UAMS Hematology Lab Exam 3
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Normal range for PT
12.6-14.6 seconds (INR of 1)
Normal range for PTT
25-35 seconds
Normal range for Fibrinogen
220-498 mg/dL
Normal range for Thrombin Time
<21 seconds
Normal range for Bleeding Time
2-9 minutes
Normal range for Platelet Count
150,000-450,000 /uL
What factors are a part of the intrinsic system?
XII, XI, IX, VIII
What factors are a part of the extrinsic system?
III (tissue factor) and VII
What factors are a part of the common pathway?
X, V, II, I (and XIII?)
What tests test the common pathway?
PT, PTT, TT, and Fibrinogen
What are the vitamin K factors?
II, VII, IX, X
What are the consumable factors?
I, V, VIII, XIII
What factors are present in aged serum?
VII, IX, XI, XII
What factors are present in absorbed plasma?
I, V, VIII, XI, and XII
Factor I
fibrinogen
Factor II
Prothrombin
Factor III
tissue factor/thromboplastin
Factor IV
Calcium
Factor V
ProAcclerin/Labile Factor
Factor VII
Proconvertin, Stable Factor
Factor VIII
Antihemophilic factor (AHF)
What is VIII:C?
It is a smaller portion of the factor VIII molecule. It is also the coagulant portion of the molecule. A deficiency of this is termed Hemophilia A.
What is VIII:vWF?
It is a larger portion of the factor VIII molecule that serves as a carrier protein for VIII:C. This piece is necessary for platelet adhesion to collage.
- attaches collagen to glycoprotein IB on platelet surface.
What does the bleeding time, ristocetin aggregation, vWFR:Co, and vWF:Ag tests look like for Hemophilia A?
all normal
What does the bleeding time, ristocetin aggregation, vWFR:Co, and vWF:Ag tests look like for vWF disease?
all abnormal
What inheritance is Hemophilia A?
recessive, X-linked
What is the inheritance of vWF disease?
dominant, autosomal
What do platelet aggregation studies measure?
Measures primary aggregation and secondary aggregation when combined with various agonists such as ADP.
What does ADP do?
Encourages primary platelet aggregation, followed by a lag phase in which the platelets are undergoing shape change and secretion, followed by secondary aggregation. Abnormal ADP graph could indicate: Platelet membrane defect, aspirin use, or storage pool defect.
What does a normal platelet aggregation graph look like?
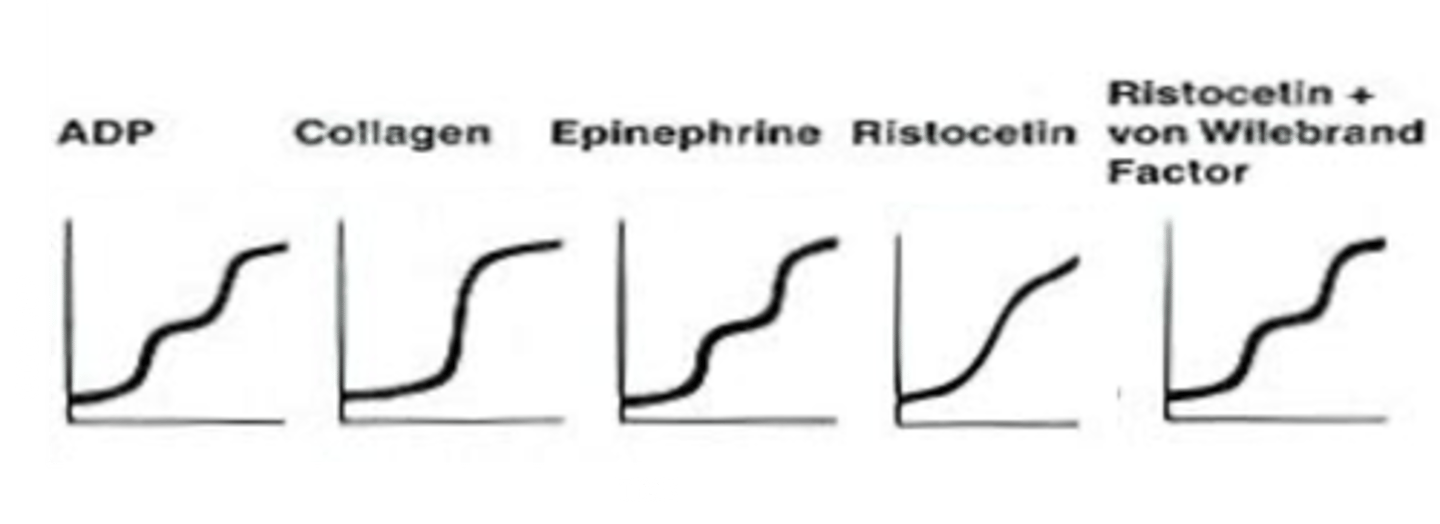

What does collagen do during platelet aggregation?
binds GPIa/IIa and GPVI but induces no primary aggregation.
What does an abnormal collagen graph indicate?
Aspirin use, storage pool defect, or release defect
What does epinephrine do during platelet aggregation?
binds to platelet receptors to activate platelets through the same pathway as ADP
What does an abnormal epinephrine graph indicate?
storage pool defect or membrane defect
What is ristocetin?
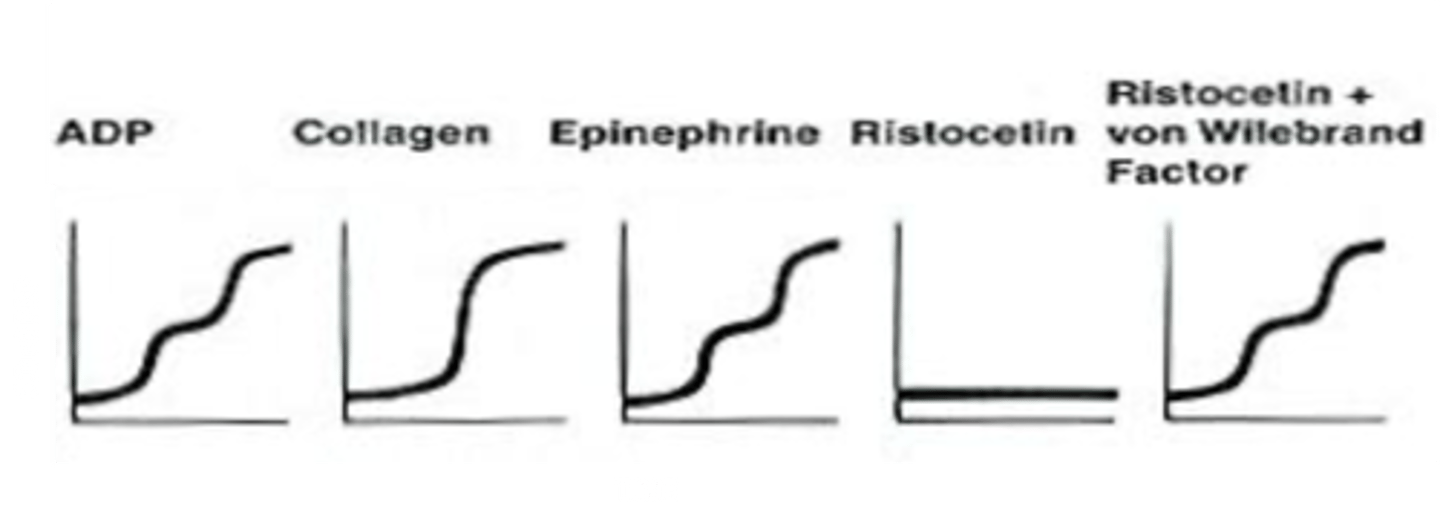
an antibiotic that encourages platelet aggregation in the presence of vWF. No aggregation will occur with ristocetin in vWF disease.
What happens when vWF and ristocetin are both present in vWF disease?
primary and secondary aggregation occur as normal
What does the platelet aggregation graph look like in vWF disease?
Notice there is no aggregation with ristocetin. Remember, ristocetin only allows for aggregation in the presence of vWF.

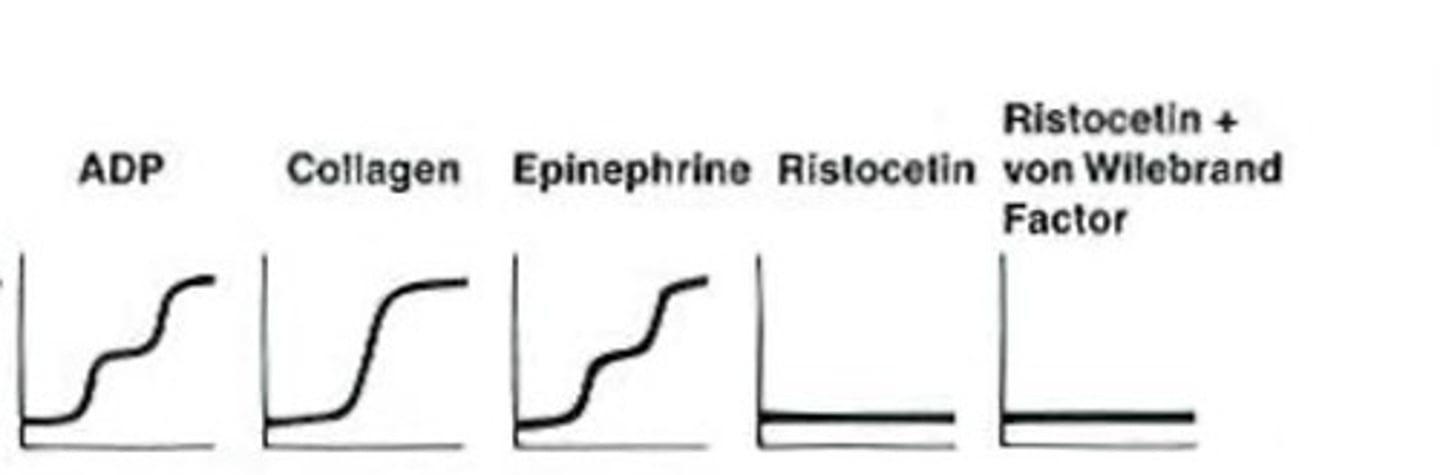
What does the platelet aggregation graph look like in Bernard Soulier Disease?
Bernard Soulier occurs when the GPIb complex is missing from the platelet surface.
- causes platelets to lack the ability to bind to vWF
- abnormal aggregation graph with ristocetin and ristocetin plus vWF
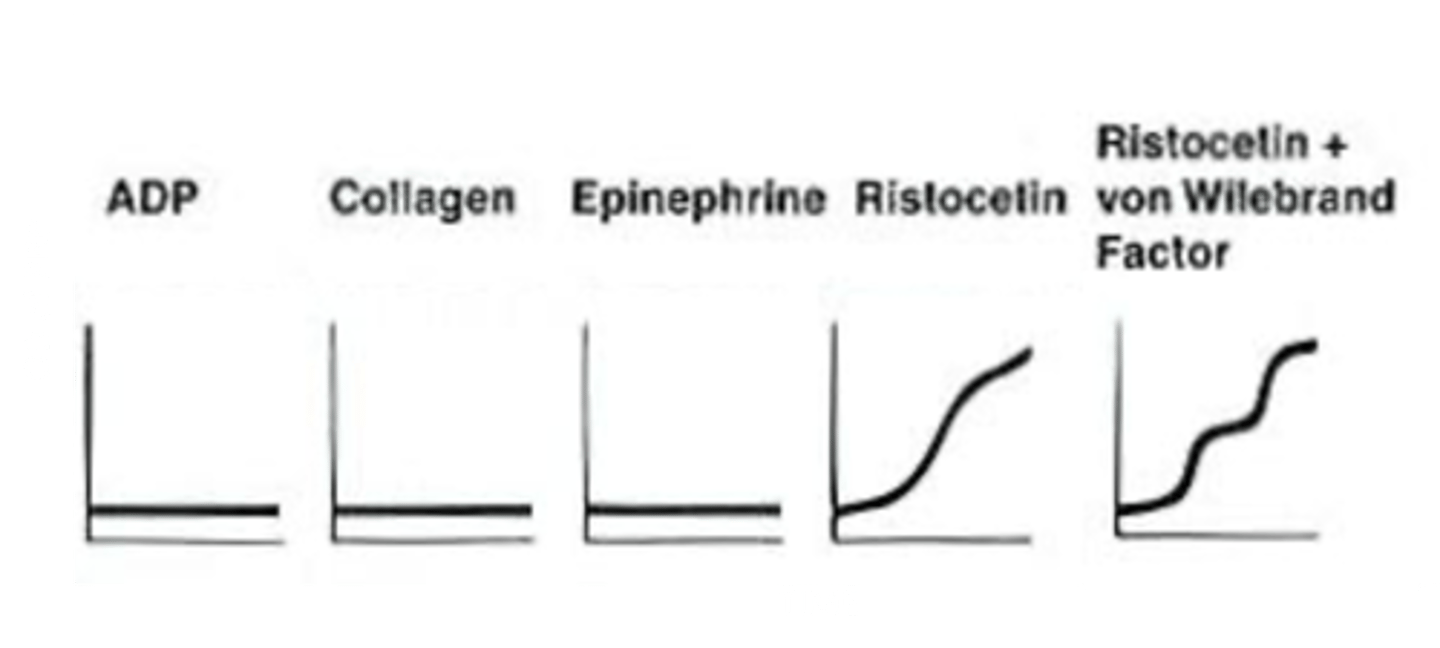
What does the platelet aggregation graph look like in Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia?
Defective platelet membrane GP IIb/IIIa.
- unable to bind to fibrinogen
- ristocetin has the ability to induce binding of vWF
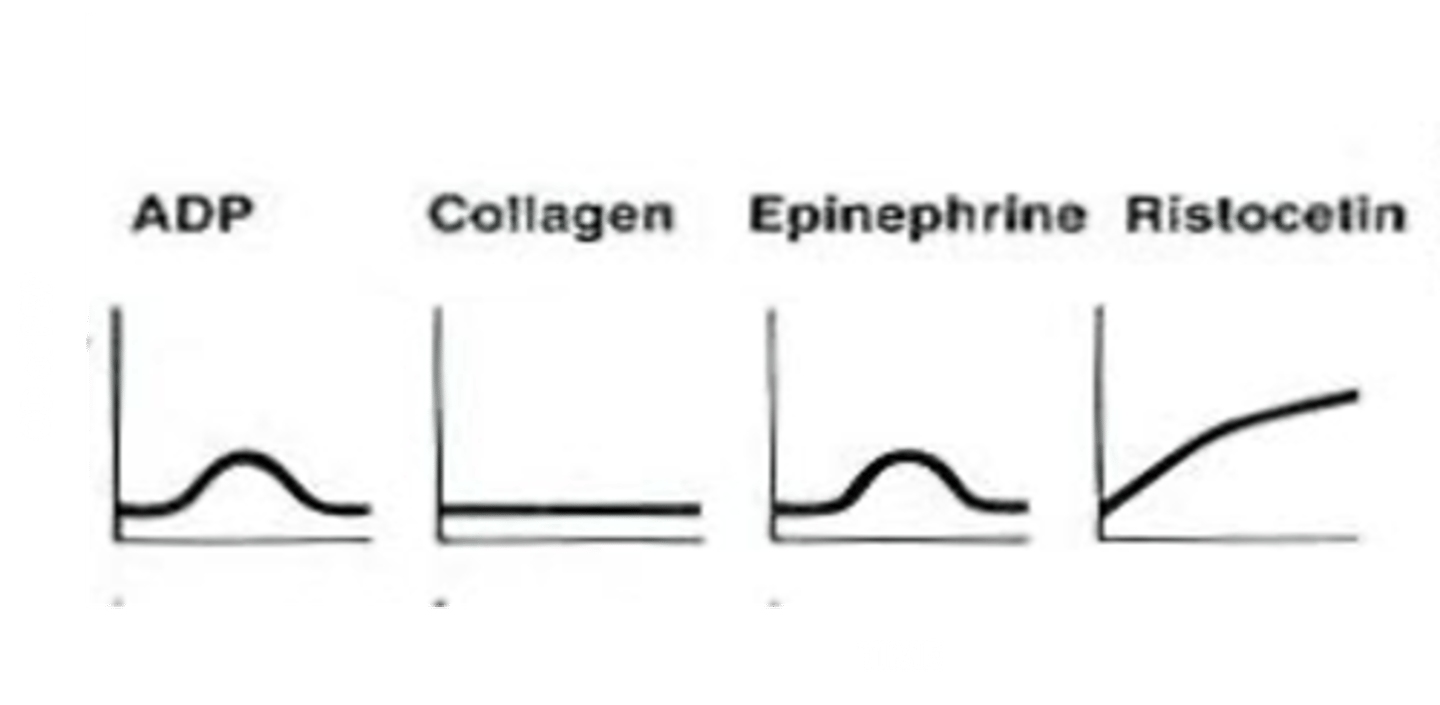
What does the platelet aggregation graph look like in Aspirin Ingestion/Storage Pool (alpha or dense granule) defect?
ADP and Epinephrine will initiate a primary aggregation, but secondary aggregation does not occur. Low dose of collagen is unable to induce aggregation.
What does aspirin do to platelet aggregation?
aspirin inhibits cyclooxyrgenase, which converts arachidonic acid into Thromboxane A2, which is needed for storage granule secretion to enable secondary platelet aggregation
Factor IX
Christmas factor
Factor X
Stuart-Prower factor
Factor XI
Plasma Antecedent
Factor XII
Hageman factor
What is factor XII deficiency associated with?
CLOTTING!
Factor XIII
Fibrin-stabilizing factor (FSF)
What test is used to detect Factor XIII deficiency?
urea solubility test
- clots from normal patients are stable for 24 hours in solution
- Factor XIII deficient clots will dissolve rapidly
What will the lab results look like in DIC?
- decreased platelets
- Schistocytes on PB smear
- prolonged PT and PTT
- prolonged bleeding time
- decreased fibrinogen
- increased FSP and D-dimer
What is Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)?
hyaline thrombi, composed of platelets and vWF, occurring in arterioles and capillaries
What is TTP caused by?
due to lack of ADAMTS-13 molecule that cleaves large vWF molecules.
What will lab results look like for TTP?
- decreased hemoglobin
- decreased platelets
- signs of hemolysis
- schistocytes on PB smear
- normal PT and pTT
- normal fibrinogen
- normal FSP and D-dimer
- associated with neurological manifestations
What is Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)?
an autoimmune disorder, results in platelet antibody formation and excess destruction of platelets
What do lab results look like for ITP?
- normal RBC morphology
- normal PT, PTT and Fibrinogen
- decreased platelet count
- prolonged bleeding time
- positive Platelet IgG Antibody Screen
What factors do protein C and S inhibit?
V and VIII
How is the protein C pathway activated?
by thrombin binding to thrombomodulin
What is anti-thrombin III?
serine protease inhibitor
What must heparin bind to in order to exert its anticoagulant effect?
anti-thrombin III
What is Factor V Leiden?
Mutated form of factor V that lacks cleavage site for deactivation by proteins C and S. Patient will be unable to stop the clotting process.
What are non-specific anticoagulant or antibody?
antibodies that are found in patients with auto inflammatory conditions (I.e. systemic lupus erythrematosus). Sometimes thought to be an antibody formed to receptors on the platelet membrane.
If patient plasma is mixed with normal plasma, and the PTT corrects, what is suspected?
Factor deficiency
If patient plasma is mixed with normal plasma, and the PTT does NOT correct, what is suspected?
Lupus anticoagulant or factor inhibitor
Hemophilia A
Factor VIII deficiency
Hemophilia B
Factor IX deficiency