Lecture 21 - Community Ecology: Mutualism and Symbiosis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Define symbiosis.
Two species live together.
Define mutualism.
An interaction between two species that benefit both parties.
What are the categories of mutualism?
Nutritional Mutualism
Defensive Mutualism
Dispersal Mutualism
What is an example of nutritional mutualism?
Legumes and Rhizobia:
bacteria live on nodules and they take atmospheric nitrogen and fix it into a form that plants use for growth. As a reward, they get carbohydrates from the plant.
Mycorrhizal Fungi
They colonise plant roots and they try to get phosphorous or water to provide for their plant host. The plant then gives them carbohydrates as a reward.
What is an example of defensive mutualism?
Ants and Plants
exchanging food for protection
What is an example of dispersal mutualism?
Plant and animal seed dispersers
exchange seed dispersal for food
Plants and animal pollinators
exchange pollination for food
What is an example of a mutualism between humans and a wild animal?
Yao people of Mozambique harvest wild honey but cannot find the bee’s nests easily.
However, the bird Honeyguides eats bees was and knows where the nests are, but cannot access the nests easily.
Hence, the Yao people and Honeyguides have a mutualistic relationship as the birds lead the Yao people to the nests and the Yao people leave the wax for the birds to eat.
What did Claire Spottisoode do?
She is a ornithologist, someone who studies birds.
She did a playback experiment with the Honeyguides to see if the noise the Yao people make to get the birds’ attention is something that the Honeyguides can recognise.
The birds could recognise it and it resulted in the likelihood of the birds showing the Yao people to the bees nest to increase.
How do you represent mutualism in a Lotka-Volterra model for inter-specific competition?
Instead of having a negative sign where the population size of one species negatively affects the population size of another species, there is now a positive effect.
Hence, positive sign instead of negative size.
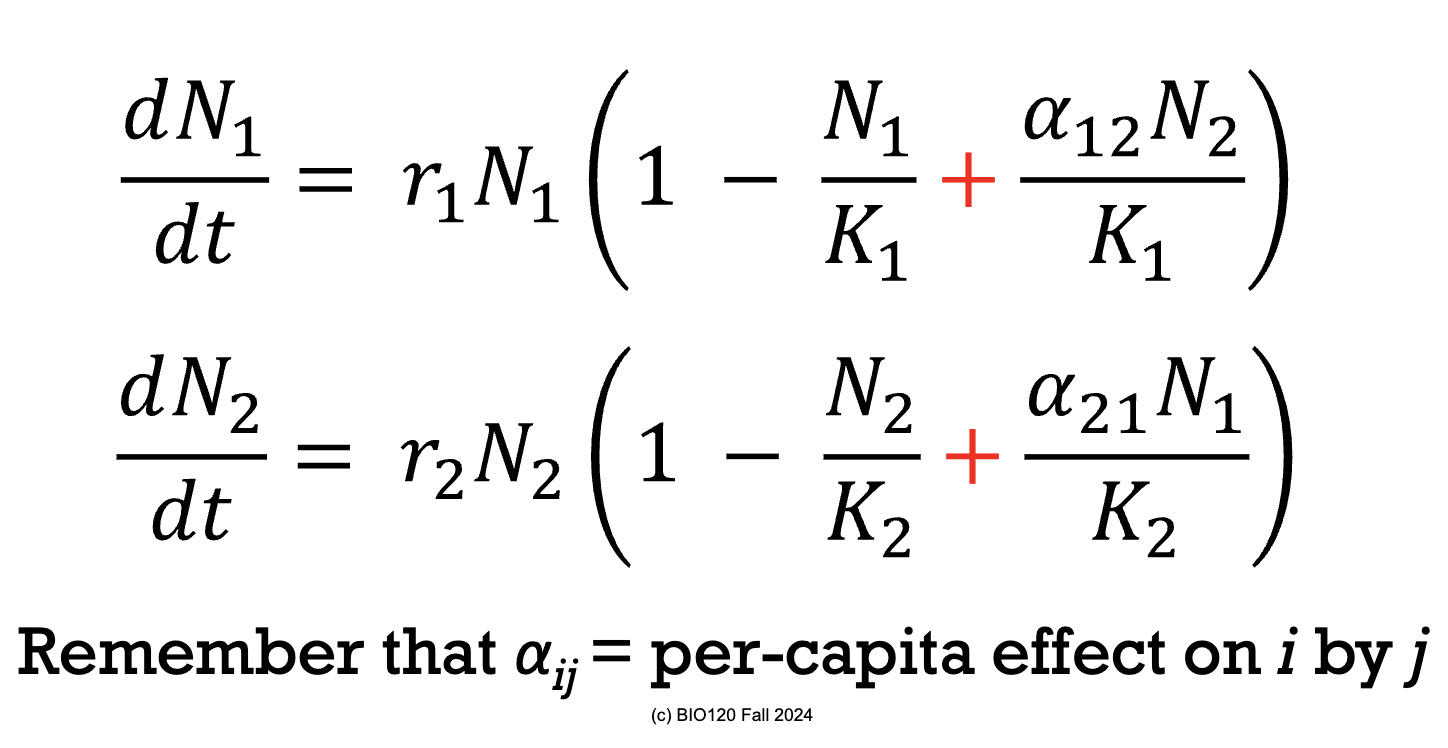
What does the α mean in the mutualism Lotka-Volterra model for inter-specific competition?
α now shows how one species benefits the other species.
What is a limitation to the mutualism Lotka-Volterra model for inter-specific competition?
If both populations reach their carrying capacity the term
N1/K1 = 1
Therefore, the first part of the term becomes 1-1 = 0, meaning that the term in the brackets becomes positive and the population can grow beyond its carrying capacity.
Hence, the growth rate of species 1 will increase as the population of species 2 increases. The increase in the species 1 population will then increase the growth rate of species 2. This will go on and on.
Both species will grow beyond its carrying capacity with no limits (faster than exponential growth).
THIS IS UNREALISTIC.
What limits the population growth of mutualists?
Strong intra-specific competition
Another species like a predator or competitor hinders growth
Diminishing returns as the population grows
When are runaway population growth rates generated?
When there is positive feedback amongst mutualists.
Define invasional meltdown.
The process where two non-native species facilitate one another’s rapid spread.
What is an example of invasional meltdown?
Spring ephemerals.
Their seeds are dispersed by ants. There is a fleshy coating around the seeds which is what attracts the ants for seed dispersal.
Define mesocosm.
An artificial ecological community that you stock with species of interest.
What is an example of mutualism helping each other prosper?
Prof Frederickson made mesocosms and put invasive and native ants inside. The plants that formed were then observed after a year.
First, the native ants dispersed native seeds and so the mesocosm was filled with native plants.
However, the invasive ants dispersed invasive seeds. Hence, the mesocosm was almost entirely filled with invasive plants.
Hence, pairs of species can really help each other prosper (invasive helped invasive, native helped native).
What is an example of parasitic mutualism?
Cleaner fish feed on parasites that are on the body of client fish. The cleaner fish then gain food while the client fish benefit from having fewer parasites (gnathiids) on their body.
There are ‘cleaning stations’ where client fish can go to get their parasites removed by them (like a grooming service).
Through research, ecologists noticed that the removal of cleaner fish increased the parasite abundance on client fish.
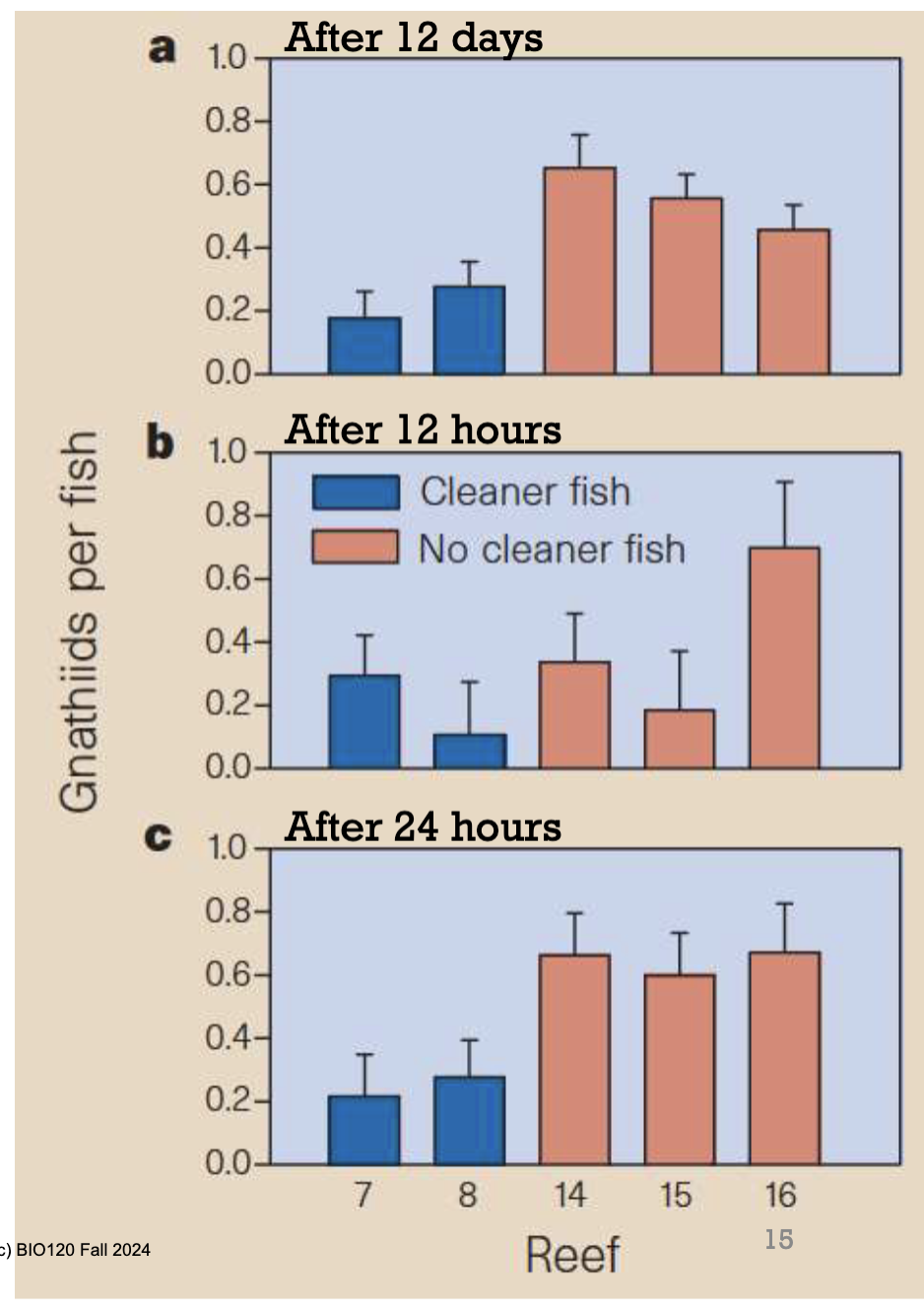
How has the impact on mutualism between cleaner and client fish affect species diversity of other reef fish?
Redouan Bshary added and removed cleaner fish in reefs and observed what happened to diversity.
He found that when cleaner fish were removed, the number of fish species went down.
However, when cleaner fish were added, the number of fish species increased.
Hence, in this example mutualism increased species diversity because the addition of cleaner fish attracted more client fish, increasing diversity in the reef.
Does mutualism always increase species diversity?
No. It can go either way.
*think about the ant that killed other trees if they were close by talked about in the lab notebook.
What did Darwin predict about the Orchid, Angraecum Sesquipedale?
He noticed that there was a very long nectar spur and didn’t know how a species could pollinate it (because the spur is so long and no one had ever observed an insect with that long of a mouth piece).
However, he predicted that there was an insect with a long enough mouth to pollinate the orchid.
What was Darwin’s prediction about the benefits of having a longer nectar spur?
He thought it would force the insect to go deeper into the flower and come into contact with the pollen receiving parts of the flower. Thus, improving pollination for the flower.
Why did the Darwins orchid have such a long nectar spur? What is this an example of?
In order for the insects to get more pollen down the long nectar spur, they would have to have longer mouth parts. Hence, as the insects evolved longer mouth parts, the flowers evolved longer nectar spurs to improve their pollination.
This then created these really exaggerated traits in both species.
This is an example of co-evolution (reciprocal evolution).
*not sure it’s true but there are similar cases and it’s Darwin’s prediction.
What is an example of bacterial symbionts?
Nancy Moran found that…
Aphids feed on phloem sap, which is rich in sugar, but low in amino acids.
To get amino acids, aphids have intracellular bacteria called Buchnera that provide them with essential amino acids. This is a bacterial symbiotic relationship.
Buchnera is vertically transmitted and are passed in aphid eggs from their moms.
What is the genome size of vertically transmitted endosymbionts?
Small.
Why is the genome size of vertically transmitted endosymbionts small?
Because bacteria loses genes that they no longer need thanks to their new lifestyle.
nicely protected in the host cell - so don’t need as many defences
or they both make the same resource so the bacteria can eventually stop producing it
How are most mutualisms transmitted?
Horizontally.
So every generation has to find a new partner, not passed on from their moms.
Are mutualisms usually one-to-one or many-to-many interactions?
Many-to-many interactions.
Define microbiomes.
All the microbes living together in a community or their collective genomes.
How are microbes useful?
New technology has allowed scientists to sequence highly conserved genes (genes that evolve slowly). Through this, scientists can identify microbes and study them.
This is great because microbes have been found to benefit people, rather than harm them.
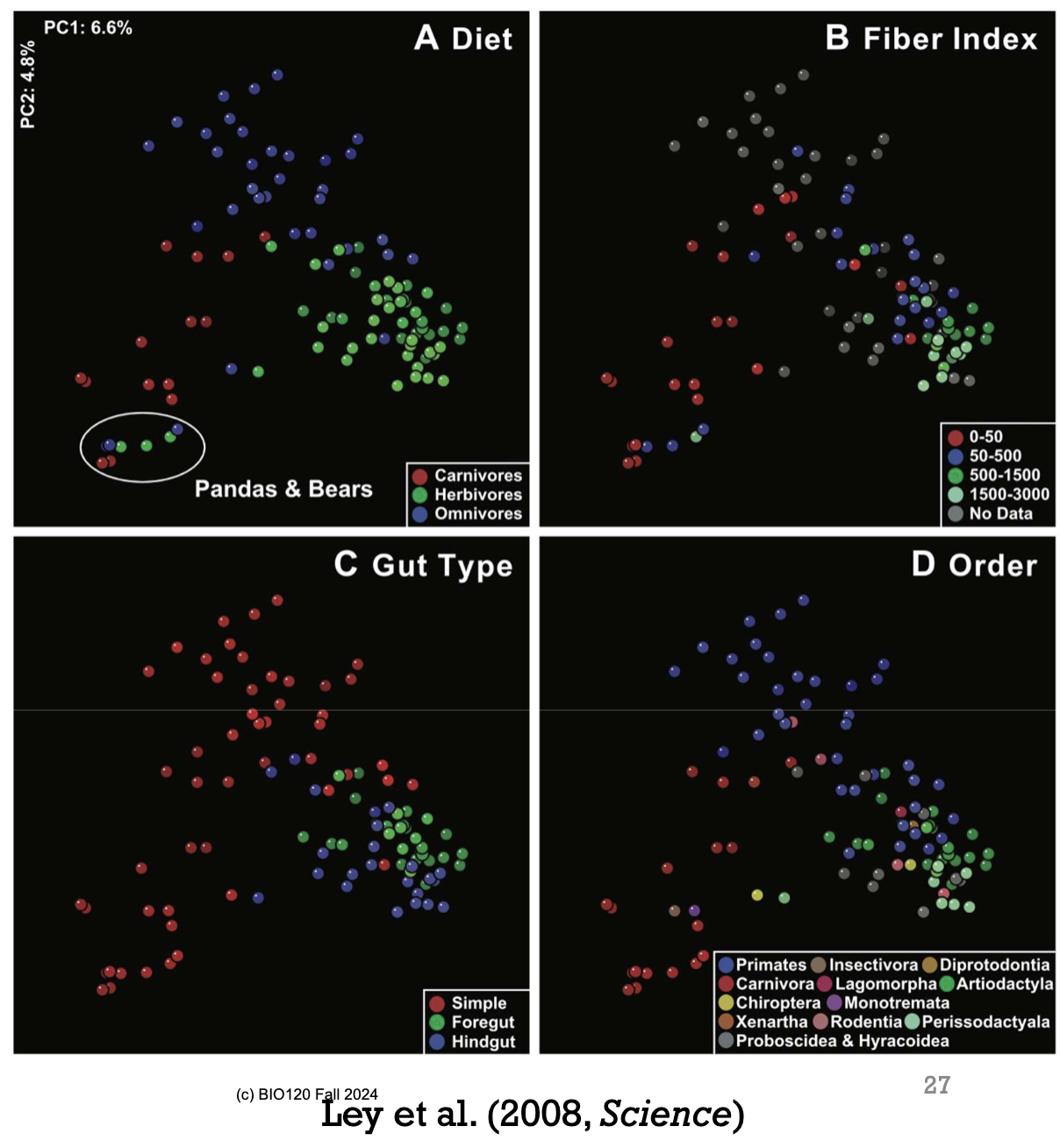
What did Ruth Ley discover about microbiomes in mammalian guts?
The microbiomes in mammalian guts reflect the diet, phylogeny and morphology of species.
In the image, the dots represent different species. Dots that are close together have similar microbiomes, whereas dots that are far apart have very different microbiomes. The colours represent factors of interest (red = carnivore, green = herbivore, blue = omnivore).