Organization and function of the cerebrum
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
cerebral cortex
thinking, memory, voluntary motor movements & sensory perception
grey matter
(somas of neurons) on outside
white matter
(axons of neurons that are myelinated with fat) on inside
Cerebral Deep Grey Matter
basal nuclei (ganglia)
limbic system
Spinal Cord
grey matter inside, white matter outside (to contact the muscles)
superficial grey matter (neurons)
Gyri = hills
Sulci = groves
Left hemisphere of brain
logic and reasoning (math, language etc)
right hemisphere of brain
creative brain, spacial orientation, object recognition
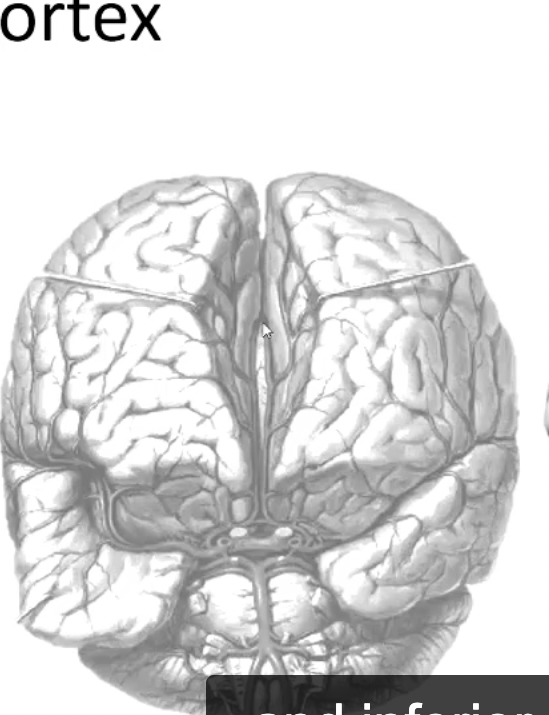
longitudinal fissure contains
falx cerebri, superior and inferior sagital sinus
primary motor cortex (pre central gyrus)
motor neurons can be found there
send their axons through the cortex, brain stem and into the spinal cord to talk to muscle for movement
mostly controls structures of the face and hands (homunculus man)
primary sensory cortex (post central gyrus)
sensations from the body (touch, pressure, position, pain, temp)
anterior
mostly motor
posterior
mostly sensory
frontal lobe
intelect, planning
parietal lobe
somatosensory cortex
association cortex (remember sensations)
common integrative area (all senses put together: vission, taste, hearing smell to give you picture of your environment)
temporal lobe
auditory cortex (hearing)
association cortex (remember sounds)
limbic system (regulates emotions and forms memories
occipital lobe
visual cortex (sight)
association cortex (remember sights)
frontal eye field (frontal lobe)
voluntary eye movement
Broca’s Area (frontal lobe)
speech (move mouth muscles to speak)
Wernicke’s Area (temporal lobe)
dictionary (responsible for deciphering language)
insular cortex (deep in the frontal, parietal and temporal lobe)
balance
emotional context to sensation (good pain, bad pain)
Olfaction (frontal lobe above eyeballs)
smell (what smell is it)
primary Gustatory Cortex
taste chemoreception and food preference
Commissural Fibers
between hemispheres
(e.g., corpus callosum,
anterior commissure)
Association Fibers
within hemispheres between lobes
fornix
Projection Fibers
to distant parts of the CNS
(e.g., internal capsule) (cortex to spinal cord / vise versa)
Basal Nuclei
motor memory, initiate/stop movements, early motor learning, skills/habits
Basal Nuclei structures
Caudate (head)
lentiform nucleus (putamen and globus palliduc)
caudate (tail)
Basal Nuclei related structures
substantia nigra of midbrain - dopamine
Huntington’s Chorea
Neurodegeneration in striatum = increased movement (no stop signal)
Parkinson’s
Lack of dopamine acting on the striatum = difficulties start / stopping movements (since dopamine is needed to carry info out of basal nuclei)
Information Pathway in Basal Nuclei
Premotor > BN > Thalamus > premotor
limbic system
emotions + memories
Hippocampus
who, what, when, why
• long-term memory formation
(consolidation)
• output via fornix
Fornix
connects hippo to mammillary bodies
Mammillary Bodies
olfactory relay nucleus (sensations for smell come through and get forwarded to other parts of the brain to be processed)
• emotion (good or bad ??)
Amygdala
visual input from eyes (scanning for threats)
will make a response if it is dangerous (fight/flight/freeze)
emotional memories (good bad???)
talks to hypothalamus
Pathway for Limbic system
info from hippocampus and amygdala is sent to the mamillary bodies via the fornix
information travels to the thalamus via the mammillothalamic tract.
From the thalamus the information is sent to the PFC and cingulate cortex (gyrus) via the anterior thalamic tract.
Hippocampal formation
takes senses and makes it a memory (consolidation)
info flows in and out of the entorhinal cortex
entorhinal cortex
internal map; your gps
prefrontal cortex
regulates attention / importance
Cingulate gyrus (reality checker)
major connecting hub between cerebral cortex and limbic system
dysfunction can cause Schizophrenia
Episodic memory
1) Sensations (current or past)
cingulate cortex =
reality check
2) Sensations relayed to
hippocampus via EC
3) Hippocampus & EC impart
context (W’s)
4) Consolidated information
relayed to mammillary
bodies (emotion) via fornix
(inner arc)
5) Output to ant. thalamus,
then to cingulate cortex and
PFC (ant. thalamic tract)
6) If important – long term
storage in the cortex
(consolidation)
Amnesia
memory loss of facts or experiences
Anterograde amnesia
refers to a deficit in the ability to form new memories following the time of brain injury.
Retrograde amnesia
refers to a loss of long-term memories.
Declarative memory
memories you can recount (short term and long term)
episodes (episodic) or facts (semantic)
short term memory (Declarative)
thalamus
amygdala
hippocampus
long term memory (Declarative)
somatosensory, visual, cortexes etc.
procedural memories (muscle memory)
cerebellum
basal nuclei
Cerebellum
vision, balance, position (novel tasks)
basal nuclei stores
early experiences (ex. walking for the first time) (skills/habits)
Thalamus determines
whether to use the basal nuclei or cerebellum to preform a task