injury prevention
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
injury evaluation process
a logical, systematic process before giving care (WILL change)
anatomy
structure
physiology
function
biomechanics
the the body moves normally
pathomechanics
how the body moves abnormally (physiology goes wrong)
accurate evaluations require…
a systematic plan
inflammatory effects
body responding in a normal, healthy manner post injury
contralateral
opposite side
ipsilateral
same side, different place
bilateral
left and right (looking at both sides adds a degree of reference
etiology
using the healthy side to show movement to determine how injury happened, then think of anatomy (structure determines function)
purpose of etiology
allows for bilateral comparison
congenital
had since birth
chromobidity
something going on that’s abnormal that adds to a previous injury
most important step in injury evaluation model
history
7-step injury evaluation model (steps)
history
observation/inspection
(physical exam process)
palpation
range of motion tests
ligamentous tests
special tests
neurological tests
history step
starts conversation, open-ended questions, ask questions and listen to answers
**establishes mechanisms of injury**
determines structures involved
onset/duration of symptoms
sounds/sensations felt at the time of injury
prior medical history
sign
something objective (can see)
examples of a sign
gait/limping, ecchymosis, swelling, spasm, cramping, redness, bleeding
symptom
something subjective (can’t see, patient must tell you)
symptom examples
shortness of breath, fatigue, nauseous, headache, numbness, tingling, pain, weakness, achy
palpation
examination by touch, contact should be gentle but firm, start distal to injury
ligamentous testing
application of a specific stress to test the integrity of isolated ligaments (laxity and instability)
laxity
clinical signs, professional feeling for looseness/teather of ligament
instability
symptom—subjective
patient feeling “giving out”
conditions warranting terminating eval
cardiovascular or respiratory arrest/distress
head or neck injury
profuse bleeding
fractures/dislocations
peripheral nerve injuries
other soft tissue trauma
mechanical injury
some force is implemented onto body, body will react by swelling, bleeding, etc
(depends on type/amount of force)
physical stress theory
body’s tissue will respond depending on the amount of force and the direction of force
(creates redness, swelling, heat, pain)
tissue loading
compression, tensile load, shearing
compression
collision, something being pinched
tensile load
muscle tear
shearing
dislocation, abrasion
musculoskeletal injuries
strains, tendinitis, heterotrophic ossifications, bursitis
bony injuries
exostosis, agpophysitis, fractures
joint injuries
sprains, subluxations, dislocations, osteochondral defects, osteochondritis dessicans, arthritis
strains
stretching or tearing of a muscle or tendon (eccentric muscle contraction, dynamic overload, predisposing factors?)
1st degree strain
overstretching and mircotearing, no gross fiber disruption
mild pain and tenderness
full arom and prom
pain with resisted contraction
2nd degree strain
further stretching and partial tearing
immediate pain, localized tenderness, and disability
varying degrees of swelling, ecchymosis, decreased rom, and decreases strength
3rd degree strain
complete rupture
audible pop
immediate pain
loss of function and palpable defect
muscle hemorrhage and diffuse swelling
tendinitis
microtrauma, inflammation occurring in overuse conditions
heterotrophic ossifications
formation of bone within a muscle belly’s fascia (treat with ice and compress, let it naturally heal)
bursitis
inflammation of the bursa sacs (localized swelling)
sprain
injury to ligament or capsular structure (graded based on amount of laxity)
dislocation
(luxation), goes out and stays out
severe stretching or complete disruption of ligaments
subluxation
goes out, comes back in
osteochondritis dessicans
dislodged fragments of bones
osteochondral defects
fractures of a bone’s articular cartilage, progressive softening of cartilage
agpophysitis
growing pains, inflammation of growth plate, muscle pulling away from bone
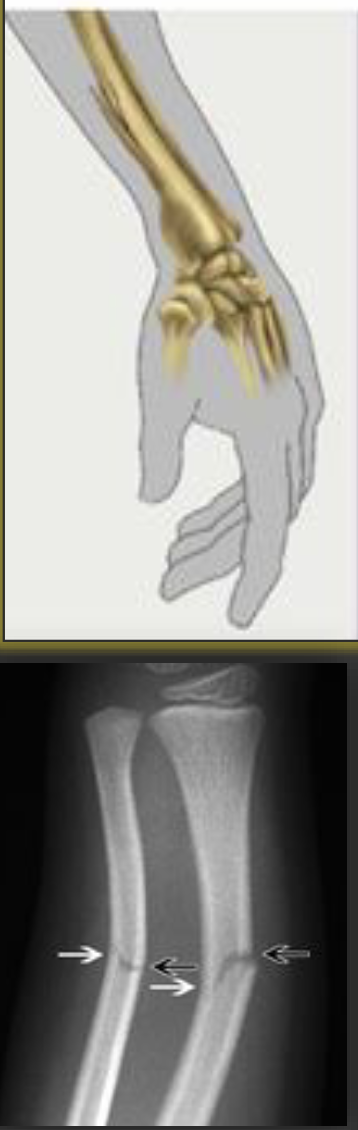
greenstick fracture
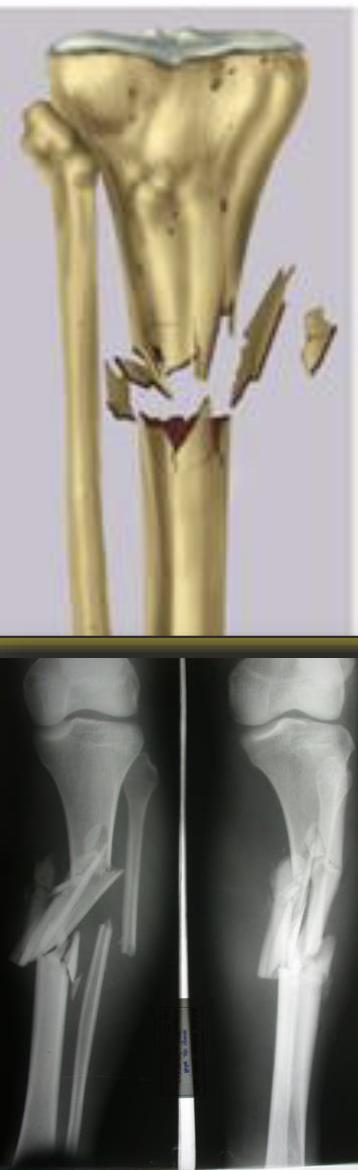
comminuted fracture
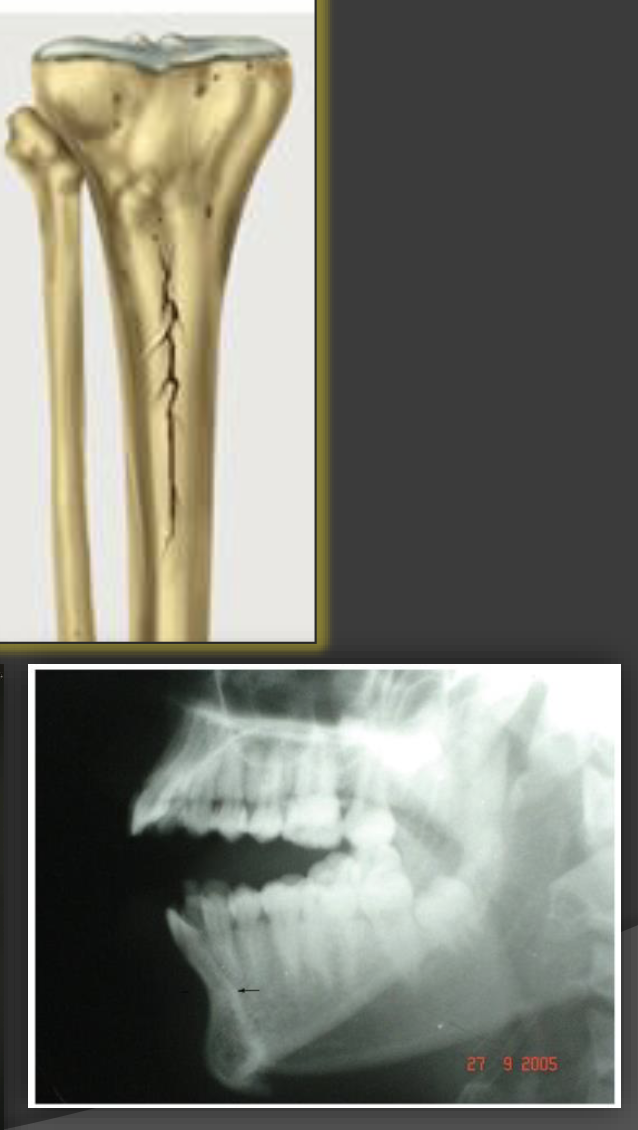
linear fracture
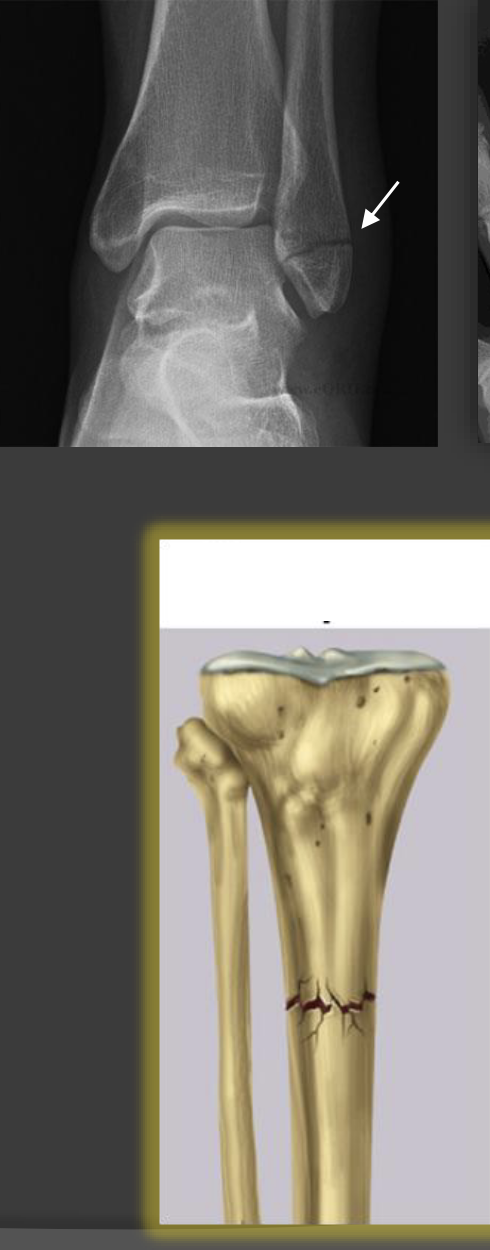
transferred, nondisplaced fracture
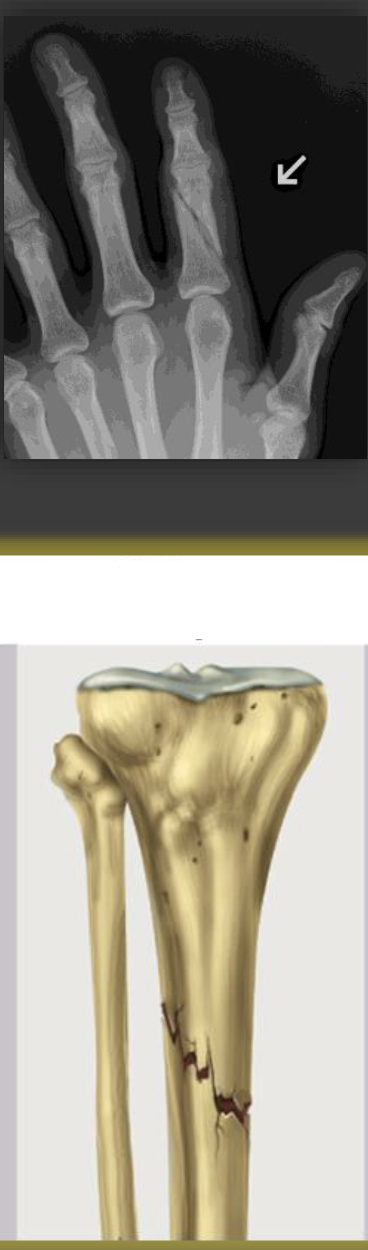
oblique, nondisplaced fracture
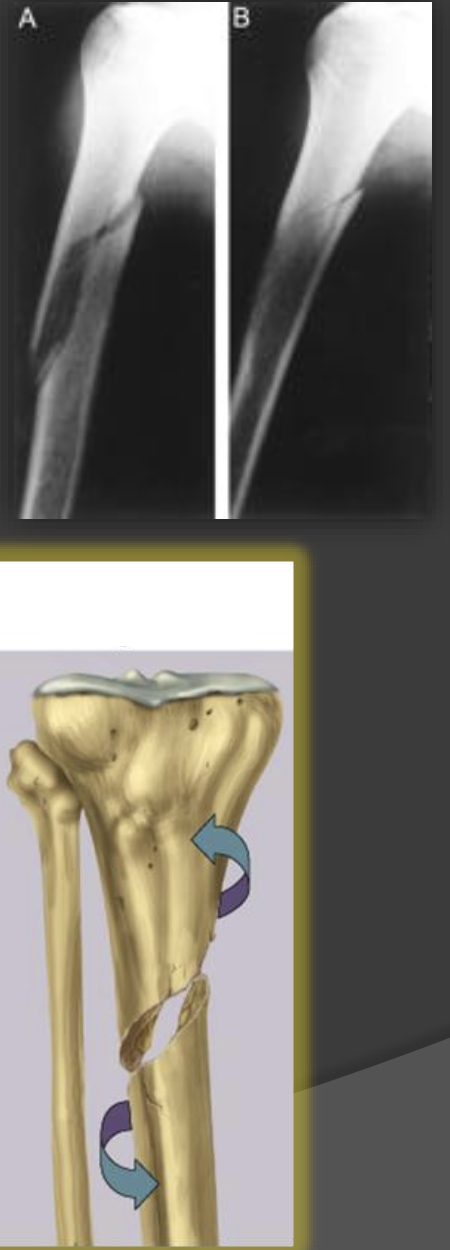
spiral fracture
stress fractures
nondescript initial findings
causes: change in workout, equipment, playing surfaces, frequency, duration, intensity
epiphyseal fracture
weak growth plate