D and F block elements(JEE), Thermodynamics(JEE) - chemistry, Chemical bonding(JEE), The Periodic table(JEE), Atomic structure(JEE), Coordination Compounds(JEE)
1/351
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
352 Terms
D and F elements belong to ___ group
3-12
outer electronic configuration of D block
(n-1)d¹⁻¹⁰ ns¹⁻²
outer electronic configuration of D block is (n-1)d¹⁻¹⁰ ns¹⁻². what is the exception for this rule?
Pd (4d¹⁰ 5S⁰)
D block has more than one typical metallic structure, what is/are the exception to this?
Zn, Cd, Hg, Mn
why do D block elements have more melting point?
there is more involvement of (n-1)d electrons(covalent bonding) in addition to interatomic metallic bonding
in a graph of MP(melting point) plotted against Z(Atomic number), the curve peaks at dˣ configuration, where x=___
5
metal metal bonds are more uncommon in 5d and 4d series compared to 3d series. true or false?
false(more common in 5d and 4d)
for ions of the same charge, radius _______(increases/decreases) with increasing at. no. Why?
decreases, due to increasing nuclear charge
Zr and Hf have similar atomic radius. this is a consequence of ____
lanthanide effect
density significantly _____ from Ti to Cu
increases
ns electrons are lost before (n-1)d electrons. True or false?
true
True or false: differentiating electron enters ns orbital first
false, differentiating electron enters the (n-1)d orbital
factors affecting IE
attraction to nucleus, inter electron repulsion, exchange energy
name the transition metal exhibiting +1 oxidation state
Cu
name the transition metal exhibiting highest oxidation state
Mn(+7)
what are the oxidation states shown by Fe
2, 3, 4, 6
oxidation states exhibited by Scandium
+3
elements showing the largest number of oxidation states have dˣ configuration, where x=_
5
usually lower oxidation states are favored by heaver members of the p block. Is this trend continued in the d block?
no
true or false: Mo(VI) and W(VI) are less stable than Cr(VI)
false(higher oxidation states of d block are more stable in heavier elements)
MoO3(hehe moo) and WO3 are stronger oxidizing agents than CrO3. true or false?
False(since Mo(VI) and W(VI) are more stable than Cr(VI)
higher oxidation states form
fluorides and oxides
why do higher oxidation states form halides?
due to high lattice energy as in the case of CoF3 or high bond enthalpy as in the case of VF5 and CrF6
highest oxidation state of Mn is found in
MnO3F
fluorides are more stable at low oxidation state. true or false?
false
oxygen stabilizes higher oxidation states better than fluorine. true or false?
true
highest Mn fluoride is?
MnF4
highest Mn oxide is?
Mn2O7
magnetic moment is calculated using the formula
√(n(n+2)) BM
catalytic activity of d block is due to?
multiple oxidation states, ability to form complexes
state 4 properties of interstitial compounds
high melting point, hard, retain metallic conductivity, chemically inert
_____ interstitial compounds approach diamond in hardness
boride
alloys are formed when atomic radii are within ___ % of each other
15
lanthanoids have ___ stable oxidation states
1
actinoids have one stable oxidation state. true or false?
false
characteristics of lanthanoids(3)
tarnish rapidly in air, silvery white metals, soft
hardness _____ with increase in atomic number for lanthanoids
increases
the hardest lanthanoid is
Samarium
lanthanoids are coloured in aqueous solutions. the exceptions are:
La, Ce
stability of half filled configuration is found in ____ in lanthanoids
Gadolinium
earlier members of the lanthanoid series are similar to ___, higher members are similar to ___
Ca, Al
mischmetal contains ___% lanthanoid
95
TiO is used in manufacture of ___
pigments
MnO2 is used in the manufacture of ____
dry cell batteries
formula for Ziegler catalyst
TiCl₄
Wacker's process uses the catalyst ___
PdCl2
a compound has empty d orbitals yet is coloured, give a reason for this
due to charge transfer
MnO₄¯ has no d electrons, yet is coloured, why?
due to charge transfer phenomenon
how many of the following are interstitial compounds?
TiC, Mn₄N, Fe₃H
3
___ and ___ do not form amalgams
Fe and Pt
Nichrome consists of
Ni, Fe, Cr
german silver consists of
Cu, Ni, Zn
Gun metal consists of
Cu, Sn, Zn
Devarda's alloy consists of
Cu, Al, Zn
Duralumin consists of
Cu, Al, Mn, Mg
how is potassium dichromate prepared
fusion of chromite ore with sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate in excess air to form chromate, which is made to react with conc. H2SO4 to form dichromate
chromite ore
FeO.Cr2O3
colour of dichromate solution
orange red
when alkali is added to dichromate solution, what is the colour change? what happens when it is acidified
orange red to yellow, back to orange red when acidified
how is potassium permanganate prepared
fusion of MnO2 with alkali metal hydroxide and oxidizing agent like KNO3
common oxidation states of actinides
+3 and +4
what is the difference between a closed system and an isolated system
for a closed system there is no mass exchange, for an isolated system there is neither mass exchange nor energy exchange
intensive property
mass / size independent
extensive property
mass/size dependent
state function
path independent
path function
path dependent
internal energy depends on ___
temperature
formula for internal energy
ΔU=Q+W
sign convention for work done
work done by the system is negative, work done on the system is positive
heat released by the system is ___(positive or negative)
negative
graph of P vs V for isothermal processes
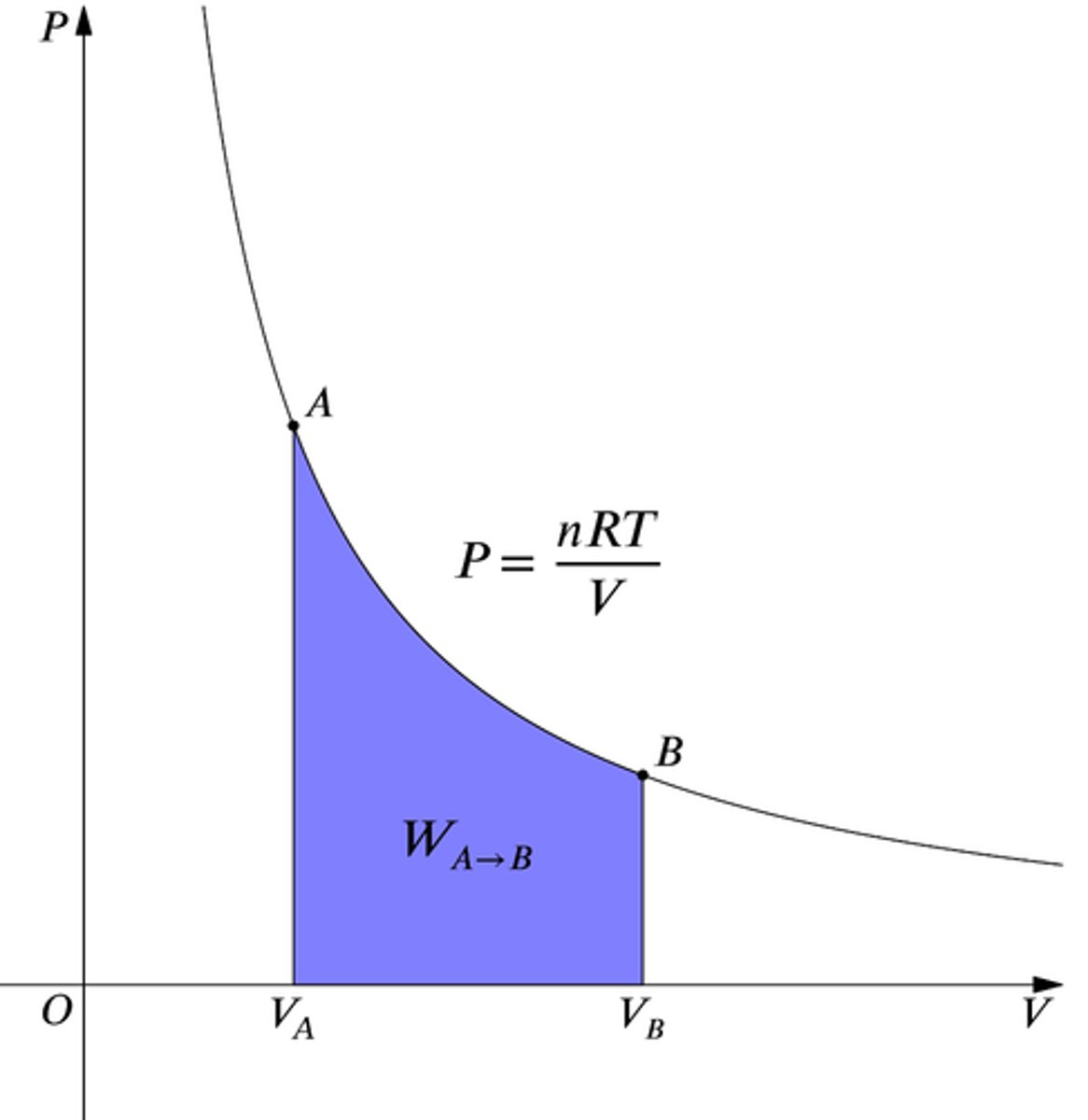
if volume increases, temperature __
increases
constant external pressure applied implies that the process is ____(reversible/irreversible)
irreversible
heat capacity
Q/t(amount of heat absorbed by system to increase its temperature by 1⁰C
specific heat capacity
Cₛ=Q/mΔt
molar heat capacity
Cₘ=Q/nΔt
Mayer's relation
Cp - Cv = R
for isothermal processes, heat capacity =
infinity
for adiabatic processes, heat capacity=
0
condition for adiabatic process
PVˠ = constant
formula for ɣ in terms of degree of freedom
1+2/f
formula for ɣ in terms of Cp and Cv
Cp/Cv
formula for Cv in terms of degree of freedom and R
ᶠᴿ/₂
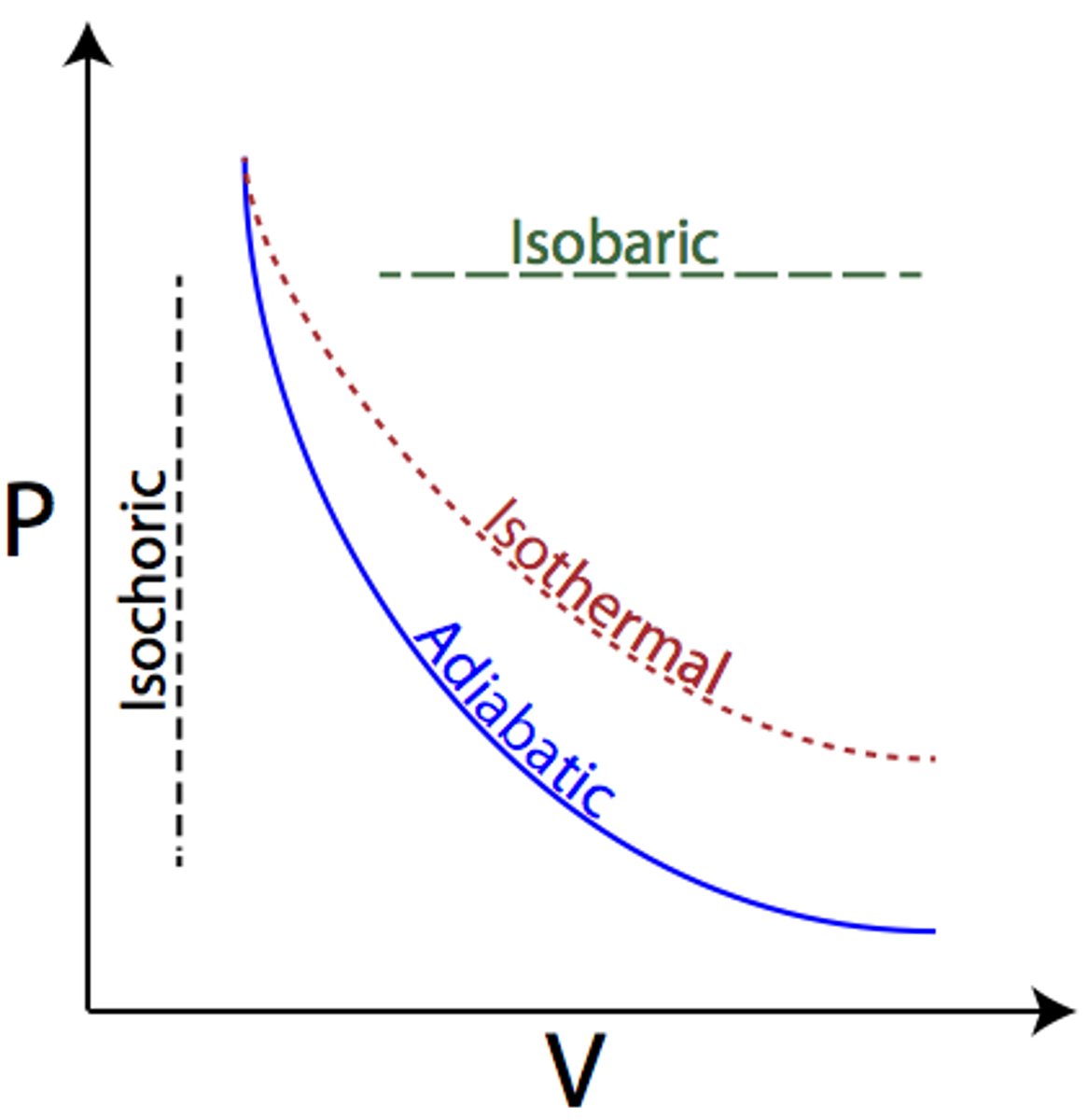
how would you identify isothermal and adiabatic process for P vs V graph?
adiabatic process has more slope
for an isothermal reversible process, work done=
-nRTln(V₂/V₁) = -nRTln(P₁/P₂)
for an isothermal irreversible process, work done =?
-Pₑₓₜ(ΔV) = -Pₑₓₜ( nRT/P₂ - nRT/P₁)
ΔH for isothermal process
0(ΔH=Qp = mCpΔT)
for adiabatic process, work done is
nRT/ɣ-1
for irreversible adiabatic process, work done is
-Pₑₓₜ(ΔV) = -Pₑₓₜ( nRT/P₂ - nRT/P₁)
in a cyclic process, clockwise curve represents ____(positive/negative) work done
positive
condition for polytropic processes
PVˣ
work done in a polytropic process
nRT/x-1
for a polytropic process, if x=infinity, the type of process is
isochoric
for a polytropic process, if x=1, the type of process is
isothermal
for a polytropic process, if x=0, the type of process is
isobaric
for a polytropic process, if x=ɣ, the type of process is
adiabatic
for a monoatomic gas, ratio of P to V is 1. what is the value of Cm?
P/V=1 => PV⁻¹ = constant =>x=-1,
Mayer's relation: Cm = Cvₘ + R/(1-x)
= 2R
what is the modified Mayer's relation for polytropic processes
Cm = Cvₘ + R/1-x
what is the value of universal gas constant
25/3 J/mol K or 2 cal/mol K
relation between ΔH and ΔU
ΔH=ΔU+ΔngRT