thermodynamics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
what are state functions?
there is no memory in the system
don’t need to know how values were reached
what is an extensive quality?
what is an intensive quality?
extensive depends on amount e.g. mass/vol
intensive is independent of amount e.g. temperature
extensive / amount gives intensive or extensive?
intensive
what is the equation for work?
involving pressure?
work = force x distance
work = pressure x area x distance moved
what is the equation for pressure?
pressure = force / area
when does a system do work against the atmosphere?
when the reaction involves expansion of the system
why is work done by the system on the surroundings negative?
the system loses energy
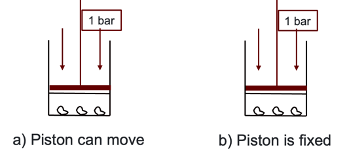
why does the temperature increases less when the piston can move?
some energy is used to move the piston (do work) so less energy to increase the temperature
what is internal energy?
what is the symbol?
the total energy of the system
U
How to calculate enthalpy using internal energy?
H = U + PV
PV is work due to atmosphere
what is ΔU?
the energy transferred as heat when the volume of the system is constant
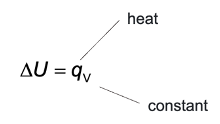
what is ΔH?
energy transferred as heat when the pressure of the system is constant

Is heat, q, a state function?
Is work, w, a state function?
No, they both depend on the conditions
What is a path function?
One where the conditions must be specified
Why is ΔU ≈ ΔH?
For which conditions?
change in volume for a reaction is likely to be negligible when only liquids or solids involved
this does not apply to gases
what is Hess’ law?
the total energy change is independent of the path taken
what is heat capacity?
the energy as heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1K
what is the equation for heat capacity?
is it a state or path function?

is heat capacity intensive or extensive?
extensive as depends on amount
what is molar and specific heat capacity? (equations?)
intensive or extensive?
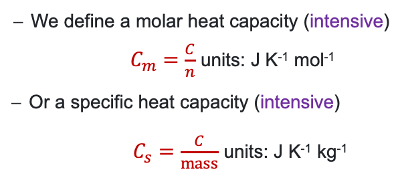
What happens if heat supplied to a gas at constant pressure?
Heat is used to increase internal energy (increases T), also doing work as gas expands
What is heat capacity at constant volume equation?
Constant pressure?
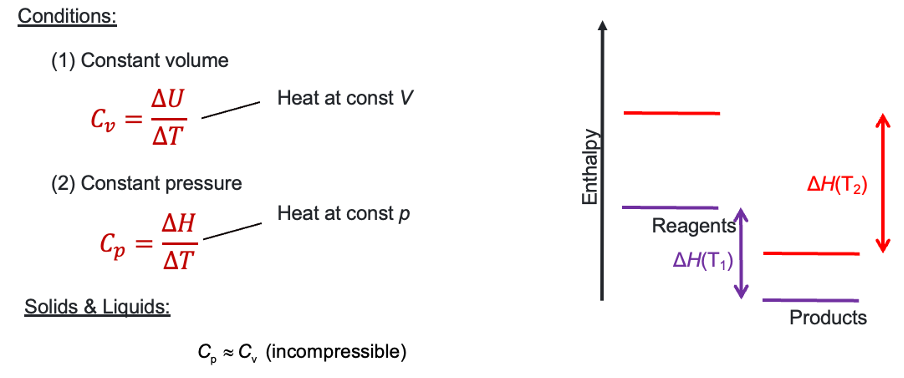
for a gas at same ∆T, is Cp or Cv bigger?
at constant pressure, energy also used to do work so more energy needed to give same ∆T
∆H = ∆U + PV so for same ∆T, Cp is bigger
why is Cp ≈ Cv for solids and liquids?
incompressible
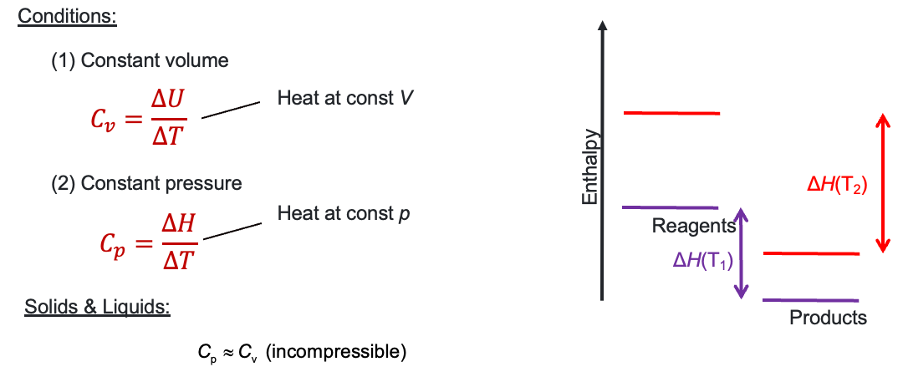
For T1 and T2, does products or reagents have the greater Cp?
reagents as change in enthalpy of reagents is much greater
both undergone same ΔT.
Does the entropy of the universe increase or decrease for a spontaneous reaction?
Increase
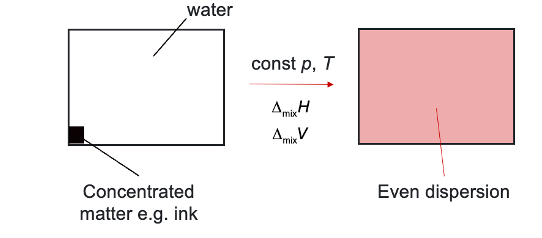
ideal mixing by diffusion
when do substances form an ideal mixture?
when ΔmixH = 0 and ΔmixV = 0
is entropy change positive or negative when mixing?
positive
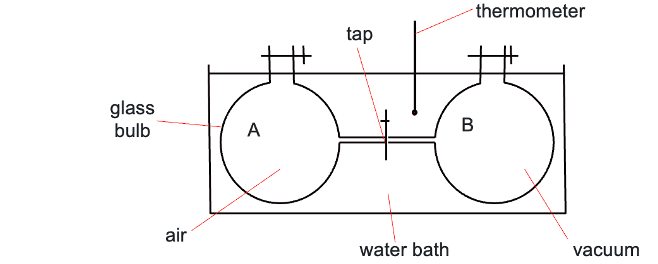
joule gas expansion
what happens when tap between A and B is opened?
ΔT?
work done?
air rushes into B, ΔT = 0
gas in A moves through tap into B until equal amount in both
water bath keeps it constant temperature
no work is done, ΔU = ΔH = 0
entropy equation using heat
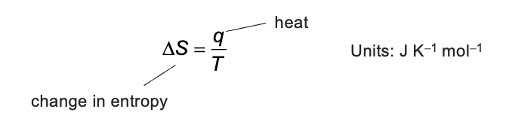
how does combined entropy of system and surroundings change during spontaneous irreversible reactions?
increases
ΔS system + ΔS surroundings >0
how does combined entropy of system and surroundings change during reversible processes?
stays constant
ΔS system + ΔS surroundings = 0
ΔS system = - ΔS surroundings
ΔS total ≥ 0
ΔS equation using volume?
does entropy increase/decrease as volume increases?
same amount of gas distributed over larger vol, so more disorder

ΔS equation using pressure?
does entropy increase/decrease with increasing pressure?
entropy decreases with increases pressure

does entropy increase or decrease with increasing temperature?
increases
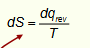
how does this show that entropy increases with temperature?
(integrate with Cp or Cv)
what is the best organised physical state of absolute entropy?
why?
the perfect crystal
the spatial relationship between each molecule is identical
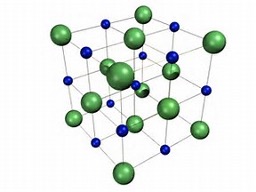
how to calculate absolute entropy?
the area under a graph of Cp / T vs T
experimentally measure Cp at different temperatures
Work done when ΔrG < 0
the more negative, the more work can be done by the system
Work done when ΔrG = 0
no work can be extracted from a system at equilibrium
what does it mean when ΔrG > 0?
the reverse process is spontaneous