L9 Mucosal and neonatal immunity
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Skin and mucosal sites
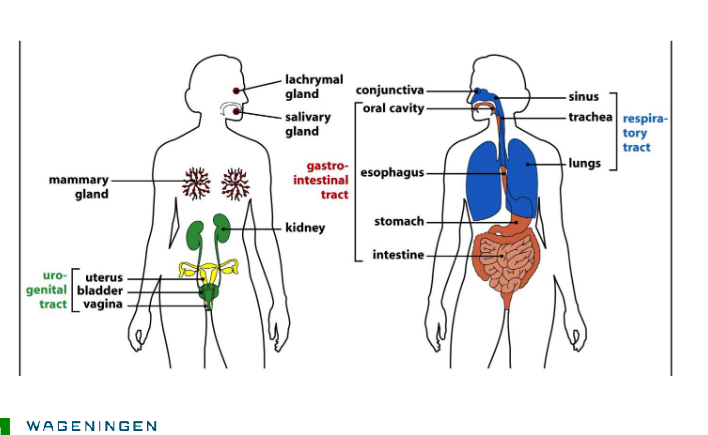
Lung and intestine a person of 1.5 m:
Skin = 2 m2, lung 100 m2, intestine 300 m2
Skin
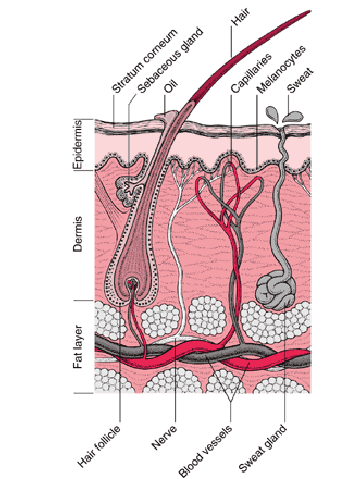
Protective properties of skin
Innate
Physical barrier
Microbiota (10^12 bact/m2)
Antibacterial substances like lysozyme, fatty acids etc
Adaptive
Langershans (dendritic) cells (2% of dermal cells)
T cells (CD8+ and y/d T cells)
Macrophages
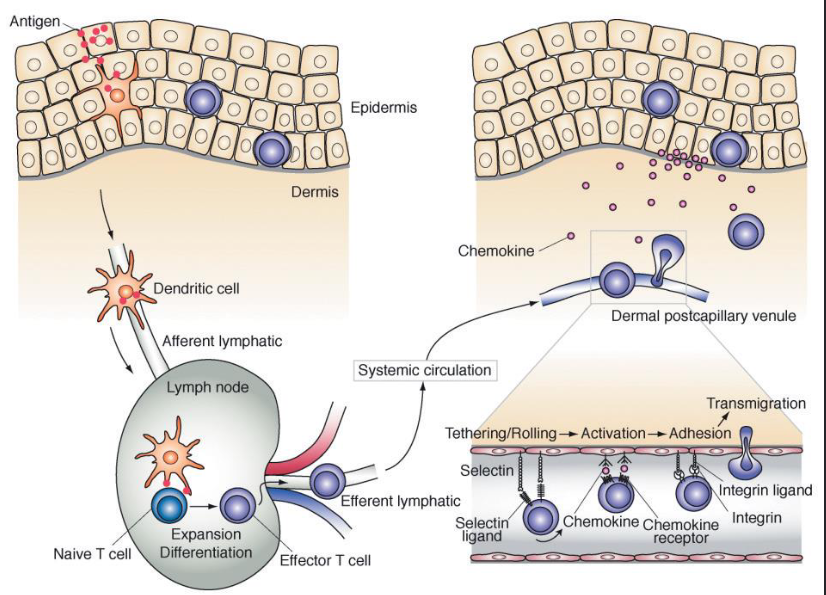
Mucosal immunity
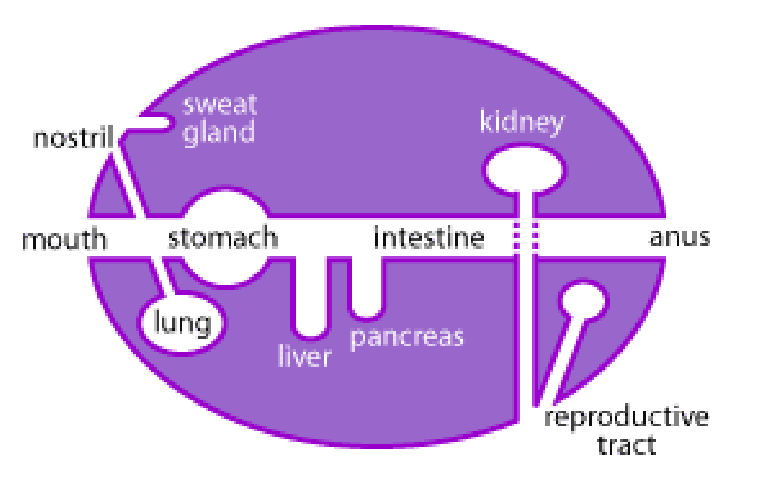
Innate surface protection mechanisms
Sneezing, coughing, vomiting
Microbiota on skin, in intestine and urogenital tract
pH, anaerobiasis
Lysozyme
Secretions (tears, mucus, saliva etc) containing antimicrobial peptides
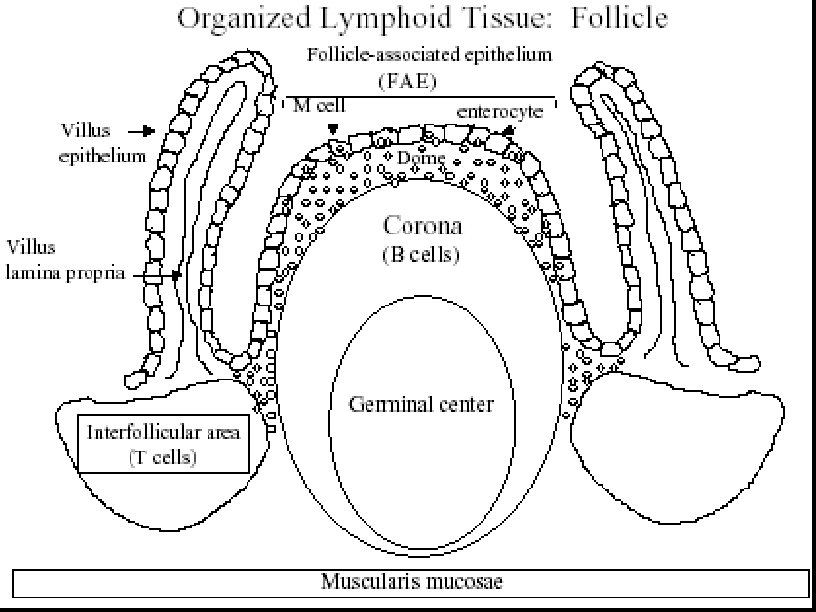
Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
Inductive lymphoid tissue
GALT - GUT
peyer’s patch, (PP)
Appendix
Isolated lymphoid follicles
BAL - bronchus
SALT/DALT - salivary/duct
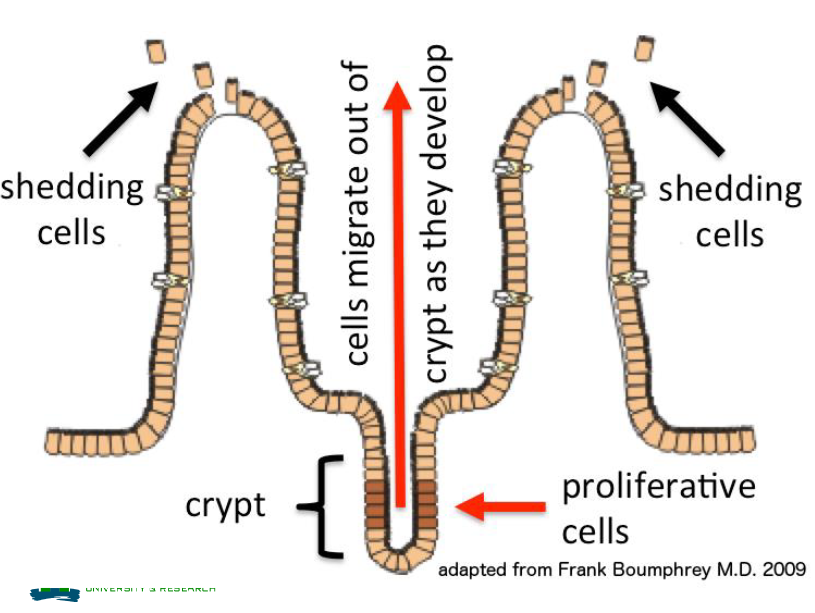
Intestinal mucosa = surface of
2 tennis courts
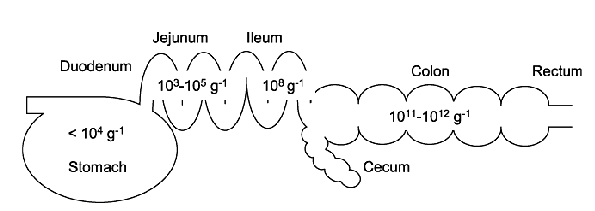
Bacterial numbers along the intestinal tract
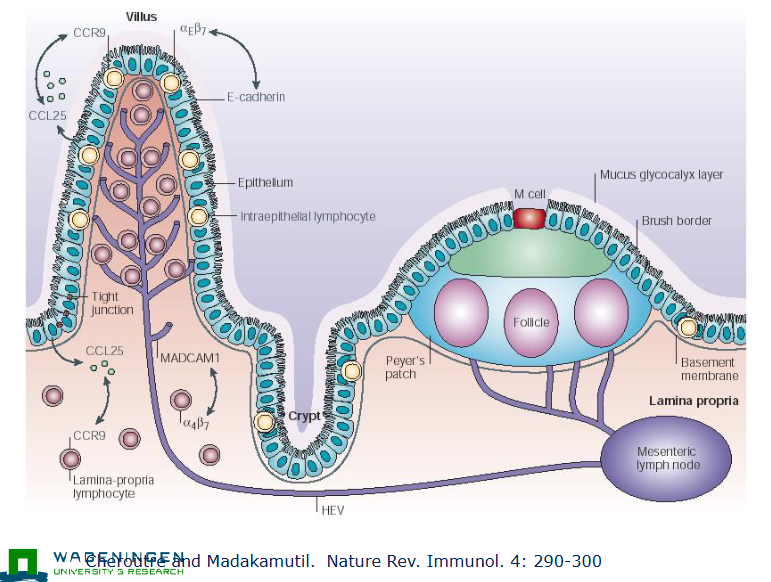
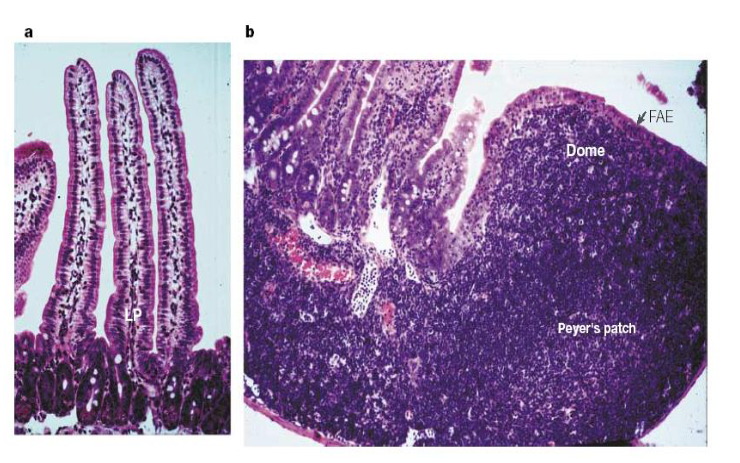
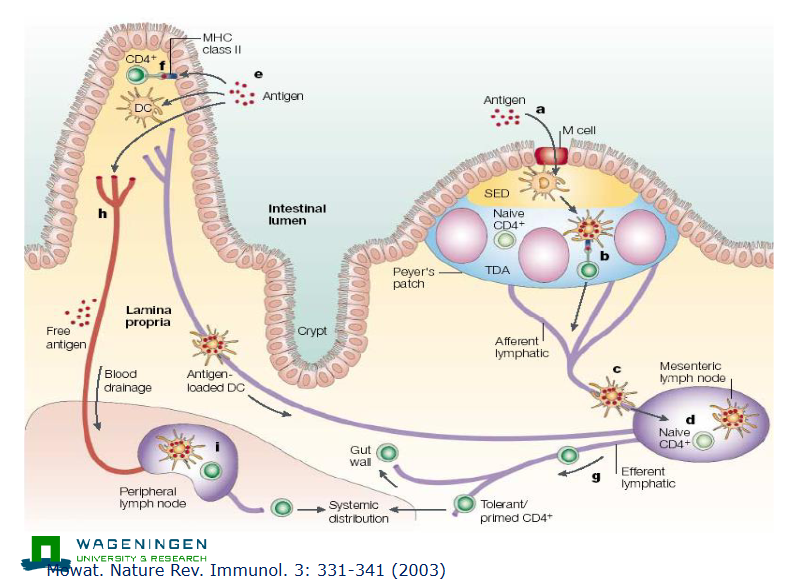
M cells facilitate
antigen uptakeO
Organized lymphoid tissue: follicle
Dendritic cells sample antigen (locations):
Directly in the itnestinal lumen
Sampling form M cells in the Peyer’s patches
From (apoptotic) epithelial cells
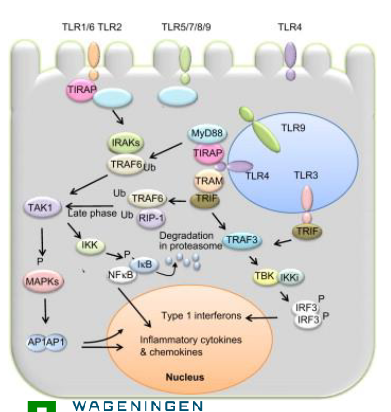
TLR signaling involved in maintance of mucosal homeostasis
TLR2 activation on intestinal epithelium stimulates production of tight junction proteins
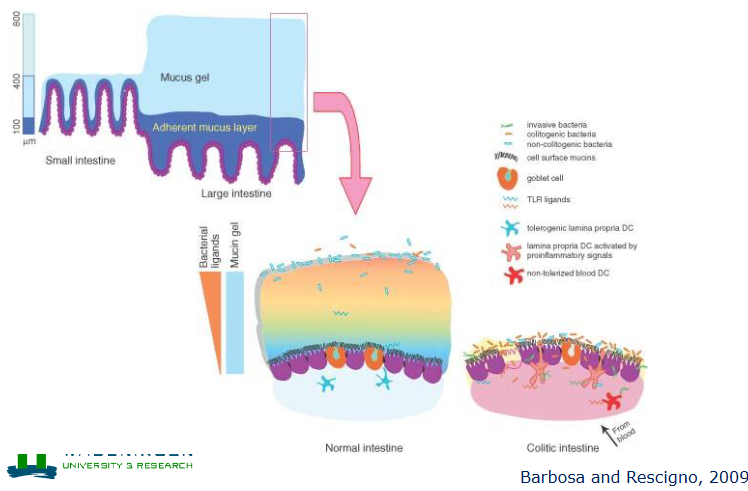
Barrier function (leaky gut)
Mucus layer inhibits direct interaction of bacteria with mucosal epithelium
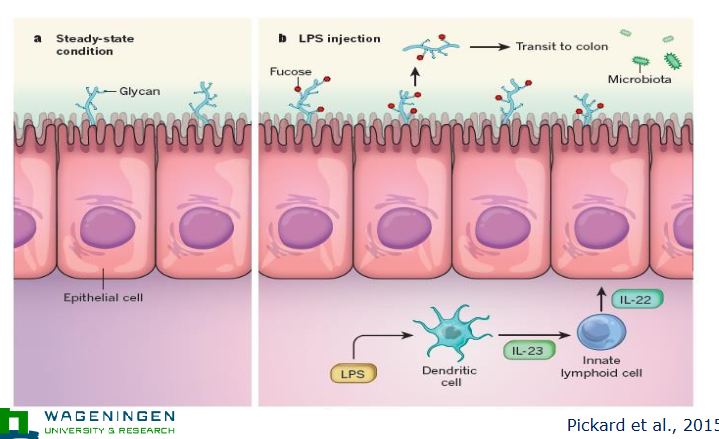
Innate immune system induces fucosylation of intestinal epithelium to sustain host-microbe symbiosis in sickness
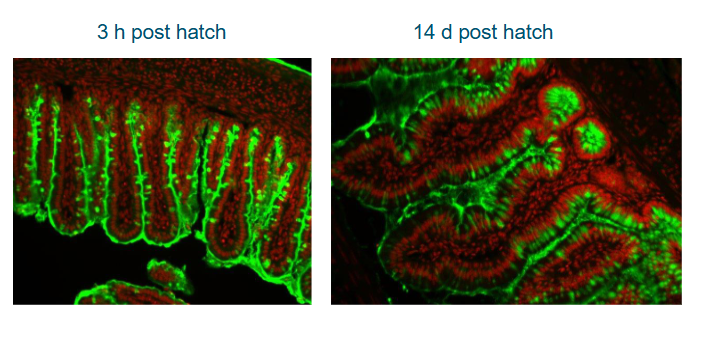
Chciken have terminal fucsoe residues
Goblet cells
Mucus production
Paneth cells
Antimicrobial molecules
Mucus layer
Glycosylated molecules

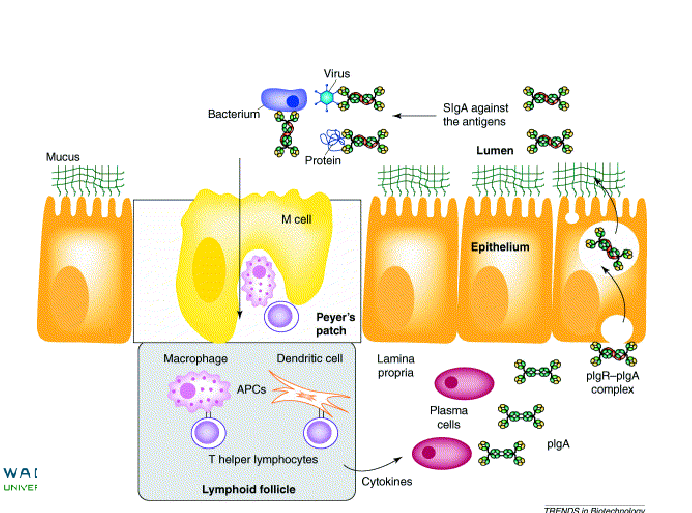
Common mucosal immune system
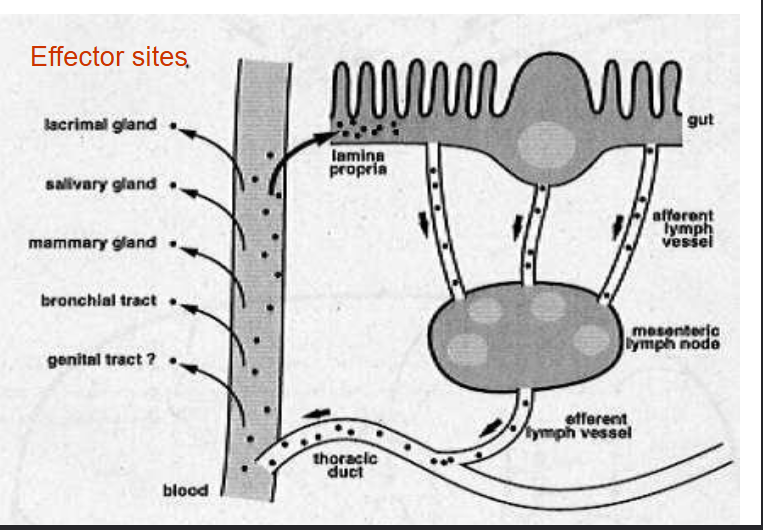
Secretory IgA productoin
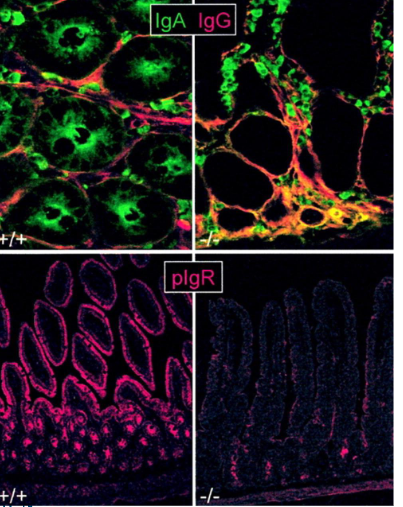
Lack op eptihelial IgA transport in pIgR -/- mice
Structure of sIgA
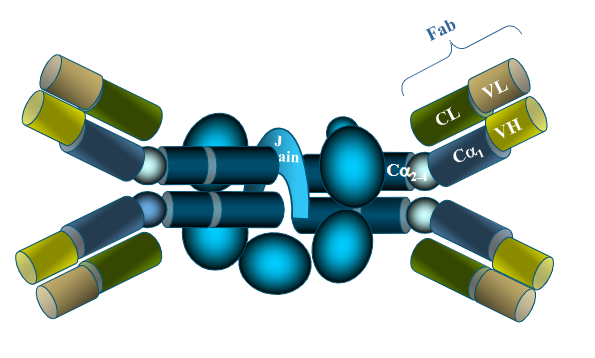
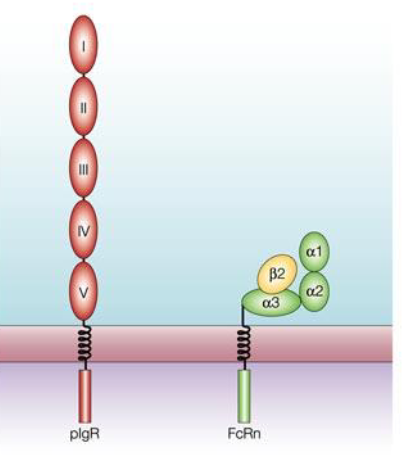
pIgR
polymeric immunoglobulin receptor
SC
secretory component, free form bound to pIgA, scavenger function
TGF - B
Isotype swithc
IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10
Proliferation
IL-6
Terminal differentiation
Mucosal IgA
2 subclasses in humans
IgA1, monomeric, predominant IgA in serum
IgA2, polymeric, predominantly found in external secretion
J-chain, required for formation of polymeric IgA, J-chain gko mice-monomeric IgA but is secreted
Loss of 13 aa in hing region reduces susceptibility of IgA2 to proteolyctic cleavage
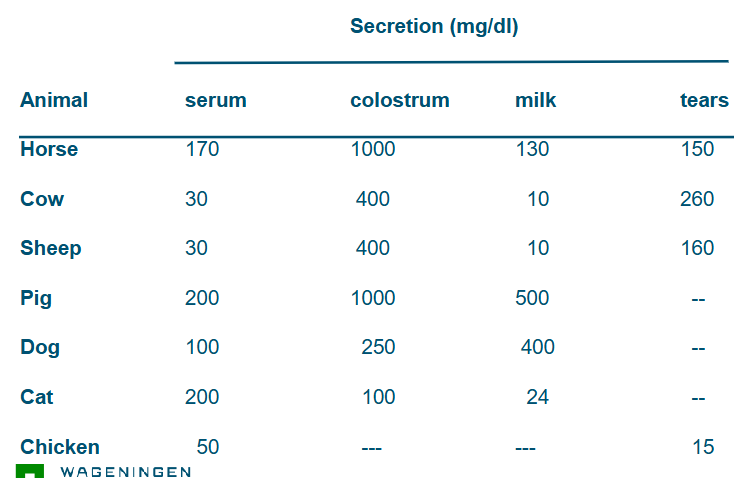
sIgA levels in domestic animals
E
Evidence for protection via IgA
Influenza - passive transfer of monoclonal IgA was protective, not IgG
Backpack - anti-rota virus IgA hybdridomas
V. cholerae - passive transfer of IgA was sufficient for protection
S. typhimurium - IgA protected against oral, not systemic challenge
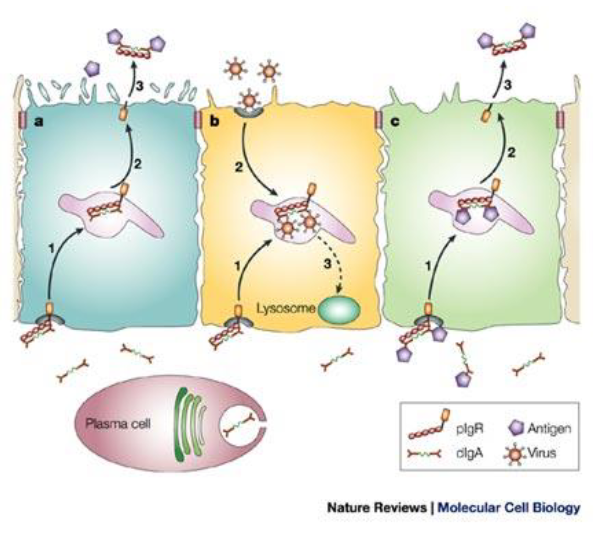
Transport of IgA
PIgA/pIgM binds to pIgR - basolateral membrane
Endocytosis and transcytosis
Disulfide bonds link pIgR to pIgA
Cleavage event, secretory component, SC
SC stabilizes pIgA and makes it resistant to proteolytic cleavage
Changes in immune parameters of hibernating squirrels
Adaptive immune responses after systemic immunization are suppressed during hibernation
In squirrels lymphocyte numbers and IgA are increased in mucosal tissuesI
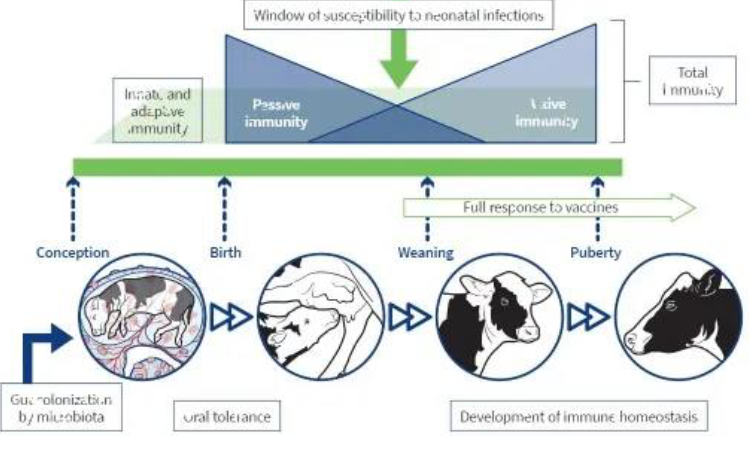
mmunity in the fetus
Fetus - natural transplant, a stranger in a strange land
Tolerance - no rejection
TH2/TH1 regulation
Development immune ssytem in the fetus
Fetus sensitive for infections, e.g. BVDV and IBR
Protection of fetus by maternal immune system
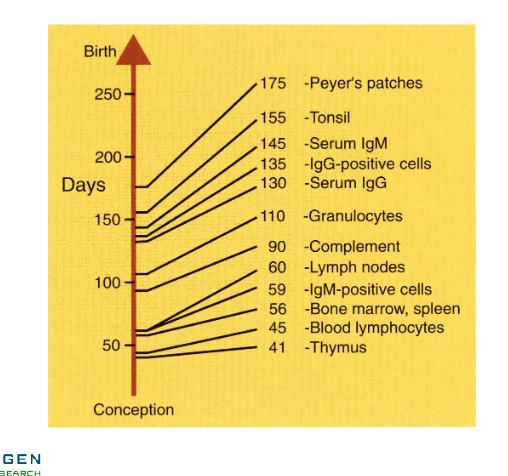
Development immune system in the fetal calf
From thymus, blood lymphocytes, bone marrow, spleen, IgM-positive cells, lymph nodes, complement, granulocytes, serum igG, IgG positive cells, serum IgM, tonsil, Peyer’s patches
Effect of BVD virus on development dependent on the timing of infection
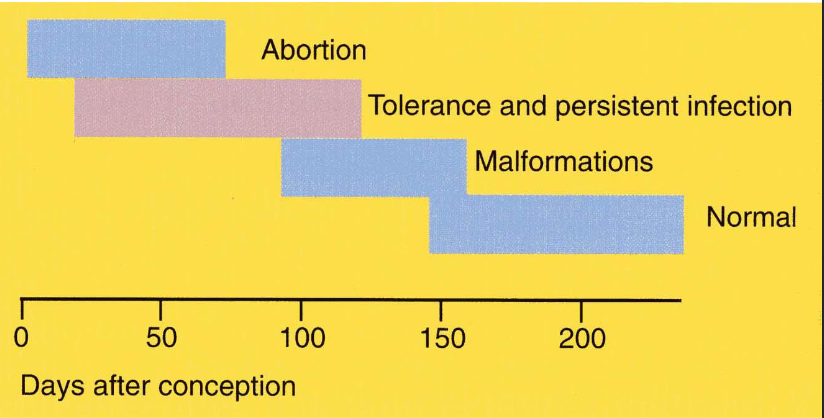
BVD in pregnanyy, what happends?
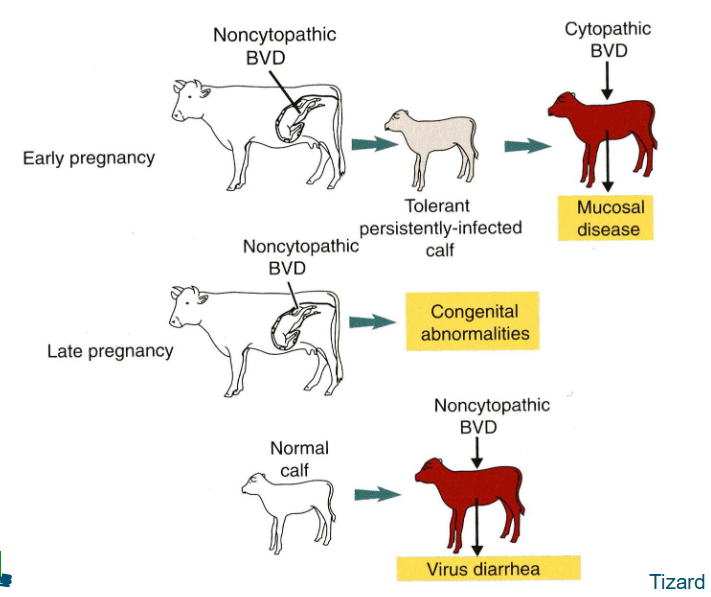
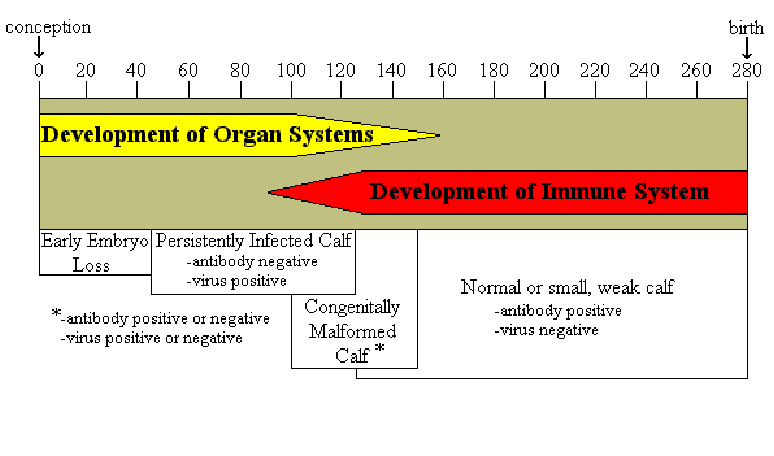
T
Transfer of immunity from mother to offspring
placenta in:
humans
cats and dogs
ruminants
horses, pigs
humans - hemochorial
cats and dogs - endothelialchorial
ruminants - epithelialchorial
horses and pigs - epithelialchorial
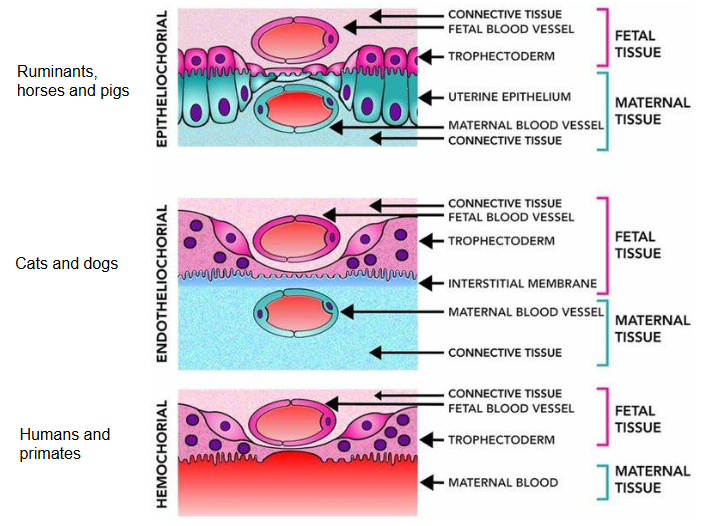
ruminants are depenten on colostrum and milk to obtain
Ig
in human, … passes the placenta
… and .. is provided via colostrum and milk
IgG
IgA and IgM
Tissue layers and placenta type
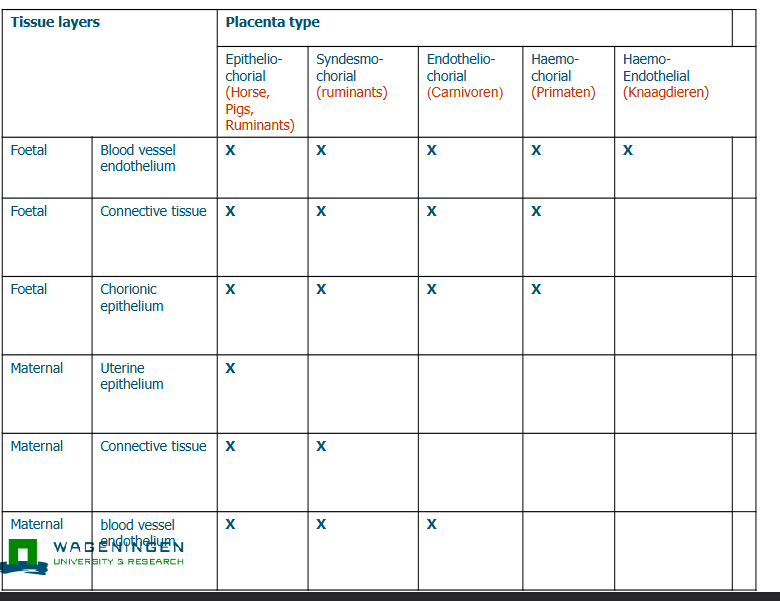
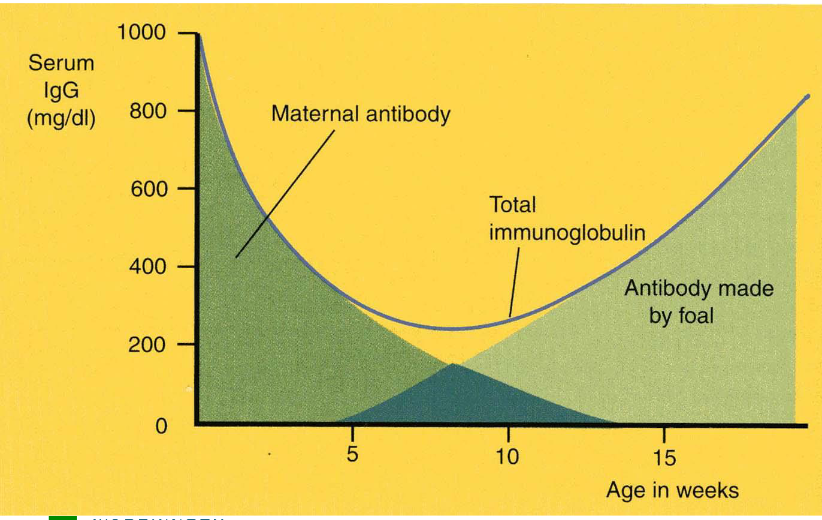
Maternal antibody transfer
Maternal antibodies reflect the infection/vacccination history of the mother
Maternal imprinting?
Ruminants, horses and pigs need colostrum to obtain maternal Ig
Cats and dogs limited transfer of Maternal IgG
Humans (primates) have in utero transfer of IgG
Composition (e.g. concentrations of Ig isotypes) of colostrum differs between species
Maternal Ig uptake: Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)
FcRn expression on enterocytes maximal at first 24 h post delivery