Organization of the Nervous System
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Dorsal
upper side/Back
ventral
bottom side/stomach side
anterior/rostral
towards head
posterior/caudal
towards tail
medial
closer to middles
lateral
closer to side
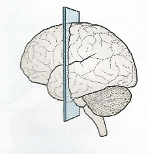
sagittal plane
down middle
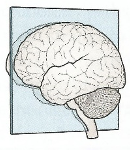
axial plane
top and bottom
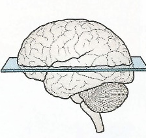
coronal plane
front and back
ipsilateral
same side
contralateral
opposite side
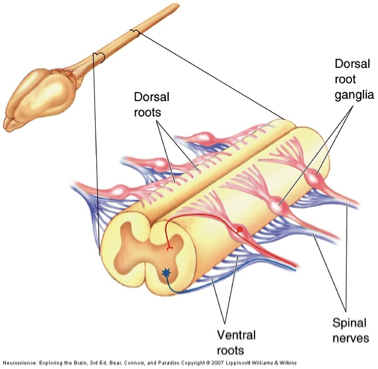
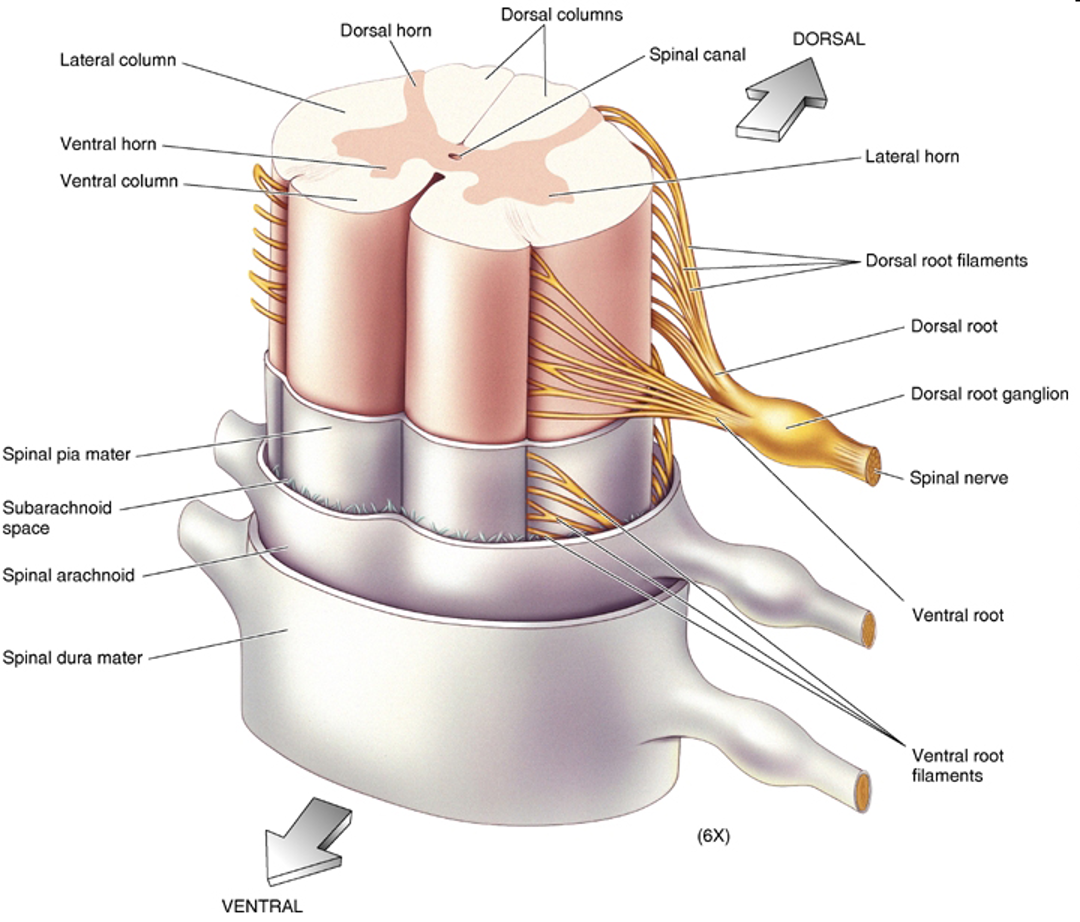
Spinal cord components
dorsal root
somatic and visceral sensory afferents
Dorsal root ganglia
somas of sensory afferents
ventral roots
somatic and visceral motor (efferents)
spinal nerves
mixed
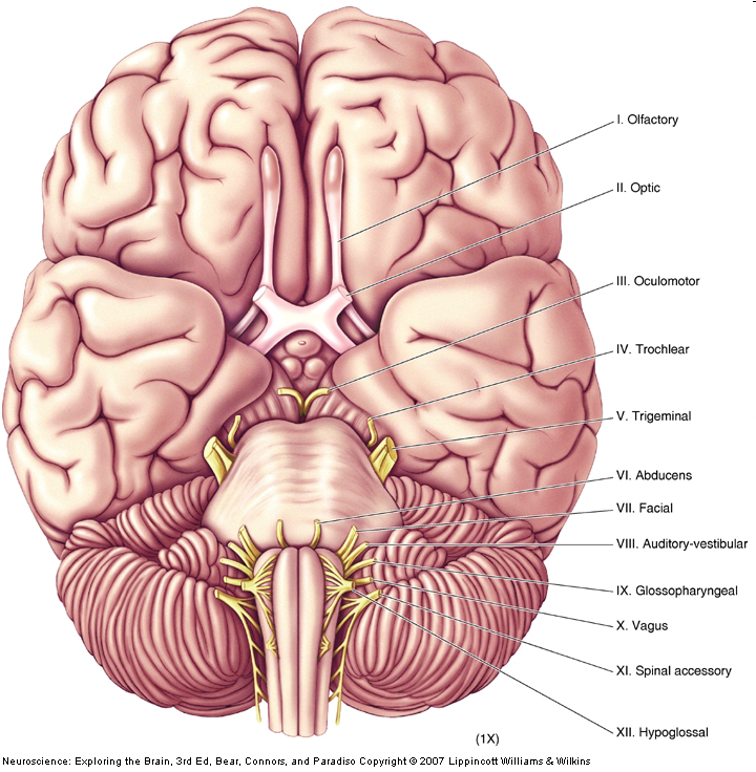
Cranial nerves
12
mostly innervate the head
axons from CNS, somatic PNS, visceral PNS
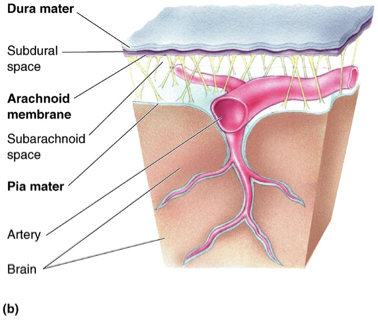
meninges
3 membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
dura mater
arachnoid trabeculae
pia mater
subarachnoid space
CSF circulates in after coming from ventricles
blood vessels
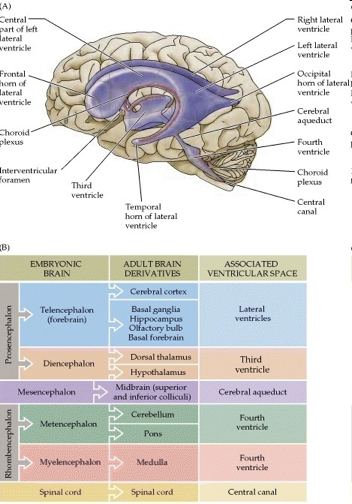
ventricular system
ventricles and CSF
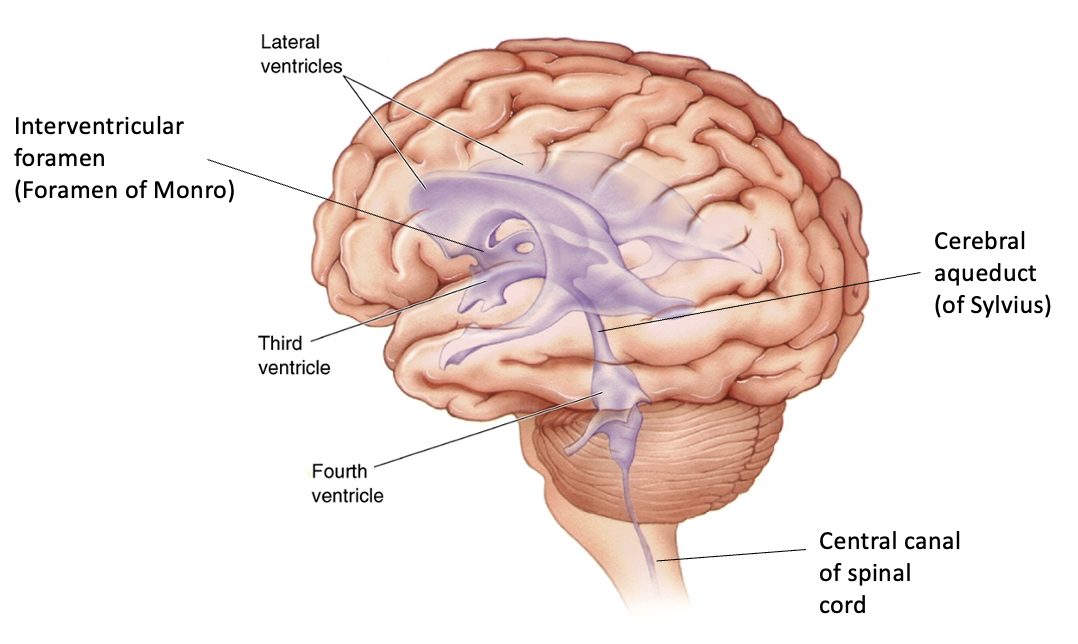
ventricles
cerebrospinal fluid-filled caverns and canals inside brain
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
produced by choroid plexus in ventricles
protects brain by cushioning it
conduit for hypothalamic peptide hormones
circulates through ventricles → subarachnoid space → reabsorbed in arachnoid villi and arachnoid granulations into venous sinuses
dura mater
tough outermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord
periosteal layer
meningeal layer
superior sagittal sinus
on the outer surface of the brain that collects blood from the brain's superficial veins and drains it into the transverse sinuses
choroid plexus
specialized ependymal cells surrounding capillaries in ventricles that produce CSF

subdural hematoma
trauma damages tiny veins within the meninges
Blood accumulates rapidly, causing pressure to rise within the brain
Results in loss of consciousness, paralysis or death

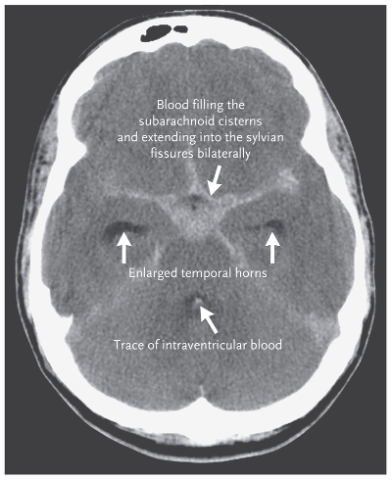
subarachnoid hemorrhage
sudden bleeding into the subarachnoid space (csf mixes with blood)
Symptoms include sudden, severe headache, usually with loss or impairment of consciousness.
frequently a sign of a ruptured aneurysm
MRI over CT
more detail
doesn’t require x rays
uses info on how hydrogen atoms respond in the brain to perturbations of a strong magnetic field
Functional MRI
active neurons have increased blood flow
detect changes in regional blood flow and blood O2 in the brain
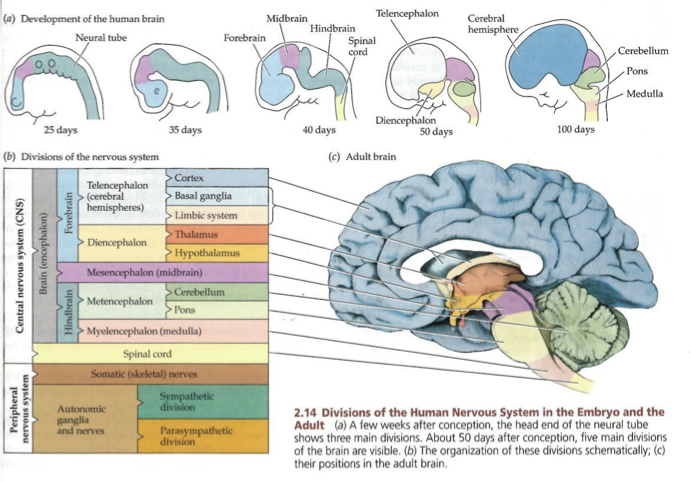
CNS development
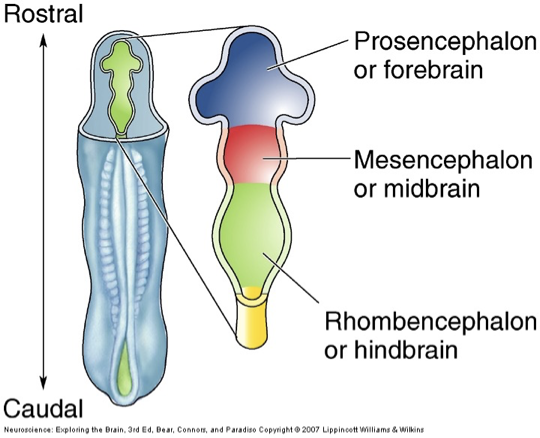
forms from walls of a fluid filled neural tube
inside of the tube becomes ventricular system
rostral → prosencephalon of forebrain
mesencephalon/midbrain
caudal → rhombencephalon of hind brain
neural tube development
5 major divisions of brain, development
differentiation
process by which structures become complex and specialized
ex. retina derived from forebrain
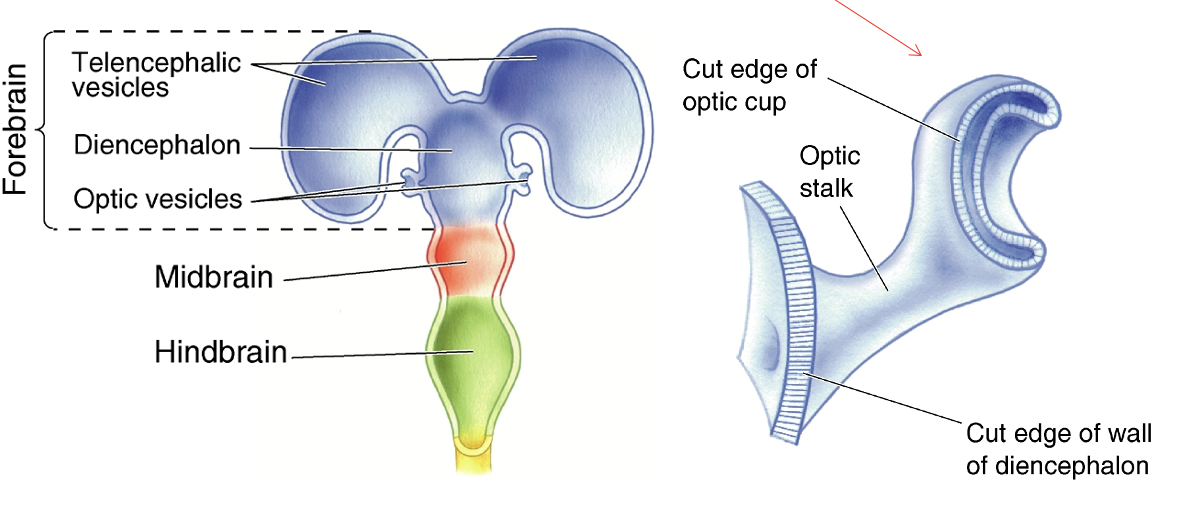
Brain derivation chart
Forebrain structural features
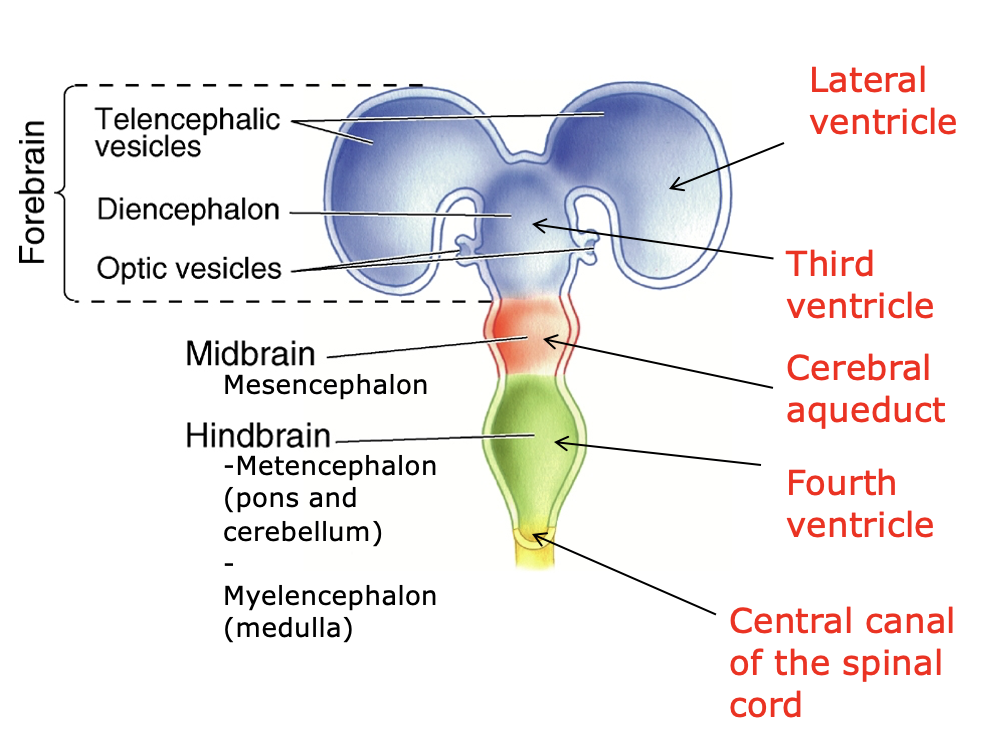
telencephalon
diencephalon
telencephalon
cerebral hemispheres
olfactory bulbs
basal telencephalon (forebrain)
hippocampus
basal ganglia
amygdala
lateral ventricles
diencephalon
thalamus
hypothalamus
third ventricle
cerebral cortex
analyze sensory input and command motor output
thalamus
gateway to the cortex
axons from thalamus to cortex pass through the internal capsule
carry info from contralateral (opposite) side of the body

hypothalamus
controls
autonomic nervous system
endocrine system
homeostatic behaviors (Eating, drinking)
midbrain structure-function relationships
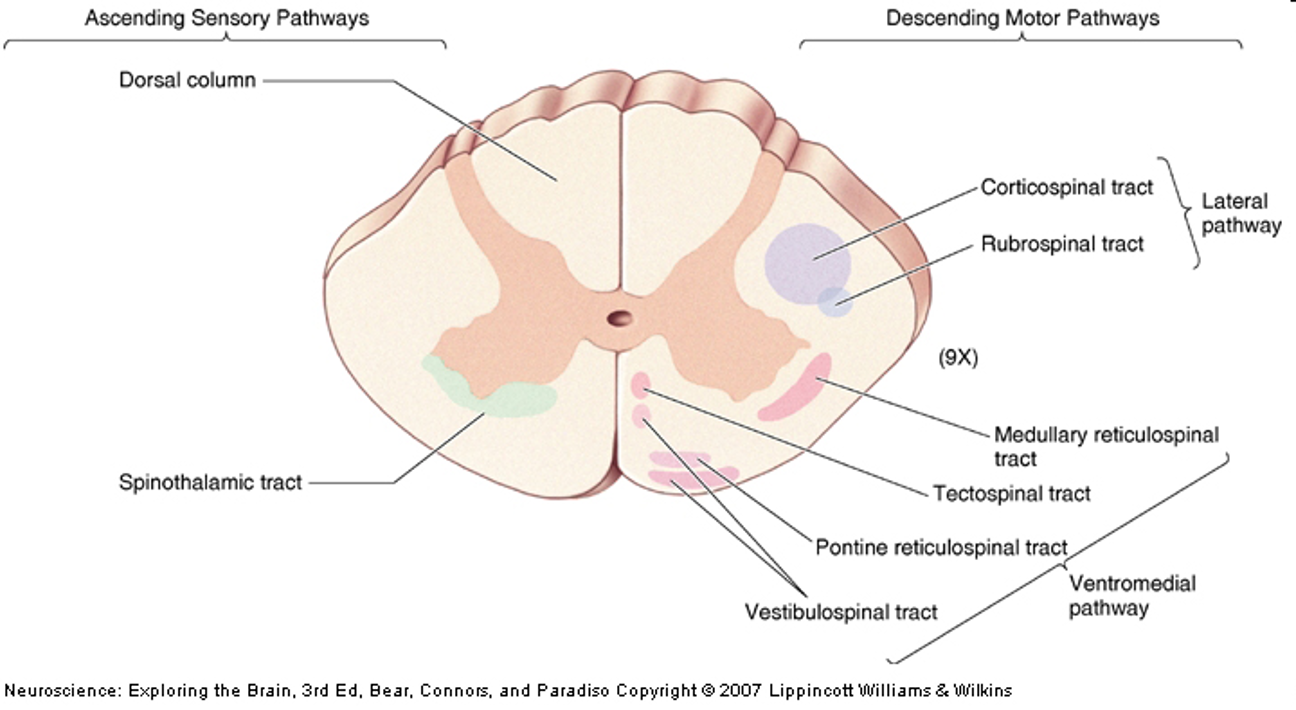
descending axons
descending from cortex to brain stem and spinal cord, motor systems
ex. corticospinal tract: motor cortex to spinal motor neurons
ascending axons
info conduit from spinal cord and brainstem to forebrain, sensory system
tectum
superior colliculus (sensory info from eye)
inferior colliculus (sensory info from ear)
tegmentum
substantia nigra - part of basal ganglia
red nucleus - control voluntary movement
origin of rubrospinal tract
pons
pontine nuclei receive inputs from corticospinal tract axons
relays info to contralateral cerebellum
cerebellum
coordination of movements
corticospinal fibers
continue toward the spinal cord in medullary pyramids
spinal cord
ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) spinal tracts
types of cerebral cortex
neocortex
archicortex
paleocortex
neocortex
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal lobes
in mammals
6 layers
brodmann’s areas: 52 areas that differ in cytoarchitecture
evolution:
amount of cortex has changed but not the structure
primary sensory areas, primary motor area
expansion of secondary (association) areas
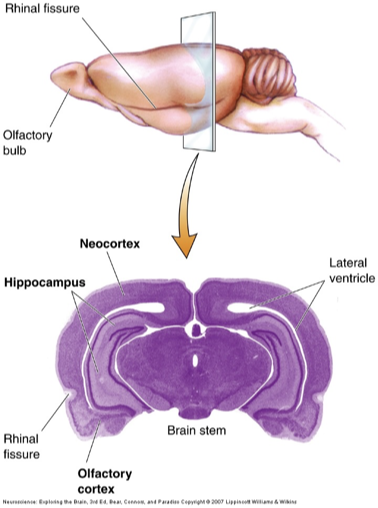
archicortex
hippocampus
paleocortex
olfactory cortex/piriform lobe
separated from neocortex by rhinal fissure
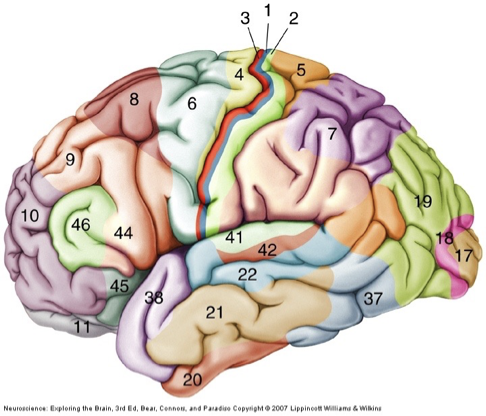
Primary motor cortex
M1, area 4
initiation of complex voluntary movement
Supplementary motor area (SMA) and premotor area (PMA)
area 6
motor planning
Parietal-Temporal-Occipital association cortex
analysis of sensory inputs
constructs representation of our sensory world
prefrontal association cortex
executive function
abstract thought
decision making
anticipating consequences of action