Ch. 26 - Fluids
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Body Fluid Compartments
Intracellular Fluid Compartment (ICF)
Extracellular Fluid Compartment (ECF)
Extracellular Fluid Compartment
One-third of water outside of cells
Body’s “internal environment”
External environment of cells
Divided into:
Plasma – fluid portion of blood
Interstitial Fluid (IF) – fluid in spaces between cells
Intracellular Fluid Compartment
Two-thirds by volume in cells
25 L (of 40 L body water) in average male
Electrolytes
Chemical compounds that dissociate into ions in water
Can conduct electrical current
Includes inorganic salts, inorganic & organic acids/bases, some proteins
Greater osmotic power than nonelectrolytes
Water moves according to osmotic gradients
Water moves from lesser osmolality to greater osmolality (concentration)
Electrolytes have greatest ability to cause fluid shifts
Nonelectrolytes
Chemical compounds with covalent bonds that prevent them from dissociating in solution
Not electrically charged
Most are organic molecules (glucose, lipids, creatinine, urea)
Fluid Movement
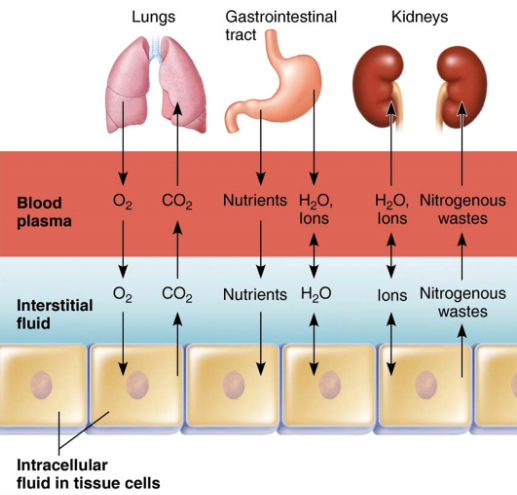
sources
of body water:
Typically 2500 ml per day
Ingested liquids and foods
Metabolic water (water of oxidation)- body water produced by cellular metabolism
Metabolic water
body water produced by cellular metabolism
routes
of water loss:
Insensible Water Loss
Vapor in expired air from lungs
Diffusion through skin
Sensible Water Loss (measurable)
Urine (60%)
Obvious sweat
Feces
Insensible
Vapor in expired air from lungs
Diffusion through skin
Sensible
Urine (60%)
Obvious sweat
Feces
regulation
of water intake/output:
Healthy people – osmolality of body fluids = 280-300 mOsm
Rise in plasma osmolality triggers thirst and release of ADH
Decline in plasma osmolality inhibits thirst and ADH release
Water and Na+ are closely tied together
Na+ acts as “water magnet”
Thirst and ADH mechanisms act independently of Na+
Thirst Mechanism
Driving force for water intake
Governed by hypothalamic thirst center
Osmoreceptors – detect ECF osmolality through changes in plasma membrane stretch
Dry Mouth – increase in blood osmotic pressures causes decrease in saliva production
Decrease in blood volume (or pressure) – signaled by baroreceptors
Collective cause of thirst sensation
Antidiuretic Hormone
Low ADH levels = most water not reabsorbed in kidneys = dilute urine = reduced volume of body fluids
High ADH levels = nearly all water is reabsorbed in kidneys = concentrated urine
Osmoreceptors of hypothalamus trigger or inhibit ADH release from posterior pituitary gland
Low ADH
most water not reabsorbed in kidneys = dilute urine = reduced volume of body fluids
High ADH
nearly all water is reabsorbed in kidneys = concentrated urine
Dehydration
fluid loss
Edema
accumulation of fluid in interstitial space leading to swelling