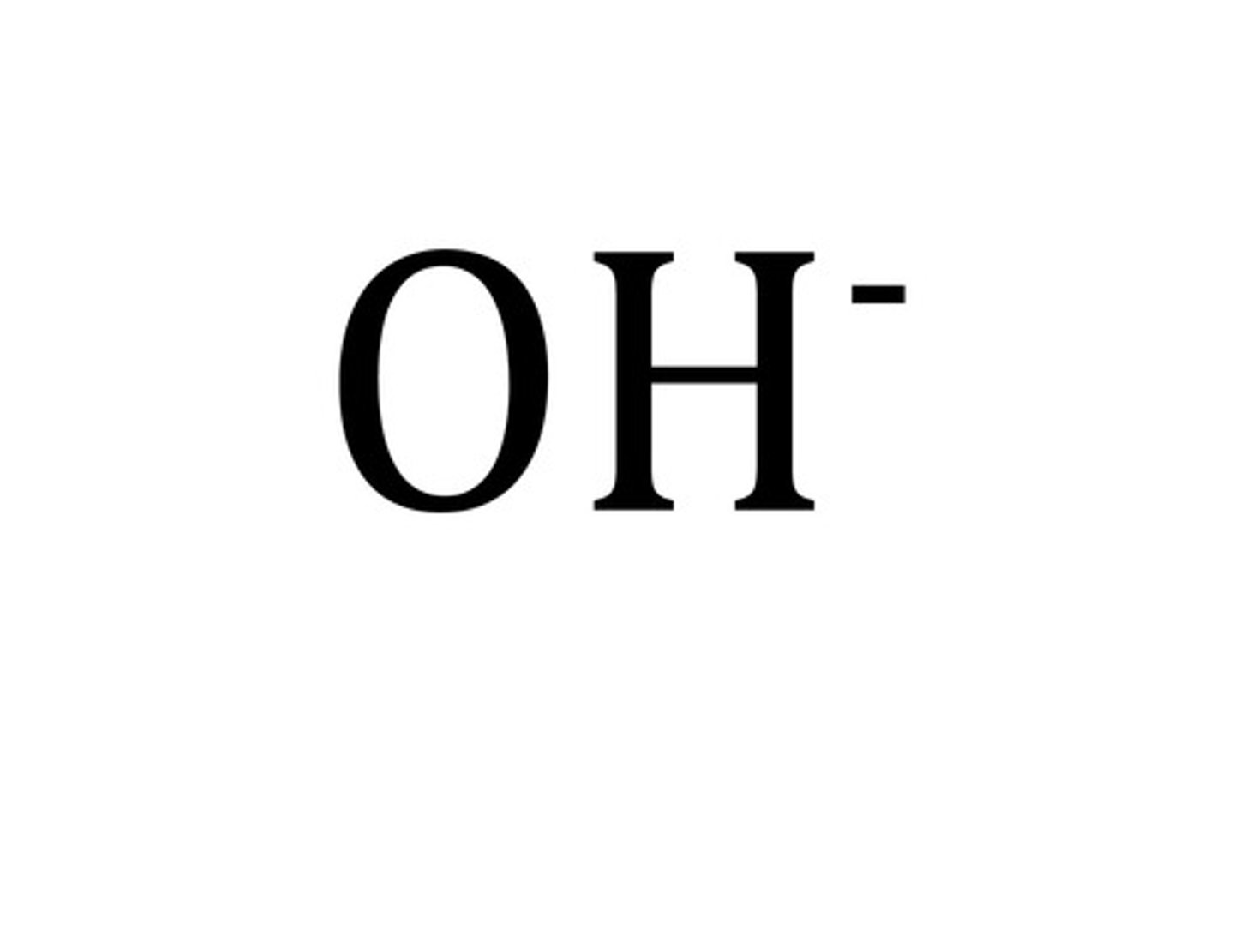Strong Acids and Bases
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Hydrochloric Acid
HCl is a strong acid
Sulfuric Acid
H2SO4 is a strong acid. It is made of the sulfate ion and hydrogen.

Nitric Acid
HNO3 is a strong acid. It is made of the nitrate ion and hydrogen.

Hydrobromic acid
HBr is a strong acid
Hydroiodic acid
HI is a strong acid
perchloric acid
HClO4 is a strong acid. It is made of the perchlorate ion and hydrogen.
Sodium Hydroxide
NaOH is a strong BASE

Acetic Acid (Vinegar)
HC2H3O2 is a weak acid. It is made of the acetate ion and a hydrogen.
Lithium hydroxide
LiOH is a strong base
Potassium hydroxide
KOH is a strong base
Calcium Hydroxide
Ca(OH)2 is a strong base
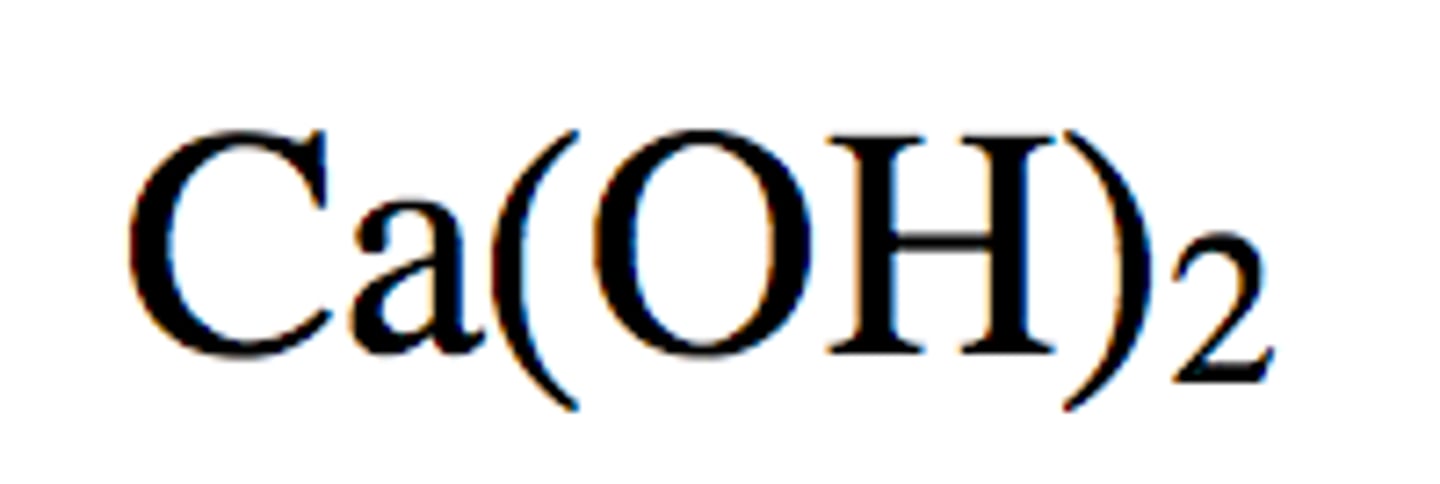
Strontium hydroxide is a strong base
Sr(OH)2
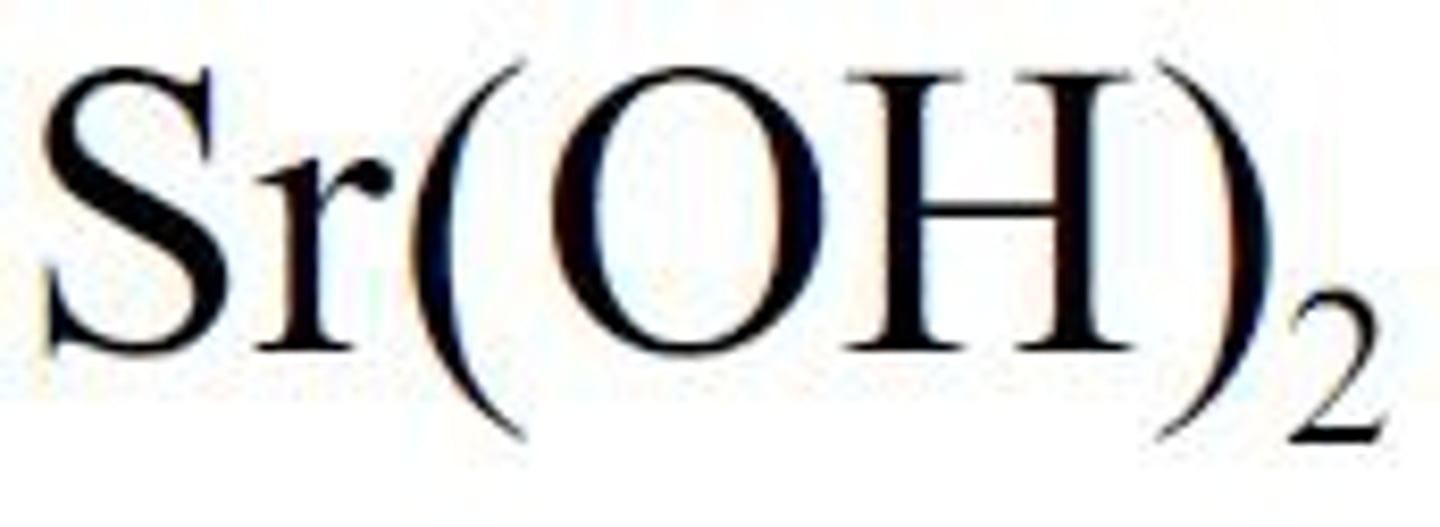
Barium hydroxide is a strong base
Ba(OH)2
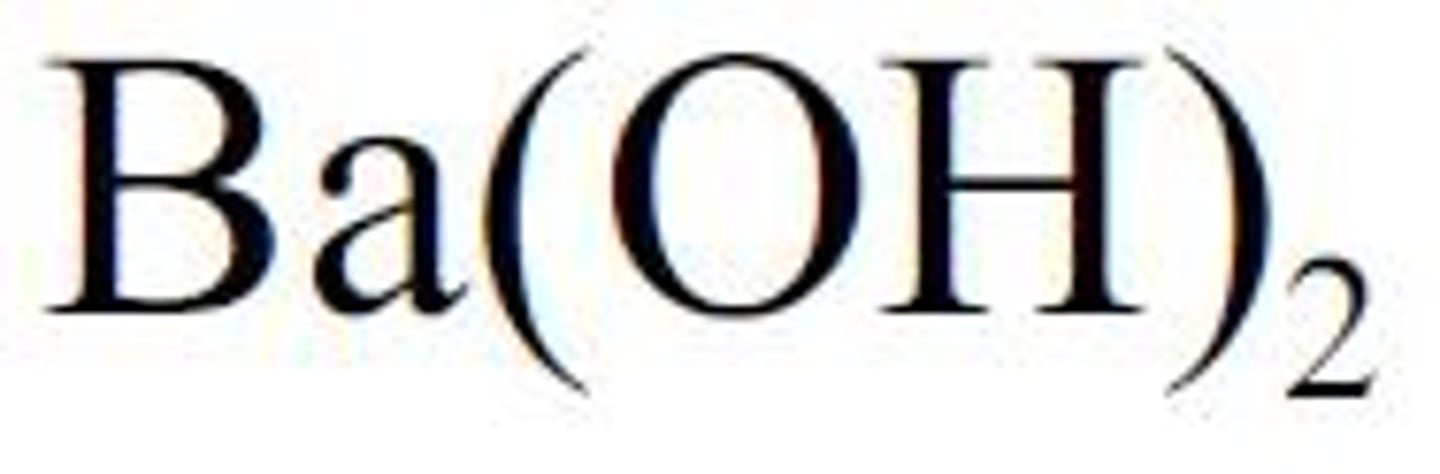
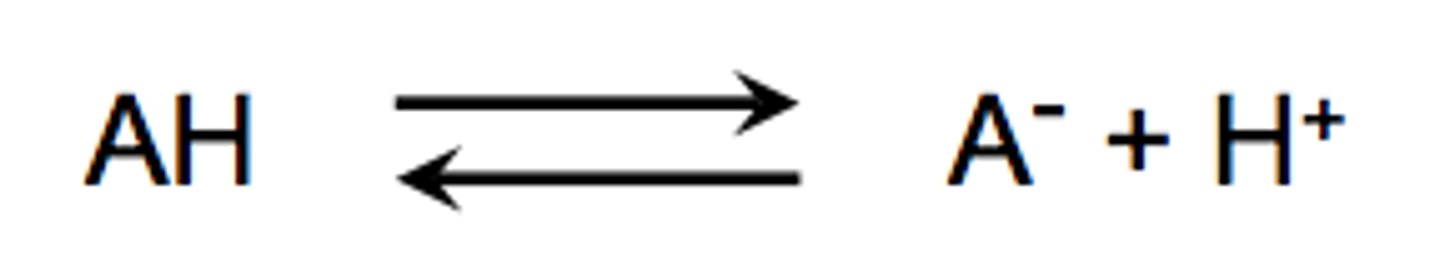
Strong acids ionize
completely
Weak acids ionize
only a little
Strong acids have a large
Ka value because there are many more products than reactants
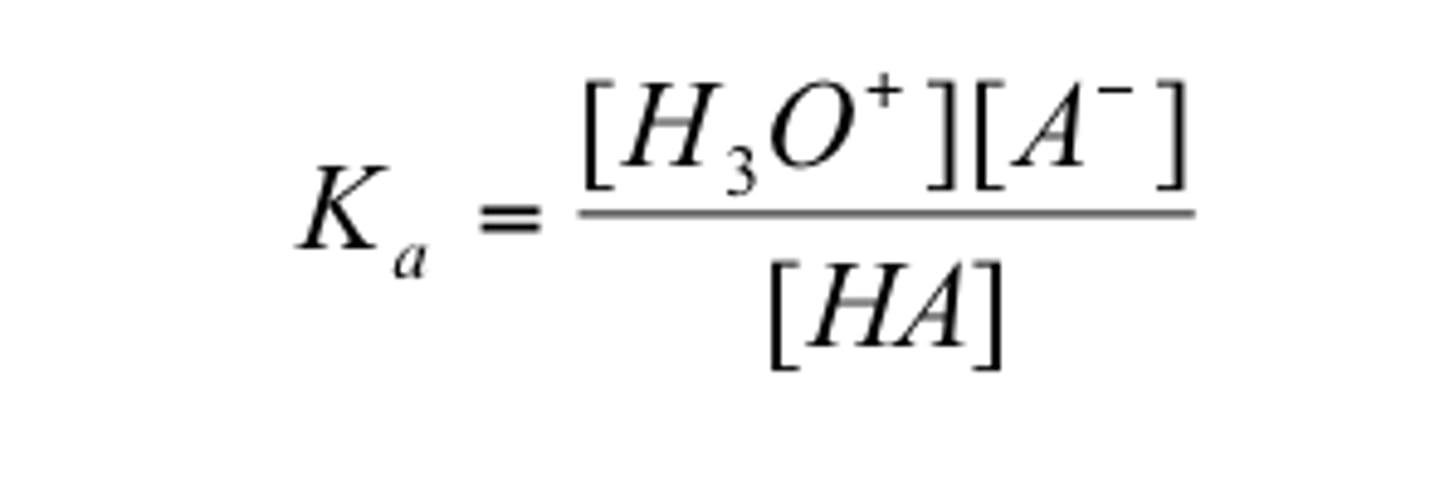
Weak acids have small
Ka values because there are few products and more reactants.
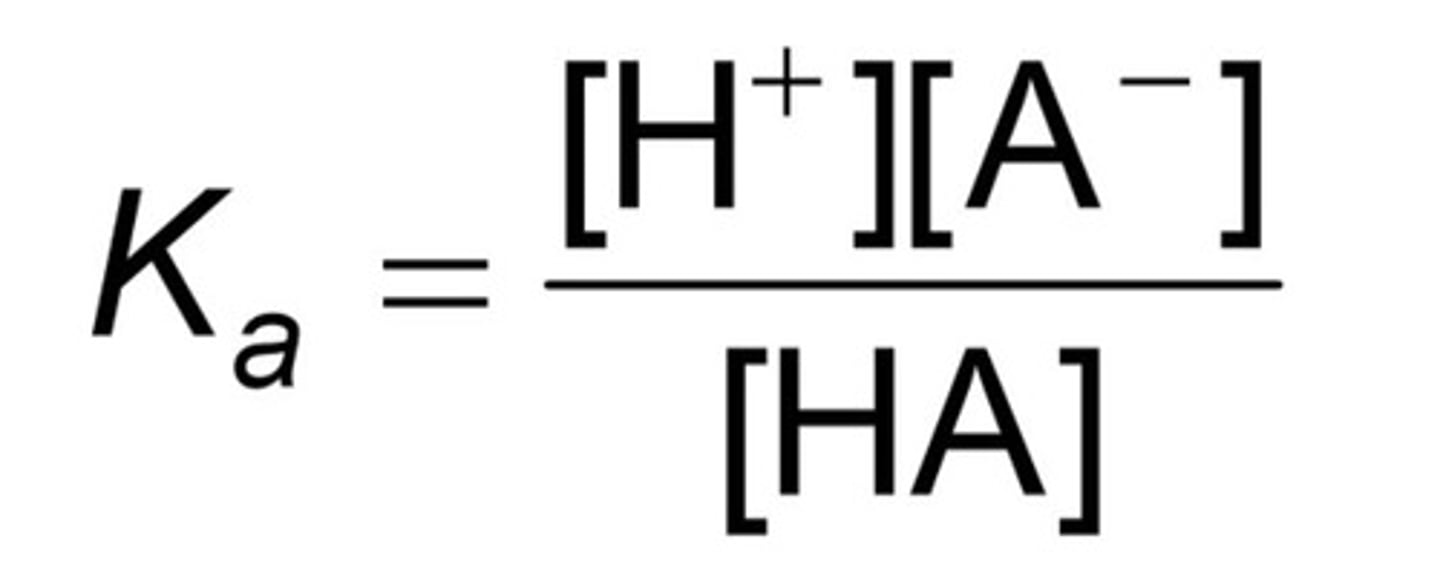
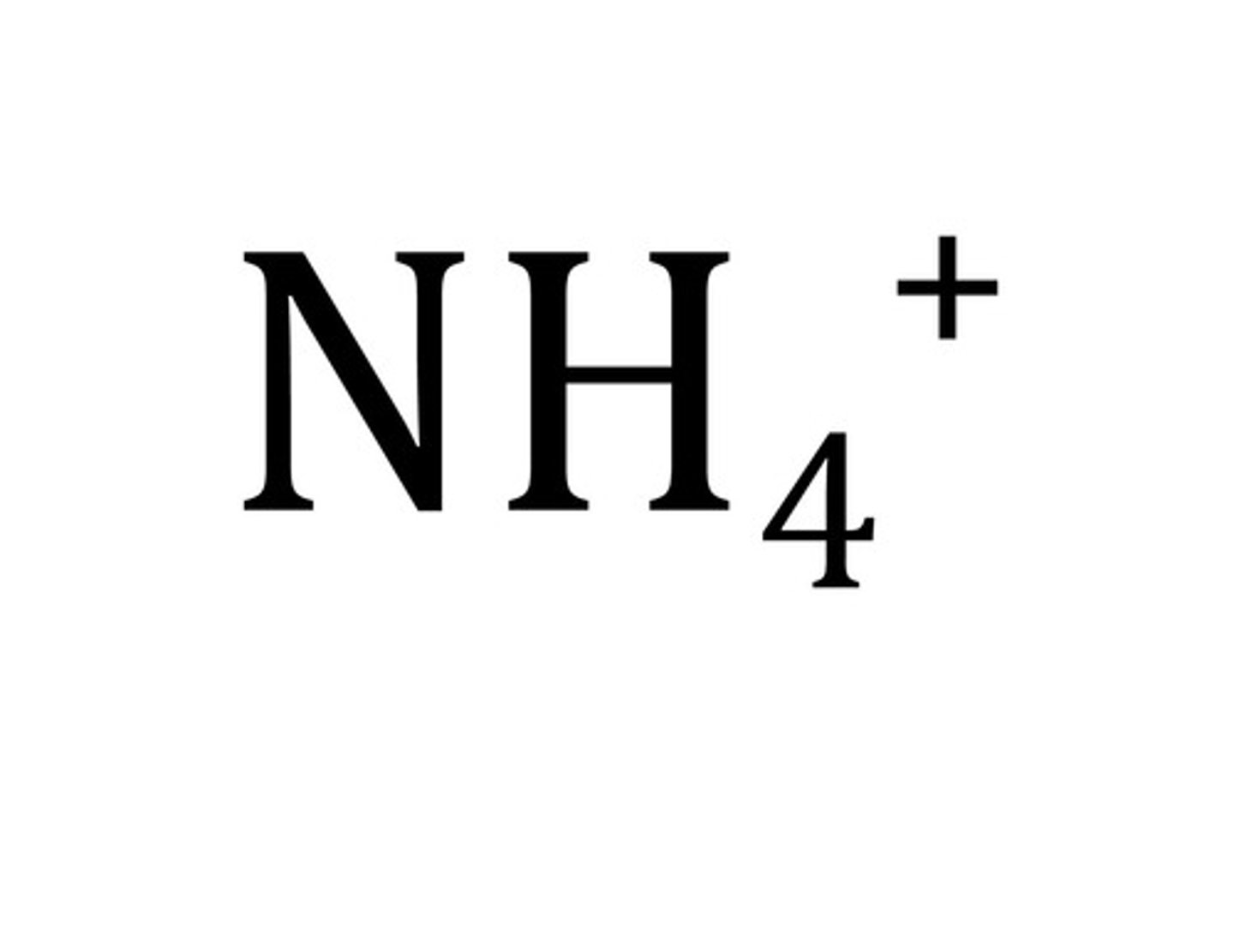
NH_3 (Ammonia) is a
Bronsted Lowry Base. It accepts a proton to become ammonium NH4+.
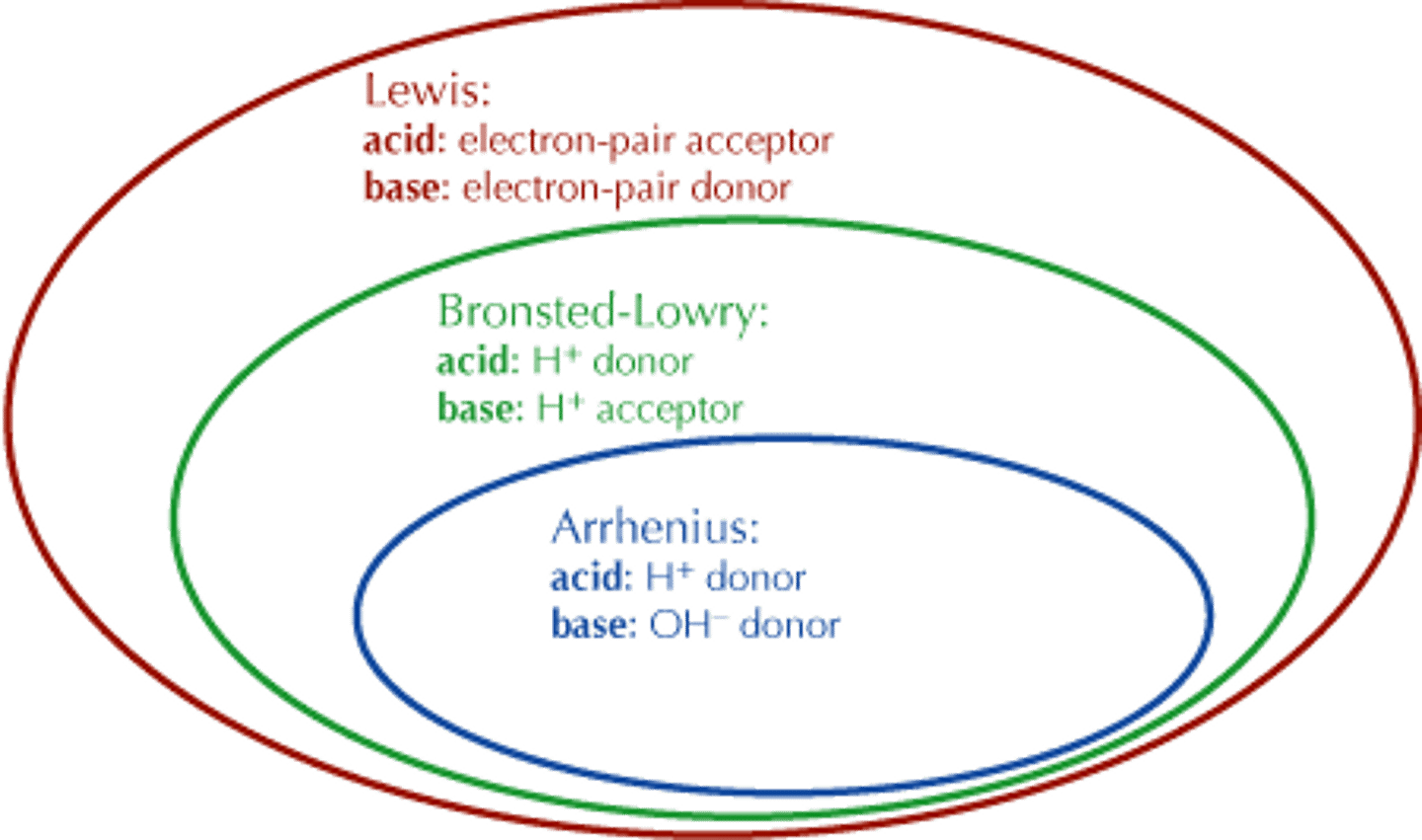
All Bronsted Lowry Bases are
Lewis Bases.
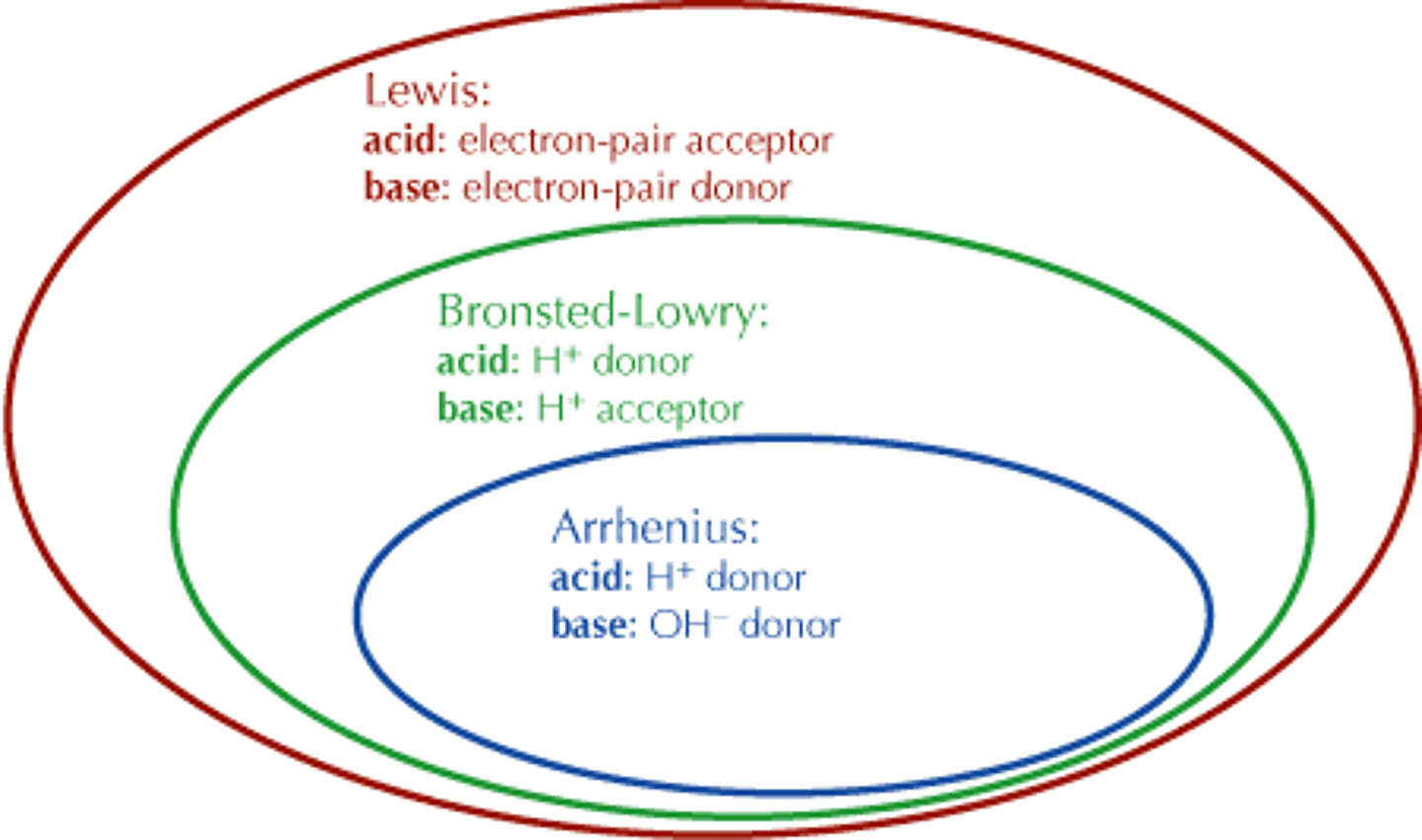
All Arrhenius Acids are
Bronsted Lowry acids
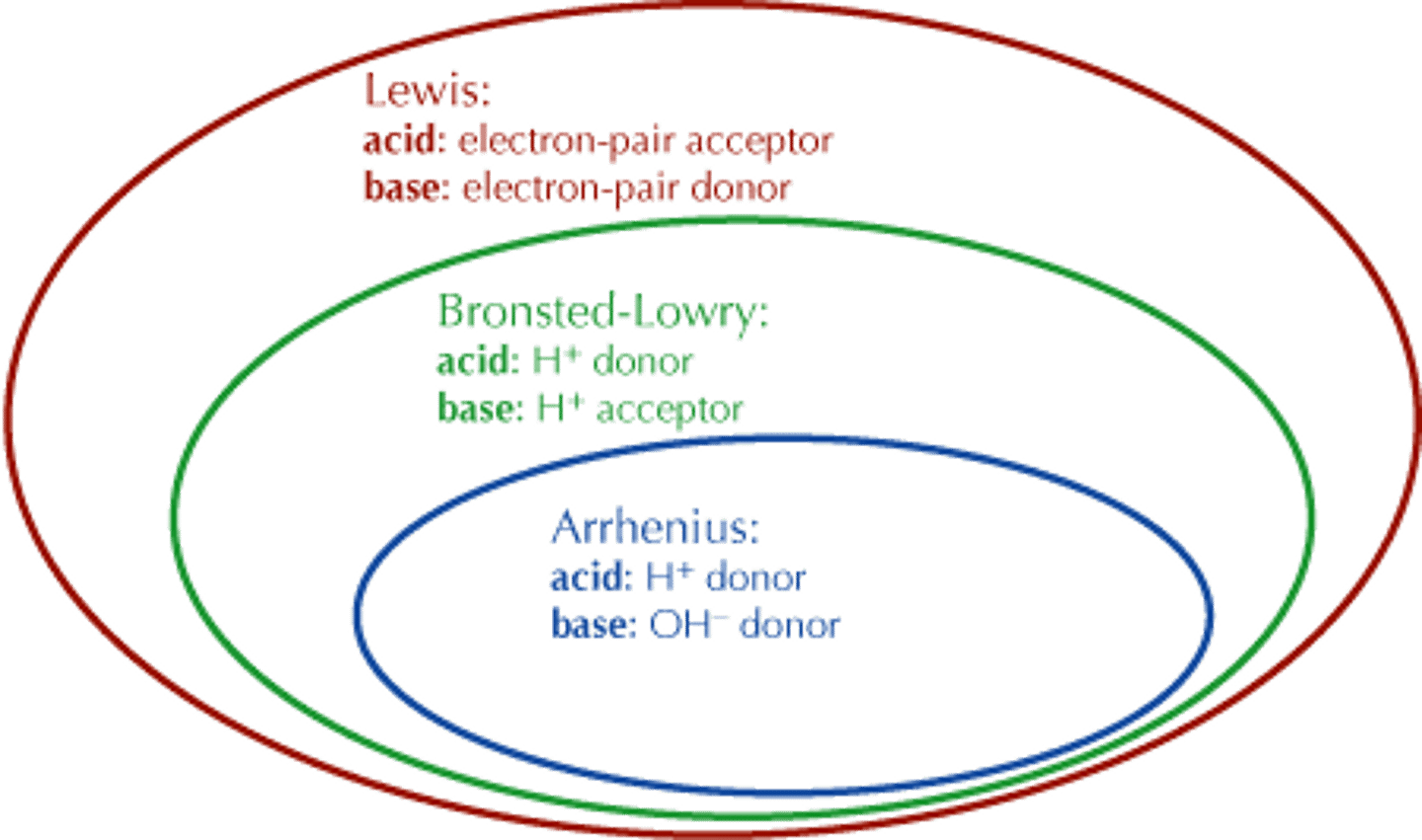
NOT all Lewis Acids are
Bronsted Lowry acids or Arrhenius acids.
Arrhenius acids have these at the front and are aqueous. They release these.
H+
Arrhenius bases release
hydroxide ions. OH-
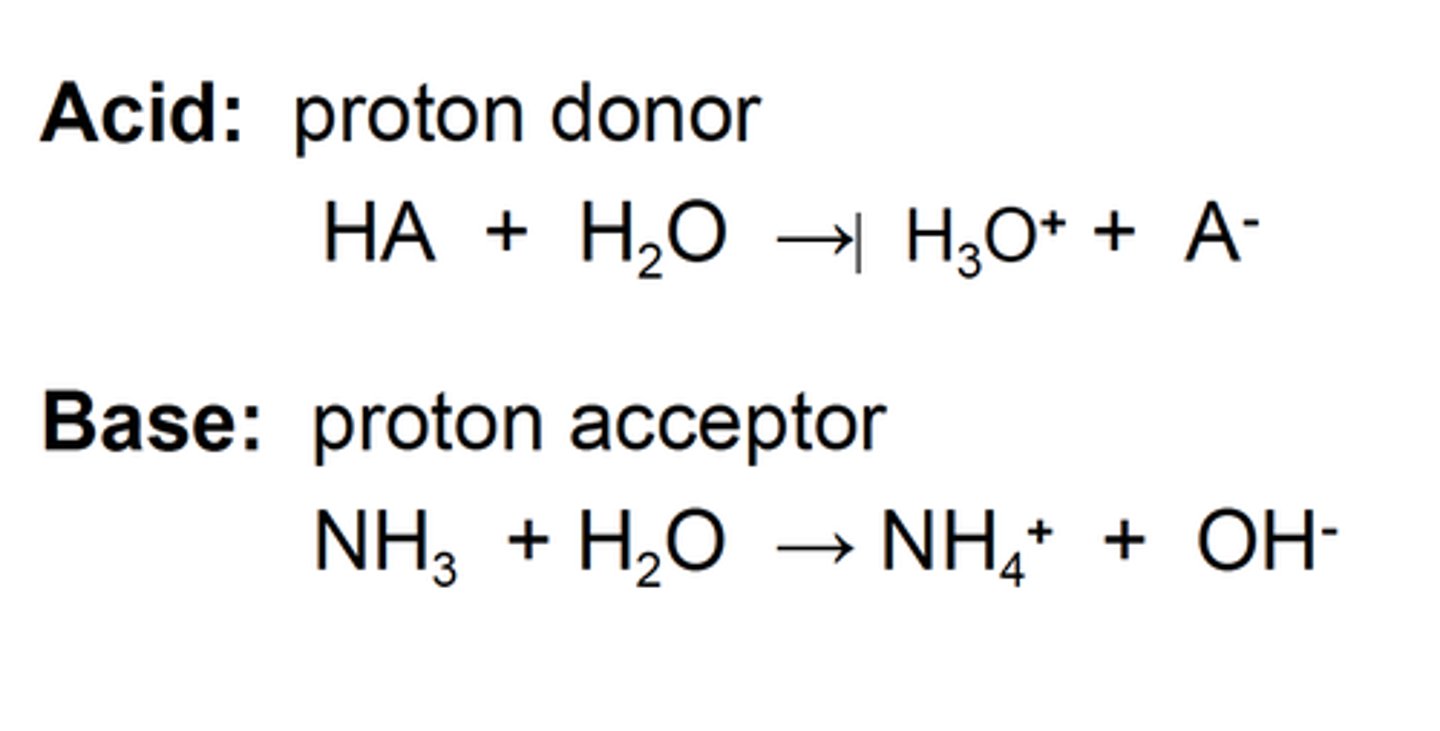
Bronsted Lowry acids are
proton donors.
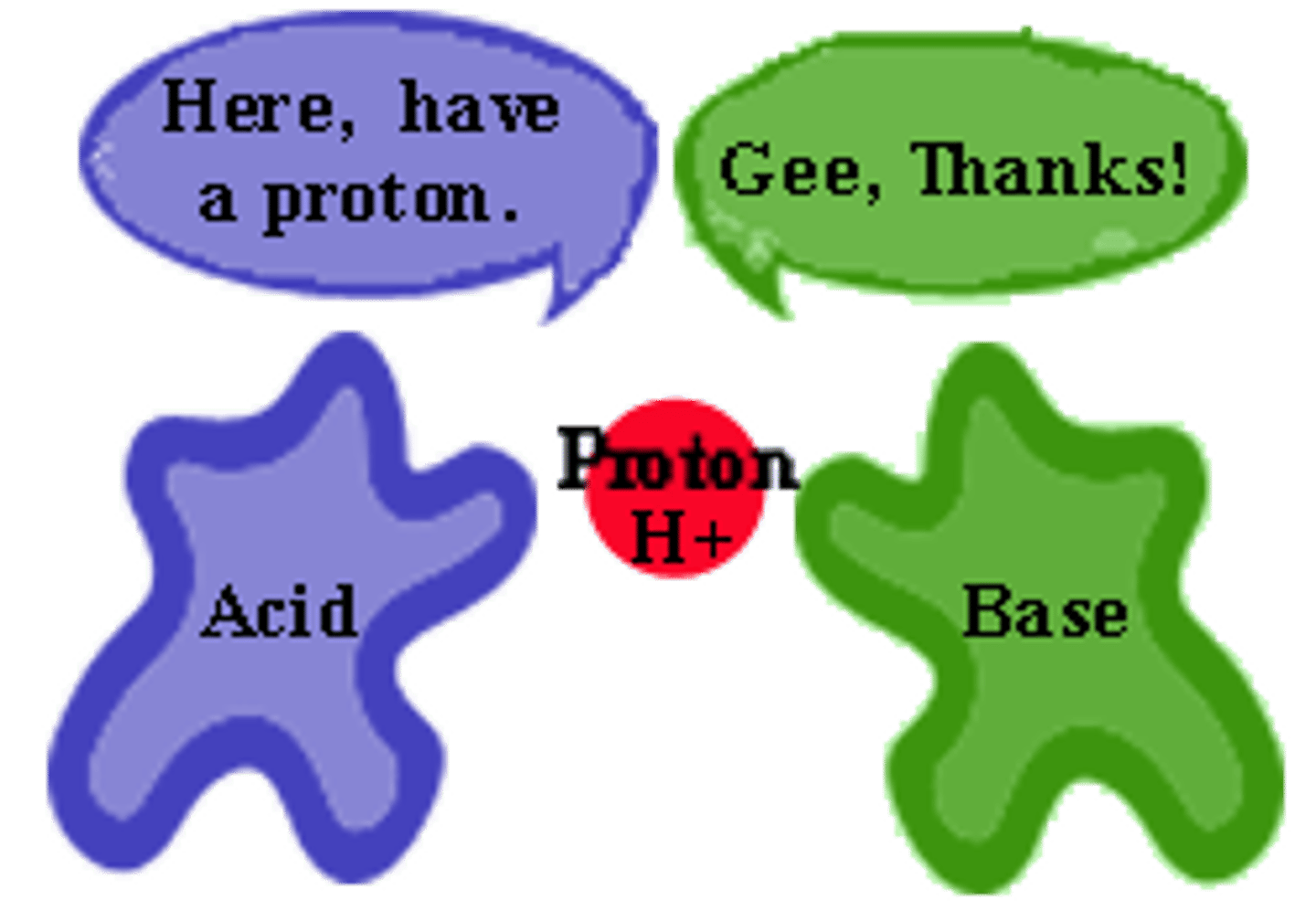
Bronsted Lowry bases are
proton acceptors
Lewis acids are
electron acceptors
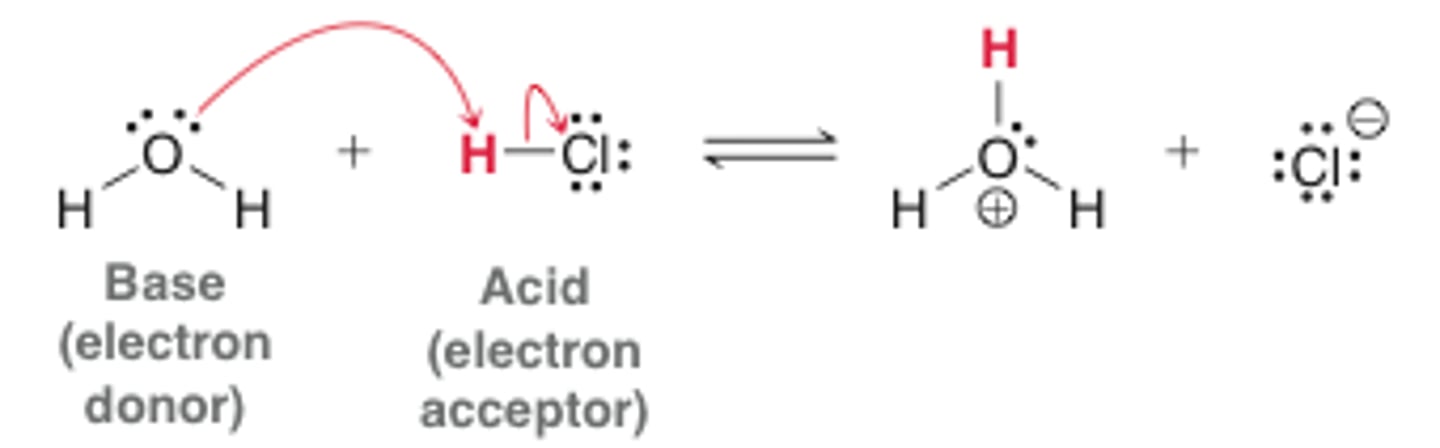
Lewis bases are
electron donors
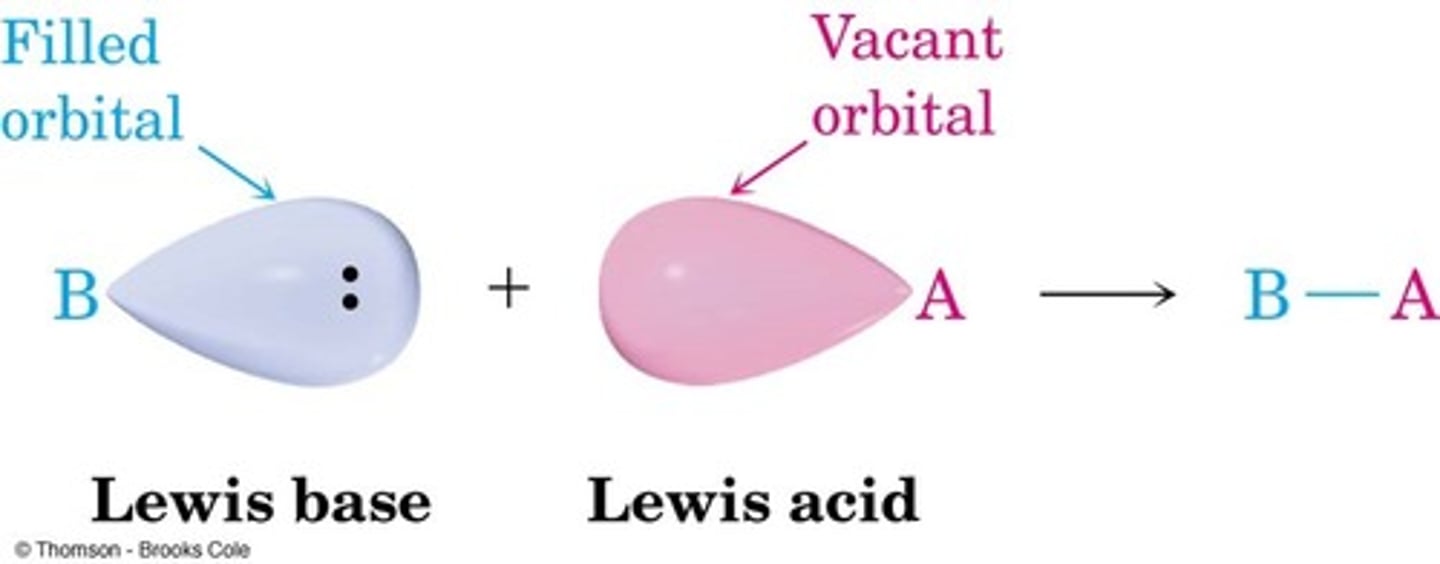
Salts are made from the
anion of the acid and the cation of the base
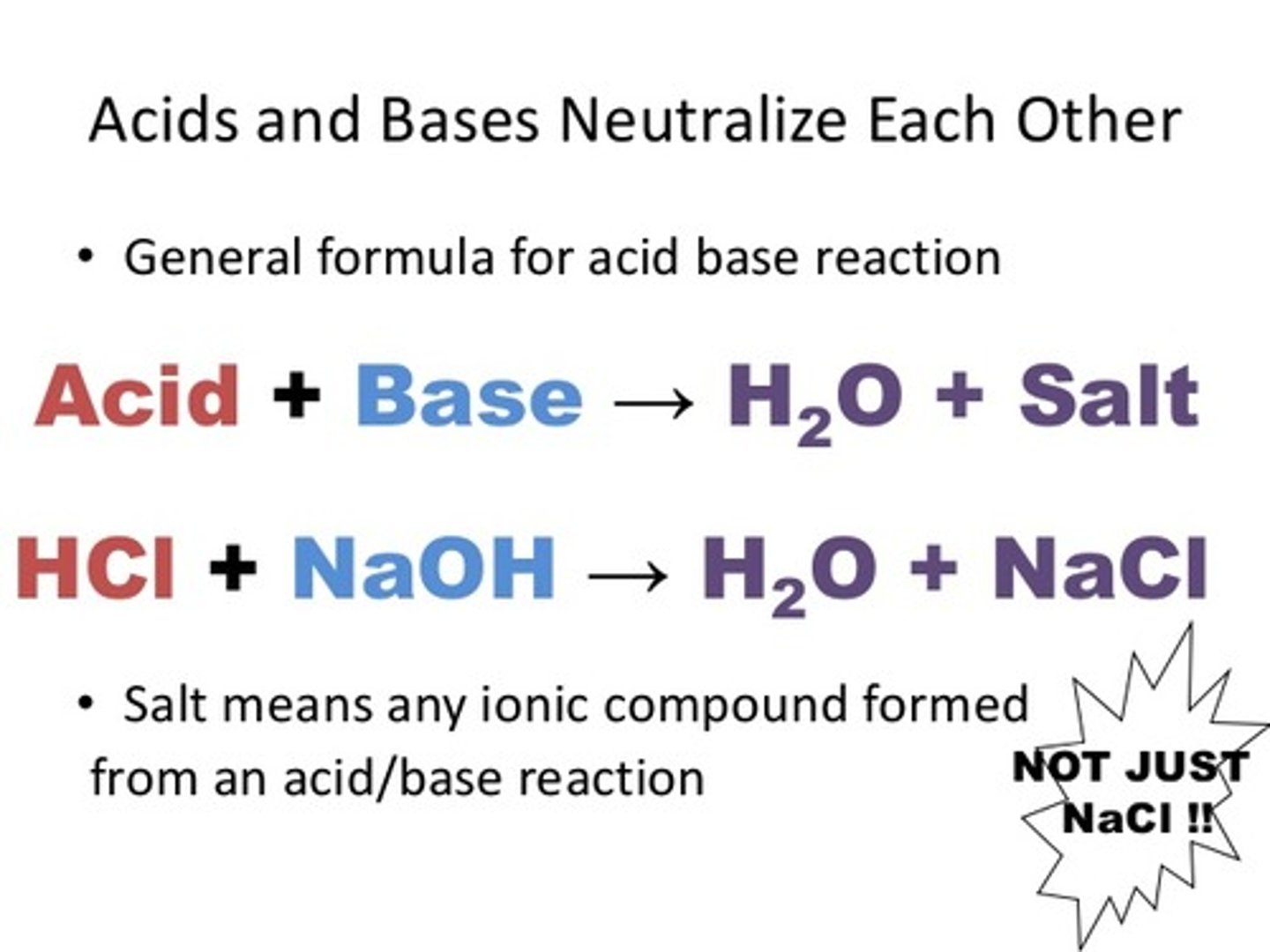
What is the salt created from Ba(OH)2 and H2SO4?
BaSO4 -- This is barium sulfate.
What is the salt created from KOH and H3PO4?
K3PO4 - remember to put charges on top and swap and drop! PO4 has a charge of -3. K has a charge of +1.
Using MaVa = MbVb what does Ma stand for?
molarity of the acid
MaVa = MbVb. What does Vb stand for?
Volume of the base.
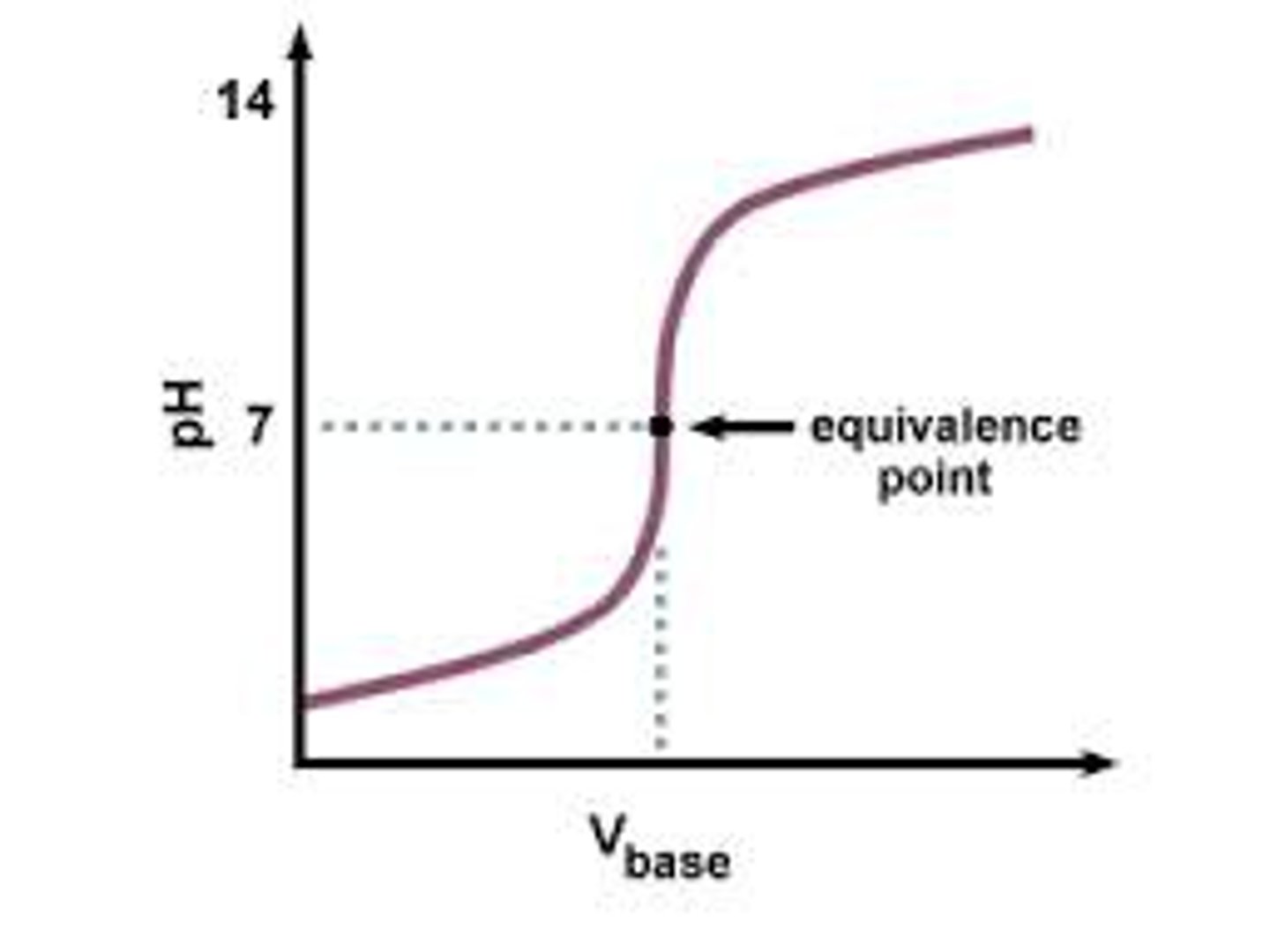
The equivalence point is
the point in a titration where the number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of moles of hydroxide ions
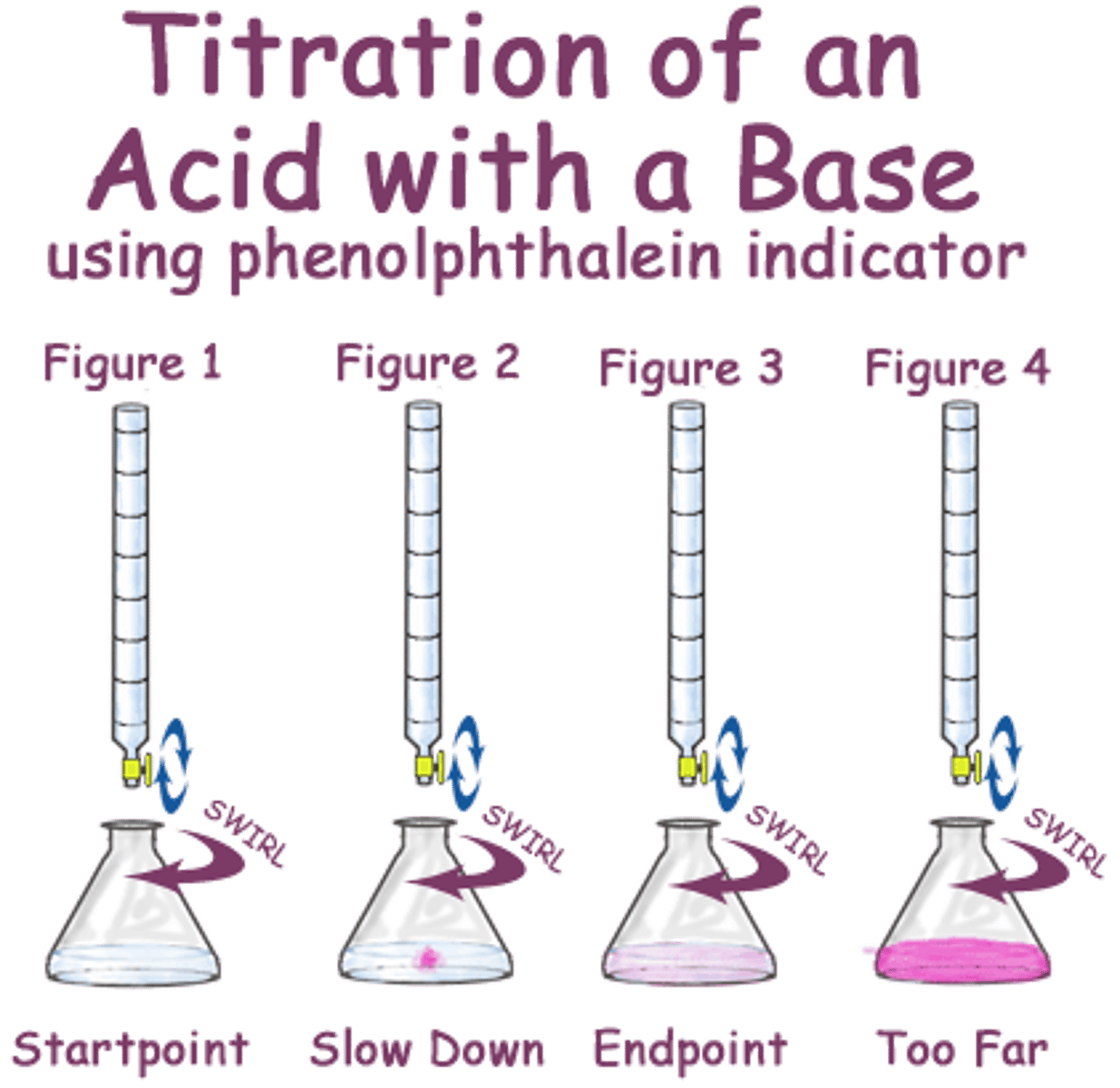
The end point
the point in a titration at which an indicator changes color
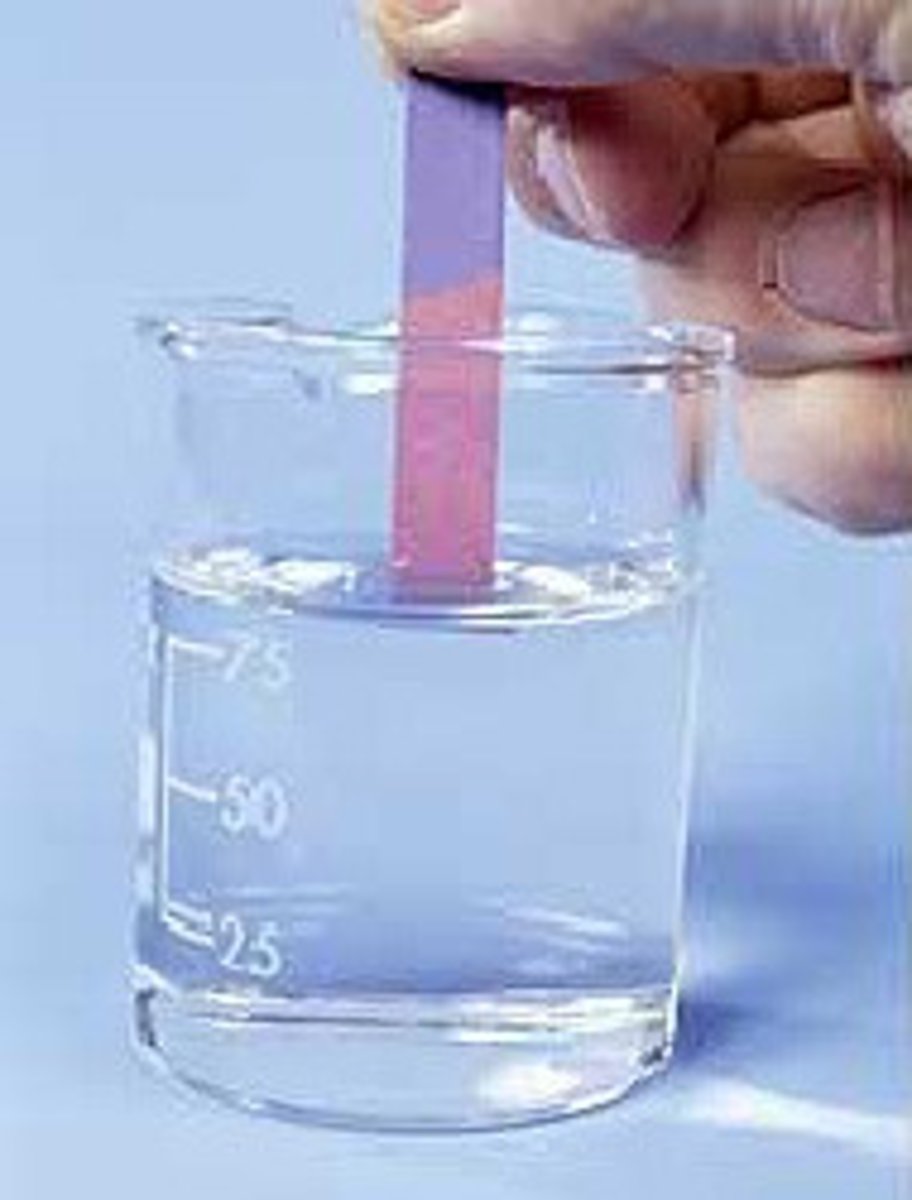
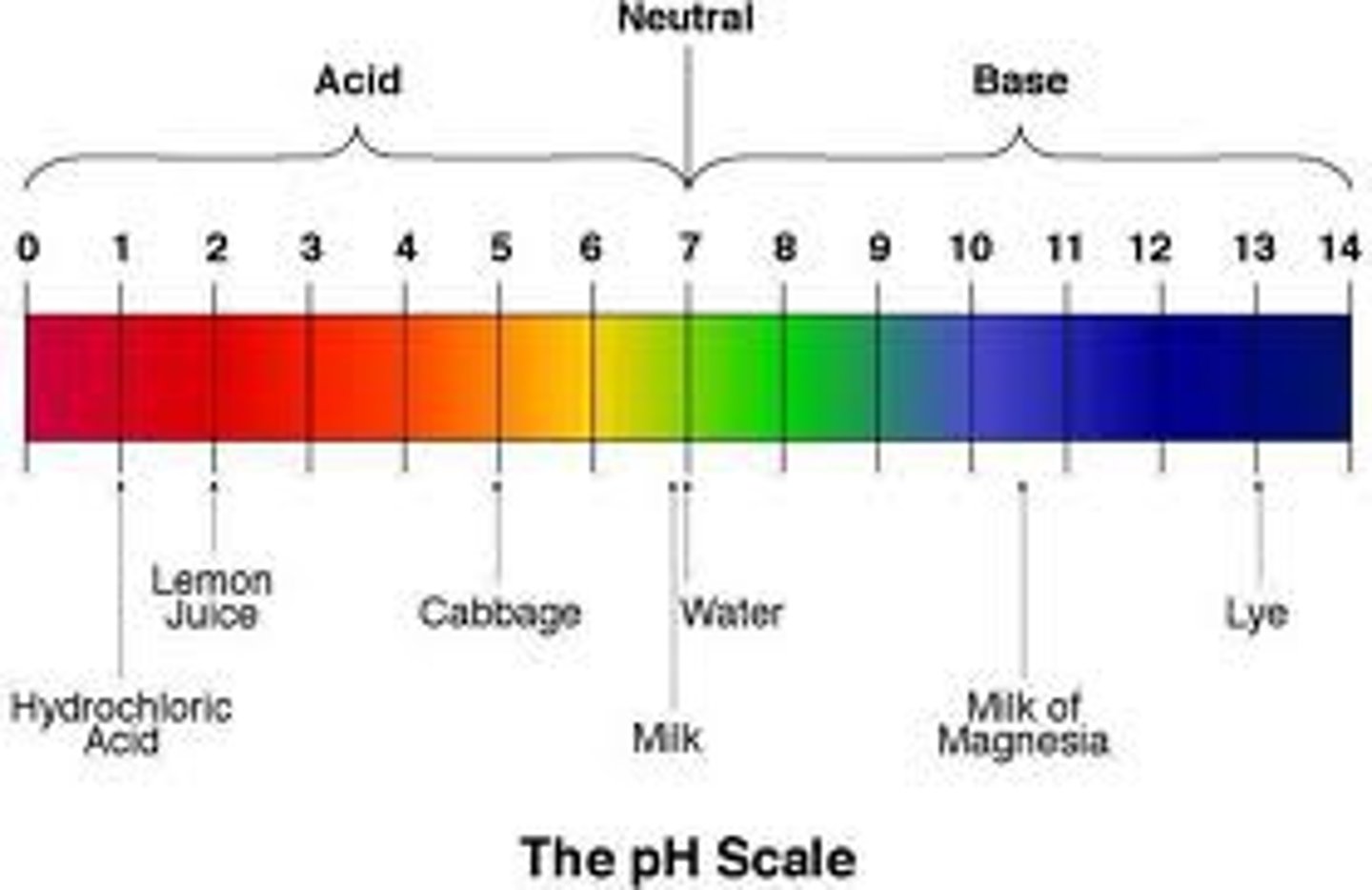
Acids turn litmus paper
red

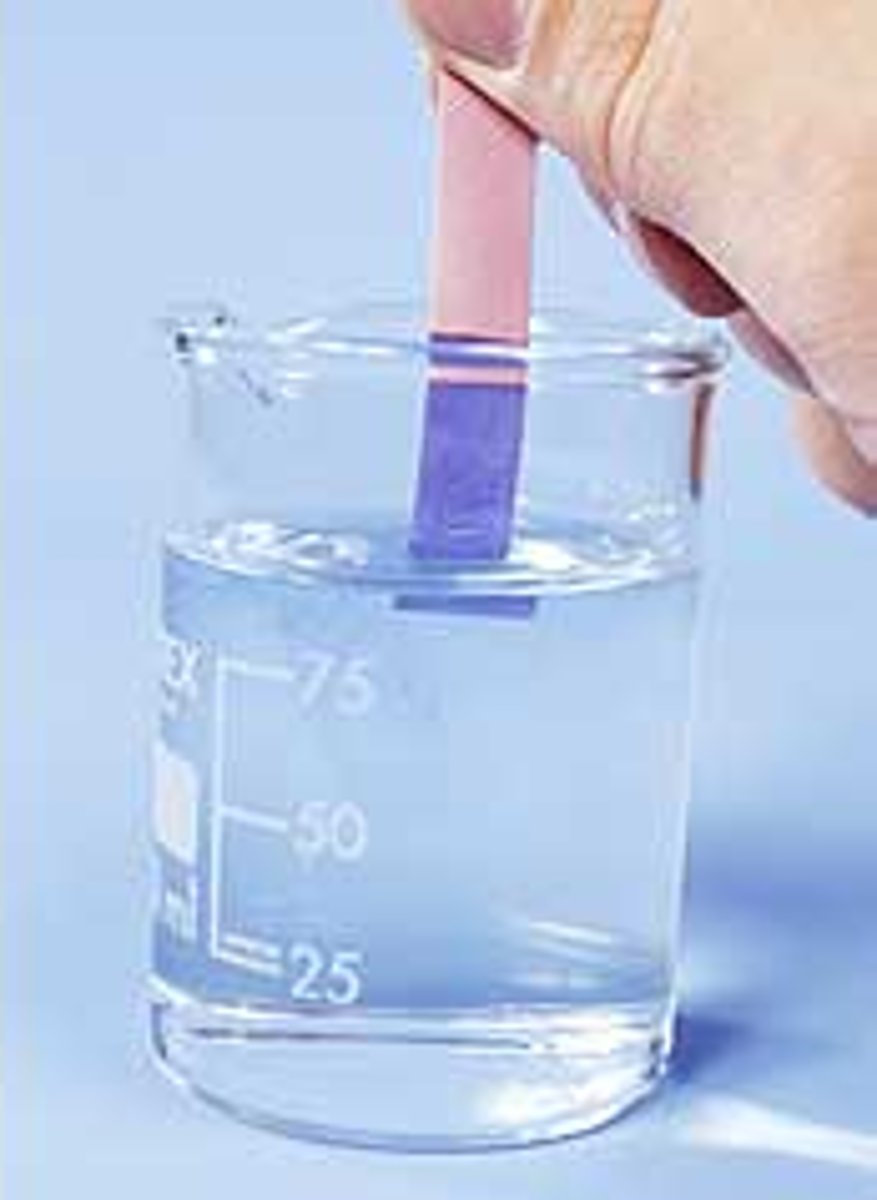
Bases turn litmus paper
blue

a pH below 7 indicates:
excess of h+ ions, and an acidic solution
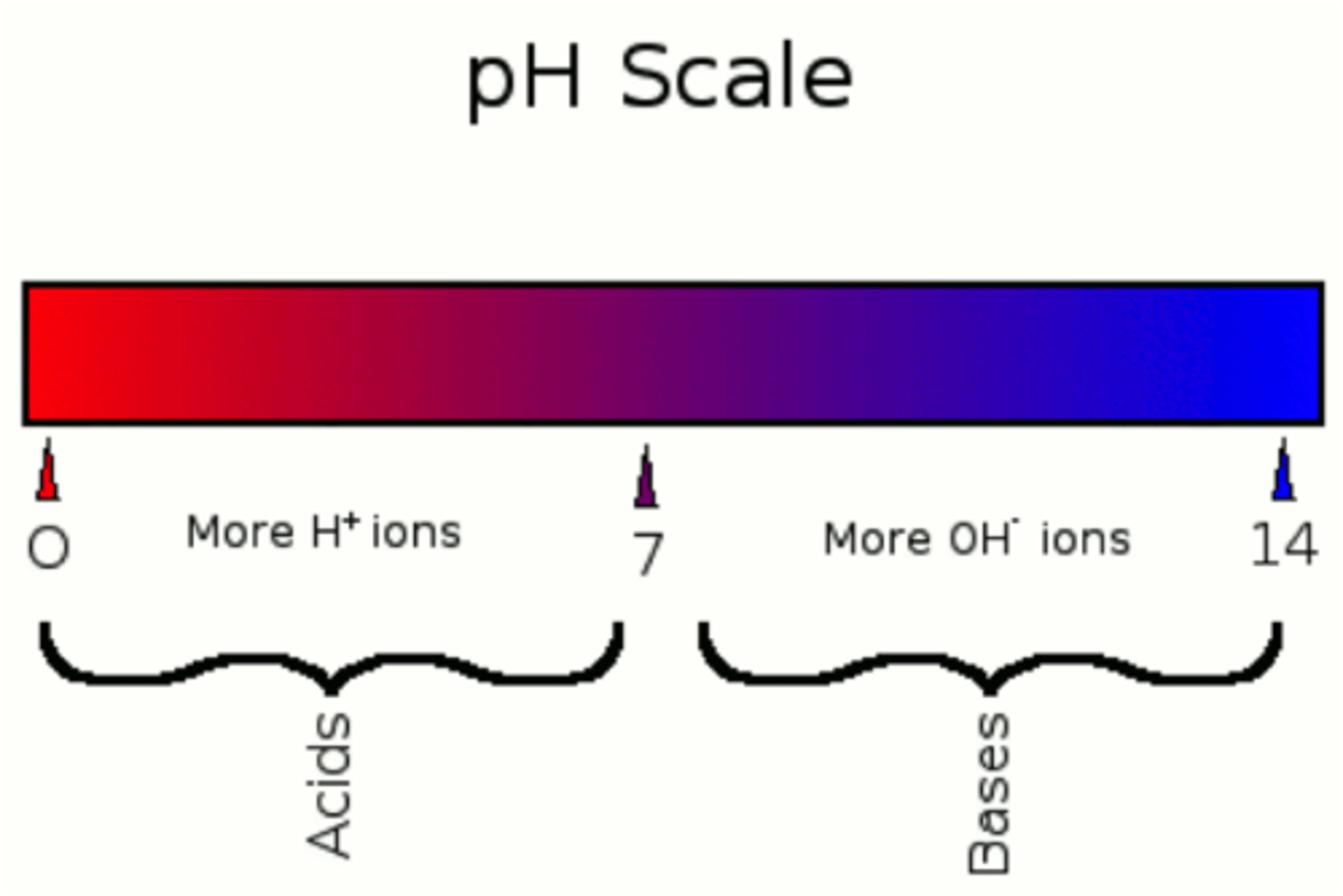
a pH above 7 indicates:
base
percent dissociation
Amount dissociated M / initial concentration M x 100%
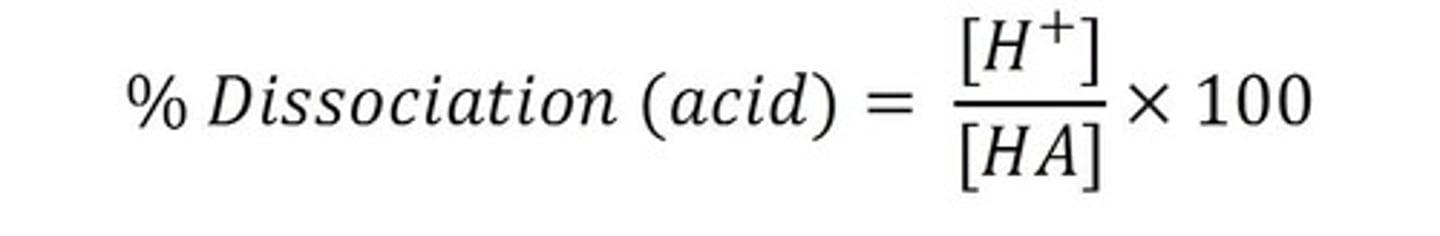
Hydronium ion formula
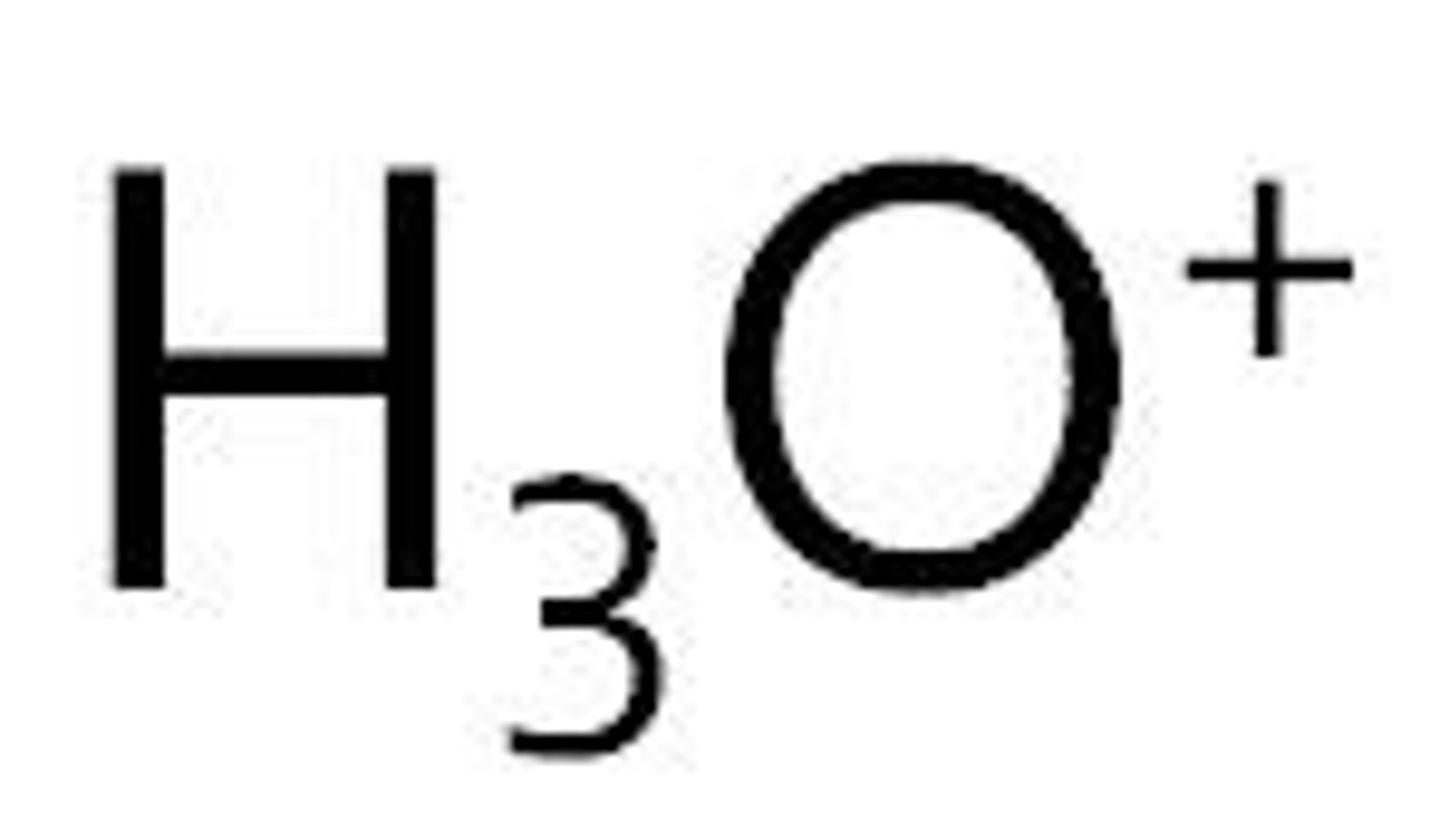
Hydroxide ion