PMP Prep Section 6: Project Management Components
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
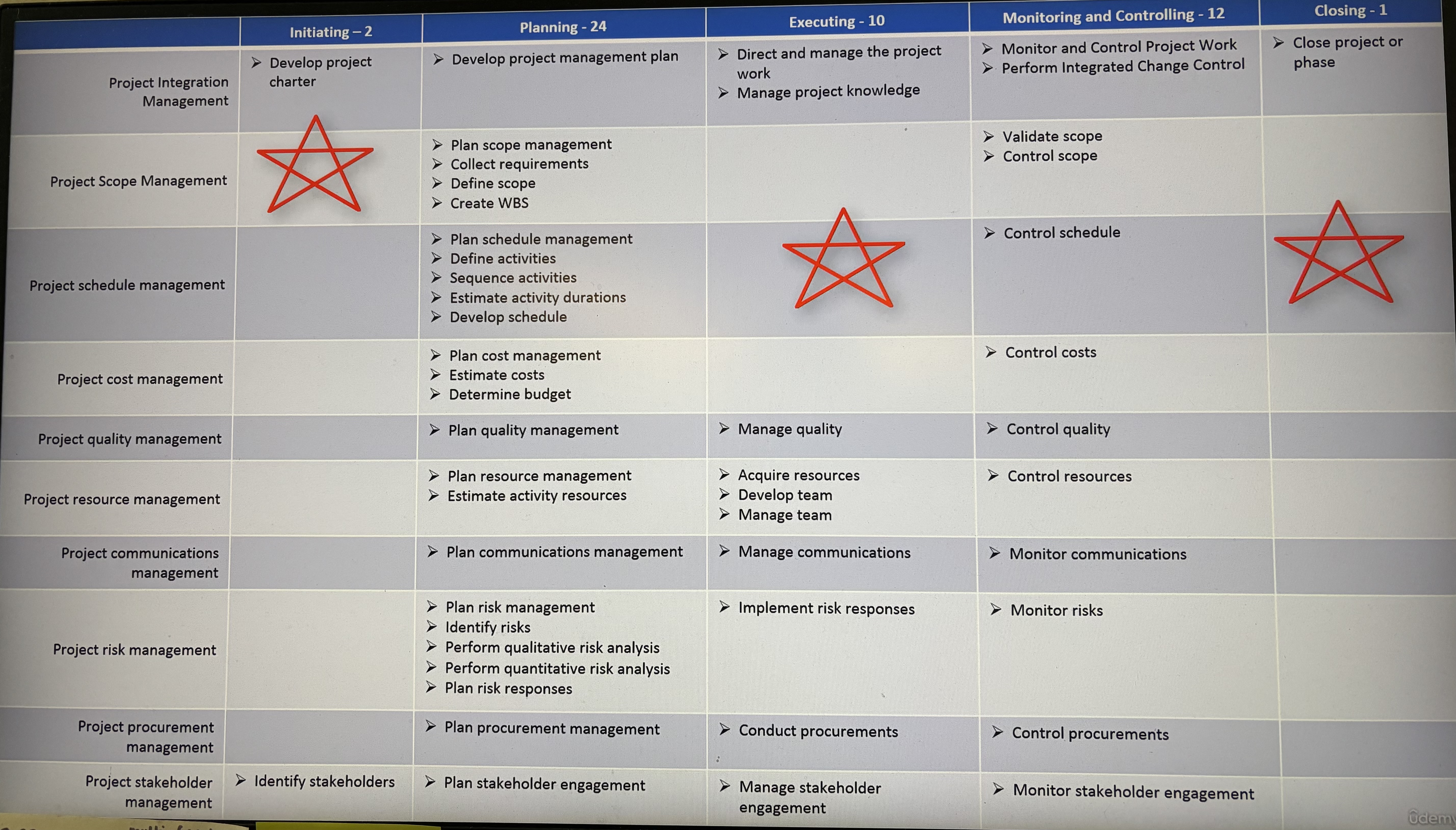
Project Management Process Groups (5)
Initiating
Planning
Executing
Monitoring and Controlling
Closing
Project Management Knowledge Areas (9)
Project Integration Management
Project Scope Management
Project Schedule Management
Project Cost Management
Project Quality Management
Project Resource Management
Project Communication Management
Project Risk Management
Project Procurement Management
Project Stakeholder Management
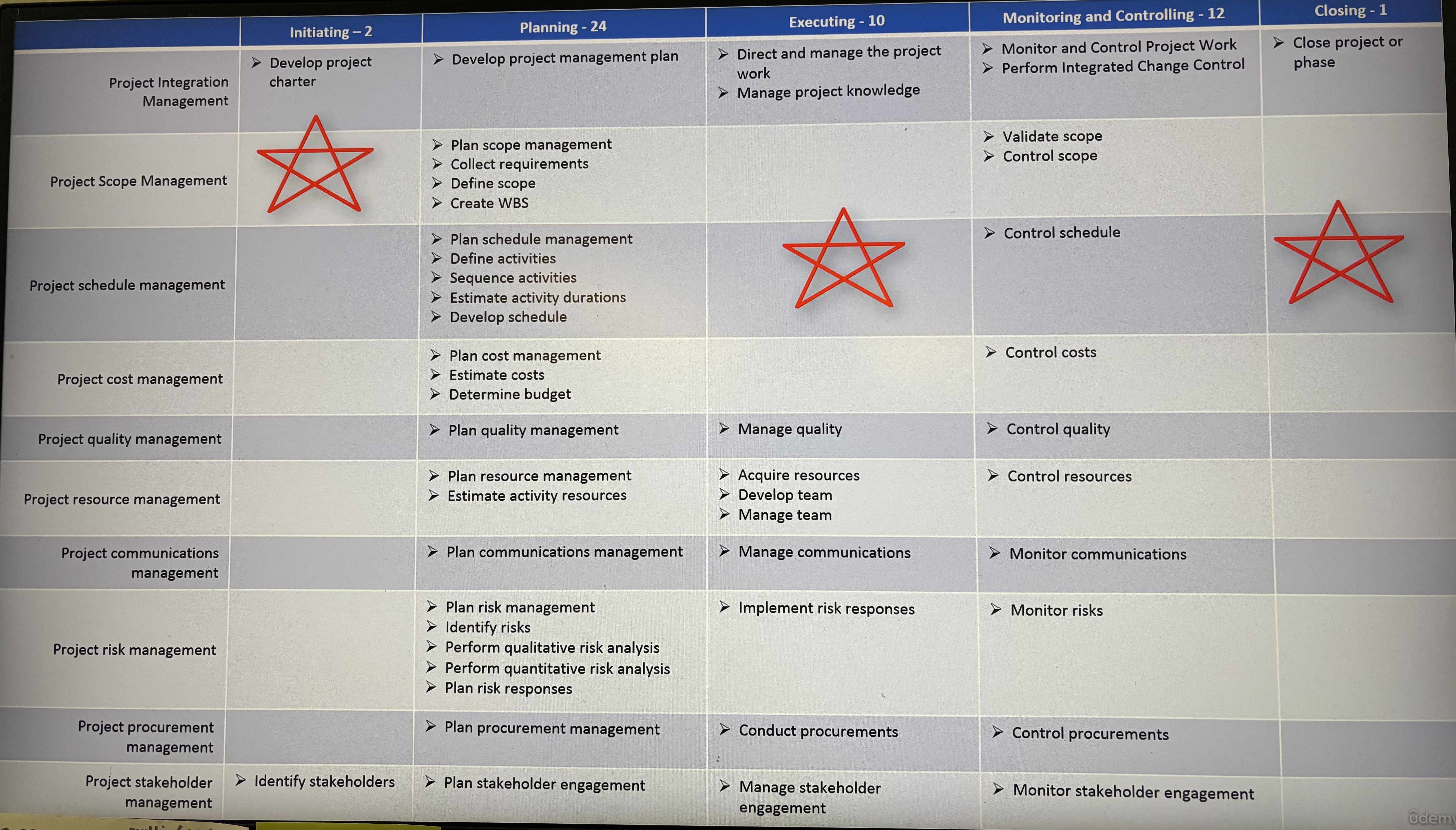
PMP processes
know these!!!
First process group you work with when starting a new project?
Initiating
How many project management processes exist within Initiating?
2:
develop project charter
identify stakeholders
First process you address when starting a new project?
Develop project charter
Project Charter
document created at the beginning of project - officially launches project, authorizes PM, and allows project to exist within the organization
How many processes in Planning?
24
develop project management plan
plan scope management
collect project requirements
define project scope
create work breakdown structure
plan schedule management
define project activities
sequence project activities
estimate activity duration
develop project schedule
plan cost management
estimate project costs
establish project budget
plan quality management
plan resource management
estimate activity resources
plan communication management
plan risk management
identify project risks
perform qualitative risk analysis
perform quantitative risk analysis
plan risk responses
plan procurement management
plan stakeholder engagement
“Collect requirements” process
Process to gather stakeholder requirements your project is required to satisfy to consider project complete
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project scope management
“Define Activities” process
Define exact activities need to be completed in order to define exact elements of WBS and scope (after scope and WBS are already created)
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project schedule management
“Plan procurement management” process
Identify and plan procurements for the project based on project needs, organizational procedures, and project budget
Process group:
Planning
Knowledge area: Project procurement management
“Create WBS” process
Document where project scope is decomposed
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project scope management
“Determine budget” process
Examine aggregate costs of individual elements to create budget and cost baseline - done after creating WBS
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project cost management
“Define scope” process
Define what is and what is not included in the project, based on stakeholder requirements
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project scope management
“Estimate activity durations” process
Create time estimates for the duration of the project work and project for stakeholders
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project schedule management
Plan resource management
Establishes ground rules, management, discipline, rewards, recognition system, and other facets of human resource management for the project
Organizational rules and structure may restrict the extent of this process
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project resource management
Plan risk responses
Counteract identified risk events after risk identification
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project risk management
Identify risks
Iterative project management process that examines project for risks that may threaten project objectives
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project risk management
Estimate activity resources
Determines quantity of people, materials, equipment, and other necessities to complete project work
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project resource management
Plan risk management
Defines risk management approach to be used within the project
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project risk management
Perform qualitative risk analysis
In-depth review of identified risks, based on the outputs of qualitative risk analysis
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project risk management
Plan communications management
Defines who will get what information and when
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project communications management
Develop project schedule
Examine project team calendars, resources availability, organization calendars, an duration of project work to schedule when project work may take place
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project schedule management
Develop project management plan
Creates overall project management plan to communicate intent and method of accomplishing project objectives
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project integration management
Plan quality management
Define conformance to requirements, organizational policies, adherence to project scope, quality assurance, and quality control activities
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: project quality management
Estimate costs
Evaluate costs of resources and activities for each element in WBS to predict cost of project
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project cost management
Sequence activities
Examine project work and put activities in the correct order
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project schedule management
Perform quantitative risk analysis
Quick subjective review of identified risks to determine which risk events demand additional analysis
Process group: Planning
Knowledge area: Project risk management
How many processes in Executing process group?
10:
direct and manage project work
manage project knowledge
manage quality
acquire resources
perform team development
manage project team
manage communications
implement risk responses
conduct procurements
manage stakeholder engagement
Direct and Manage project work
Project manager ensures project team and any vendors are completing project work as defined in project management plan
Process group: Executing
Knowledge area: Project integration management
Acquire resources
Add team members to project
Process group: Executing
Knowledge area: Project resource management
Develop team
Conducting activities to help project team members to know and rely on each other
Process group: Executing
Knowledge area: Project resource management
Manage team
Communicate expectations and what is required of team members
Process group: Executing
Knowledge area: Project resource management
Conduct procurements
Actual purchasing of project resources
Process group: Executing
Knowledge area: Project procurement management
Implement risk responses
Execute risk response when triggers or thresholds are apparent
Process group: Executing
Knowledge area: Project risk management
How many Monitoring and Controlling Processes?
12
monitor and control project work
perform integrated change control
validate scope
control scope
control schedule
control costs
control quality
control resources
monitor communications
monitor risks
control procurements
monitor stakeholder engagement
Control procurements
Procurement process to monitor vendors and project manager’s organization to ensure both parties are keeping terms of the contract
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project procurement management
control scope
Prevent unapproved changes from entering project scope
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project scope management
Control schedule
Process that helps project team prevent changes to project schedule due to errors, risks, and unapproved project changes
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project schedule management
Monitor risks
Project team works to monitor existing risks for any changes in probability or impact
Occurs after risks have been identified, analyzed, and responded to
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project risk management
Monitor communications
Ensures management, customers, and stakeholders are kept informed on project performance according to communications management plan
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project procurement management
Perform integrated change control
Examines project change to determine its full effect on all areas of project
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project integration management
Monitor and control project work
Project team confirms that project work is being completed according to plan
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project integration management
Validate scope
Project stakeholders, particularly customers, inspect project work to confirm that work is completed in project is accurate
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project scope
Control costs
Ensures costs are controlled, tracked, and documented throughout the project
Process group: Monitoring and Controlling
Knowledge area: project cost management
How many project Closing processes?
1:
Close project or phase
Manage Quality Processes
often influenced by regulations, standards, guidelines, and organizational requirements
Process group: Executing
Knowledge area: project quality management
True or false: quality control should always happen before scope validation
True
What will customers often need to do at the end of a project phase?
complete scope validation process
customer inspects work to confirm project work is accurate up until this point
PM then completes close project or phase process to close second phase and allow third phase to commence
How often will you developer a project charter?
Typically only done once, but can be re-done at each phase of the project if necessary
How often will you identify project stakeholders?
Happens throughout the project, but should occur as early as possibly
Work Performance Data
raw data and facts about project work
status of project work assignments
percent complete
in progress
start/finish dates
data can include:
activity costs
number of change requests
defects
duration
Work Performance Information
analyzed work performance data
usable info to make decisions
enables you to act upon data
Work Performance Reports
How you package information so it becomes communicable
helps stakeholders make decision
examples:
status reports
memos
dashboards
project updates
Order that Work Performance aspects are transformed
data → information → reports
Key facts about Tailoring the Process for your project
choose what processes should be used on a project
determine what depth the process should be used
remember not every process is needed on every project
be aware the larger the project the more processes are likely needed
Steps to Tailor Processes to your Project
identify relevant knowledge areas
recognize processes that reside in these knowledge areas
tailor these processes to fit your specific project, considering its priority and characteristics
understand that every knowledge area and process offers more opportunities for tailoring
Primary types of project life cycles / environments
Predictive
Iterative / Incremental
Adaptive
Predictive life cycles
plan-driven
waterfall approach
predicts project life cycle
scope changes are tightly controlled
Iterative / Incremental Life Cycles
phases repeat through iterations
iterations create deliverables
detailed scope is elaborated for each iteration
changes to project scope are expected
Adaptive Life Cycles
change-driven
agile project management
rapid iterations of project work
works through backlog of requirements
changes to project scope are expected
Are Adaptive Life Cycles be Iterative or Incremental?
Adaptive Life Cycles can be either iterative or incremental
Business documents
documents that serve as inputs and outputs throughout project processes
Examples of business documents
project business case
project charter
project management plan
benefits management plan
Phase gate
Review conducted at end of project phase before moving to next phase
Ensures prior phase is:
fully completed
financially accounted for
signed off on
How are business documents tied to phase gate?
Business doc attached to phase gate would include:
review of what was supposed to be spent
scheduled completion date for that phase
deliverables expected
Exceptions Report / Variance Reports
needed when actual project performance differs from goals in business documents
explains why target or KPI was not hit - explains why project was late, over budget, etc.
Kill point
another word for Phase Gate- opportunity to “kill” the project based on performance
ex: if you’re more than 30% over budget at the end of X phase, we will not move the project forward
Possible phase gate decisions
continue to next phase
continue to next phase with modification
end project
remain in current phase
repeat current phase or elements of it
Project Business Case
economic feasibility study - confirms if we can afford to do the project
explains validity of benefits
informs future project decisions
developed and maintained by project sponsor
defines issue to be solved or opportunity
identifies affected stakeholders and high-level scope
helps organization determine if we should take on project, including defining:
root cause of problem/opportunity
gap analysis of capabilities
known risks
critical success factors
decision criteria
Who is responsible for Project Business Case?
Project sponsor is accountable for development and maintenance of this document
Project manager is responsible for providing recommendatiosn
Typical Project Recommendation Options proposed by Business Case
do nothing
do minimum work possible
do more than minimum work possible
Project Benefits Management Plan
Plan describing how benefits will be created for the organization by a project
addresses 3 main questions:
how will you create benefits?
how will you maximize benefits?
how will you sustain benefits?
6 components of Project Benefits Management plan
target benefits: expected tangible/intangible value
strategic alignment: how project aligns to business strategies
timeframe: benefits by phase - short-term, long-term, or ongoing
metrics: measures to show if benefits are realized
assumptions: believed but not proven
risks: what could threaten benefits
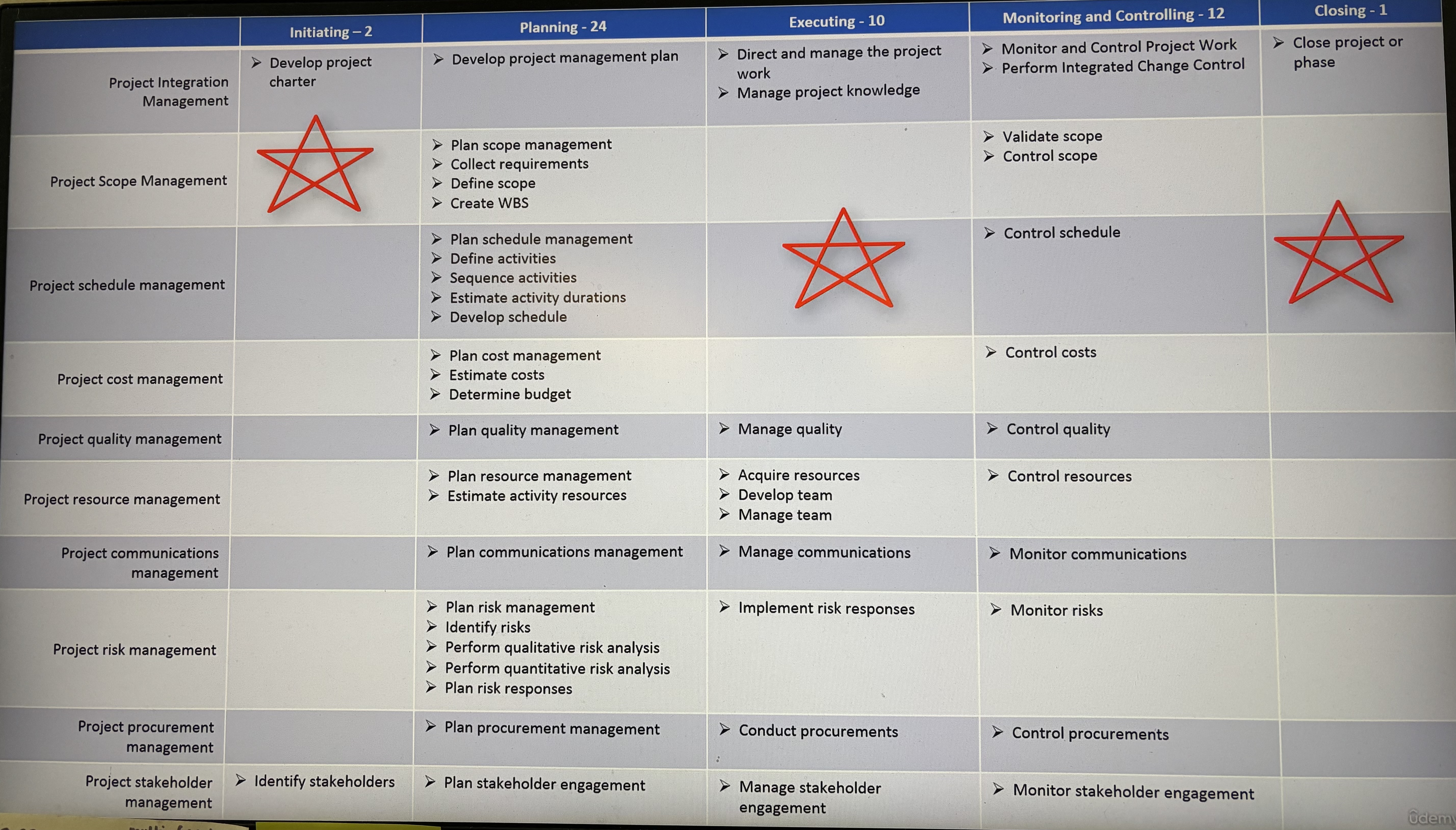
MEMORIZE THIS
MEMORIZE THIS