3.2 Inflation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Inflation
Sustained increase in general price level
Deflation
Sustained decrease in general price level
Disinflation
When inflation occurs at a lower rate. Prices are still increasing, but at a slower rate
CPI
Measures cost of living for typical households, comparing value of a ‘basket of goods+services‘ from 1 year to the base year.
Inflation Rate
Change in CPI divided by initial CPI
Limitations of Inflation Rate
CPI may not entirely reflect consumption patterns of households
Cannot account for discounts sales
Cannot account for new products/substitutes
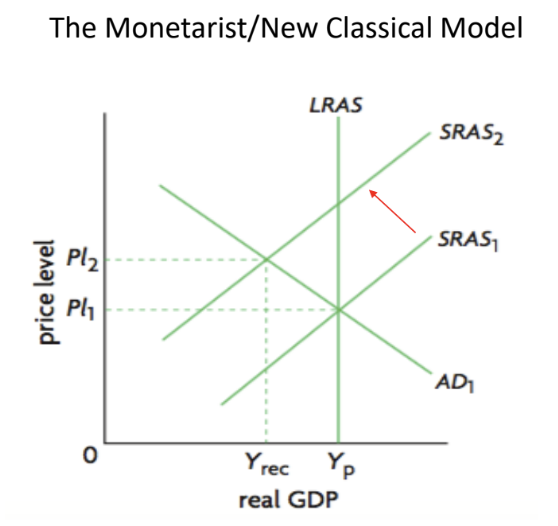
Cost Push Inflation
Caused by increase in COP, cuasing a fall in AS (aka Stagflation)
Only occurs in Monetarist Model
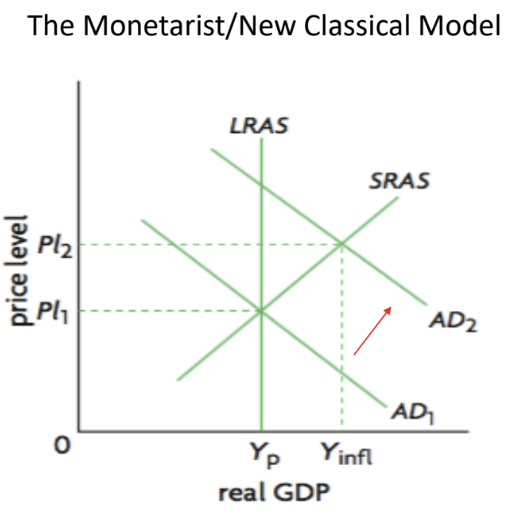
Demand Pull Inflation
Caused by excess AD in the economy (inflationary gap)
Purchasing Power
Quantity of products which can be bought with money
Consequences of Inflation (FIREW)
Firms
Firms spend more money on menu costs
Firms may be cautious about making future investments due to fluctuating price levels
International Competitiveness
If domestic IR > foreign IR, our exports are relatively more expensive
Redistribution Effects
Pensioners, people on fixed wages lose out (typically low income households)
Hence government has to spend more $ on welfare for them
Effects on Economic Growth
(X-M) component
I component
Wage Price Spiral
Trade unions argue for higher wages for workers due to the higher cost of living
Firms comply, but their COP is higher, so they pass it on to consumers
Hence cost of living increases, spirals
Hyperinflation
When the price level increases by more than 50% per month
Deflationary Spiral
AD Falls
So price level falls
Firms lay off workers due to falling profits (from lower prices) + lower AD
Unemployment rises, consumers have less disp. income, so AD. falls