reproduction and Mieosis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Reproduction
the production of offspring
asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is faster but provides no variety in offspring,
sexual reproduction
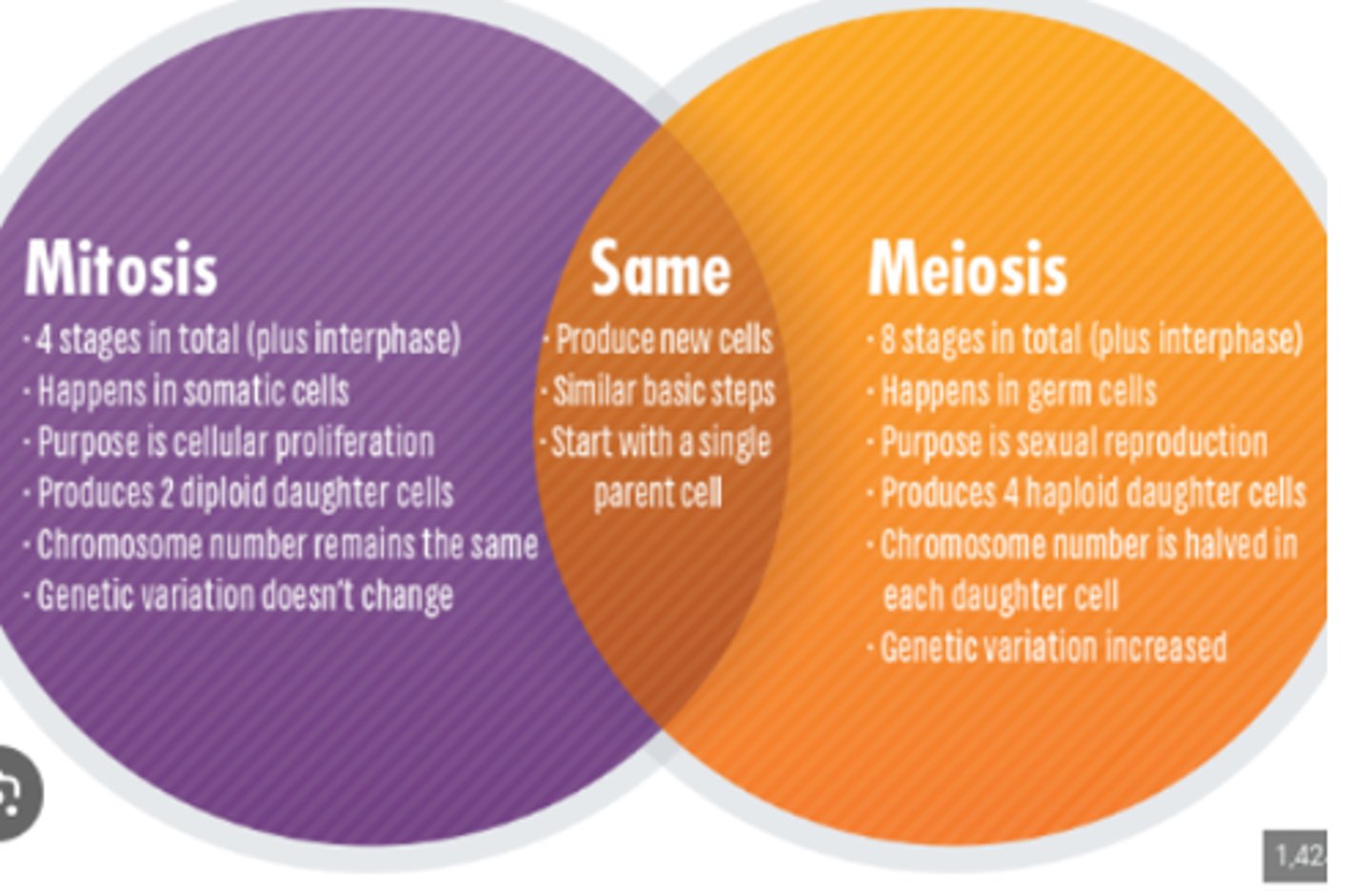
Sexual, provides significantly more variety and takes much longer and more energy, Requires an egg and a sperm, and goes through Mitosis and Meiosis( goes through PMAT twice)
Gametes
a haploid cell the fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization
Zygotes
the diploid product of the fusion of haploid gametes (a fertilized egg).
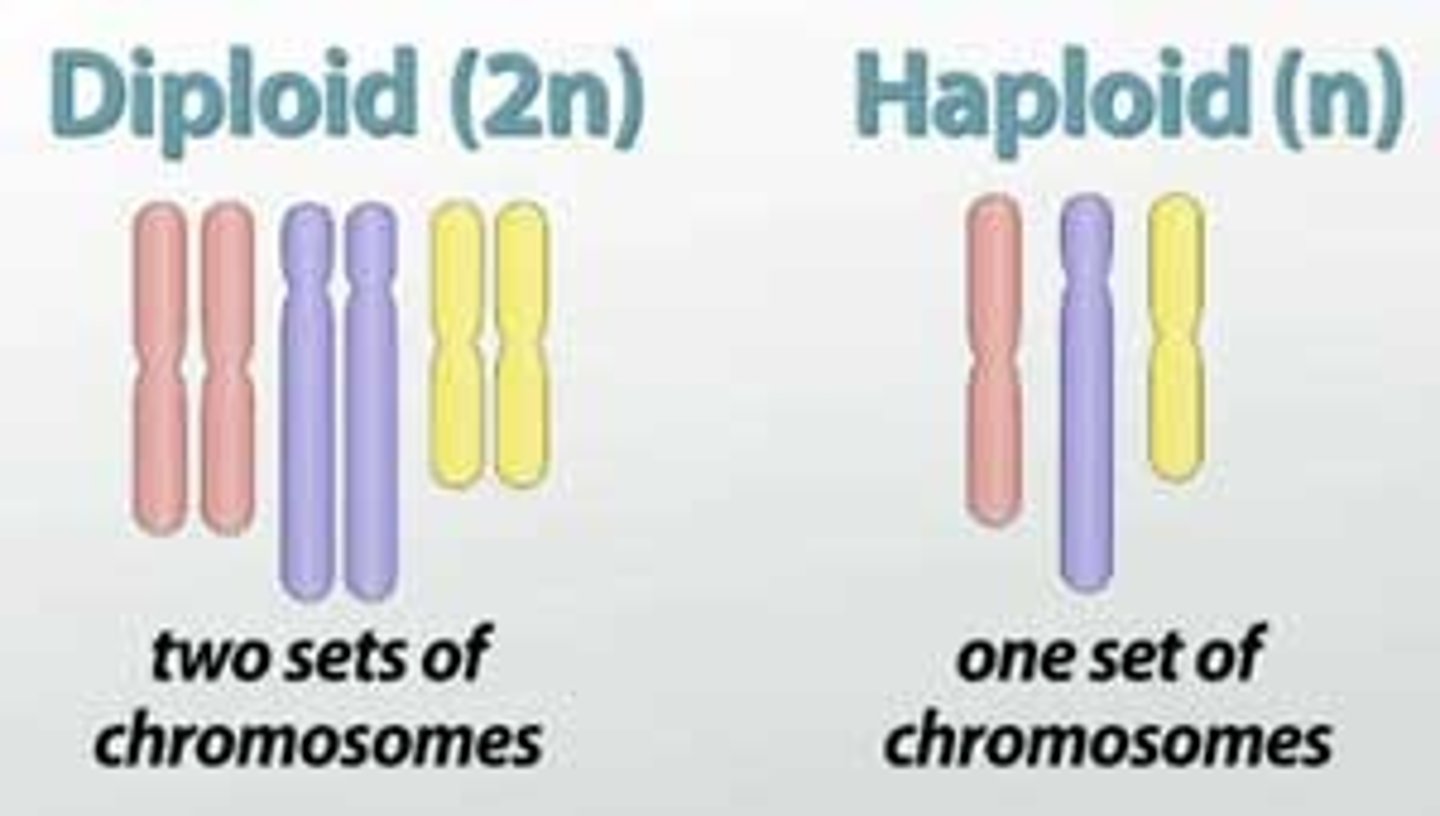
Diploid
(genetics) an organism or cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number
Haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Homolagus chromosomes
chromosomes of the same height that express the same feture such as controlling eye color.
sister chromatids

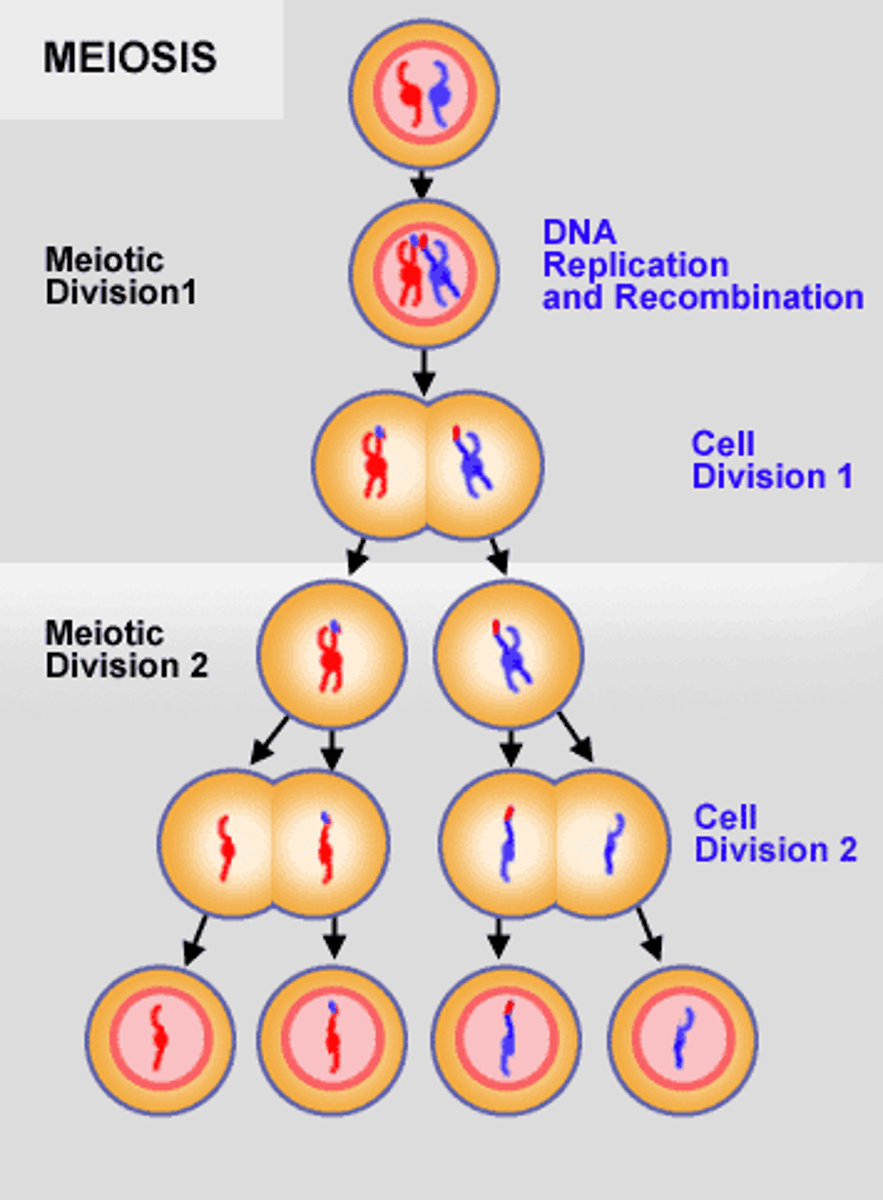
Meiosis
This is the process in which it happens during only sexual reproduction where it takes chromosomes from the mother and father and performs the actions of cross over (homolagus pairs) and then separates after sharing DNA into Diploids and seperates into their own cells

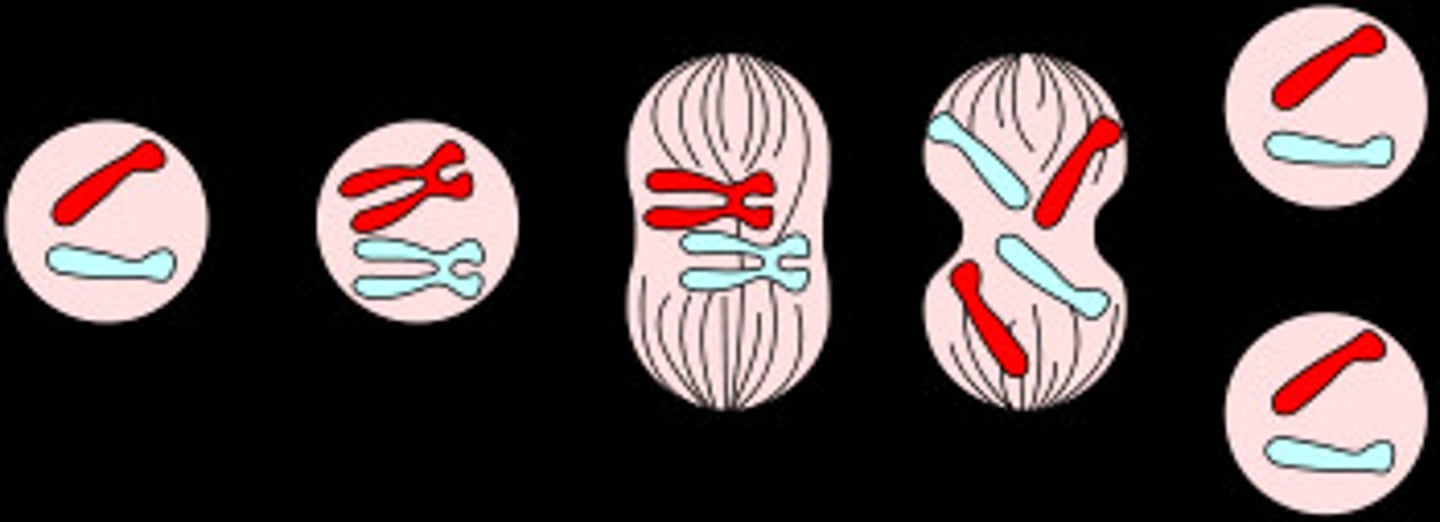
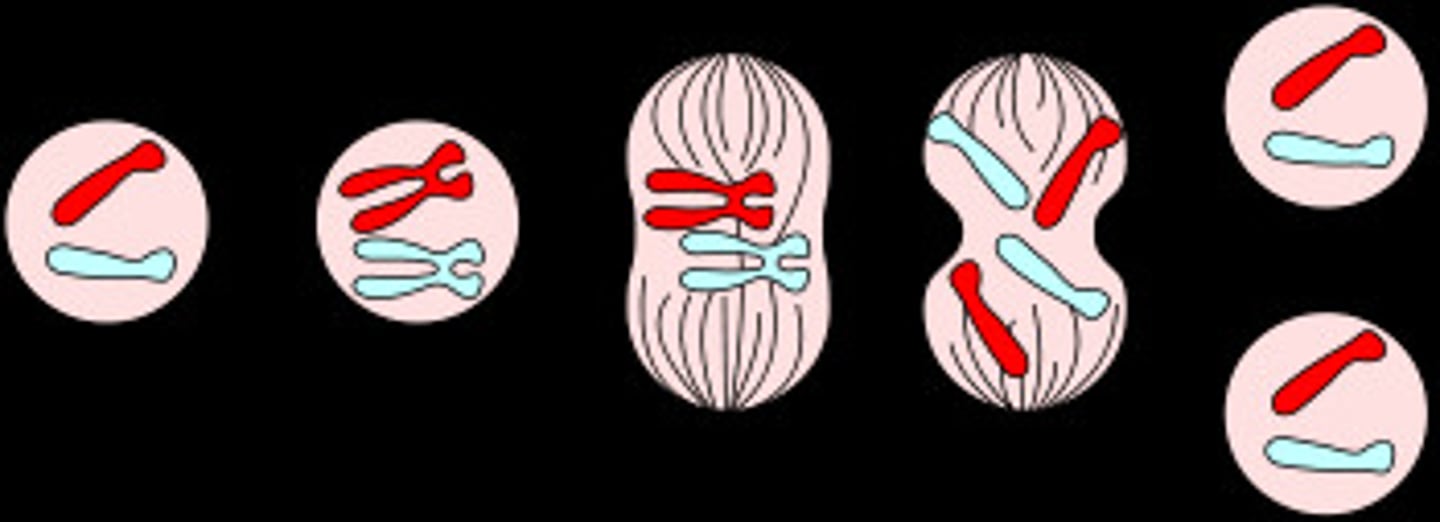
mitosis
this is the process which happens after meiosis and also happens in asexual reproduction where a chromosome is separated into sister chromatids and the other sister chromatid is creates and then they split off. (PMAT)
Fertilization
Process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells join to form a new cell
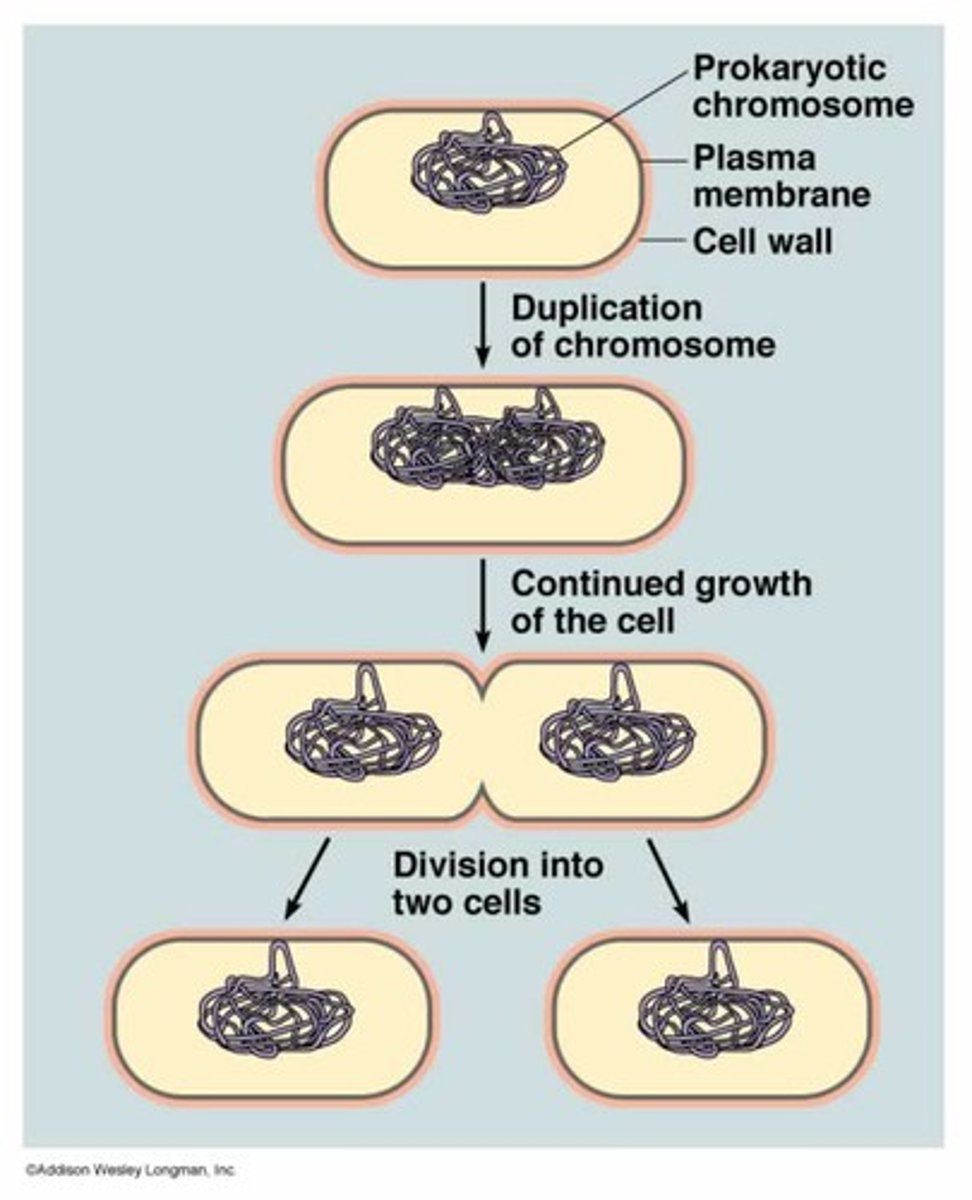
binary fission
a type of asexual reproduction in which the cell splits in half with each cell having identical copies of the DNA
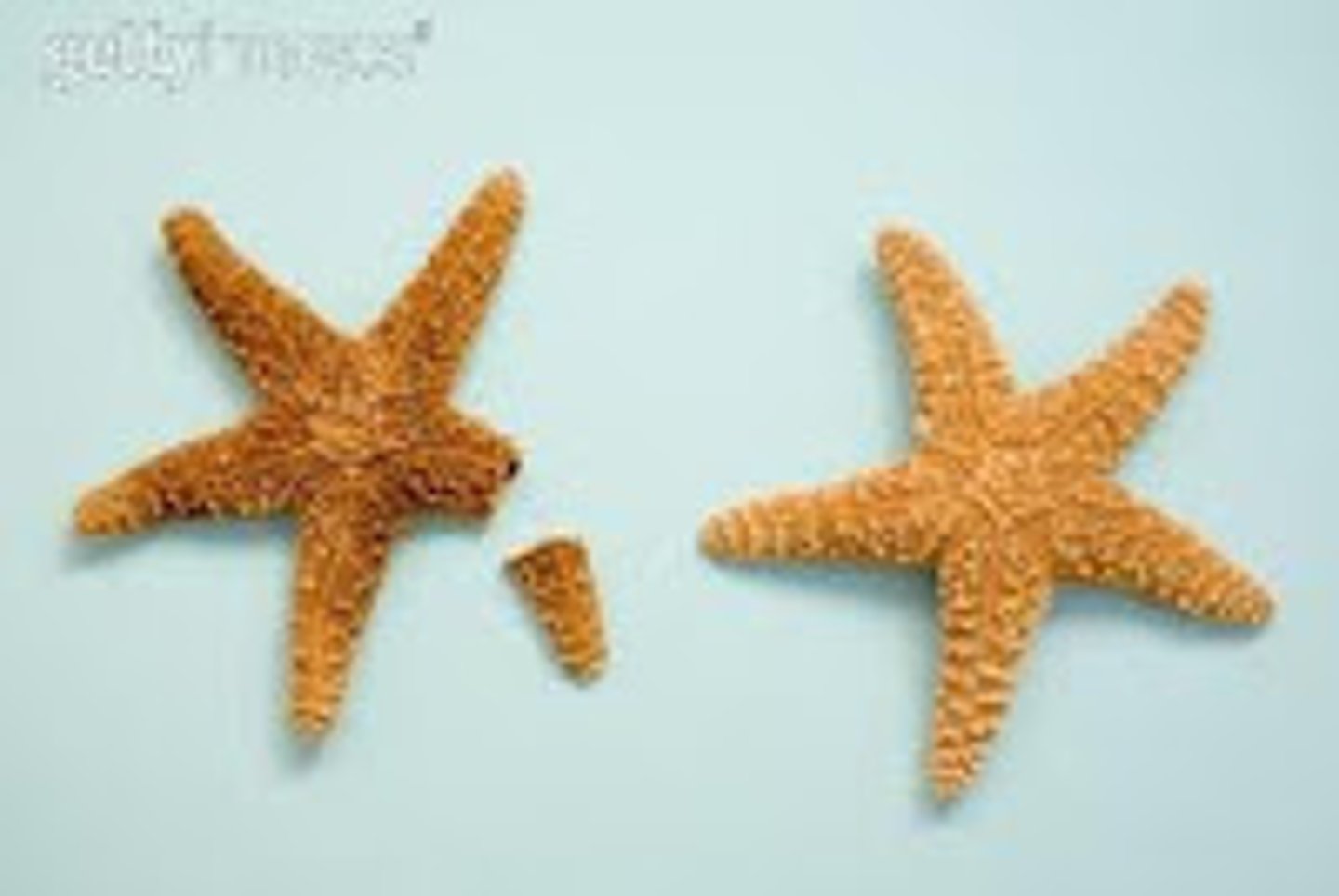
Fragmentation
this is the process in which a part is separated from the rest of the organism and then it grows back the rest of the organism in the form of a copy (asexual reproduction)

Budding
this is the process in which a part is separated from the rest of the organism and then it regenerates the rest of the organism as another organism.

Crossover
this is the exchamge of dna in homologous pairs
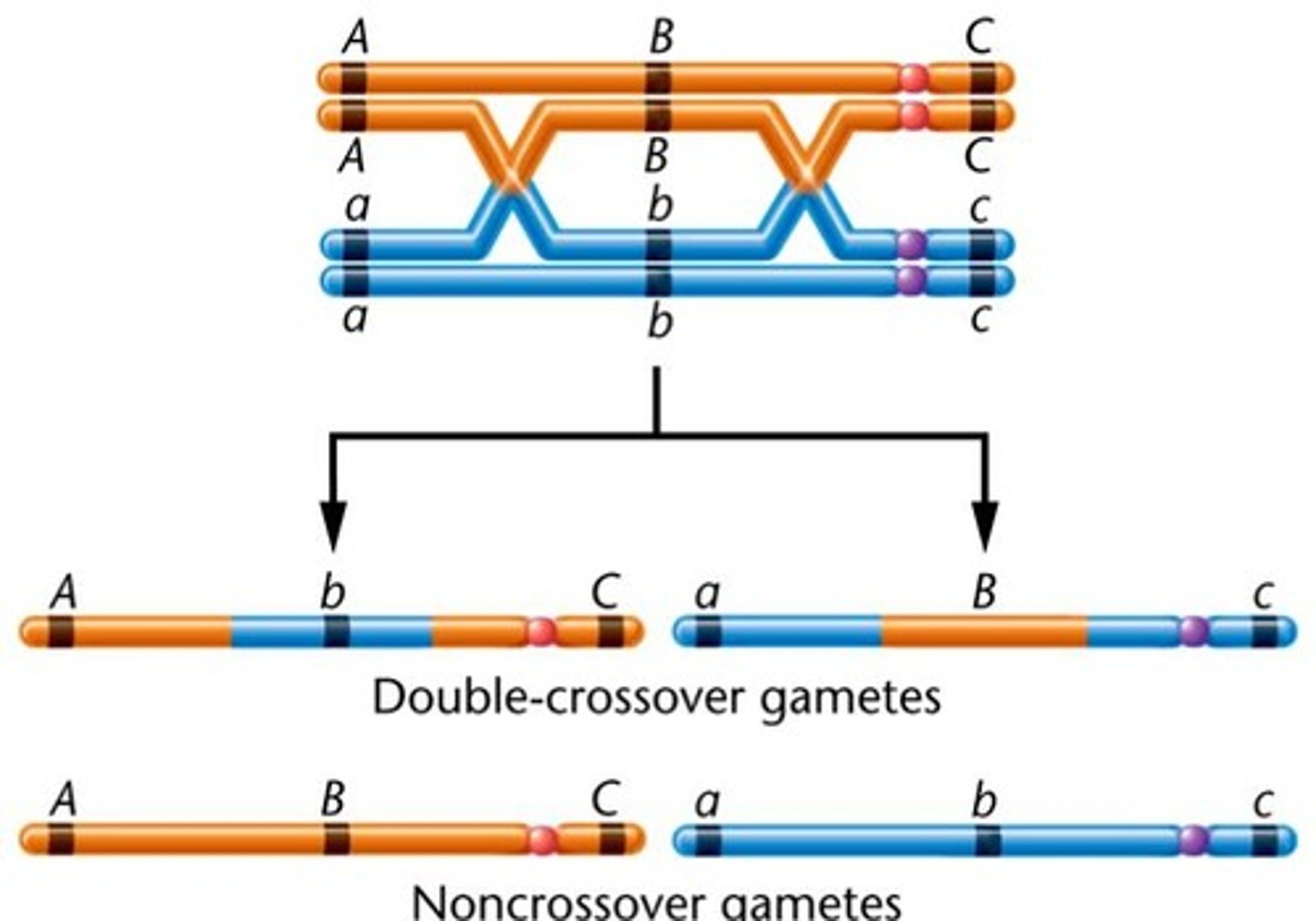
recombant chromosomes
this is chromosomes that have had dna swapped or crossed over between the parent cells
Independant Asortment
the process in which the cells can have varying dna based on the possibilities of the exchangement of genes
Pathogenesis
this is the production of a zygote from an unfertilized egg(asexual reproduction)
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
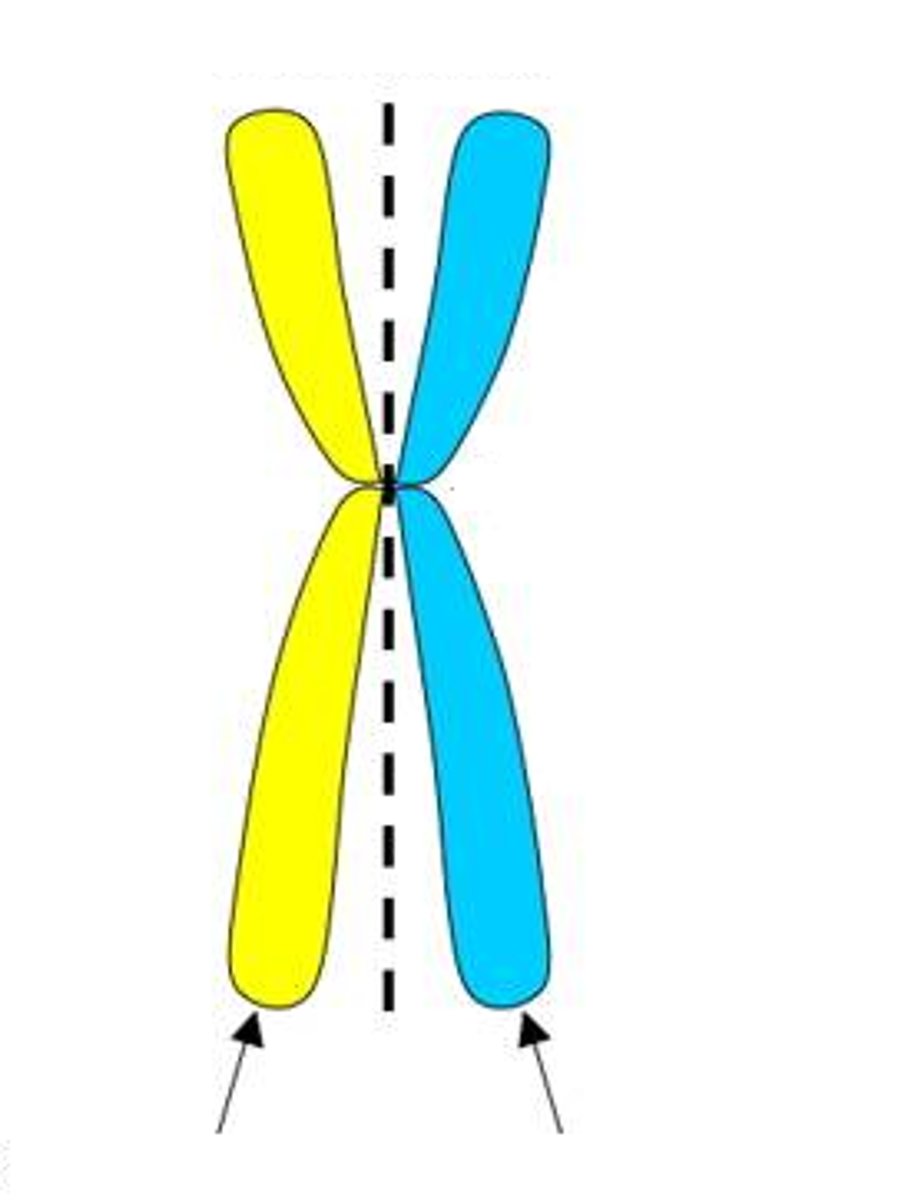
non-sister chromatids
chromatids belonging to homologous chromosomes

sister chromatids
Nondisjunction
this is when in meiosis the chromosomes do not separate evenly.
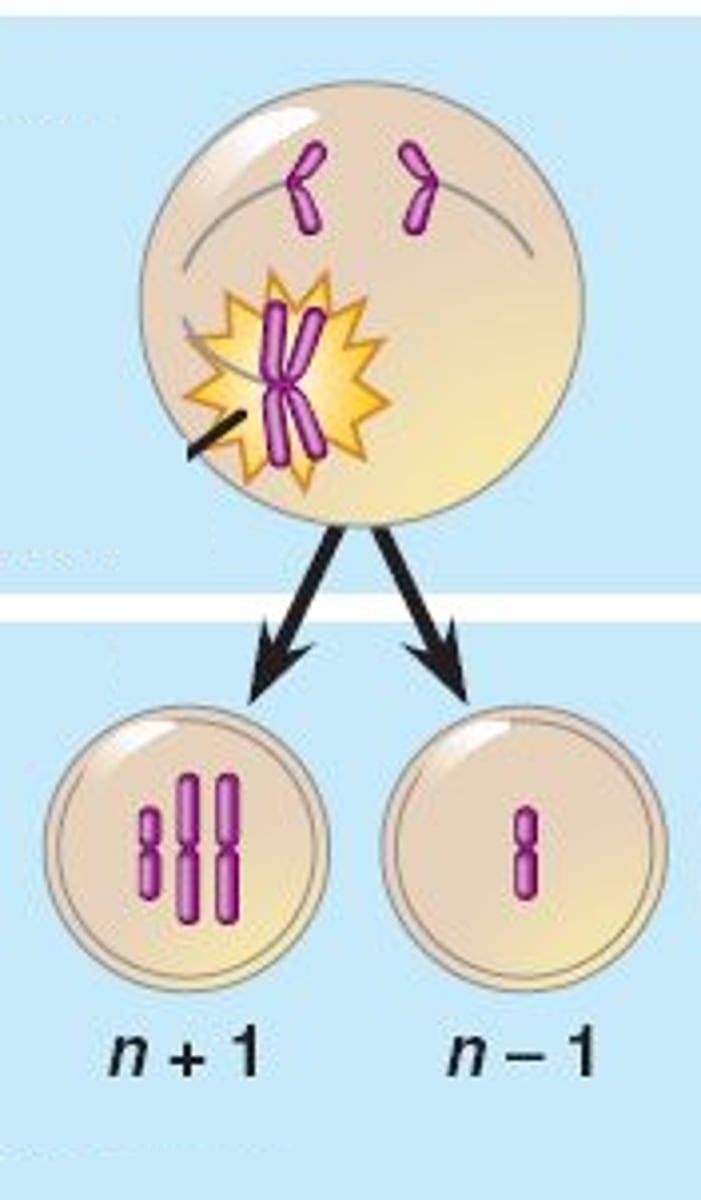
aneuploidy
this is the result of nondisjunction in which is defined by an uneven number of chromosomes
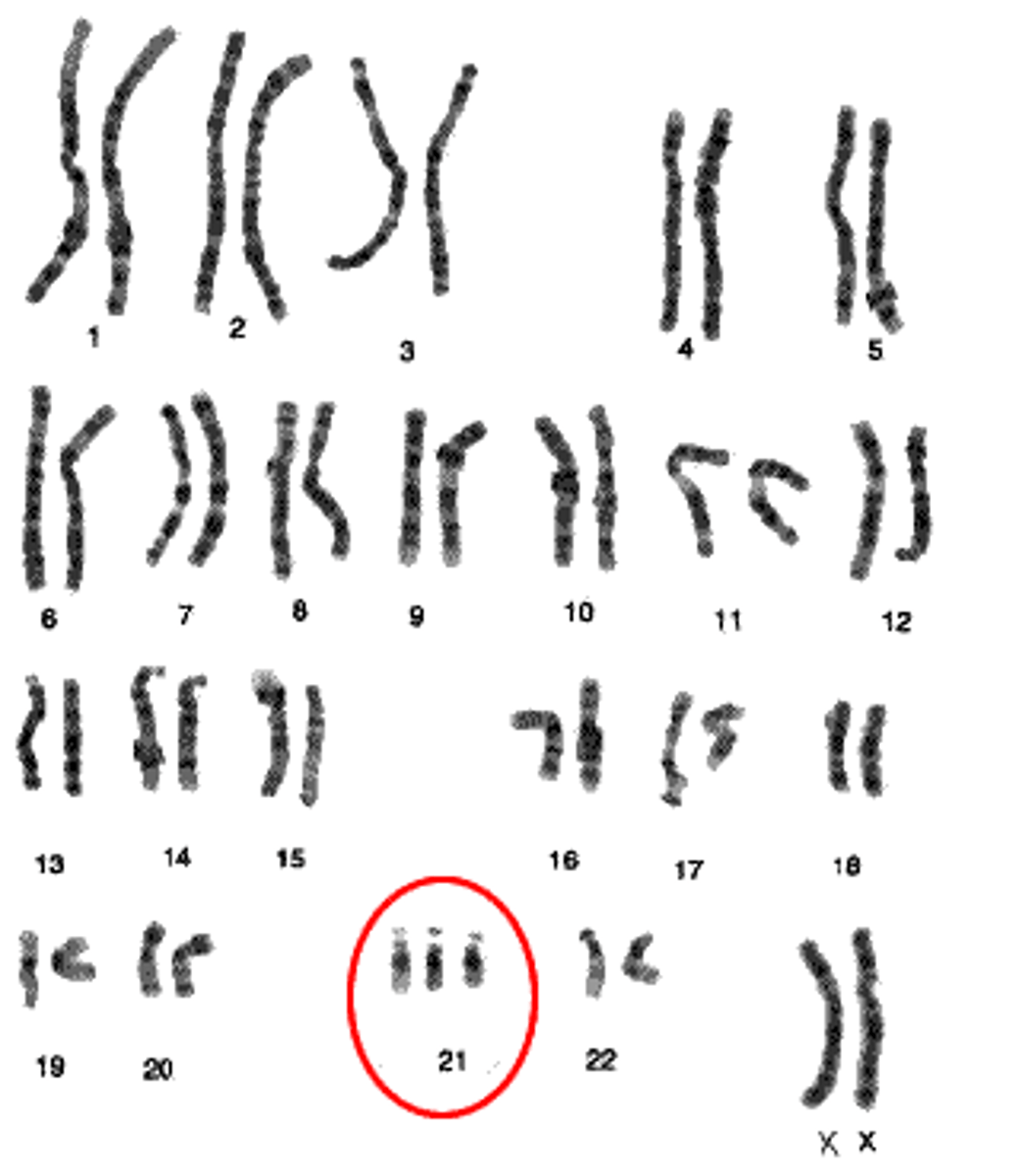
Karyotype
this is the complete set of chromosomes lined up bu the same gene, allows to determine genders and other things such as having more or less chromosomes which lead to problems such as down syndrome
down syndrome
has an extra chromosome of number 21
turner syndrome
this is when there is a missing x or partial x in their sex chromosome, leads to delayed puberty and developmental things. They are also known to be infertile.
Extra copy of the X chromosome
Klinefelter syndrome, delayed or incomplete puberty as well as the possibility to be infertile
mieosis number of chromosomes after
1/2 starting value
Mitosis number of chromosomes after
the same as before
how many chromosomes do humans have?
46 chromosomes, 23 pairs
independant assortment
the possibilities of the variation of genes

where dose crossover occur
what happens in prophase 2
spindle fibers form and chromosomes condense
mieosis vs mitosis
mieosis vs mitosis