L11 - Oceans and atmospheric circulation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Why are oceans in constant motion?
The earth rotates → generates angular momentum and centrifugal force → creates the Coriolis effect
Wind over the oceans creates shear force → drags water with it
The surface of the ocean is not flat → gravitational forcing of water from high areas to low areas
Density → density can vary with temperature and salinity → as water cools, it gets more saline and density increases, causing water to sink → causes ocean currents.
What causes the Coriolis Effect?
Occurs because all objects on earth have the same angular velocity, but the velocity of different points on earth varies.
Water at the poles travels slower than water at equator.
In the northern hemisphere, as you move water in one direction, it is deflected to the right of its direction of travel.
What causes Ekman spirals?
The Coriolis Effect
When large bodies of water are moved, laminar flow occurs → the water moves in blocks and slides over each other.
The average movement of water is perpendicular to the wind direction, which is a consequence of the Coriolis force.
What happens during Ekman spirals?
In the northern hemisphere, there will be a displacement to the right of the direction of movement.
The shear force from the wind that pushes the water across will be affected by the Coriolis effect, so will be deflected to the right.
As the layers decrease, they will move further right of the direction of travel → the Coriolis effect will further this for each decreasing layer.
What does the Ekman spiral create?
A spiral is created where the amount of movement is gradually decreasing until the bottom of the spiral, at which this water will be stationary.
Movement is decreased because the energy is being converted from kinetic to heat due to friction.
What happens during upwelling?
In the northern hemisphere: because of the Ekman transport, the water is deflected to the right.
Water from below upwells to fill the gap left by this movement.
The water that comes up from the depth is usually enriched in nutrients
This is why certain areas of the ocean have very rich fisheries.
If the wind is blowing in the opposite direction, downwelling occurs.
During thermohaline circulation, what happens as water is evaporated?
Pure water is evaporated from the oceans to form clouds
This makes the ocean left behind become a more concentrated solution of salt.
During thermohaline circulation, what happens as ice sheets are formed?
The formation of ice sheets will increase the salinity of the water.
The water that will freeze will be pure water
How does thermohaline circulation work?
As water moves towards the poles, it will get colder because the solar radiation is less intense.
It becomes more dense and sinks
Water from the equator will flow north to fill that hole.
Gulf Stream waters can be 15oC warmer and can be a major flow of energy from the equators to the poles: results in us having warm summers and winters.
Major concern that this circulation is about to collapse
How is incoming solar radiation distributed?
Because of the tilt of the earth, distribution is not constant
At mid-latitudes, the radiation this the earth perpendicular to the earths surface, resulting in fairly intense radiation.
When the light hits the northern and southern latitudes, the earths surface is at an angle, resulting in the light being spread over a greater area, reducing the intensity.
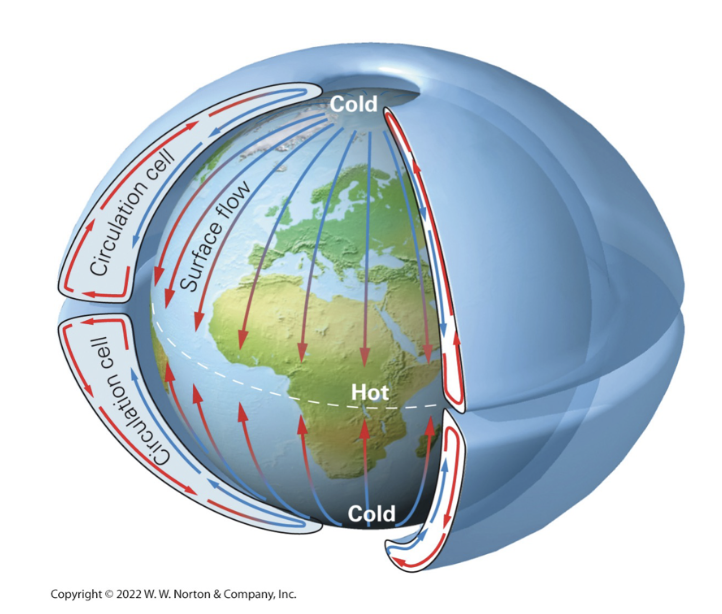
How would global atmospheric circulation work on a stationary earth?
It will be hotter around the equator due to intense solar radiation, causing the air to expand, become less dense, and rise.
At the poles it will be a lot colder: air stops expanding, shrinks, and becomes more dense.
This creates a circulation where the air rises at the equator, flows towards the north poles where it cools and sinks, and flows from north to south.
How does global atmospheric circulation occur on a rotating earth?
The Coriolis Effect affects air currents
As this hot air rises and travels north, it is deflected to the east.
At about 30oN, it cools down and sinks.
At ground level, trade winds travel from east to west by the time you reach the equator.
What controls climate?
Latitudes
Altitudes
Proximity to oceans
Ocean currents
How do altitudes influence climate?
Colder as altitude increases, reducing pressure, causing air to expand
Expanding air consumes heat energy.
How does proximity to climates control climate?
Oceans warm and cool more slowly than continents
There are greater temperature extremes at the continents
At the continents closer to oceans, there will be less variation between summer and winter
How do monsoons form in winter seasons?
In the winter season, because the land warms and cool more rapidly, the air over the Himalayas gets very cold and sinks, travelling to the ocean.
The air over the Indian Ocean is warm so it rises.
This generates an anticlockwise circulation system where the air is pulled from the Tibetan Plateau across the Indian Ocean, collecting water vapour until the air rises, cools, and rain falls over the Himalayas
How do monsoons form in summer seasons?
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) shifts to the Himalayas alays because the land heats up so much, causing the air to heat up and rise over the Himalayas.
The downwelling circulation is now over the Indian Ocean, where it travels over the ocean, absorbing moisture, begins to heat up and rise, then cools down again and causes significant rainfall.
What happens during a La Niña period?
There will be areas of low pressure in the west.
The air is rising and cooling, water vapour condense, and it rains.
One of the features of this system is that the flow of air from east to west pulls water in that direction too, causing upwelling of this colder, nutrient-rich water onto the South American coastlines
What happens during El Niño years?
The high pressure areas are now in the west
Air flows across the pacific, gathering moisture, rises in the east, condenses, and there is rainfall.
What are the consequences of an El Niño period?
Droughts and forest fires in the east (e.g. Australia)
Large amounts of rain and flooding in the west
Coastal upwelling in South America stops: fisheries die off, causing food security and water quality issues.
How do monsoons and El Niño/La Niña periods affect rice production?
Rice production in India dips during El Niño years (less rainfall: monsoons significantly affected: crop yield decreases)
Higher production happens in La Niña years.
What happens during positive years of the North Atlantic Oscillation?
There are areas of low pressure around Greenland and areas of high pressure in the Azores.
This forces moist air into Northern Europe, and dry air in the mediterranean
What happens during negative years of the North Atlantic Oscillation?
Low pressure moves south of Greenland, high pressure moves off the Azores, and pushes wet weather into the mediterranean