Environmental Economics (Environ 235) Exam 2
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Benefit Cost Analysis (BCA)
decision making framework in which all costs and benefits are measured and compared in monetary units
static efficiency
efficiency at a particular point in time
dynamic efficiency
maximizes the present value of net benefits across time
Present Value Equation
y=x/(1+r)^N
Risk Neutrality
indifference between a certain outcome with a given value and a set of risky outcomes with the same expected value
risk averse
Reluctant to take any kind of risk.
risk loving
refers to a person's willingness to take bets with negative expected values
precautionary principle
a principle based on the belief that action should be taken to decrease the probability of a catastrophic outcome of a policy
distributional effect
who is receiving benefits vs. who is receiving costs of a certain policy
tangible vs intangible benefits
Tangible Benefits: Can be quantified and measured easily.
Intangible Benefits: Results from an intuitive belief that the system provides
Cost Surveys
easy to lie, inflate cost necessary
Engineering costs
tends to miss specifics and understates actual costs
discount rate
"discounts" future to present value
risk-free rate of return
the rate of return on risk-free investments. The interest rates on short-term U.S. government bonds are commonly used to measure this rate
risk premium
the excess return required from an investment in a risky asset over that required from a risk-free investment
cost effective analysis
Compares alternative projects or plans to determine the least costly way to achieve desired goals. Usually, some index or point system is developed to measure the effectiveness of the proposal in meeting the goals and objectives.
impact analysis
report detailing all aspects of a proposed action without monetization or optimization to avoid bias
total economic value
is an approach to compare the benefits and costs associated with ecosystems
total economic cost
use + option + nonuse values
direct use value
value of engaging directly with amenity
indirect use value
ecosystem benefits that are not valued in markets, such as flood prevention and pollution absorption
option value
the worth of something we might use later
nonuse value
bequest + existence value
bequest value
future generations' possible use
existence value
the worth of knowing that something exists, even if we never experience it ourselves
endowment effect
the tendency of people to be unwilling to sell a good they already own even if they are offered a price that is greater than the price they would be willing to pay to buy the good if they didn't already own it
revealed valuation
uses existing market to obtain data on an good/service
direct revealed
uses market of good to understand how society values it
indirect revealed
uses travel costs, hedonic models and/or defensive expenditure to estimate value
Travel Cost Method
the value a person will spend on traveling to a location for an activity
Hedonic Model
property values and wage models
defensive expenditures
The amount of money people are willing to pay to protect themselves against pollution damages. Examples are expenditures on sunscreen, noise proofing, bottled water, and air purifiers.
direct stated preference methods
surveys directly asking WTP and WTA
strategic bias
respondents do not reveal true WTP to influence outcome
social desirability bias
the tendency for people to say what they believe is appropriate or acceptable
information bias
when too much or too little information is provided
starting point bias
respondents are influenced by the values listed in the survey
hypothetical bias
the possibility that people respond differently to hypothetical situations than to having to pay real money
interviewer bias
effects of interviewers on respondents that lead to biased answers
payment vehicle bias
They are influenced by the type of payment mentioned in the survey, such as taxes or donations
indirect stated methods
choice experiments and contingent ranking
choice experiments
presents alternative resource or use options, each of which are defined by various attributes including price
contingent ranking
a survey method in which respondents are asked to rank a list of alternatives
value transfer valuation
uses values developed at different time, location or context
benefit function transfer
uses models developed in other research
meta analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
Schaefer Growth Model
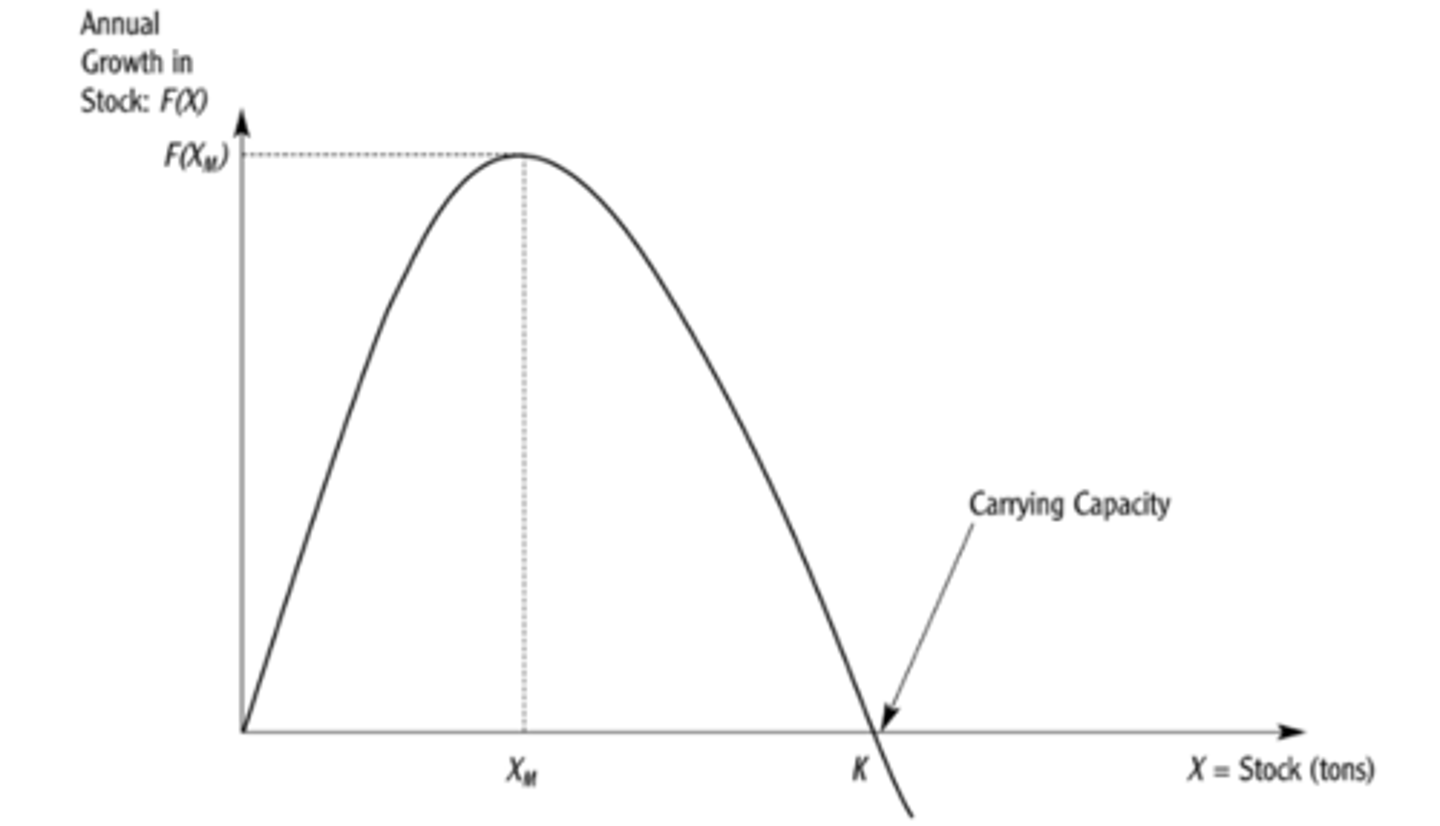
economic model assumptions
species price is constant, cost of effort is constant, harvest is positively correlated with efficiency and stock sizes, sustainable harvest
sole ownership
well defined property rights maintain incentive to harvest at efficient effort level
open access
undefined property rights incentives overexploitation
aquaculture
controlled raising and harvesting of marine species
concerns of aquaculture
not all species can be raised in aquaculture, fish feed is still wild-caught, invasive species, disease and pollution
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
the seazone extending 200 nautical miles from the coast over which a state has special rights as to the exploration and use of marine resources
Gear Restrictions and Fishing Seasons
artificially raise costs
taxes on effort/harvest
wealth transfer to governemt
Catch Share Programs
type of management system that dedicates a secure share of fish or fishing area, to individual fishermen, communities or fishery associations
ITQ (individual transferable quota)
A fishery management program in which individual fishers are given a total allowable catch of fish in a season that they can either catch or sell.
problems with ITQ
high grading and bycatch
high grading
selectively taking the best and leaving the rest.
marine protected areas
areas of ocean partially protected from human activities
marine reserves
an area of the ocean designated for no activities, beneficial when fishery is severely overexploited