Anatomy and Physiology - Skeletal System
1/186
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science Olympiad 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
Skeletal System
Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement.
206
Number of bones in the human body
the cranium
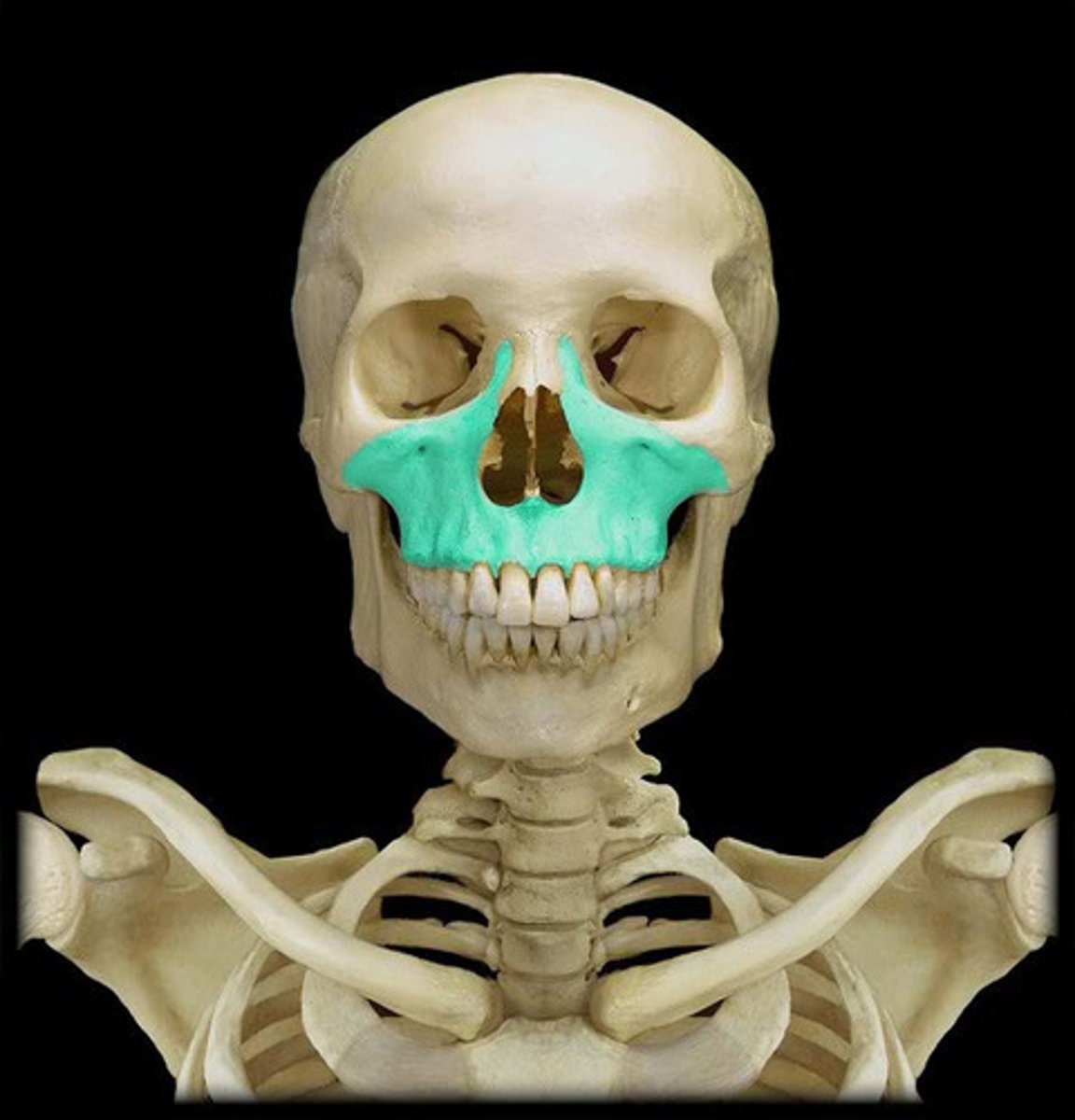
the maxilla
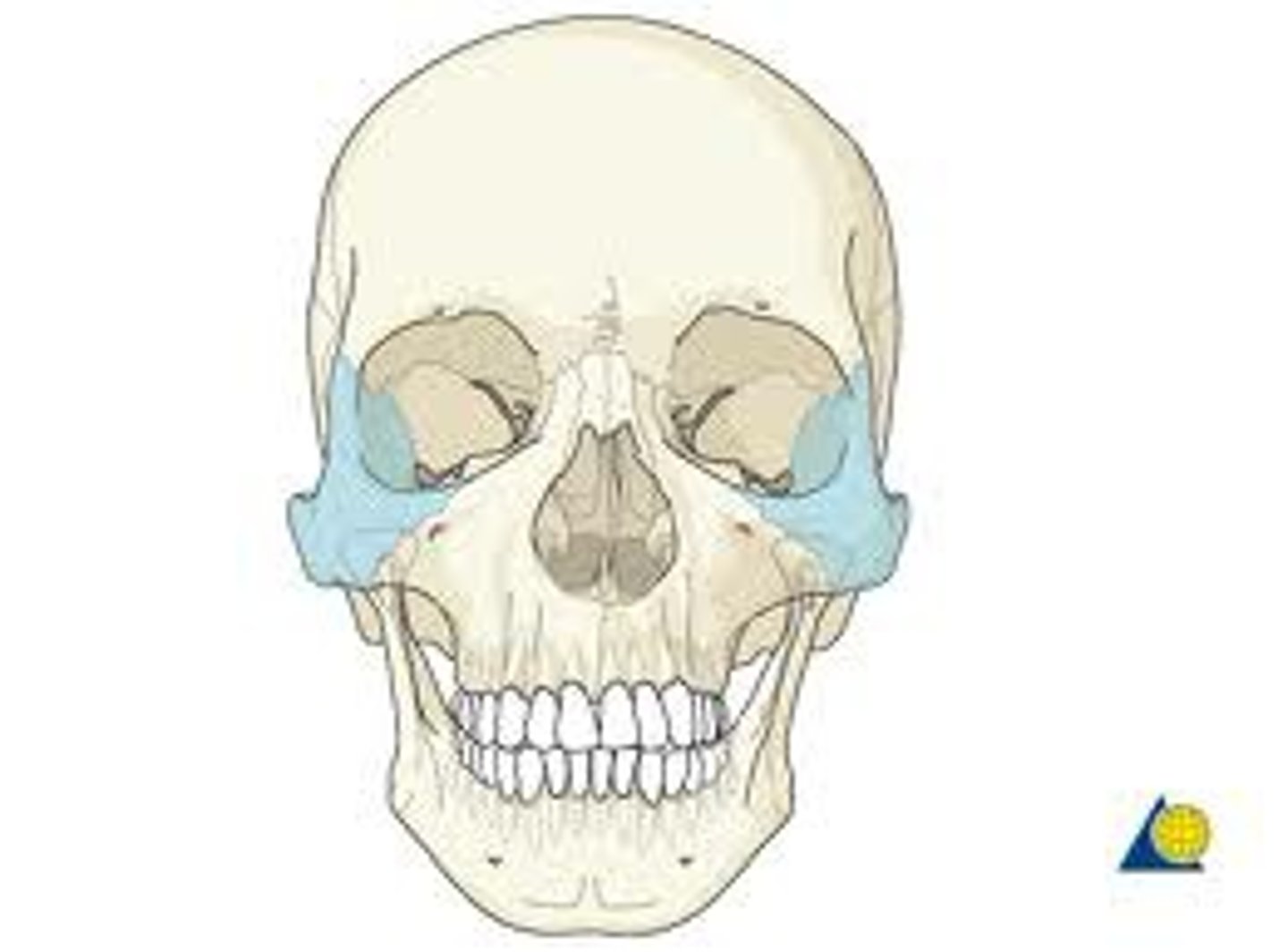
the zygoma
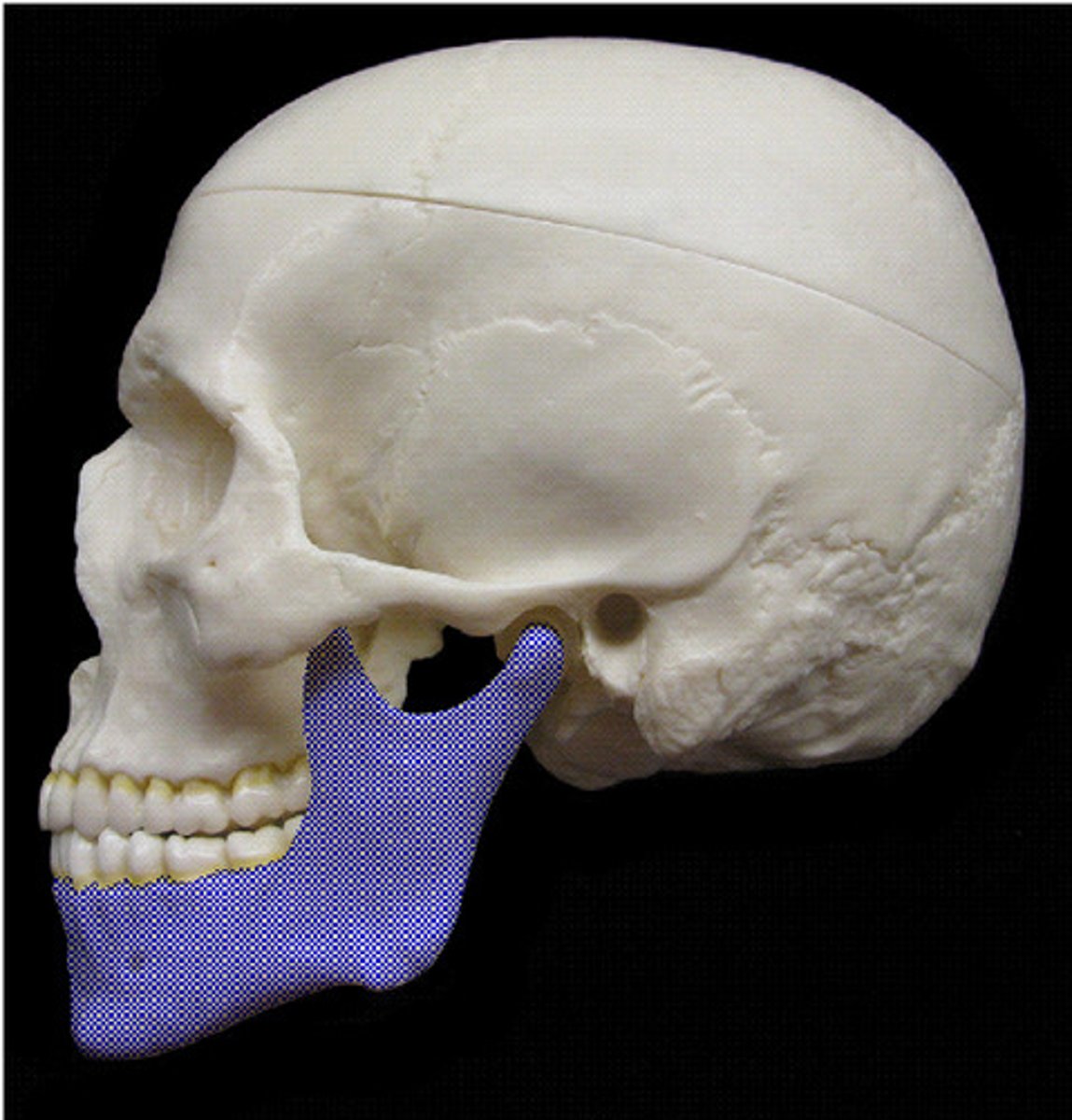
the mandible
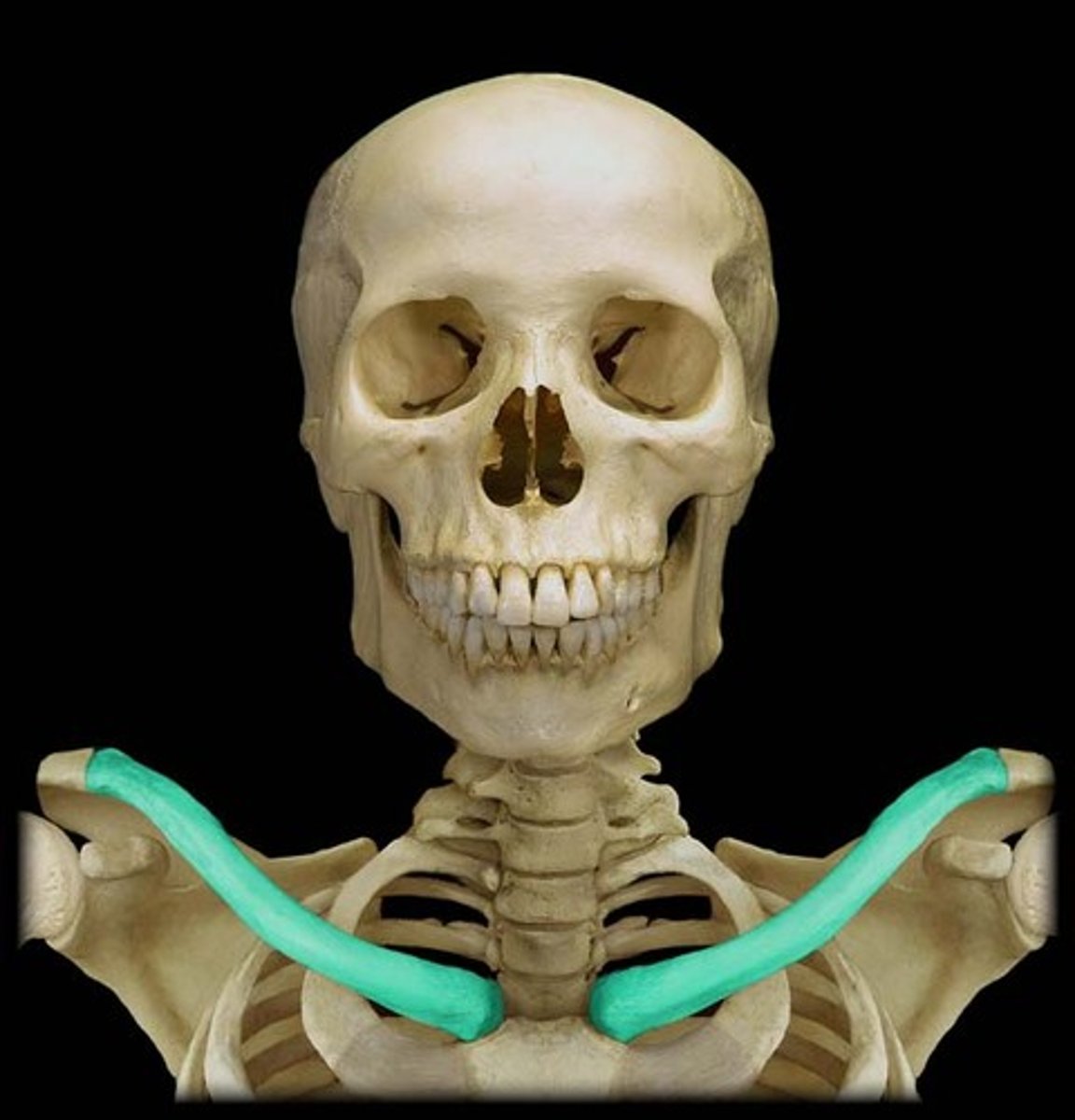
the clavicle
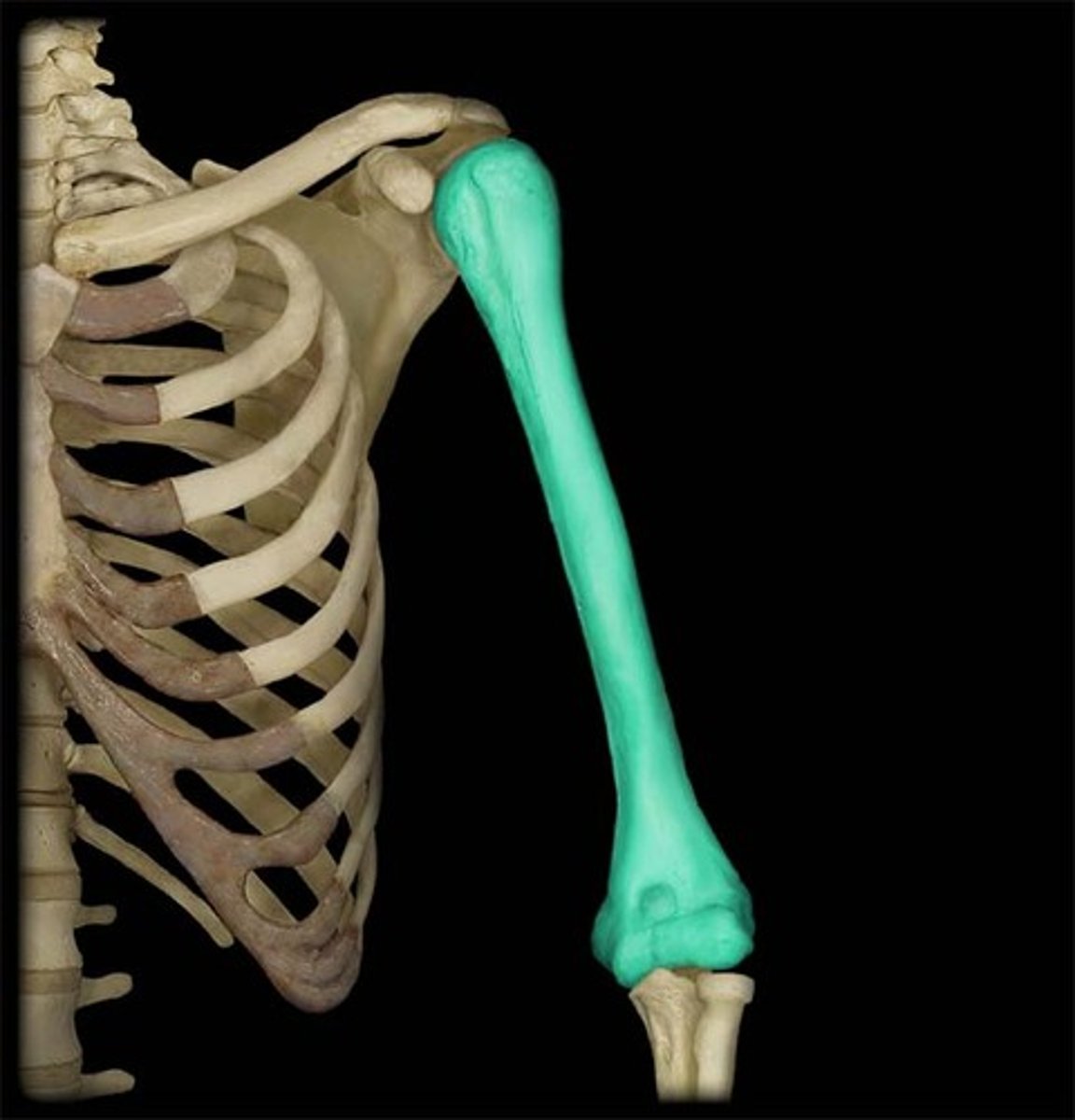
the humerous
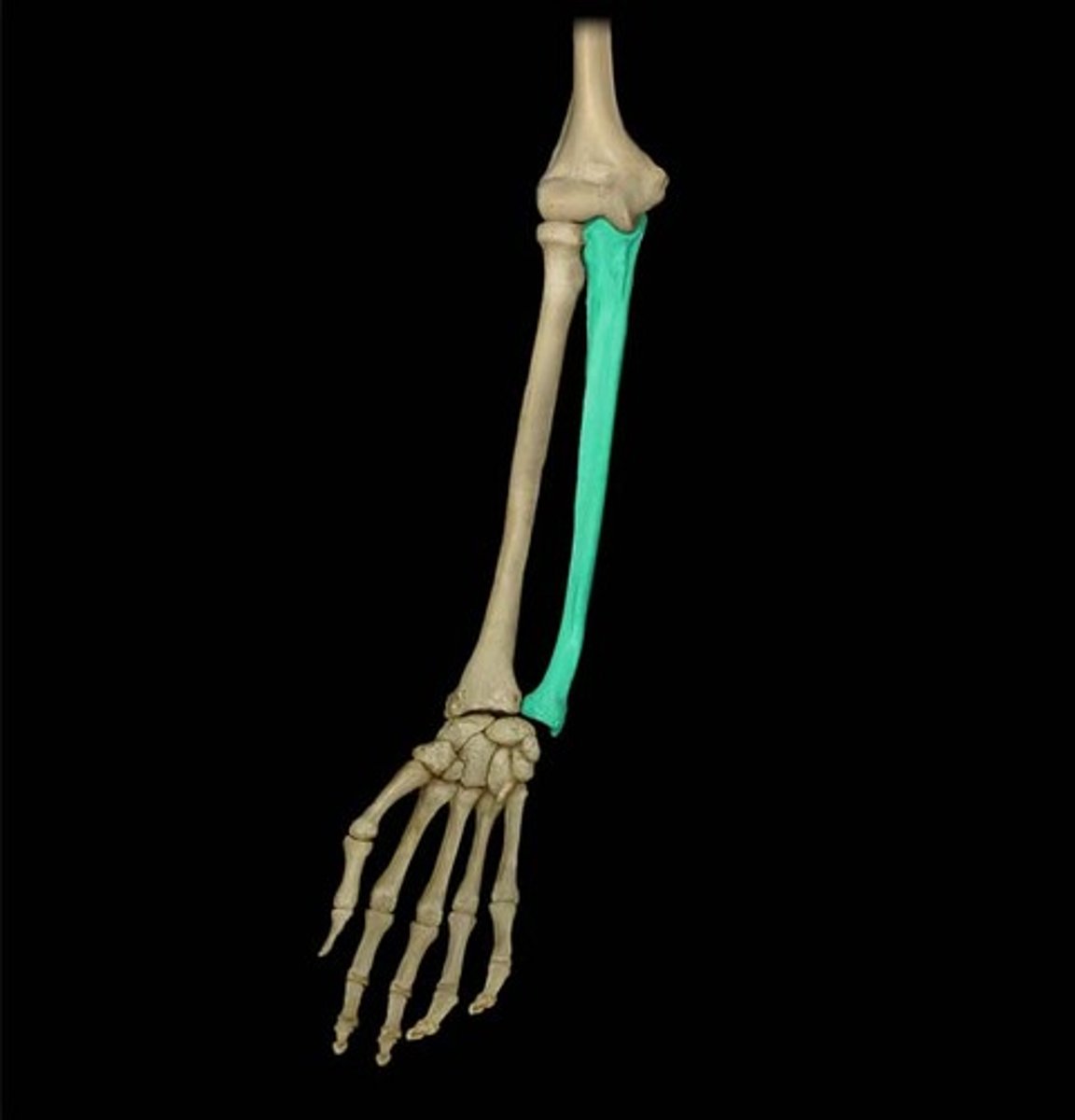
the ulna
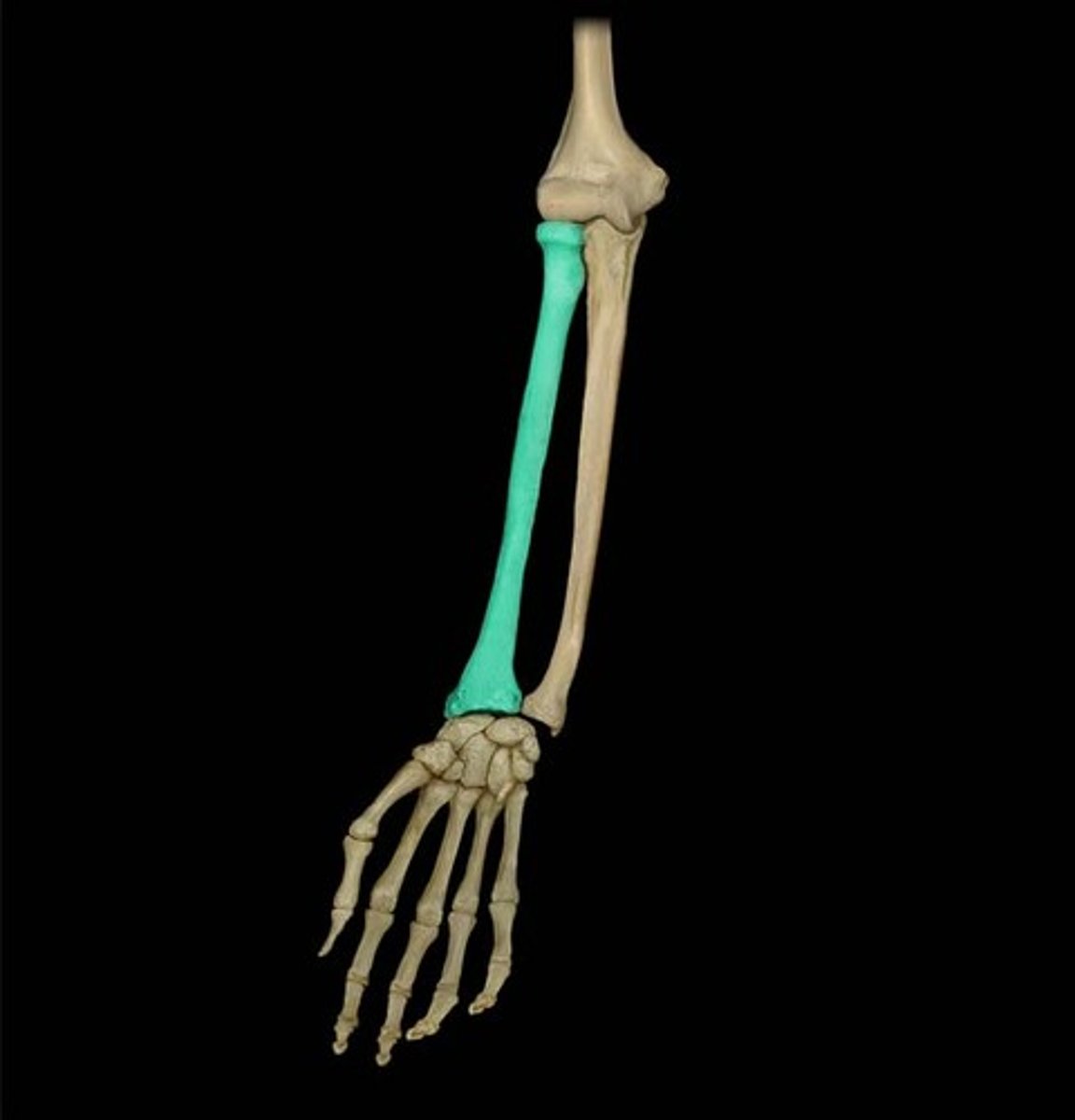
the radius
the carpals
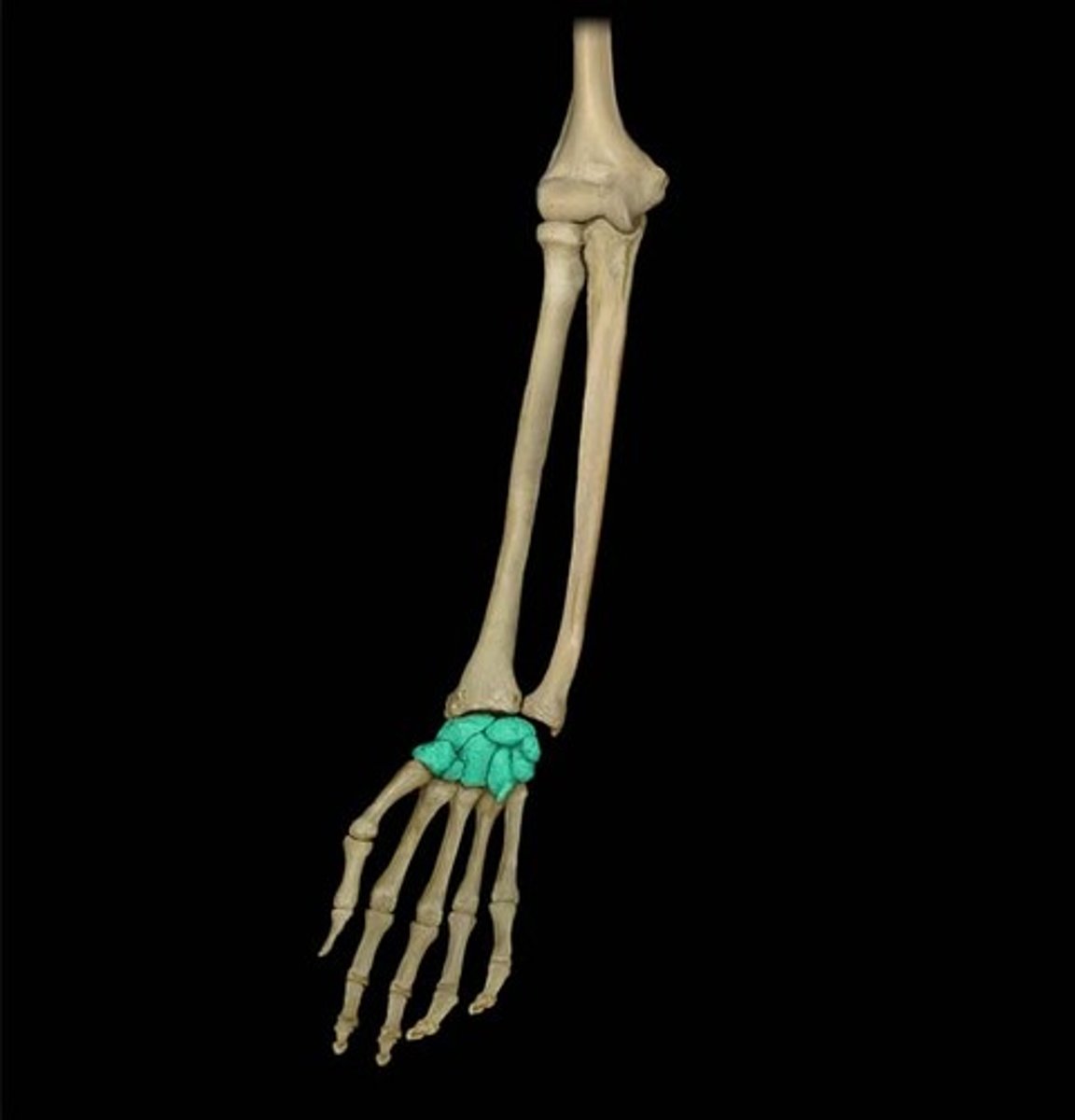
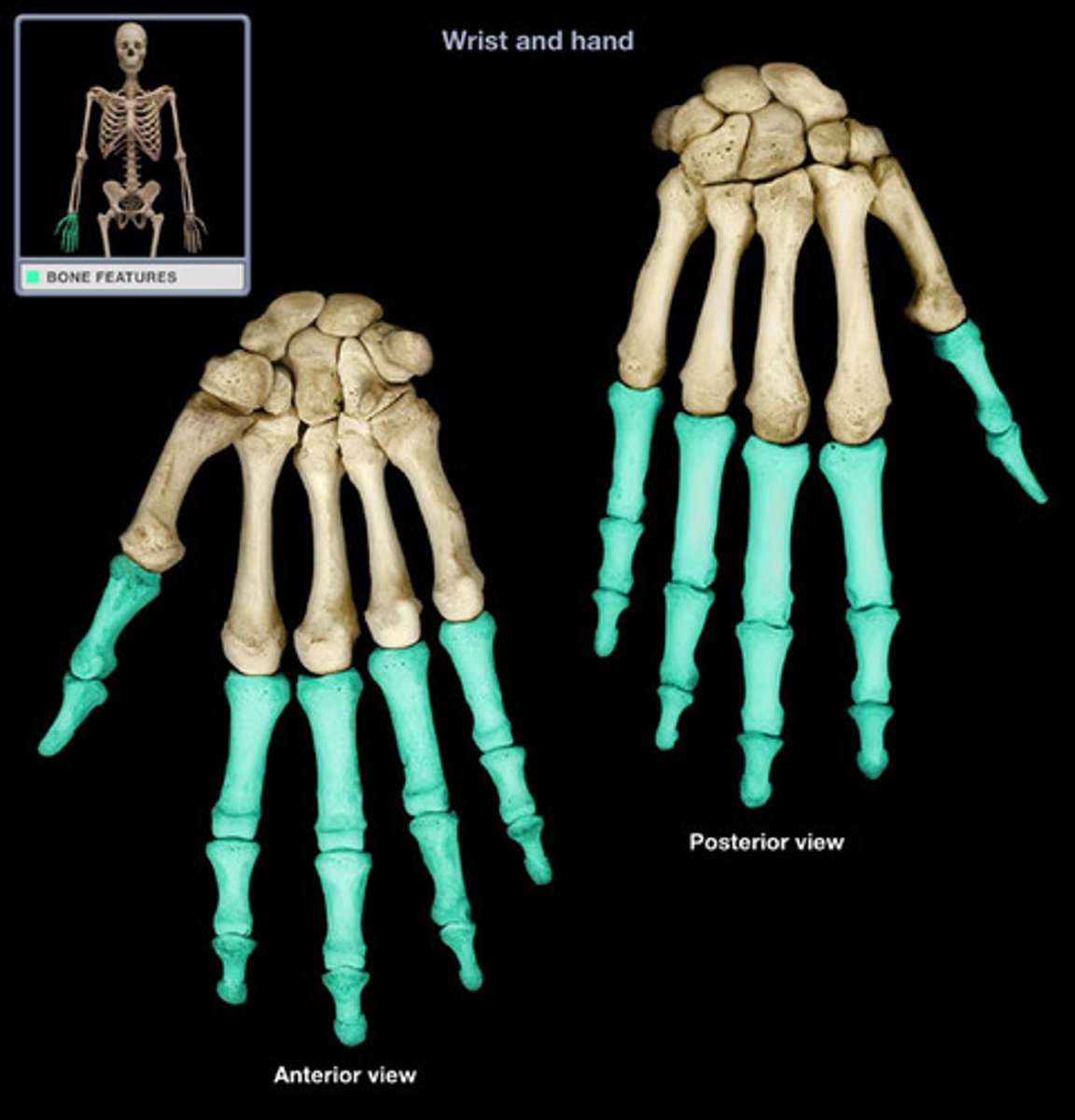
the metacarpals
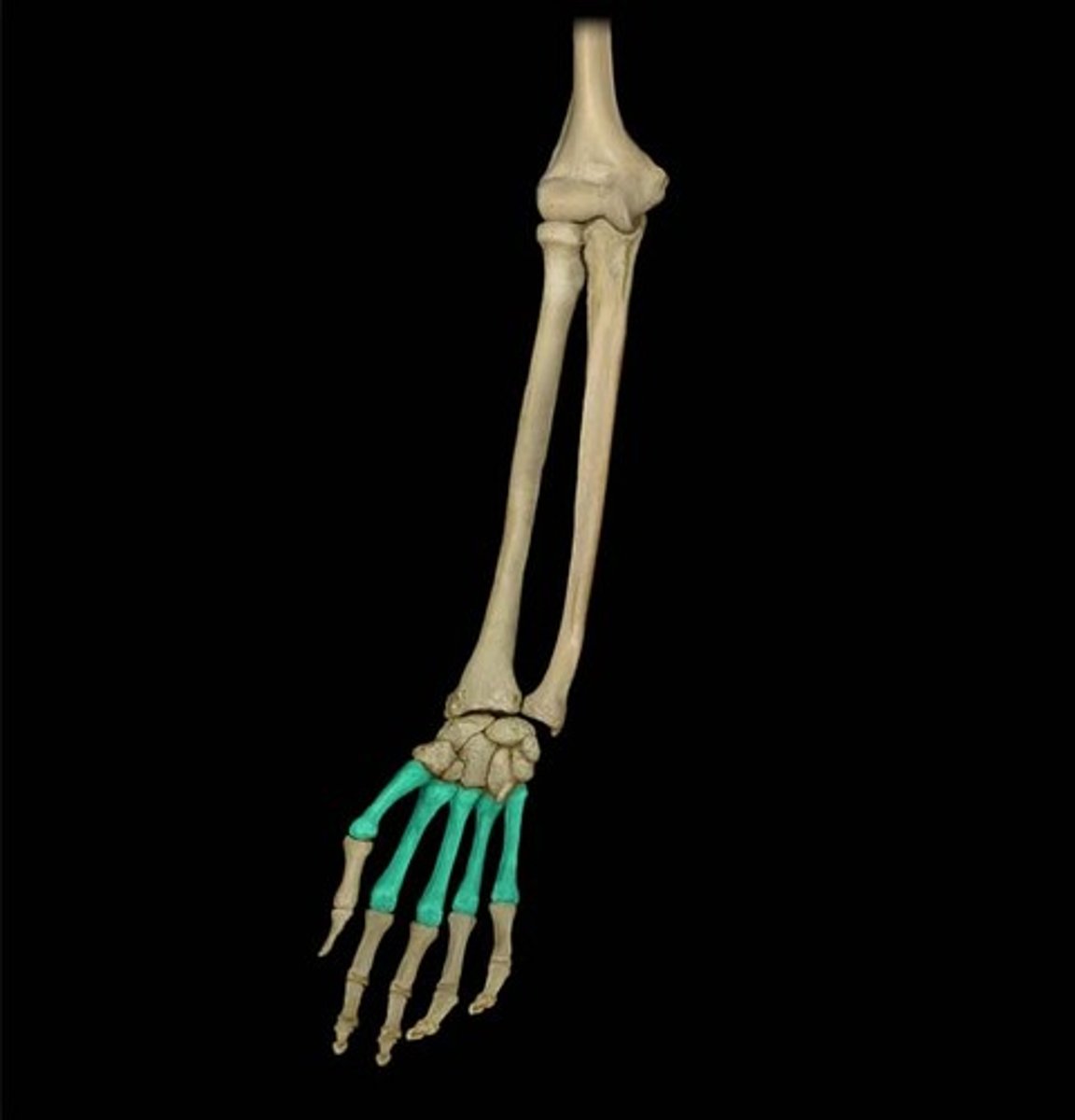
the phalanges
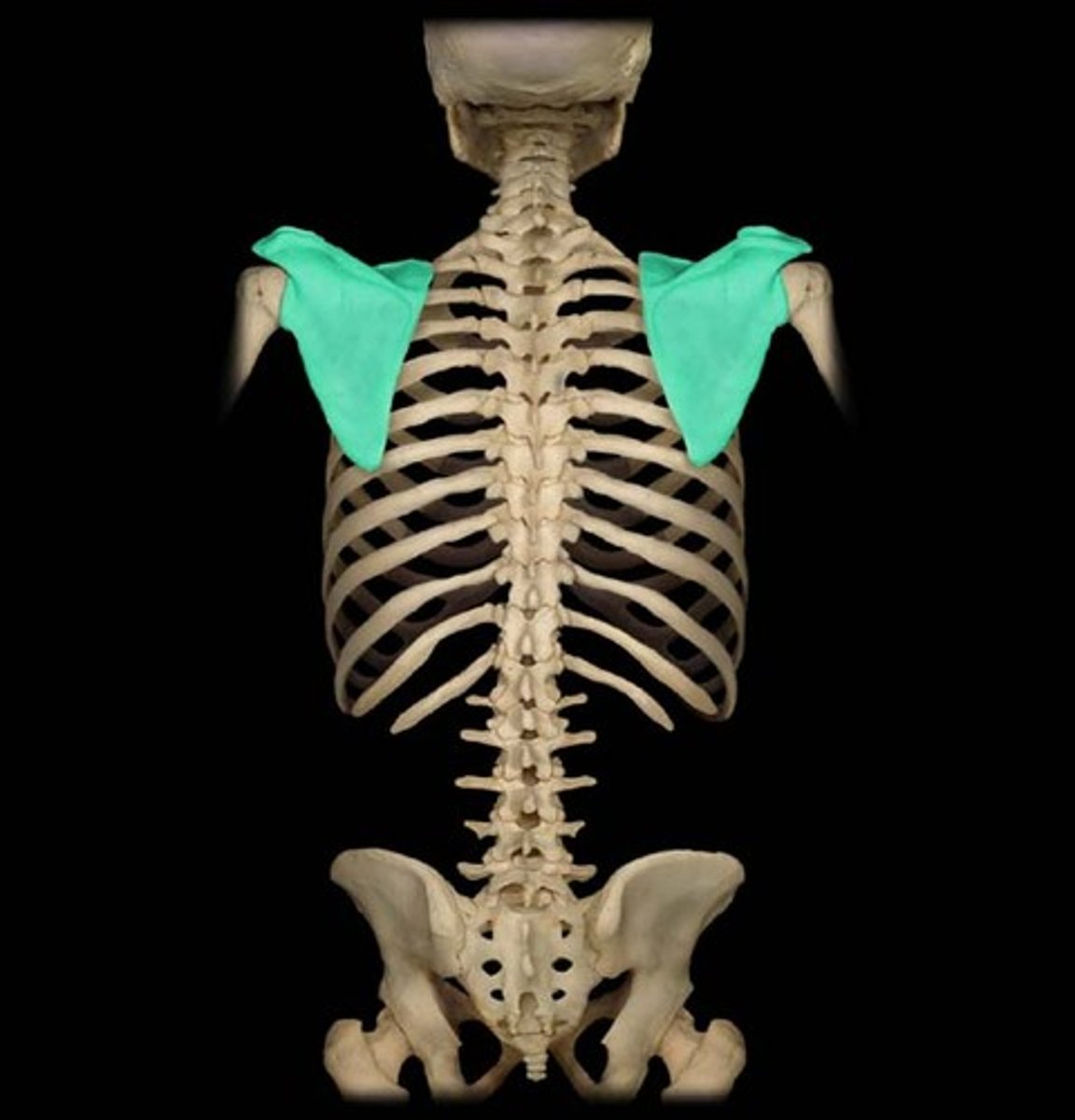
the scapula
the sternum
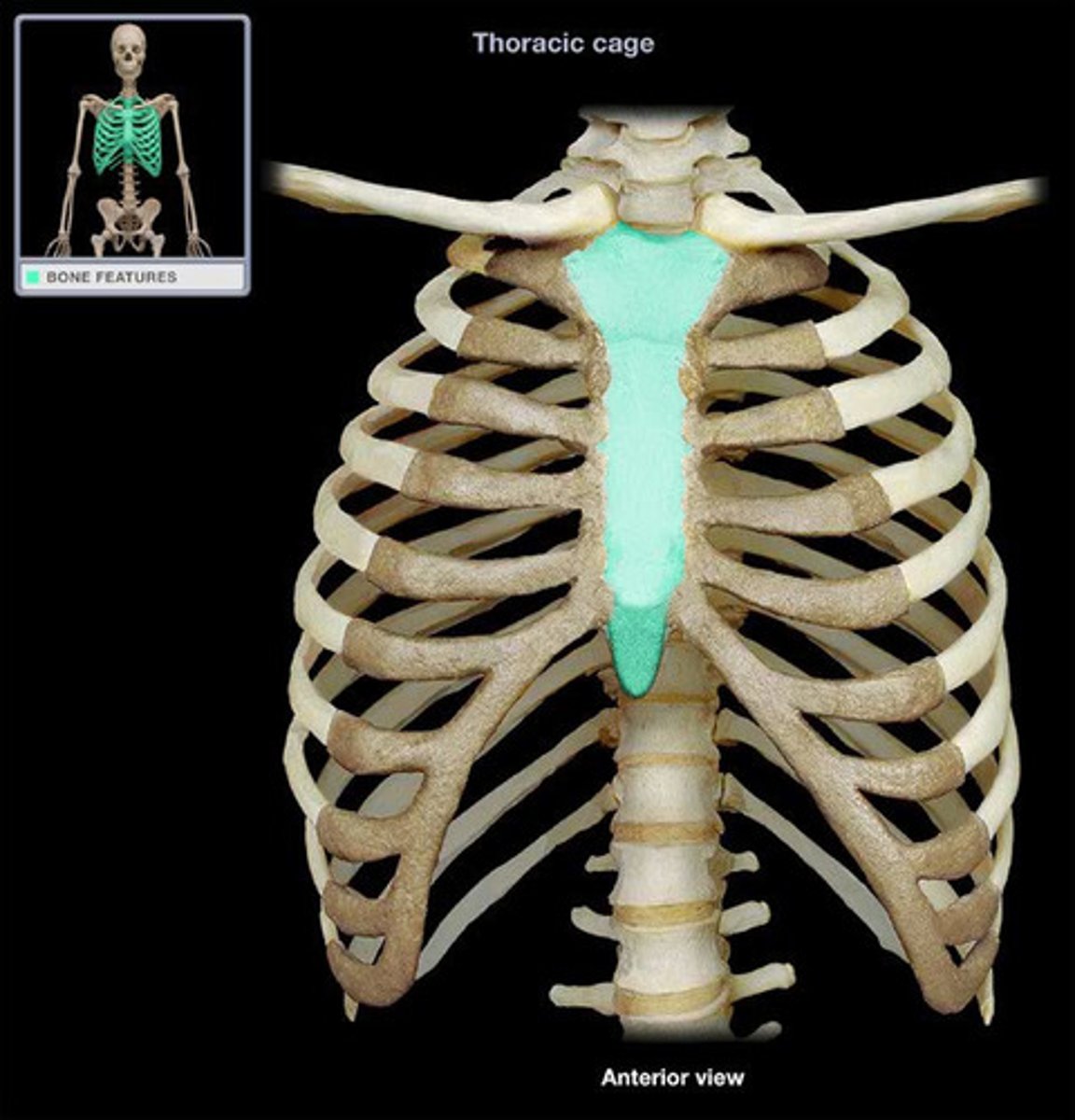
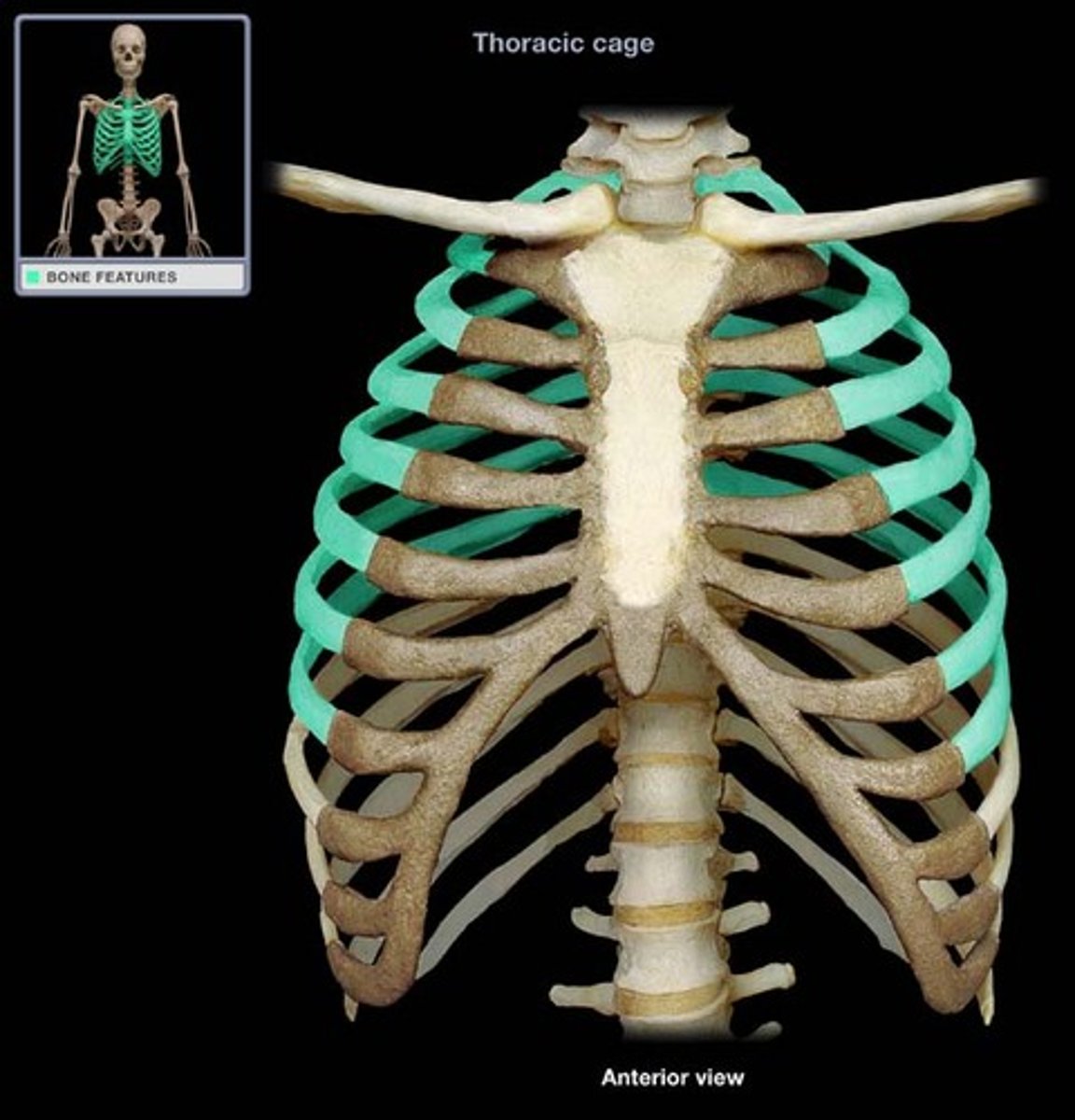
the ribs
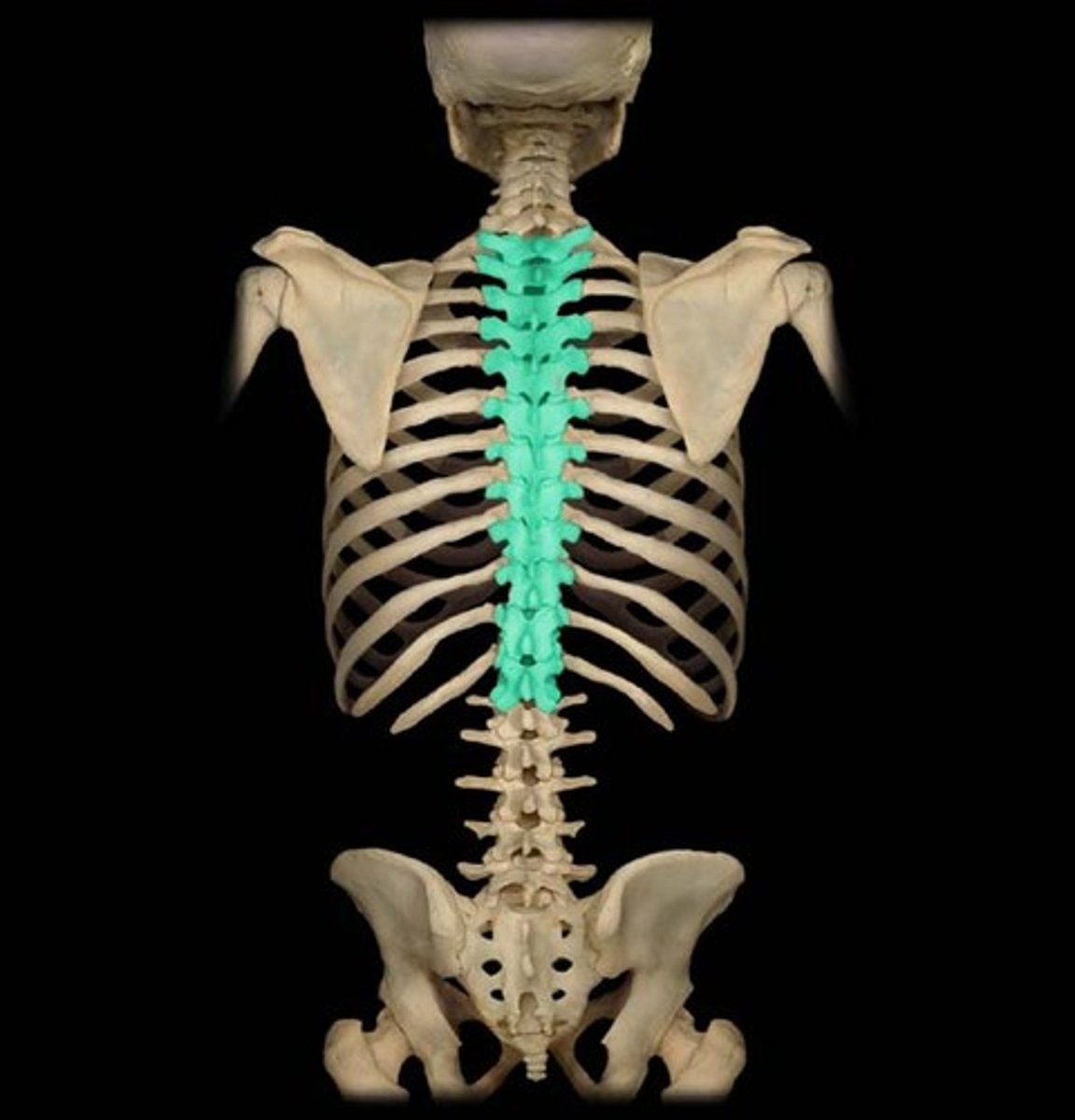
the vertebral column
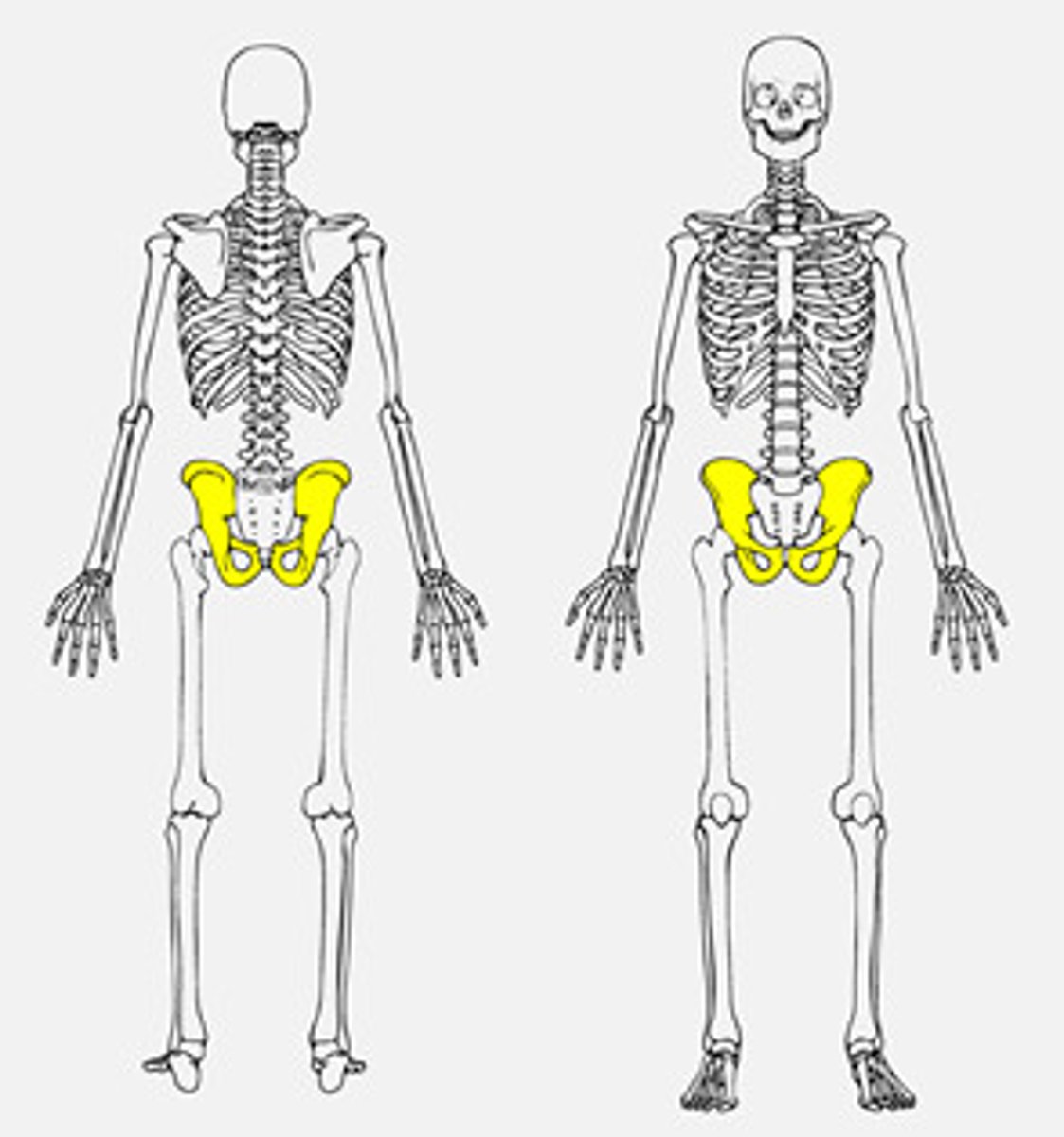
the pelvis
the coccyx
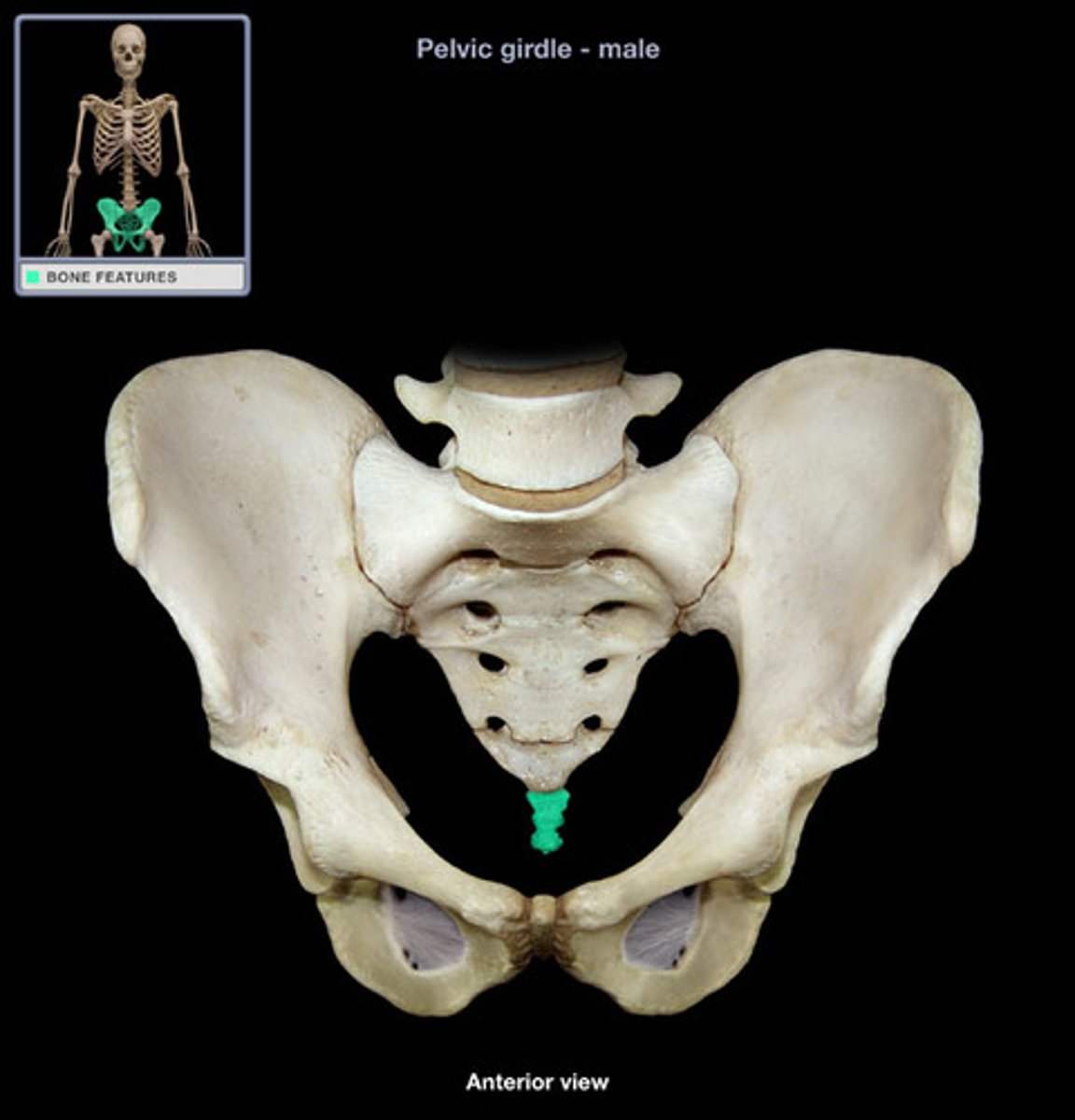
the femur
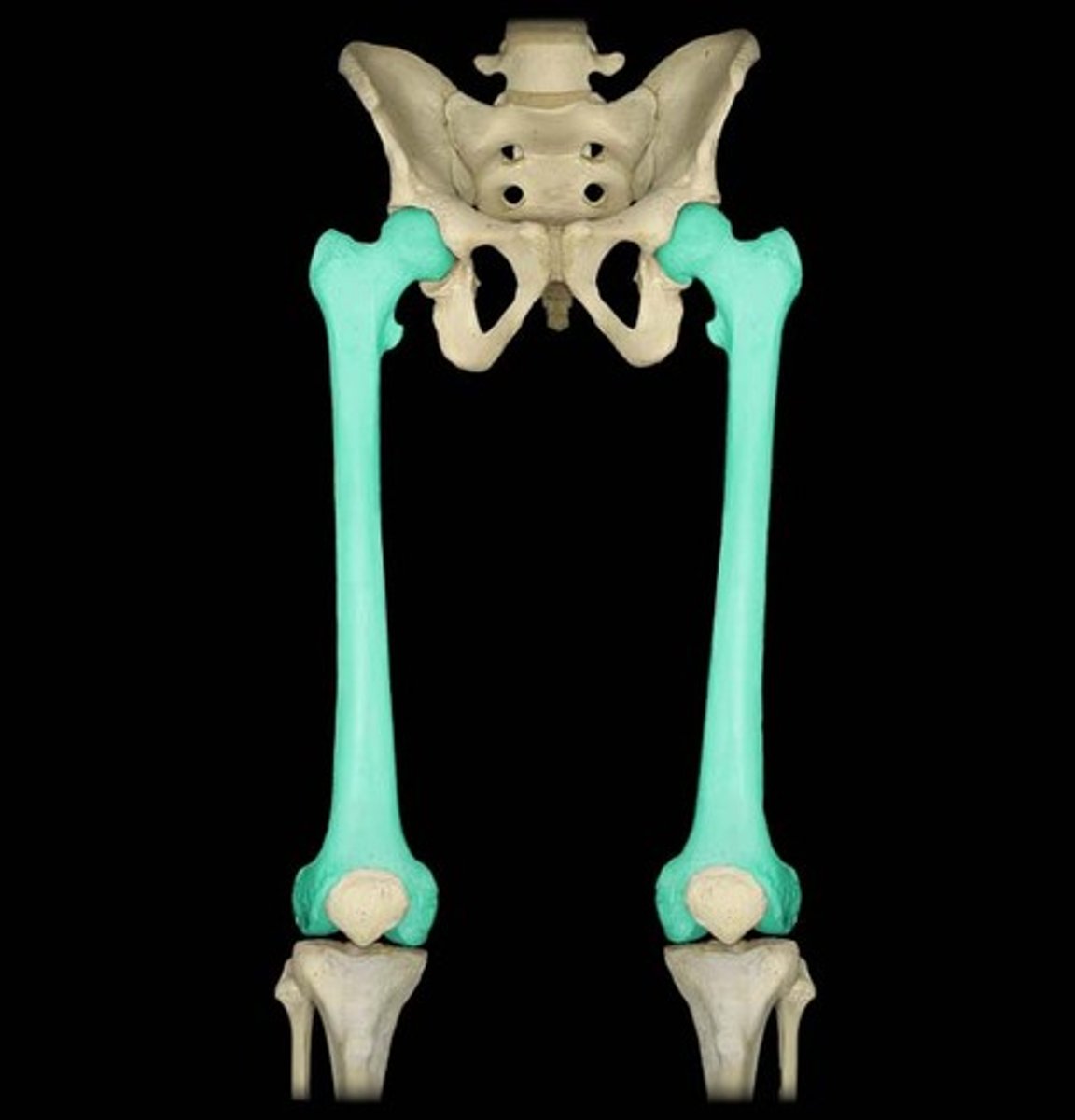
the patella
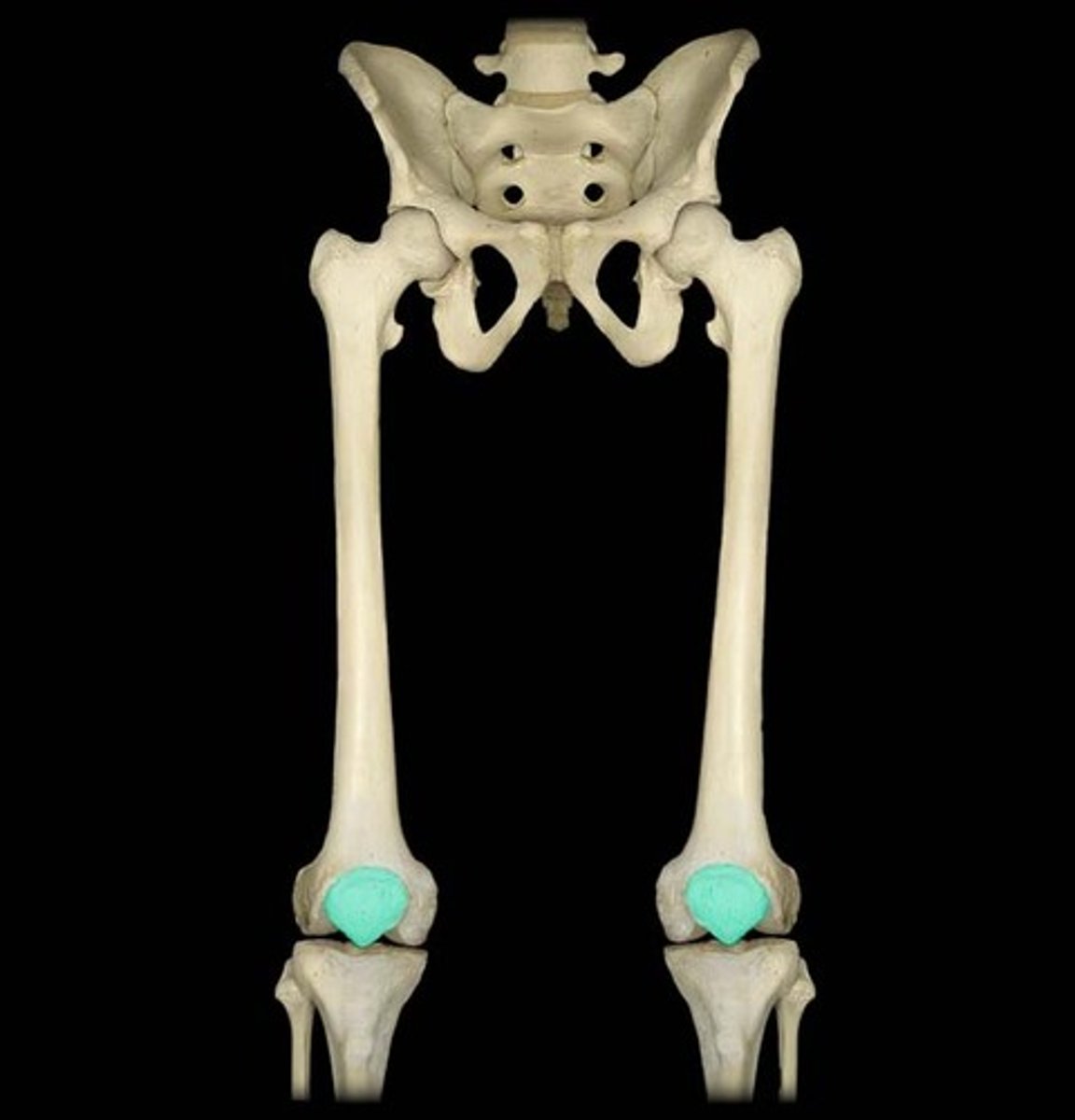
the tibia
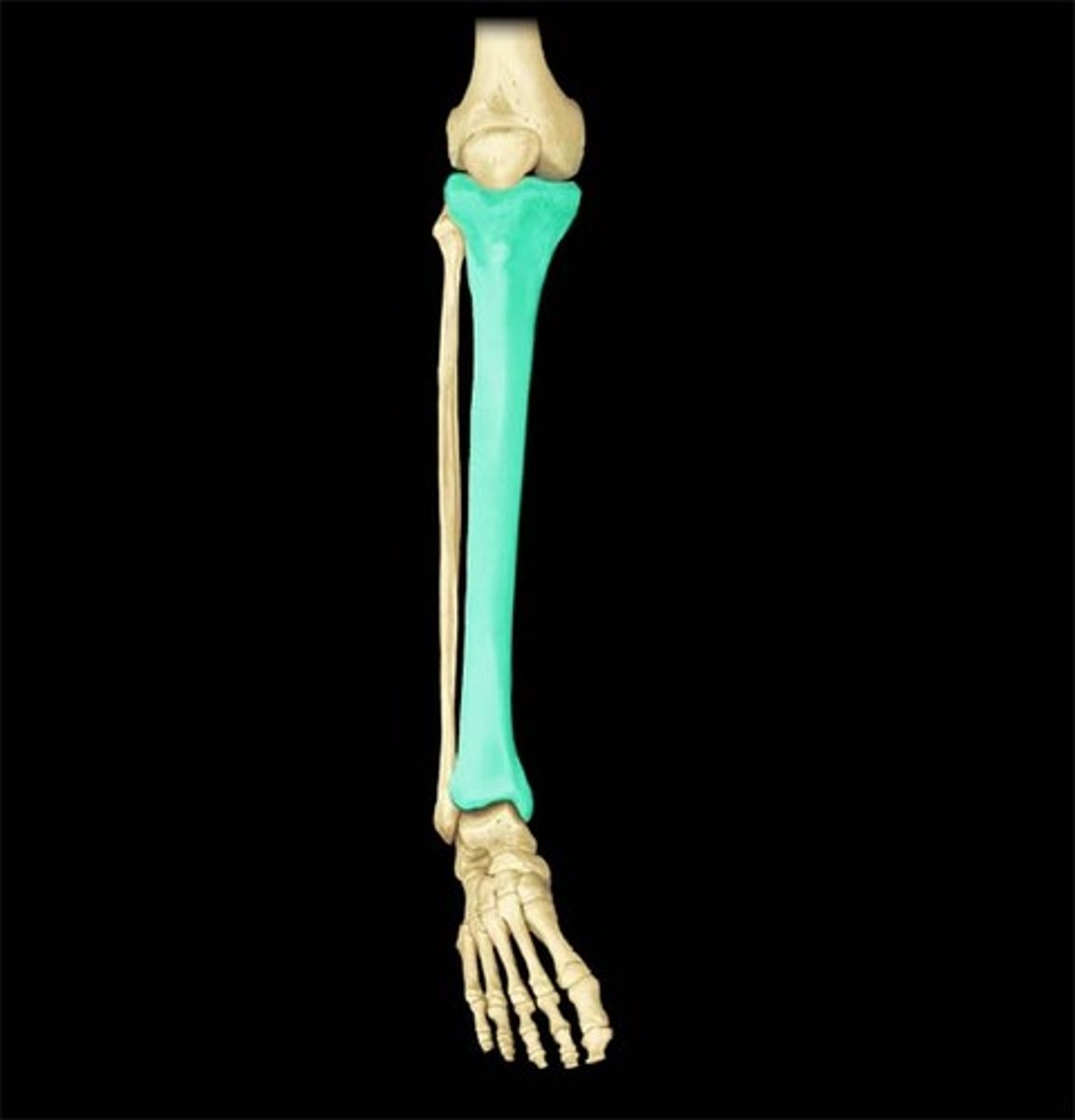
the fibula
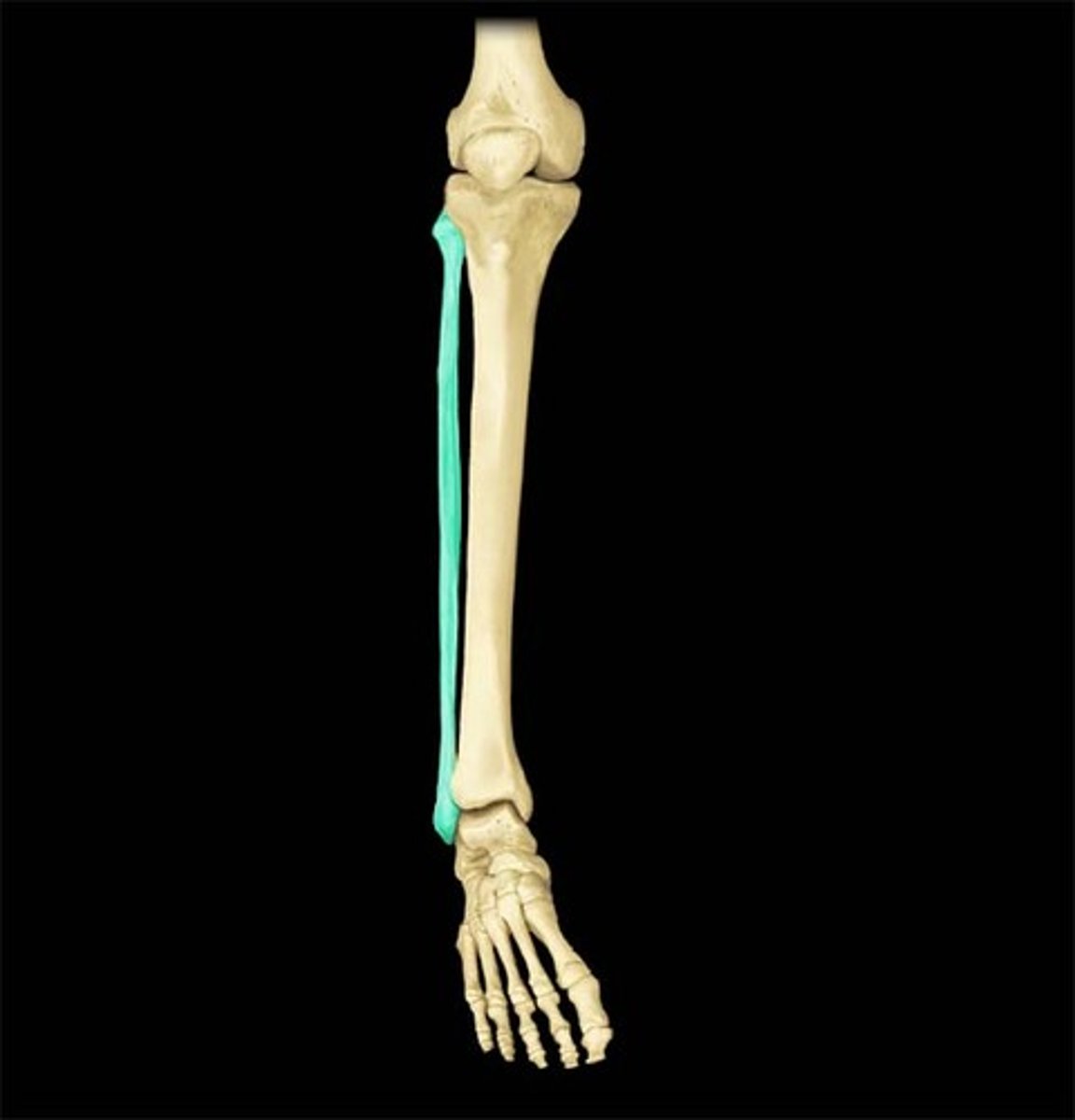
the tarsals
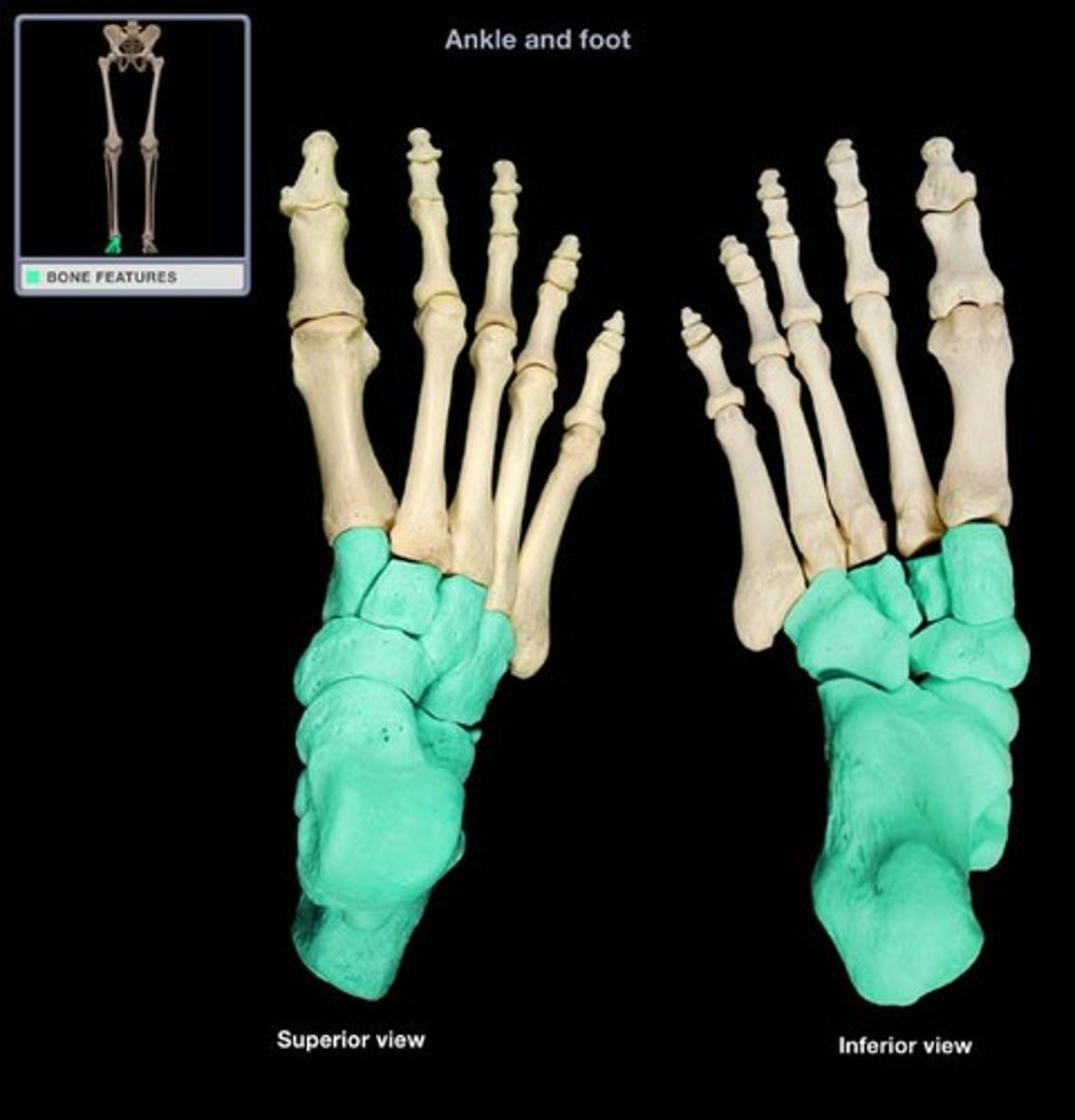
the metatarsals
Homeostasis
maintains a balance between the outside body temperature and internal body temperature.
levels of organization in the body
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, human body
Smallest/basic level of organization
cells
Four types of tissue
muscle, connective, nerve, epithelial
muscle tissue
body tissue that contracts and relaxes
connective tissue
Tissue that joins, protects, insulates, supports and cushions.
nerve tissue
tissue that carries messages back and forth between the brain, spinal cord, and every other part of the body
epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities inside the body.
Bones
Living organs; store minerals, and produce blood cells
Main parts of the bone
Compact bone, spongy bone, marrow, and periosteum
compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the periosteum and can resist shock and stress
spongy bone
bone tissue that is porous, provides strength, and aids in making new blood cells
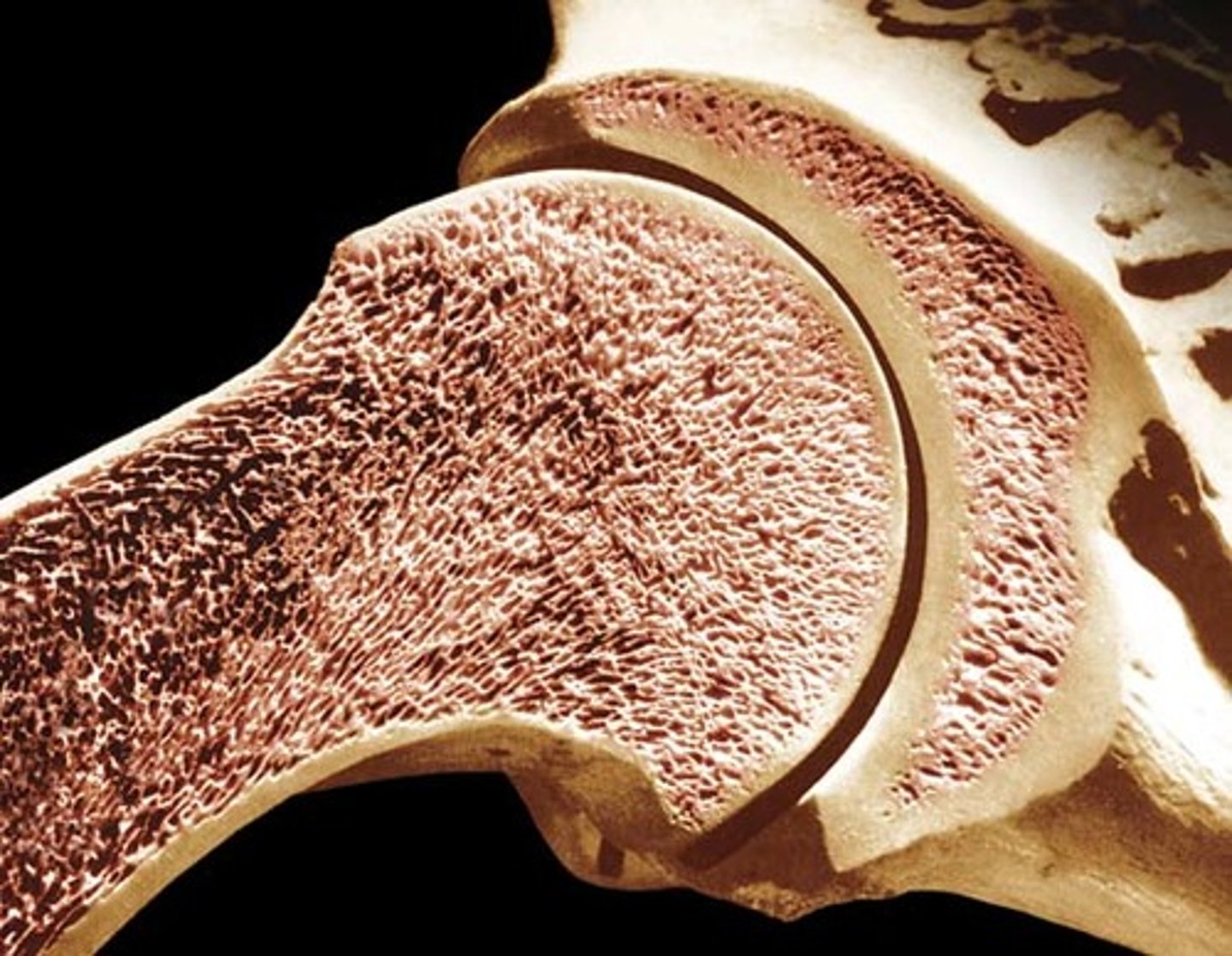
Periosteum
tough membrane covering the bone; ligaments and tendons are attached to it
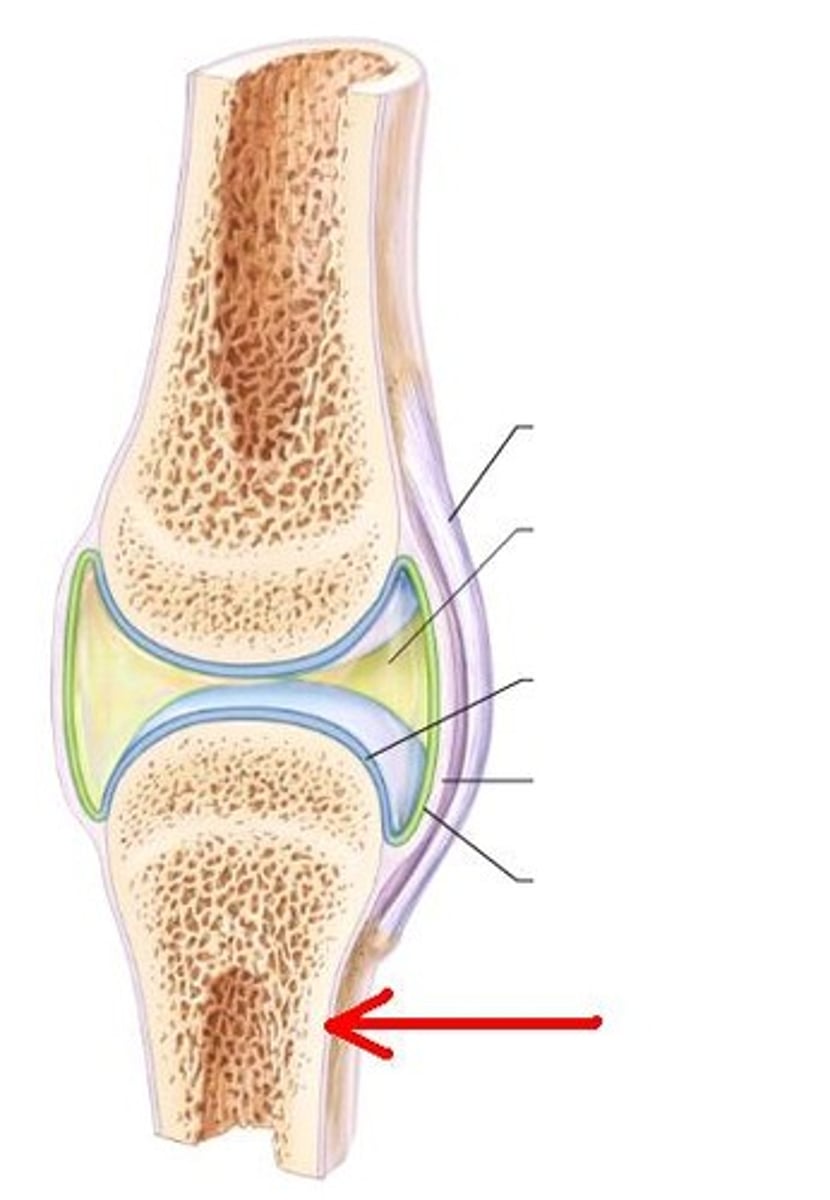
red marrow
produces red blood cells
yellow marrow
found in the cavities of long bones; stores fat
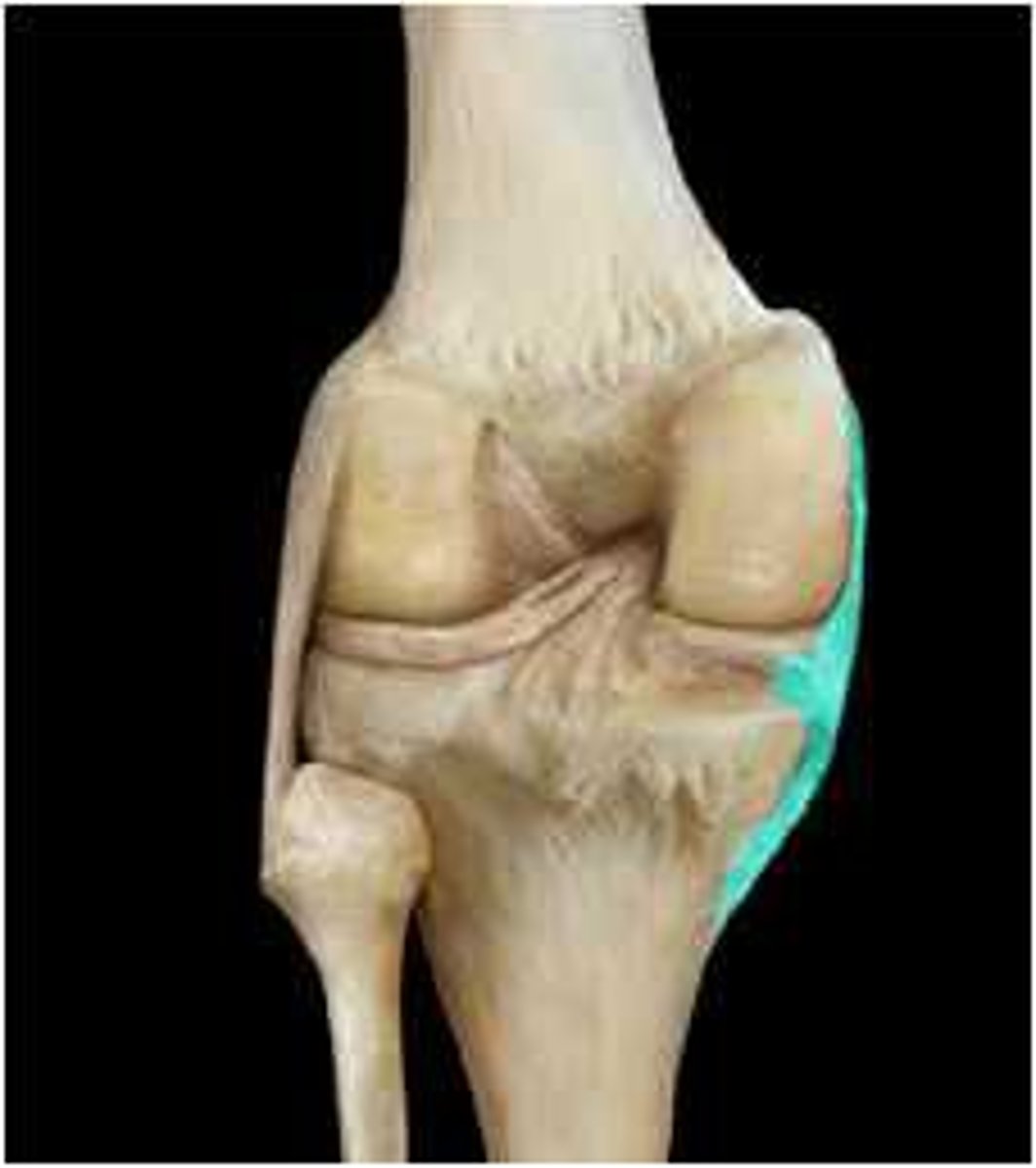
ligaments
strong band of connective tissue; connects bone to bone
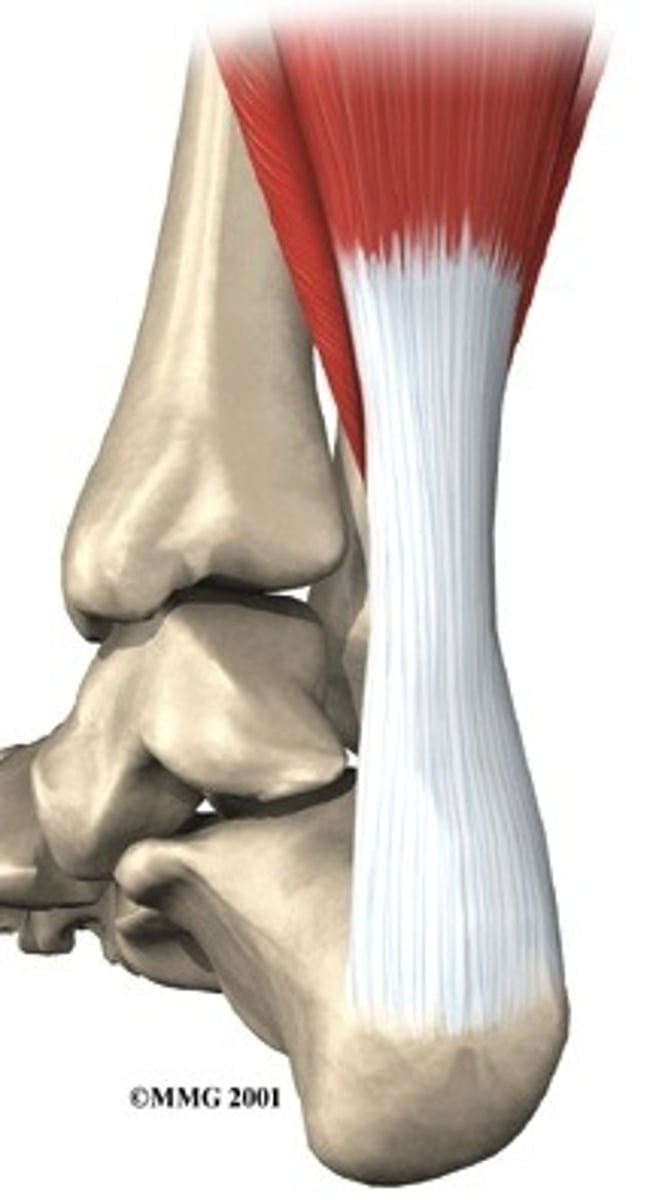
tendon
a tough connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone
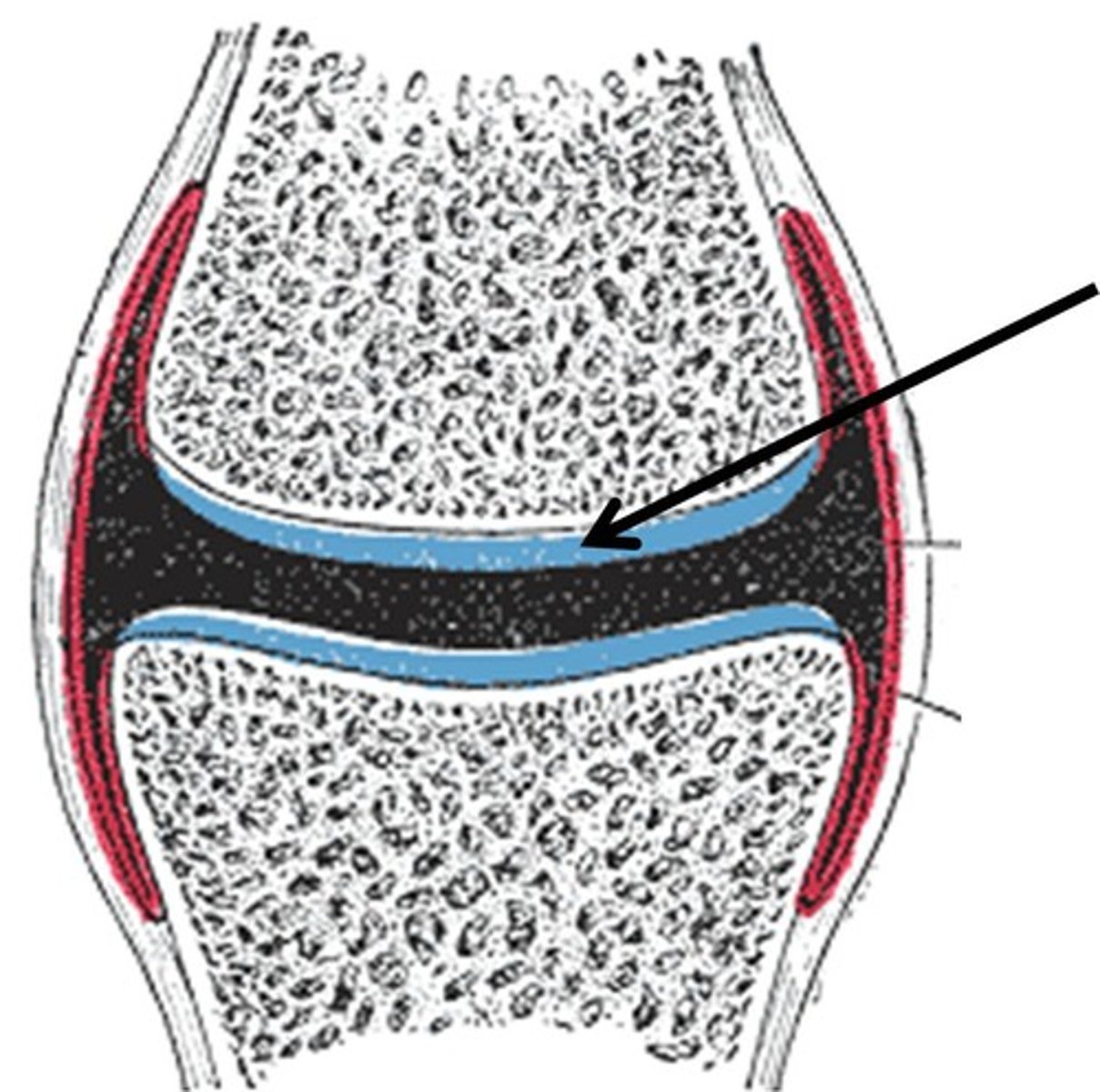
cartilage
tissue found at ends of bones and acts as a cushion between bones or where joints form
blood vessels
vessels that carry nutrients to the bone and wastes away
bone marrow
A soft tissue inside the bone that produces blood cells
joints
place where two or more bones join together
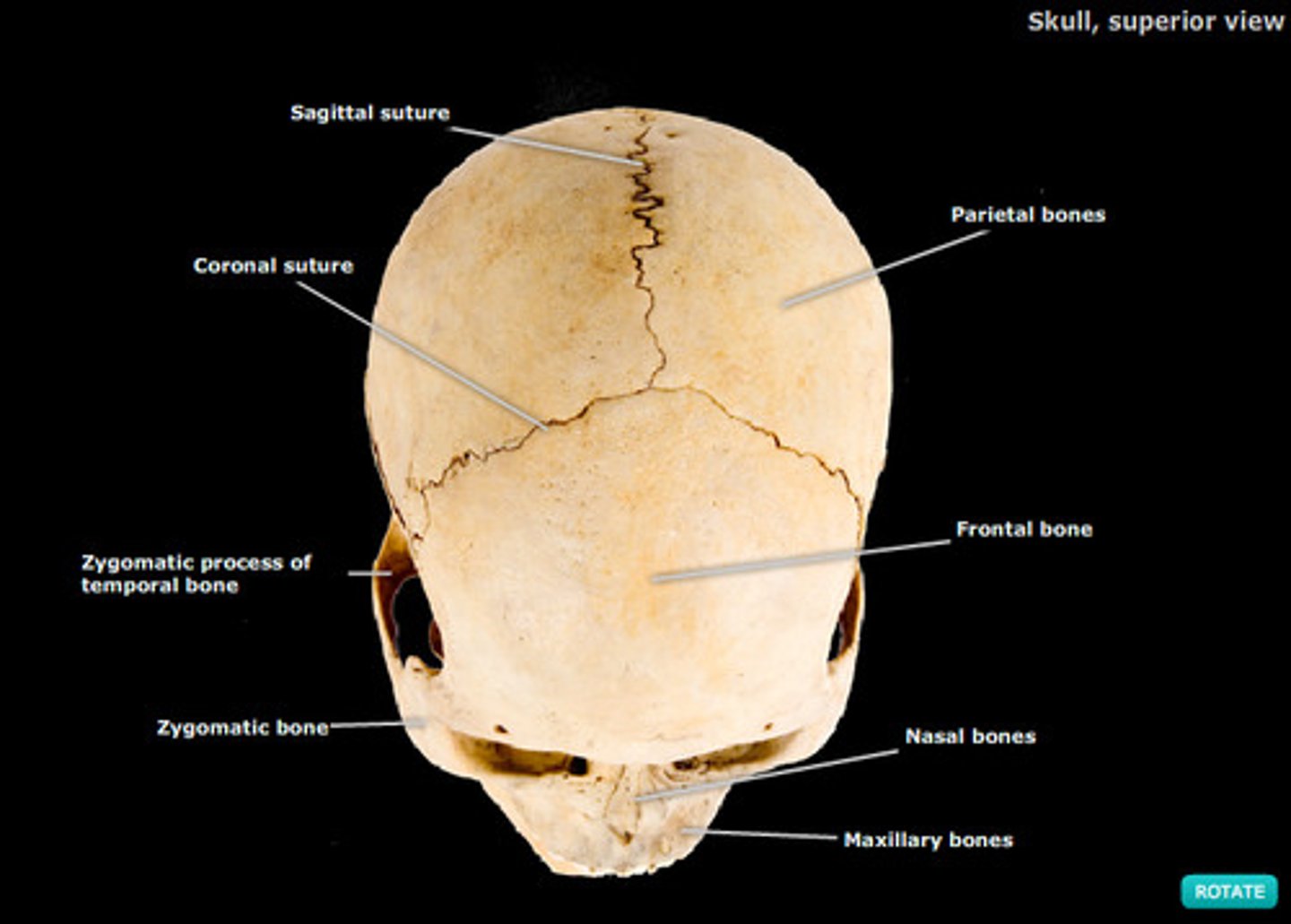
fixed joint
a joint that does not move; the skull
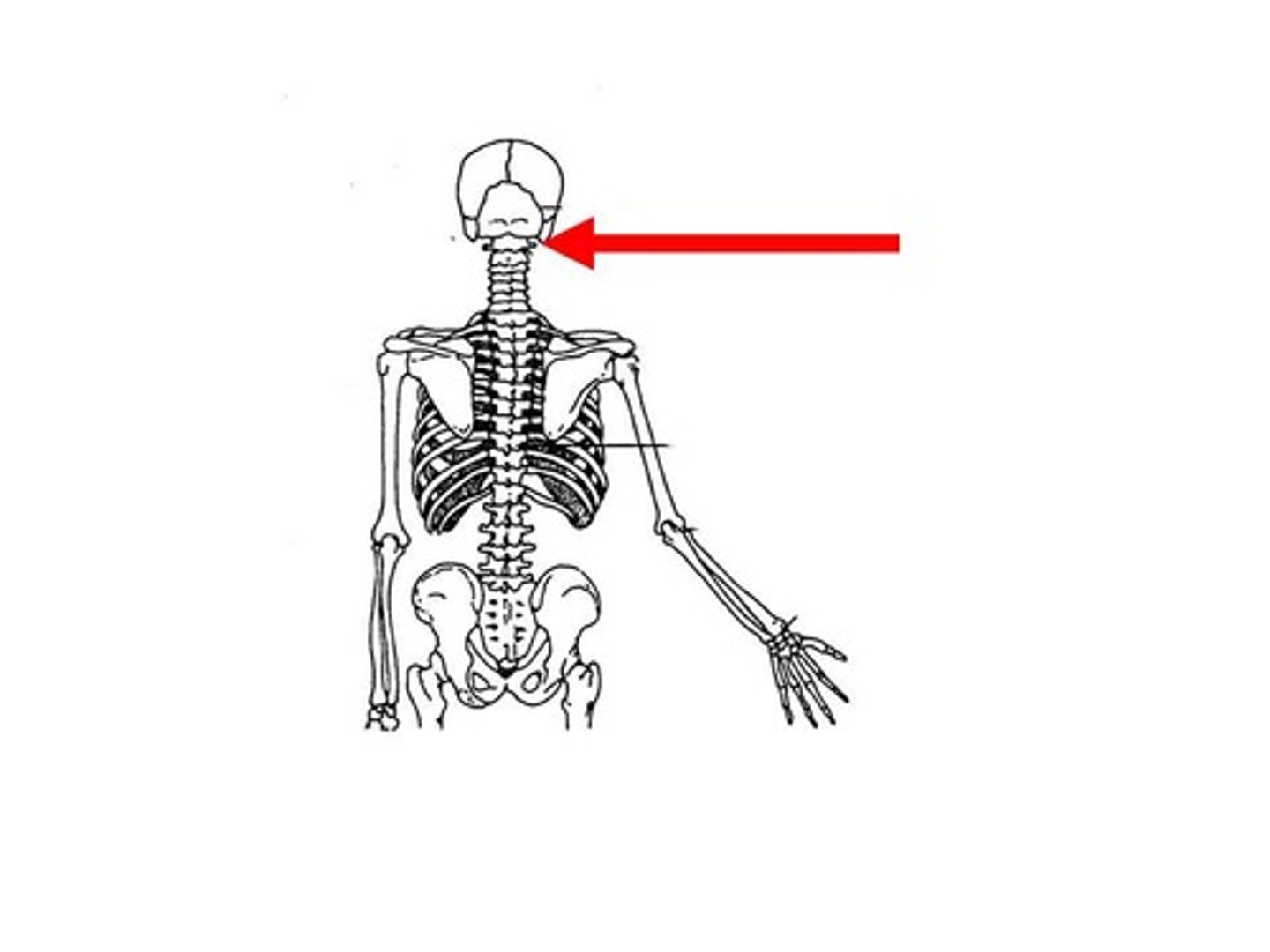
pivot joint
Allows limited rotation; the neck
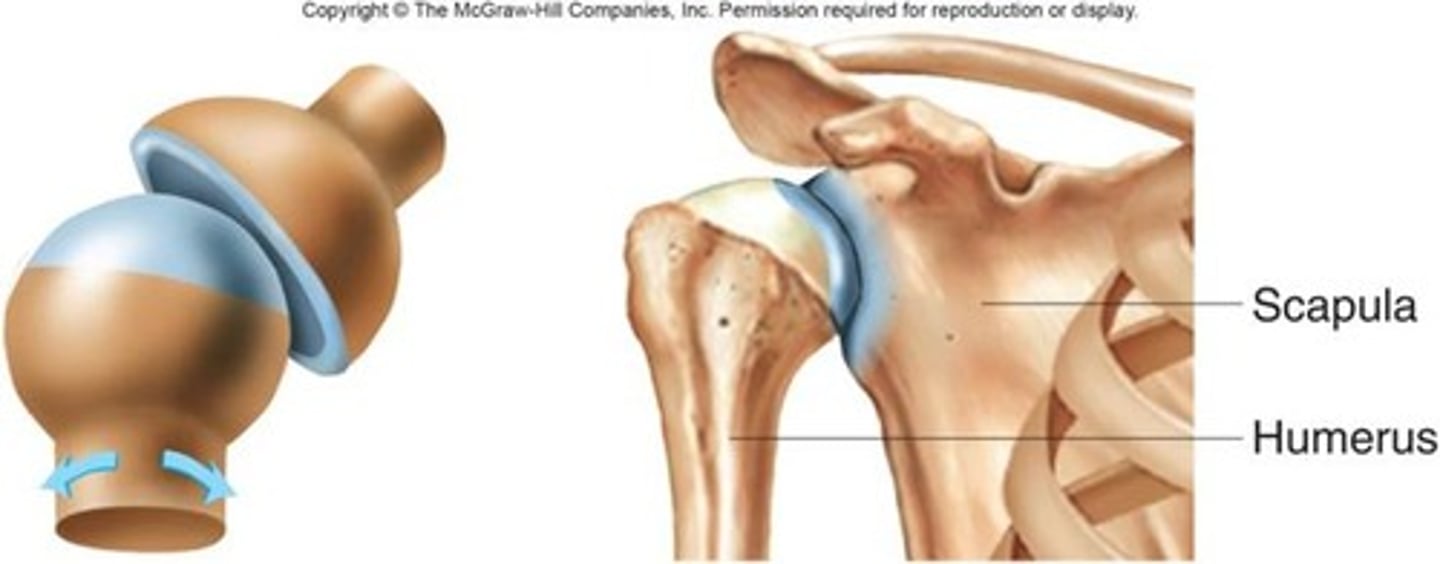
ball and socket joint
allows movement in all directions; the hip and shoulder
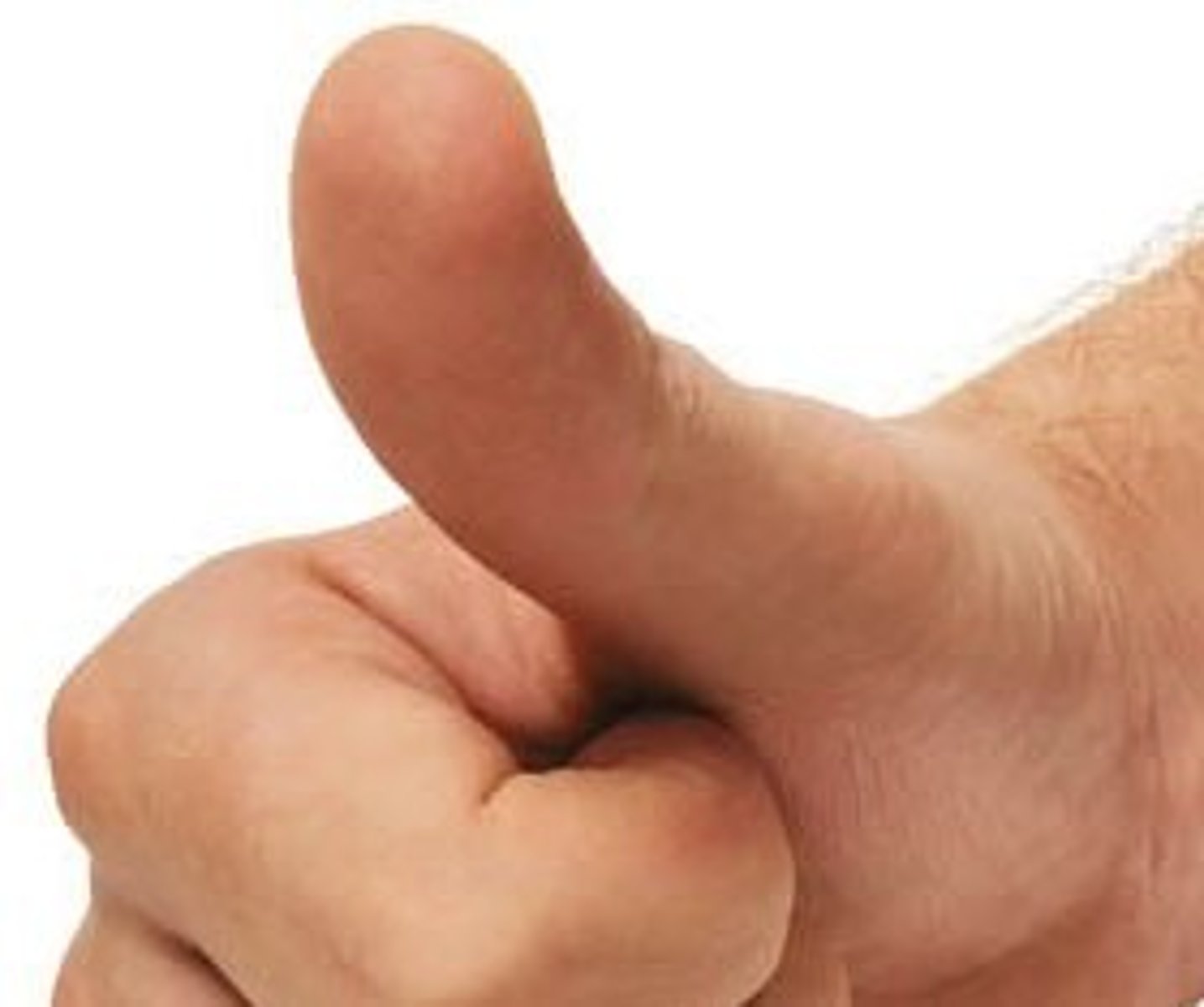
saddle joint
allows movement in two directions; the thumb

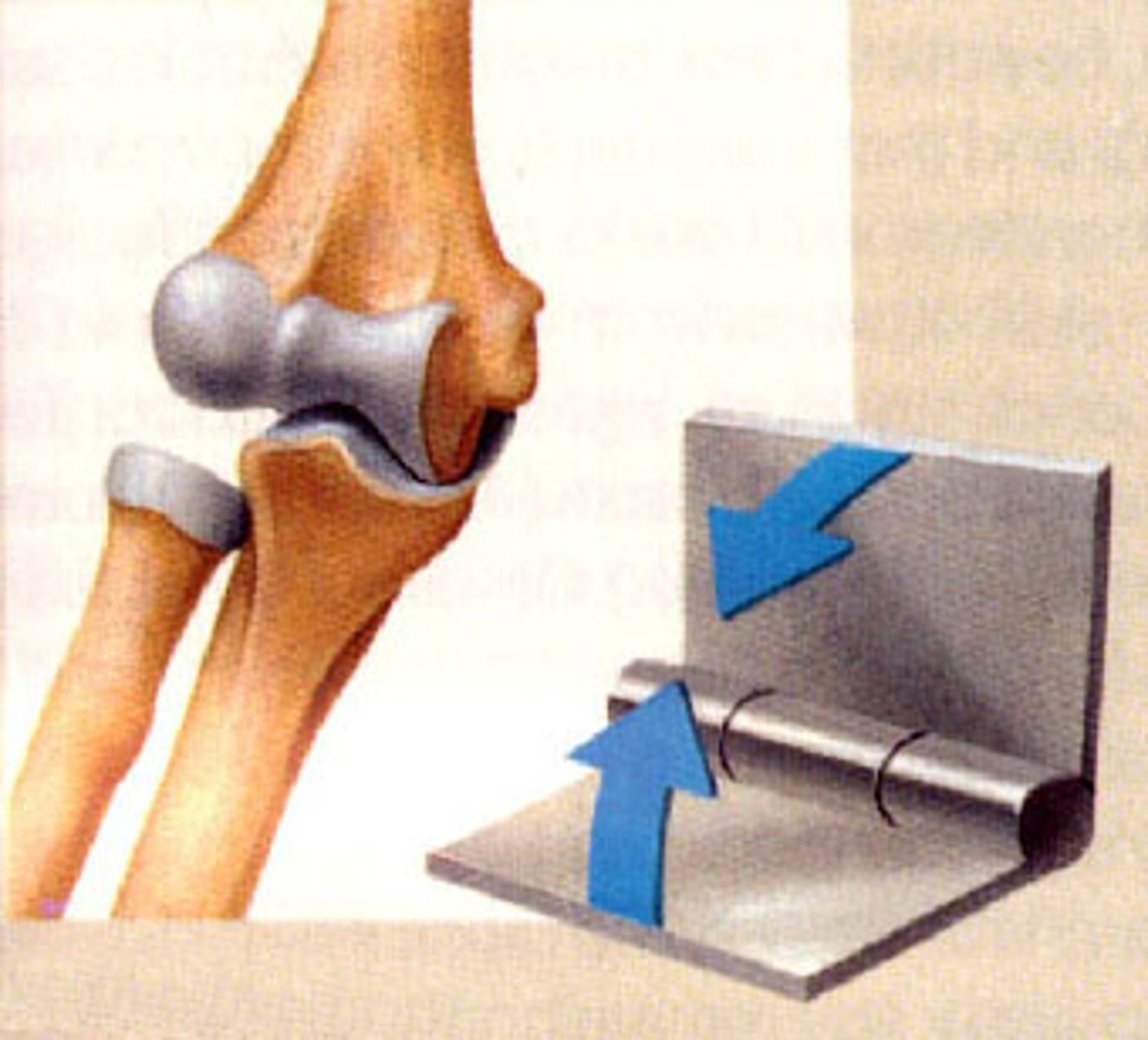
hinge joint
allows movement in one direction; the elbow, knee, or fingers
gliding joint
Allows one bone to slide over another; wrist and ankle
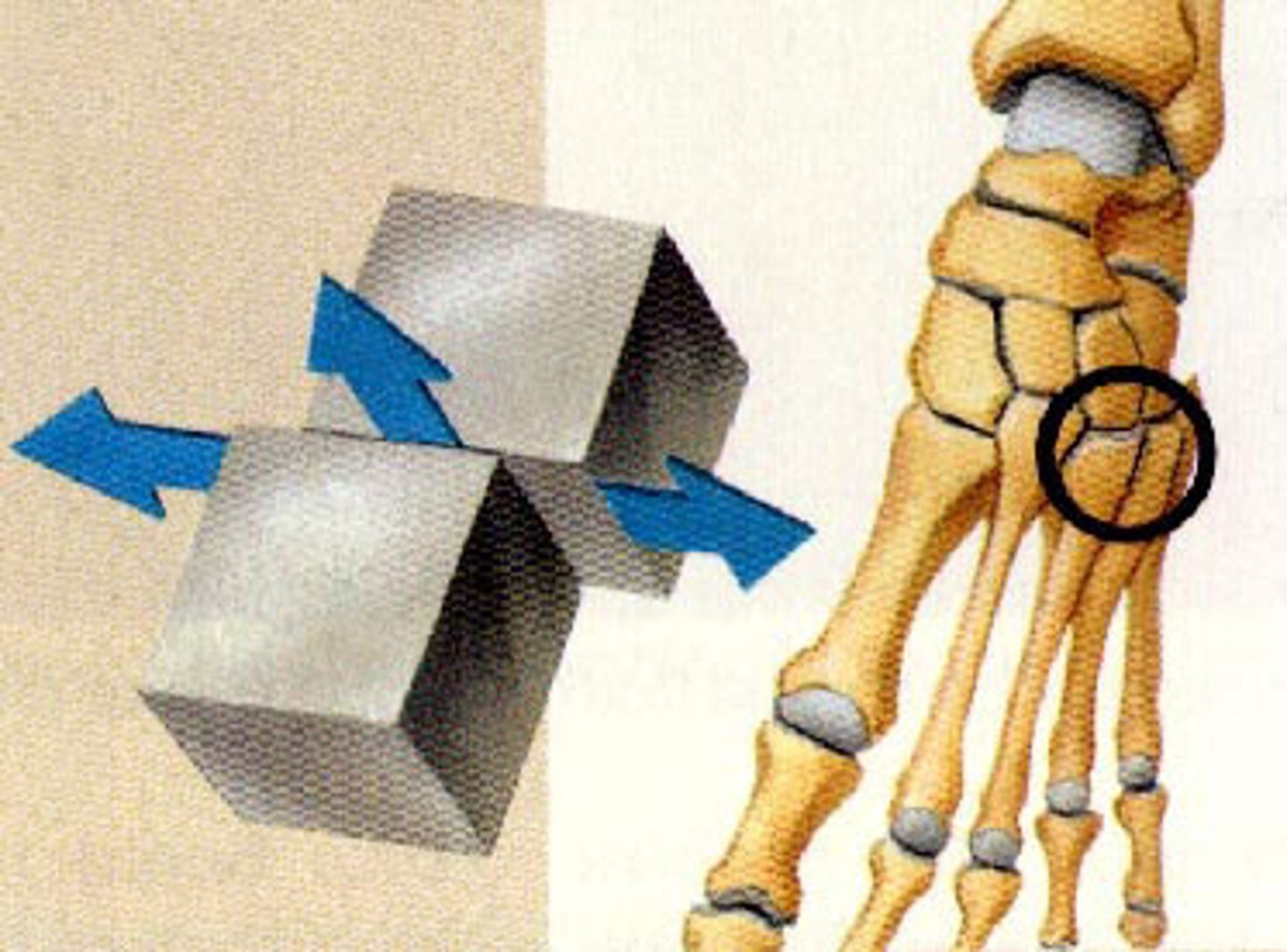
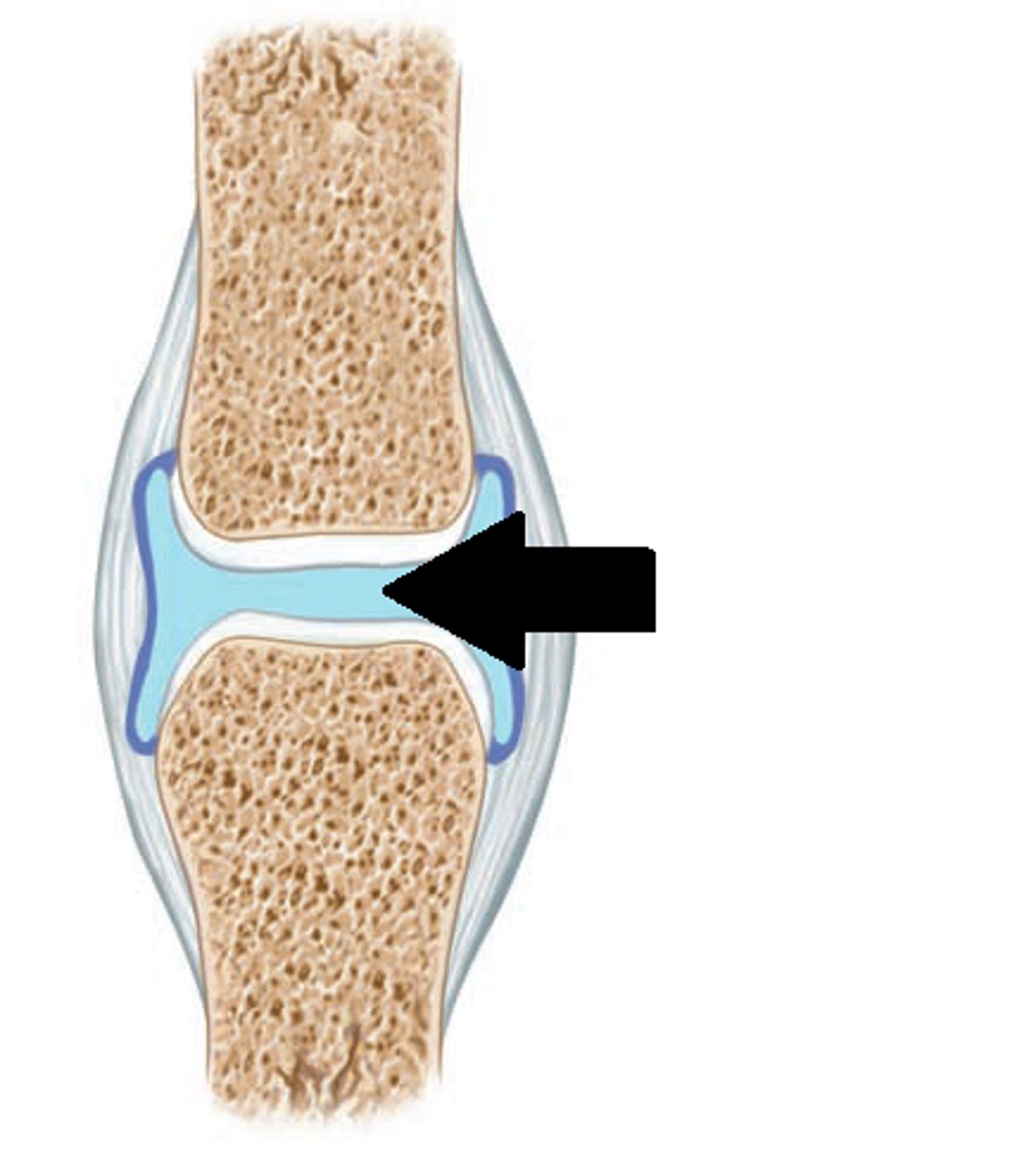
synovial fluid
reduces friction between bones; popping sound is an air bubble
cranium
skull
maxilla
upper jawbone
mandible
lower jawbone
zygoma
cheekbone
clavicle
collarbone
humerous
upper arm bone
ulna
lesser forearm bone (on pinky side)
radius
main forearm bone (on thumb side)
carpals
wrist bones
metacarpals
hand bones
phalanges
finger bones and toe bones
scapula
shoulder blade
sternum
breastbone
ribs
bones surrounding the chest cavity
vertebral column
spine
pelvis
hip bone
coccyx
vestigial structure - the tailbone
femur
upper leg bone or thighbone
patella
kneecap
tibia
shin bone
fibula
calf bone
tarsals
ankle bones
Metatarsals
foot bones
Makes bones strong
calcium
axial skeleton
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the cranium, sternum, rib cage, and vertebral column
appendicular skeleton
Part of the skeleton that attaches to the axial skeleton and has the limbs attached to it
Functions of the Skeletal System
1. Support
2. Movement
3. Blood cell formation (hemopoiesis)
4. Protection of internal organs
5. Detoxification (removal of poisons)
6. Provision for muscle attachment
7. Mineral storage (particularly calcium and phosphorus)
Axial Skeleton
Consists of 80 bones, in the skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and hyoid bone
Appendicular Skeleton
126 bones, upper and lower extermities plus two girdles. Half of the bones in the body are in the hands and feet
Long Bones
longer than they are wide; shaft and 2 ends. Ex: Humerous
Short Bones
roughly cube shaped. Ex: ankle and wrist bones
Sesamoid Bones
short bones, but with tendons. Ex: Patella
Irregular Bones
odd shapes, do not fit into the other classes. Ex: Vertebrae
Flat Bones
Thin, flat and often curved. Ex: sternum, scapulae, ribs, most skull bones.
cevical vertebrae
7 bones, top of the spine. transverse formina, bifid spinous process, vertebral prominens. Contains Atlas and Axis.
Atlas
Supports the head.
Axis
pivots to turn the head
thoracic Vertebrae
12 bones, middle of the spine. long spinous process, rib facets. Ribs attach here.
Lumbar Vertebrae
5 bones, bottom of the spine. Large bodies, short spinous processes
Saacrum
five saacral vertebrae fused, protects reproductive, excretory, and digestive organs. good cite for muscle attachment in the legs
coccyx
3-5 fused coccyx vertebrae
Ball & Socket join
allows for a full range of motion Ex: hip, shoulder
Pivot
one bone pivots in the arch of another Ex: Axis and Atlas
Saddle
two directional movement between thumb and trapezium carpel Ex: thumb
Hinge
door hinge- bending and extending Ex: elbow, knee, finger joints
Ellipsoid
side to side and back and forth Ex: radius end into carpal bones
Plane or Gliding
least movable- side to side only Ex: between vertebrae