Cheat Sheet 10: Protists and Fungi Overview
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Kingdom Protista
Taxonomic group of eukaryotic organisms.
Plant-like Protists
Photosynthetic autotrophs, e.g., red algae.
Fungus-like Protists
Reproduce via spores, similar to fungi.
Animal-like Protists
Also known as protozoa, mostly unicellular.
Amoeba
Example of animal-like protist using pseudopodia.
Pseudopodia
Temporary arm-like projections for movement.
Cilia
Hair-like structures for movement in protists.
Flagella
Tail-like structures for motility in protists.
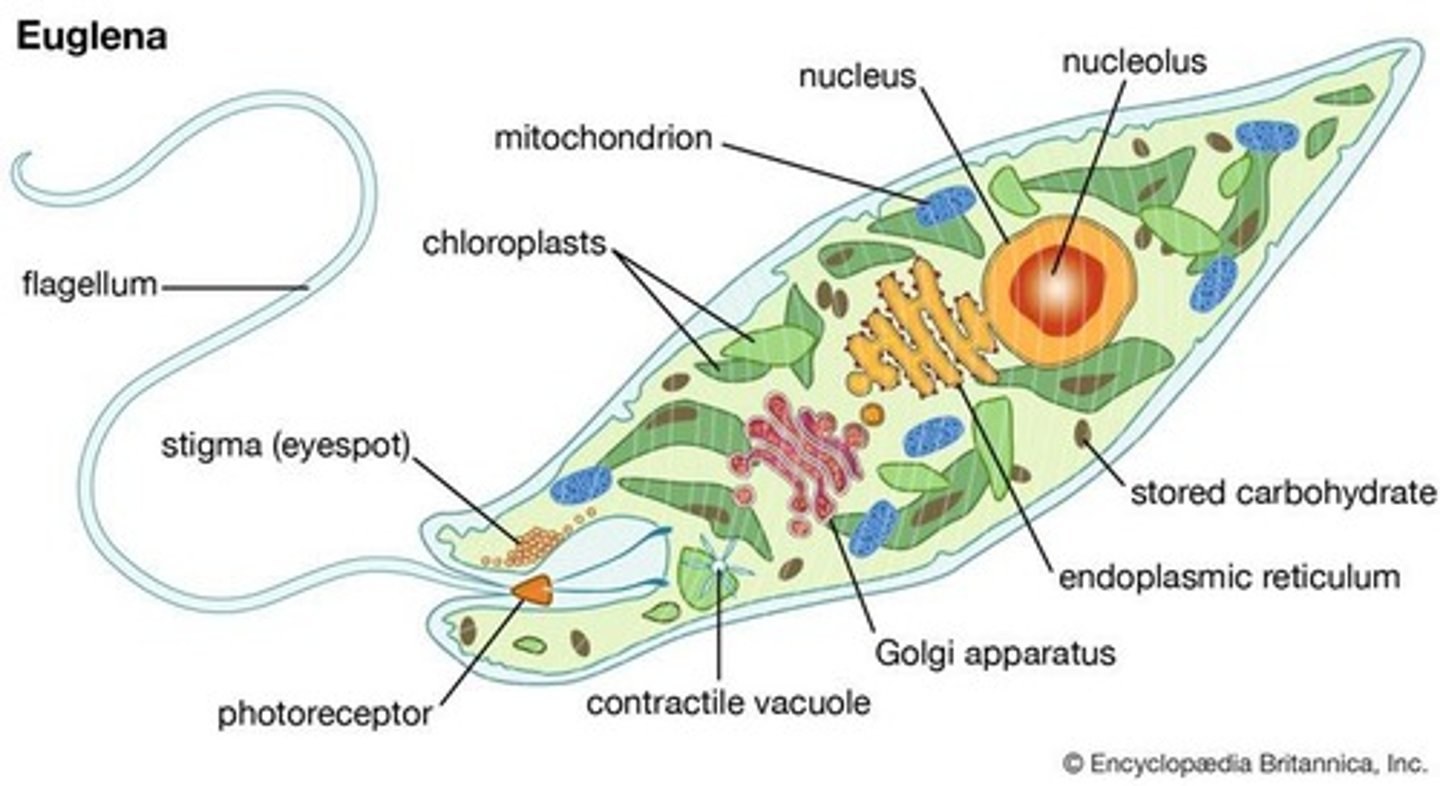
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume organic matter for energy.
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food via photosynthesis.
Mycelium
Network of fungal filaments connecting fungi.
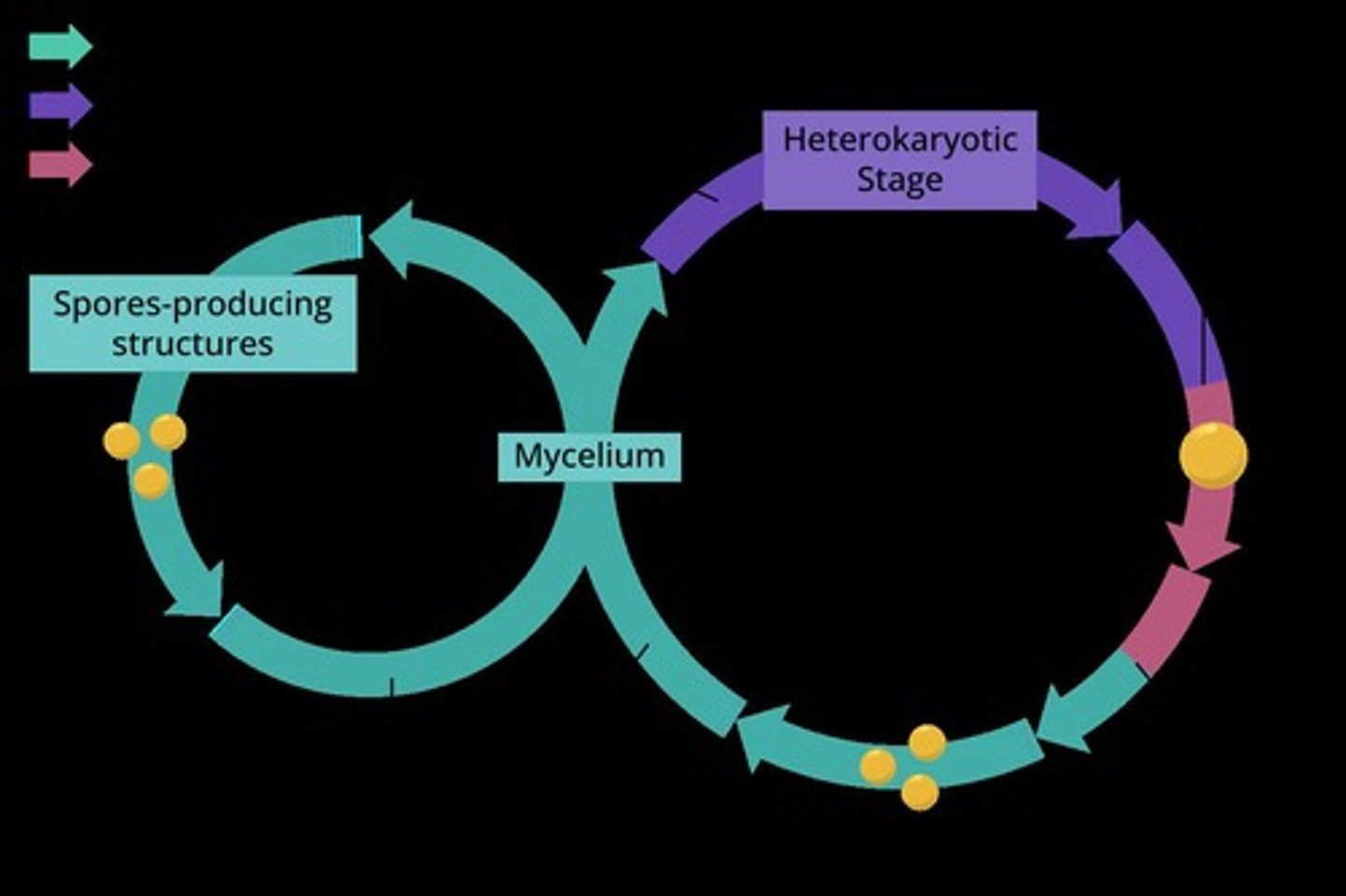
Hyphae
Filamentous branches produced by multicellular fungi.
Chitin
Structural component in fungal cell walls.
Sporangium
Organ where meiosis occurs and spores form.
Rhizoids
Branching hyphae that anchor fungi to substrates.
Septate Hyphae
Hyphae with septa separating individual cells.
Coenocytic Hyphae
Multinucleated hyphae without septa.
Filamentous Fungi
Multicellular fungi including molds and mushrooms.
Non-filamentous Fungi
Unicellular fungi, primarily yeasts.
Asexual Reproduction
Reproduction without the fusion of gametes.
Sexual Reproduction
Involves the fusion of gametes.
Saprobes
Decomposers feeding on non-living organic matter.
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing food particles by protists.
Eukaryotic Organisms
Cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Moist Environments
Preferred habitats for many protists.
Symbiotic Relationships
Interactions between different species benefiting one or both.
Undergoes asexual reproduction by budding
Non-filamentous fungi