Ocean Currents and Tides
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to ocean currents, tides, and coastal processes from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Surface Ocean Currents
Caused by friction between wind and the ocean surface.
Ekman Spiral
Spiral movement of water caused by wind and Coriolis Effect.
Ocean Gyres
Five major gyres include North & South Pacific, North & South Atlantic, Indian Ocean.
Coriolis Effect
Effect that causes ocean currents to deflect.
Gyres
They affect global climate by transferring warm water to poles and cold water to the equator.
Upwelling
The rise of cold, nutrient-rich water due to surface current movement.
Warm Currents
They make coastlines humid.
Cold Currents
They make coastlines dry.
Deep Ocean Circulation
Driven by density differences from temperature and salinity, known as thermohaline circulation.
Deep Ocean Water Origin
Typically originates from cold, salty surface water in high latitudes.
Global Conveyor Belt
A model of thermohaline circulation moving through major oceans.
Wave Energy
Powered by wind energy.
Parts of a Wave
Three key parts include crest, trough, wave base.
Wave Size Factors
Affected by wind speed, wind duration, and fetch.
Waves at Shore
They slow down, grow taller, and break upon reaching the shore.
Wave Abrasion
Grinding action of rock fragments in water.
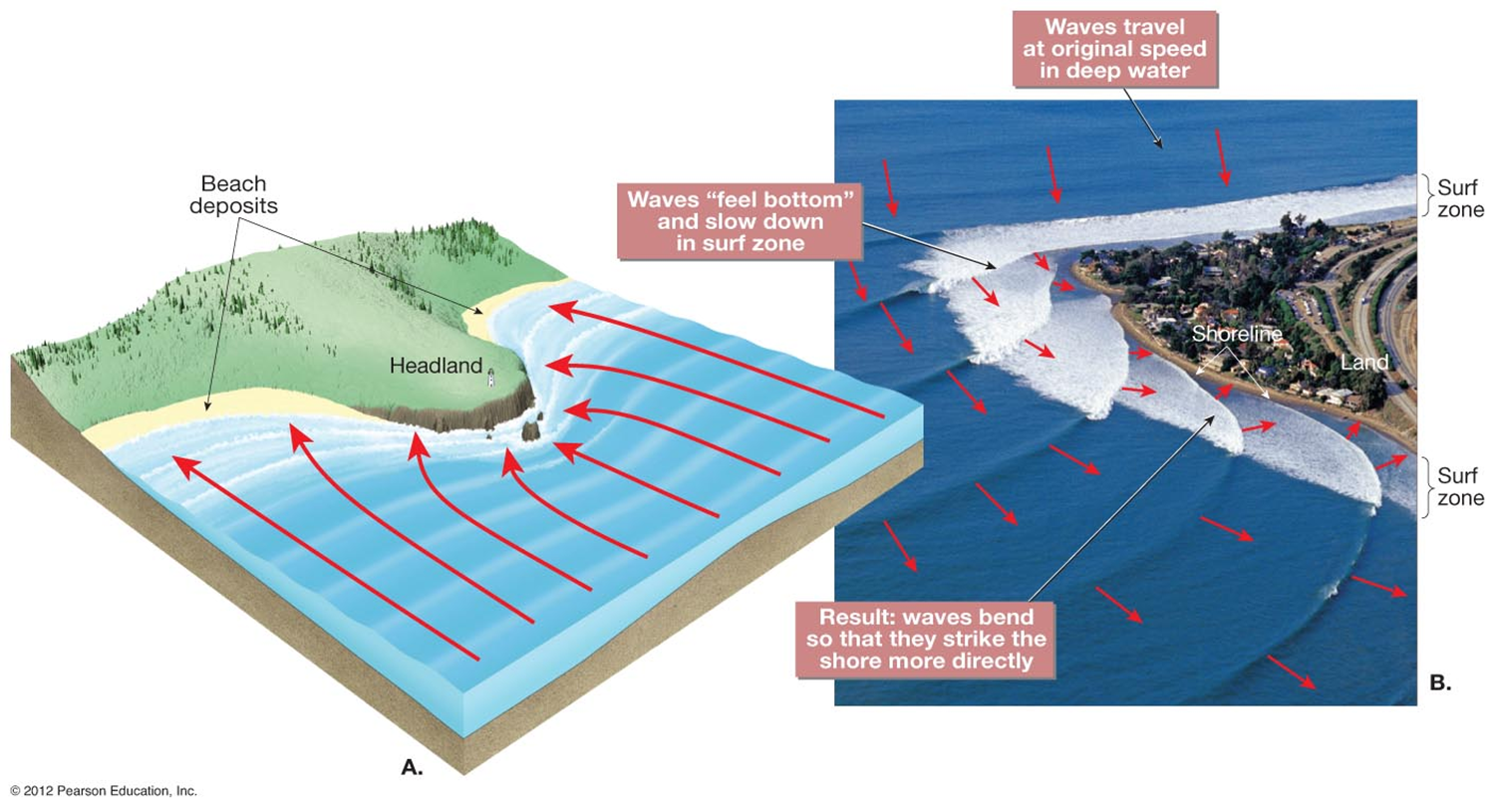
Wave Refraction
Bending of waves to strike the shoreline head-on.
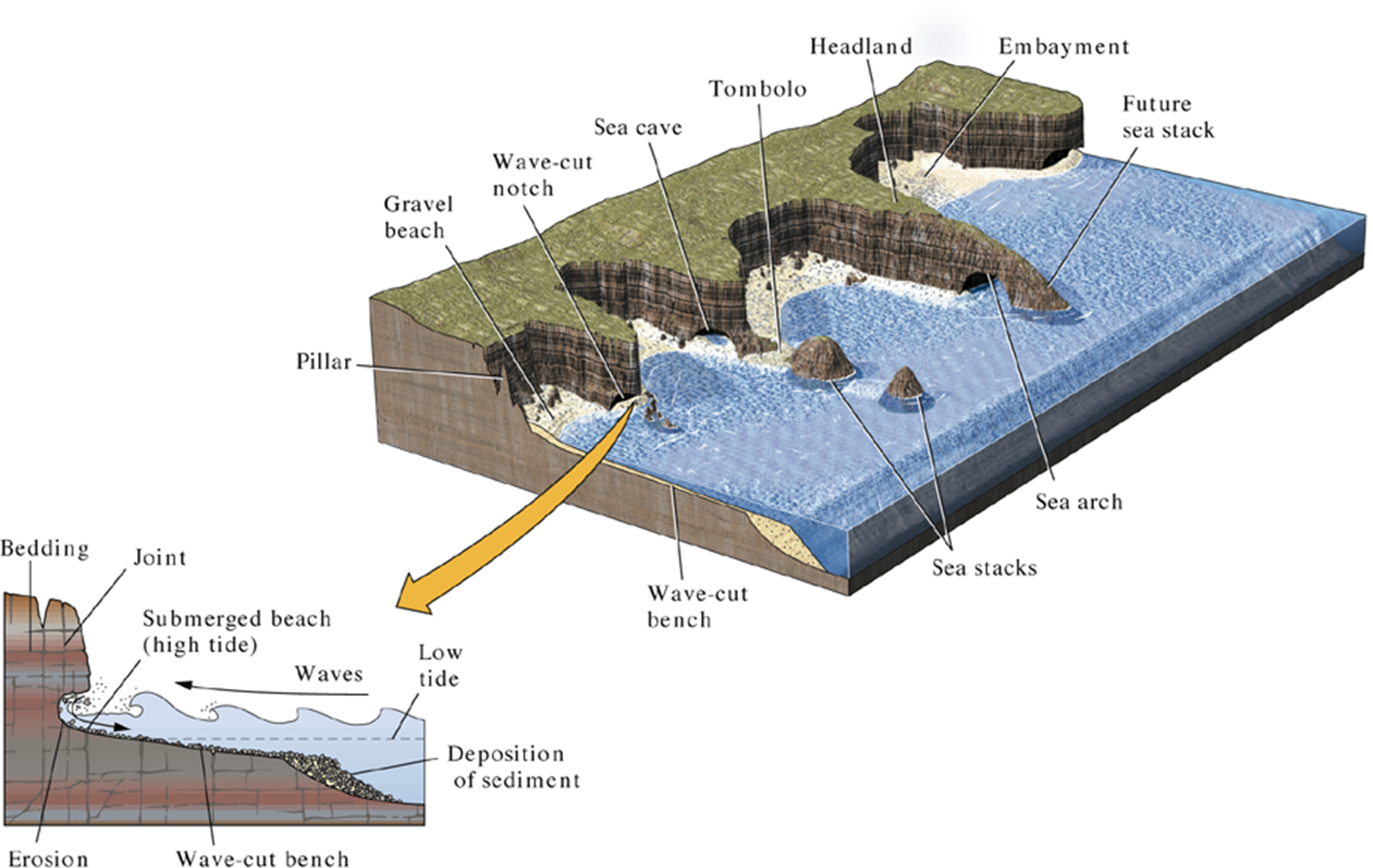
Erosional Coastal Features
Include sea stacks, sea arches, and cliffs.
Beach Drift
Sediment moves in a zigzag along the shore.
Longshore Drift
Sediment moves parallel to shore due to current in surf zone.
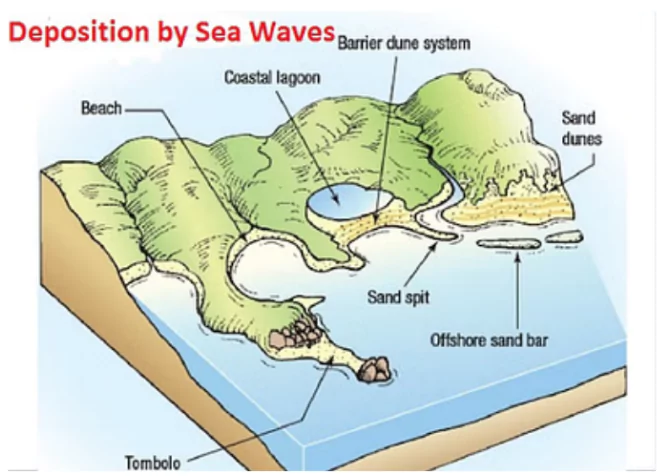
Depositional Coastal Features
Include spits, baymouth bars, and tombolos.
Hard Stabilization Types
Include groins, breakwaters, seawalls, and jetties.
Soft Alternatives to Hard Stabilization
Include beach nourishment and population relocation.
Emergent Coast
Occurs when a coastline rises or sea level falls.
Submergent Coast
Occurs when a coastline sinks or sea level rises.
Tides Causes
Caused by the Moon's gravity, Sun's gravity, and centripetal force.
Spring Tide
Characterized by high tidal range during full or new moon.
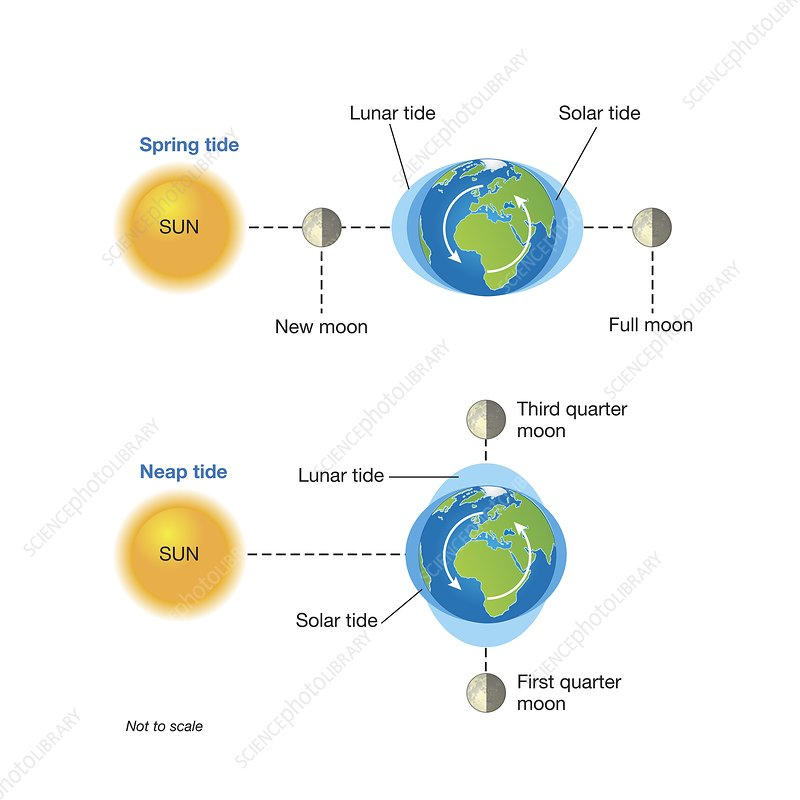
Neap Tide
Characterized by low tidal range during 1st or 3rd quarter moons.
Tidal Patterns
Include diurnal, semidiurnal, and mixed.
Flood Current
Tidal water moving inland.
Ebb Current
Tidal water moving seaward.
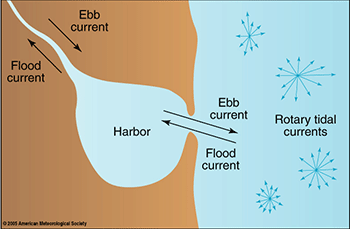
Tidal Currents Effects
Can create tidal flats and tidal deltas.