BIPN 100 Lecture #1 Terms - Emergent Properties in Physiology and Introduction to Neurons
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintenance of stable internal environment conditions; dynamic steady state
What are the internal environments of Homeostasis?
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Extracellular Fluid (ECF) - also includes interstitial fluid (ISF), fluid between cells
What are the different steps of the Homeostatic Reflex Loop?
Stimulus— change in environment
Sensor— specialized receptor, monitors regulated variable
Integrating Center— the control
Effector— caries out response
Response/Compensatory Mechanism— response that returns homeostasis
Negative Feedback Control
Homeostatic, keeps system at/near setpoint by opposing or removing signals (ex. blood pressure)
Positive Feedback Control
response reinforces stimulus, further moving stimulus away from normal value until event (ex. uterine contractions when pregnant)
Law of Mass Balance
amount of a substance in the body remains constant
any gain must be offset by an equal loss
Name some of the parts of a neuron.
Plasma membrane
Dendrites
Soma/Cell Body
Axon Hillock
Axon
Axon Terminal
Synapse
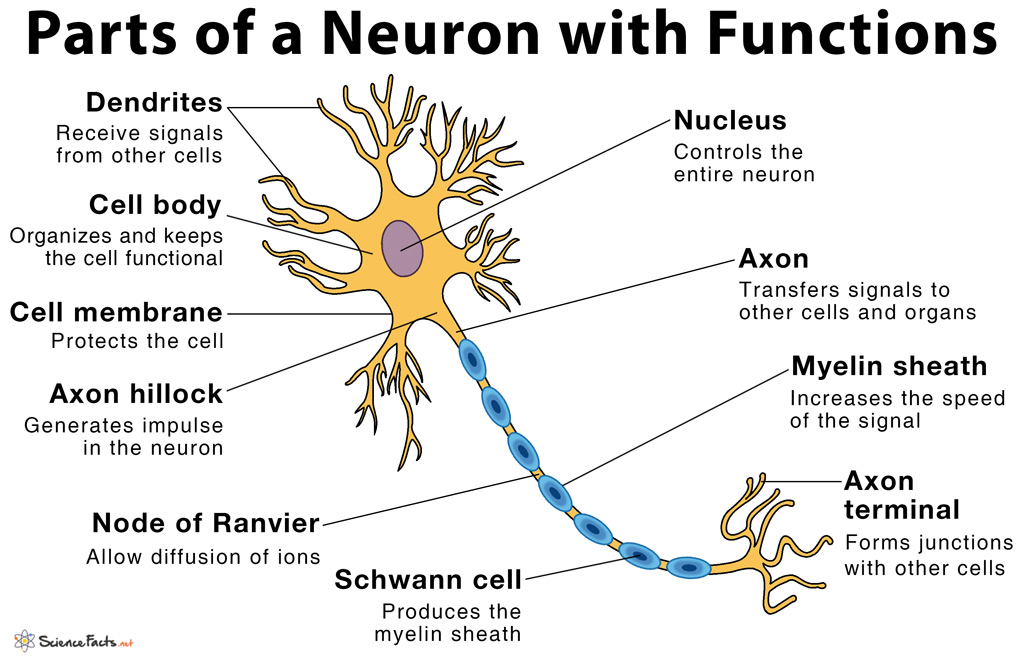
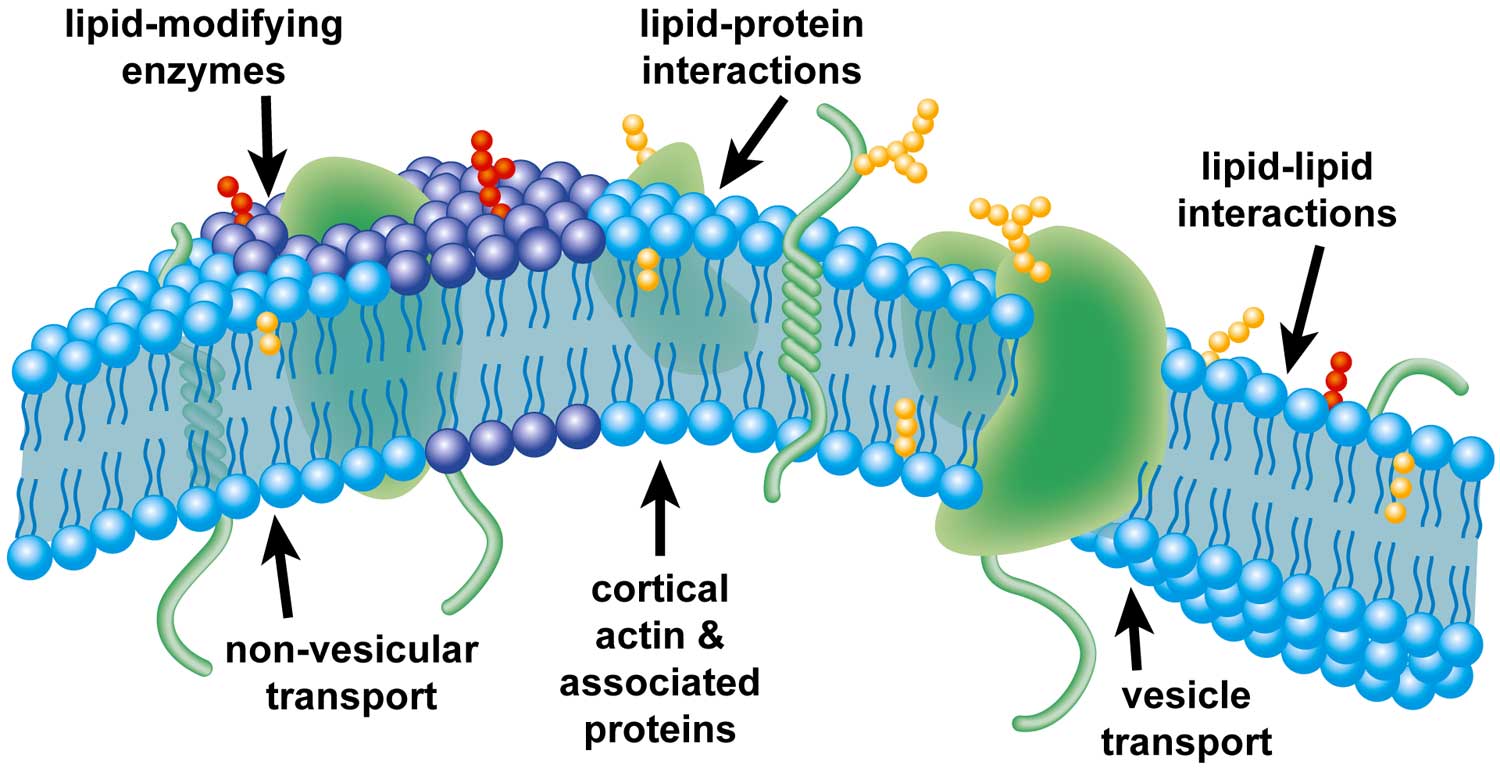
Plasma Membrane
consists of both lipids and proteins where receptors and channels allow specific molecules to pass through
Dendrites
thin, branched processes that RECEIVES incoming info from other neurons
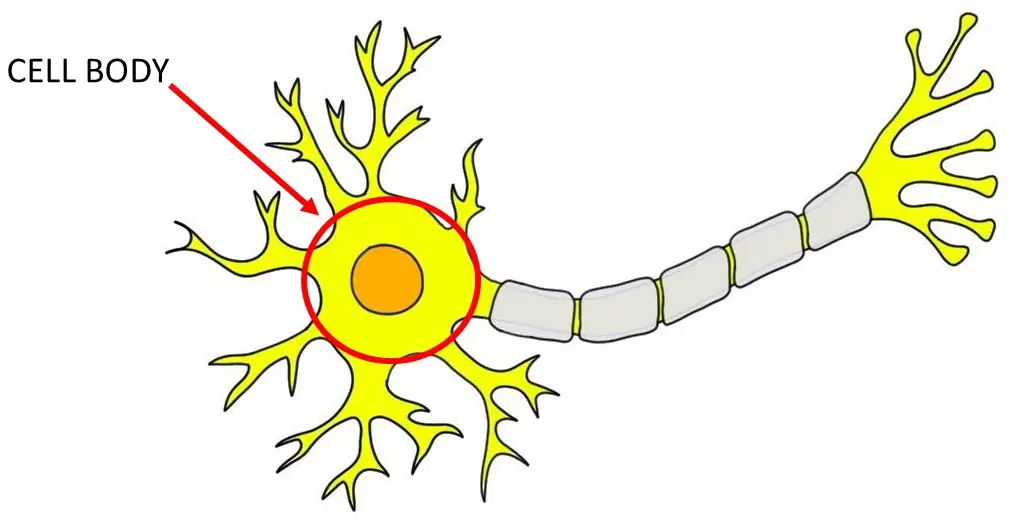
Soma/Cell Body
the spherical part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and organelles necessary for cell function
function: integrates inputs from dendrites
Axon
long extension from the soma to transmit outgoing electrical signals
function: axon transport moves vesicles down/up axon
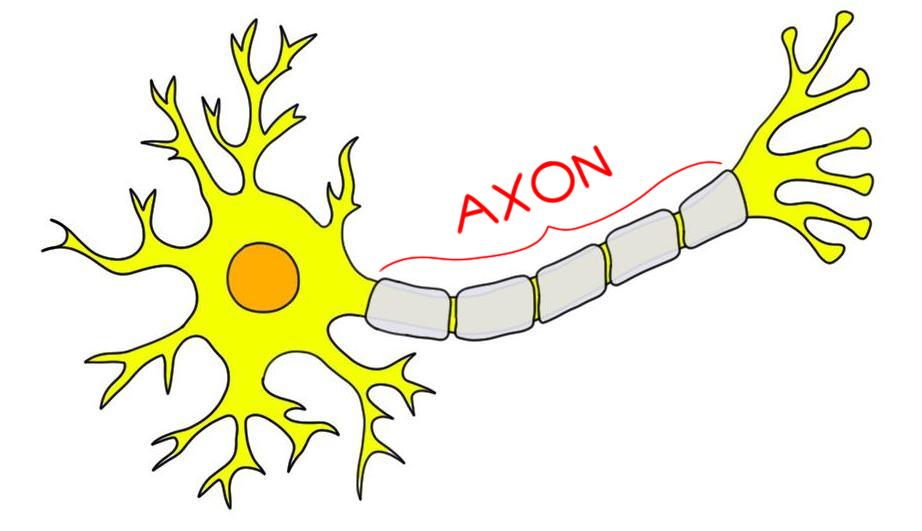
Axon Terminal
enlarged button-shaped that is the end of an axon
function: stores and secretes chemical messengers; electrical signal to release
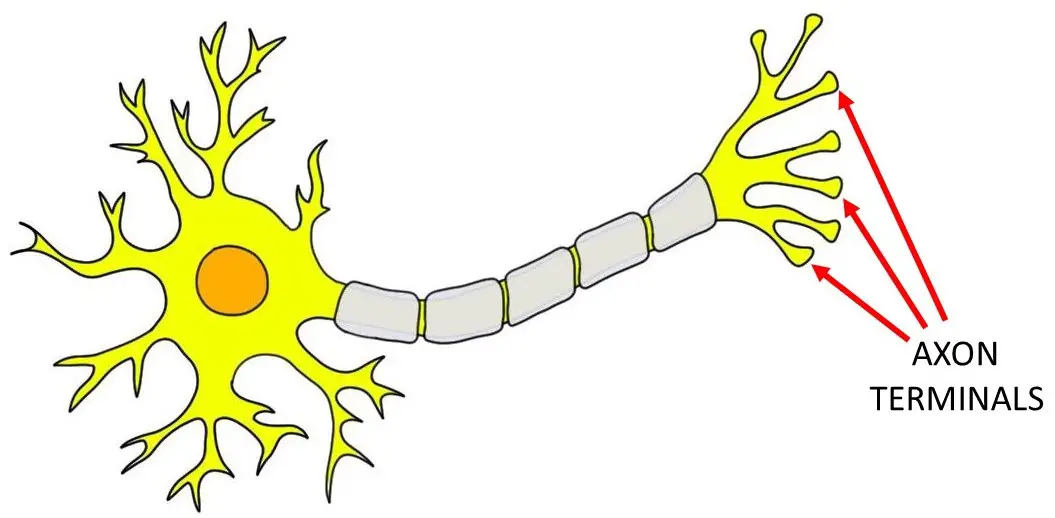
Synapse
junction between axon terminal of presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic target cell
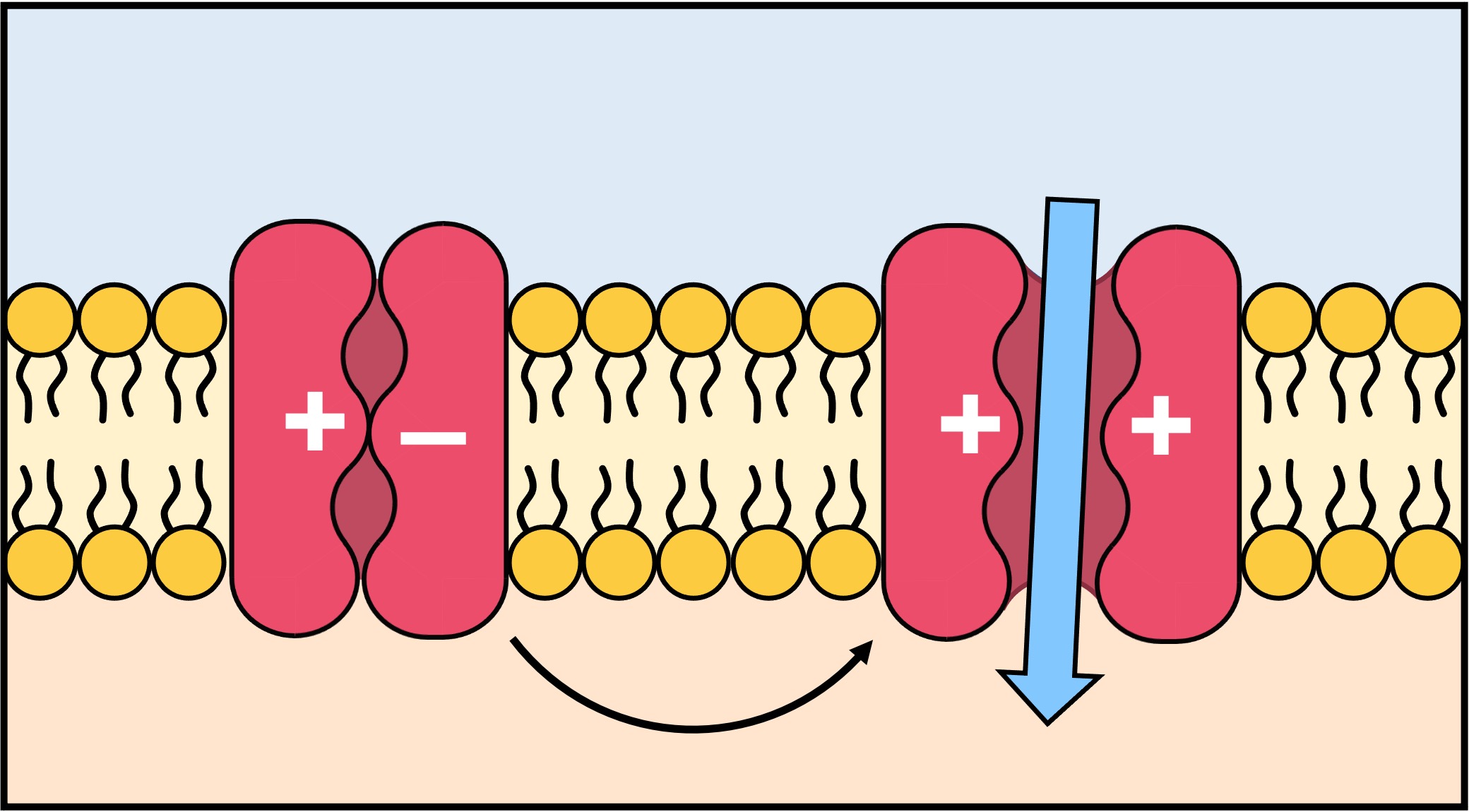
Ion Channels
membrane proteins w/ selective permeability for particular ions
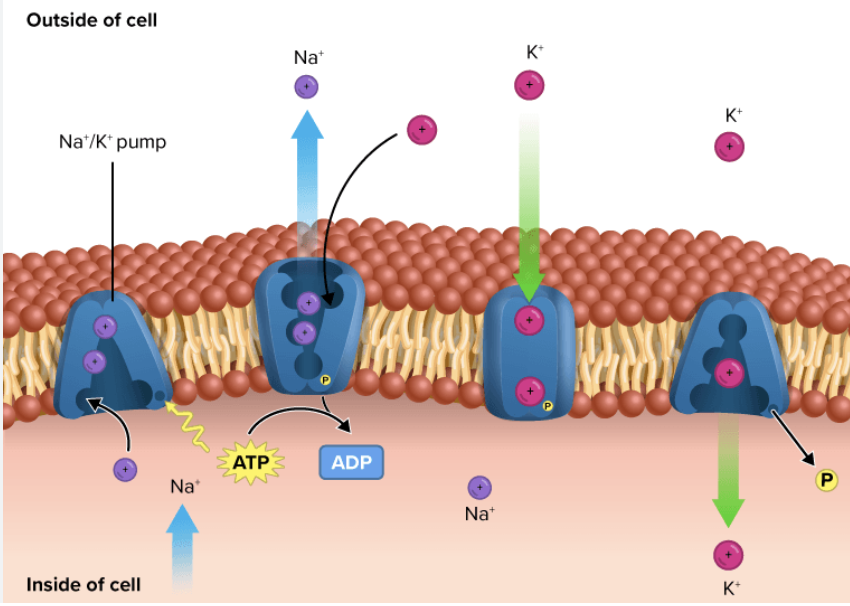
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Na+-K+-ATPase
carrier membrane protein, maintains resting membrane potential
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
nerves and ganglia
What are 3 different types of neurons?
Afferent Neurons
Interneurons
Efferent Neurons
Afferent Neurons
PNS, sends sensory information towards the CNS
function: receives sensory info
Interneurons
CNS, integrate inputs and communicates w/ other interneurons and efferent neurons
function: integrate sensory info to produce response
Efferent Neurons
carry info to effector organs (muscle, glands, etc) away from CNS
function: send motor/autonomic messages