topic 5: communication and the internet
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
WAN
uses satellites and radio waves to connect and usually spreads over a a wide geographical area
internet
a collection of inter-connected networks
WWW
a method of accessing information on the internet
HTTP
the protocol governing the transfer of hypertext web pages across the internet
ISP
internet service provider provides access to the internet for private individuals and businesses
web servers
stores and distributes web pages
URL
a web address
DNS
translates domain names into IP addresses
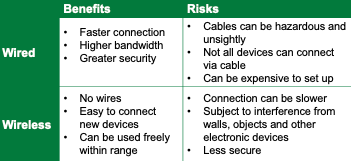
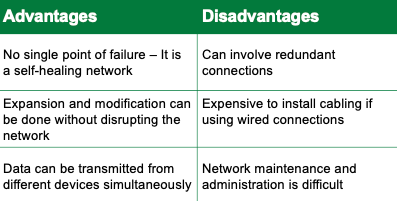
wired vs wireless
LAN
covers a relatively small geographical area
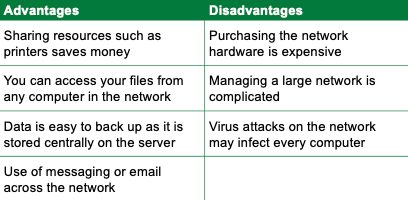
advantages and disadvantages of networking
PAN
a network communicating between computer devices
bandwidth
the amount of data that can be carried at a time
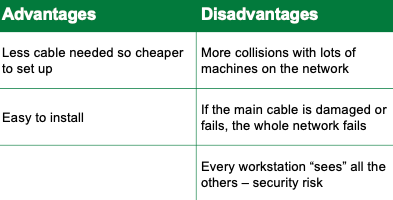
bus
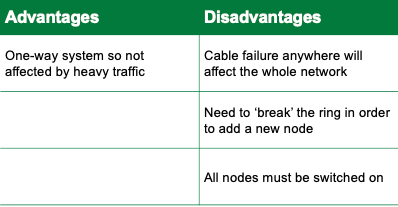
ring
star
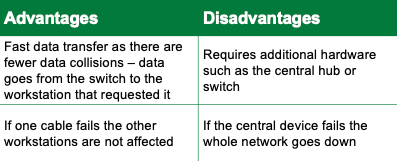
mesh
router
sends data packets on their way in the best direction
hub
when a packet of data is received, it broadcasts the packet to all devices on the network
switch
send packets to the intended recipient using its mac address
advantages of a client server
all data can be backed up centrally
security is better as data is held in one location
users can log in from any computer on the network
advantages of peer to peer
easier to set up
no special software is requires
individual computers share a printer, router, modem and other hardware
users can communicate directly with each other and share each others’ files
drawbacks of peer to peer
viruses and malware are easily transferred over this type of network
data recovery and backup is not done centrally
packet header
contains packet number, total number of packets in the transmission, source address, destination address
SMTP
protocol for sending emails between servers
POP
holds email for individual until picked up then deletes it from the server
IMAP
stores emails on a server so it can be accessed and edited from anywhere
TCP
how messages are broken up into packets and reassembled at the destination
TCP/IP protocol stack
application
transport
network
link
application layer
encodes data sent so it can be understood be recipient (FTTP or FTP)
transport layer
sets up communication between two computers
network layer
attaches the IP address of the sender so the recipient will know who sent it
link
the physical hardware that connects the two hosts
physical security
controlling access to critical parts of a network using physical methods
malware
malicious software designed to disrupt the use of a computer system
social engineering
the art of manipulating or conning individuals into giving away private information
phishing
a trick email the seems legitimate that tricks user into giving up personal data
shoulder surfing
direct observation of a user entering their security details
software patch
an update to a program to improve it or fix a bug
DoS attack
attempts to flood a website server with an overwhelming number of data requests