Heat, Work, and Efficiency
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Heat
The act of transferring thermal energy from a body with hotter temperature to one with cooler temperature.
Temperature
The measure of the average kinetic energy of particles.
Heat Transfer
A process that occurs whenever there is a change in temperature. When energy is transferred from a high temperature object to a low-temperature object.
its always HOT → COLD.
What is thermal equilibrium?
When 2 objects have the same temperature, energy can no longer be transferred.
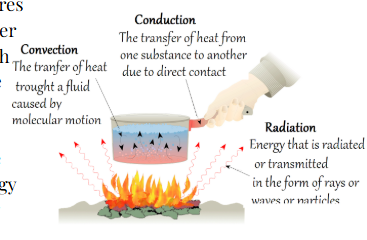
Modes of heat transfer
1) Conduction
Energy transfer between two objects of different temperature through DIRECT CONTACT
2) Convection
When energy is transferred through fluids moving from one location to another
3) Radiation
When energy travels through electromagnetic waves.
Heat and Work
Heat → Energy transfer
Work → Energy transferred when an object is moved against force
HEAT CAN DO WORK
Heat transfer can be used to do work, an example of this is cooking rice. When rice boils (this is convection), the cover may move upwards due to bubbles (this is where the work is done).
Heat Flow
Natural or spontaneous flow of heat
From a higher temp to a lower one. Used to do work where external energy is not required to happen
Non-spontaneous process
Heat flows from lower temp to higher. Work should be done on the system which requires mechanical energy.
Heat engines
This is a system that converts heat into work by taking heat from the reservoir, the hot body, to carry out work. There is a discharge of some heat to the sink, which is a cold body. Which is a “waste” of heat.
Thermal Efficiency: The ratio of the useful work done to the heat output.
We can only have 100% efficiency if there is no energy being wasted, but this is impossible. An example is an automobile’s internal combustion engine.
(Engines of a car are only 35% efficient. For every 100 joules of thermal energy produced, only 35 joules are used to move the car.)
Types of engines
External combustion engine
The combustion of fuel takes place externally. I.e. steam engine.
Internal Combustion engine
The combustion of fuel takes place inside. i.e. two stroke and four stroke petrol and diesel engine.