Unit 1 Test Review A&P Honors
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail, largest organ of the human body; separate internal from external environment
skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. Made up of bones and joints; bone marrow makes blood cells
Muscular System
enables movement of the body and internal organs
lymphatic system
Composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs. Provides defense against infection.
respiratory system
Brings oxygen into the body. Gets rid of carbon dioxide.
digestive system
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
endocrine system
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells.
urinary system
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water, electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood.
reproductive system
system of organs involved in producing offspring
negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
positive feedback
Feedback that tends to magnify a process or increase its output.
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
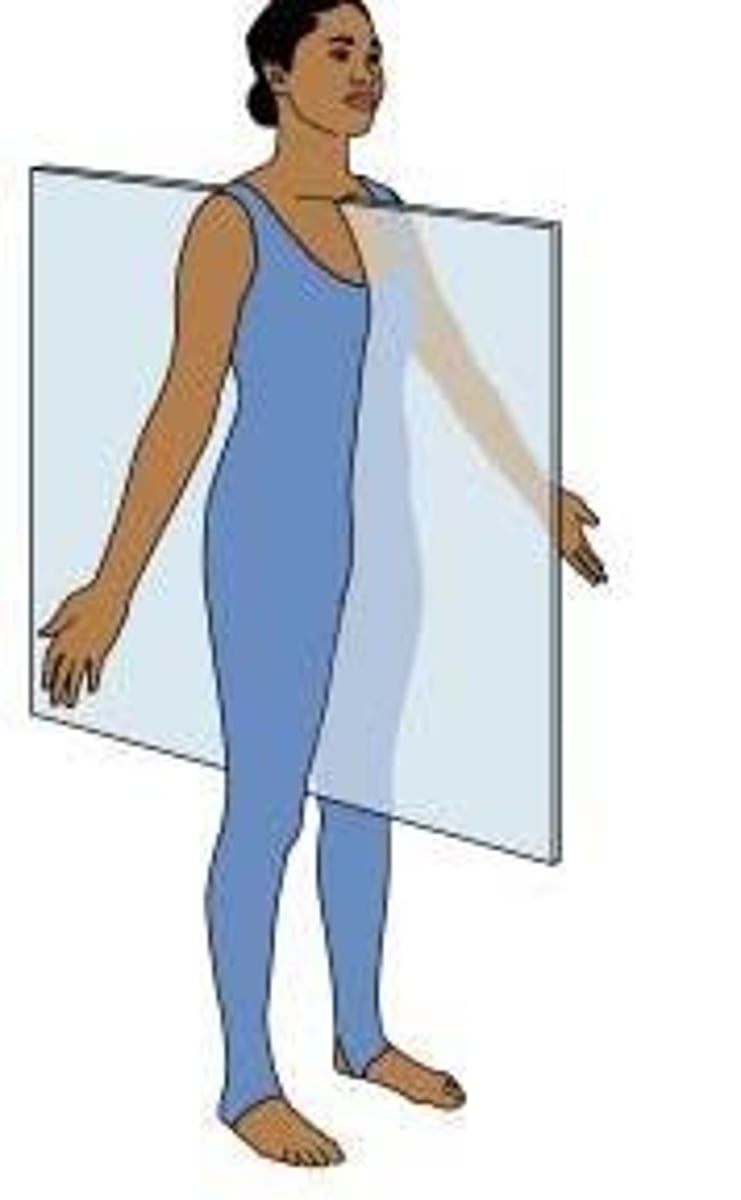
saggital/median plane
divides the body into left and right halves
frontal (coronal) plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
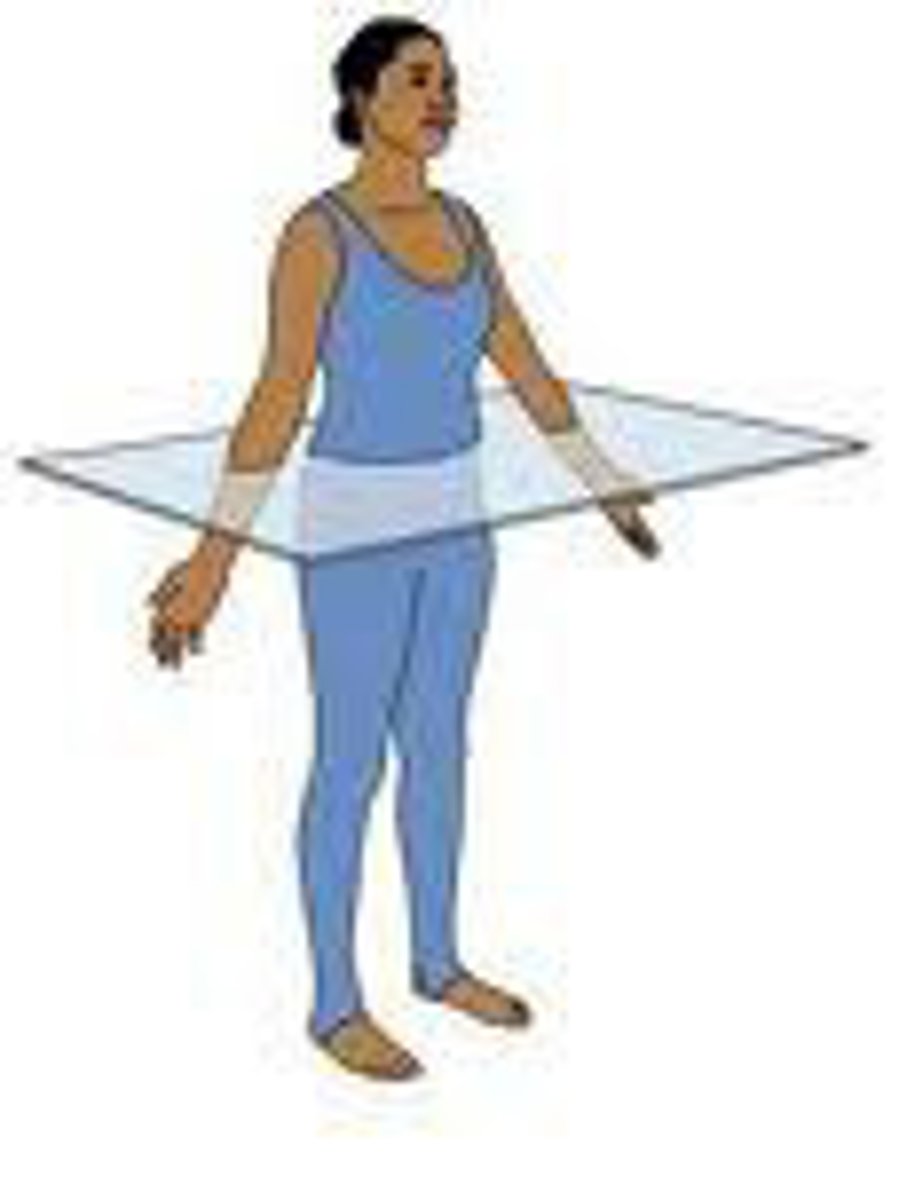
transverse
Divides body into upper and lower parts
superior
toward the head
inferior
away from the head
anterior (ventral)
front of the body
posterior (dorsal)
back of body
medial
Toward the midline of the body
lateral
Away from the midline of the body towards sides
intermediate
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
superficial
near the surface
deep
away from the surface
thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs
abdominal cavity
contains primarily the major organs of digestion
ventral cavity
thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
dorsal cavity
includes the cranial and spinal cavities.
apical
tip
basal
bottom
contralateral
opposite side
ipsilateral
same side
peripheral
on the edge, not important
visceral
pertaining to the internal organs
parietal
pertaining to the outer wall of the body cavity
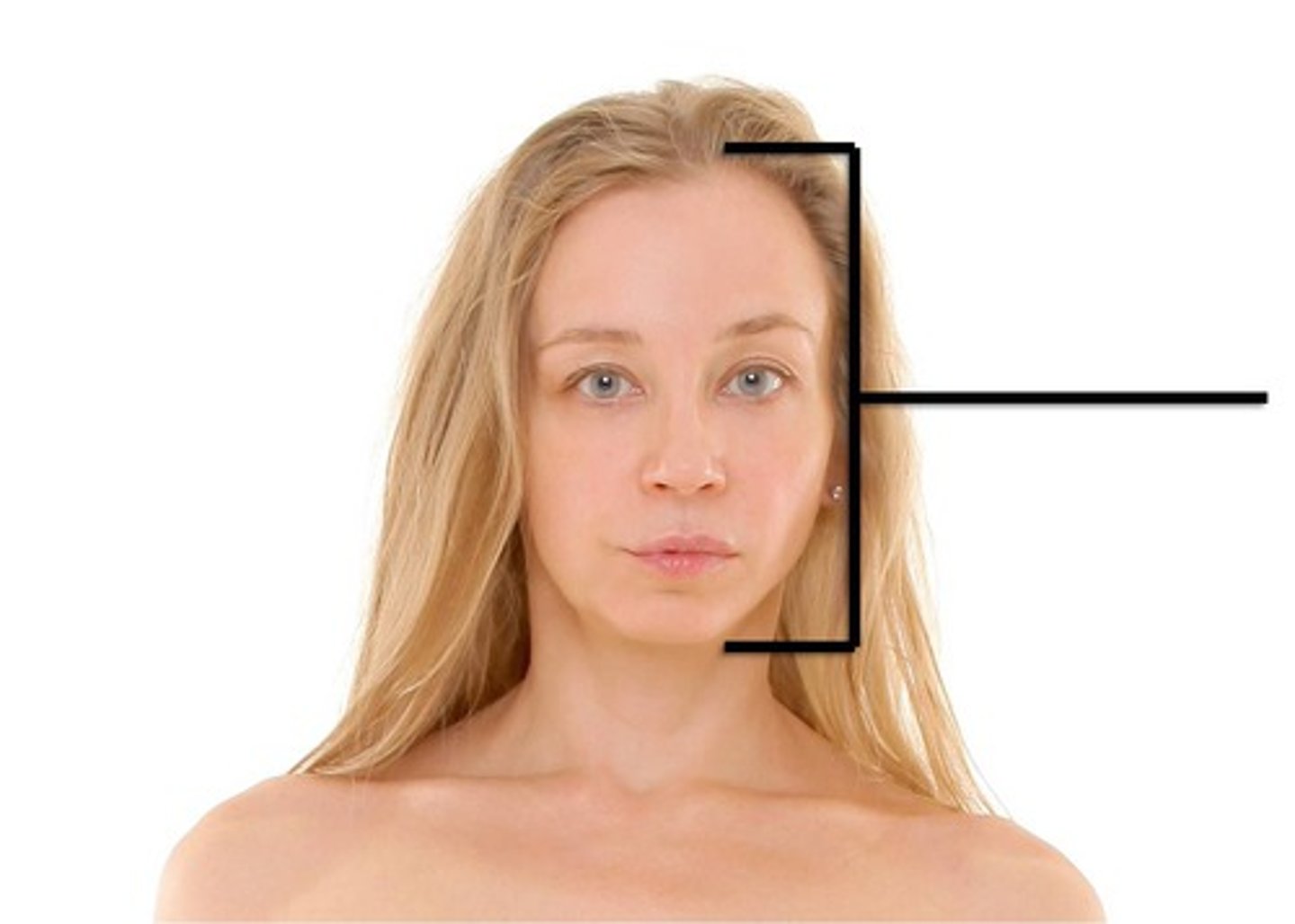
frontal region
forehead
orbital region
eyes
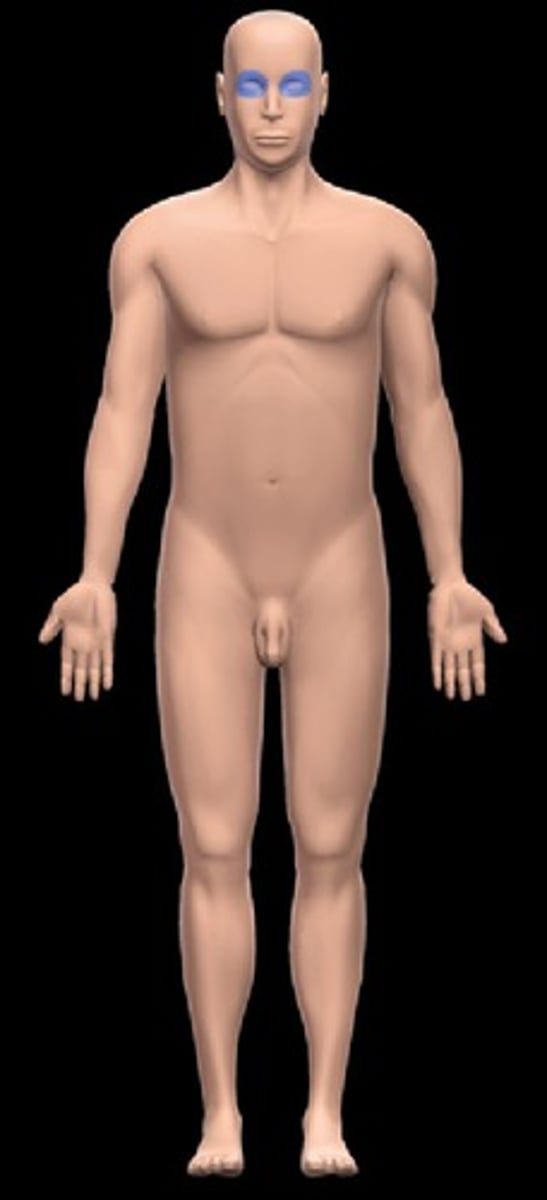
nasal
nose region
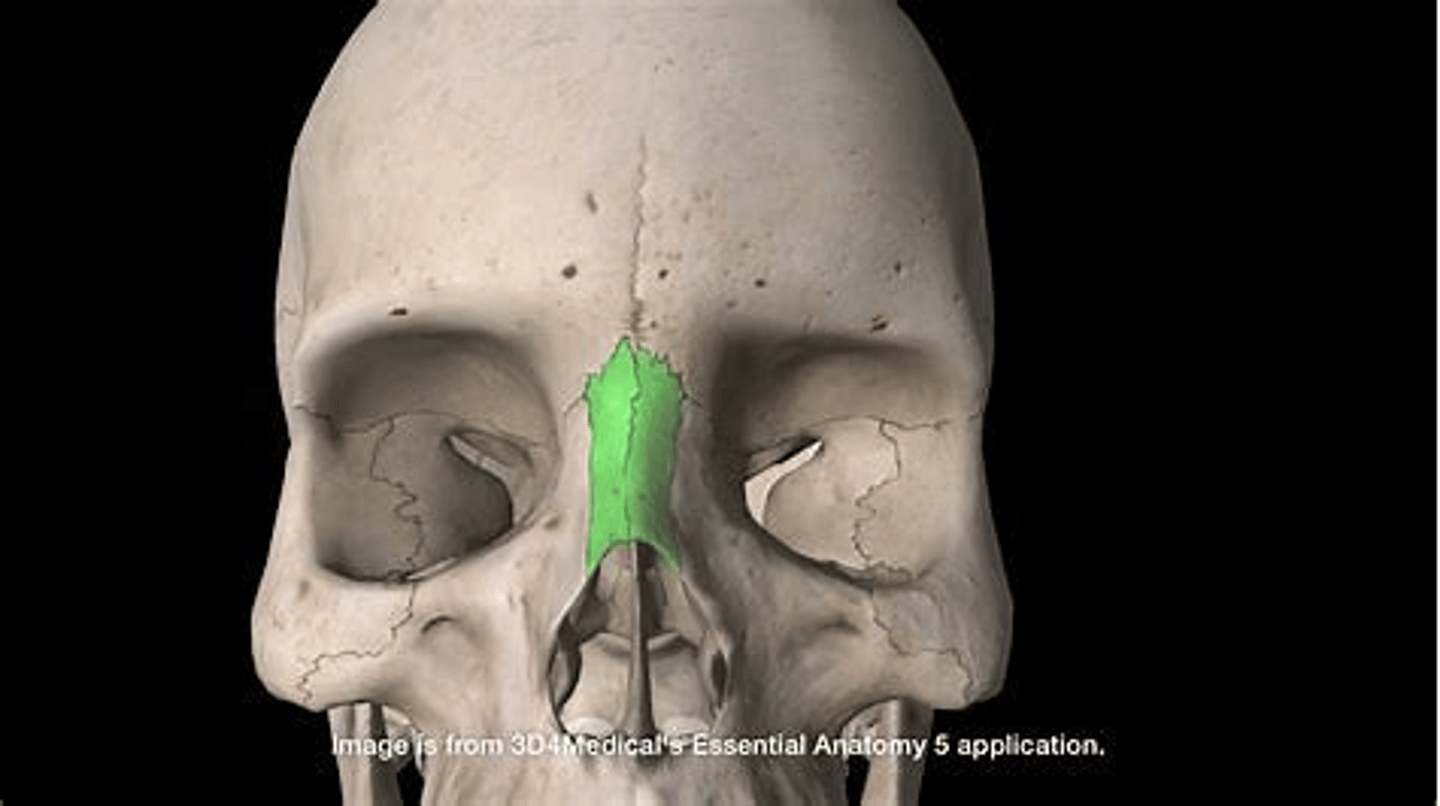
mental region
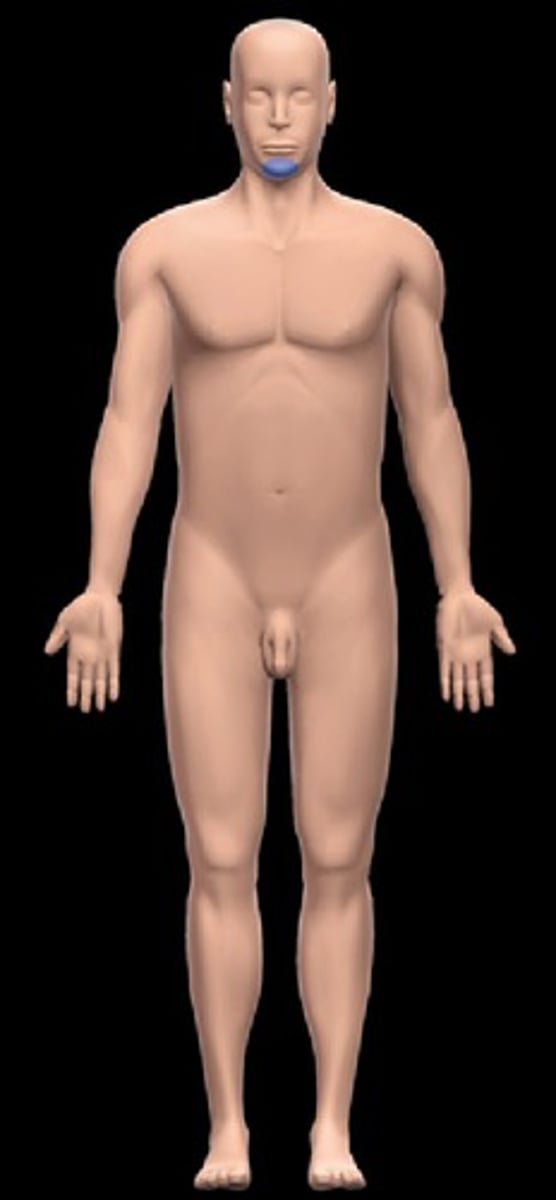
Cephalic
Head
Buccal
Cheek
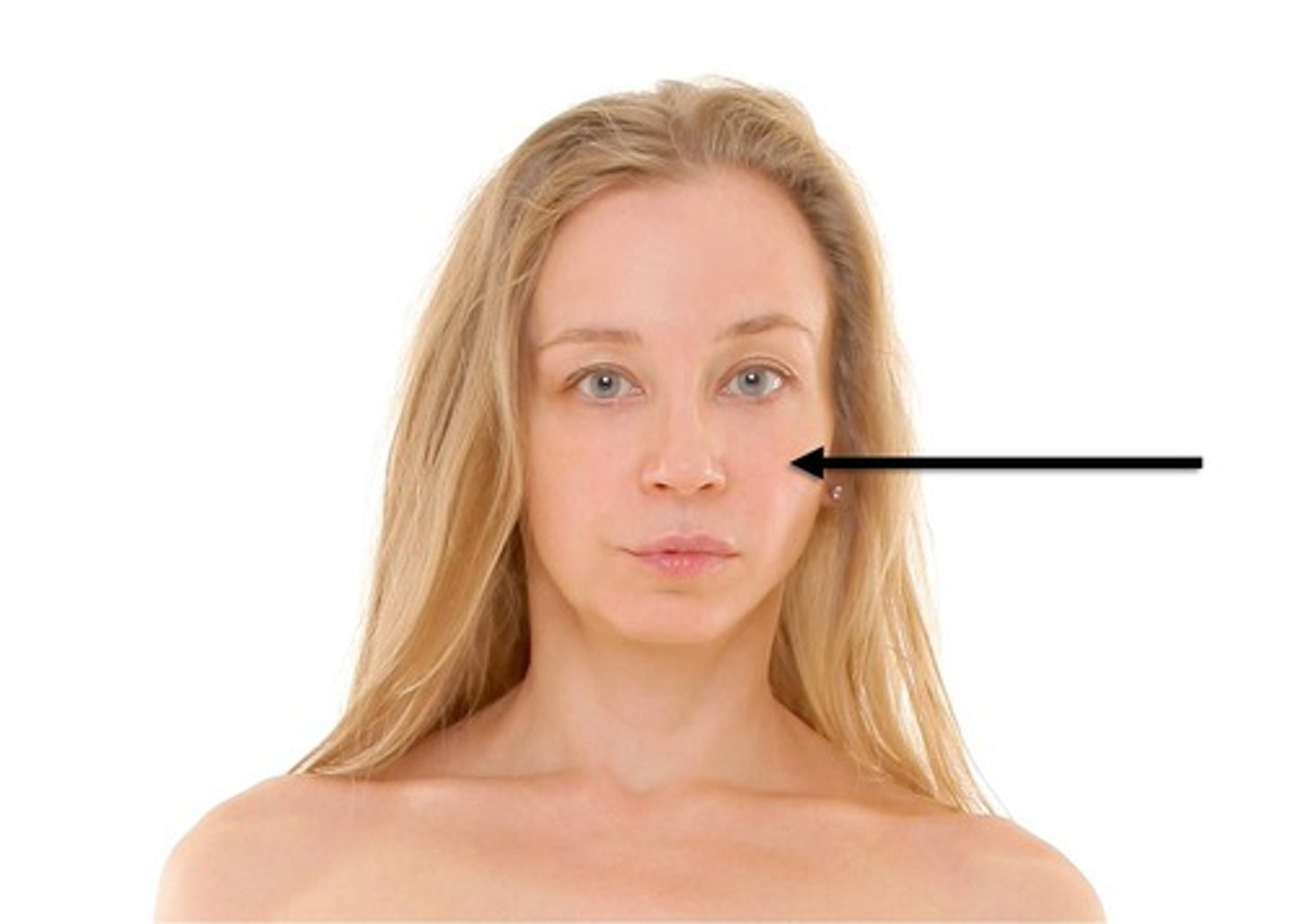
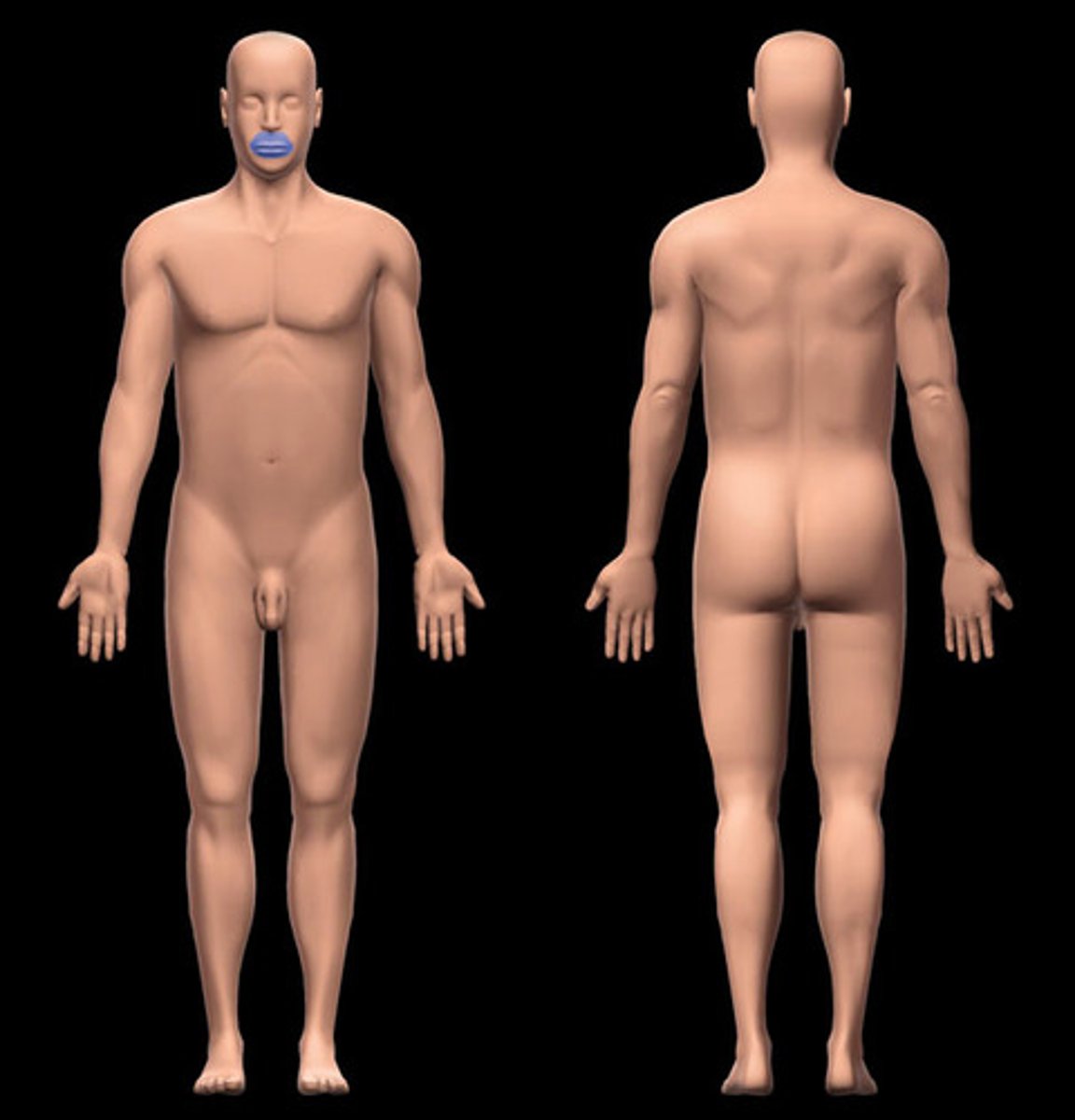
Oral
Mouth
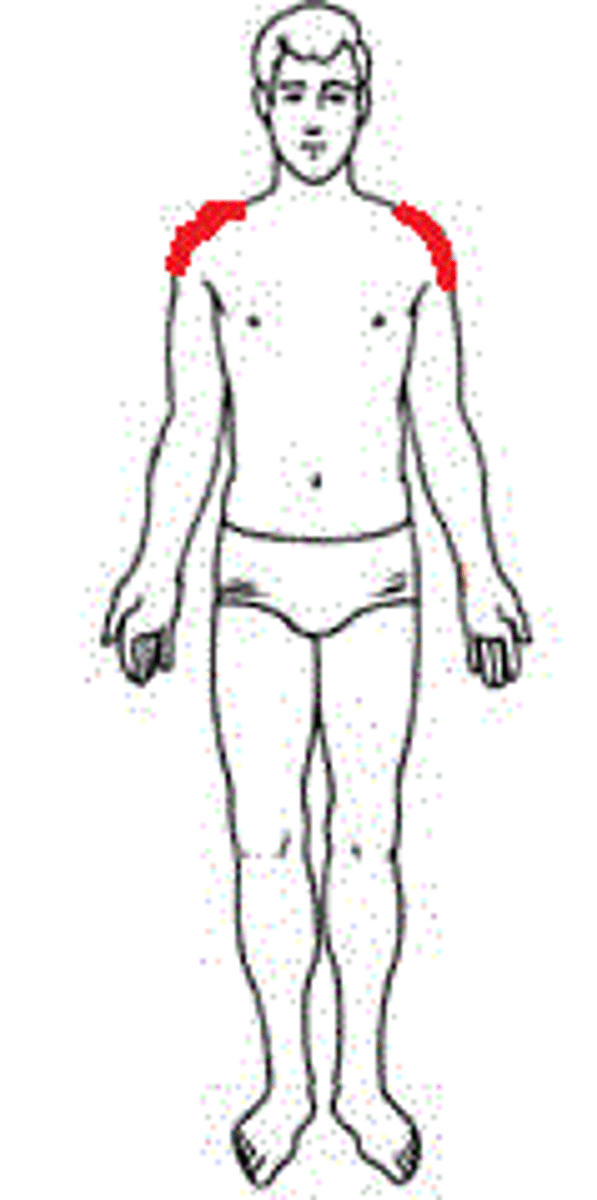
Acromial
Shoulder
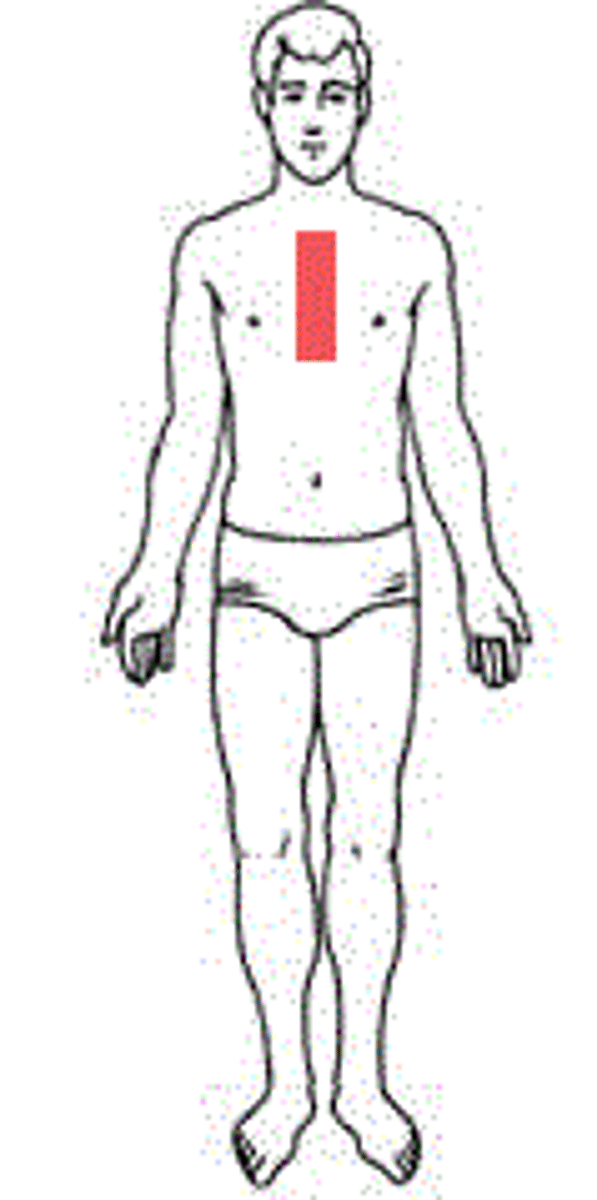
Sternal
Middle thorax
Pectoral (thoracic)
Chest
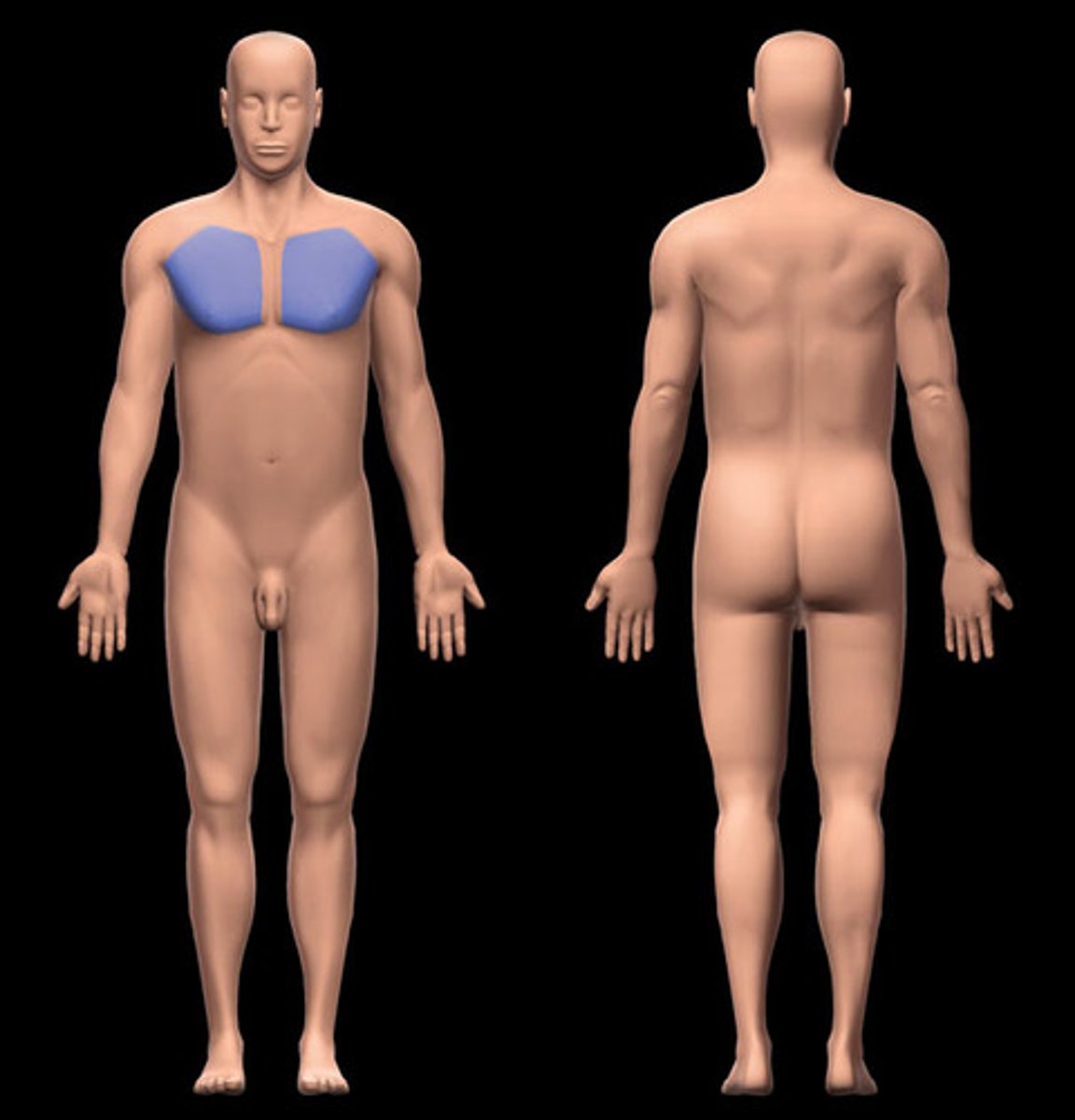
Axillary
Armpit
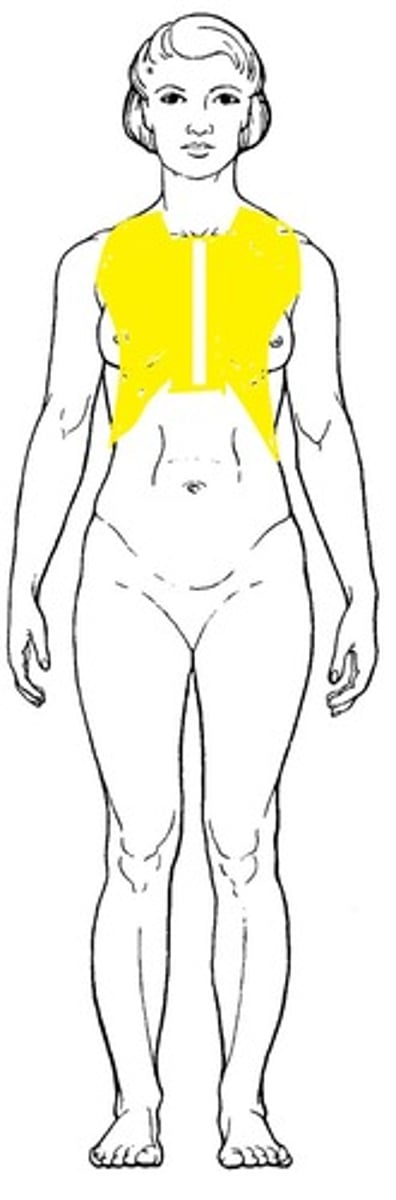
Mammary
Breast
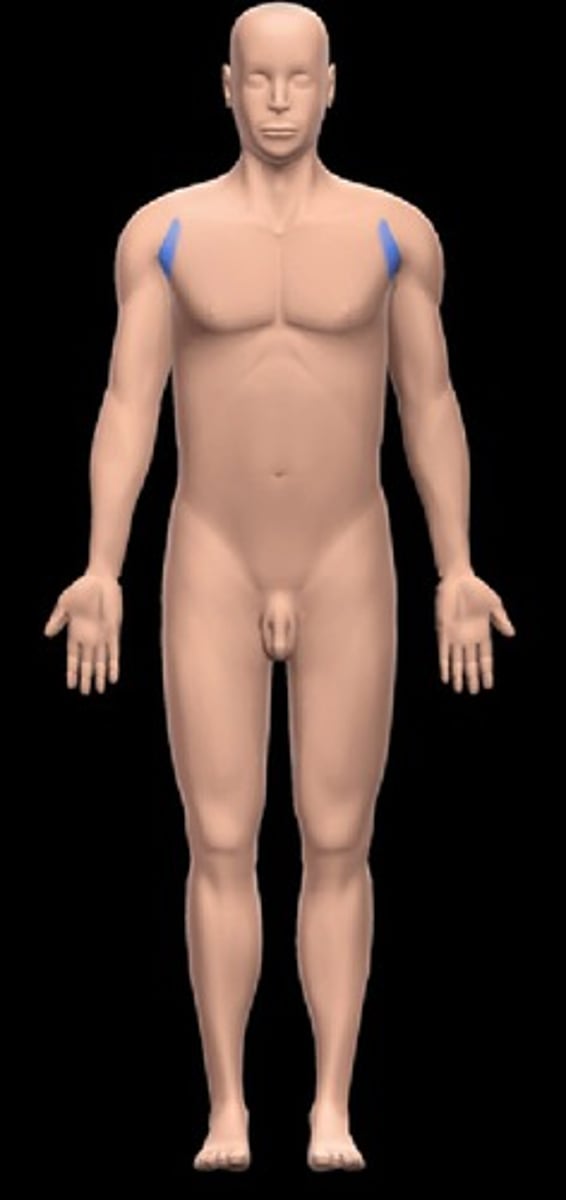
Brachial
Arm
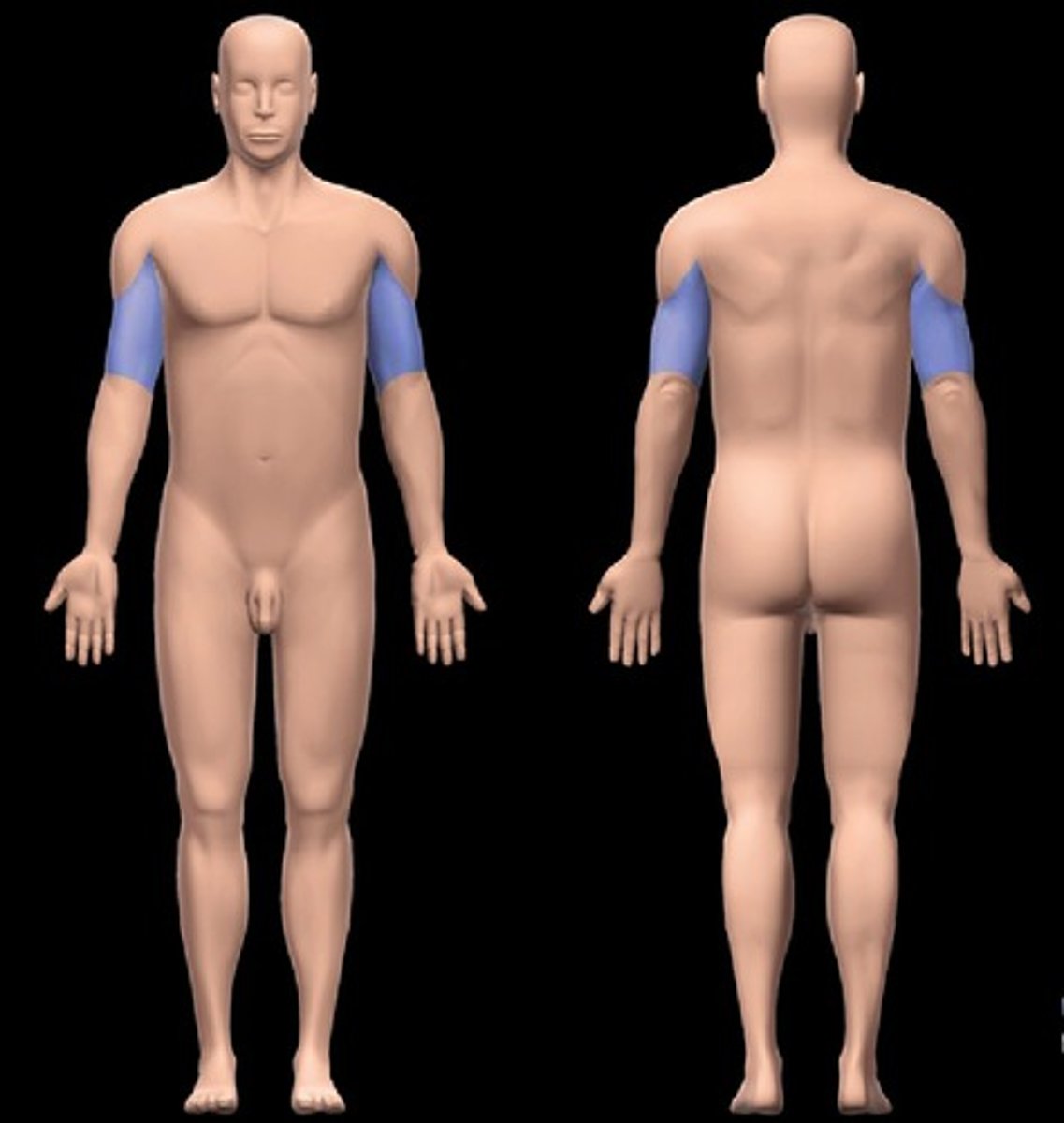
Antecubital
Anterior elbow
Umbilical
Navel, bellybutton
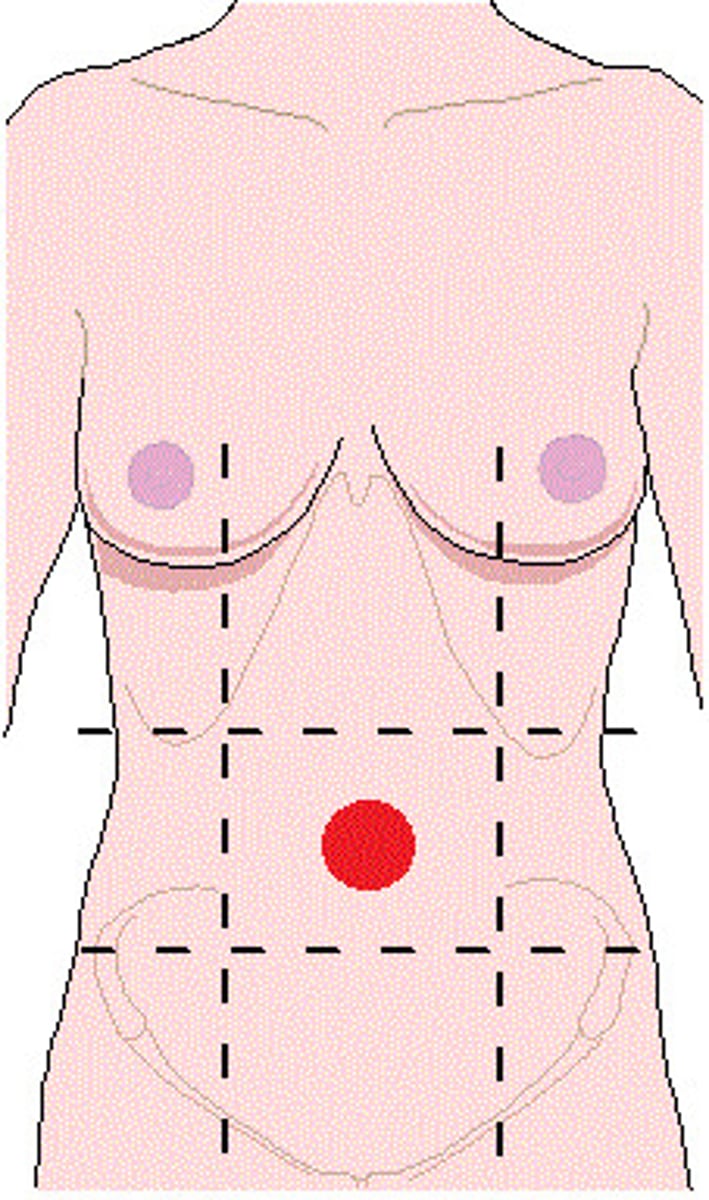
Abdominal
Abdomen
Inguinal
Groin
Antebrachial
Forearm
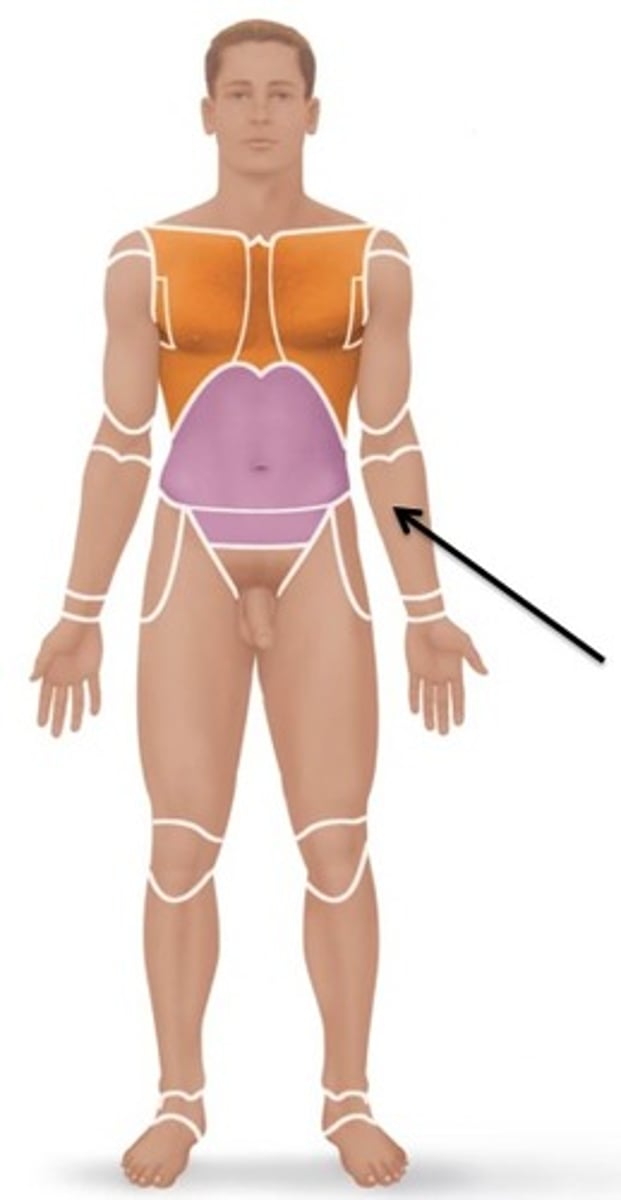
Carpal
Wrist
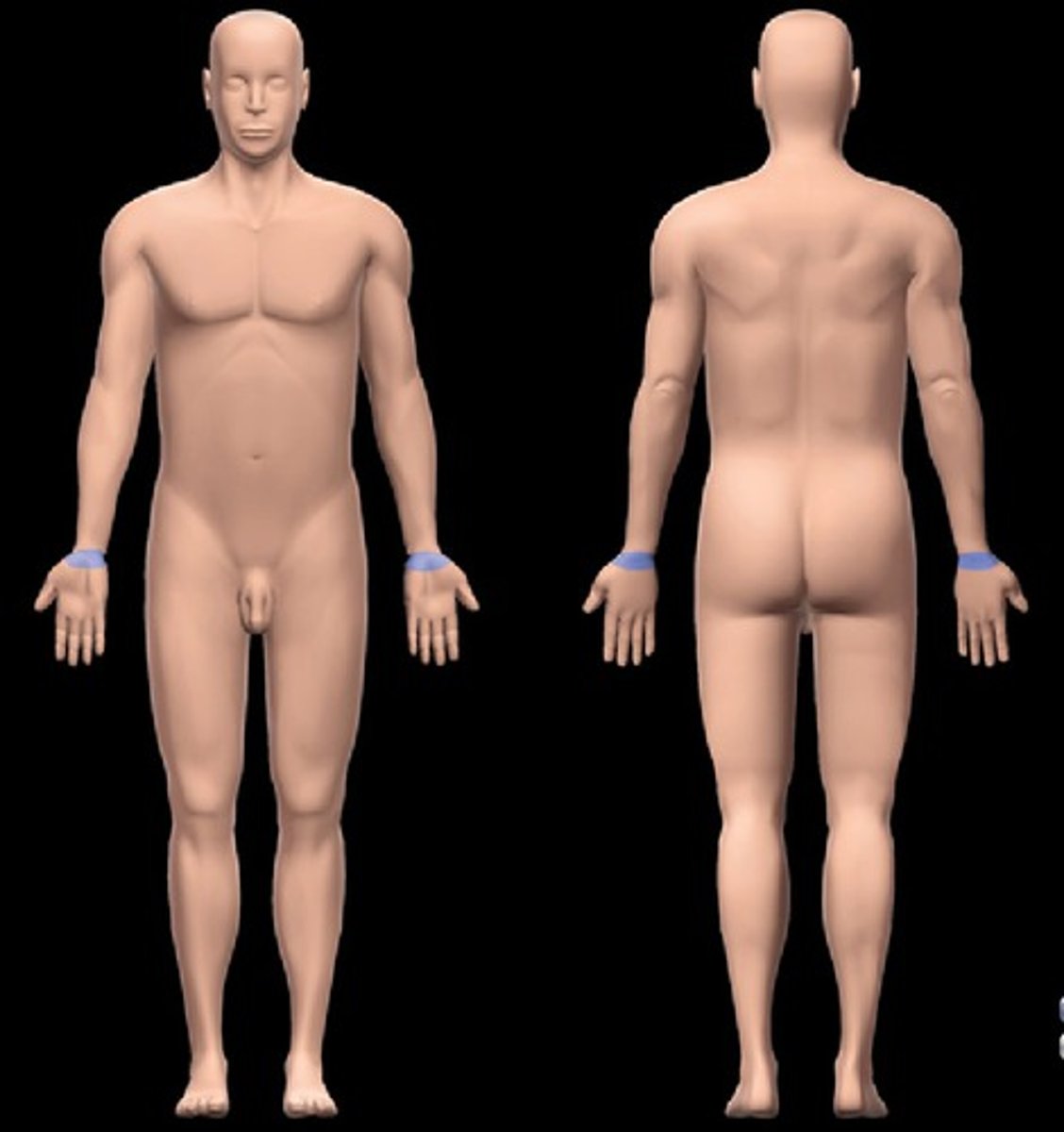
Coxal
Hip
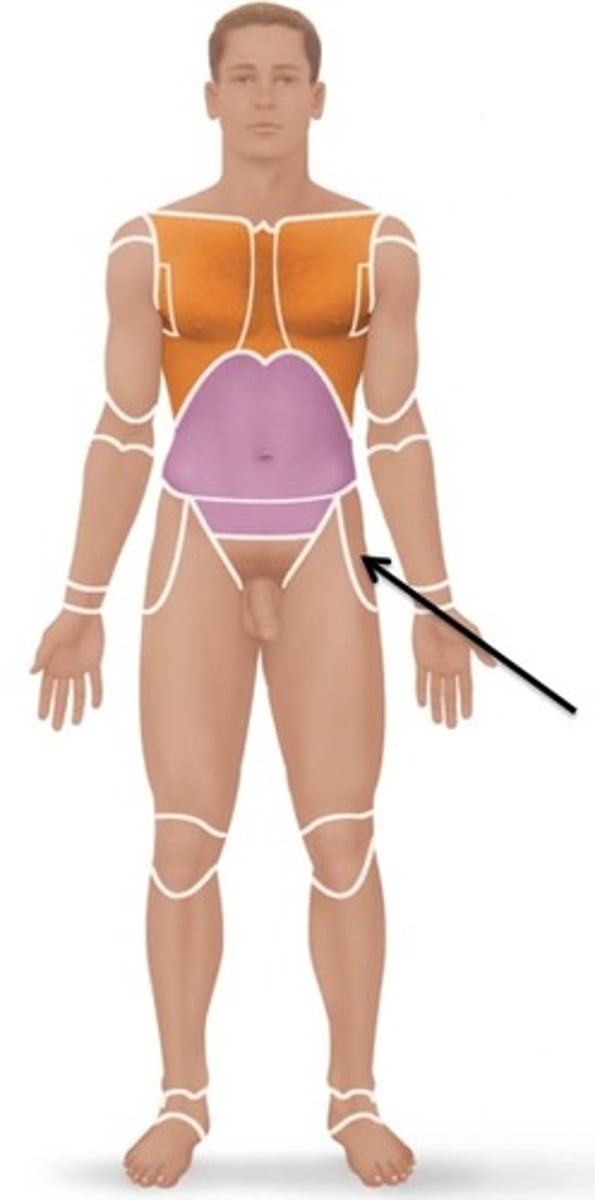
Palmar
Palm

Digital
Finger or toe
Genital (pubic)
Reproductive
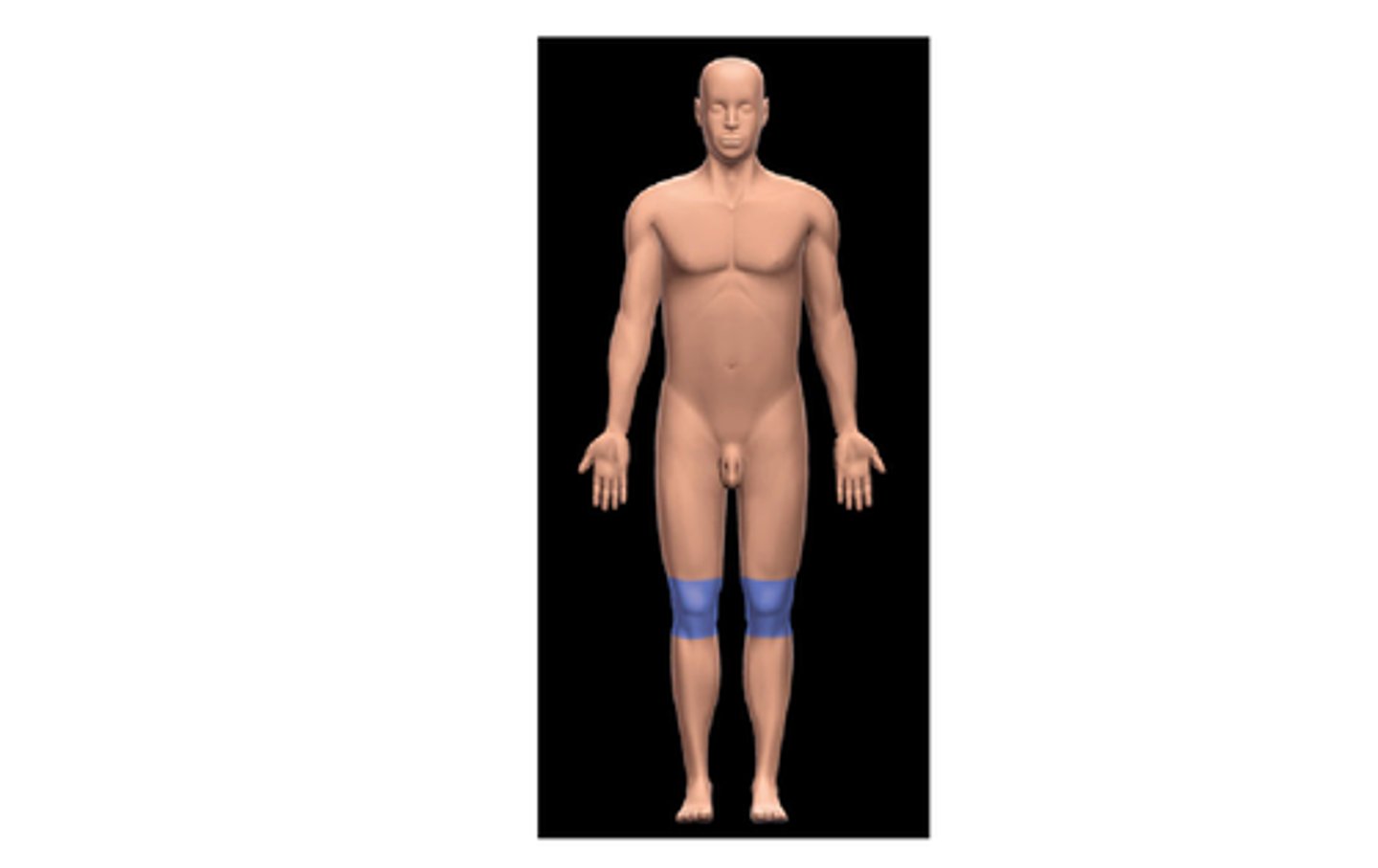
Patellar
Knee
Crural
shin region
Tarsal
Ankle
Pedal
Foot
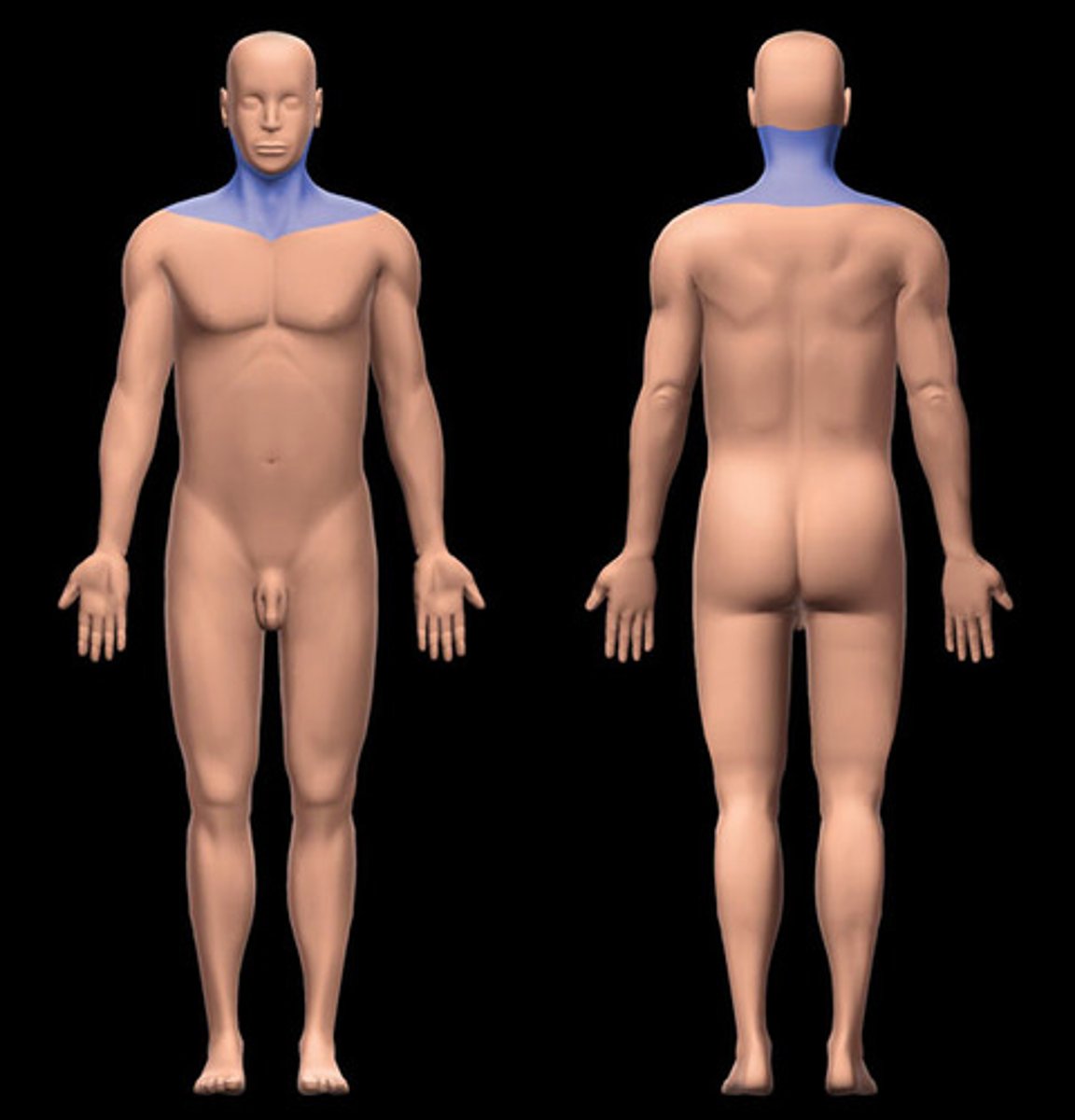
Cervical
Neck
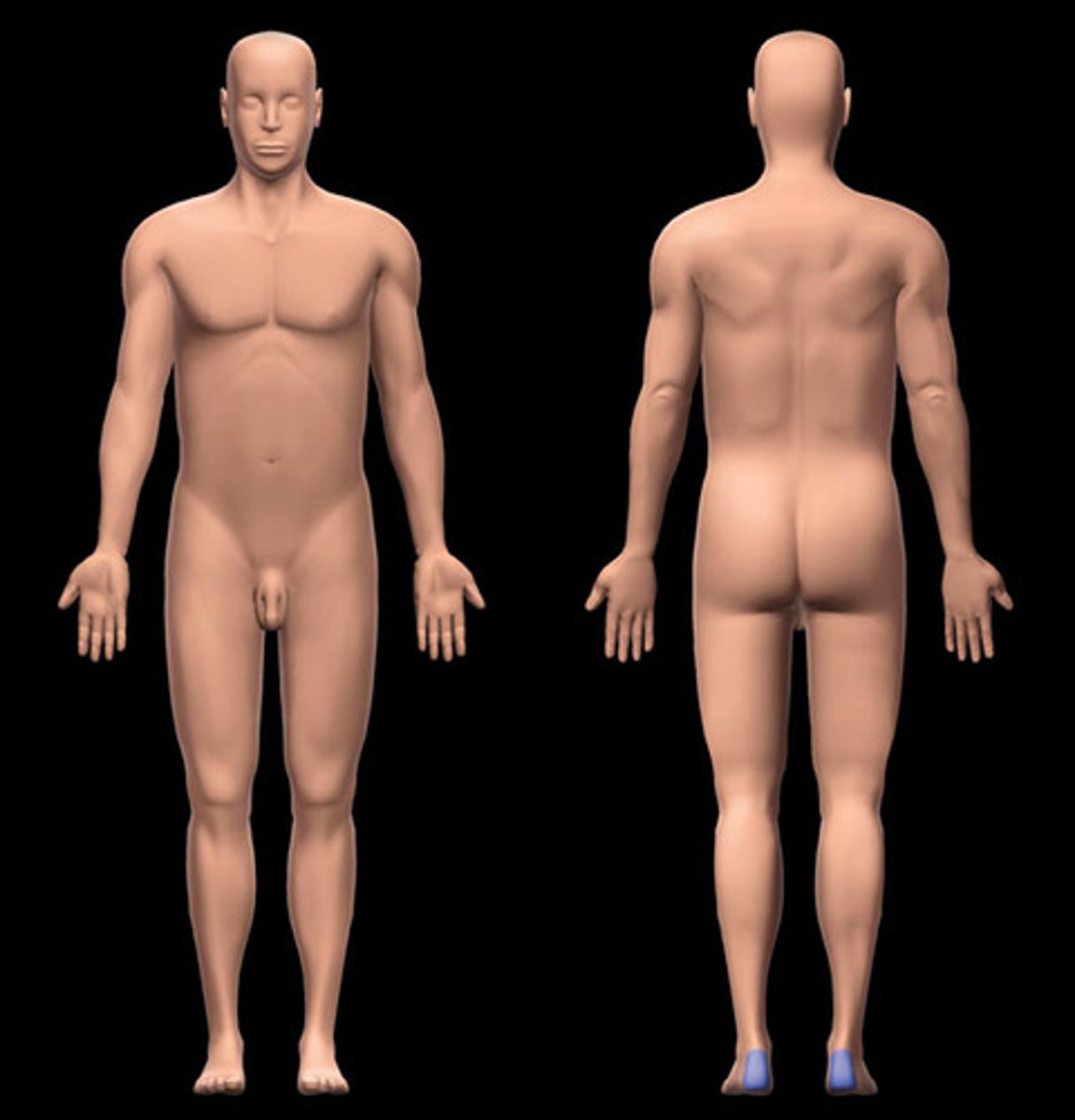
Calcaneal
heel of foot (posterior)
Cephalic
head
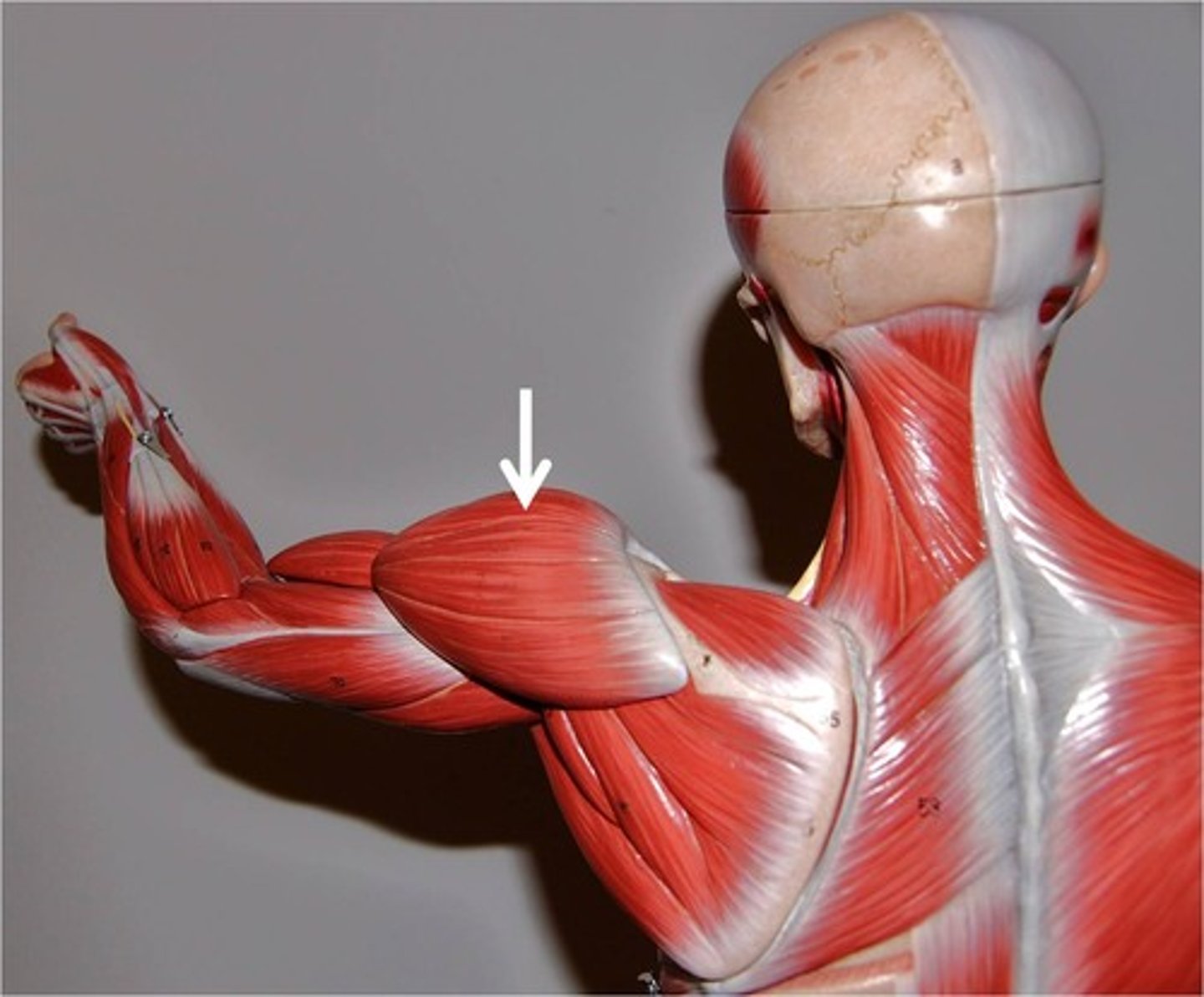
Deltoid
curve of shoulder formed by deltoid muscle
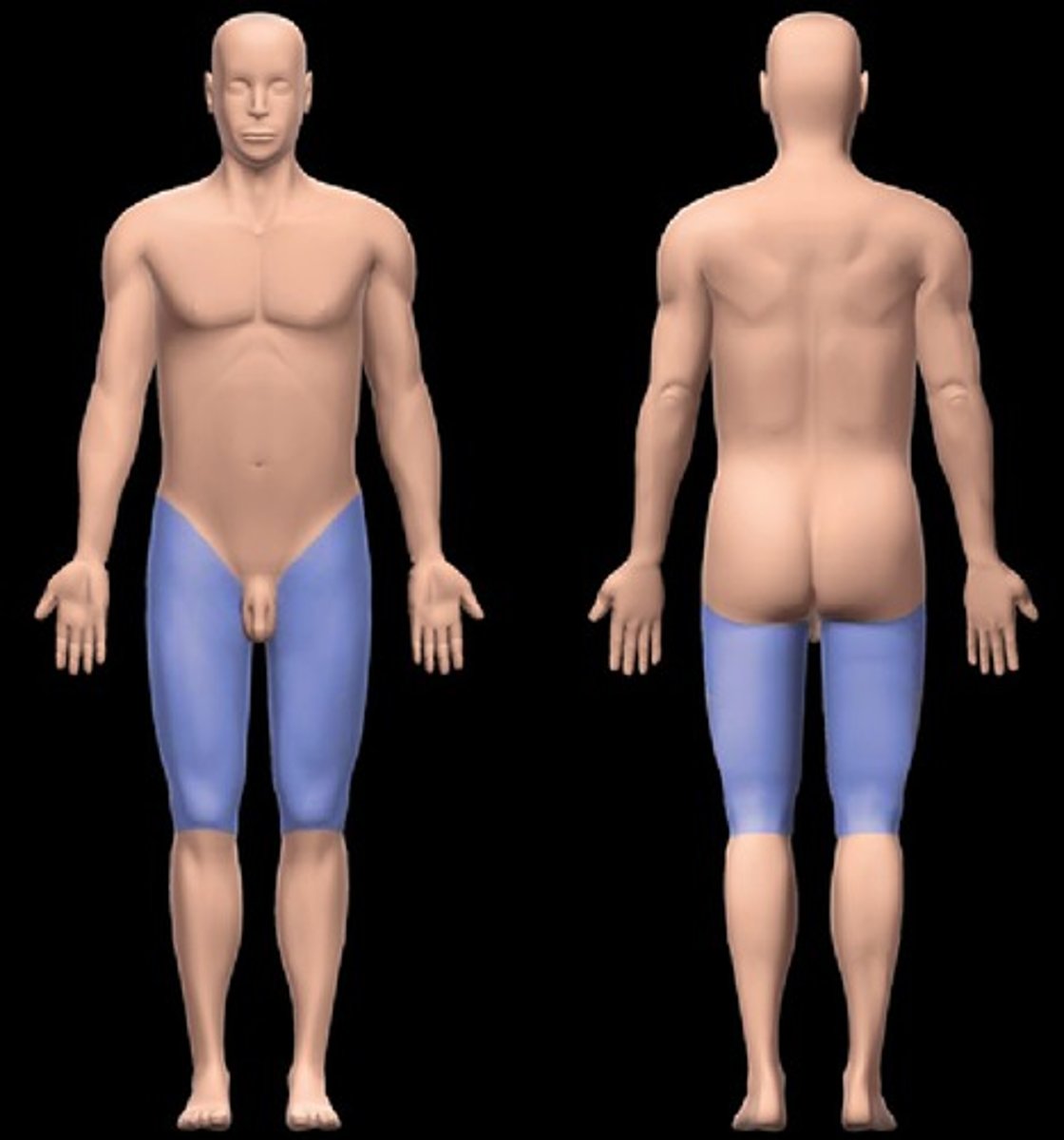
Femoral
thigh
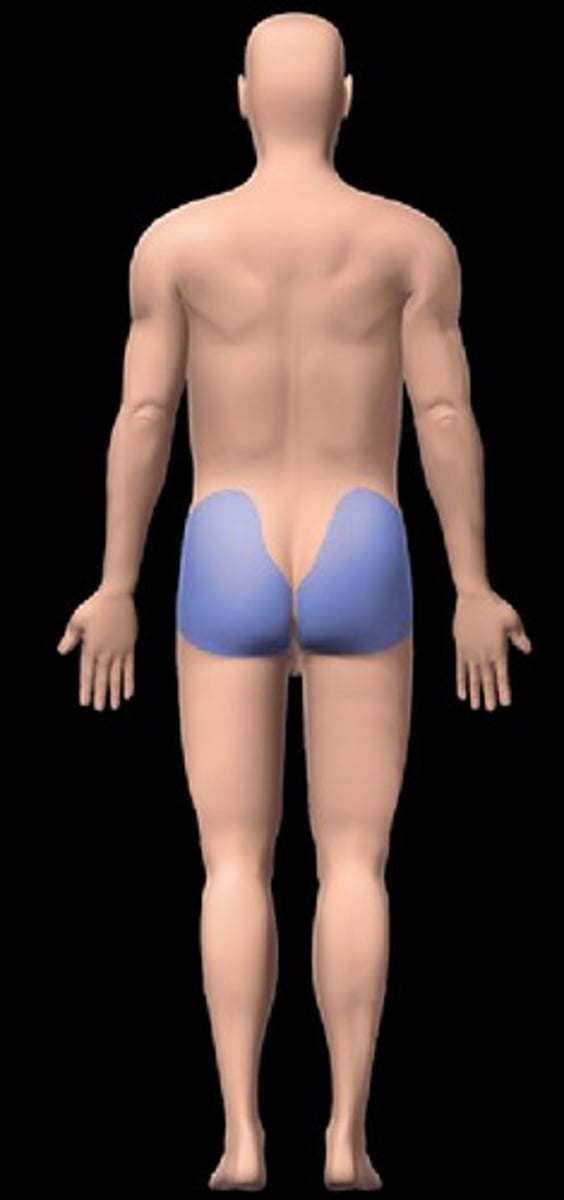
Gluteal
buttock
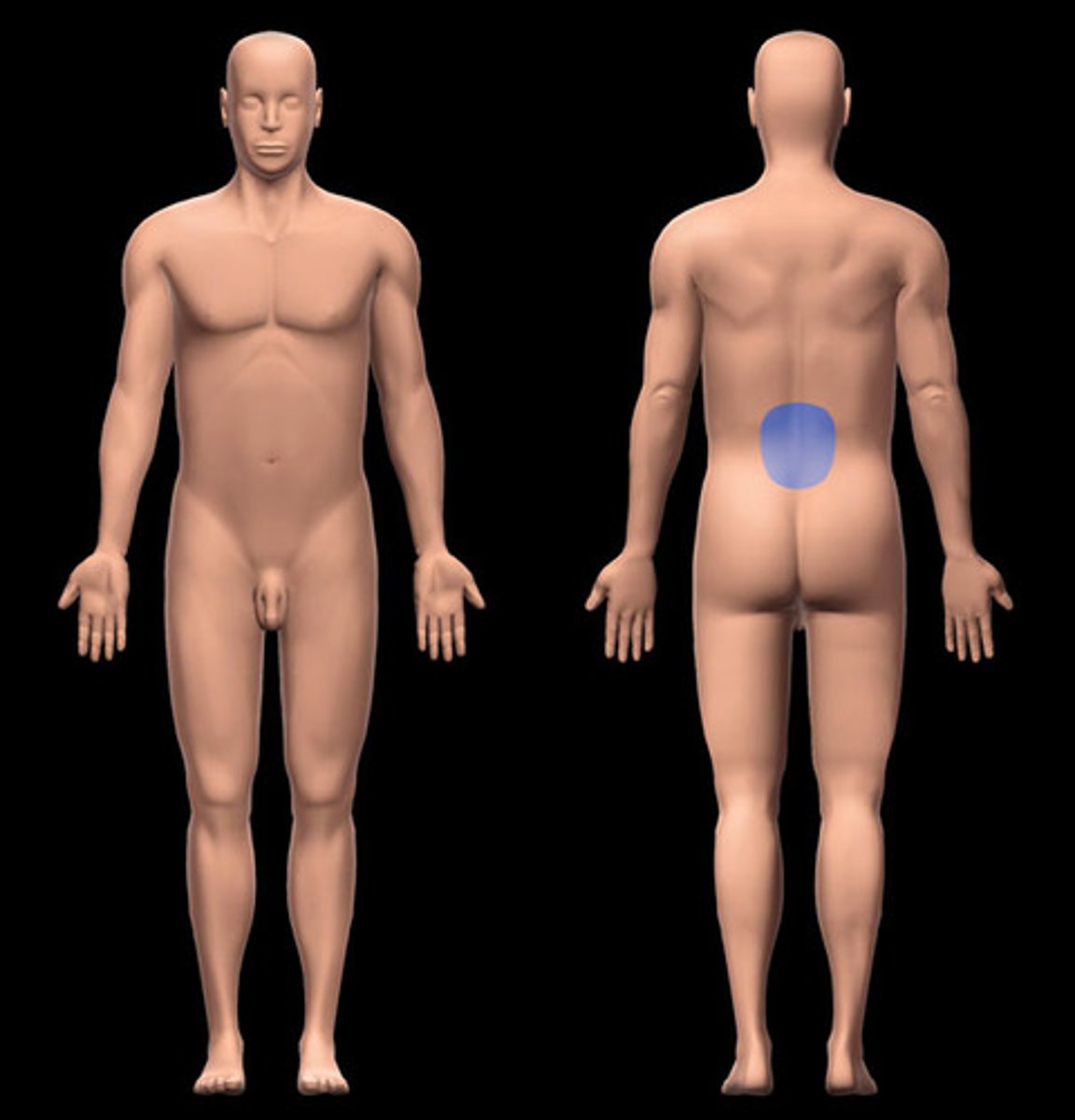
Lumbar
area of back between ribs and hips
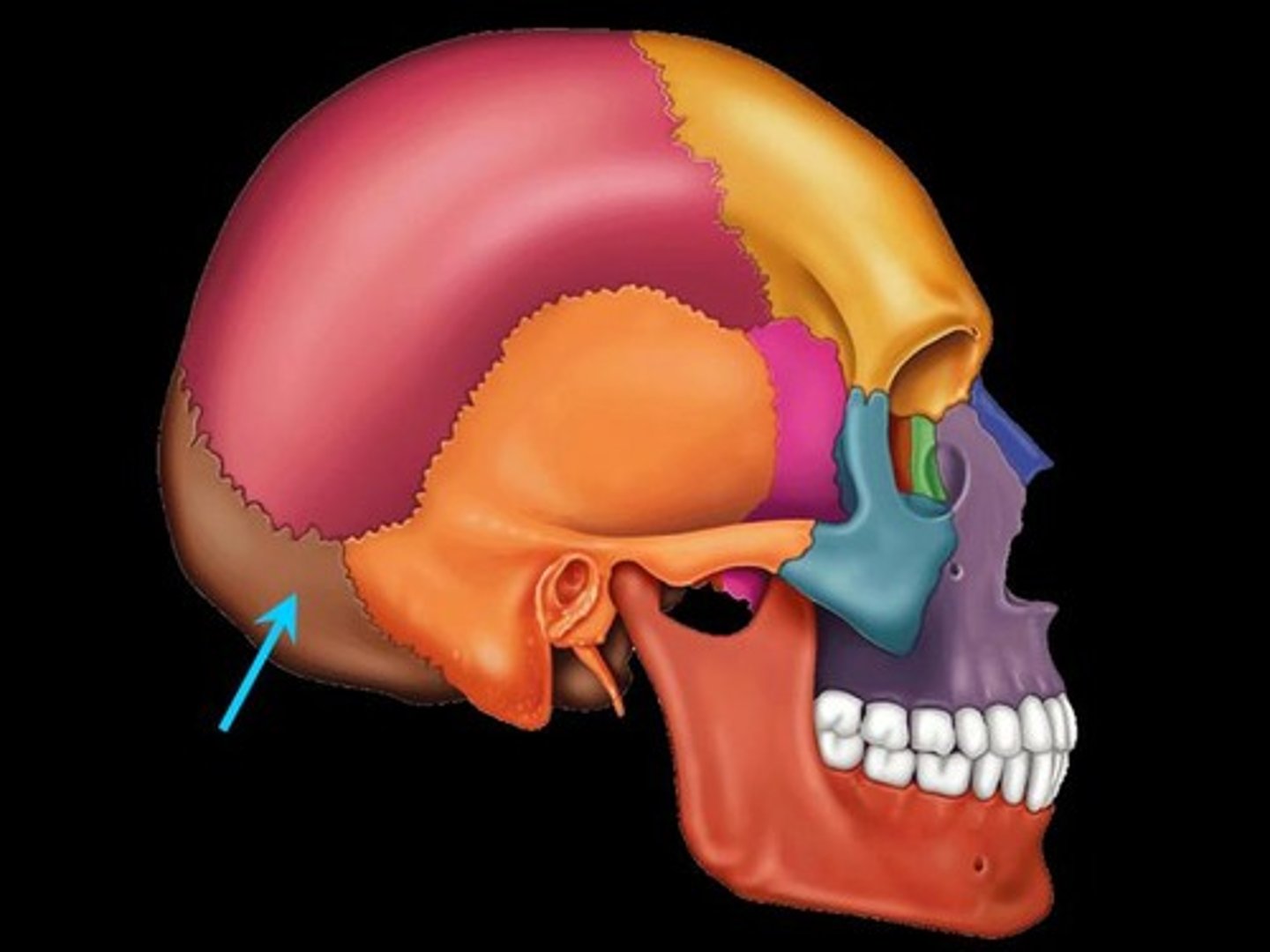
Occipital
posterior surface of head
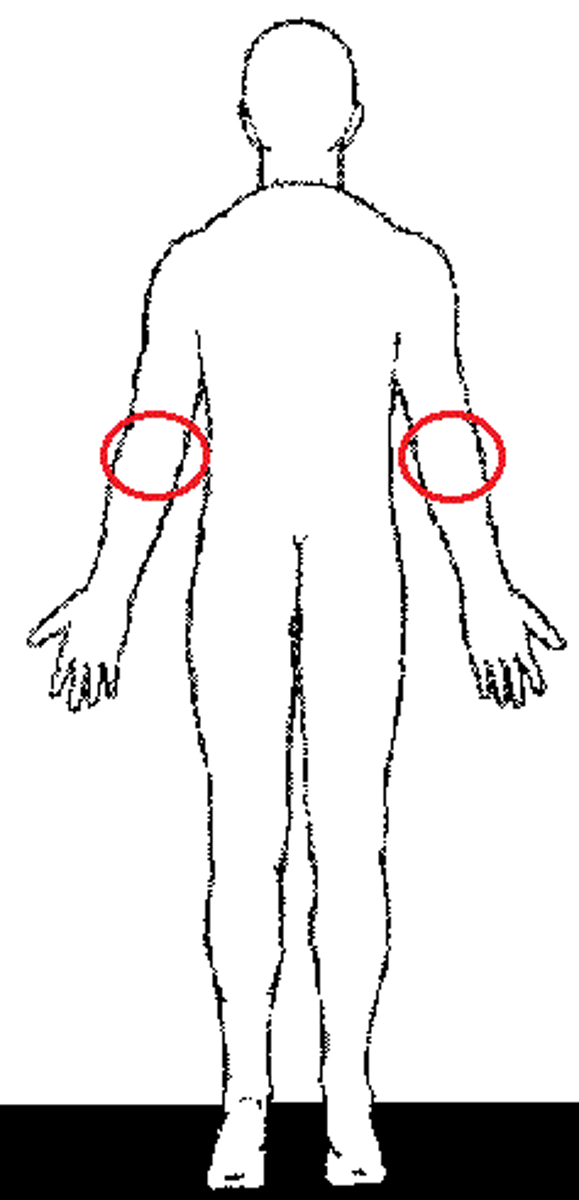
Olecranal
posterior surface of elbow
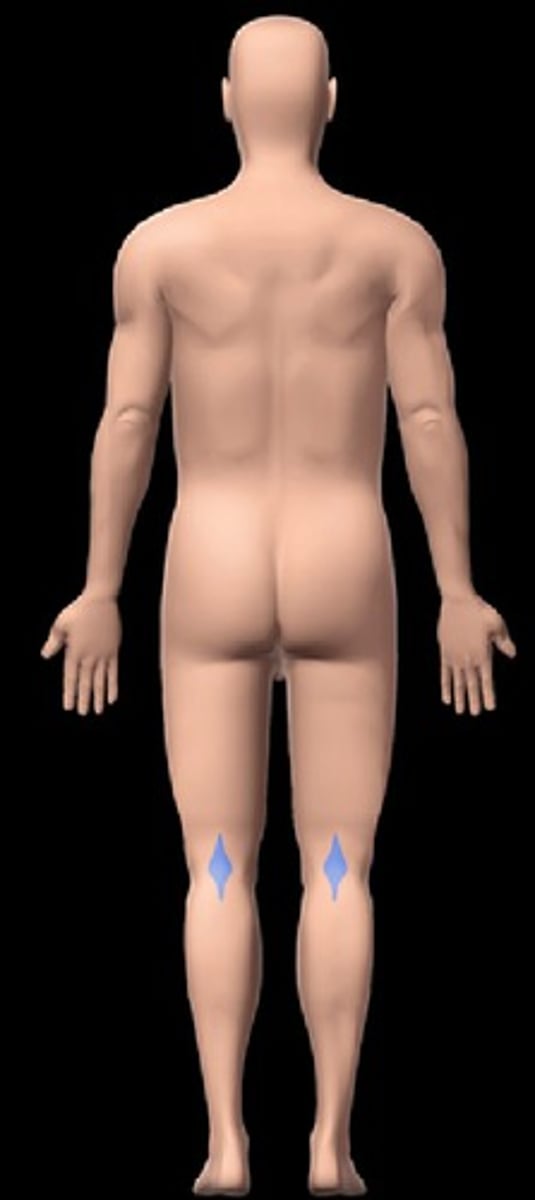
Popliteal
posterior knee area
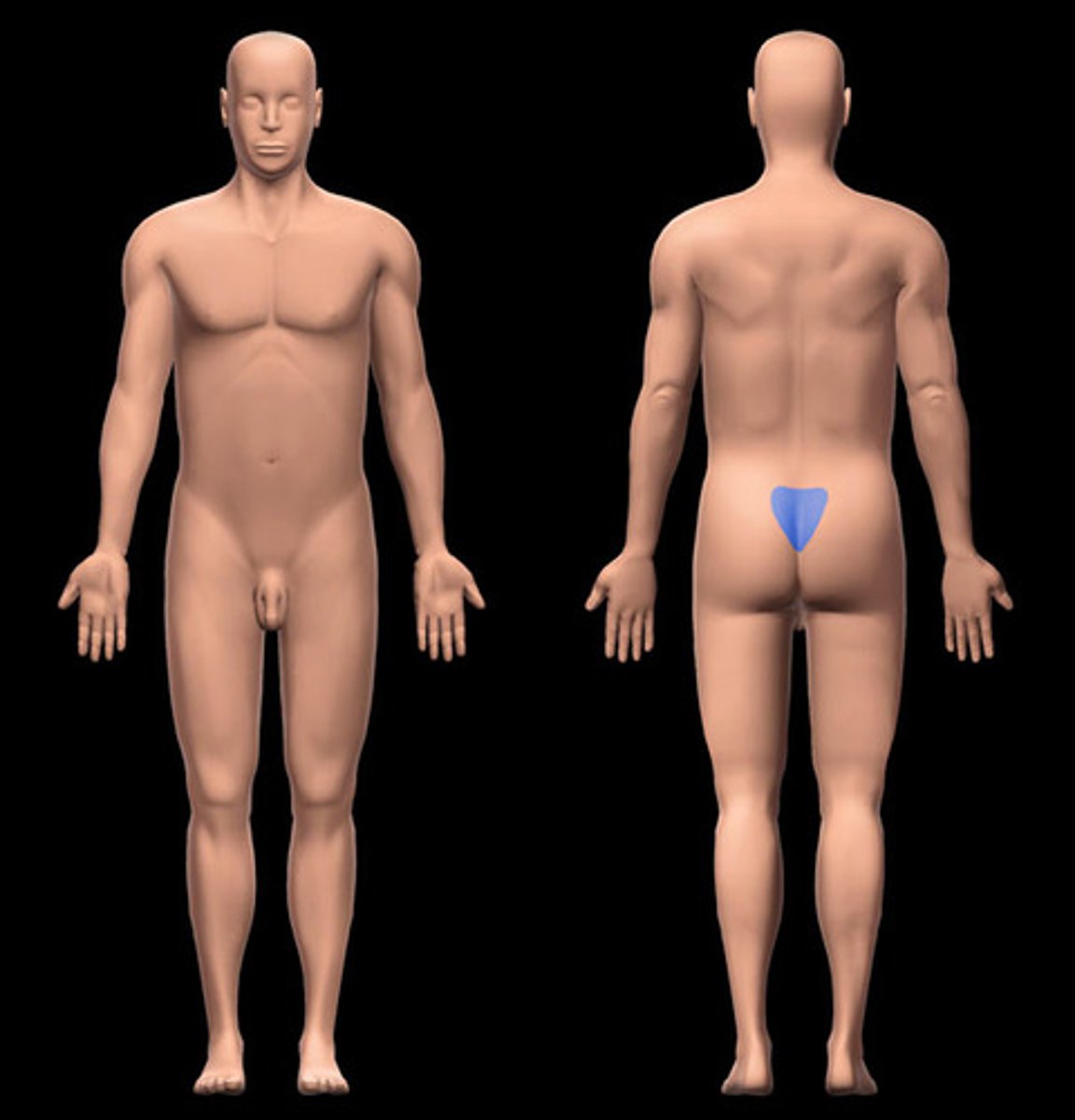
Sacral
area between hips
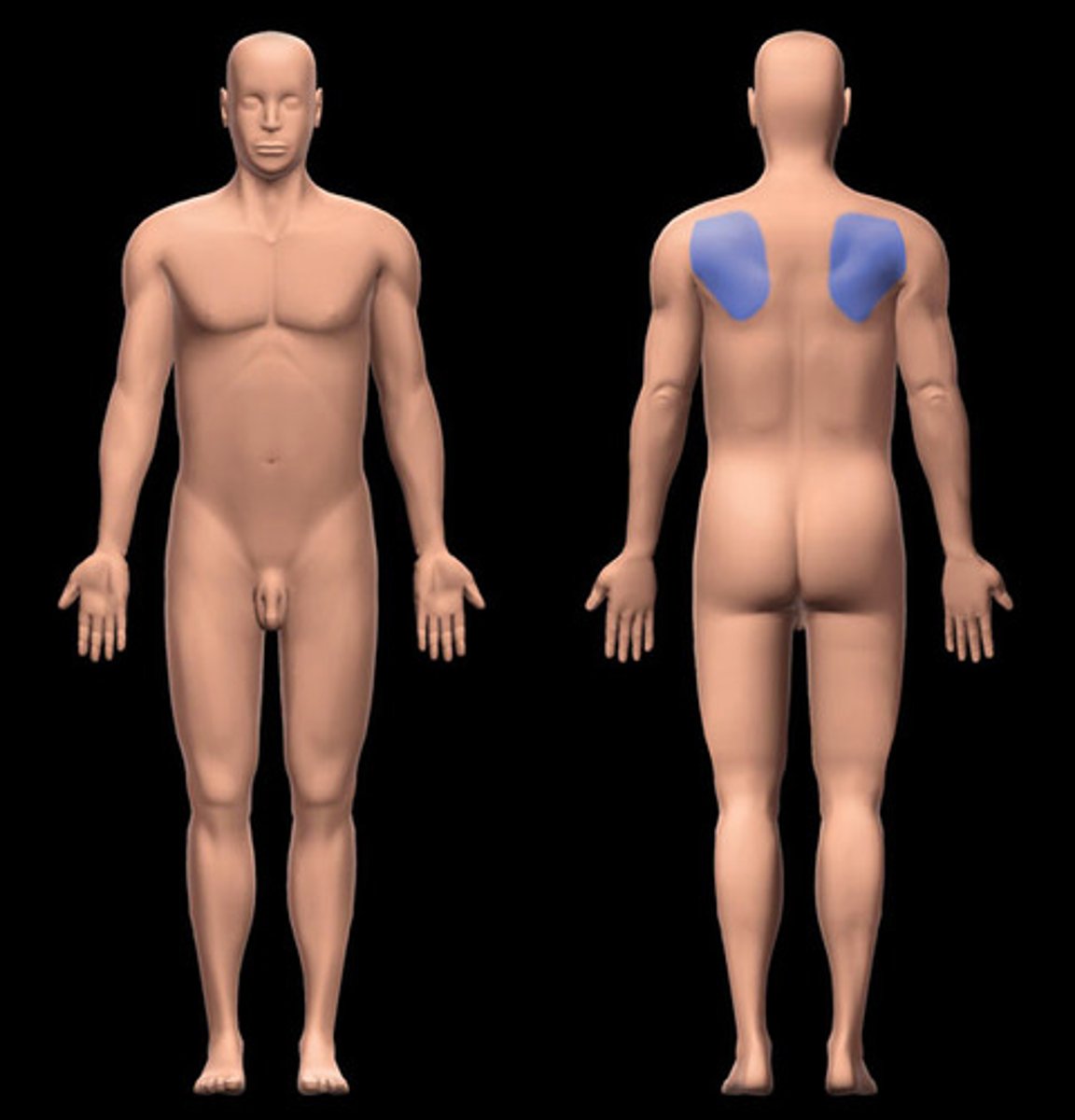
Scapular
shoulder blade region
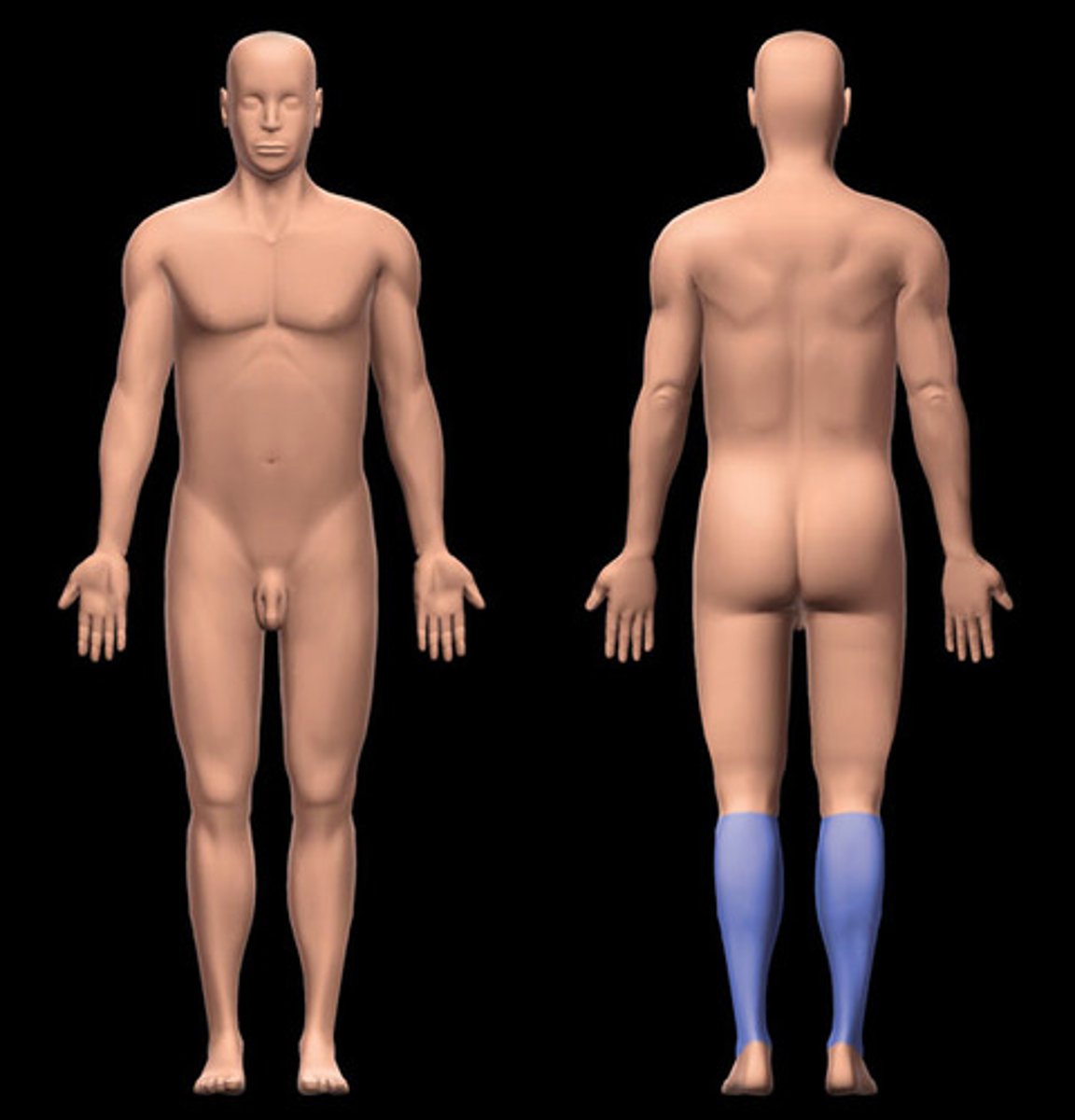
Sural
posterior of lower leg; calf
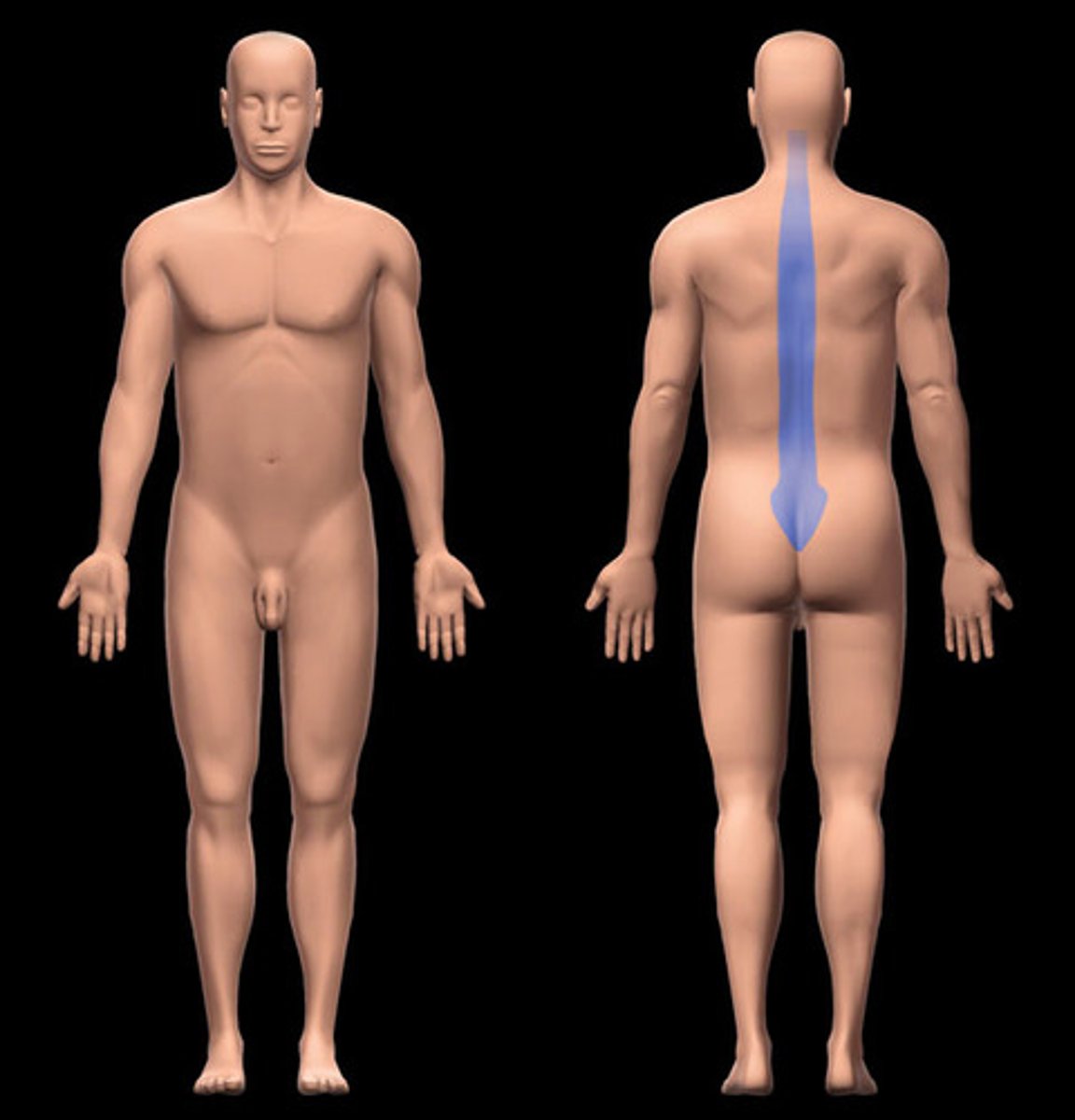
Vertebral
area of spine
Plantar
sole of the foot
organic molecule
Carbon containing compounds that make up living things; four classes of organic molecules are CARBOHYDRATES, LIPIDS, PROTEINS, AND NUCLEIC ACIDS
carbohydrate
Organic molecule that functions in short term energy storage
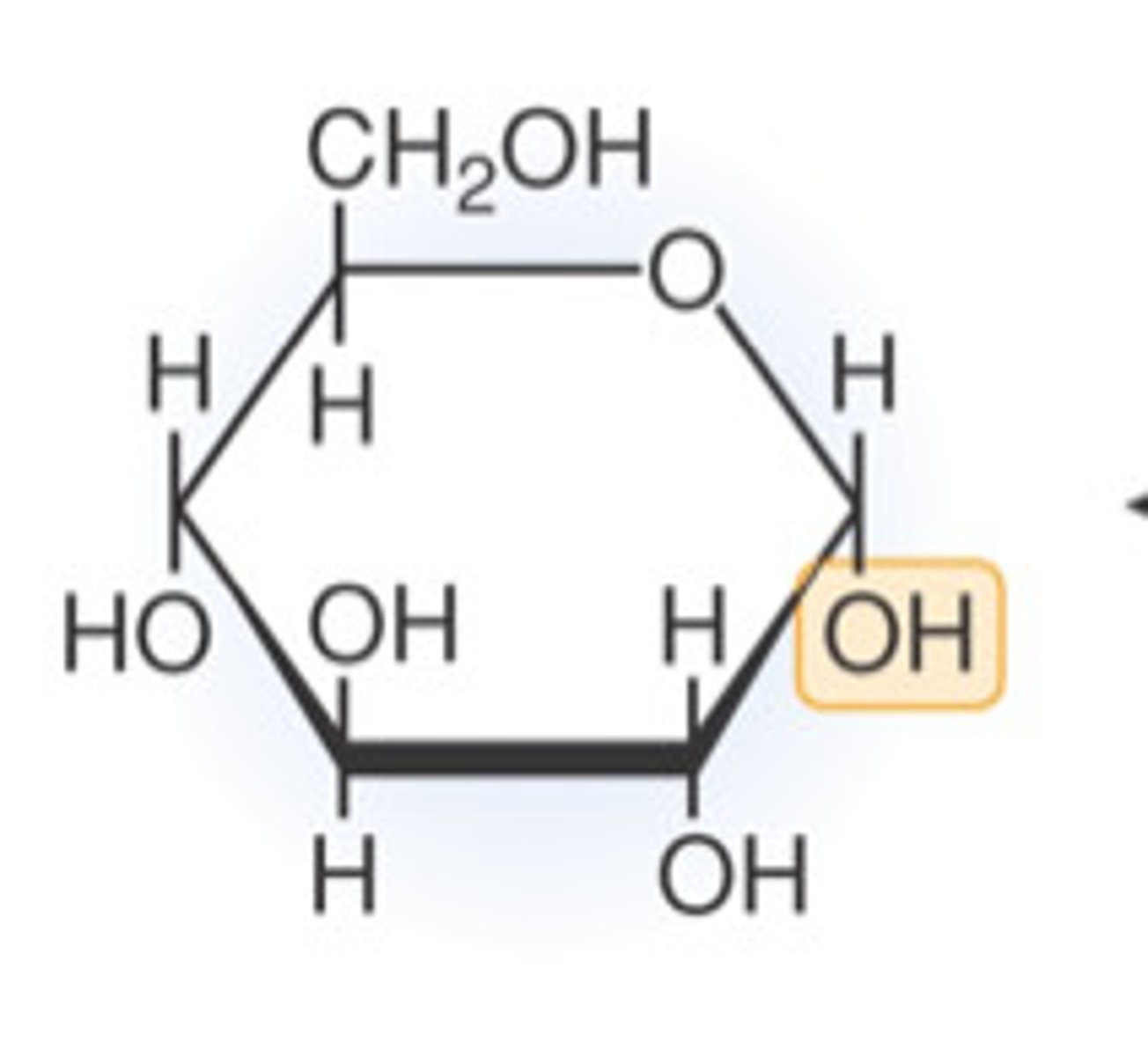
glucose
Monosaccharide, short term energy storage; blood sugar; C6H12O6
glycogen
Complex Carbohydrate; energy storage in animals; polysaccharide
starch
Complex Carbohydrate; energy storage in plant cells; polysaccharide

cellulose
Complex Carbohydrate; structural support in plants
lipid
Organic molecule that functions in long term energy storage and insulation
fatty acid
subunit of a lipid; long hydrocarbon chain
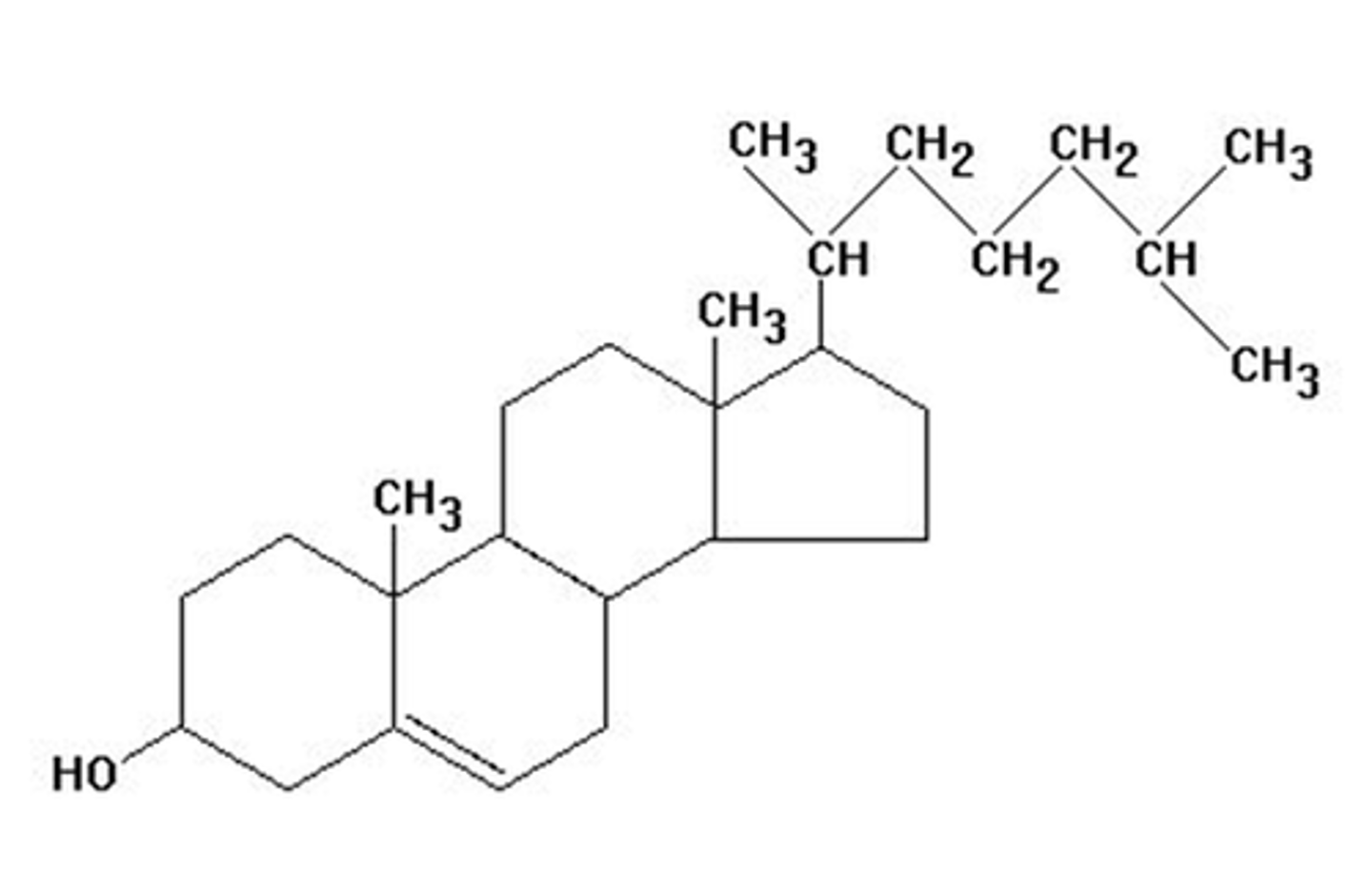
steroid
lipid molecule made from cholesterol containing 4 fused carbon rings; testosterone and estrogen are example; or can be used for "mad' gains in gym
protein
organic molecule built up of amino acids

amino acid
monomer of protein
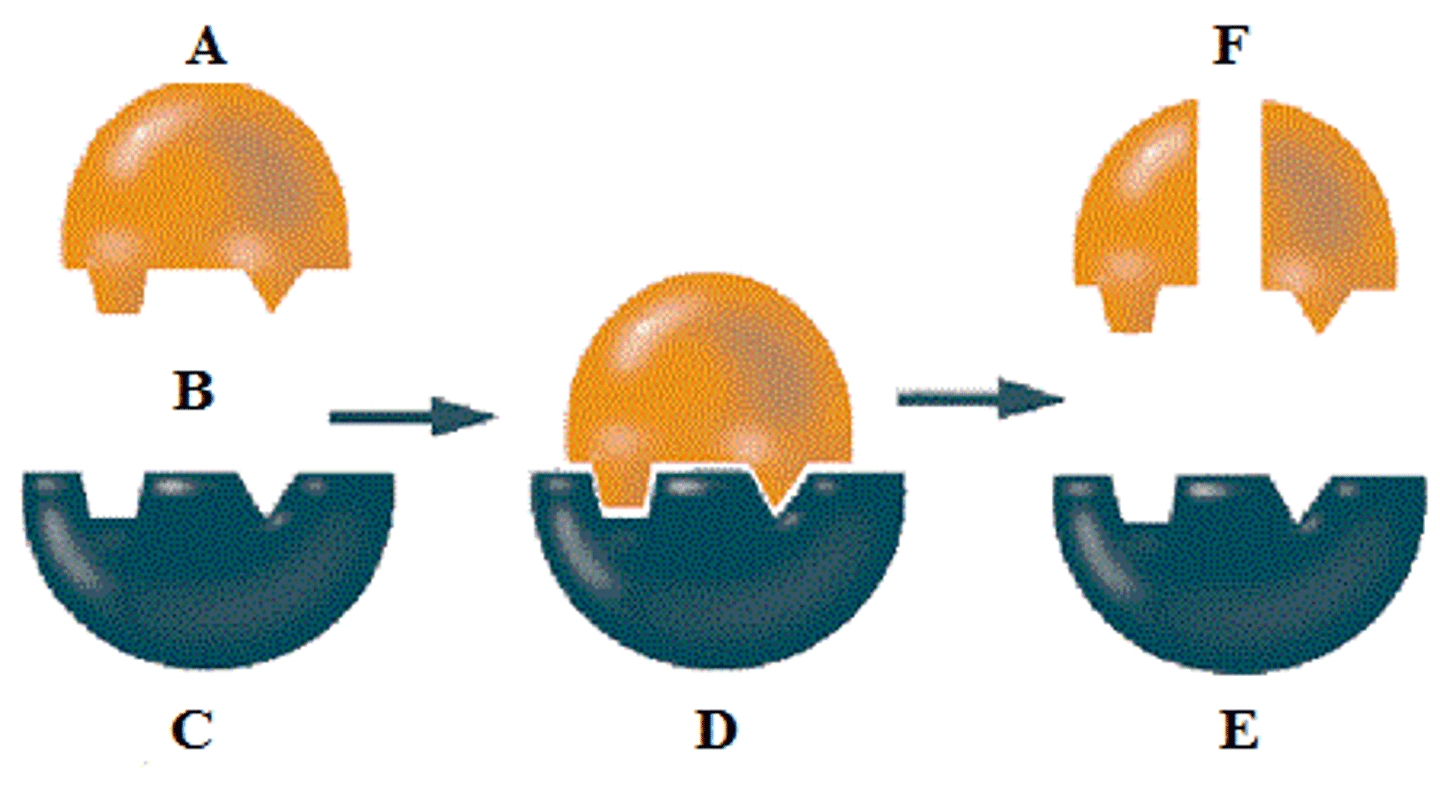
enzyme
protein molecule that controls chemical reactions and cell processes
polypeptide
Chains of amino acids that make up proteins
monosaccharide
single sugar such as glucose
polysaccharide
many sugars such as starch, cellulose, or glycogen
monomer
mono = one ... a single subunit of an organic molecule. Also called the building block. Think individual lego
polymer
poly = many ... a macromolecule. This is what is created when lots of monomers come together. Think lego castle
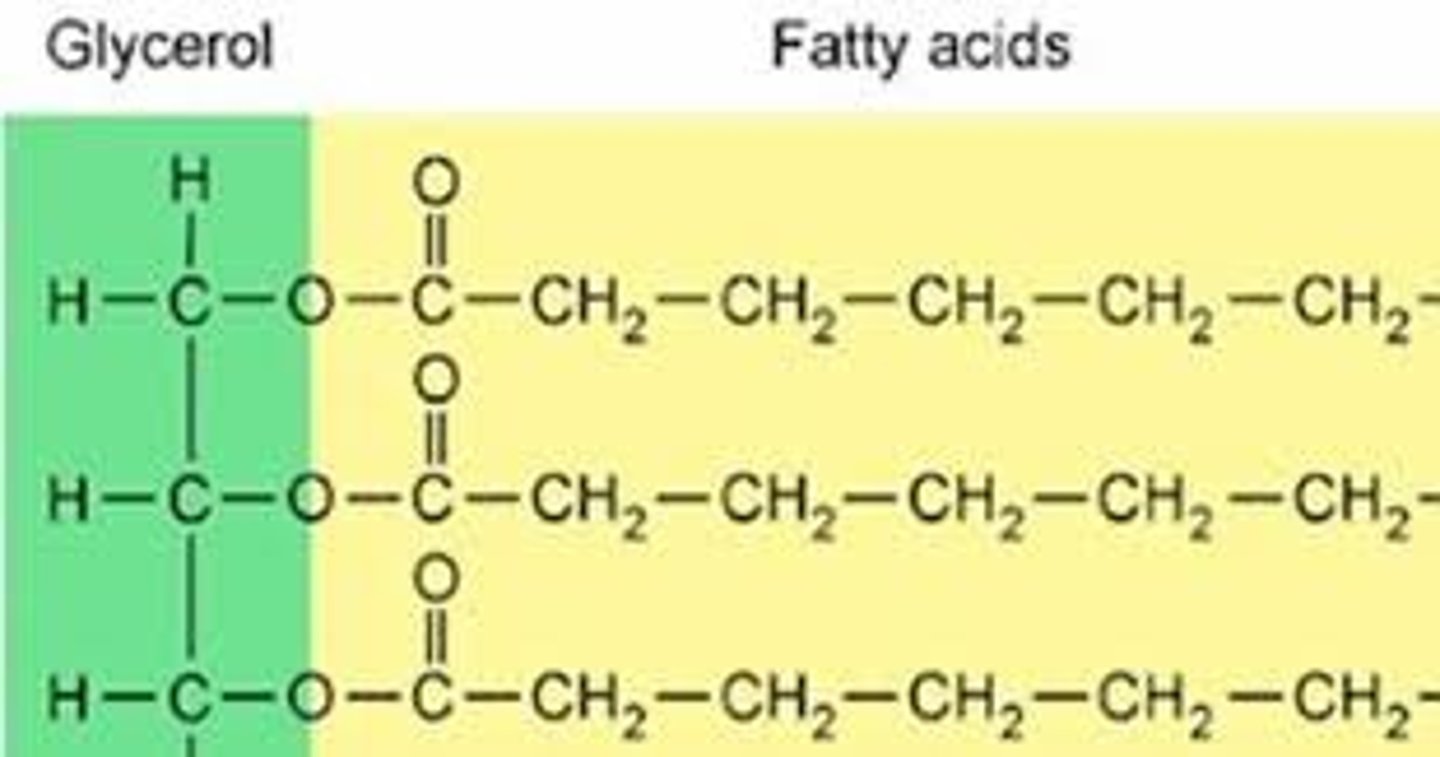
fat (triglyceride)
A large lipid molecule made from an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids; a triglyceride. Most fats function as energy-storage molecules.
Organic Elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids.