Medical Condition and Injury
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
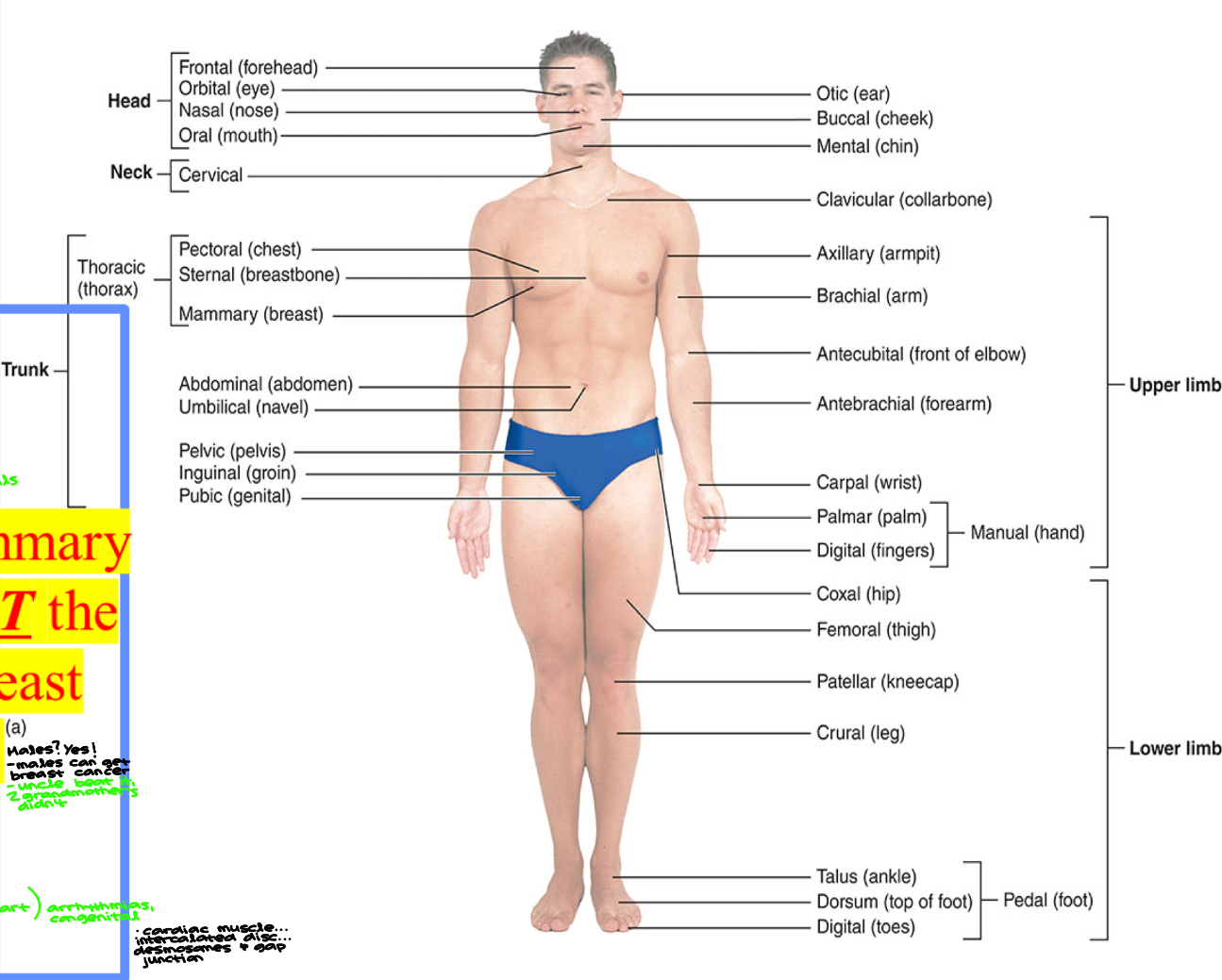
Anatomy has its own vocabulary for surface regions (anterior)
NOTE- Mammary Gland (all mammals) is NOT the same as breast tissue !! Males? Yes !
Males can get breast cancer, uncle beat it… 2 grandmothers didn’t
Adipose tissue around → just primates
Heart disease! #1 in women?
#1 killer in U.S.
Issued w/ heart valves & blood vessels that innervate heart → arrhythmias, congenital
Cardiac muscle… intercalated disc… desmosomes & gap junction
2015
NM hiking trail… foot got hung up & all quad tendons on left side detached
One hip replaced in ‘18, other in ‘19, reconstructed knee
Left knee bucked out at Auburn game going down steps
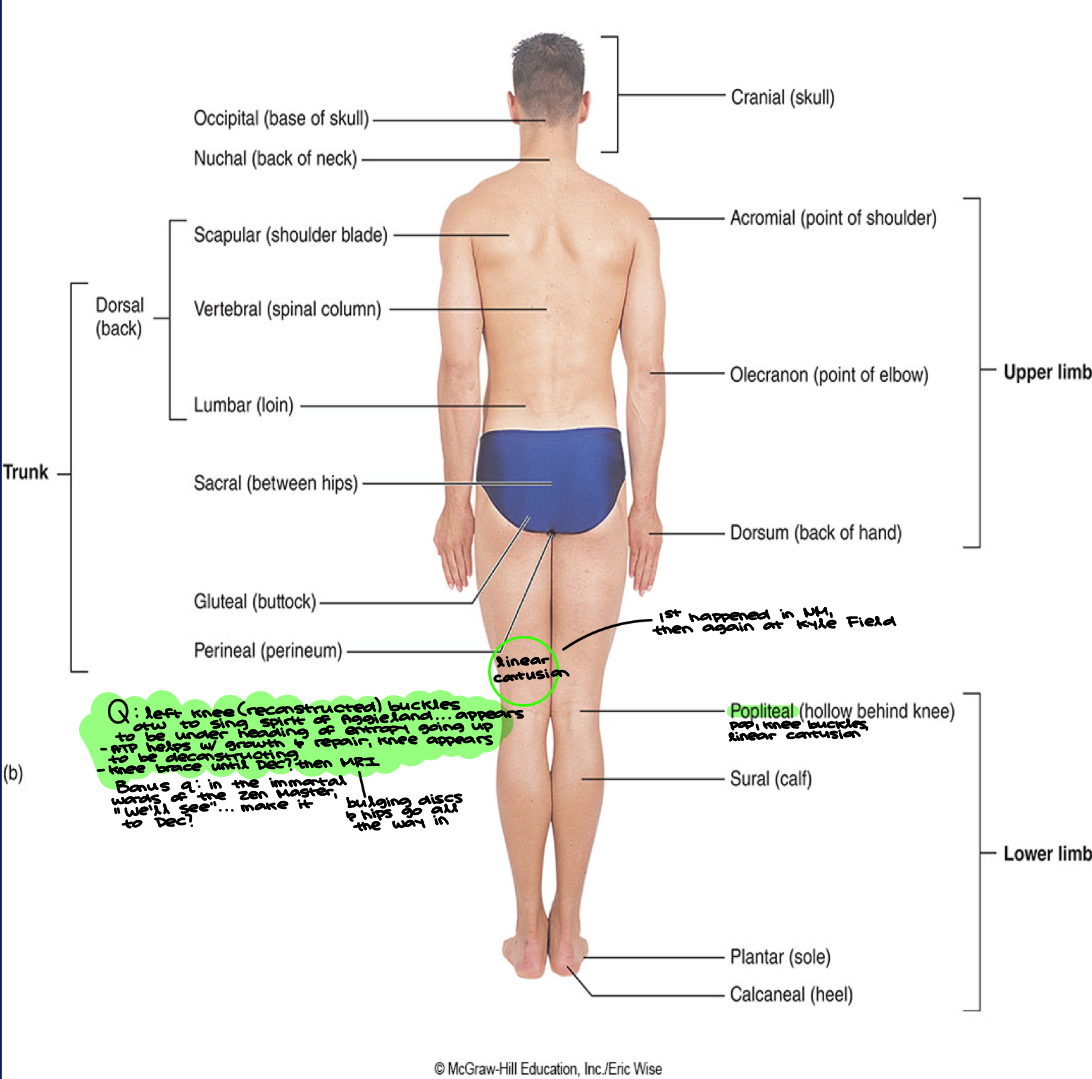
Anatomy has its own vocabulary surface regions- (posterior)
7, 12, 5, 5, & 4 = #’s; MRI?? Yes!
CPL = Aub!
Remember- “cervi” or “cervical” is neck in G/L; cervical vertebrae are in the neck
Reminder: know vertebrae types and numbers
Cervix is a neck-like structure in female reproductive tract
Question on Exam
Left knee (reconstructed) buckles on the way to sing spirit of Aggieland… appears to be under heading of entropy going up
ATP helps w/ growth and repair, knee appears to be deconstructing
Knee brace until Dec? then MRI (bulging discs and hips go all the way in)
Linear contusion in popliteal area (hollow behind knee)… pop, knee buckles, linear contusion
1st happened in NM, then again at Kyle Field
Bonus Question
In the immortal words of the zen master, “we'll see”… make it to Dec?
Review
5 bone remodeling hormones, 5 epiphyseal growth plate zones
Osteogenesis Imperfecta & **Osteoporosis; 99% of all Ca++ in bones hydroxyapatite. **Menopause **E2 & P4 (osteoblast stim!) are way down = 2 of 5 hormones (remodeling)
E2: estrogen, P4: progesterone… 2 of 5 hormones, stimulate osteoblasts
Women go through menopause and get osteoporosis way more
-osis/-otic: condition of, por: hole, osteo: bone, osteoporosis: condition of little holes in bone
Sprains vs strains ***BACK for a later exam!
**Arthritis, **inflammation and **NSAIDs (and their effects on enzymes)** Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, Exs: Ibuprofen (Advil)- Comp Inh. of COX (cyclooxygenase) = **antipyretics (fever down)
Inflammation is a defense… fine until it becomes chemically inflammed
Inflammation 101: 1) Get to it 2) Remove it 3) Repair it
Supposed to feel pain associated w/ pressure
Antipyretics is a defense, keeps fever down… pyr: heat
(Review)- Last but NOT least, our defenses can paradoxically lead to physiological conditions becoming worse. GUESS- Vomiting & Diarrhea (defenses)… ***dehydration = (EI)
dehydration leads to electrolyte imbalance
Dehydration continued
Water has a high specific heat which means you need a lot of energy into system to change its temp.
need to be hydrated to regulate temp., dehydration an issue
easier to stay cool when hyperhydrated
(OI) = Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Brittle Bone Disease):
Symptoms include: whites of the **eye (sclera)** are ***blue instead (5), short stature, loose joints, hearing loss, breathing problems and problems with the teeth. Papillary reflexes (nervous sys.); bloodshot eyes; Horizontal gaze nystagmus = Field sobriety test (not fluid movement of eye = “tick”)
2013: Dad yellow/green in sclera → scan → grapefruit sized tumor on liver… early detection is key
**eye (sclera)** are ***blue instead (5)
shine a light in someone’s eyes → dilate less light → constrict
bloodshot lower eyelid… quick & simple diagnostic
spin them around, stop, will eyes only follow tip of pin? if impaired, eyes will tick instead of eyes moving back & forth
Cause: Lack of collagen type I (triple helix, there are **28 types of collagen and collagen has at least one segment that is a triple helix of its own collagen fibril components)
Genetics- In 90% of cases, the **COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes and hereditary in an **autosomal (non-sex chromosomes, 1-22) *dominant**; Allele does **NOT mean fitness of individual) manner. **Note- There are 19 different genes that are associated with at least **21 documented types of OI
does not add to sustainability
recessive does not code for functional… does missense or nonsense
1 gene, 2 alleles, 3 genotypes → basis for Hardy-Weinburg
dominant, recessive, hetero
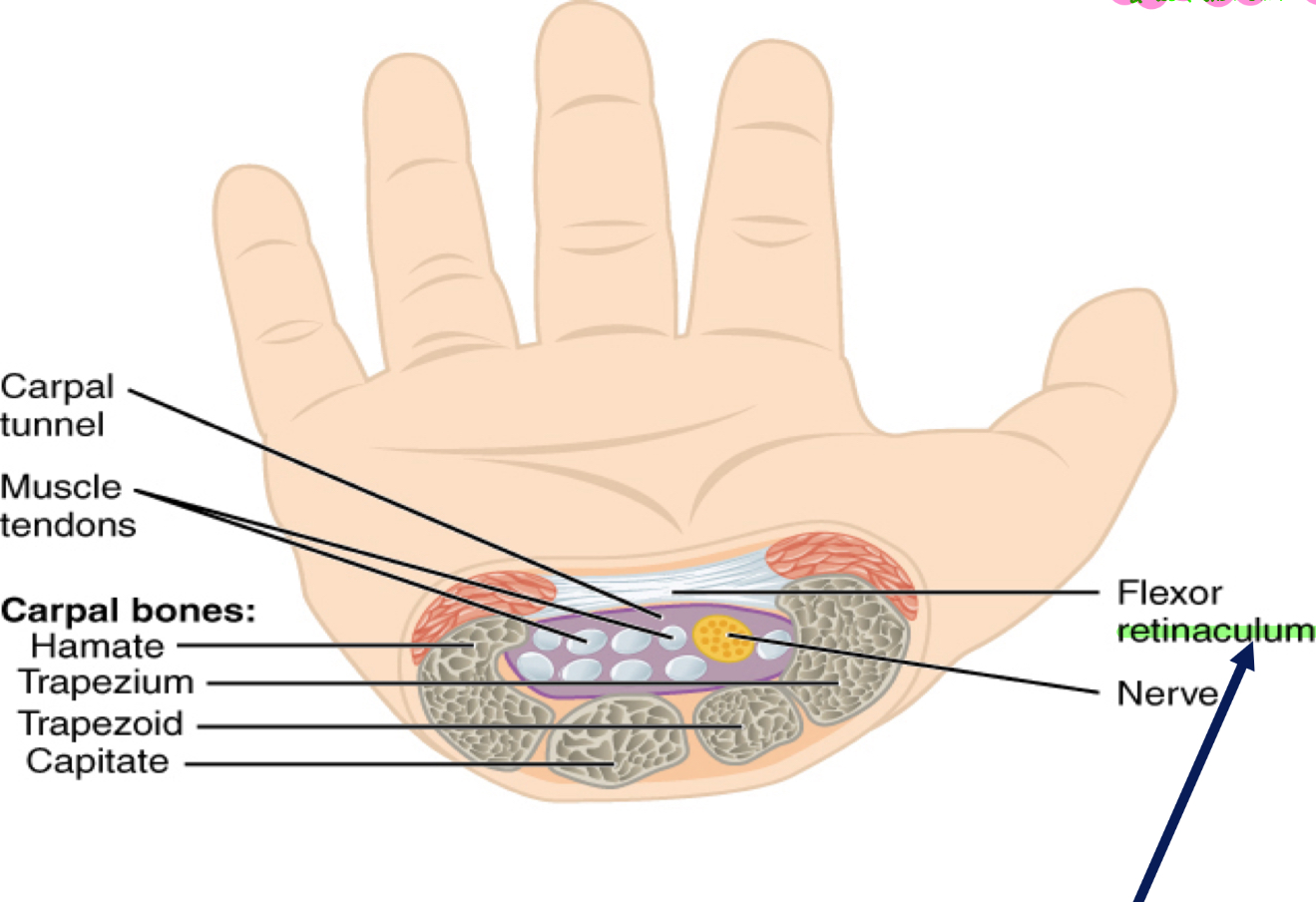
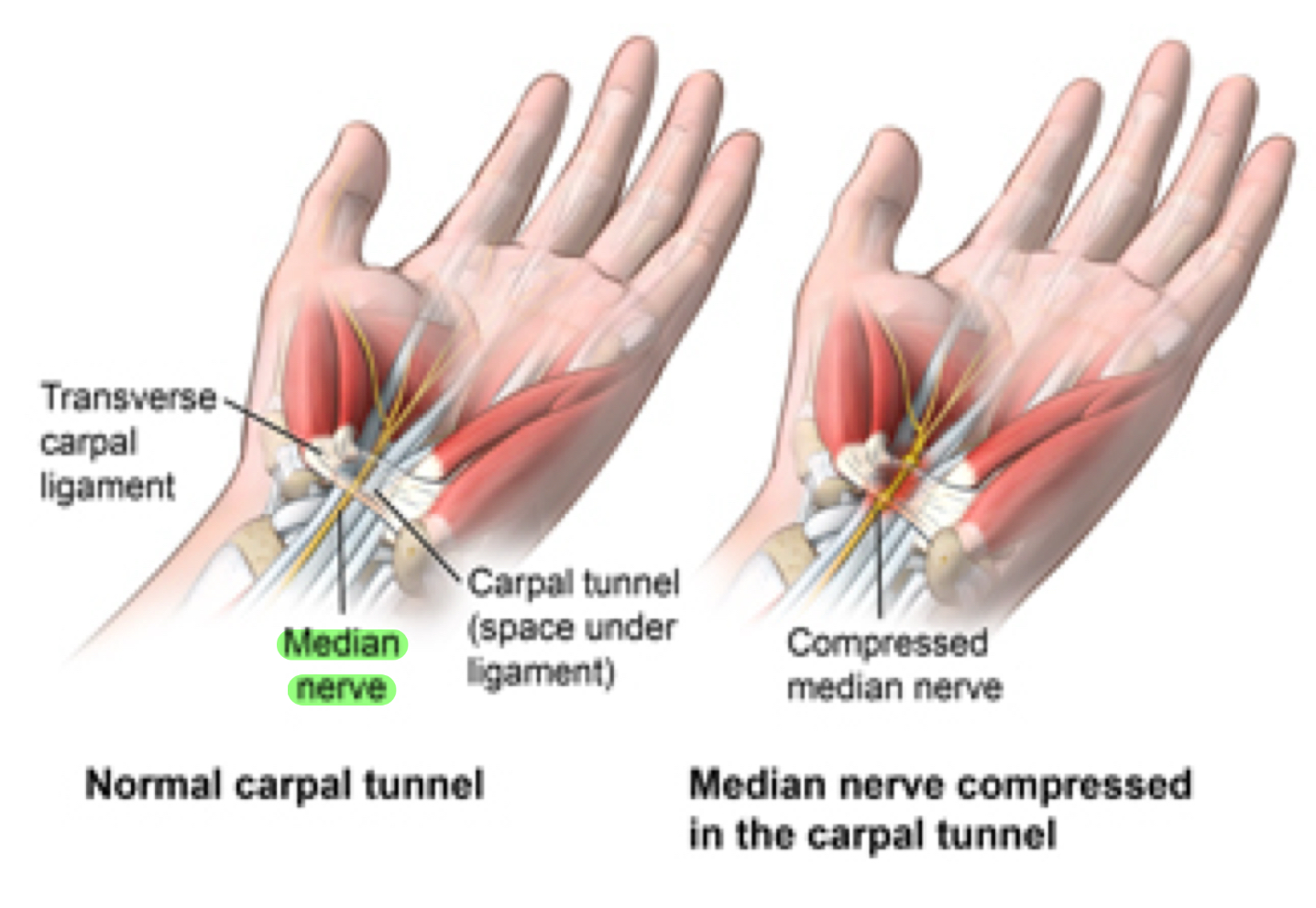
Carpal Tunnel (anatomical ref.):
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by pressure on the ****median nerve***. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway surrounded by bones and ligaments on the palm side of the hand. When the median nerve is compressed, symptoms can include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and arm. ***WRIST!!!- Flex, extend, **abduct & **adduct… 1 letter makes a huge difference
The anatomy of the wrist, health problems and possibly repetitive hand motions can contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome
Proper treatment usually relives tingling and numbness and restores wrist and hand function
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (will happen w/ excessive use of mouse)
CPL had it and the chiropractor fixed it
Put several electrodes on forearm to highest setting
Muscles contract… was trying to fatigue muscles of forearm and put less pressure on MEDIAN nerve
When fatigue was over, was trying to maybe get some of those muscles to rearrange themselves in a way that didn’t continue to put pressure on nerve
**Retinaculum = Band of thickened deep fascia usually around tendons
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 2
“Pop/Crack a joint = SOUND? = Gases escaping the joint
Left knee buckling is not the same kind of popping
Tommy John Surgery
Tommy John Surgery (sports that involve throwing!!):
**Ulnar collateral ligament** (replaced w/ a tendon not a ligament, overhand pitching, major surgery takes time to heal, can come back stronger) reconstruction, colloquially known as Tommy John surgery** (TJS), is a surgical graft procedure where the ulnar collateral ligament in the medial elbow is replaced with either a ******tendon** from (1) elsewhere in the patient’s body, OR with one (2) from a deceased donor. The procedure is common among collegiate and professional athletes in several sports, particularly baseball. **Aponeurosis = takes the place of a tendon (pearly white in color)
The ulnar collateral ligament **(UCL) can become stretched, frayed or torn through the repetitive stress of the throwing motion. The risk of injury to the UCL is believed to be extremely high, as the amount of stress through the structure approached its ultimate tensile strength during a hard throw
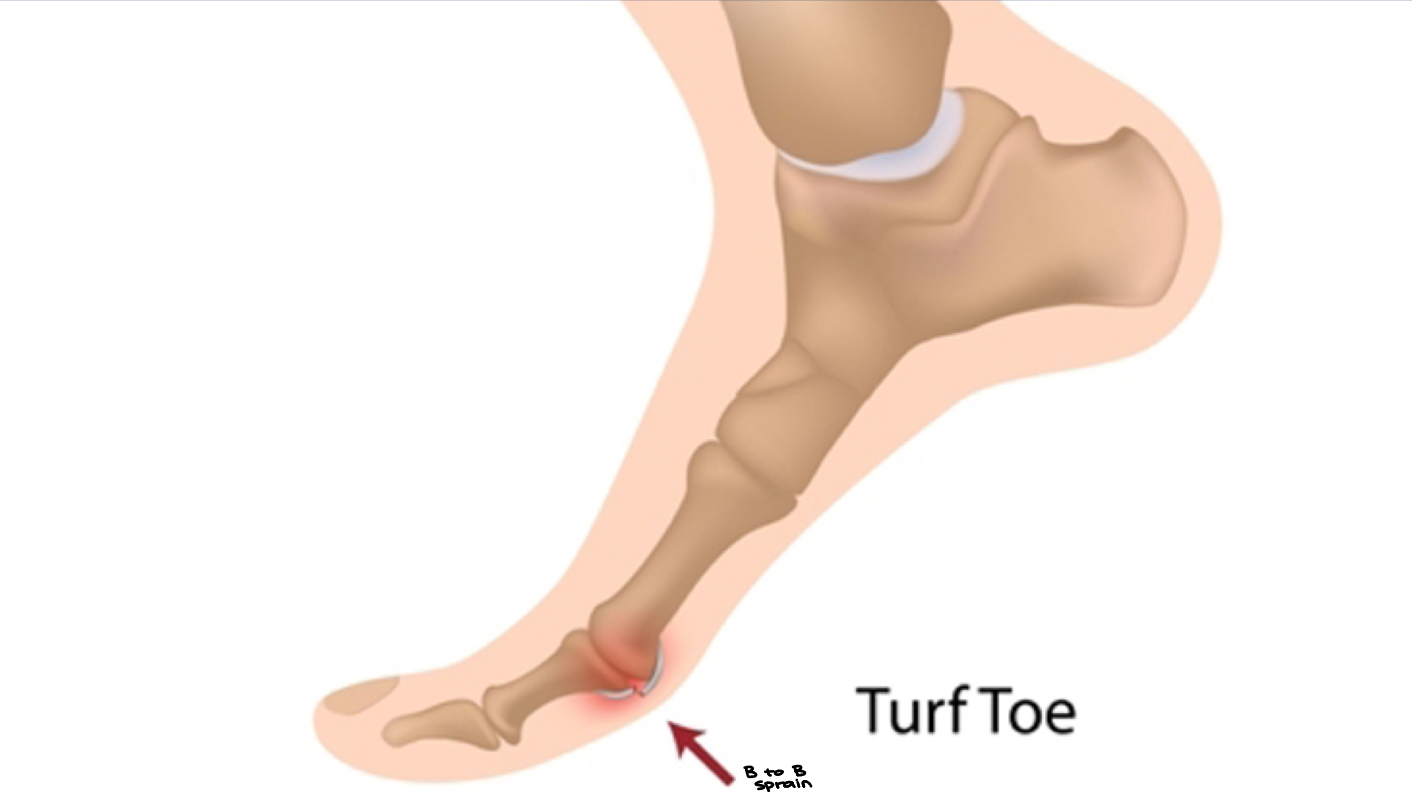
Turf Toe = Hallux (thumb is pollux)
Turf toe:
A turf toe injury refers to a ligament sprain of the big toe joint that occurs on turf surfaces. This may cause tenderness and swelling around the big toe joint
Turf toe injuries occur when the big toe joint bends beyond its normal range of motion, thus spraining the ligaments that support the joint. If the big toe continues to bend uninterruptedly, this injury can become far more severe in nature
The term turf toe was first coined by Bowers and Martin after they noticed and increase in **ligament sprains (should there be a massive inflammation of the distal segment of the hallux) OR a dislocation of the big toe joint amongst college football players following the installation of an artificial turf at West Virginia University
The authors stated that a combination of flexible football shows and hard artificial surfaces increased the risk of turf toe injury
in 1996 switched over to grass… helps w/ ACL, MCL, etc.
Turf Toe 2
Swelling → pressure → pain
5 signs of inflammation! Pressure is NOT one = PAIN!! Pharm & pain & vet school! Kill most of the pain but NOT all
Pain is an evolutionary significant mechanism to tell vertebrate you are wounded so we can repair it
Animals: difference w/ regards to pharmacology associated w/ pain
Question: joint is a condyloid joint, it can flex, extend, aDuct, & aBduct
Parity… supinator & pronator teres
A Separated Shoulder vs a Dislocated Shoulder
A **separated shoulder, also known as **acromioclavicular joint injury is a common injury to the **AC joint. The AC joint is located at the outer end of the clavicle (“cleido”) where it attaches to the acromion of the scapula
clavicle is the most commonly broken bone in human body
dad went hunting, went off road, broke clavicle, never got it fixed b/c of orthopedic surgeon
next year he breaks ankle while filling a feeder… wet, fell on rock wrong → got it fixed but kept screws in
**A dislocated shoulder is trauma to the **GH joint**- Glenohumeral Joint = humerus and glenoid fossa
Symptoms include non-radiating pain which may make it difficult to move the shoulder
The presence of swelling or Contusion = **bruising (damaged blood vessel… RBCs being broken down… Fe2+ (in hemoglobin) must be dealt with) and a deformity in the shoulder is also common depending on how severe the dislocation is. Ref: color change
will change color b/c of repairing of blood vessels and b/c iron is being dealt w/, can’t let it float around hazardly
Question on Exam… contusions
CPL walking down front row & left knee buckles, contusion in popliteal area (linear), needs MRI (review MRI from exam 1)
bruises change color… iron being broken down
Have to repair damaged blood vessels
Iron is reactive, can’t let it go all over the place
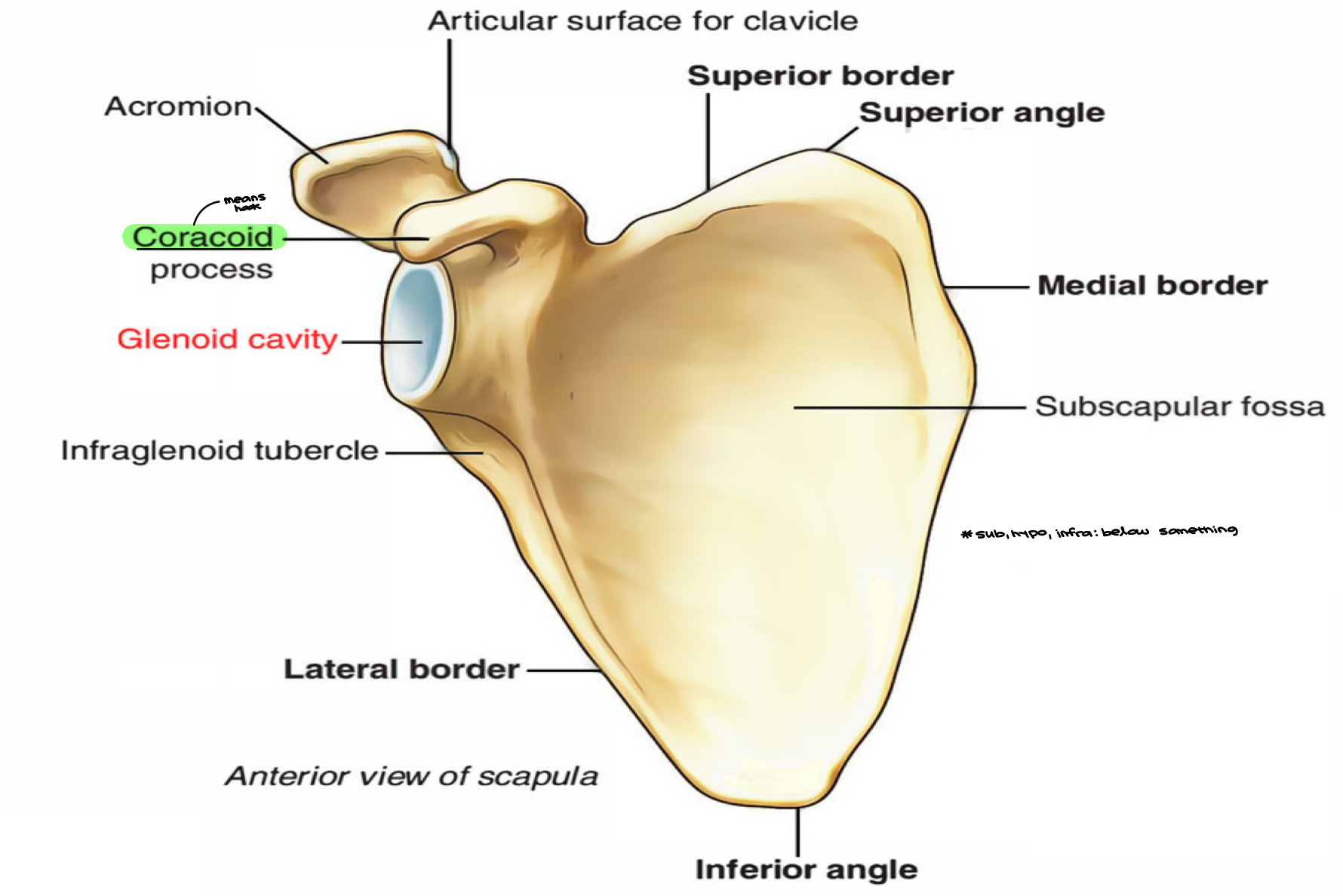
Coracoid process: means hook
Sub, hypo, infra: below something
Obligate Aerobes- Use O2 as the terminal electron acceptor of the ETC
-O2 is reduced to water. **CUT in the SKIN!!!
RBCs don’t have mitochondria or DNA, leukocytes do
Know what obligate anaerobes use as their terminal electron acceptor! *(CO2; SO42-)? Dead organisms smell bad
Still make ATP, but oxygen is a poison to them
Don’t have 3 enzymes
Use CO2 & reduce it to CH4 (methane)
SO42- reduced to hydrogen sulfide
Obligate aerobes (like us!) **have the enzymes **catalase and SOD (superoxide dismutase) and **glutathione (*GSH, by itself → tripeptide, GSH) peroxidase (*GPX, 1 of 3 enzymes). Obligate anaerobes do NOT have these two enzymes! To wit, oxygen is a POISON to obligate anaerobes: **make H2O2 → water and O2 (Bubbles!!!) → KILLS obligate anaerobe (NOT have 3 enzymes !!!)
SOD makes H2O2 (from the reactive oxygen metabolites) and catalase breaks down H2O2 down into O2 and H2O2. Why? Because oxygen is a reactive molecule aerobes make plenty of reactive oxidative intermediates using O2
GSH → glutathione *(cysteine can scavage free radicals = Antioxidant)
most ubiquitous tripeptide found in higher vertebrates
glutamate, cysteine, glycine
Reference to a cut on one’s hand. What do you see if H2O2 is poured into the cut??? Why pour hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into the cut?
*5 fluids: aqueous humor of the eye, blood, lymph, bile, interstitial fluid
Antiperspirants vs Deodorant
Antiperspirants work on the apocrine, sudoriforous glands of the axillary region
Deodorant interacts w/ thiol alcohols
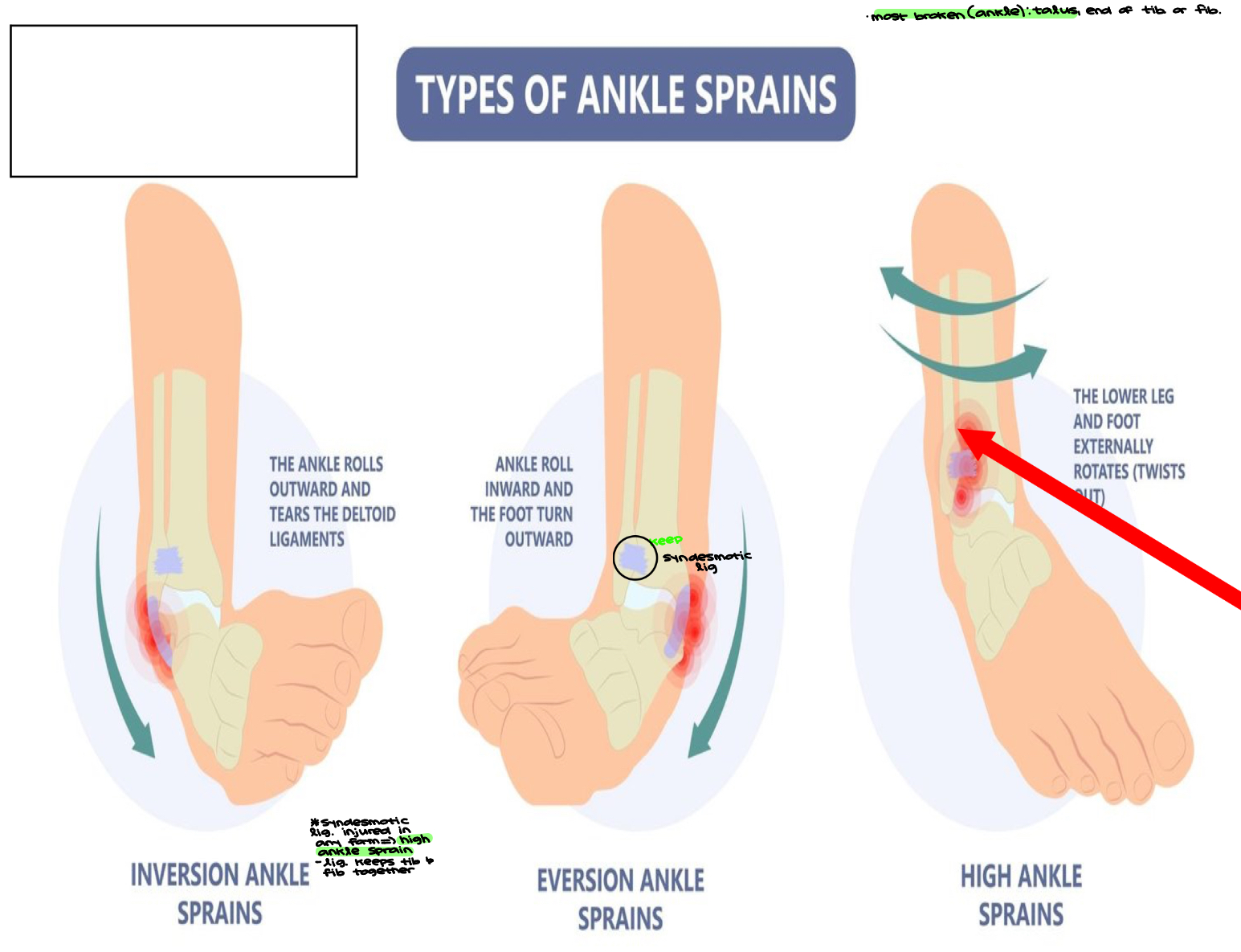
High Ankle Sprain:
A high ankle sprain is also known as a syndesmotic ankle sprain. This type of sprain is a stretching and twisting of the **syndesmotic ligaments** that connect the tibia and fibula of the lower leg. ***The fibula is the NON-weight bearing bone of the lower leg! (tibia is the weight-bearing bone) ***Interstitial space = space between cells!!
The “high ankle” component of the term comes from the sprain being characterized as pain or discomfort “above the ankle.” LONG TIME TO HEAL !?!?!? Why !?! Think level of vascularity. Think cells that are highly perfused w/ blood/O2; Friendly reminder- cells that are MORE than ****6-8 cell lengths away from capillary bed do NOT receive as much blood ERGO, nutrients and gases much DIFFUSE to these tissues!
Types of ankle sprains
Most broken (ankle): talus, end of tib. or fib.
Syndesmotic lig. injured in any form → high ankle sprain
ligament keeps tibia and fibula together
Don’t confuse high ankle sprain with broken ankle
Broken bone
A ****broken bone** is commonly referred to as a fracture of that bone. Speak the language of broken bones
Factors such as the direction and extent of the break are all considered prior to the diagnosis of the fracture
Also, has the fracture **penetrated the skin (compound, goes through skin) and are there **pieces (comminuted) of the bone visible at the site of the fracture? These elements are considered as well
**Blunt force trauma** (Joe Brrr, turf toe, high ankle sprain)… leads to the fracture and/or contusion (bruise) = hockey puck hits anterior crest of tibia
****Add depression fracture (cranium); Ex = Hammer to cranium and bone fragment is dislodged towards brain = perfect impression of the actual impact
Forensics… (1) hair follicle has DNA (2) ^
Depression: takes place of whatever object, directly into superior aspect, leaves a perfect outline
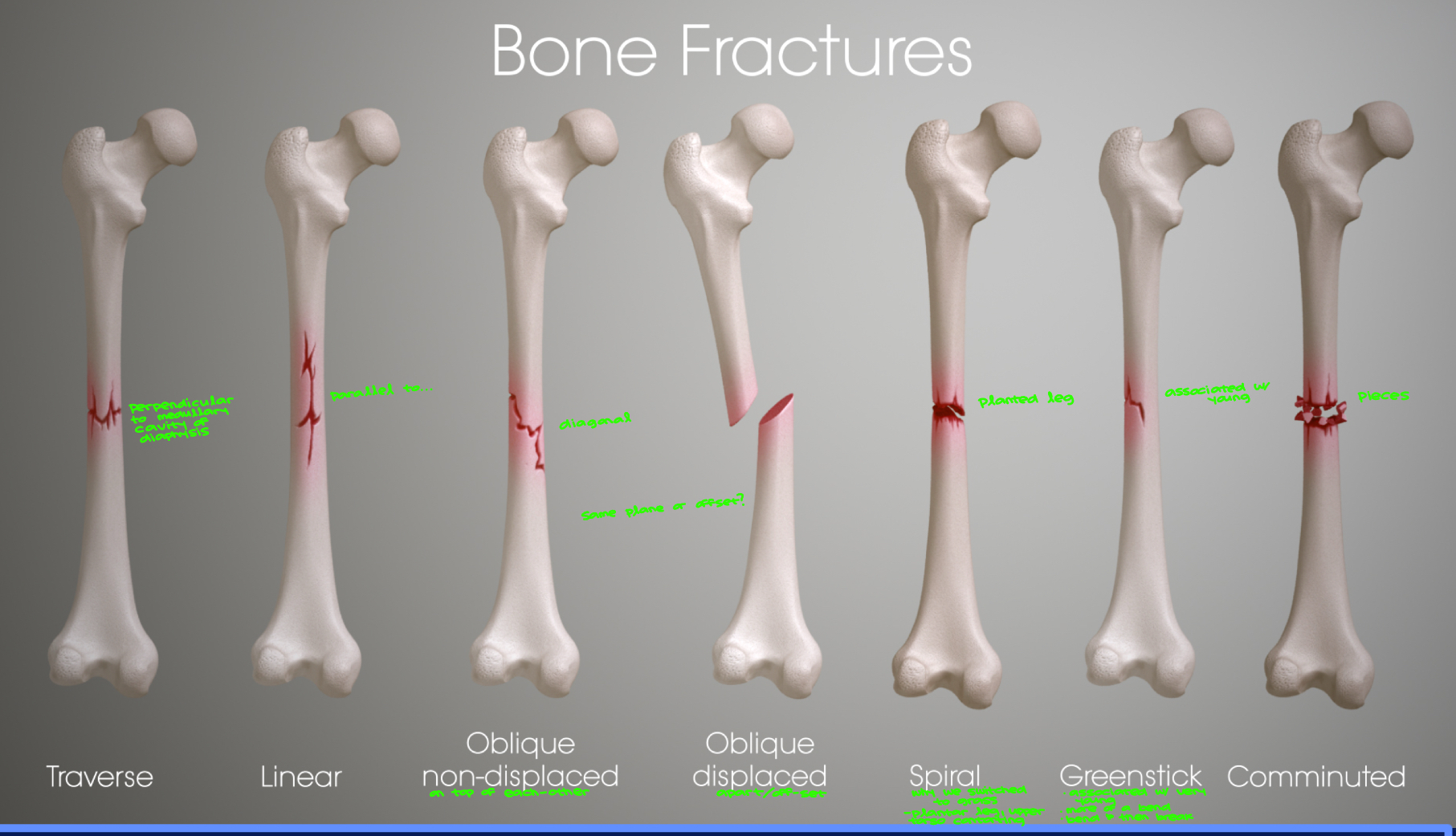
Bone Fractures
Oblique fractures are when the break is at an angle. A compound fracture has broken the skin. **Transverse and Traverse are the same!!
Traverse: perpendicular to medullary cavity of diaphysis
Linear: parallel to…
Oblique non-displaced: diagonal, on top of each other
Oblique displaced: apart/off-set
same plane or offset?
Spiral: planted leg… why we switched to grass. plantar leg, upper torso contorting
Greenstick: associated w/ young… bend then break
Comminuted: pieces
Greenstick fracture
A greenstick fracture typically happens in the very young. The bone bends then it breaks
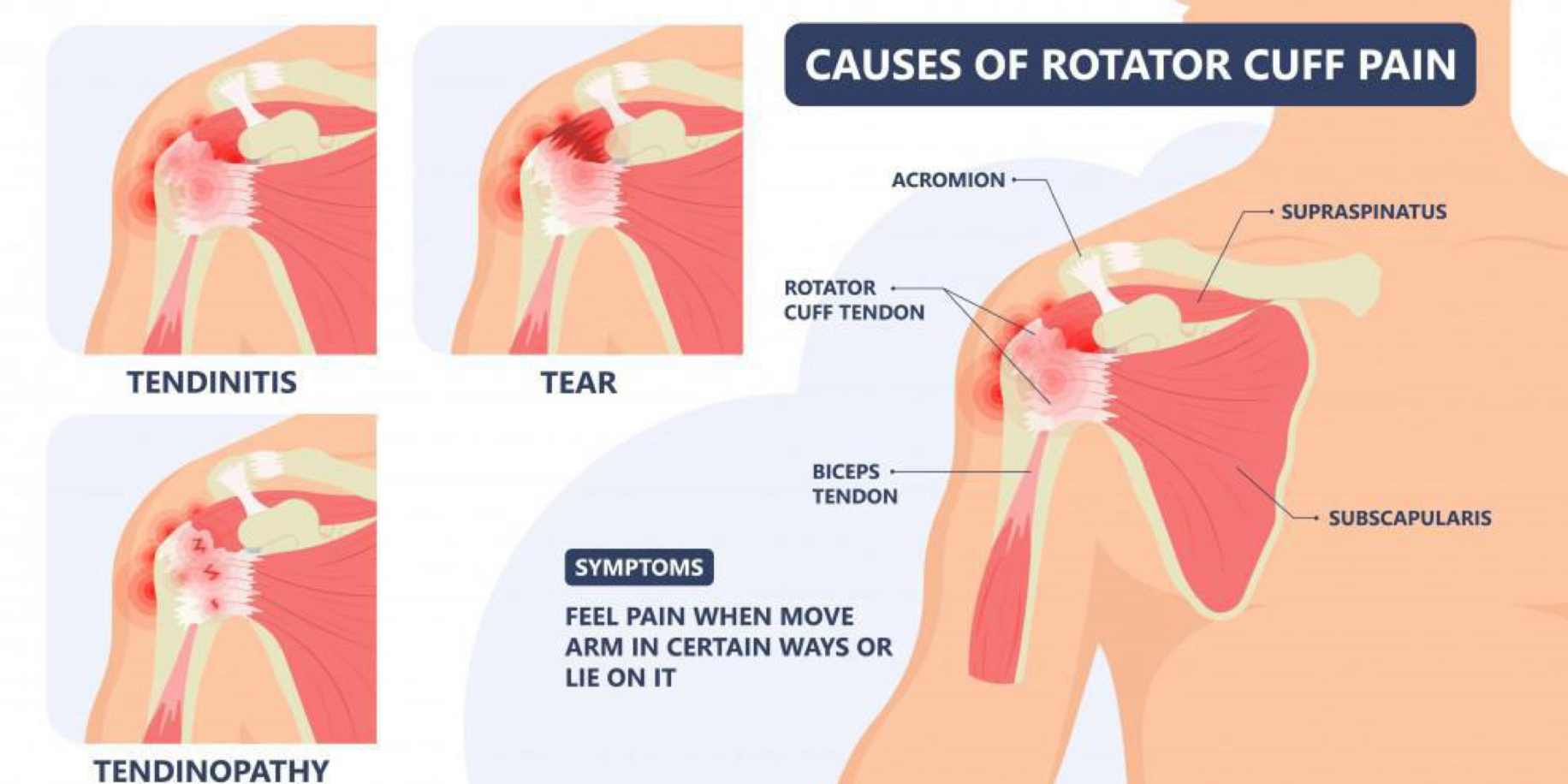
Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff (helps stabilize shoulder socket) is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion
Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the (1) supraspinatus muscle, the (2) infraspinatus muscle, (3) teres ***minor** muscle, and the (4) subscapularis muscle. The rotator cuff muscles are important in shoulder movements and in **maintaining glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) stability
2nd GH… glenohumeral & growth hormone
2 HAs… hyaluronic acid & hydroxyapatite
These muscles arise from the scapula and connect to the head of the humerus, forming a cuff at the shoulder joint. They hold the head of the humerus in the small and shallow glenoid fossa of the scapula
Clavicle is most commonly broken bone in body
Causes of Rotator Cuff Pain
A *****tendinopathy is pain, swelling or tenderness typically due to overuse
-pathy: overuse/swelling… leads to pressure… leads to pain & tenderness
**Bruise/**Contusion (**deep bone bruise***) Leakage… lymphatic sys pick it up!! Swelling = **Edema
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates (leakage of blood, **lymph fluid**) into the surrounding interstitial (#5) tissued. Most bruises occur close enough to the epidermis such that the bleeding causes a (**hemoglobin = **Fe2+ = TOXIC) ***visible discoloration. The bruise then remains visible until the blood is either absorbed by tissues or cleared by immune system action. Bruises which do not blanch (**blanching** = skin has whitish appearance caused by diminished blood flow to that region) under pressure can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, or bone
hema or hemo = blood… or emia/emic
Why do bruises change color? (1) vessels are being ruptured (2) iron is being transported out
blanching: inflammation, push, turns white (ant bite)
Inflammation Basics
Inflammation (from Latin: inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators (mediators of inflammation). The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair
******The five cardinal signs are heat, pain (via pressure), redness, swelling, and loss of function**
(next week) Mediators of Inflammation- Included among these mediators are (1). arachidonic acid derivatives (leukotrienes and prostaglandins) (5), (2). vasoactive peptides (-kinins), (3). phospholipid mediators (platelet activating factor), and (4). cytokines (interleukins and other bio-response modifiers); Ref to cyclooxygenase = **COX enzymes; Histamine = Sources (Mast Cells)!!!
Review 2
**Osteogenesis Imperfecta (collagen!) & **Osteoporosis
**Sprains vs strains (back!!0
**Arthritis, inflammation, and **NSAIDs (and their effects on enzymes) **Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, Exs: Ibuprofen (Advil) - Comp Inh. of COX (cyclooxygenase) = **antipyretics (fever down)
Last but NOT least, our defenses can, paradoxically lead to physiological conditions becoming worse
Active Transport (AT) vs Passive Transport
Active Transport → energy into sys
(A) 1° (primary AT) → use ATP directly → “ATPase” Ex: Na+/K+ ATPase pump
(B) 2° (secondary) AT → uses ATP indirectly Ex: Na+/glucose co-transport system
Passive Transport → no energy into sys
(A) Ex: diffusion… spray perfume, goes from high conc. & is going to start colliding w/ air molecules, goes in diff. directions
(B) Osmosis: water does moving
“U-Tube
(C) Facilitated Diffusion → PROTEIN
Integral Protein → found w/in cell membrane
Channels
Channels (3 types)
“leak” channel → K+ leak channel
voltage-gated channels (excitable tissues, Na+, K+)
ligand-gated receptor/channel
Ligand is a molecule that binds either NT or hormone… have to be hydrophilic b/c they bind to cell surface receptor
Latin ligande, to bind or tie off
Receptor becomes channel b/c of MIFCC
Molecular Interaction Facilitates Conformational Change (MIFCC)
Integral Protein → found w/in cell membrane
Carriers
Ex: Na+/glucose co-transport system
Univ. of Florida… Gatorade early ‘60s
2° AT symport
Integral protein
Oral rehydration therapy
Integral Protein → found w/in cell membrane
Pumps
Ex: Na+/K+ ATPase pump
“ATPase”
1° AT
ATP hydrolysis
+∆G rxn → -∆G rxn
“∆S” → entropy disorder
∆G = ∆H-T∆S
ATP hydrolysis → -∆G rxn… -∆H, +∆S
ATP → ADP + PO4 → +∆G rxn → -∆G rxn… ATP hydrolysis, coupled together… can’t happen spont., not happening thermodynamically
Against gradient, potassium wants out, keeps getting pushed in
Sodium wants in, gets pumped out
ATP hydrolysis makes things in nature that don’t want to happen thermodynamically happen
Ex: biosynthesis +∆G → -∆G
ATP hydrolysis can couple rxn, make something that doesn’t want to happen thermodynamically happen
Integral Protein → found w/in cell membrane
Receptors
Going to be on cell surface
Pharmacology- study of drugs & drug interactions
*Antibiotics (kill bacteria) vs Antimycotic fungi (kill fungi)
Pharm 101 → attack something that pathogen *has that host does *NOT
Ex of antibiotic targets
peptidoglycan biosyn. enzymes (if don’t have, can’t divide via binary fission)
30s/50s (svedberg) → 70s ribosomes humans: 40s/60s → 80s
one small “circular” chromosome → DNA gyrase “supercoils” (enzymes)
cyanide will kill bacteria, but also humans b/c it uncouples ETC
humans don’t have cell walls
mitochondrial ribosomes are closer to bacterial 70s ribosomes
no nucleus… nucleoid region
Antimyocotics (kill fungi) → Fungacidal (dead)
Targets:
(A) Chitial biosyn. enzymes (NOT CHITON)
(B) Eagosterol (fungal version of cholesterol… steroidal lipid)
bacteria have defenses against our antiobiotics
drug will go into bacterium, break down w/ an enzyme, pump it out