Oncology 4 (Mast Cell Tumor)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Mast cell tumors are called the ____ !
great imitator — because they can look like anything and have a wide range of biologic behavior
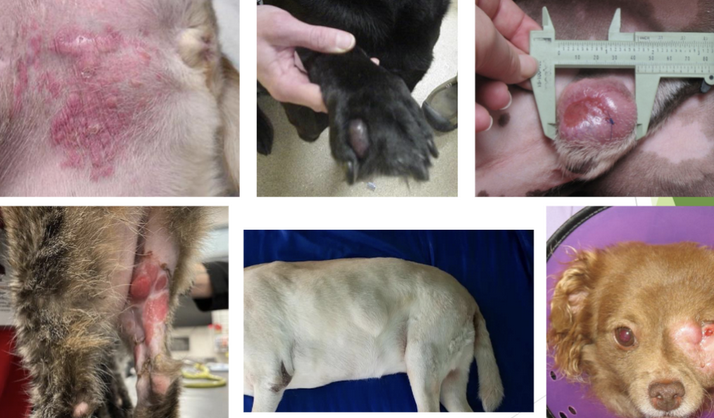
How common are MCT?
Most common cutaneous tumor in dogs (16-21%)
What is the signalment (age, breeds) associated with MCT?
~9 yo
Boxers, boston terriers, Labs, pugs, bulldogs, mixed
What type of cells are mast cells and where are they found normally?
round cells
normally in lungs, liver, skin, GI, lymphoid tissue
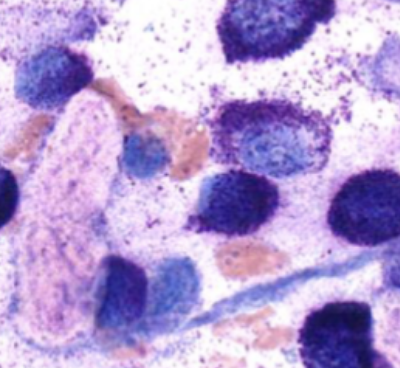
What are the roles of mast cells?
wound healing, induction of innate immune response, anti-parasitic activity
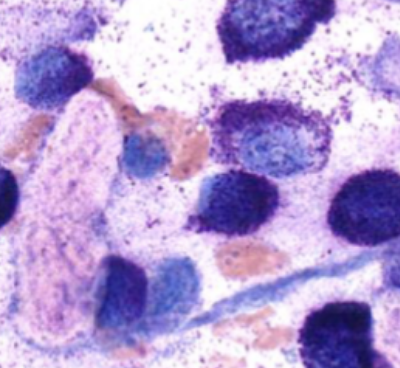
Mast cell granules contain _________ which causes _______.
- heparin, histamine, proteases, preformed TNF-alpha
- vasodilation, vascular leakage, smooth muscle constriction
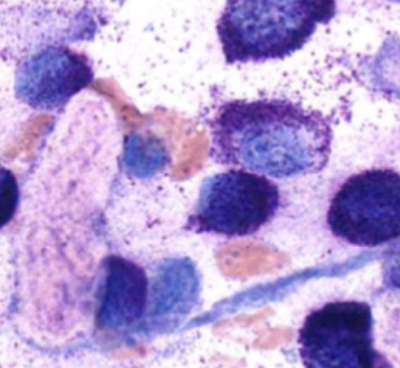
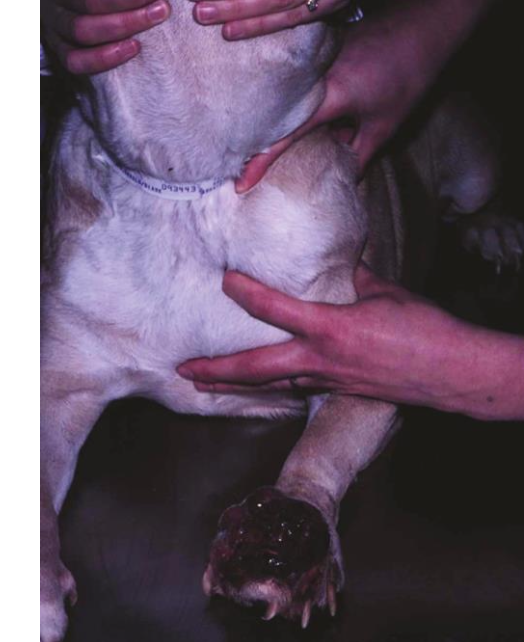
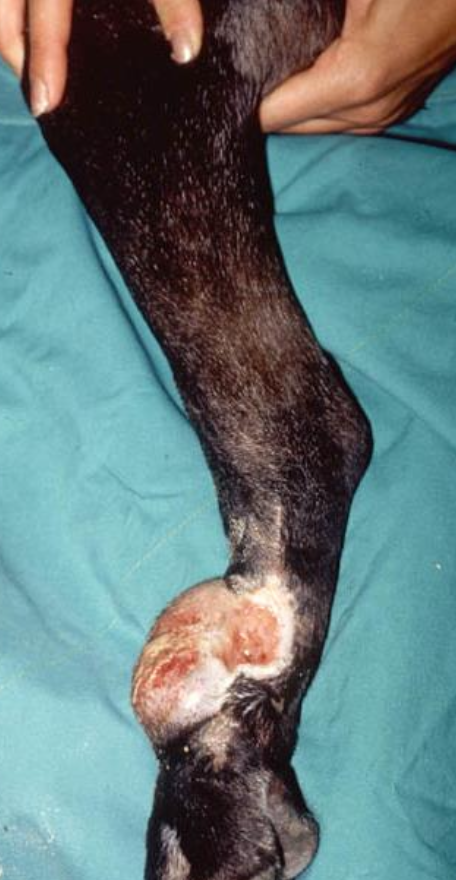
How do MCT lesions present clinically?
most are cutaneous or subcutaneous
most are solitary (11-14% of dogs multiple lesions)
majority located on trunks or limbs
True or False? MCT only present cutaneously.
False. There is a visceral form (disseminated or systemic mastocytosis) and primary GI form which is rare.
What is the patient history like in MCT?
mass “comes and goes” or “appeared overnight”
redness, swelling, pain
Darier’s sign = local degranulation from mast cell degranulation after manipulation
More rarely → v/d, fever, collapse
What is the etiology of MCT?
mostly unknown, multiple genetic links under investigation
suspected receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) KIT
RTKs convey ___ signals from outside the cell to inside the cell.
growth factor
What is c-kit?
proto-oncogene that encodes for KIT (a RTK)
___ binds to KIT to promote ___, ___, ___ of normal mast cells.
Stem cell factor (SCF),
proliferation, differentiation, maturation
How are MCT and c-kit associated?
20-30% of grade 2/3 tumors have an ACTIVATING mutation of c-kit
→ SCF-independent activation of KIT → upregulation of signal transduction
c-kit mutation is linked to _____
increased risk of local reoccurence, metastasis, and worse outcome in MCT
Common mutation sites in c-kit?
Exons 11, 12 (juxtamembrane), and 8, 9 (extracellular).
What is the first-line diagnostic test for MCT?
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology.
What stains are best to visualize mast cell granules?
Giemsa or toluidine blue.

Why might granules not stain with Diff-Quik?
Mast cell granules may appear unstained with this method.

What should be administered before FNA a possible MCT?
Diphenhydramine (to reduce degranulation reactions).
What type of biopsy confirms diagnosis and grading of MCT?
Incisional or excisional biopsy with histopathology.
What are the five major prognostic factors for MCTs?
Histologic grade,
Stage,
c-kit status,
Proliferation rate,
Other factors (breed, size, location).
What is the Patnaik grading system?
3-tier system: Grade 1 (low), Grade 2 (intermediate), Grade 3 (high).

Median survival time (MST) for Grade 3 tumors?
~278 days (9.2 months)
MST for Grade 1–2 tumors?
> 3 years.
__ % of low or intermediate grade MCT resulted in death of patient. ☹
15-30%
What is the Kiupel grading system?
2-tier system: Low grade (MST > 2 yrs), High grade (MST < 4 months).

Which organs are most commonly affected by metastasis?
Lymph nodes → spleen → liver (rarely lungs).
How common is metastasis in high-grade MCTs?
55–96%
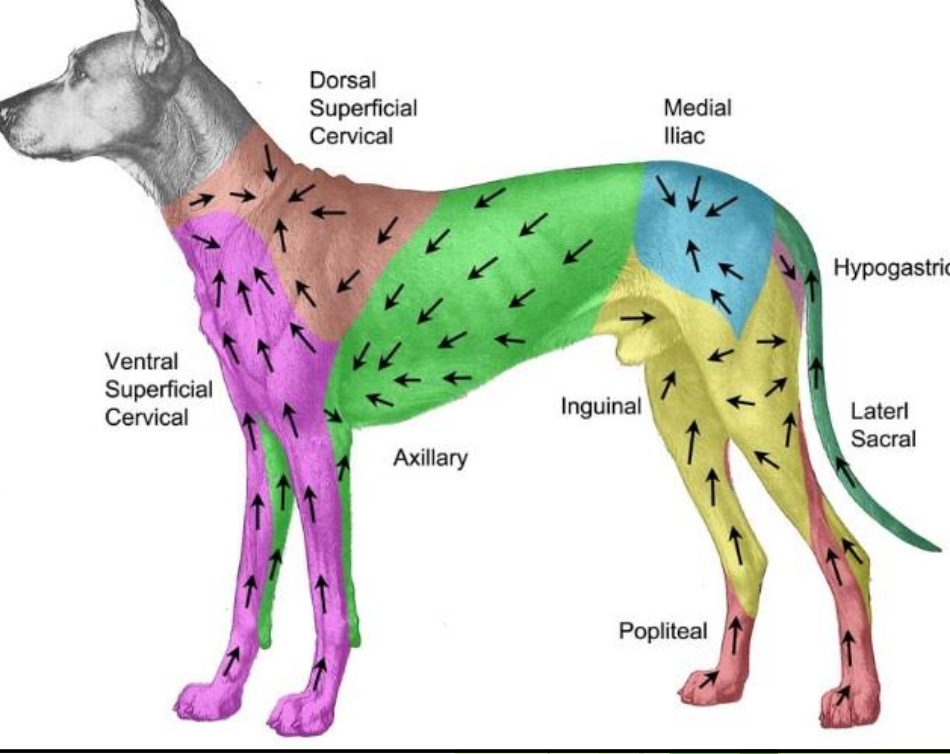
What staging tests are recommended?
LN FNA (sentinel lymph node mapping), abdominal ultrasound, liver/spleen aspirates, ± thoracic radiographs
What is the purpose of a buffy coat smear?
To check for circulating mast cells (though nonspecific) aka peripherla mastocytosis
What is the MCT Prognostic Panel used for?
Predicting biologic behavior, especially for intermediate-grade tumors.
BUT EXPENSIVE.
Most helpful for grade 2/intermediate grade MCT or if behavior is in question
What KIT IHC staining pattern indicates worse prognosis?
Diffuse cytoplasmic staining of CD117 (KIT).
What mitotic index indicates poor prognosis?
> 5 mitoses per HPF
What does increased Ki67 indicate?
Higher proliferation rate → worse prognosis.
What are the treatment modalities for MCT?
surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or combination

What is the treatment of choice for localized MCTs?
Wide surgical excision.
Recommended surgical margins for MCT?
2–3 cm lateral and 1 fascial plane deep.
What % of low/intermediate-grade MCT recur after surgery?
20–30%
When is radiation indicated for MCT?
When microscopic disease remains after surgery or re-excision is not possible.

When is chemotherapy used for MCT?
For high-risk, metastatic, or recurrent disease; as adjuvant therapy.
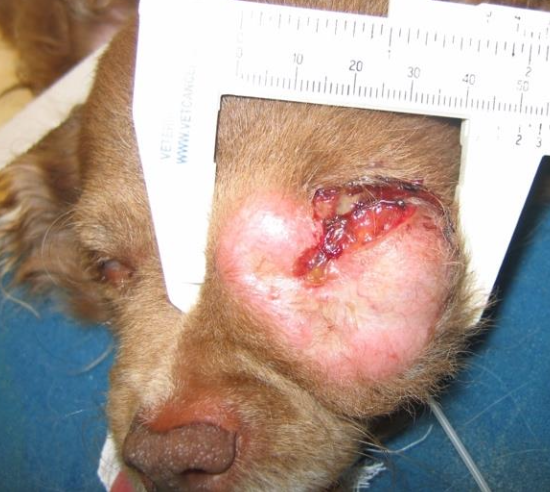
Common drugs used in MCT chemotherapy?
Vinblastine, Palladia, lomustine (CCNU), hydroxyurea, chlorambucil, vinorelbine ± prednisone.

Typical chemotherapy response rate for gross MCT disease?
10–60%
What tyrosine kinase inhibitor is FDA-approved for canine MCT?
Toceranib phosphate (Palladia)

What pathways does Palladia inhibit?
VEGFR2, PDGFR, KIT

Approximate overall response rate to Palladia?
60% (43% response + 17% stable disease)

What supportive medications can be considered?
Antihistamines, steroids
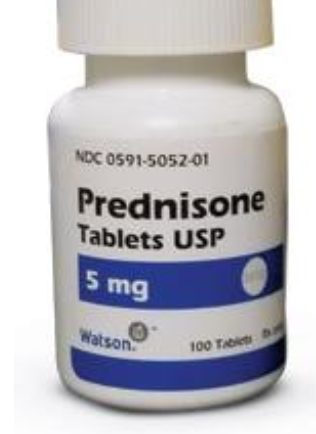
Which H1 blocker is recommended?
Diphenhydramine
Which H2 blocker is recommended?
Famotidine
Omeprazole (not a H2 blocker, PPI that is used also)
What steroid can help reduce tumor swelling and mast cell activity? How?
Prednisone
Inhibit MCT proliferation and induce apoptosis in vitro, may decrease peritumor edema clinically
Prednisone response rate for intermediate/high-grade MCT as a single-agent?
~24%, short duration (weeks)
When should you consider supportive treatments with MCT?
if P has gross disease or as part of chemo protocol