Redox Titrations (chptr 15)
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Learning Objectives: (1) be able to explain conceptually what a redox reaction is, and (2) be able to complete calculations to determine the three regions of a redox titration curve.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Antioxidants are… ?
substances that neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that can damage cells and cause disease.
What are antioxidant assays?
Antioxidant assays are laboratory methods used to measure the ability of compounds to scavenge free radicals and prevent oxidative stress in biological systems.
What do we need for quantitative redox reactions?
a 1:1 molar equivalency —> STOICHIOMETRY
a way to check if the reaction is proceeding as intended —> COLORIMETRY or ELECTRICAL POTENTIAL READING
Potentiometry
the use of electrodes to measure voltages that provide chemical information
Electrode
conducts electrons into or out of a chemical species in a redox reaction
inert or counter electrode
an electrode that does not participate in the redox chemistry except as a conductor of electrons (i.e. Pt)
indicator or working electrode
an electrode that responds to analyte
reference electrode
and electrode that has a constant potential
About indicator electrodes:
Two Broad Classes:
Metal Electrodes
they develop an electric potential in response to a redox reaction at the metal surface (i.e. Pt (inert))
Pt is what’s most commonly used
Purpose = to transmit electrons to or from species in solution
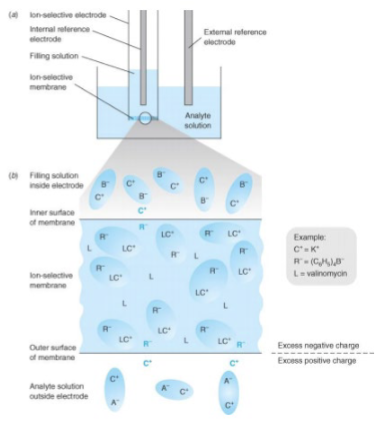
Ion-Selective Electrodes
selective binding of one type of ion to a membrane generates an electric potential
DO NOT involve redox processes
The net driving force for a reaction is expressed by… ?
the Nernst Equation
The two terms include the driving force under standard conditions, Eo, and a term showing the dependence on reagent concentrations, or, really, activities
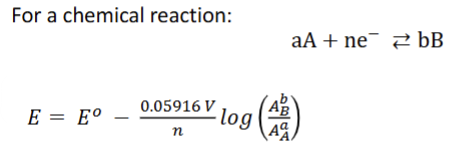
Redox Titration
based on an oxidation-reduction reaction between analyte and titrantto determine the concentration of an unknown solution.
What is the significance of the redox titration curve?
The redox titration curve is significant as it illustrates the relationship between the volume of titrant added and the potential of the solution, allowing for the determination of the endpoint of the titration, helping to identify the concentration of the analyte and providing insights into the redox behavior of the system.
Many RedOx reactions are… ?
atom-transfer reactions
Equivalence point is marked by… ?
a steep rise in voltage.
The voltage at any point of a titration depends on… ?
the ratio of reactants
synmmetric redox titration curve when it’s a 1:1
asymmetric when it’s not 1:1
Redox Indicator
a compound that changes color when it goes from its oxidized to its reduced state
Gran Plot
uses data from well before the equivalence point (Veq) to locate Veq