Reliability and Validity
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
consistently, repeated, constant, variance
reliability is the extent to which a measured value can be obtained _____ with _____ assessment in _____ conditions, concept of _____ is used to estimate
confidence, conclusions, performance
without reliability, cannot have _____ in data or draw rational _____ about stable/changing _____ of patients
relative reliability
coefficient reflect true variance as a proportion of the total variance in a set of scores
group, ICC, kappa, 1, more, unit, different
relative reliability is used for _____ comparisons, uses _____ ratio/_____, closer to _____ = _____ reliable to identify true difference, no _____ of measurement, allows comparing _____ tests
absolute reliability
indicate how much of a measured value may be due to error
individuals, SEM, range, true, units, same
absolute reliability is used for looking at _____, use _____ to find _____ where _____ score will fall, includes _____ of measurement, only compare to tests with _____
specific context, application, population, skill, training, trials
reliability of a measure exists in a _____ that is relevant to its _____, including the _____/rater _____ or _____/number of _____
all or none, some, sufficient, application
reliability is not _____, exists to _____ extent in any instrument, must judge if it is _____ for intended _____
generalizability, error, controlled, unexplained variance
concept of _____ states there are many sources of _____ and some can be _____ to improve reliability, reduces _____
classical measurement, random
_____ theory states that all error is _____
random error, test retest error, rater error, true score
observed score is made up of _____, _____, _____, and _____
test retest, rater, alternate forms, internal consistency
four types of reliability
test retest
assesses the measurement instrument’s consistency
rater
assesses the consistency of 1 or more raters
alternate forms, recall
_____ compare two versions of an instrument, minimize _____ effect with subjects
internal consistency
extent to which items of a multi-item test are successful in measuring various aspects of the same characteristic and nothing else
instrument, raters
test retest reliability is ability of _____ to measure performance consistently, most meaningful for measures that do not rely on _____
interval, fatigue, learning, memory, genuine change
with test retest reliability _____ between tests must be considered, far enough to avoid _____ or _____/_____ effects but close enough to avoid _____ in target variable
carryover, pretrials
_____ is idea that from practice or learning on initial trial altered performance on subsequent trials, neutralize with _____
testing effects
_____ is the idea that act of measurement changes the outcome
systematic error
carryover and testing effects may show up as _____
intrarater, bias, subjective, blinding, rater skill
_____ reliability is stability of data recorded by one rater across trials, possibility of _____ especially when _____ criteria is used, control by _____, same as test retest when _____ is relevant to accuracy
interrater, intrarater reliability, each rater, same response, simultaneously, independently
_____ reliability is stability of data recorded by two or more raters, _____ of _____ should be established first, best when all raters measure the _____ (_____ but _____)
generalizability, clinic, assume, similar
many studies choose to use only one rater to collect data to improve consistency but sacrifice _____ to _____, if interrater reliability has not been established cannot _____ other raters would obtain _____ results
ICC, kappa, categorical, SEM, correlation, cronbach’s alpha
test retest and rater reliability use _____ or _____ (used for _____ variables) coefficient, _____ in clinical situations, alternate forms uses _____ coefficients, and internal consistency uses _____
change, pretest, posttest, error, cancel, true score, error
reliability is necessary precondition for being able to interpret _____ scores (difference between _____ and _____), with large _____ variance, difference between trial 1 and 2 may _____ out _____ and be composed of mostly _____
regression toward the mean
tendency for extreme scores to fall closer to the mean on retesting
less extreme, no effect, groups, strong, less
RTM shows error on second test to be _____, even in conditions where treatment has _____, most dangerous when subjects are assigned _____ based on scores, measures with _____ reliability are _____ likely to exhibit
methodological research, standardizing, protocols, training, calibrating, improving, multiple, sample, variance, pilot
_____ involves the development and testing of measuring instruments for use in research or clinical practice, involves _____ measurement _____, _____ raters, _____/_____ instruments, taking _____ measurements, choosing _____ with _____ in scores, and _____ testing
confidence, accurate, relevant, apply, meaningful, intended, interpretation, application, meaning, relevance, decisions
validity relates to _____ we have that our measurement tools are giving us _____ information about a _____ construct so that we can _____ results in a _____ way, extent to which a test measures what it is _____ to, addresses the _____ and _____ of measured values (_____ and _____ to clinical _____)
discriminating, magnitude, quality, degree, predictions, future
questions addressed by validity:
is test capable of _____ among individuals with and without condition
can test evaluate _____ or _____ of a variable or _____ of change from one time to another
can we make useful and accurate _____ about patient’s _____ function based on outcome
actions, decisions, foundation
measurements have consequences for _____ and _____, validity gives _____
consistency, random error, alignment, construct, inferences
reliability relates to _____ of measurement (free of _____) while validity relates to _____ of measurement with _____ (can _____ be made)
all or none, judge, abstract, instrument, intended
reliability and validity do not consider as _____, no obvious rules to _____ measurement and possible _____ constructs, are not an absolute characteristic of _____ specific to _____ use
reliable not valid
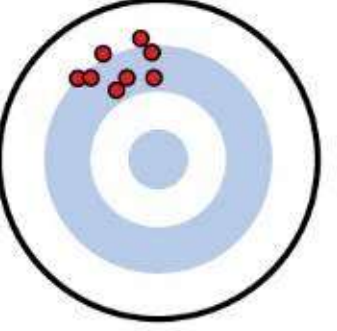
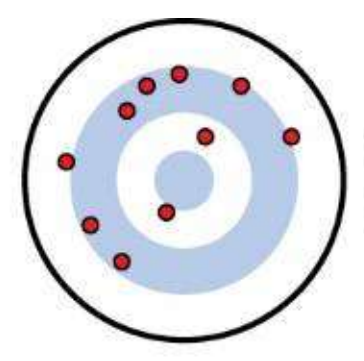
valid not reliable
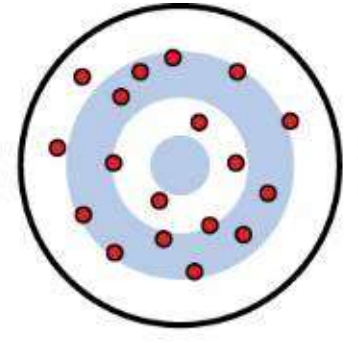
not valid not reliable
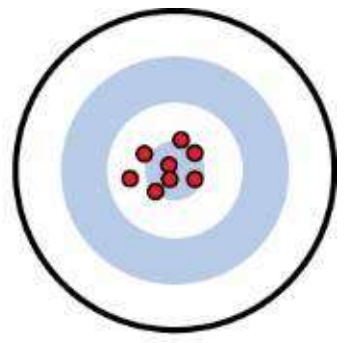
valid reliable
content, criterion related, construct
three c’s of evidence for validity
content validity
establishes that multiple items that make up measurement adequately sample the universe of content that defines the construct being measured, adequacy that complete universe of content is sampled by test’s items
full scope, number, relative importance, irrelevant
three requirements of content validity are items must adequately represent _____ of construct, _____ of items that address each component should reflect _____, should not contain _____ items
subjective, panel, first
judging content validity is a _____ process, uses _____ of experts or focus group, should be answered _____
face validity, received, understood
_____ is implication that an instrument appears to test what is intended to test, impacts how well it is _____ and its relevance is _____ by those who use it
use, after, planning, constructing
face validity is judgment by those who _____ test _____ test is developed, content validity evolves from process of _____/_____ test
criterion related validity
establishes the correspondence between a target test and a reference gold standard measure of the same construct
align, external criterion, agreement, comparing, gold standard
criterion related validity is ability of measure to _____ with results on _____ (in _____) and _____ results to _____
concurrent validity
extent to which the target test correlates with a reference standard taken at relatively the same time to reflect same incident of behavior
establish, new, sensitivity, specificity
concurrent validity is often used to _____ validity for _____ tests, comparing _____ and _____
predictive validity
extent to which the target test can predict a future reference standard, take baseline and evaluate after period of appropriate time
screening, identify, future, predict, outcomes
predictive validity is used to validate _____ measures to _____ risk factors for _____ disease/progression to _____ treatment _____
construct validity
establishes the ability of an instrument to measure the dimensions and theoretical foundation of an abstract construct
latent, inferences, known groups, convergence, divergence, factor analysis
construct validity is assessing presence of _____ trait, make _____, assess through _____ method and _____/_____, _____ statistical procedures tests
convergent validity
extent to which a test correlates with other tests of closely related constructs
divergent validity
extent to which a test is uncorrelated with tests of distinct or contrasting constructs
norm referenced, relative, representative distribution, population
_____ test is standardized assessment designed to compare and rank individuals within a defined population, how individuals perform _____ to one another, judgment is on how measured value related to _____ of _____
criterion referenced, others, goals, interventions, change, cut off, change, time
_____ test is interpreted according to a fixed standard that represents an acceptable level of performance, irrespective of how _____ perform, useful for establishing _____, planning _____, and measuring _____, use _____ scores, can _____ over _____
understand, clinical, validation, issues, adapting, cross, different
methodological studies must fully _____ construct, consider _____ context, consider several approaches to _____, consider validity _____ if _____ existing tools, _____ validate outcomes across _____ samples
external validity
can results be generalized to other persons, settings, or times
internal validity
is there evidence of a causal relationship between independent and dependent variables
history, unanticipated, maturation, development, time, attrition, experimental, testing, instrumentation, regression to the mean, selection, groups
threats to internal validity include _____ (_____ events, _____ (changes due to normal _____ or passage of _____), _____ (loss of subjects for specific reason related to _____ situation), _____ (pretest affect posttest), _____ (how it was measured), _____, and _____ (subjects assigned to experimental _____)
random assignment, blinding
ways to control threats to internal validity include _____ and _____
operational definitions, comprehensive, subgroup, time, multiple, interactions, experimental bias, behavior, influences
threats to construct validity include _____ (interpreted within context), _____ measurements (secondary), _____ differences, _____ frame, _____ treatment _____, _____ (subject changes _____, investigator _____)
selection, characteristics, convenience, adherence, compliance, setting, ecological, real world, history, contemporary
threats to external validity include influence of _____ (depend on subject _____, _____ sampling), _____ (_____ to protocol), influence of _____, _____ validity (generalization to _____), influence of _____ (older studies limited application based on _____ practices
homogenous, inclusion, exclusion criteria, random, blocking, confounders, matching, characteristics, repeated, control, efficient
strategies to control for subject variability include _____ samples based on _____/_____, _____ assignment, _____ variables by building in possible _____, _____ subjects based on similar _____, and _____ measures using subject as own _____ (most _____)
compliance
_____ relates to getting assigned treatment, being evaluated according to protocol, and adherence to protocol requirements
missing data
_____ occurs due to dropouts, missing a session, missing an outcome measure
anticipated, populations, higher
noncompliance and missing data should be _____ in study design, some _____ may have inherently _____ risk
per protocol, intention to treat
ways to analyze results with noncompliance include _____ analysis and _____ analysis
complied, removed, successful
per protocol analysis only includes subjects who _____ with protocol, noncompleters are _____, may make experimental group look more _____ compared to control group
original random, received, noncompliant, dropped out, all, underestimate
intention to treat analysis data is analyzed according to _____ assignments, regardless if treatment was _____ or if they were _____/_____, ideally includes _____ subjects, may _____ treatment effect
few, both
ITT analysis is only appropriate with _____ gaps, ideally use _____ analyses to increase strength