Biology Intro Unit
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:59 AM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Theory
- well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations
- broader than hypothesis
- broader than hypothesis
2
New cards
Prokaryote
unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus
- smaller than eukaryotes
- smaller than eukaryotes
3
New cards
eukaryote
organism whose cells contain a nucleus
4
New cards
emergent properties
due to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases
5
New cards
symbiotic relationships
The relationship between two species that live in close association with each other
- predation, parasitism, herbivory, commensalism, mutualism, competition
- predation, parasitism, herbivory, commensalism, mutualism, competition
6
New cards
commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
7
New cards
mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
8
New cards
parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and lives on the host while the other is harmed
9
New cards
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
10
New cards
fitness
how well an organism can survive and reproduce in its environment
11
New cards
phenotypic variations
differences in the physiology, anatomy, or behavior of different species or individuals of the same species (physical features)
12
New cards
evidence for evolution
1. Drug resistant pathogens
2. Homology
3. Fossil Record
4. Biogeography
2. Homology
3. Fossil Record
4. Biogeography
13
New cards
homology
similarity resulting from common ancestry
- Morphological: common physical attributes due to convergent evolution
- Molecular: two organisms share many portions of nucleic acids sequence (molecular homoplasies)
- Morphological: common physical attributes due to convergent evolution
- Molecular: two organisms share many portions of nucleic acids sequence (molecular homoplasies)
14
New cards
phylogenetic trees/cladograms
represents the history of species divergence
15
New cards
binomial nomenclature (taxonomy)
First: genus -- Second: Species name Ex: Homo Sapiens
16
New cards
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
17
New cards
molecular homoplasies
in organisms that do not appear to be closely related, the bases that their otherwise very different sequences happen to share may simply be coincidental matches
18
New cards
shared derived character
An evolutionary novelty that is unique to a clade.
19
New cards
maximum parsimony
one should first investigate the simplest explanation that is consistent with the facts.
20
New cards
Molecular clocks
A method for estimating the time required for a given amount of evolutionary change
- based on the observation that some regions of genomes evolve at constant rates.
Unreliable:
- natural selection causes bursts of genome change
- after the fossil record we have nothing to go off of
- based on the observation that some regions of genomes evolve at constant rates.
Unreliable:
- natural selection causes bursts of genome change
- after the fossil record we have nothing to go off of
21
New cards
descent with modification
each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time
22
New cards
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Ex: drug-resistant bacteria
Ex: drug-resistant bacteria
23
New cards
vestigial structures
remnants of features that served important functions in the organism's ancestors
24
New cards
analogous structures
Body parts that share a common function, but not structure
25
New cards
homologous features
features with similar structures but (maybe) different functions
26
New cards
biogeography
study of the distribution of organisms around the world
27
New cards
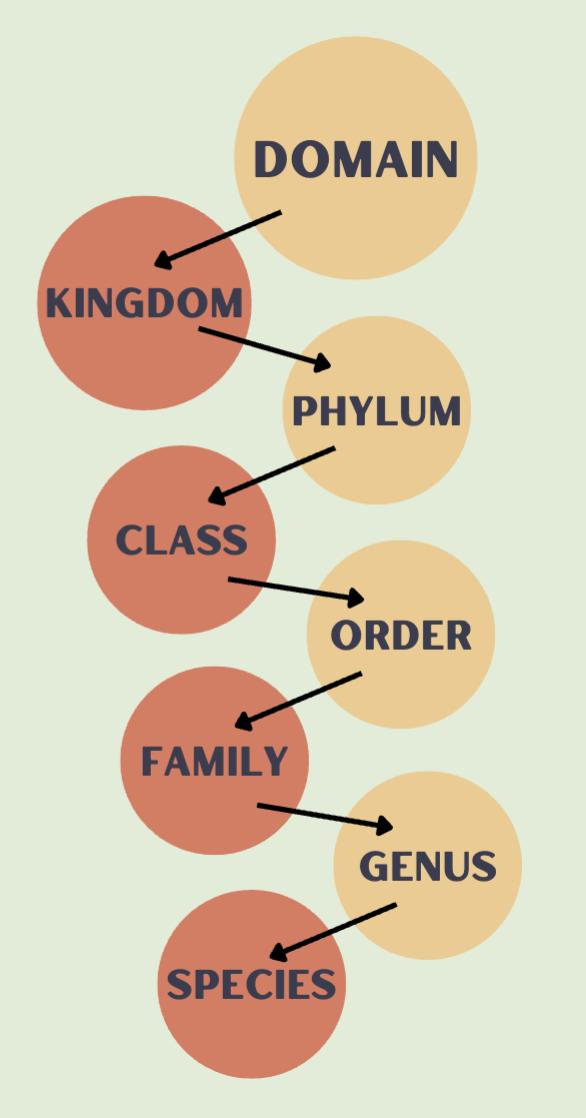
taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified
domain -> kingdom -> phylum -> class -> order -> family -> genus -> species
28
New cards
basal taxon
a lineage that diverges early in the history of a group
29
New cards
analogy
similarity between organisms due to convergent evolution
30
New cards
taxon
a group of organisms in a classification system
31
New cards
phylogenetic trees represent a \___
hypothesis
32
New cards
clade
A group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants.
33
New cards
monophyletic group
group that consists of a single ancestral species and all its descendants
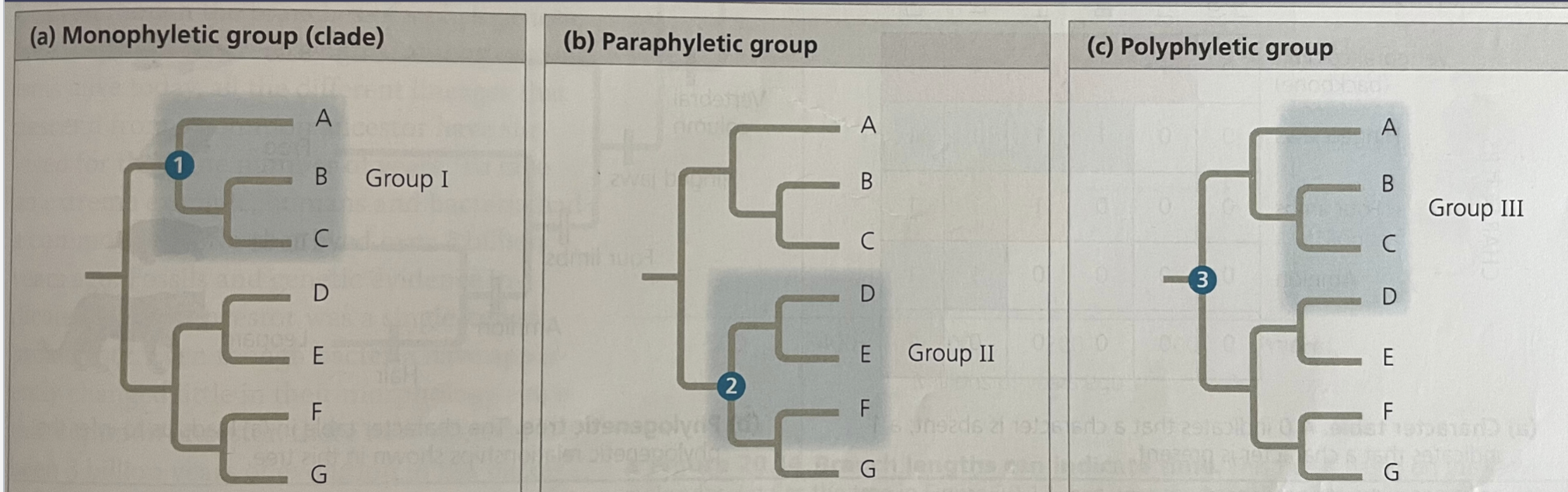
34
New cards
paraphyletic group
composed of some but not all members descending from a common ancestor
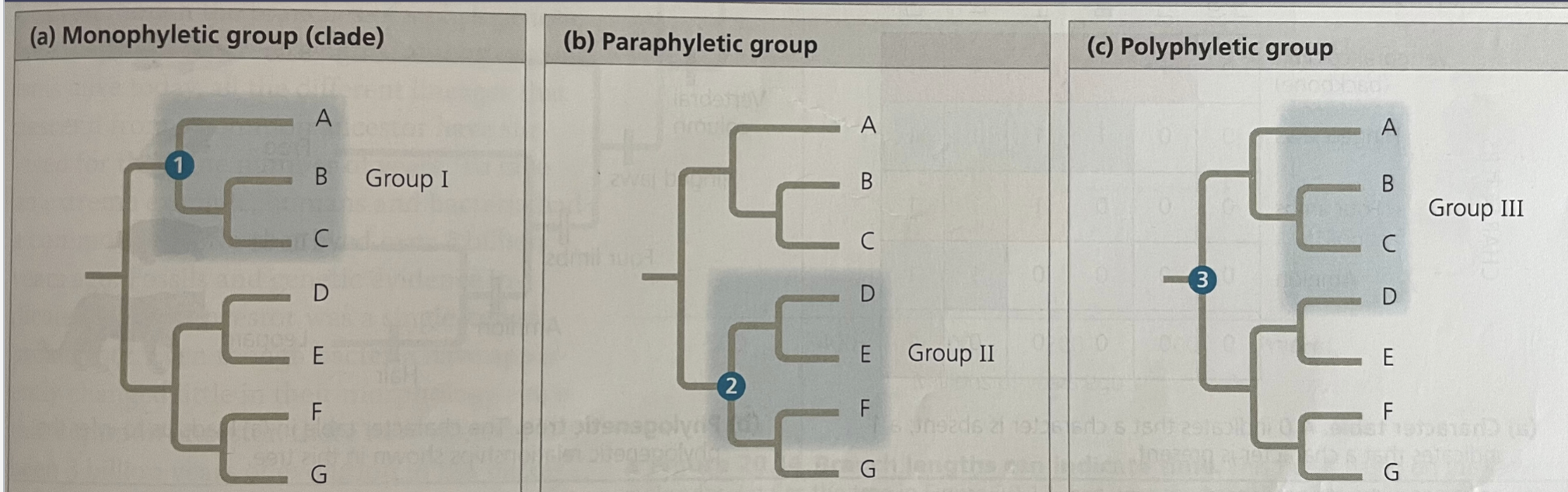
35
New cards
polyphyletic group
an unnatural group that does not include the most recent common ancestor
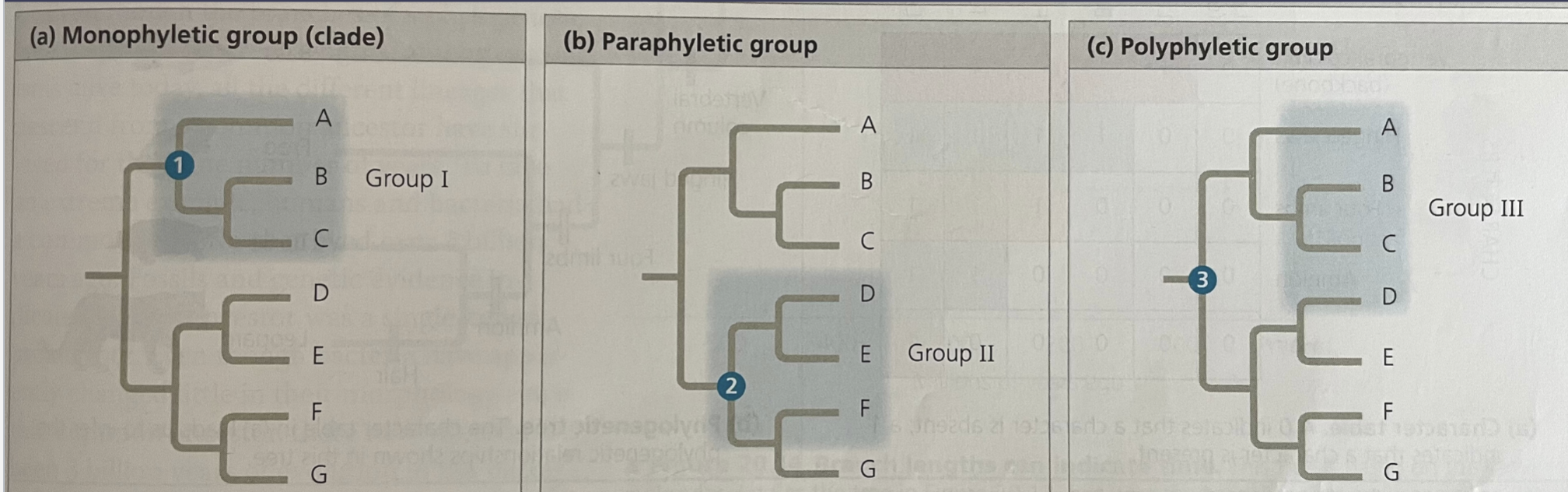
36
New cards
Three Domains
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
37
New cards
horizontal gene transfer
transfer of genes between cells of the same generation
38
New cards
mutation
random change in an organisms genome
39
New cards
dependent variable
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested. (pillbugs in each chamber)
40
New cards
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied (time)
41
New cards
species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
- Reproductive Isolation
- Reproductive Isolation
42
New cards
adaptive radiation
Evolution of many new species from a common ancestor as a result of introduction to new environments. (quickly)
43
New cards
Biology Themes
1. New properties emerge at successive levels of biological organization
2. Life's process involves the expression and transmission of genetic info
3. Life requires the transfer and transformation of energy and matter
4. Organisms interact with other organisms and the physical environment
2. Life's process involves the expression and transmission of genetic info
3. Life requires the transfer and transformation of energy and matter
4. Organisms interact with other organisms and the physical environment
44
New cards
genetic variation
The variety of different types of genes (DNA) in a species or population.
45
New cards
Consumer levels
Tertiary consumers (ex: humans and orcas) --\> Secondary consumers (eat primary consumers) --\> Primary consumers (ex: worms) --\> Producers (ex: plants)