05.B BIO Carbohydrates (PART B)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Organic compound
Compound that contains carbon bonded to hydrogen and is found in living things
Macromolecules
Aa large molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules called monomers. Organic macromolecules include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrate (Function)
An essential structural component of many cells and source of quick energy
Carbohydrate (Elements)
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen; ration 2H:1O
-ose
common suffix for sugars
sacch-
common prefix meaning sugar
-mer
suffix meaning unit
mono-
prefix for one
di-
prefix for two
poly-
prefix meaning many
Carbohydrates (Monomer)
Monosaccharide
Monomer
Simplest building block of a macromolecule
Polymer
Large molecule made up of smaller building blocks or monomers
Monosaccharide (Description)
Building block of carbohydrates; chemical formula is C6H12O6
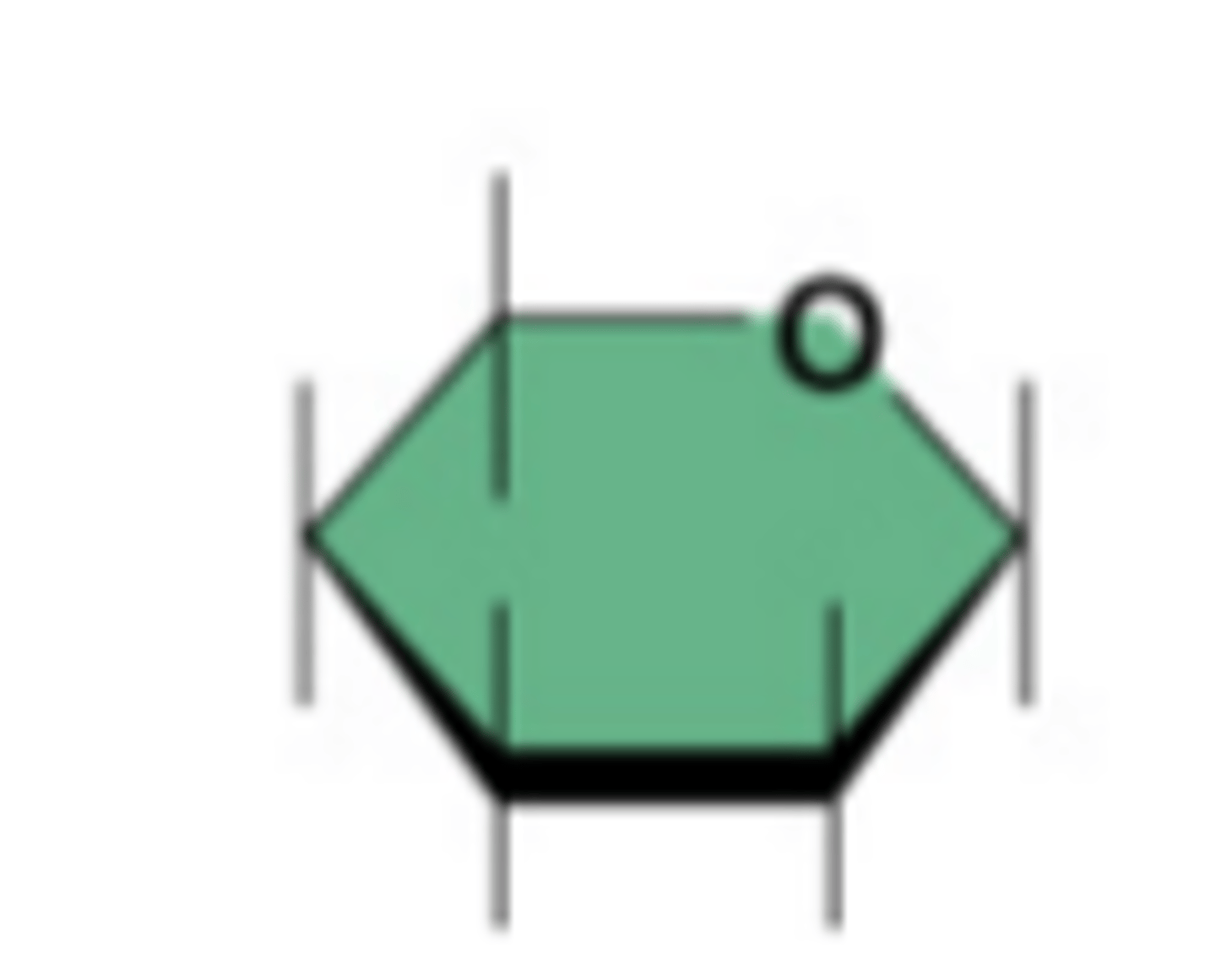
Monosaccharide (Examples)
Examples include - glucose, galactose and fructose
Glucose
A monosaccharide that is used in cellular respiration as a short-term source of energy; also the building block for starch, glycogen and cellulose; chemical formula is C6H12O6
Fructose
A monosaccharide that is naturally found in fruit and honey; chemical formula is C6H12O6
Galactose
A monosaccharide that is found in milk; chemical formula is C6H12O6
Isomers (Description)
Compounds with the same chemical formula but different structural formulas
Isomers (Examples)
Examples of compounds that have the same chemical formula but different structural formations include - glucose, galactose and fructose
Disaccharides (Description)
two sugars/monosaccharides bonded together by a covalent bond; include lactose, sucrose and maltose
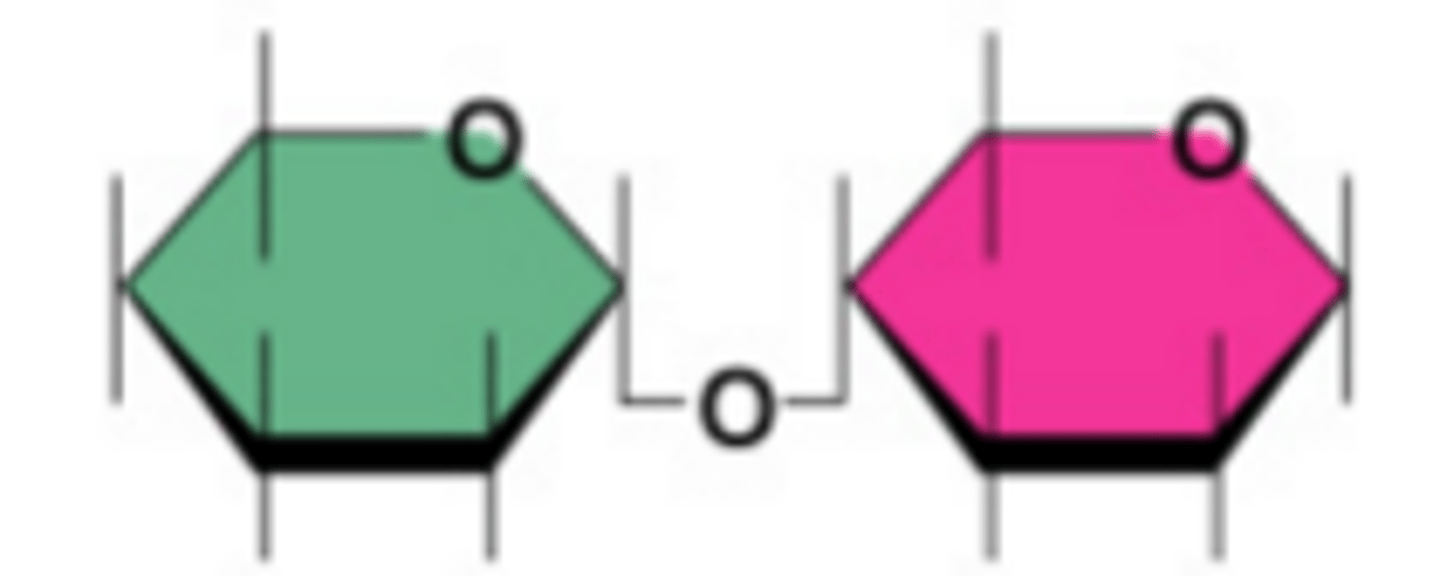
Sucrose
A disaccharide ; table sugar
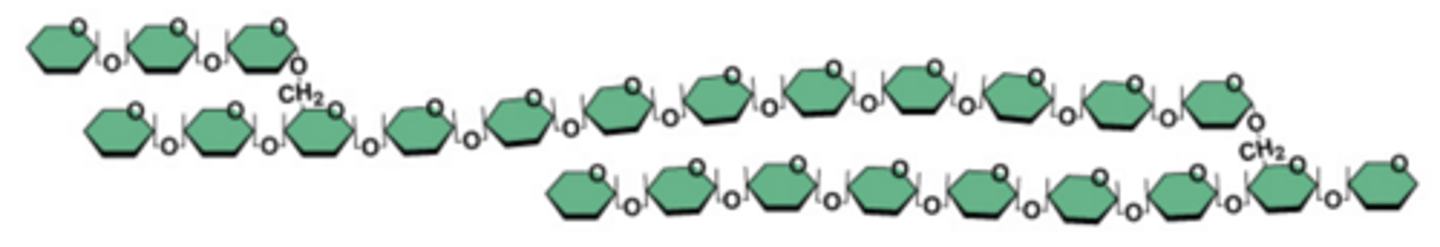
Polysaccharide (Description)
Large carbohydrate made up of many monosaccharides
Disaccharide (Examples)
Examples include - sucrose, lactose, maltose
Polysaccharide (Examples)
Examples include - starch, glycogen, and cellulose
Starch
A polysaccharide found in plants that is used for food storage
Glycogen
A polysaccharide found in animals that is used to store carbohydrates in the liver and skeletal muscles
Cellulose
A polysaccharide found in the cell wall of plants that provides structure and support that can't be digested by humans
Hydrolysis
A chemical reactions in which water is added to break bonds; breaks apart large macromolecules
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are covalently bond to each other when a water molecule is removed; for each bond broken one water molecule must be removed