Bot-Lec (Sem-1) - Chapter 1: An Introduction to Botany
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
botany
the study of plants and plant life
botanikos
Greek for botanical
botane
Greek for plant/herb
medicine
closely linked with botany for hundreds of years
primitive medicine men and witch doctors
first people to specialize in botany
cellulose
plant cell walls
eggs and sperm; spores
two adult forms of plants
multicellular eukaryotes
plant cell type
photosynthetic autotrophs
plant mode of nutrition
sexual and asexual
plant reproduction
determinate and indeterminate
plant growth
oxygen + glucose
sunlight + carbon dioxide + water =
primary producer
plants' producer level
Genesis 1: 29-30
God created plants before man because of the need for man to breathe oxygen and for food.
Theobroma cacao
scientific name of the plant from which chocolate comes from

carbon cycle
the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back
carbon enters the atmosphere as CO2
carbon cycle step 1
CO2 absorbed by plants
carbon cycle step 2
animal consumes plants, incorporating carbon into their system
carbon cycle step 3
animal and plants die, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere
carbon cycle step 4
nitrogen cycle
the series of processes by which nitrogen and its compounds are interconverted in the environment and in living organisms, including nitrogen fixation and decomposition
nitrogen fixation
process of converting nitrogen gas into nitrogen compounds that plants can absorb and use
nitrogen assimilation
the incorporation of nitrogen into organic cell substances by living organisms.
nitrogen ammonification
soil bacteria, microbes & decomposers converting waste & dead biomass back into NH3 and returning it to soil
nitrification
the process by which nitrites and nitrates are produced by bacteria in the soil
denitrification
process in which fixed nitrogen compounds are converted back into nitrogen gas and returned to the atmosphere
plant anatomy; plant morphology; plant genetics; plant physiology; plant pathology; ecology; paleobotany
branches of botany
plant anatomy/phytotomy
study of internal plant structure
plant morphology/phytomorphology
study of external plant structure
plant genetics
study of plant heredity and variation
plant physiology
study of plant function
plant pathology/phytopathology
study of plant diseases caused by biotic and abiotic agents
plant ecology
study of the interactions between plants and the environment
paleobotany
study of plant fossils
molecular level; cellular, tissue, and organelle; community and population level
plant levels of study
molecular level
biochemical, molecular and genetic functions of plants
cellular, tissue, and organelle
the anatomy and physiology of plants
community and population level
involves interactions within a species, with other species and with the environment
photosynthetic
all plants are
leaves; fruit or flowers; stems; seeds
not all plants have
hunters/gatherers
early human cultures were
plant taxonomy
oldest branch of plant study; important for distinguishing edible and non-edible plants
8000-12000 years ago
when did agriculture start
Chinese; Egyptians; Assyrian; Inca; Mayan
ancient civilizations
Empedocles
believed that plants, like animals, had soul, reason, and common sense

Aristotle
classified organisms as plant or animal

Theophrastus
father of botany; pupil of Aristotle
Carolus Linnaeus
Swedish; father of taxonomy; binomial nomenclature

Carl von Linne
birth name of Carolus Linnaeus
binomial nomenclature
the system of nomenclature in which two terms are used to denote a species of living organism, the first one indicating the genus and the second the specific epithet
bryophytes
nonvascular land plants
tracheophytes
vascular land plants
spermatophytes
seed plants
gymnosperms
a plant that produces seeds that are exposed rather than seeds enclosed in fruits
angiosperms
flowering plants that produce seeds in fruit
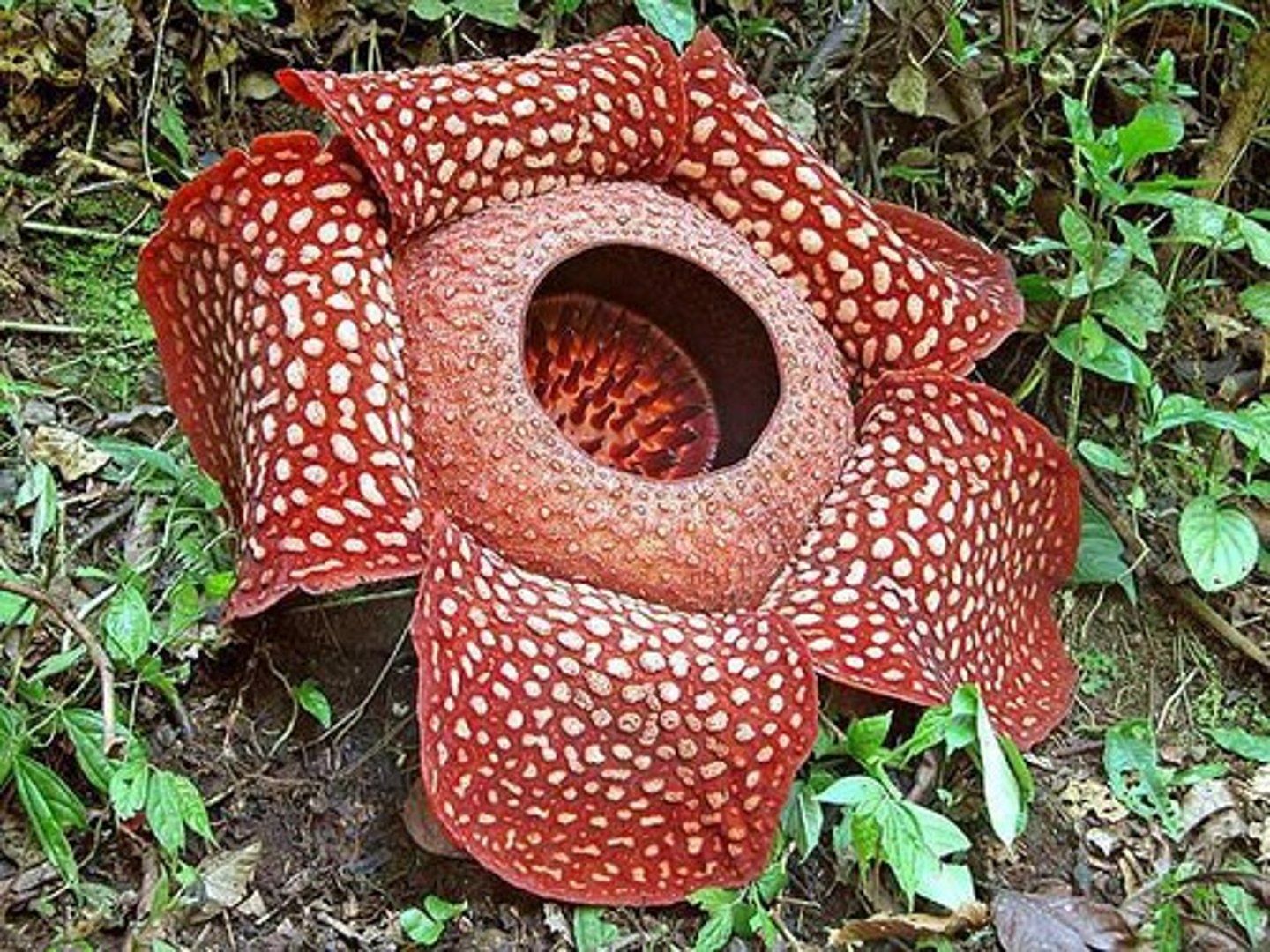
Raflessia
largest bloom in the world (~1 m)

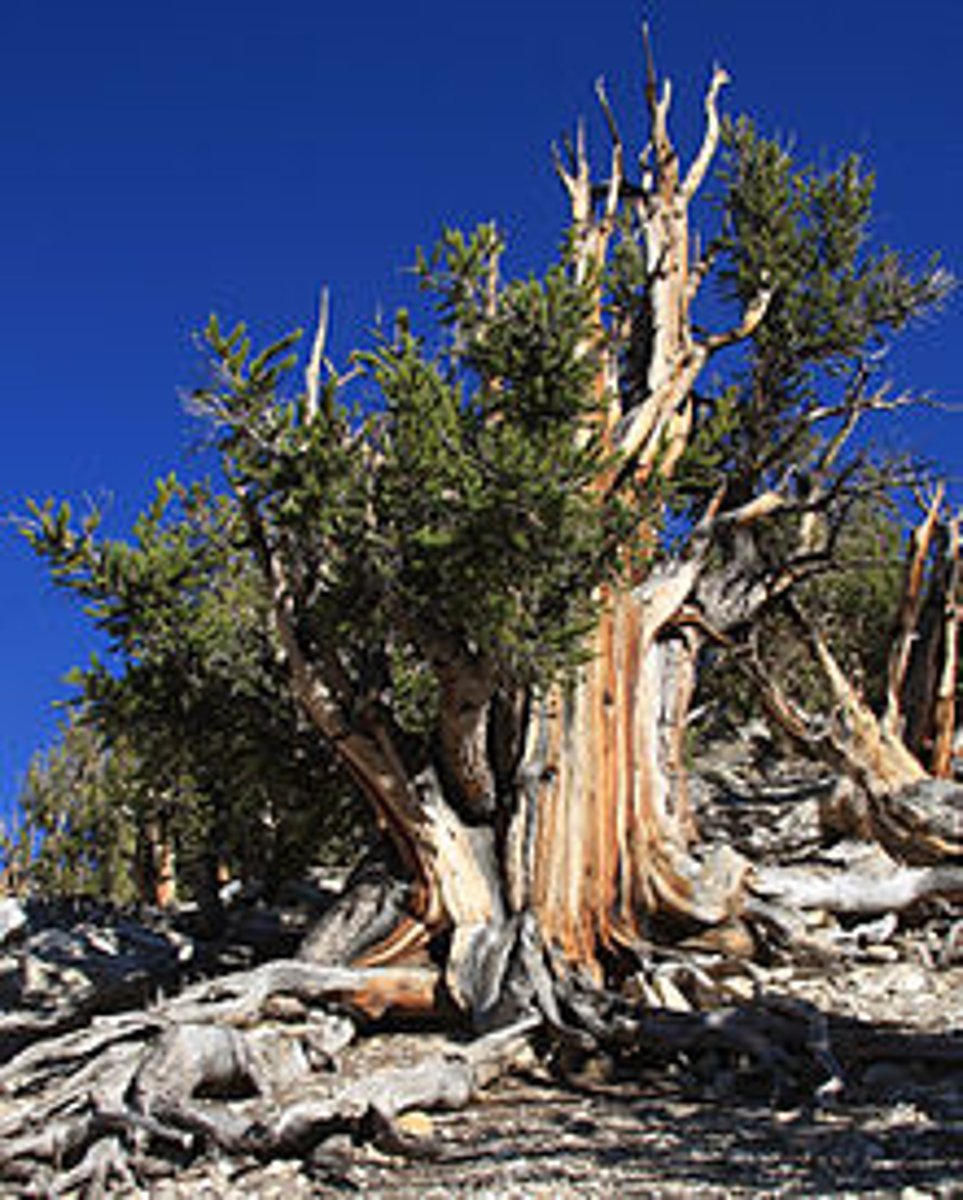
Pinus longaeva
Great Basin bristlecone pine; longest living tree in the world (~5000 years)

Sequoiadendron giganteum
giant sequoia; longest tree in the world (~100 m)

Passiflora
passion flower

oxygen
plants produce most of the ______ we breathe
Joseph Priestley
recognized that an animal's breathing "injured" air, while plants "restore air"; he conducted two experiments wherein he trapped a mouse in one sealed container and trapped another mouse in a different container, although the second one had a plant; the mouse with the plant survived longer

photosynthesis
process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches
vitamin A; vitamin C; vanillin; caffeine; morphine
plants can produce an amazing assortment of chemicals
vitamin A
supports the overall health of the skin; aids in the health, function, and repair of skin cells; has been shown to improve the skin's elasticity and thickness
vitamin C
an important substance needed for proper repair of the skin and tissues; promotes the production of collagen in the skins dermal tissues; aids in and promotes the skins healing process
vanillin
vanilla
caffeine
a mild stimulant found in coffee, tea, and several other plant-based substances
morphine
narcotic drug derived from opium, used to treat severe pain
cork
cells were first observed in
Robert Hooke
first to observe "small chambers" in cork and call them cells.

Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
first virus discovered and first virus purified
Dmitri Ivanovsky
discovered viruses
Nicotania tabacum
tobacco; first plant to be purified of virus
Gregor Mendel
Austrian Augustinian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to his eventual recognition as founder of the science of genetics (1822-1884)
law of inheritance
foundation of plant genetics and breeding
Pisum sativum
garden pea; species used in Mendel's study of peas
sickle cell anemia
a genetic disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in some red blood cells assuming an abnormal sickle shape
Norman Borlaug
Father of the Green Revolution; distinguished plant breeder, 1914-2009
Coffea arabica
coffee plant; provides for non-intoxicating social interactions; produces caffeine
25 million
number of coffee producing family farms
$65 billion
retail US sales of coffee in 2001
wines
an alcoholic drink made from grapes or other plants; dark red color

endothelin-1
chemical produced by cells in the walls of blood vessels; high concentrations can constrict blood vessels which can lead to heart disease
Roger Corder
he and his colleagues at the Queen Mary, University of London, set out to test whether drinking red wine might inhibit ET-1 production
polyphenols
in red wine; similar amount in red grape juice; not much in white or rose wine
spices
the bark, roots, seeds, buds, or berries of an aromatic plant.
$2 billion
retail sales of spices in the US in 1994
U.S.
largest provider and consumer of spices; largest floral producer
lycopene
natural compound; a pigment responsible for the red color of tomatoes and other red-hued vegetables;
yohimbine
natural compound; aphrodisiac, used for treating erectile dysfunction; derived from Pausinystalia johimbe
Pausinystalia johimbe
Yohimbe; plant that produces yohimbine compound
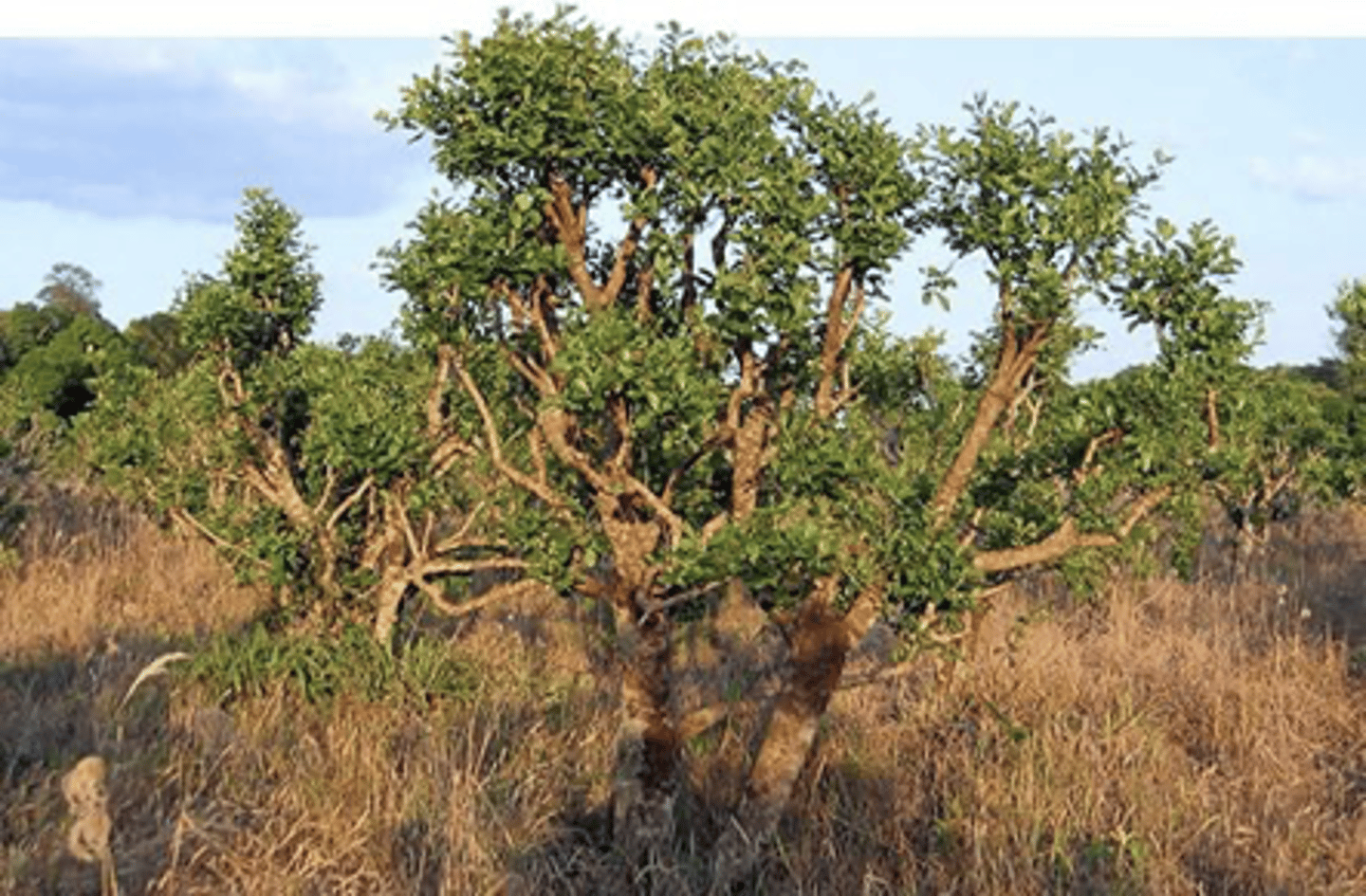

taxol
medicine; cancer drug; derived from Taxus brevifolia
Taxus brevifolia
Pacific yew tree; plant that produces taxol medicine
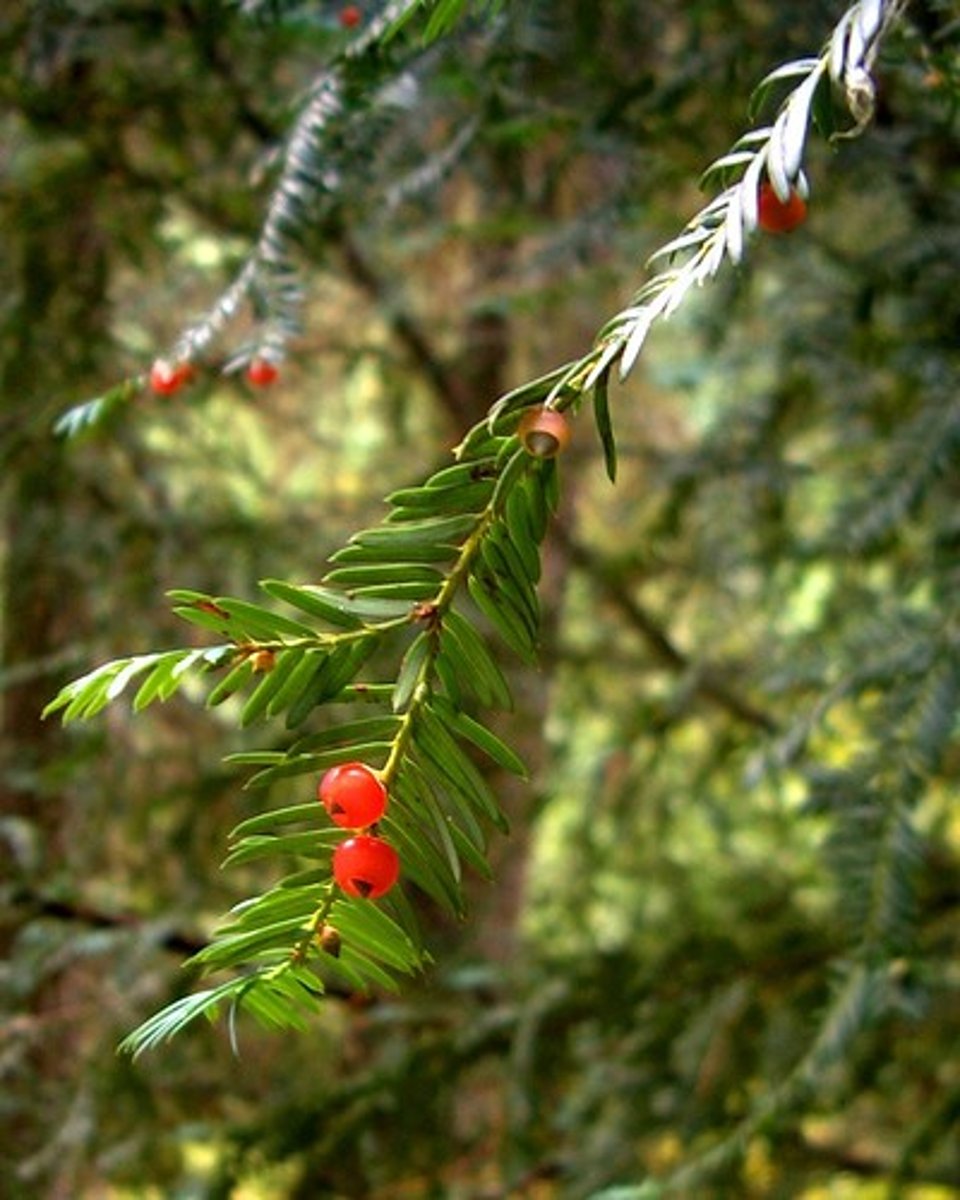

saponins
active plant constituents that produce a soap-like lather in water
ginseng
Panax; contains saponin; used for treating stomach and nervous disorders
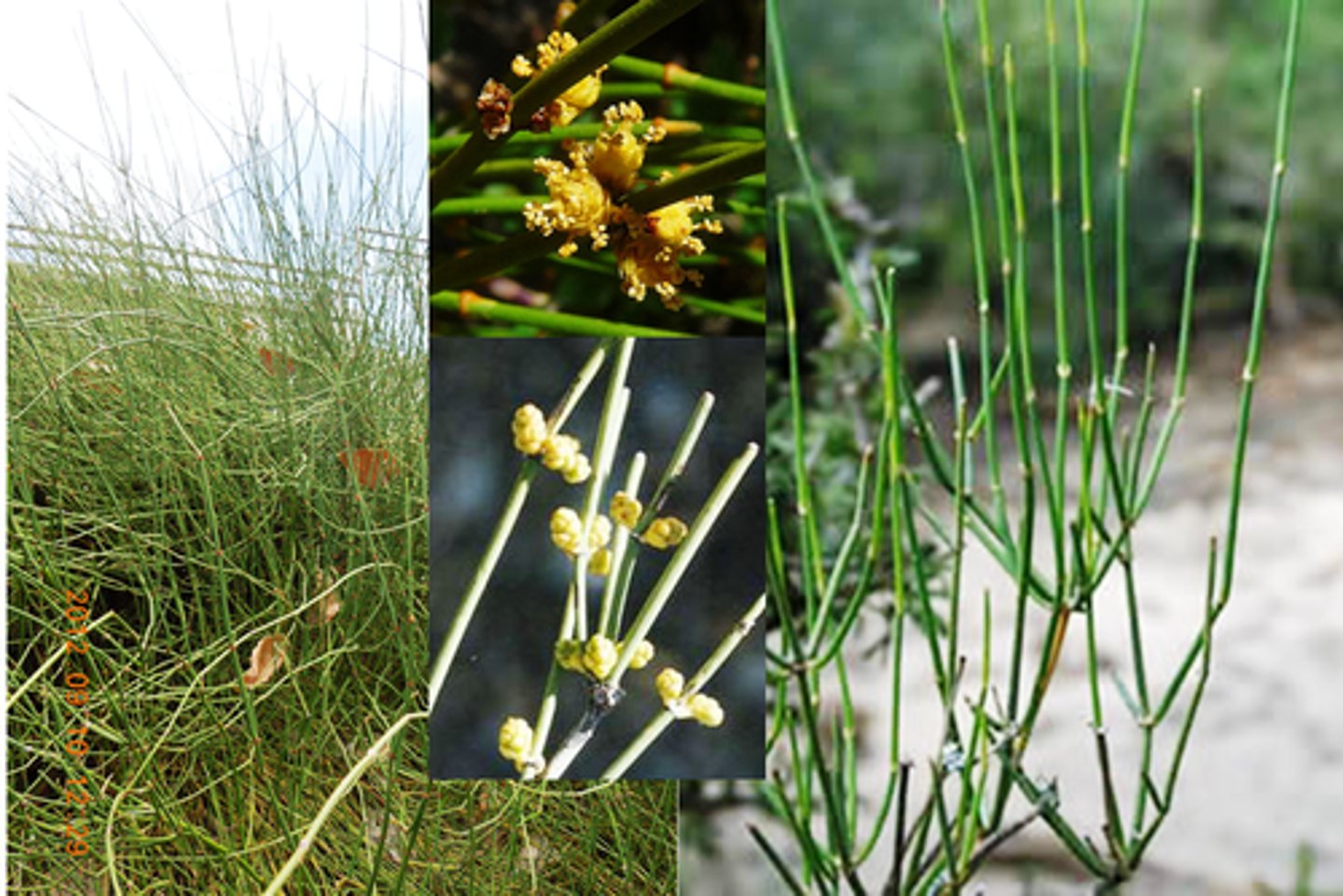
alkaloids
potent plant chemicals that contain nitrogen
ephedrine
alkaloid; cures hypotension; derived from Ephedra
Ephedra
Mormon tea plant; cures hypotension; produces ephedrine

quinine
alkaloid; used for treatment against malaria; derived from Cinchona
Cinchona
tree bark used for quinine (malaria treatment)
