular fusion protein, and calcium channels.
A new activation zone can be established by the insertion of only ___ number of these packets
2-3
what two molecules signal to induce the presynaptic differentiation
neurexin and neuroligin
a hallmark characteristic of postsynaptic structure assembly is the _________/_____________ of _______________ ______ in the cell membrane
clustering/aggregation of neurotransmitter receptors
____ a proteoglycan produced by neurons that induce AChR clustering at the postsynaptic membrane
agrin
agrin on the presynaptic nerve terminal binds to a postsynaptic receptor on the muscle fiber called
muscle-specific kinase (MuSK)
interactions between _____ and ________are necessary to achieve precise alignment between the presynaptic axon terminal with the postsynaptic AchR aggregate
Argin and MuSK
EphB and EphrinB signaling acts to aggregate postsynaptic ________ receptors in CNS
glutamate
synaptic activity also regulates the ________ of postsynaptic receptors
density
at NMJ the electrically active terminal releases Ach and the receptors are clustered at the postsynaptic membrane. This is a activity-dependent signal that suppresses extra junctional receptors by blocking transcription in extra synaptic nuclei.
The denervation of NMJ or blocking of sodium channels with tetrodotoxin, results in extra junctional ___ receptors being distributed over the entire muscle surface
ACh
What are the molecules that induce assembly of the postsynaptic structure?
agrin, MuSK, EphB/EphrinB, glutamate, AChR/ACh
retinal ganglion cells form synapses with normal ultrastructure but displayed little spontaneous synaptic activity and high failure in synaptic transmission.
When RGC was co-cultured with glial cells the spontaneous postsynaptic currents increased and fewer transmission occurred.
The conclusion to this is that glial cell signals are _____________ ________ ________ ____________ ________
required to become fully functional
How do glial cells participate in synapse formation?
Glial cells release soluble factors that promote synaptogenesis
glial cells release soluble factors. In cultures that do not have glial cells, RGC have autapse development but only very few synapses forms in absent of glial cells. When grown in glial cell presence the autapses number _____
increased
What are the molecules involved in glial cell synapse formation?
proteinase K, apolipoprotein E, cholesterol