Osmosis Clicker Questions
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Salmon face different osmoregulatory challenges in these two environments. Due to the difference in osmotic concentration between the the salmon cells and salmon’s aqueous environment, in open oceans, water _______ the salmon’s body, whereas in rivers, water _______ the salmon’s body via osmosis.
leaves; enters
To solve the problem of losing water due to osmosis in the open ocean, you expect salmon to produce ____.
A little bit of highly concentrated urine
What type of nitrogenous waste is most toxic?
Ammonia
When salmon enters freshwater to breed, it needs to pee a lot to get rid of the water that is seeping into its blood via the exposed gills. Salmon kidneys are organized much the same way as mammalian kidneys are. In which kidney structure is the salmon blood filtered to remove the water?
Bowman’s capsule
The Bowman’s capsules are located in the ___ of the kidney.
cortex
Select all: Which components of the nephron are located in the medulla?
Collecting duct
Loop of Henle
(the lower parts of the nephron)
Epithelial cells lining the proximal and distal tubules must actively pump NaCl out of the urine, rather than rely on passive transport to reabsorb NaCl. Why?
There’s more NaCl inside the epithelial cells than in the urine.
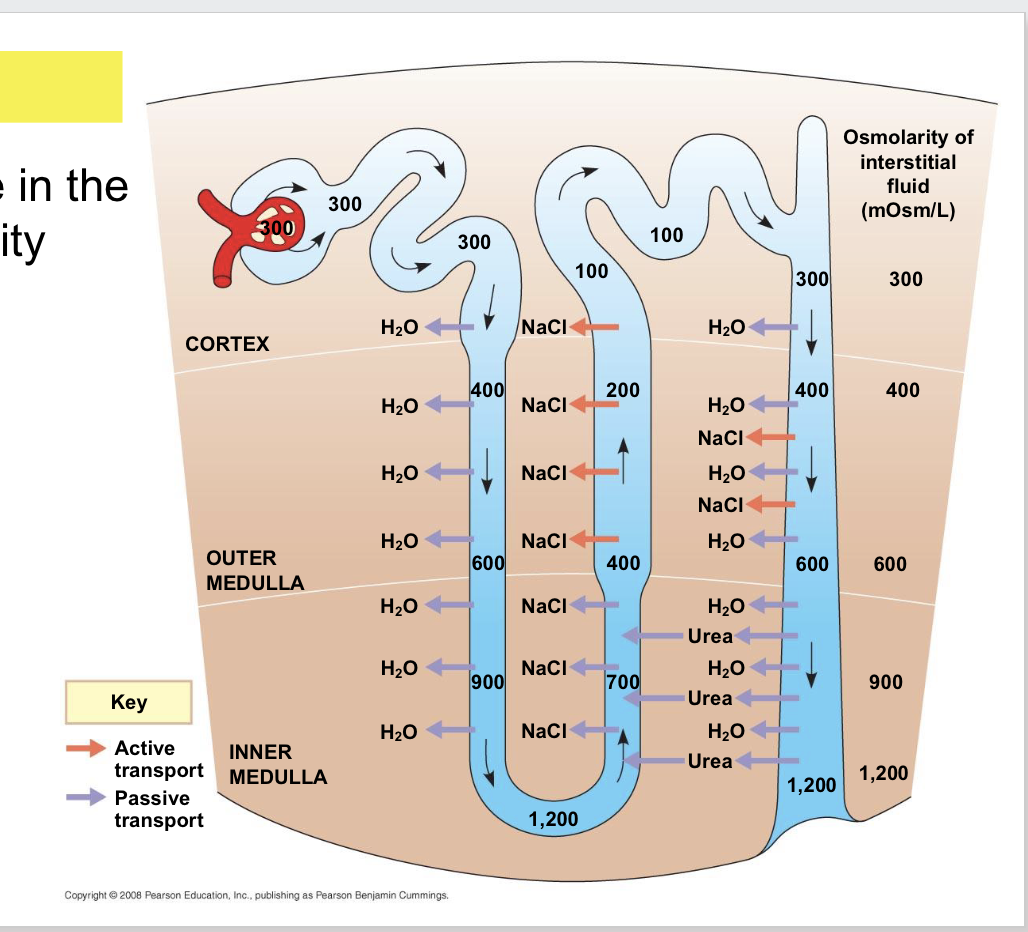
Select all that apply: Where in the nephron is water permeability tightly controlled?
Ascending loop of Henle
Collecting duct
The collecting duct of the nephron takes urine to the ___.
ureter
The process of adjusting urine concentration in response to changing salinity is
an example of________; the ability of salmon to change their urine
concentration is an example of _______.
acclimation; adaptation