APHuG Unit 1.5 - Development
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Developing
with respect to a country, making progress in technology, production, and socioeconomic welfare
Developed
Advanced economic progress; high paying jobs and full infrastructure.
Infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures for a country. Roads, power, gas, water, sewage, etc.

Commodity Chain
series of links connecting many places of production and distribution, resulting in a commodity exchanged on the world market
Gross National Product
the total value of all goods and services produced by a country's economy in a given year whether or not they're in the country
Gross Domestic Product
the total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given year
Formal Economy
the legal economy that is taxed & monitored by a government and is included in a government's GNP
Informal Economy
economic activity that is neither taxed nor monitored by the government; not included in a country's GNP
Neo-Colonialism
the entrenchment of the colonial order, such as trade and investment, under a new guise. Previous colonial powers still wield power over former colonies.
Dependency Theory
a structuralist theory that offers a critique of the modernization model of development. Based on the idea that some politics/economic relations have created arrangements that control & limit how much a country develops
World-Systems Theory
originated by Immanuel Wallerstein and illuminated by his three-tier structure, proposing that social change in the developing world is inextricably linked to the economic activities of the developed world
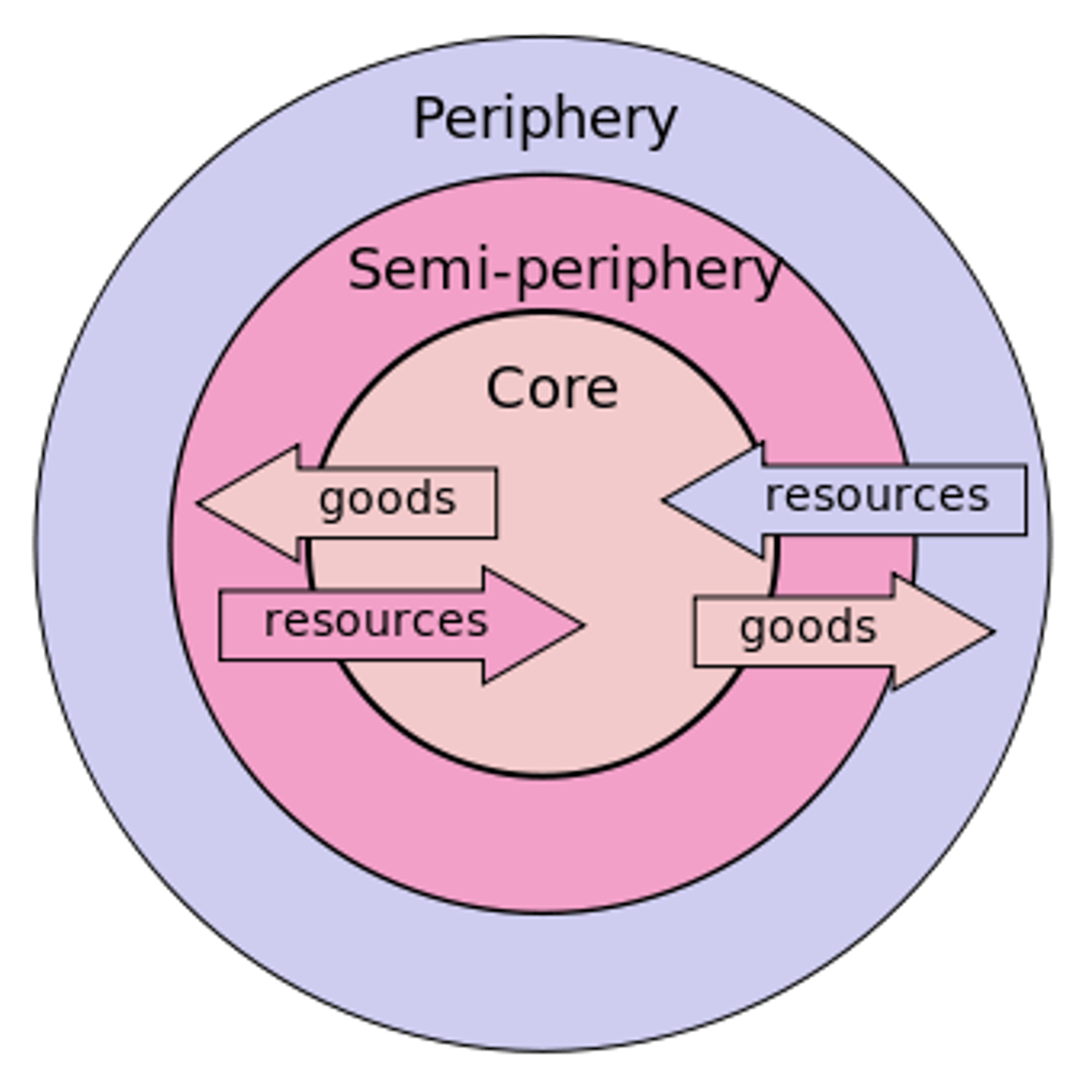
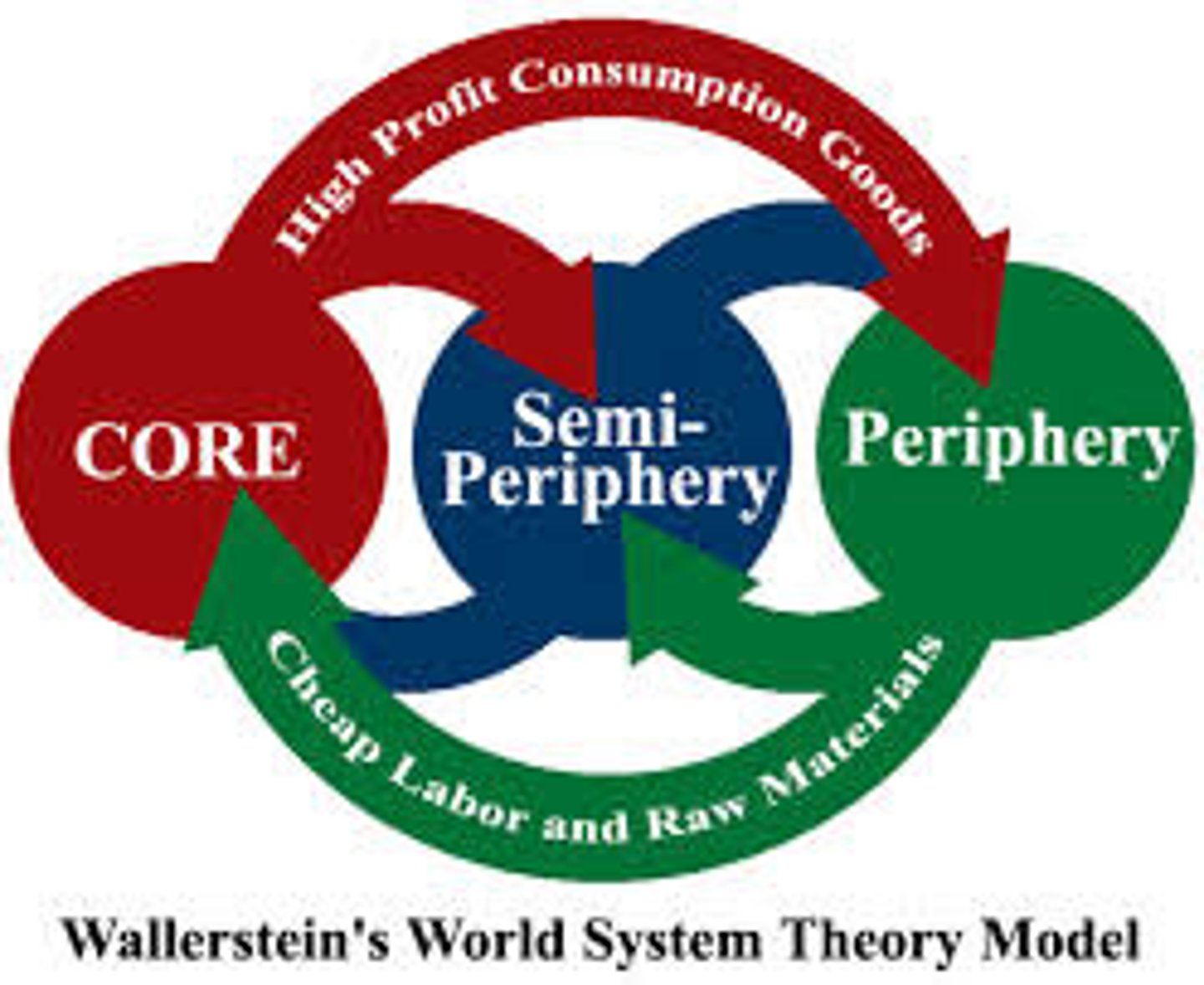
Three-Tier Structure
the division of the world into the core, the periphery, and the semi-periphery as a means to help explain the interconnections between places in the global economy
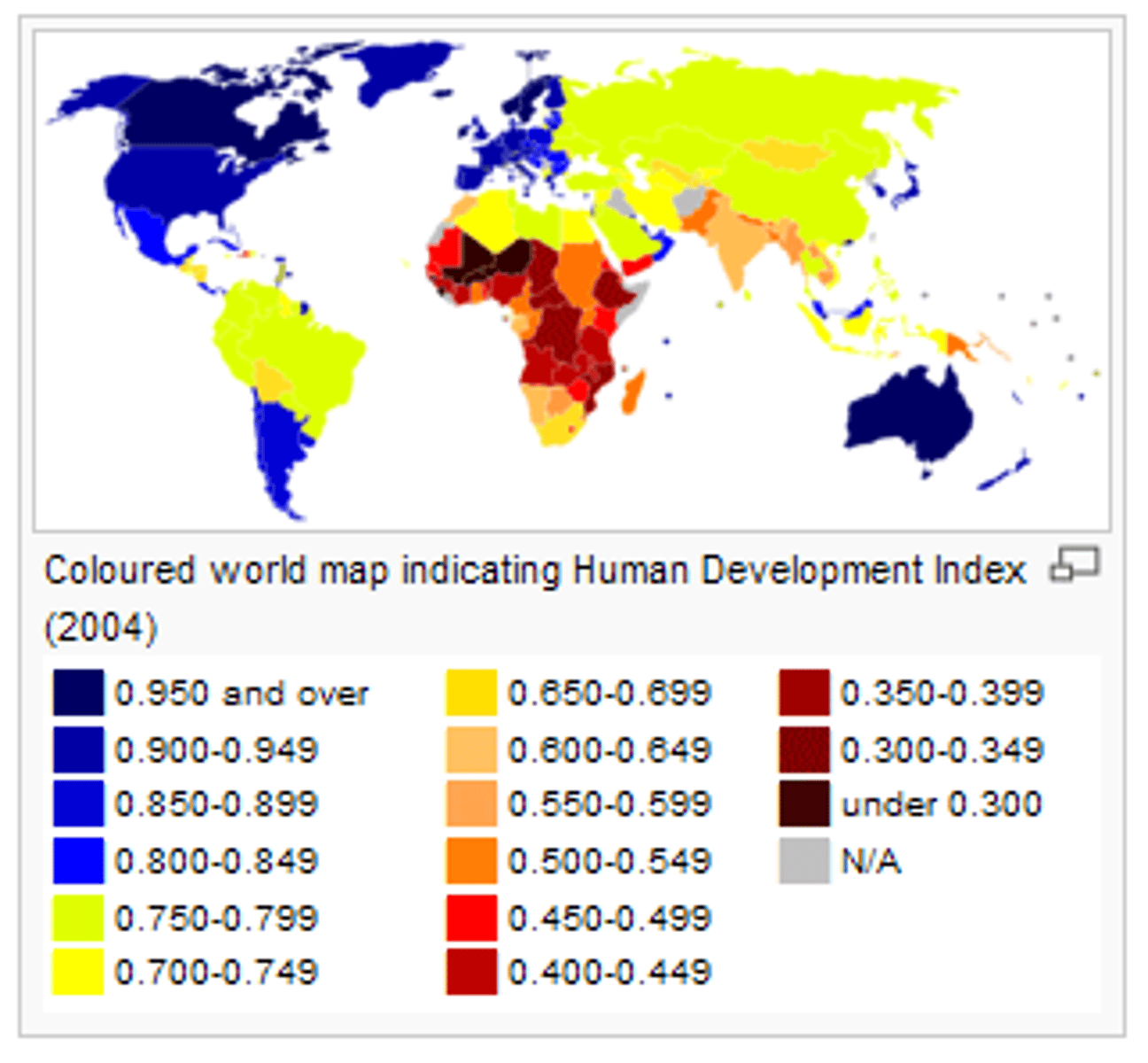
Human Development Index (HDI)
Indicator of level of development for each country, constructed by United Nations, combining income, literacy, education, and life expectancy
Gender Development Index (GDI)
An indicator constructed by the U.N. to measure the gender gap in the level of achievement in terms of income, education, and life expectancy.
Literacy Rate
The percentage of a country's people who can read and write - correlates to education and development rate.
Primary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with the direct extraction of materials from Earth's surface, generally through agriculture, although sometimes by mining, fishing, and forestry.

Secondary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with manufacturing useful products through processing, transforming, and assembling raw materials - Factories
Tertiary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with transportation, communications, and utilities, sometimes extended to the provision of all goods and services to people in exchange for payment.
Quaternary Sector
Jobs that deal with the handling and processing of knowledge and information.
Quinary Sector
Service sector industries that require a high level of specialized knowledge or technical skill. Examples include scientific research and high-level management with decisions affecting many people.
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology has transformed the process of manufacturing goods.
Industrialize
to change an economy to rely more on manufacturing and less on farming
Deindustrialize
a process of decreasing reliance on manufacturing jobs and switching to more service industry jobs.
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
The amount of money needed in one country to purchase the same goods and services in another country
Gini Coefficient
A measure of income inequality within a population, ranging from zero for complete equality to one if one person has all the income.
Gender Gap
A term that refers to the privileges afforded to males and females in a society.
Gender Inequality Index
A United Nations index, introduced in 2010, which measures a country's loss of achievement due to gender inequality, based on reproductive health, employment, and general empowerment.
Core Country
Countries that dominate trade, control the most advanced technologies, and have high levels of productivity within diversified economies.
Semi-peripheral countries
countries that supply sources of labor and raw materials to the core industrial countries and the world economy but are not themselves fully industrialized societies
Peripheral Country
A country that has a marginal role in the world economy and is dependent on core countries in its trading relationships.
Commodity
a raw material or primary agricultural product that can be bought and sold, such as copper or coffee.
Commodity Dependence
economic dependence on exports of agricultural and mineral raw materials --> ties a peripheral country to the needs of a core country
MDC
A country that has progressed relatively far along a continuum of development.
LDC
A country that is at a relatively early stage in the process of economic development