BE 359 Chapter 17: Cell Organization and Movement I - Focus on Microfilaments and Cytoskeleton
1/275
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
276 Terms
actin
a section of mouse intestine stained for ________ (red), extracellular matrix protein laminin (green), and DNA in the nucleus of each cell (blue)
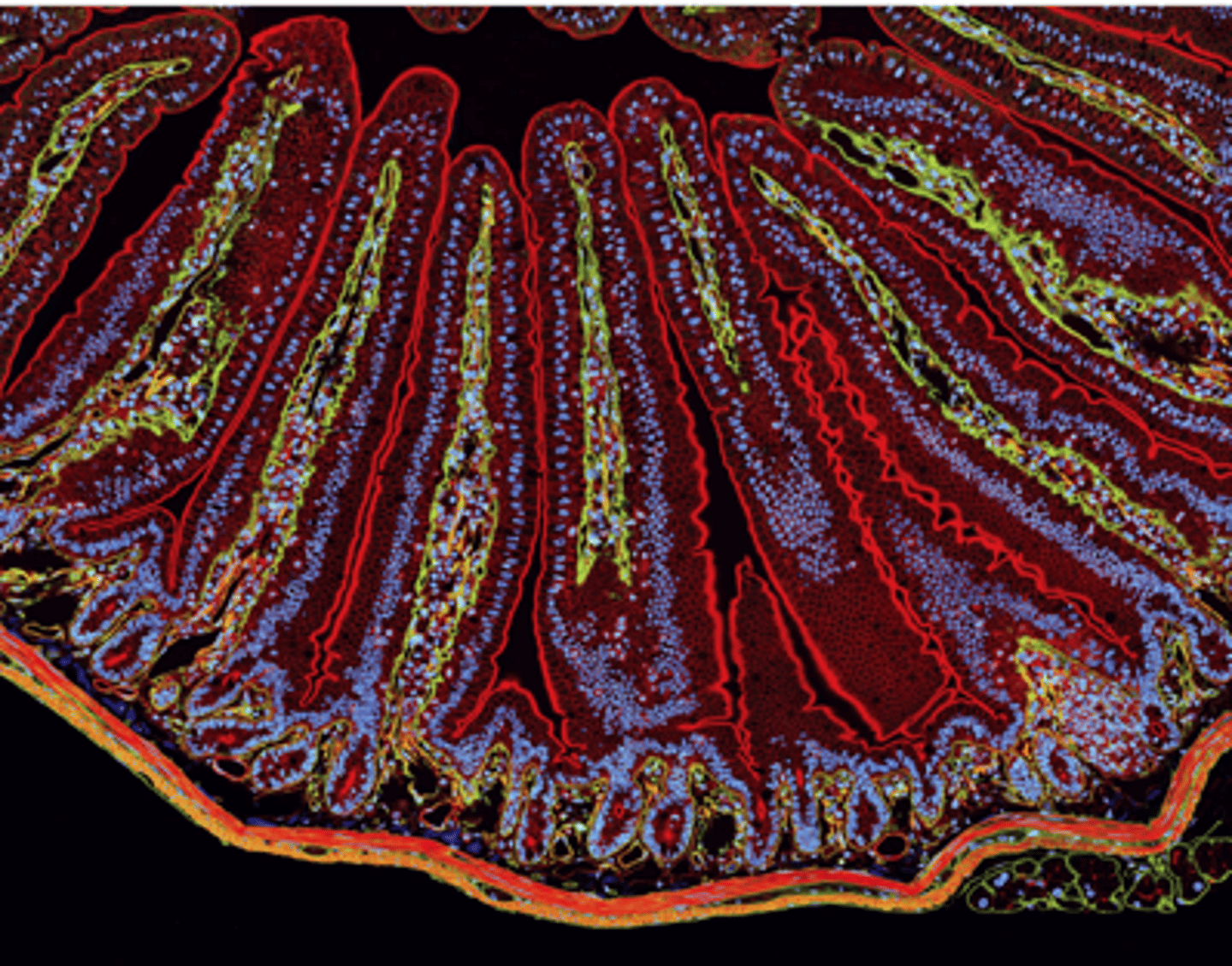
actin localization
in the microvilli, on the apical end of the epithelial cells lines the epithelium surface facing the lumen (top)
actin localization
in the smooth muscle that surrounds the intestine (bottom)
actin
a highly conserved and abundant eukaryotic cell protein
actin
cells assemble diverse structures of _________ filaments for different functions
polarized
G-actin reversibly assembles into ____________ F-actin filaments
protofilaments
G-actin reversibly assembles into polarized F-actin filaments: composed of two ___________________, in which the actin subunits all oriented in the same direction
helix
G-actin reversibly assembles into polarized F-actin filaments: protofilaments are wound around each other to form a __________ with the actin nucleotide-binding site exposed on the (−) end of each protofilament
polarizes
The distribution and organization of cytoskeleton filaments structurally ______________ different types of cells
epithelium
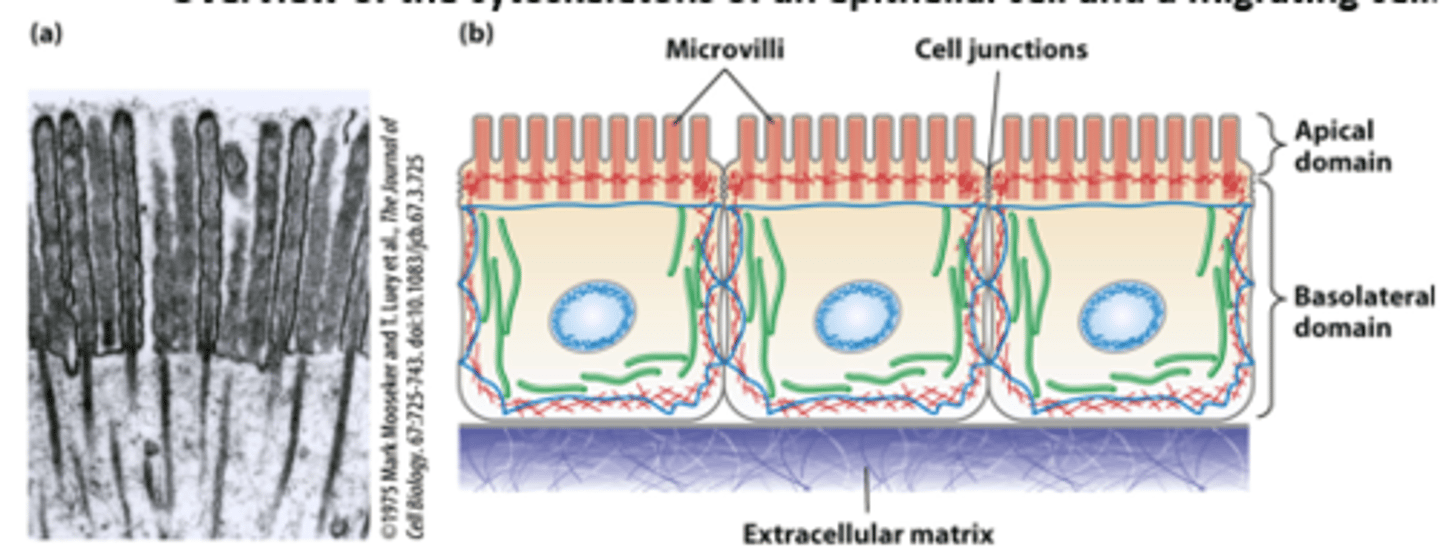
Epithelial cells lining the intestine: polarized morphology and junctions with all neighboring cells forms a tight single cell layer pavement-like _______________
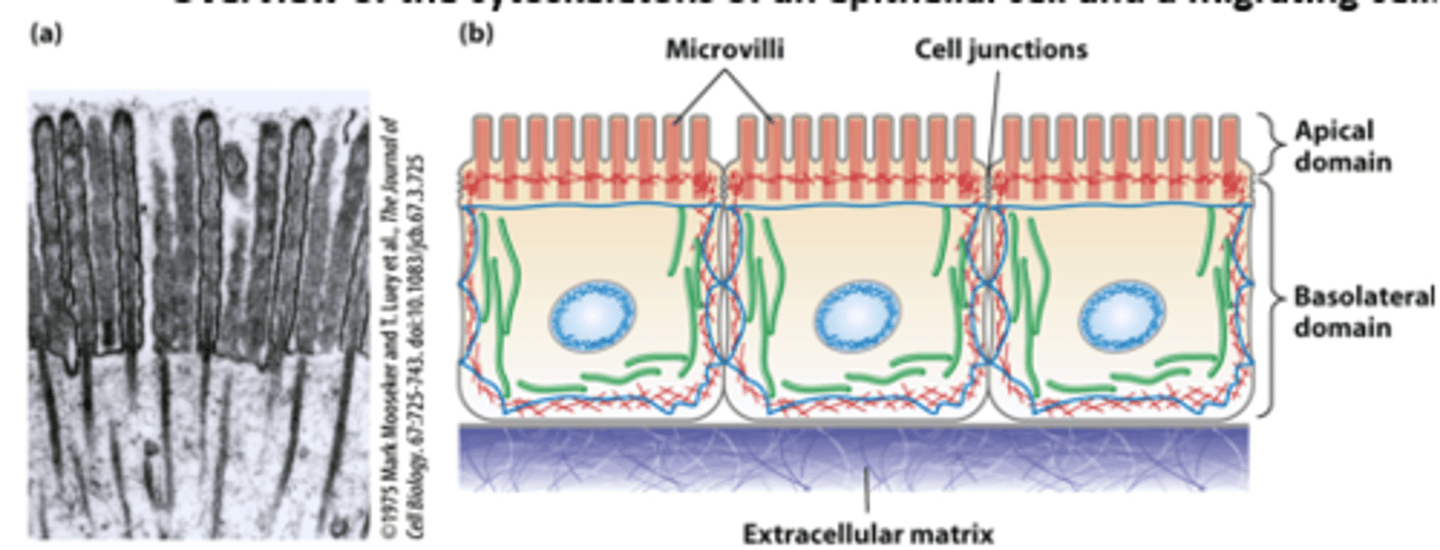
nutrients
Epithelial cells lining the intestine: ___________ (such as glucose) are imported from the intestinal lumen across the apical plasma membrane and exported across the basolateral plasma membrane into the bloodstream
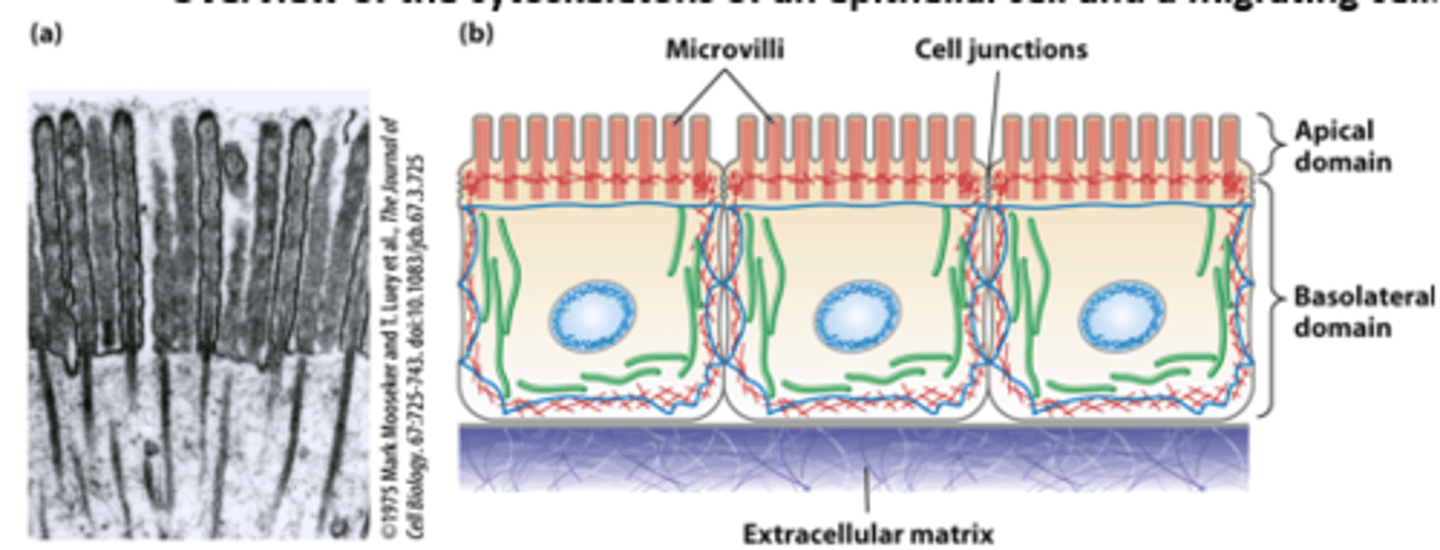
actin microfilaments
Epithelial cells lining the intestine: The highly polarized intestinal epithelial cell structure, with distinct apical and basolateral domains, is supported by the cytoskeleton - core bundles of _________ _______________ provide support to the intestinal epithelial cell apical microvilli (TEM of thin section)
infectious
A white blood cell macrophage uses a complex array of actin microfilaments at the leading edge for the processes of chemotaxis and phagocytosis to pursue, capture, and destroy ______________ agents
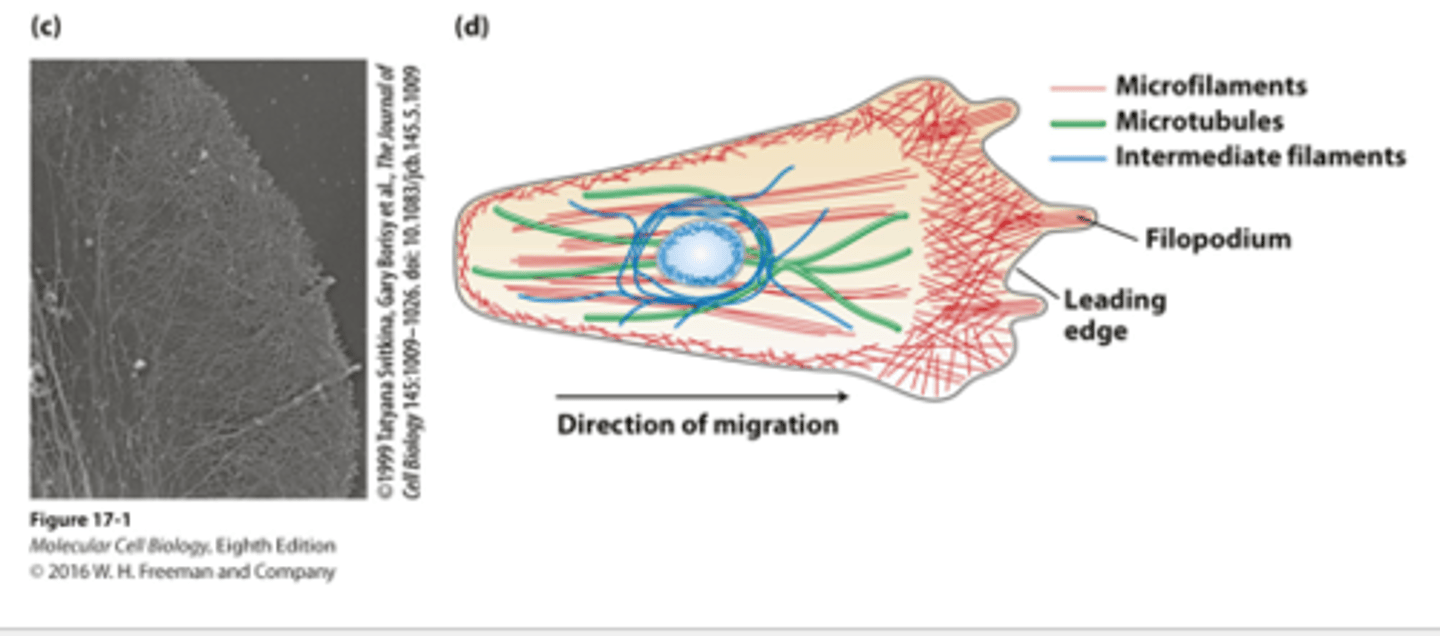
TEM
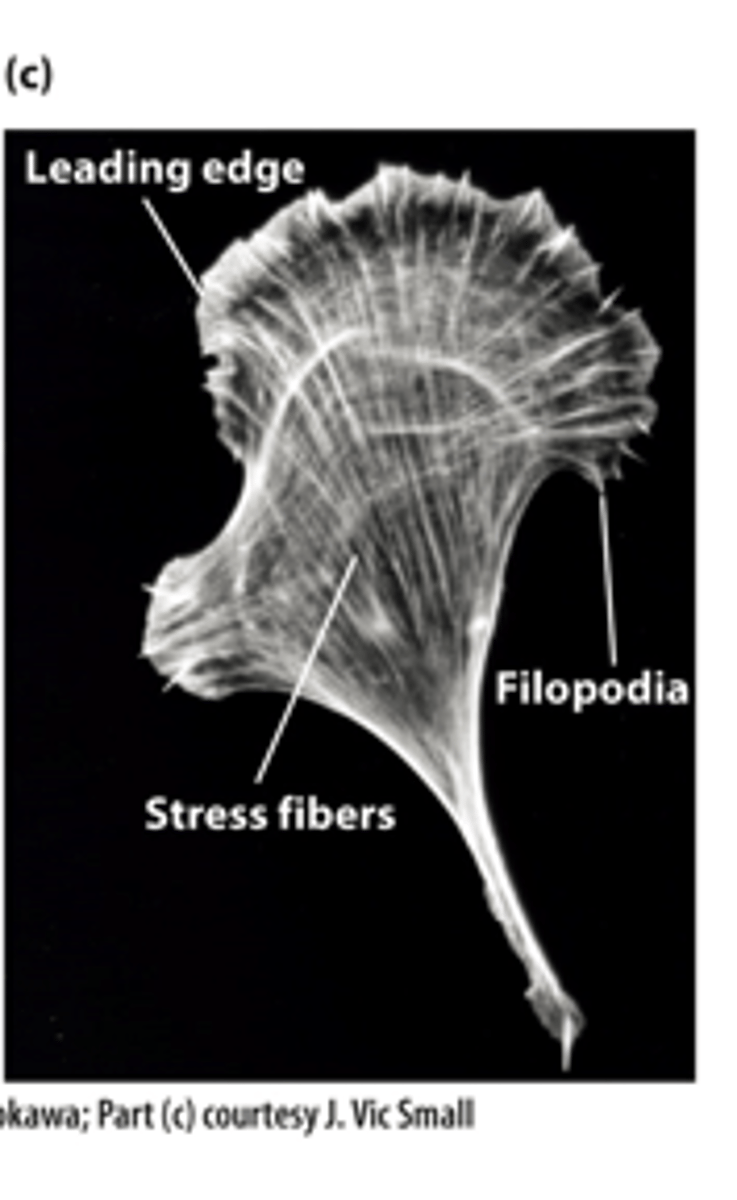
_______ of the leading edge cytoskeleton : visualized by extracting the membrane and soluble components from the cell by detergent treatment and making a metal replica of the remaining filaments
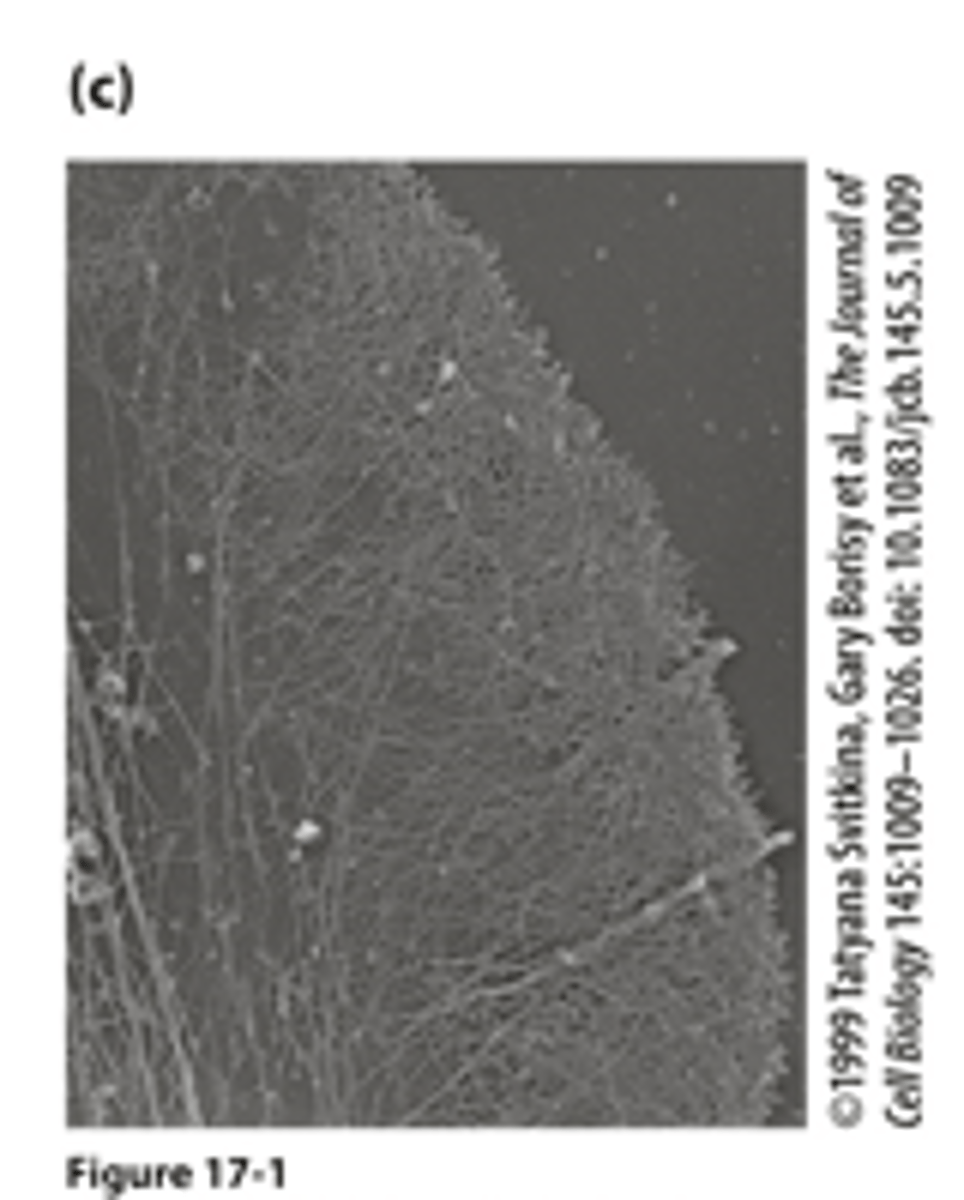
migrating
Morphologically distinct domains in a _____________ cell polarizes the cell structure with the leading edge oriented in the direction of locomotion
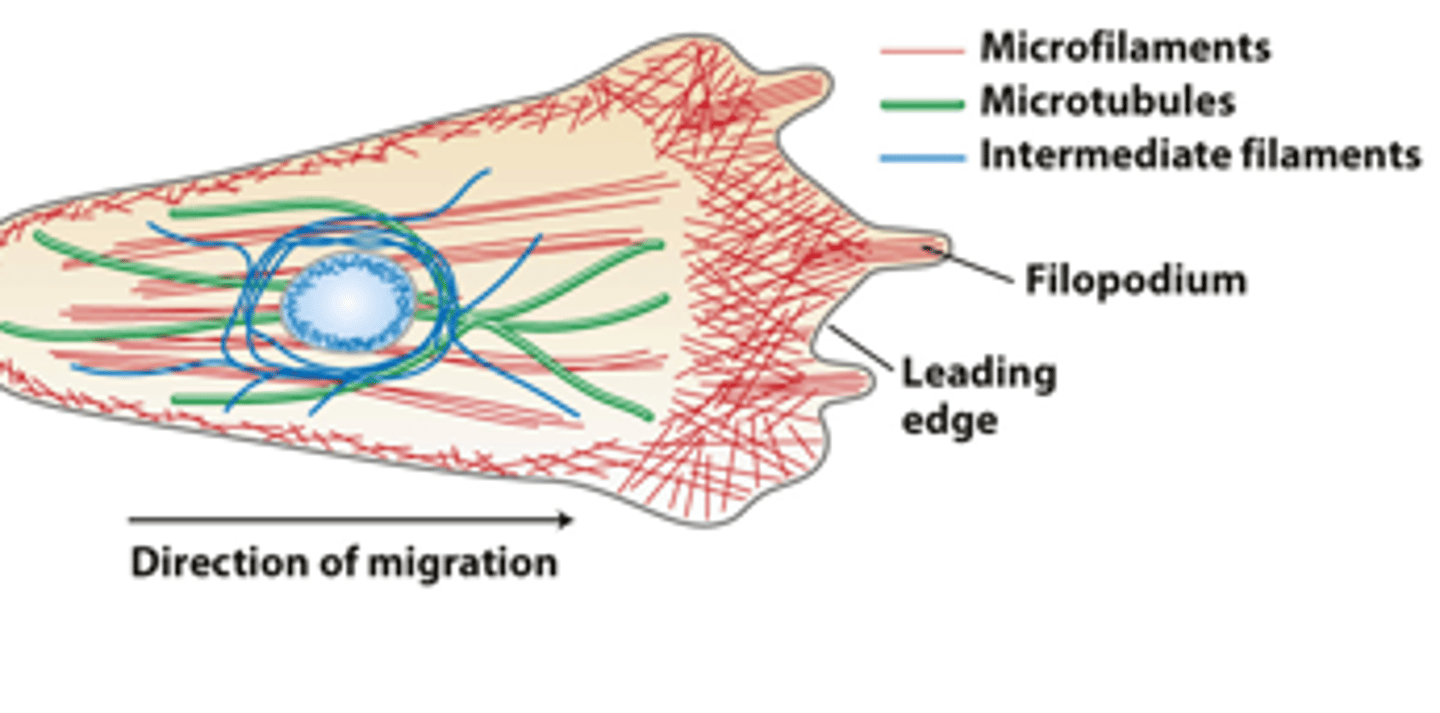
red
in overview of the cytoskeletons of an epithelial cell and a migrating cell: microfilaments are _______
green
in overview of the cytoskeletons of an epithelial cell and a migrating cell: microtubules are _________
dark blue
in overview of the cytoskeletons of an epithelial cell and a migrating cell: intermediate filaments ________ ___________
light blue
in overview of the cytoskeletons of an epithelial cell and a migrating cell: nucleus __________ ___________ oval
filament
Cells reversibly and dynamically assemble each type of ____________ from specific subunit
three
a single cell can have all __________ filament systems in its cytoskeleton
organization
Each filament system has a distinct _____________ in cells
actin microfilaments, tubulin microtubules, intermediate filaments
three types of filaments
fluorescence microscope
Each filament type can be labeled with specific fluorescent antibodies that are visible with a _________________ ___________________ (immunofluorescence microscopy).
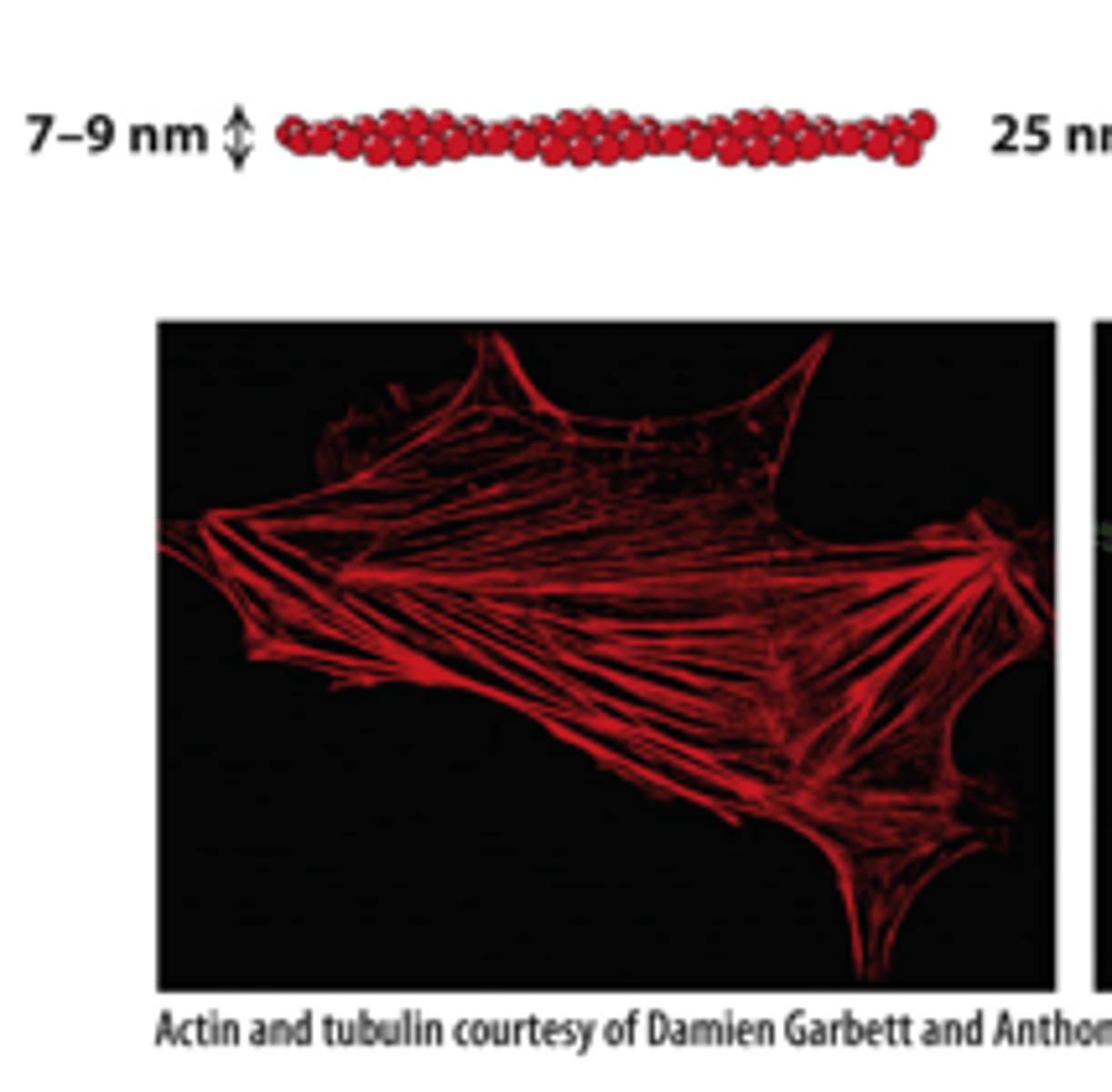
microfilaments
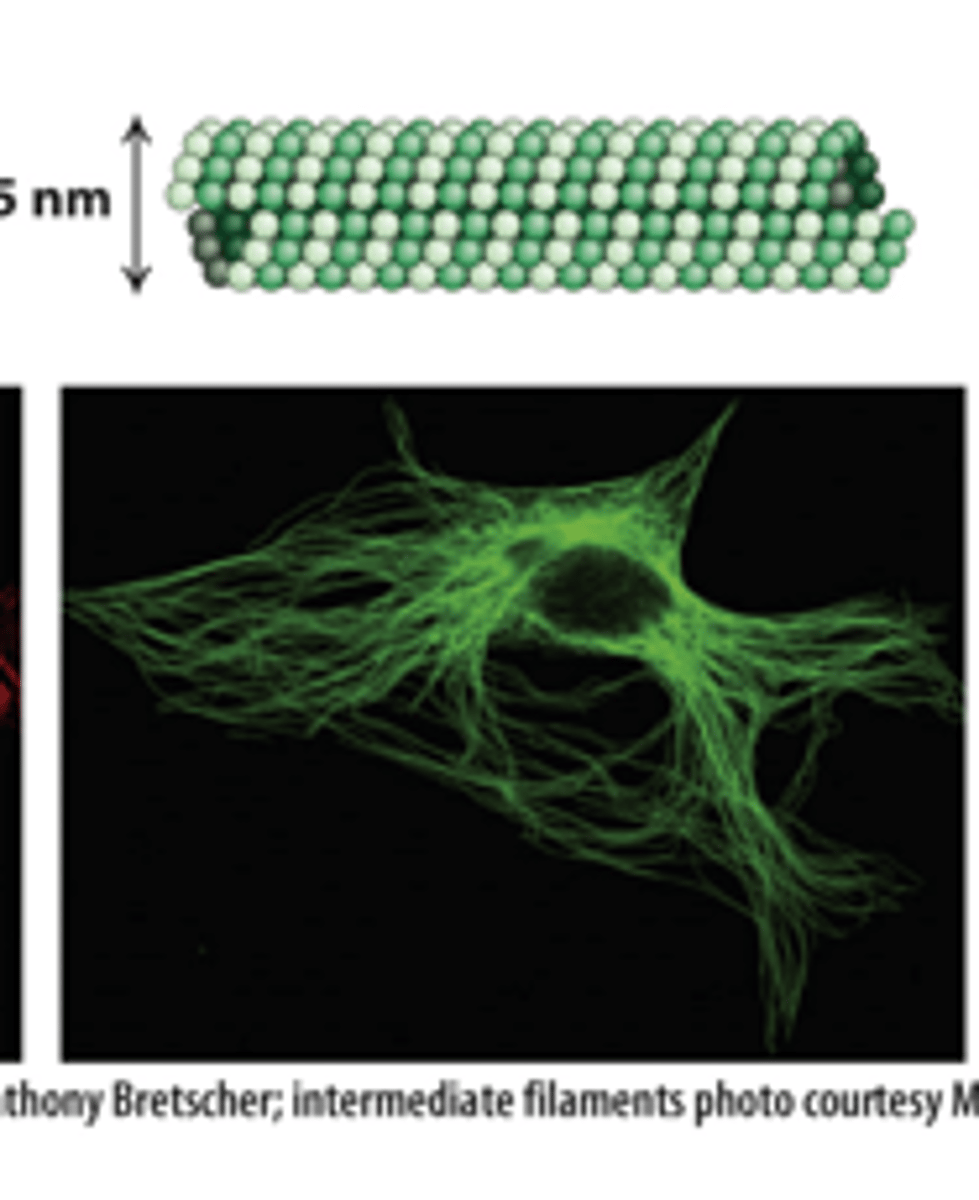
microtubules
intermediate filaments
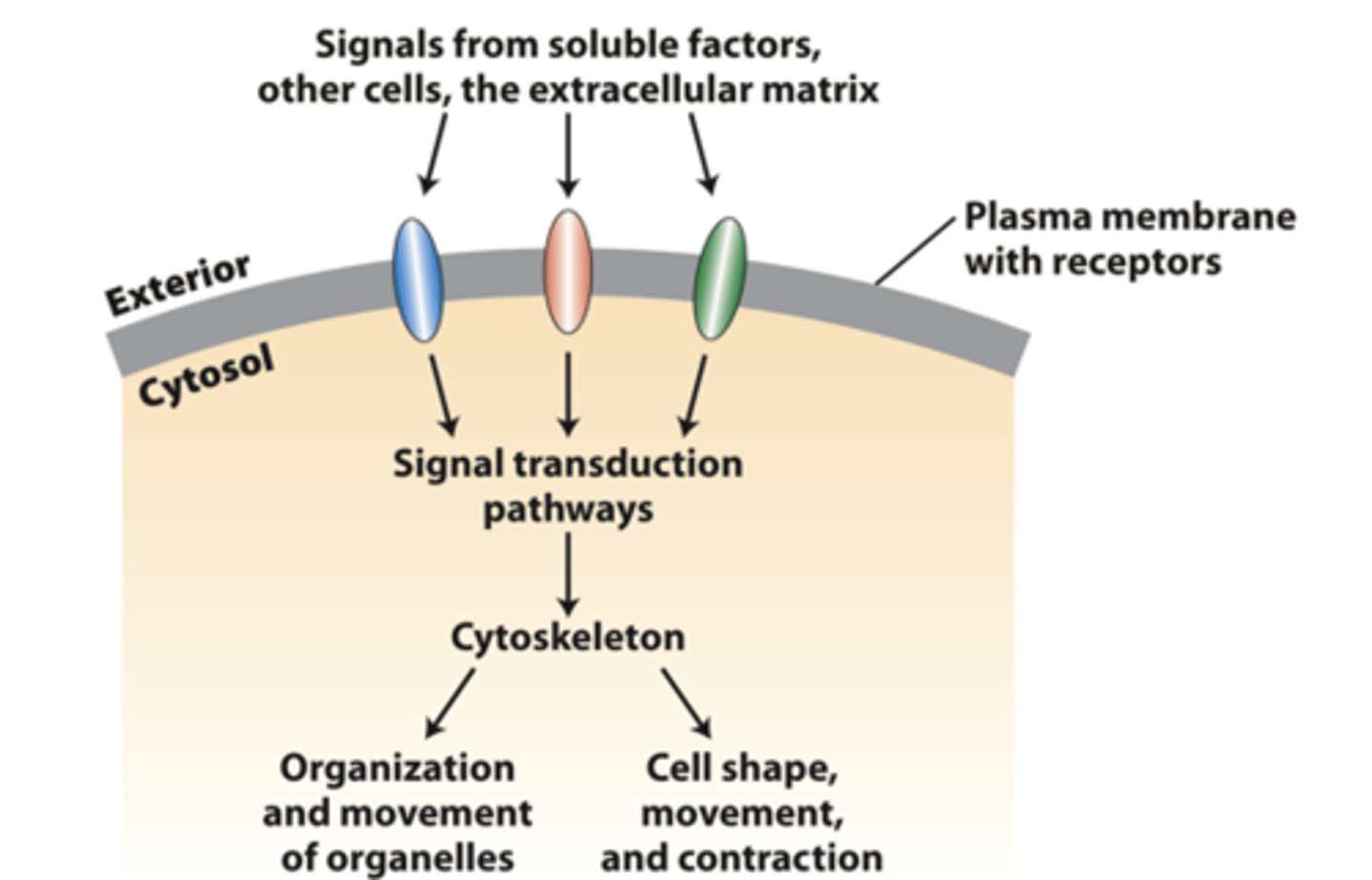
cell surface receptors
transmit external signals from the extracellular matrix, other cells, or soluble factors across the plasma membrane to activate specific cytosolic signaling pathways that regulate cytoskeleton organization and function
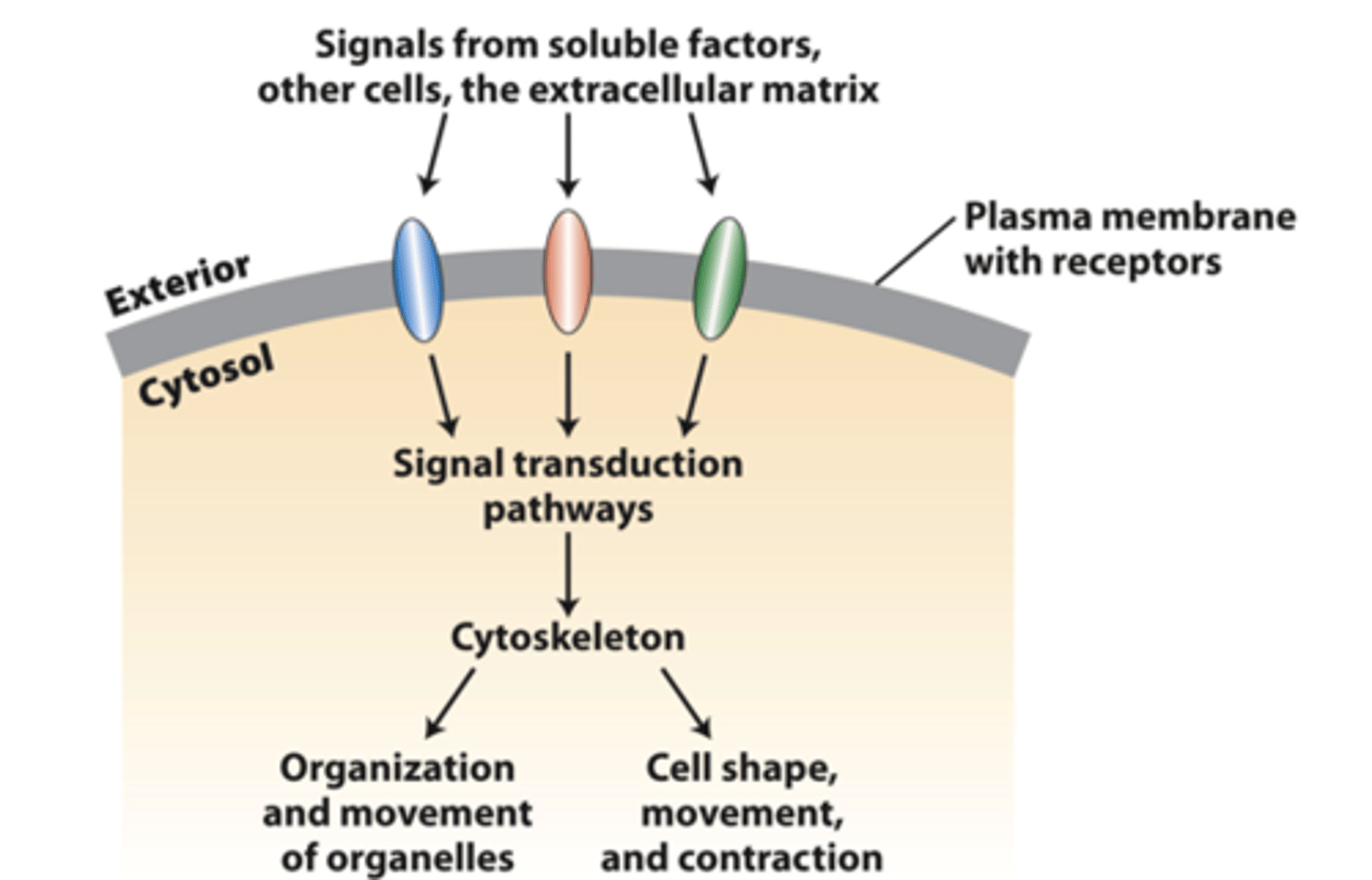
cytoskeleton
Integration of signals from more than one type of receptor leads to a variety of _________________ organizations and activities, some of which may be localized in cells
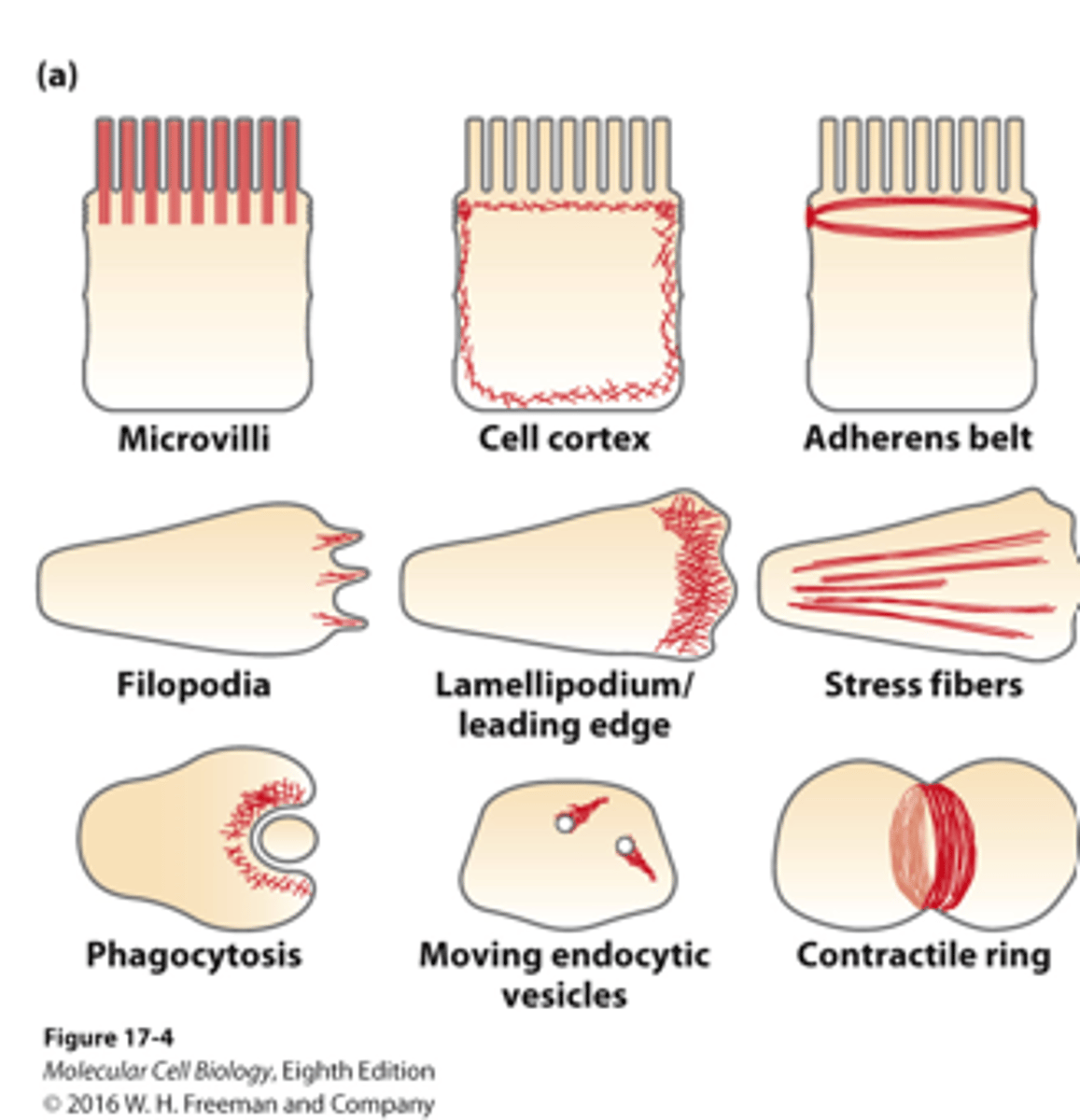
microfilaments
______________ can be organized into a variety of different structures with distinctive activities within a cell/in different types of cells
actin filaments
The apical region of a polarized epithelial cell, showing the microvillar core bundles of _________ _________________ (Sample was prepared using a rapid freeze, deep etch, rotary shadow protocol and viewed by transmission electron microscopy.)
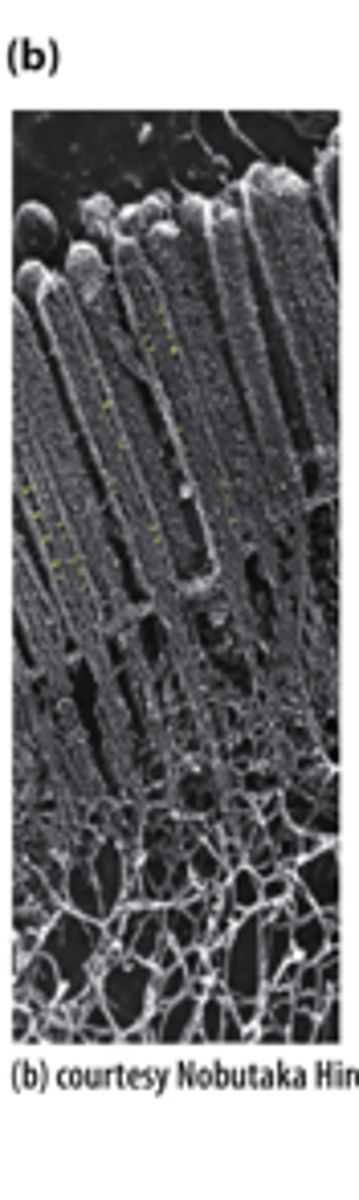
phalloidin
Staining actin microfilaments with fluorescent ____________, a drug that specifically binds F-actin, reveals different microfilament organizations in a moving cell led by the leading edge
actin
__________ is ancient, highly conserved, and abundant
eukaryotic
_____________ actin is structurally related to bacterial MreB, which also forms filaments
amoebae, animal
Actins from ____________ and ___________ actins are identical at 80 percent of their amino acid positions despite a billion years of evolution
six
________ human actin genes are expressed in different cell types, but the proteins are 93 percent identical
protein
Actin comprises up to 10 percent of the total ___________ in muscle cells and 1-5 percent in other cell types - 5 x 108 actins in a liver cell and localized concentrations of actin in cells can be 5 mM in microvilli
two
G-actin: The actin monomer structure (measuring 5.5 × 5.5 × 3.5 nm) is divided by a central cleft into ________ approximately equal-sized lobes and four subdomains, numbered I-IV
ATP, ADP
G-actin: _______/_______ binds at the bottom of the cleft and contacts both lobes
F actin
Actin monomers polymerize into a long, helical _____-__________ polymer (microfilament)
helically
Actin monomers polymerize into a long, helical F-actin polymer (microfilament): structure--filament is composed of two ___________ wound strands with a repeating unit of 28 subunits (14 in each strand) covering a distance of 72 nm.
exposed, opposite
Actin monomers polymerize into a long, helical F-actin polymer (microfilament): polarity--•the ATP-binding cleft of every actin subunit is oriented toward the same end of the filament. The filament end with an __________ binding cleft is the (−) end; the ___________ end is the (+) end.
TEM
_______-negatively stained actin filaments appear as long, flexible, and twisted strands of beaded actins
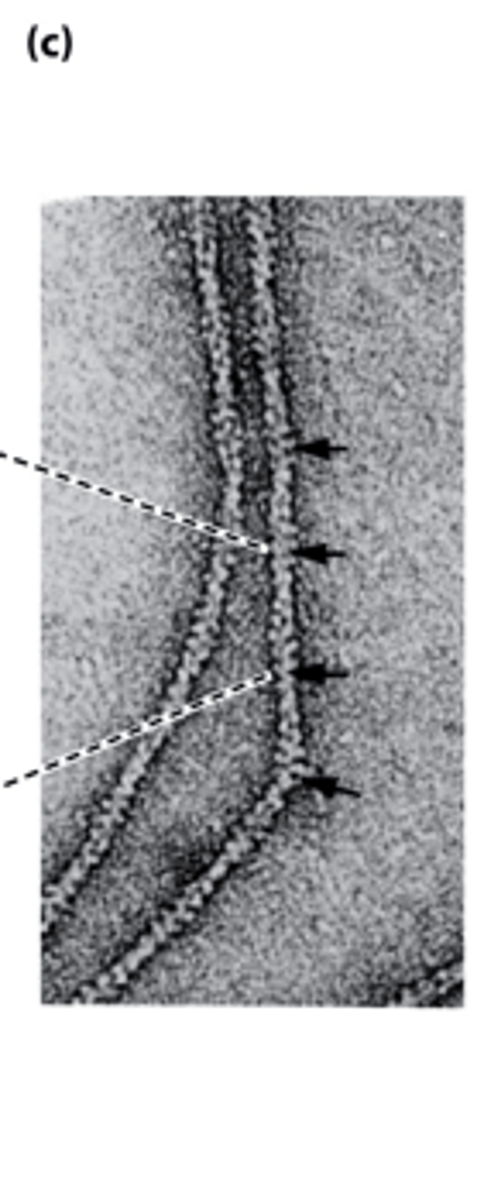
in vitro, kinetics, critical concentration
actin filament polymerization: ______ ____________ mechanism, ___________, _________ ____________
G actin, F actin
regulation of actin filament polymerization and stability by _____-_________ and _____-_________ binding proteins
in vitro
______ ________ polymerization of G-actin monomers to form F-actin filaments can be monitored by viscometry, sedimentation, fluorescence spectroscopy, or fluorescence microscopy
nucleation phase
G-actin polymerization into F-actin filaments: (lag) Inefficient formation three ATP-G-actin "nucleus/seed" (more stable than two actin associations because of the extra bonds) initiates formation of a filament
elongation phase
G-actin polymerization into F-actin filaments: Actin subunits rapidly assemble onto each end of a filament.
steady state phase
G-actin polymerization into F-actin filaments: G-actin monomers exchange with subunits at the filament ends, but there is no net change in the total length of filaments
nucleation, elongation, steady state
three phases of in vitro G-actin polymerization
short actin
Addition of _______ ________ filament "nuclei/seeds" bypasses the slow nucleation phase - elongation proceeds without any lag period
different
two ends of a myosin-decorated actin grow at ___________ rates
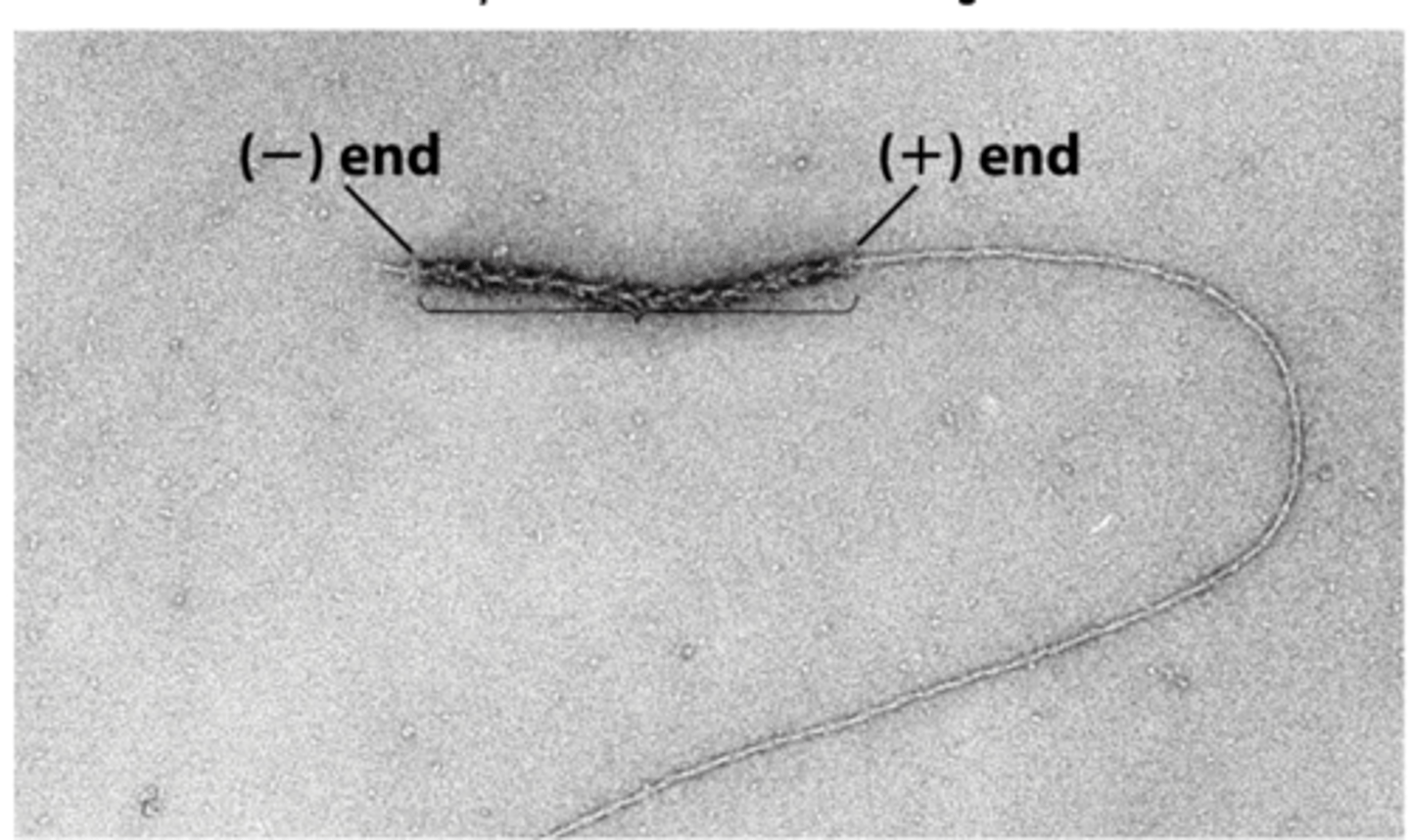
positive
actin filaments grow faster at ______________ ends
negative
actin filaments grow slower at _____________ ends
short actin
myosin-decorated actin filament experiment: ________ ________ filaments arrowhead decorated with myosin S1 heads added to G-actin nucleate (seed) actin assembly on both ends of the filament
G actin
myosin-decorated actin filament experiment: ______-__________ assembles ~10 times faster at the (+) end than at the (−) end, reflecting different ratios of on-off rates at each end
positive, negative
ATP-actin subunits assemble faster at the (____________, lower Cc) end than at the (__________, higher Cc) end of an actin filament, resulting in treadmilling at steady state
ten
Actin filament assembly-disassembly at each end: Rate of ATP-G-actin assembly is almost _______ times faster at the (+) end than at the (−) end.
similar
Actin filament assembly-disassembly at each end: Rate of ADP-G-actin disassembly is ____________ at the two ends
steady state
Actin filament assembly-disassembly at each end: At __________ __________, ATP-actin assembly on the (+, lower Cc) end is faster than actin ATP hydrolysis in the filament, giving rise to a filament with a short region of ATP-actin and regions of ADP-Pi–actin and ADP-actin toward the (−) end
filament net
Actin filament treadmilling: The _____________ ________ Cc is between the (+) end and the (-) end Cc
ATP, ADP
Actin filament treadmilling: At steady state, _______-G-actin subunits assemble preferentially on the (+) end, while _______-G-actin subunits disassemble from the (−) end.
two
Actin filament treadmilling: _________ actin subunits (blue) assemble on the (+) end. Over time, more actins assemble onto the (+) end while actins disassemble from the (-) end, and the blue subunits treadmill to the (-) end
in vitro
Treadmilling filaments can do work ______ ________
turnover
Regulation of filament _______________ by actin-binding proteins
actin binding
__________-___________ proteins regulate the rate of assembly and disassembly of actin filaments as well as the availability of G-actin for polymerization
profilin, cofilin
Regulation of filament turnover by actin-binding proteins: _________ (cycle 1), __________ (cycle 2), thymosin-beta4 cycle
prolifin
profilin (cycle 1): __________ binds to ADP-G-actin opposite the nucleotide-binding cleft, opening the cleft and catalyzing the exchange of ADP for ATP
blocks
profilin (cycle 1): Profilin binding sterically __________ ATP-G-actin assembly on the filament (-) end but allows the unblocked G-actin monomer end to assemble onto the filament (+) end
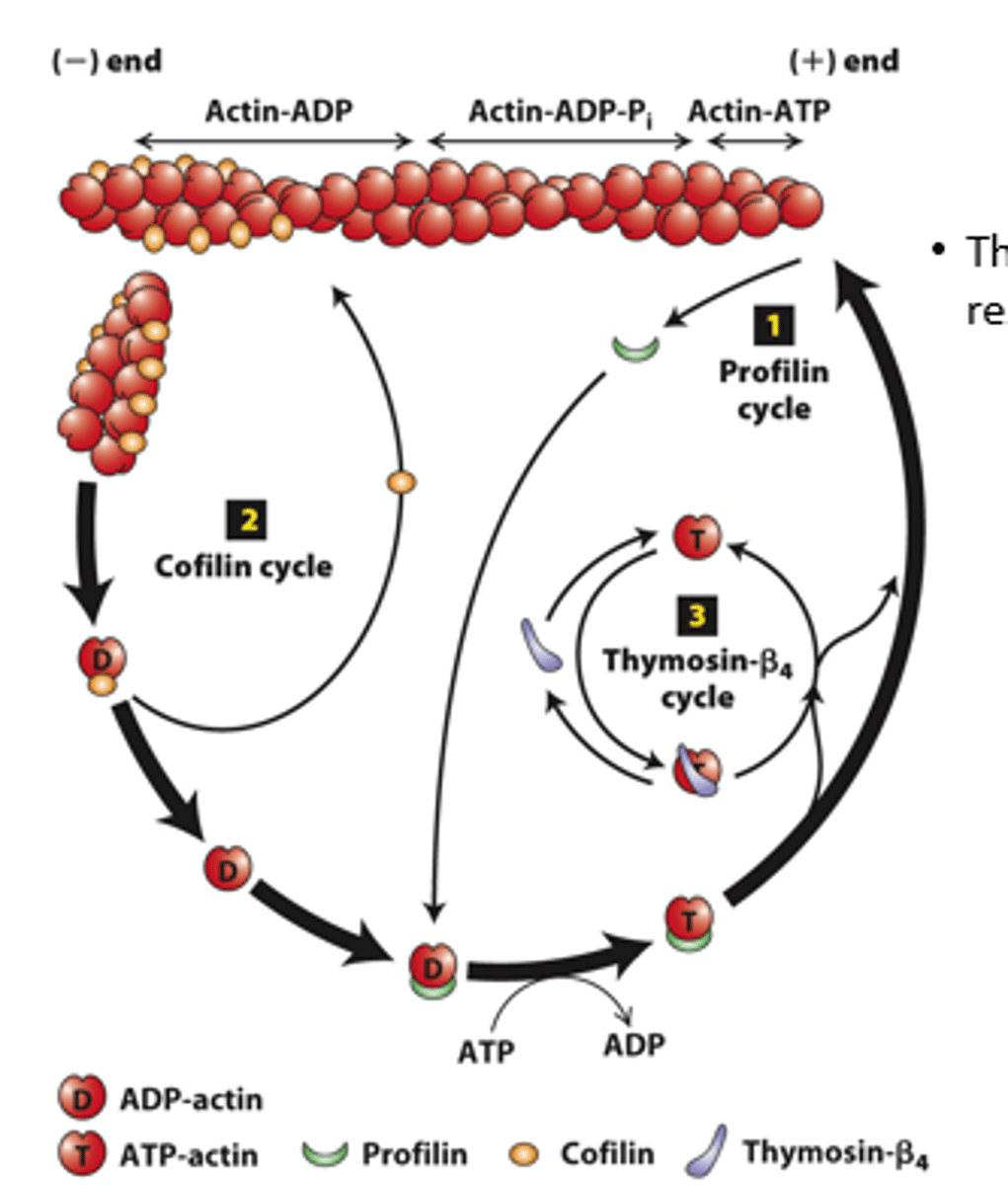
positive
profilin (cycle 1): ATP-G-actin-profilin complex assembly on the (__________) end dissociates profilin to interact with another ADP-G-actin
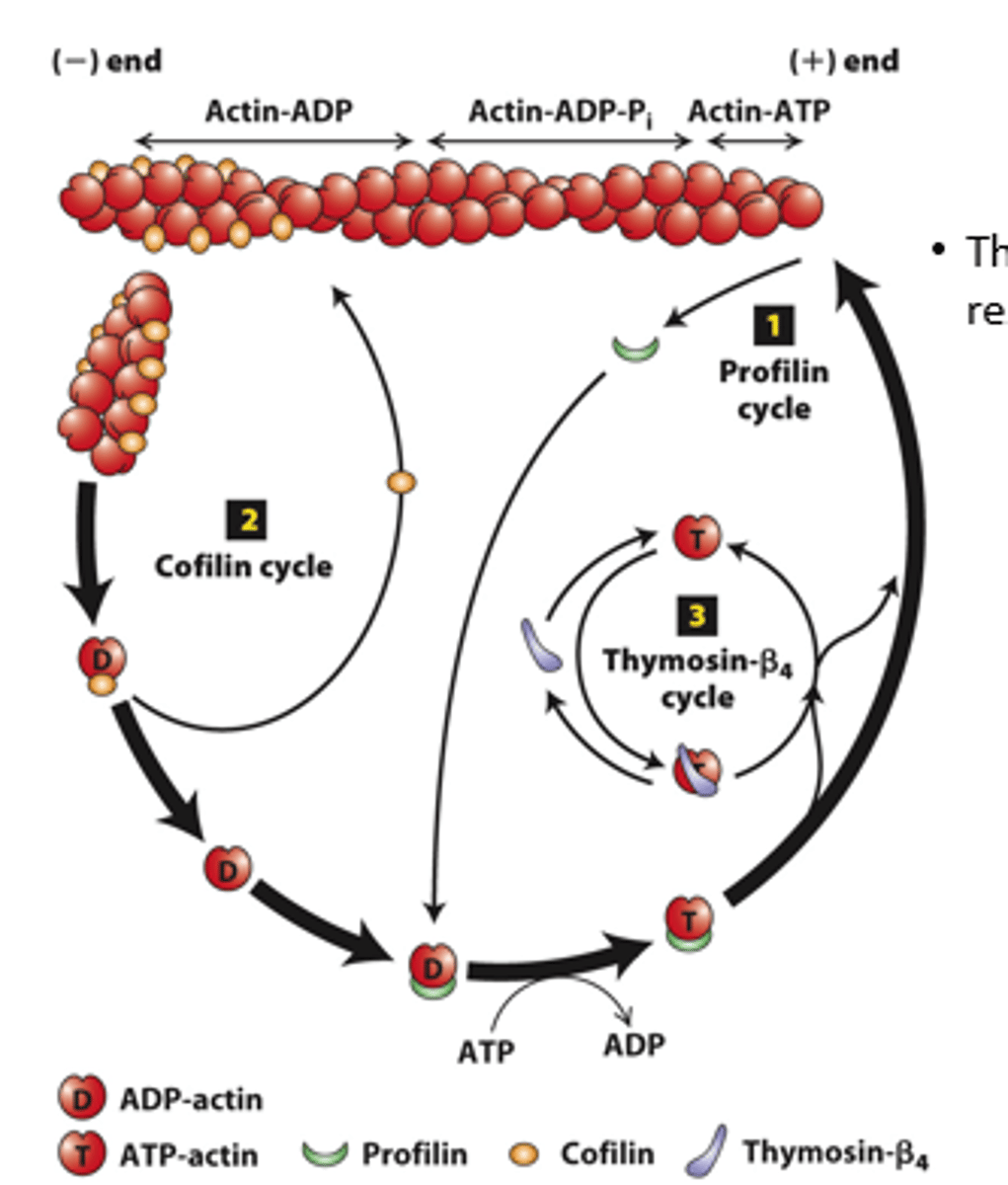
spontaneous
profilin (cycle 1): ATP-G-actin-profilin cannot initiate _______________ F-actin polymerization
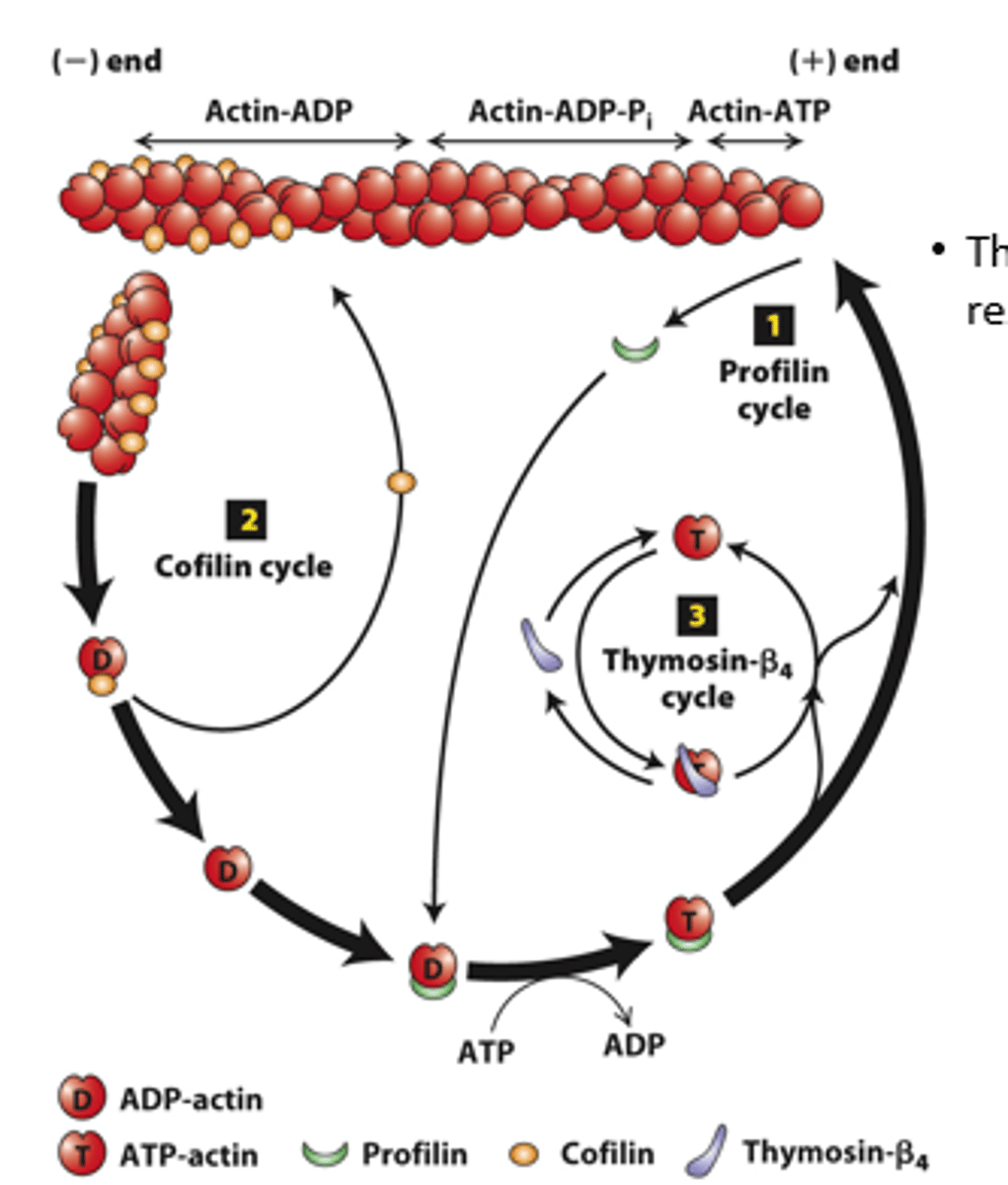
cofilin
Cofilin (cycle 2): ___________ fragments ADP-actin filament regions, enhancing overall depolymerization by making more filament (-) ends
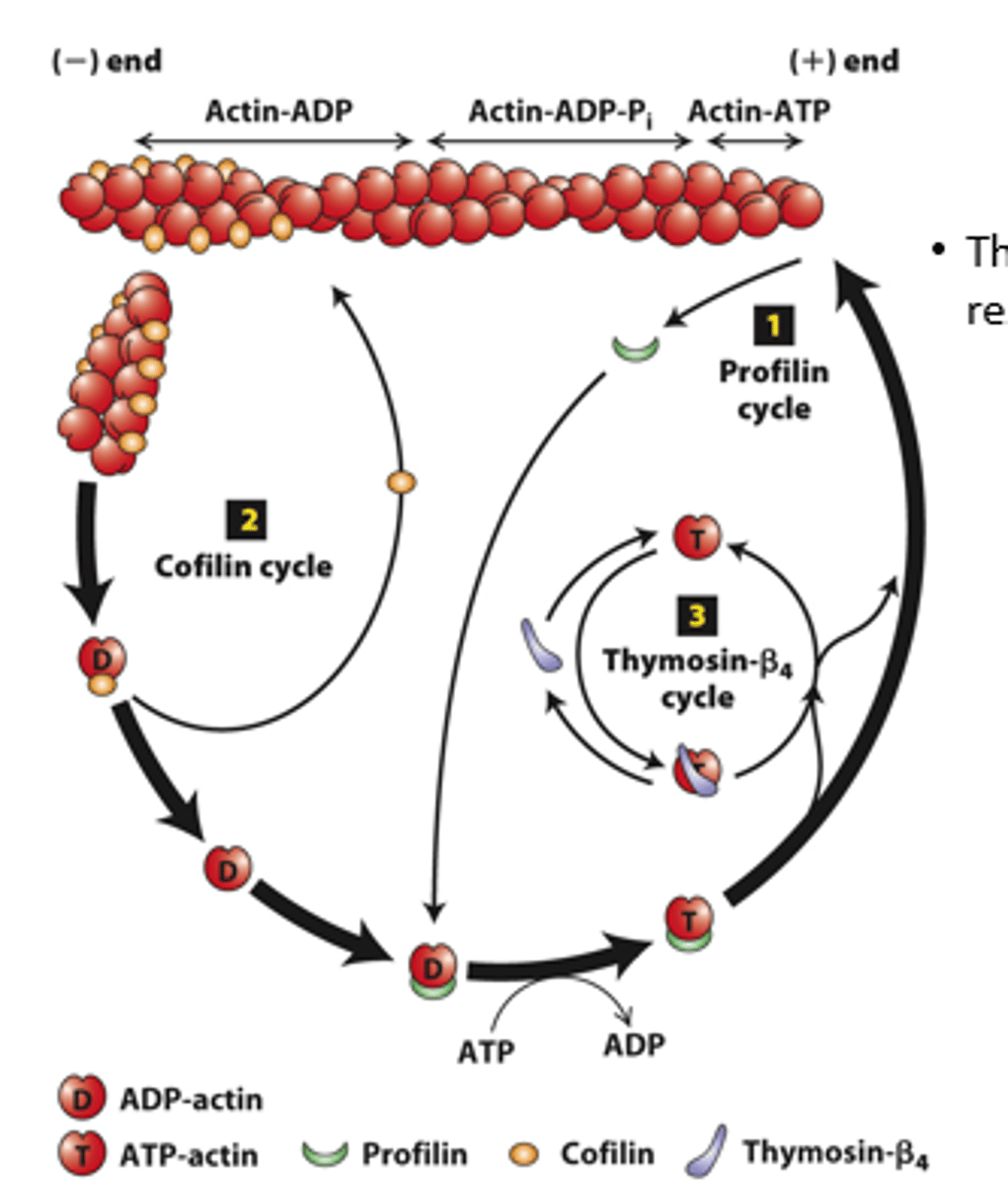
buffered
Thymosin-β4 (cycle 3): provides a ____________ reservoir of ATP-G-actin for polymerization
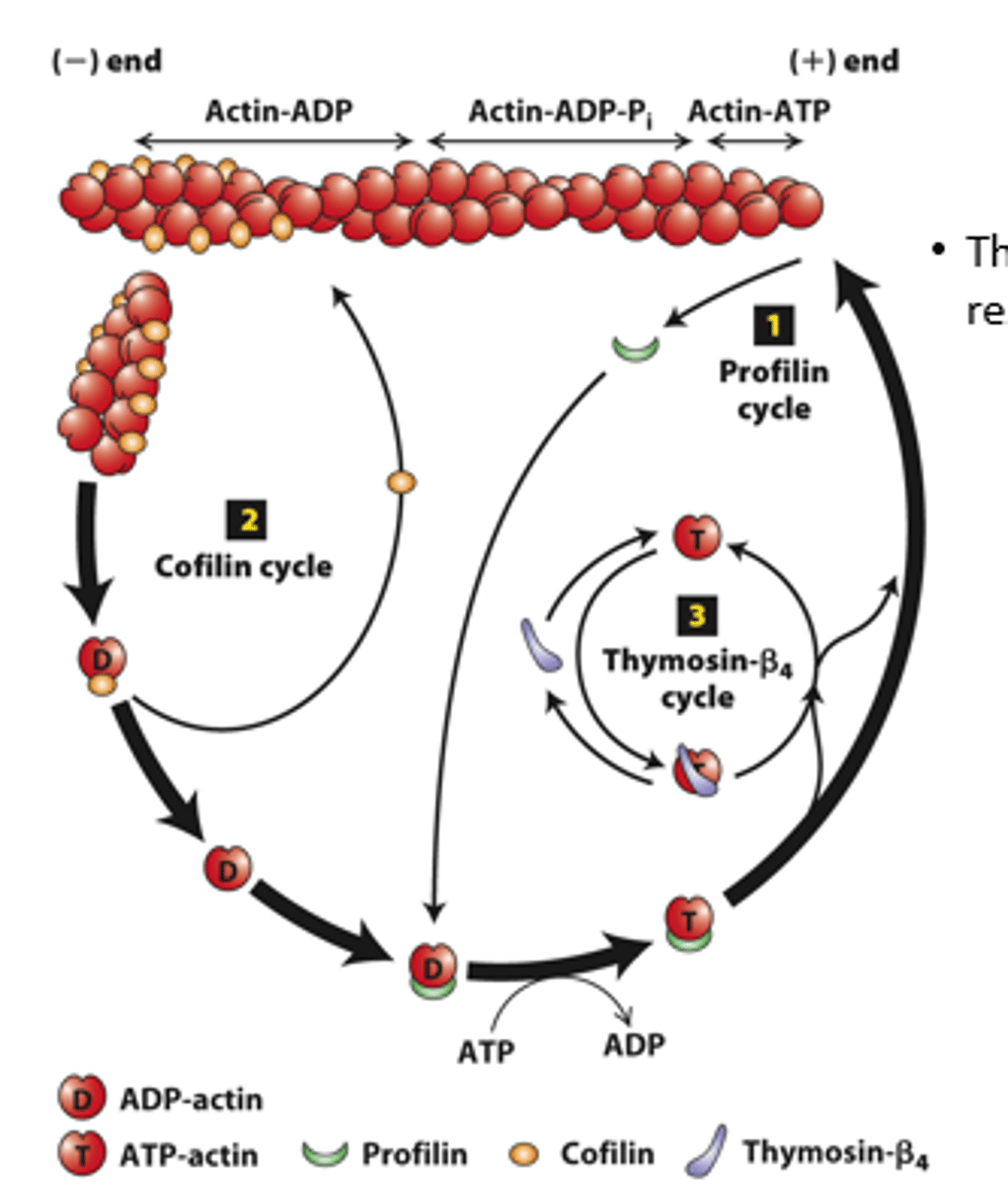
high, low
Thymosin-β4 buffers ATP-G-actin - sequesters G-actin at _______ concentration; releases G-actin at _______ concentration to polymerize
buffer
Thymosin-β4 is an abundant protein in cells and can ____________ a substantial amount of actin in a cell (220 microM of the 550 microM actin in human platelets)
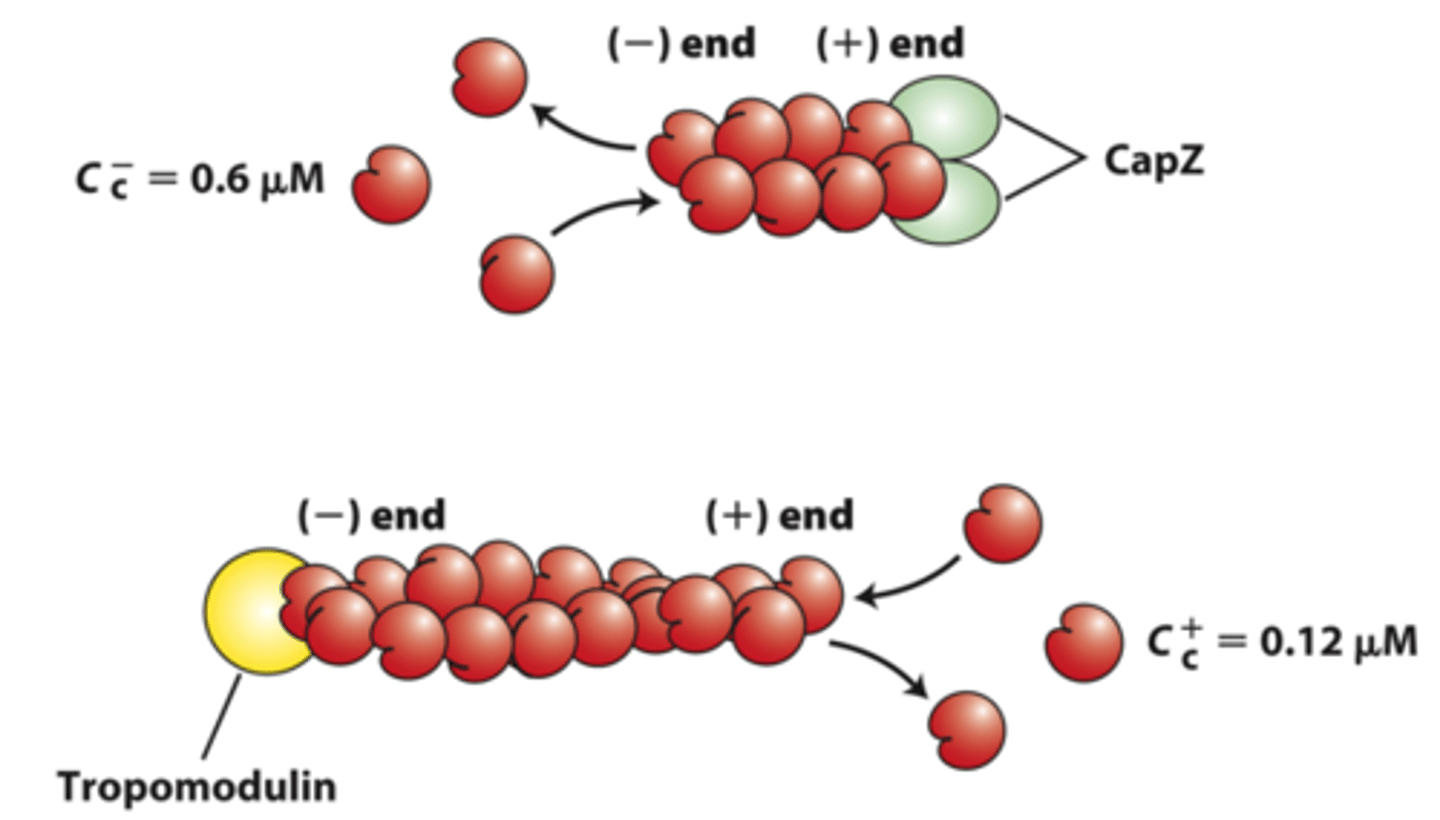
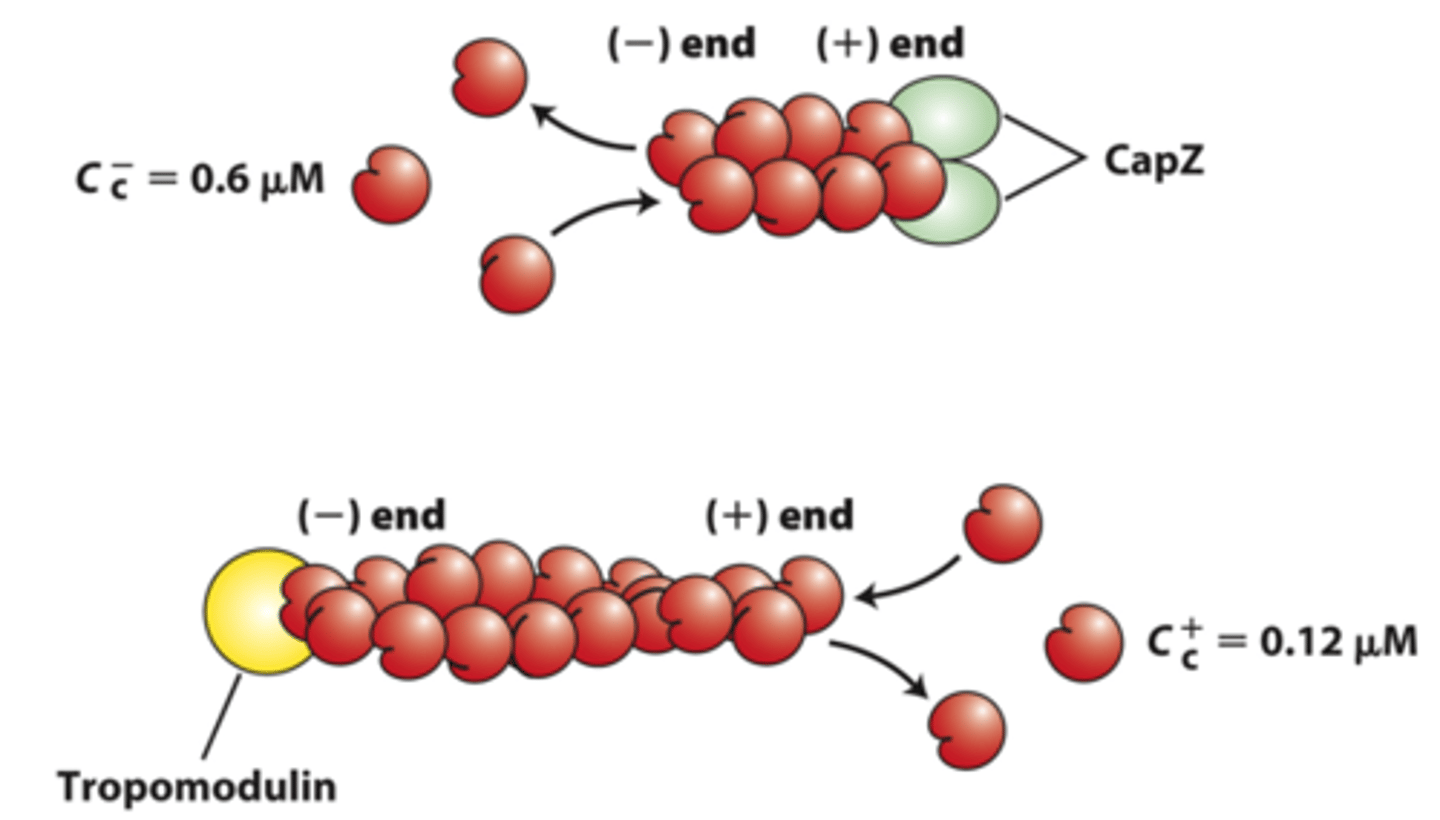
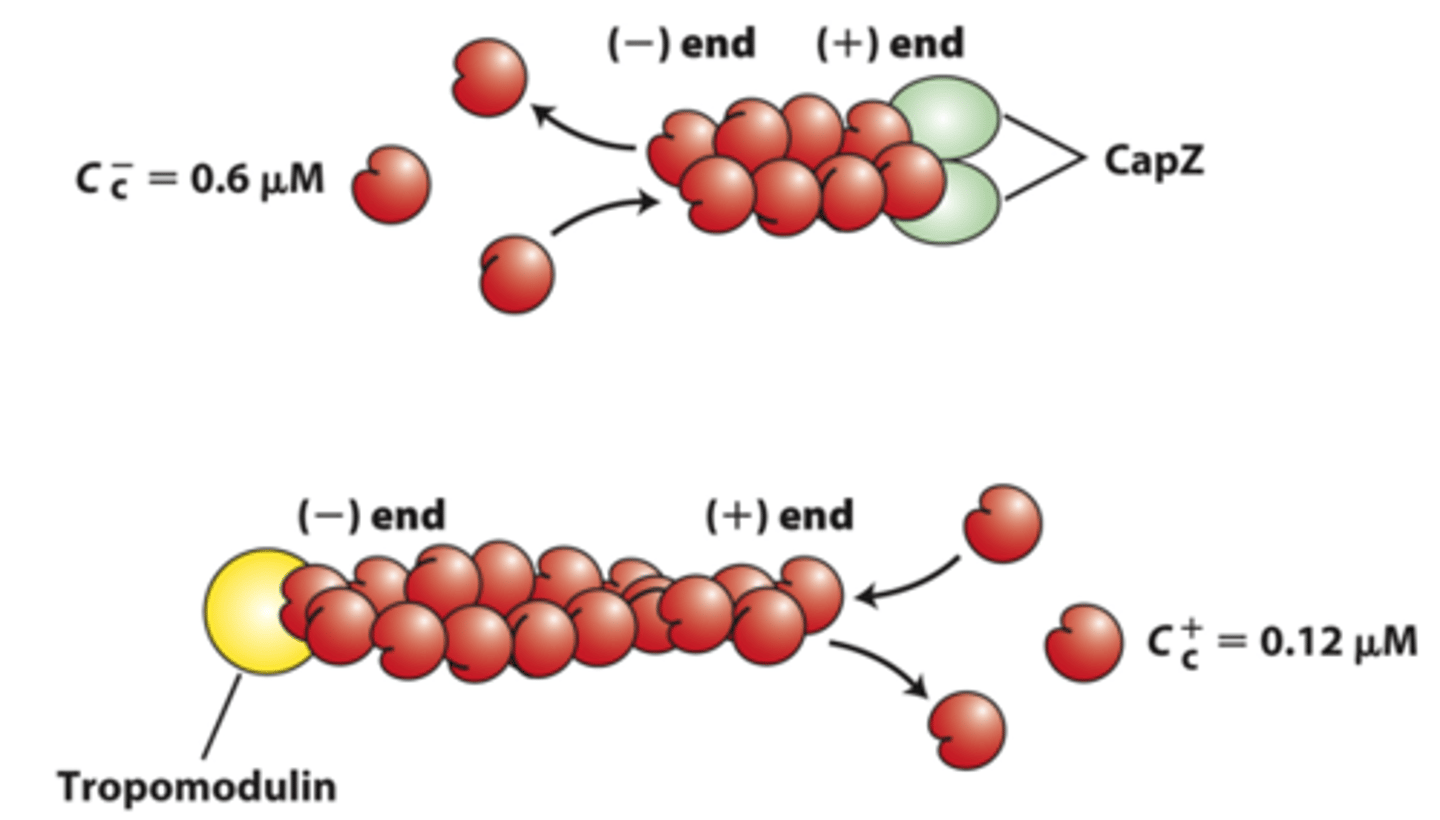
capping
_____________ proteins block assembly and disassembly at filament ends
negative
positive end capping proteins: CapZ limits actin assembly and disassembly dynamics to that at the _____________ end
gelsolin
positive end capping proteins: ____________ severs actin filaments by inserting itself between actin subunits of the helix - blocks the new (+) end. Some gelsolin family members are activated by a rise in Ca2+ concentration
functionally
_______________ different actin-based structures are nucleated by formins and Arp2/3 complexes
tropomodulin
negative end capping protein: ______________ blocks the end where filament disassembly normally occurs, thereby stabilizing the filament
Arp2/3
__________-dependent actin polymerization
pathogenic, endocytic
Arp2/3-dependent actin polymerization: moves ____________ bacteria and _________ vesicles within cells
pushes
Arp2/3-dependent actin polymerization: __________ the leading edge membrane forward in moving cells
toxins
affect the dynamics of actin polymerization
nucleate
Two major classes of actin-nucleating proteins regulated by signaling pathways ___________ actin assembly
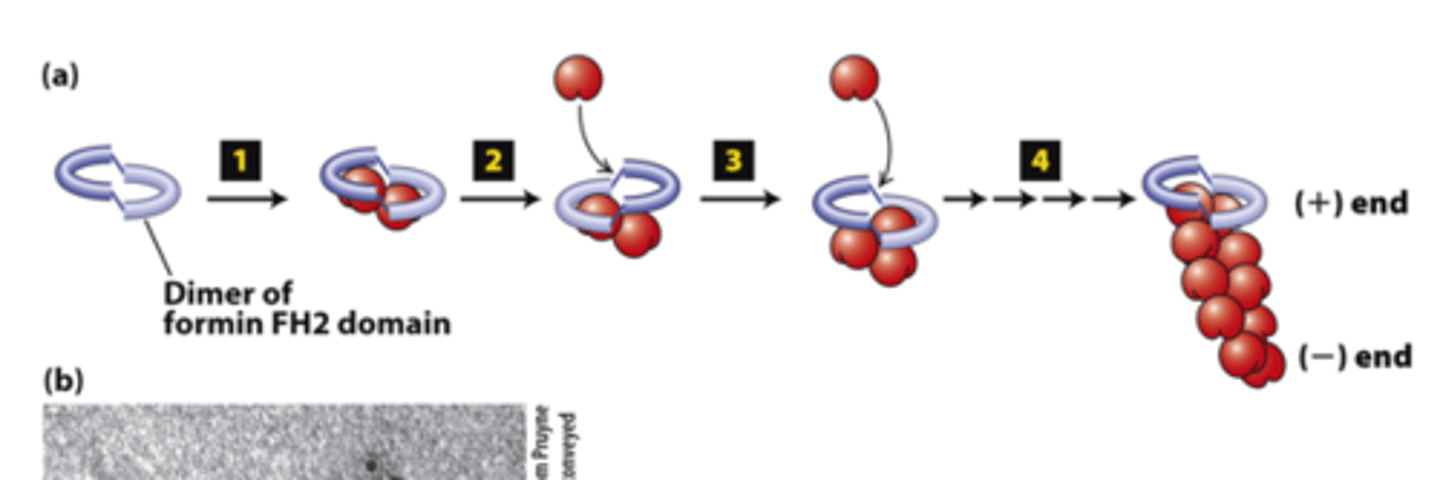
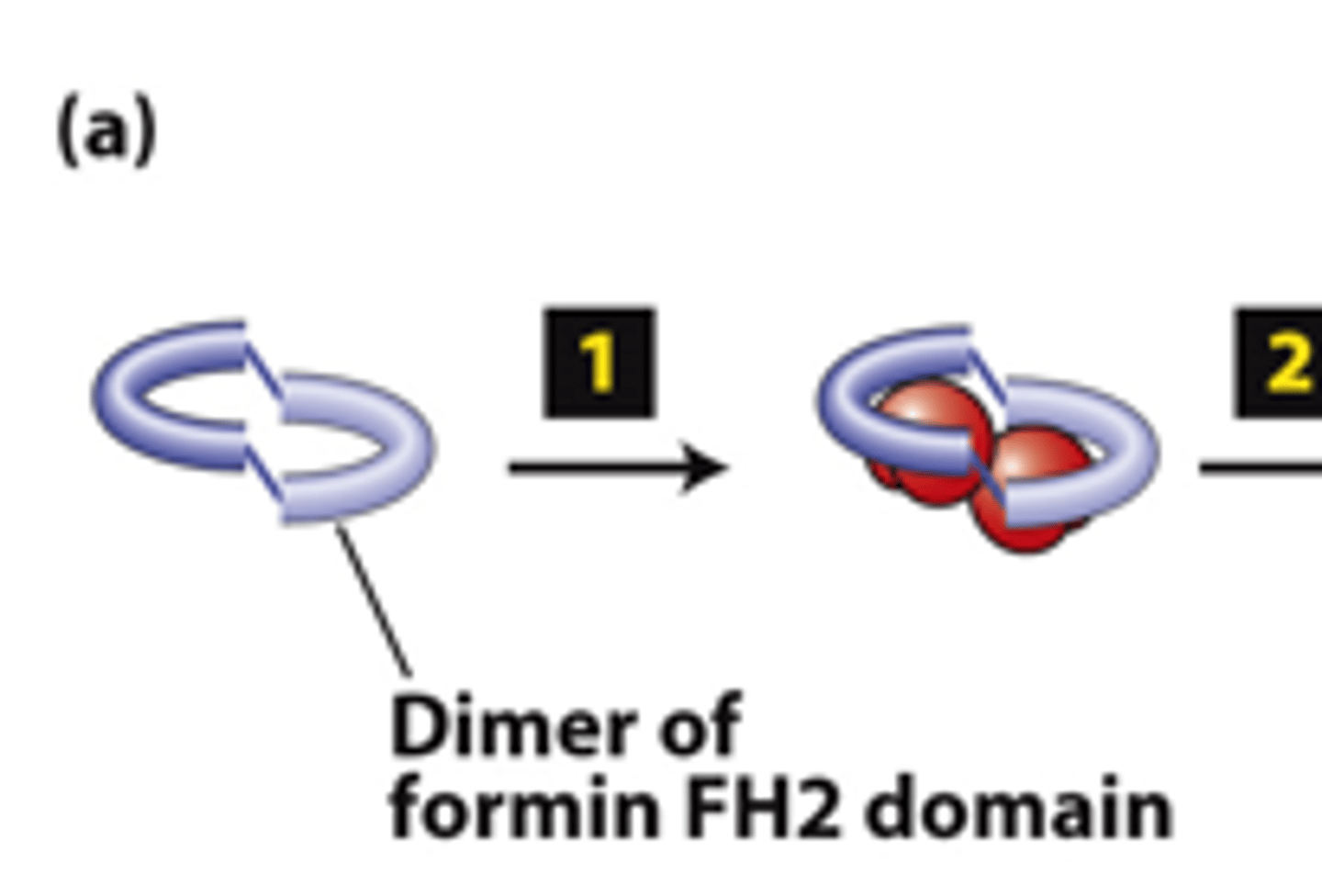
dimer
FH2 domains from two formins form a _________
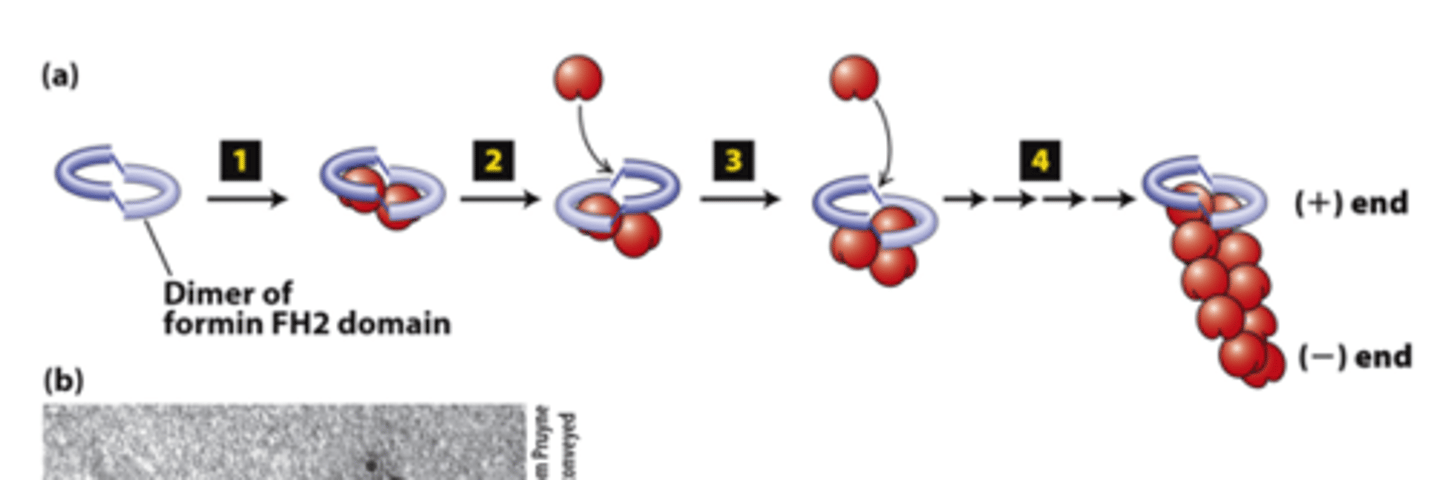
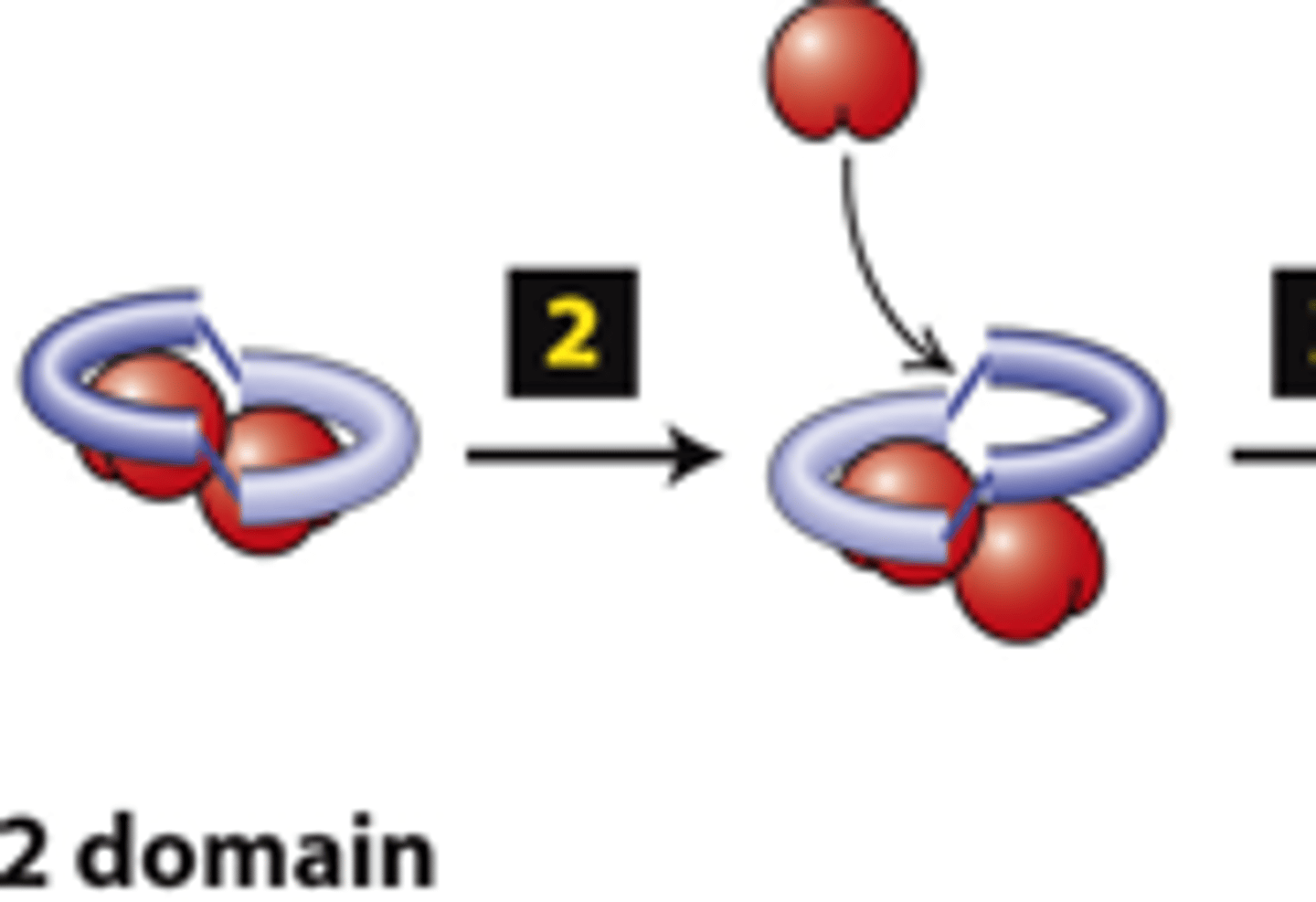
actin
FH2 domains from two forms form a dimer, step 1: The FH2 dimer binds two ________ subunits to nucleate formation of a new filament (bypasses formation of three monomer trimer seed).
positive
FH2 domains from two formins form a dimer, step 2: One FH2 domain rocks up far enough to allow assembly of one actin subunit onto a protofilament ____________ end
protofilament
FH2 domains from two formins form a dimer, step 3: The other FH2 domain rocks up far enough to allow assembly of one actin subunit onto the other ________________ (+) end.
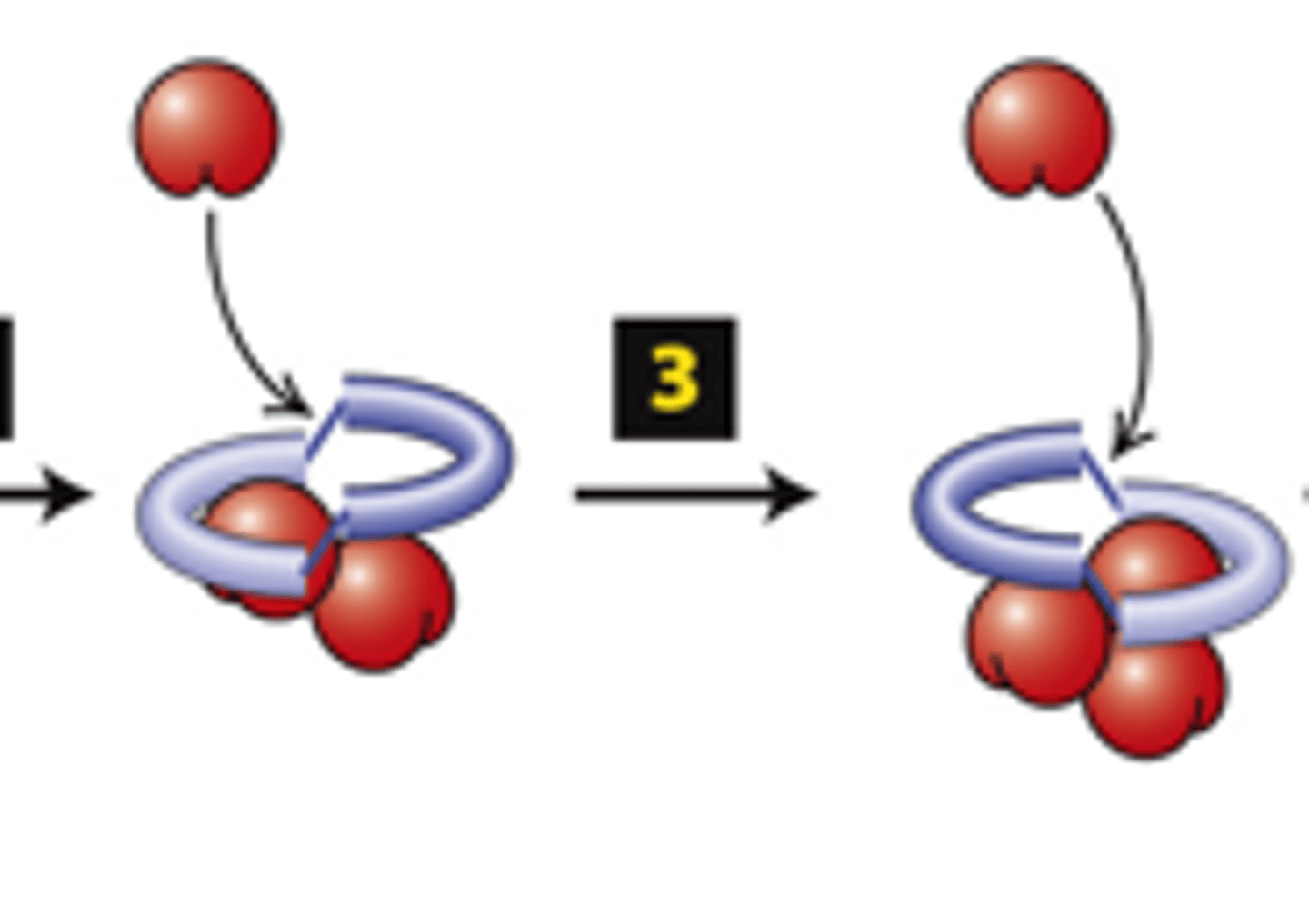
capped
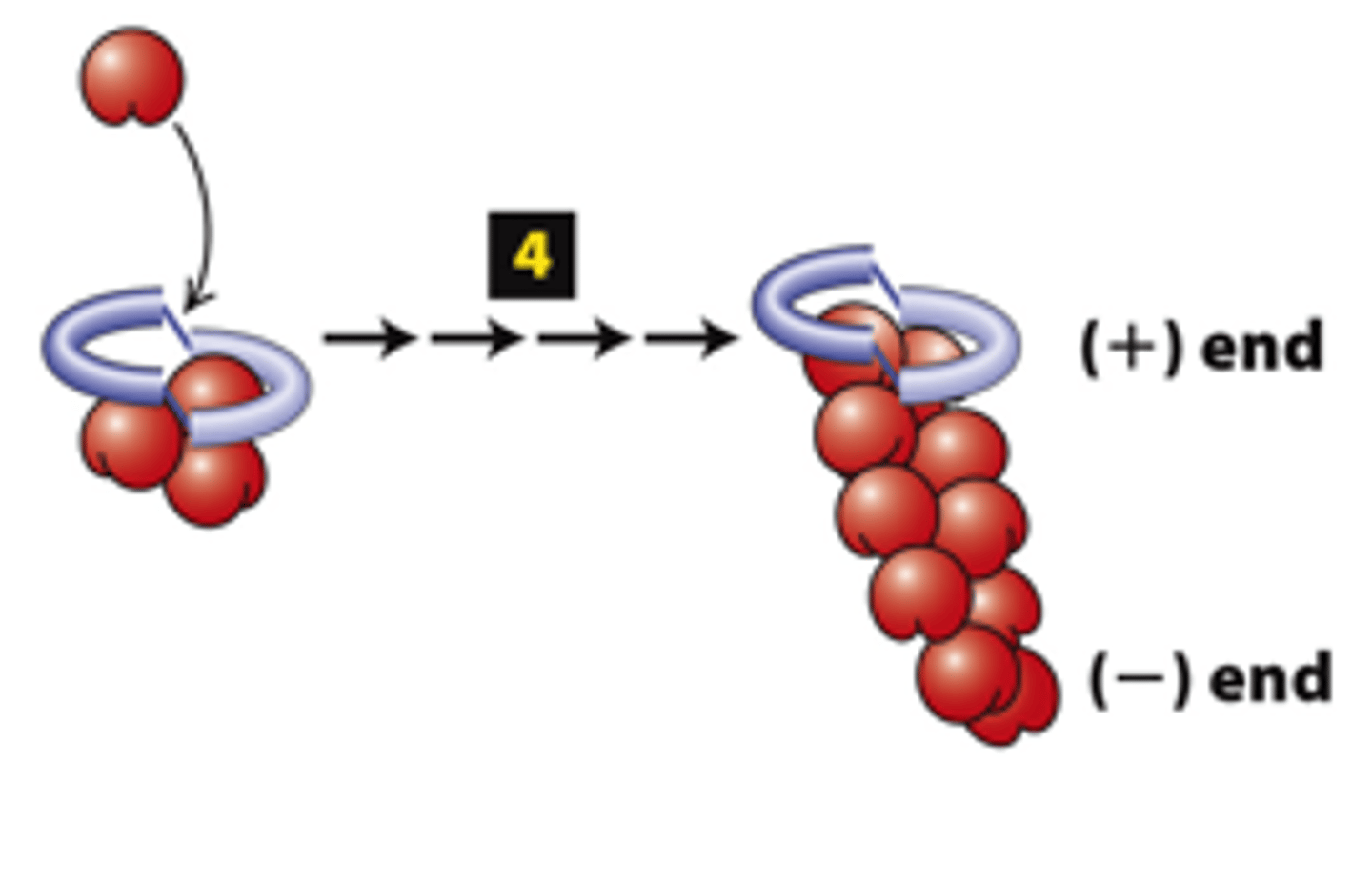
FH2 domains from two formins form a dimer, step 4: The cycle repeats to elongate an unbranched filament.
The FH2 domain protects the (+) end from being immediately ______________ by (-) end capping proteins
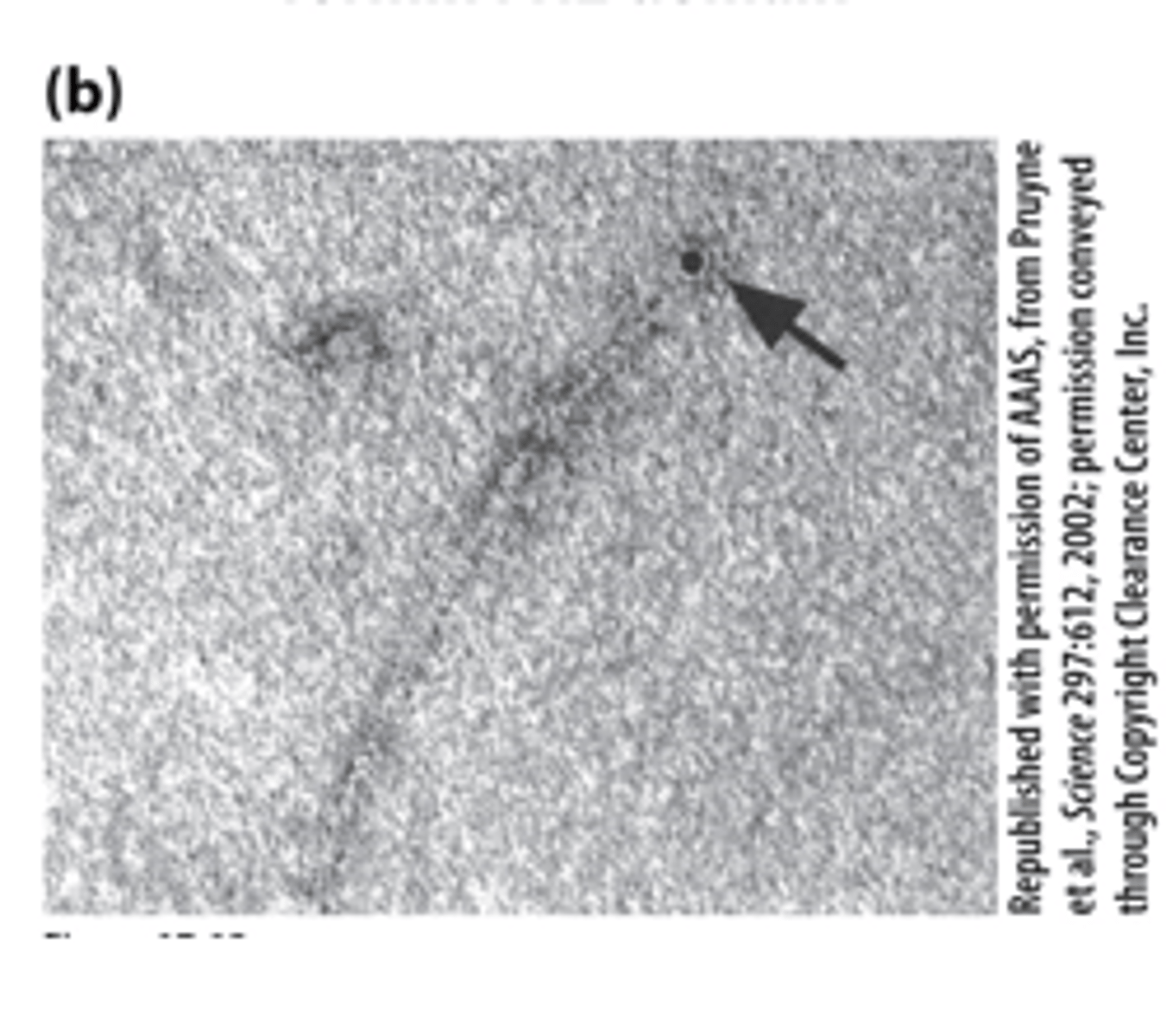
TEM
The FH2 domain of a formin labeled with colloidal gold (black dot) nucleated assembly of an actin filament--_______ of a sample negatively stained with uranyl acetate
intramolecular
regulation of formin activity by an _______________ interaction
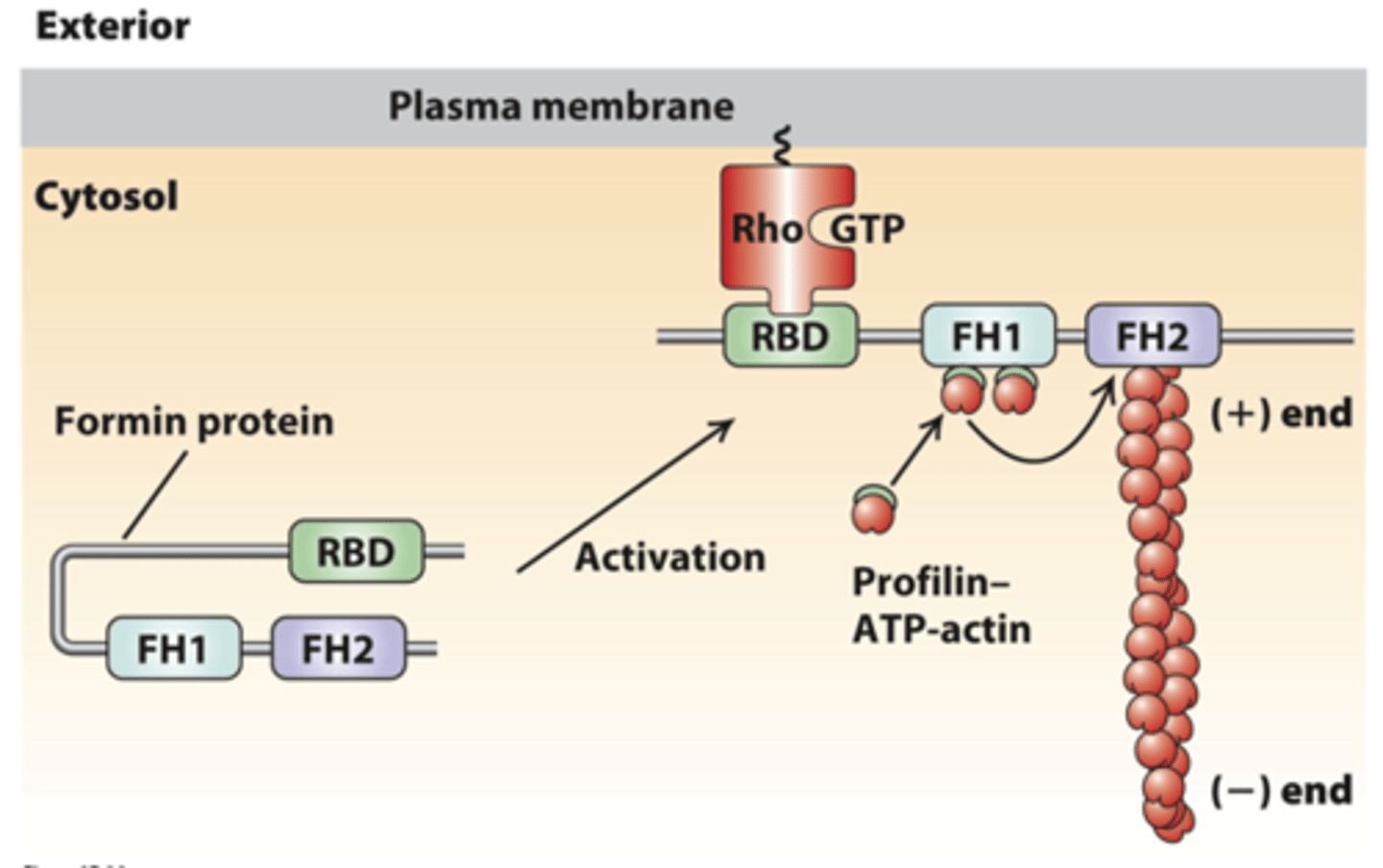
formin
regulation of formin activity by an intramolecular interaction, inactive state: __________ folds back on itself to inhibit FH2 domain activity
Rho
regulation of formin activity by an intramolecular interaction, activation: membrane receptor activation of ________ to the GTP-bound form (Rho-GTP)
Rho binding domain
regulation of formin activity by an intramolecular interaction, activation: Formin _______-____________ _____________ (RBD) binds Rho-GTP, exposing FH2 to dimerize and nucleate a new actin filament
FH1 domain
The proline-rich FH1 domain recruits profilin-ATP-G-actin complexes that can assemble on the growing filament (+) end in the adjacent FH2 domain
formins
___________ assemble long actin filaments in muscle cells, stress fibers, filopodia, and the contractile ring that forms during cytokinesis
Arp2/3
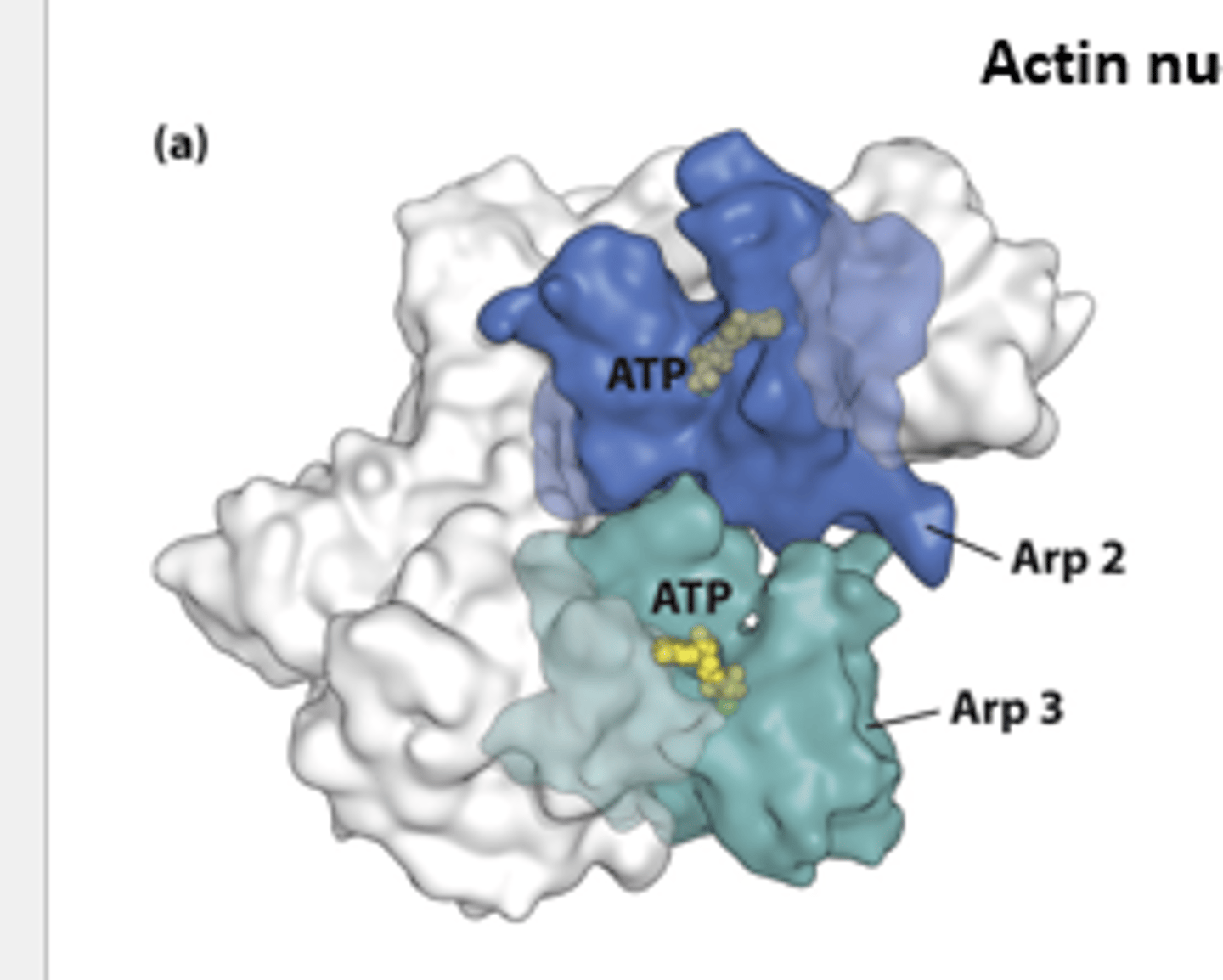
actin nucleation by the ___________ ocmplex
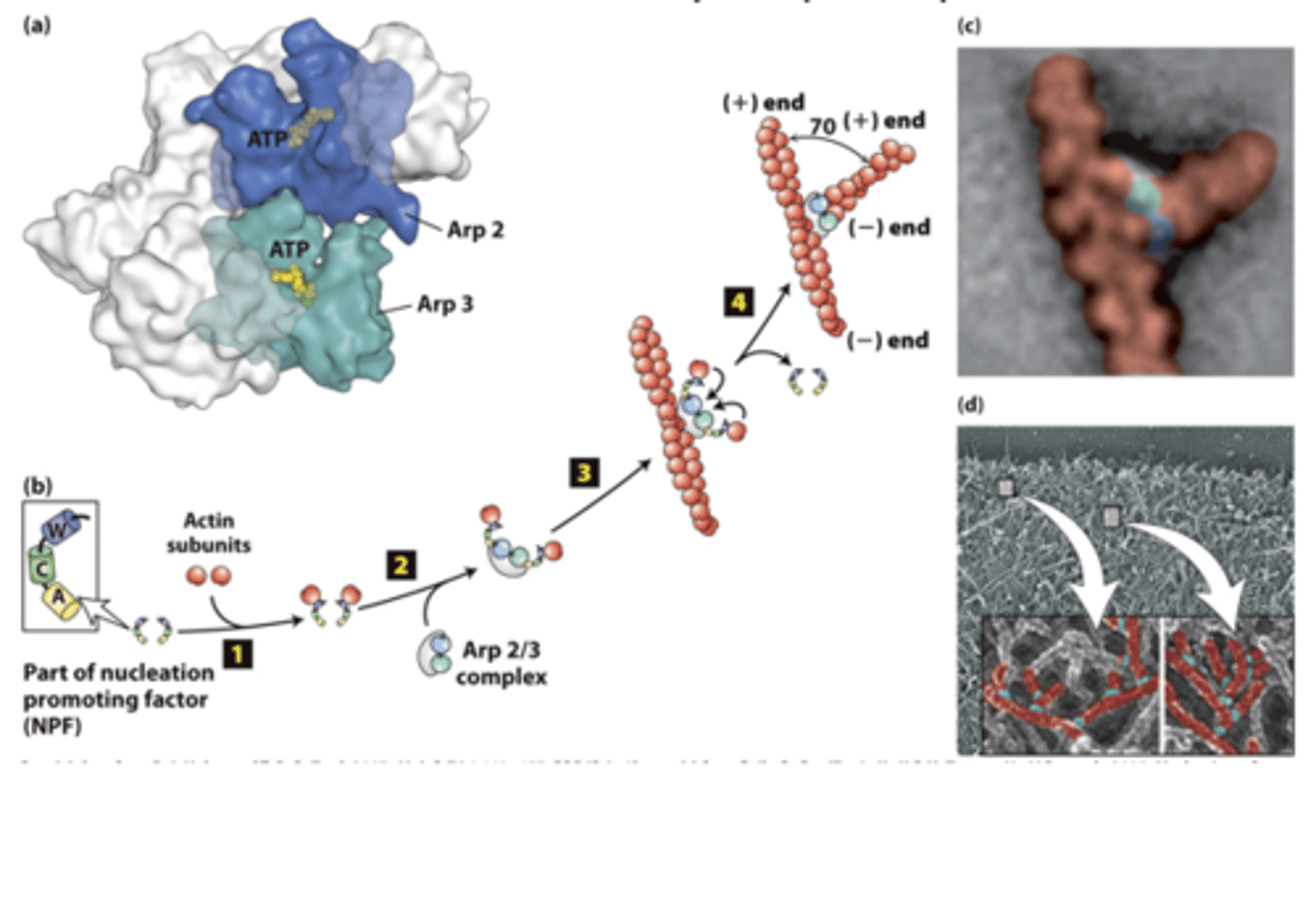
branched
The Arp2/3 complex nucleates __________filament assembly
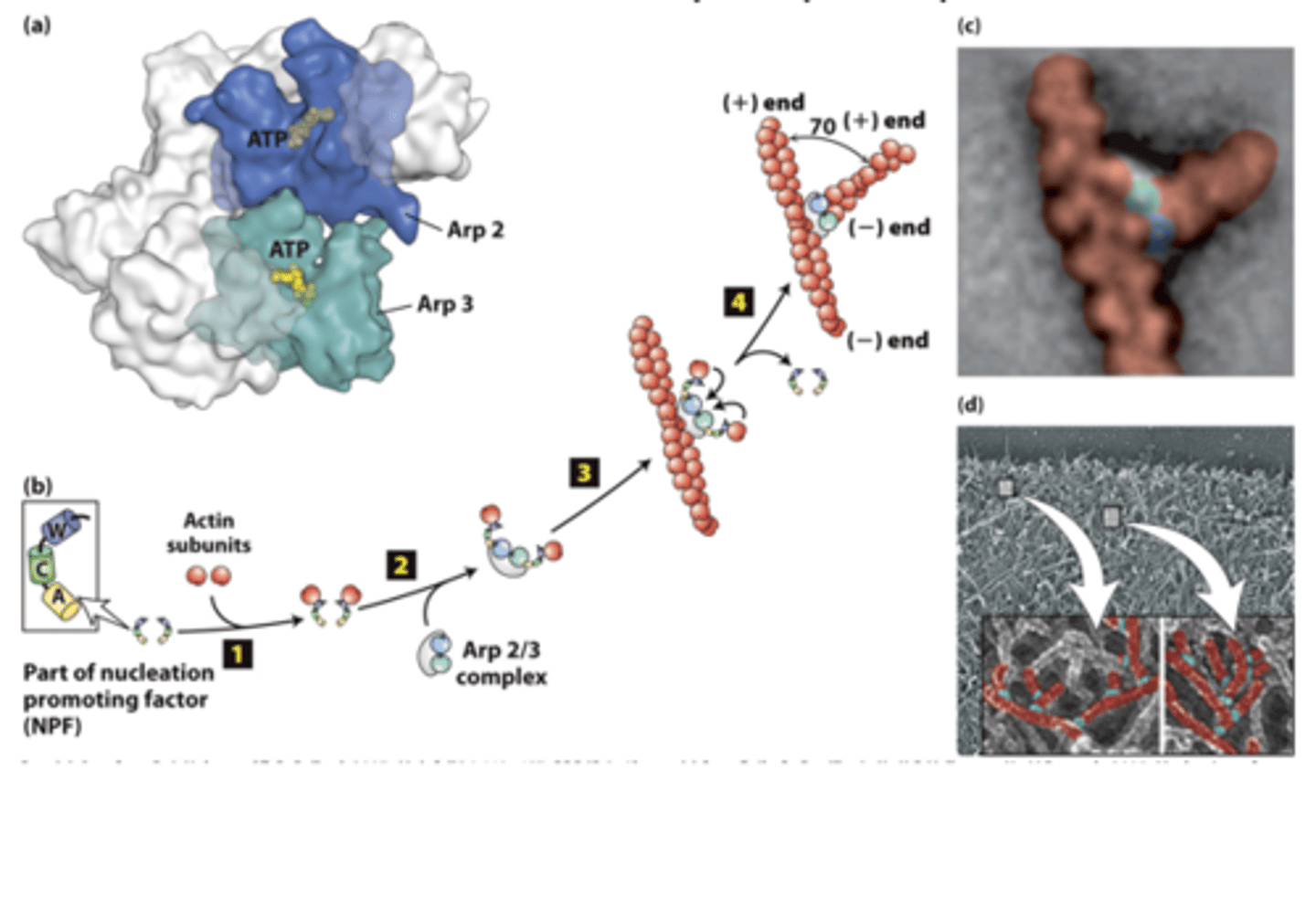
Arp2/3
X-ray crystallographic structure of the __________ complex - composed of actin-related polypeptides Arp2 (blue) and Arp3 (green) and five additional subunits (gray).