Communicable diseases
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Active immunity
Resistance in an organism that developed through the production of specific antibodies in response to a pathogen
Draw the structure of an antibody
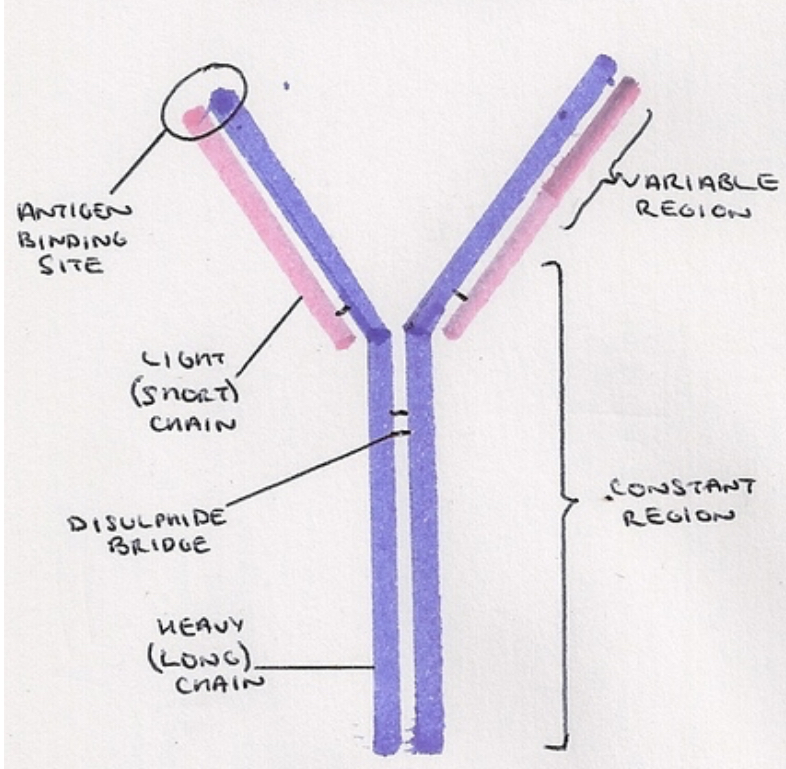
What is an antibody?
Y-shaped glycoprotein produced by B lymphocytes in response to an antigen
why is active immunity long lasting?
Memory cells are produced
Agglutinins
Chemicals that cause pathogens to clump together, allowing phagocytes to digest multiple pathogens at once
Antibiotic
A chemical or compound produced by a living organism that kills or prevents the growth of bacteria
How does bacterial resistance to antibiotics work?
Bacteria mutate to become resistant to an antibiotic, survive and reproduce very rapidly, passing on their antibiotic resistance
Antibodies
Immunoglobulins produced by B-lymphocytes in response to a specific antigen, triggering an immune response
Antigen
A chemical present on the surface of a cell that induces an immune response
Antigen-presenting cell
A macrophage captures an antigen and presents it to T cells
Artificial active immunity
The production of antibodies by the immune system following the exposure to a weakened or dead pathogen
example of artificial active immunity
Vaccinations so organism produces its own antibodies
example of artificial passive immunity
antibodies from other organisms
Example of natural activity immunity
Normal immune response
Example of passive natural immunity
Mother to baby
State 3 differences between active and passive immunity
Active is exposed to antigens, passive is not exposed to antigens
Passive only B memory cells active, active both B and T lymphocytes
Active protection is long term, passive short term
Artificial passive immunity
The immunity acquired from the administration of specific antibodies from another organism
Autoimmune disease
A condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue
Example of autoimmune diseases
Arthritis, lupus
Bacteria
Prokaryotic cells that have cell walls but lack organelles
How are pathogenic organisms harmful?
Produce toxins that damage host cells
B effector cells
A type of B lymphocyte that divides to form plasma cells
Black Sigatoka
A fungal disease in tomatoes, turning leaves black
B lymphocytes
Lymphocytes that mature in bone marrow
What are the 3 types of B lymphocytes?
Plasma cells, B effector cells and B memory cells
B memory cells
B lymphocytes that provide immunological memory
Callose
A plant polysaccharide that is deposited between the cell wall and cell membrane in cells adjacent to infected cells, serving as a defence against pathogens
Clonal selection
The identification of an antibody-producing cell with complimentary receptors to the shape of a specific antigen
Communicable disease
A disease that is caused by a pathogen and transmitted directly between organisms
Cytokines
Cell-signalling molecules produced by mast cells in damaged tissue, attracting white blood cells to the site of damage
Direct transmission
The transfer of a pathogen directly from one organism to another
Epidemic
a rapid rise in the incidence of a communicable disease at a local or national level
Expulsive reflexes
Coughs or sneezes initiated upon irritation of the respiratory tract
What is the purpose of expulsive reflexes?
They remove microorganism-containing mucus from the gaseous exchange system
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms that may cause disease
What do fungi do that can cause diseases?
Digest and destroy cells, and produce spores that can spread rapidly between organisms
Histamine
A chemical produced by mast cells in damaged tissue, making blood vessels dilate and cause their walls to become leakier
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
An infectious virus that destroys T helper cells, weakening the immune system of the body
Indirect transmission
The transfer of a pathogen indirectly between organism
How can diseases spread via indirect transmission?
Fomites, vectors or soil contamination
Inflammation
A localised response of vascular tissue to pathogens, damage or irritants
Influenza
A common infection caused by viruses that destroy ciliated epithelial cells in the gaseous exchange system, exposing airways to secondary infection
Interleukins
Cytokines produced by T helper cells that stimulate B cells
Lymphocytes
White blood cells that contribute to the specific immune response
Lysosome
A membrane-bound organelle that contains hydrolytic enzymes
Malaria
A disease caused by protoctist Plasmodium that lives within two hosts, mosquitoes and humans
Mast cells
Specialised cells in connective tissue that are important in the inflammatory response
Which chemicals do mast cells release?
Histamines and cytokines
Natural active immunity
The production of antibodies by the immune system following infection
Natural passive immunity
The immunity acquired by an infant when antibodies are transferred through the placenta from the mother
Non-specific defences
Defences that are always present and are the same for all organisms
Examples of non-specific defences
Skin, blood clotting, inflammation, mucous membranes and expulsive reflexes
Mucous membranes
The membranes lining body cavities that secrete a sticky mucus
Opsonins
Chemicals that bind to and tag foreign cells, making them easily recognisable to phagocytes
Passive immunity
Resistance in an organism acquired via the transfer of antibodies
Why is passive immunity short-term?
No memory cells are produced
Pathogen
A disease-causing microorganism
What kinds of microorganism can pathogens be?
Bacteria, viruses, fungi or protoctista
Penicillin
The first conventional, effective and safe antibiotic
Personalised medicine
A form of medical care that enables doctors to provide healthcare that is customised to an individuals genotype
Phagocytes
Specialised white blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens
What are the two types of phagocytes?
Neutrophils and macrophages
Phagocytosis
The process by which phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens
Phagolysosome
A vesicle within within a phagocyte formed by the fusion of a phagosome and lysosome
Phagosome
A vacuole inside a phagocyte in which a foreign particle is engulfed
Plasma cells
B lymphocytes that produce antibodies specific to a particular antigen
Potato blight
A disease caused by protoctist causing collapse and decay of the leaves, fruit and tubers
Primary immune response
The response of the immune system to a pathogen when it is first encountered
How many antibodies and how quickly are they produced during the primary immune response?
A small number and slowly
Ring rot
A bacterial disease in tomatoes and potatoes that results the leaves, fruit and tubers
Secondary immune response
The response of the immune system to a pathogen when it is encountered for a second or more time
How many and how quickly are antibodies produced during the secondary immune response?
Lots of antibodies, rapid production
Synthetic biology
The design and construct of new biological entities, as well as the reconstruction of pre-existing natural biological systems
T helper cells
T lymphocytes with CD4 receptors on the cell surface membrane, which bind to antigen-presenting cells and secrete interleukins
T killer cells
T lymphocytes that produce perforin, destroying pathogens with a specific antigen
T lymphocytes
Lymphocytes that mature in the thymus gland
What are the 4 types of T lymphocyte?
Helper, killer, regulator and memory
T memory cells
T lymphocytes that provide immunological memory
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
A virus that infects many species of plants, damaging the leaves, flowers, and fruit
T regulator cells
T lymphocytes that regulate the immune response by suppressing other T cells and maintaining tolerance to self-antigens
Tuberculosis (TB)
A bacterial disease that damages lung tissue and weakens the immune system
Vector
A living or non-living agent that transmits a pathogen between organisms
Viruses
Non-living infectious agents that invade host cells and take over cell metabolism, replicating within them
Describe the stages of phagocytosis
Phagocyte recognises antigen as foreign
cell membrane of phagocyte fuses around pathogen, engulfing into a vesicle
A lysosome fuses with the vacuole and empties its digestive enzymes to digest/hydrolyse the microorganism
What extra step of phagocytosis happens in macrophages?
Antigens are presented on the cell surface membrane
Useful products are taken to the cytoplasm and wasted products exocytosed