Vaccination
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Innate Immunity
First line of defense, no memory or specificity.
Adaptive Immunity
Acquired immunity with memory after exposure.
Humoral Immunity
Involves antibodies produced by B cells.
Cell Mediated Immunity
Involves Tc cells targeting infected cells.
T Helper Cells
Direct immune response type; Th1 and Th2.
Th1 Cells
Promote cell-mediated immune responses.
Th2 Cells
Promote humoral immune responses.
Variolation
Early vaccination method using smallpox scabs.
Edward Jenner
Pioneer of vaccination using cowpox.
Pasteur's Experiment
Demonstrated principles of vaccination with P. multocida.
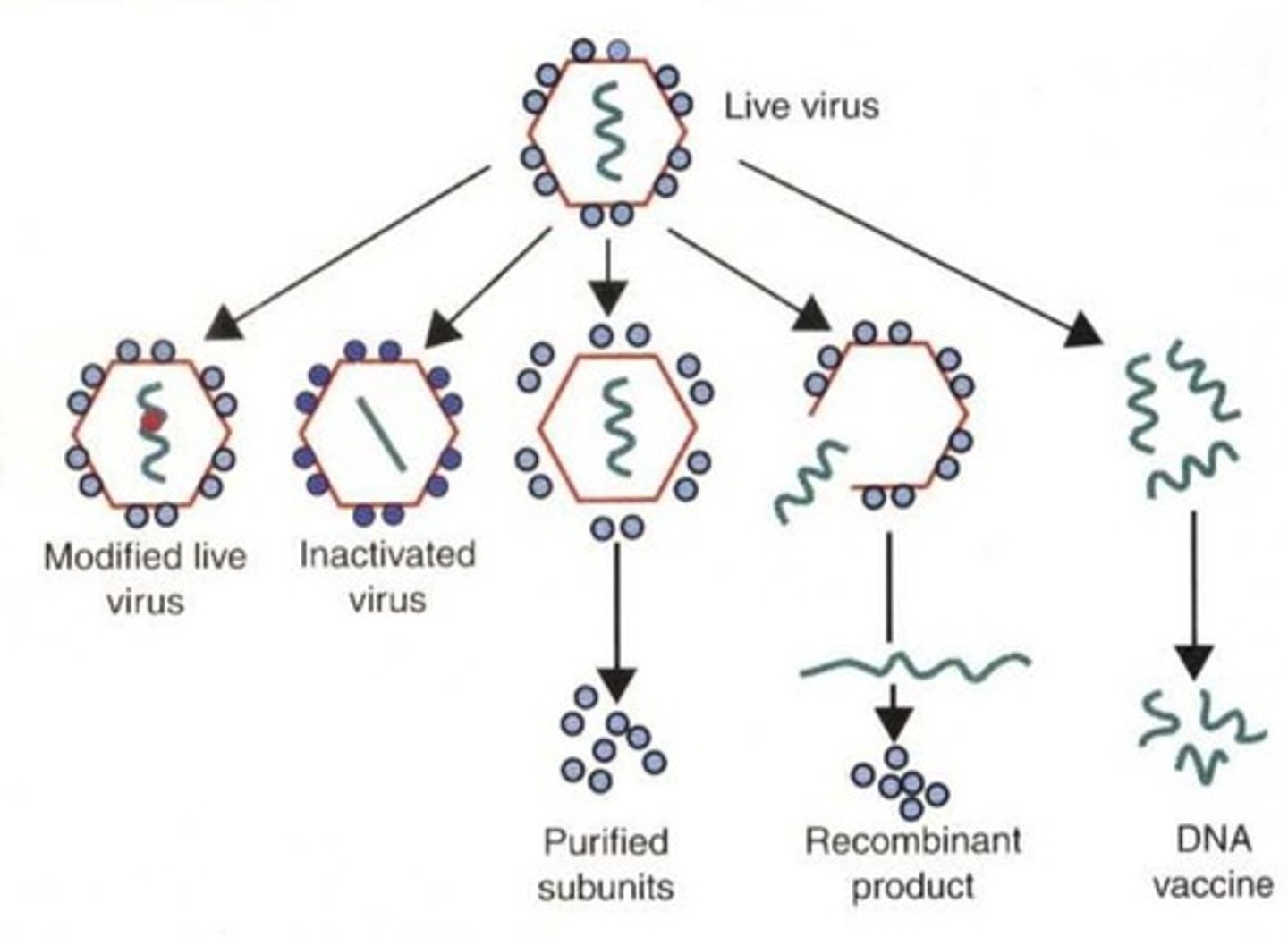
Attenuated Organism
Weakened form of pathogen used in vaccines.
Passive Immunity
Immediate protection via transferred antibodies.
Active Immunity
Long-term immunity from exposure to antigens.
Colostral Antibodies
Antibodies transferred from mother to offspring.
Antibody Titre
Measurement of antibody concentration in serum.
Antiserum
Serum containing antibodies from immunized animals.
Serum Sickness
Type III hypersensitivity reaction from passive immunization.
Clostridium tetani
Bacteria for which horses are immunized for antitoxin.
Heterologous Species
Different species receiving antibodies may react poorly.
Maternal Antibodies
Can interfere with active immune responses in young.
Pulpy Kidney Vaccine
Should not be given to lambs under 6-8 weeks.
Anaphylaxis
Severe allergic reaction potentially from repeated antibodies.
Passive Immunity
Short-term immunity acquired from another source.
Active Immunity
Long-lasting immunity developed by immune response.
Antigen Administration
Introducing an antigen to stimulate immune response.
Secondary Response
Immune response triggered by re-exposure to antigen.
Prolonged Protection
Long-lasting immunity from repeated antigen exposure.
APC Activation
Antigen-presenting cells stimulate immune response.
Cytokines
Signaling proteins that mediate immune responses.
T and B Cells
Lymphocytes involved in adaptive immunity.
T Helper Cells
Cells that assist in activating other immune cells.
MHC Class II Polymorphism
Genetic variation affecting antigen presentation.
Lymphoid Tissue
Organs where immune cells are activated.
Vaccine Safety
Requirement for vaccines to avoid adverse effects.
Clonal Selection
Process of selecting specific B-lymphocytes.
Plasma Cells
B cells that produce antibodies.
Memory Cells
Long-lived B cells that remember past infections.
Serum Antibody Titre
Concentration of antibodies in serum over time.
Anamnestic Response
Rapid antibody response upon re-exposure to antigen.
Neutralisation
Antibodies preventing virus entry into cells.
Virolysis
Destruction of viruses by antibodies in blood.
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing pathogens by immune cells.
Adjuvants
Substances enhancing immune response to vaccines.
Live Vaccines
Vaccines containing weakened pathogens that replicate.
Inactivated Vaccines
Vaccines made from killed pathogens.
Genetic Engineering
Using DNA technology to create new vaccines.
Genetically Engineered Vaccines
Vaccines made from nucleic acids for immune response.
Subunit Vaccine
Contains isolated antigens mixed with adjuvant.
Recombinant Antigens
Antigens produced through genetic engineering techniques.
Alum
Adjuvant enhancing TH2 responses and antibody production.
Genetic Attenuation
Method to weaken pathogens by gene mutation.
Thymidine Kinase (TK)
Gene essential for herpesvirus replication in neurons.
Live Recombinant Organisms
Non-pathogenic organisms used to deliver antigens.
Rabies Vaccine
Contains rabies G protein inserted into vaccinia.
Nucleic Acid Vaccines
Vaccines using purified DNA for specific antigens.
Efficacy of Vaccines
Immune response does not guarantee protection.
Herd Immunity
Population immunity reducing infection spread.
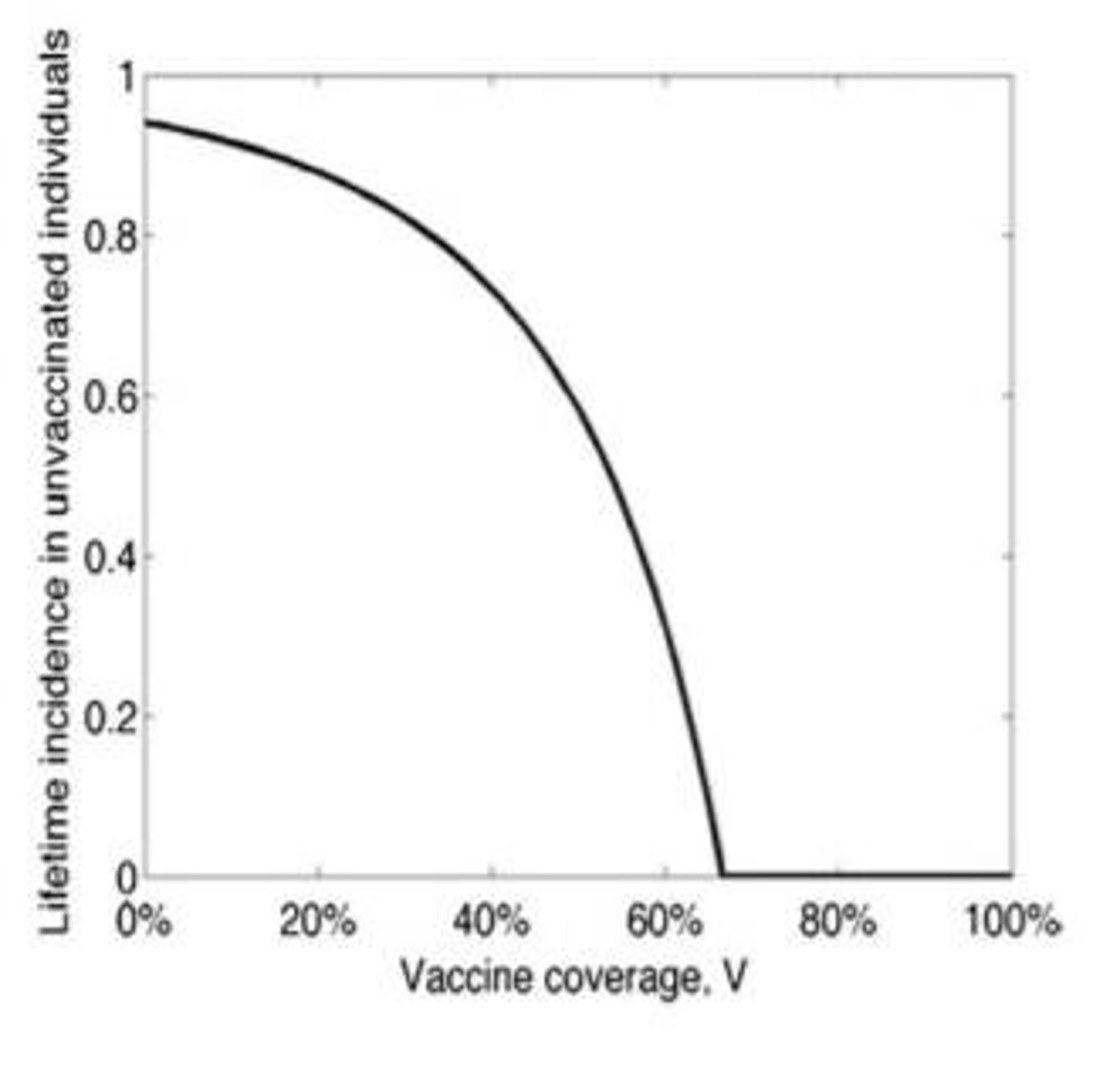
Herd Immunity Threshold
Formula: (R0 - 1)/R0 for immunity proportion.
Reproduction Number (R0)
Average secondary infections from one infected individual.
TH1 Response
Cell-mediated immune response promoted by DNA vaccines.
Adjuvants
Substances enhancing immune responses in vaccines.
Gaston Ramon
Pioneered adjuvant use in vaccine formulations.
Alexander Glenny
Demonstrated effects of alum on immune responses.
Bovine Viral Diarrhoea
Target of experimental nucleic acid vaccines.
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
Target of experimental nucleic acid vaccines.
Canine Rabies
Target of experimental nucleic acid vaccines.
Infection Transmission
Spread of disease within a population.
Susceptible Population
Individuals at risk of infection without immunity.