Chapter 17: Digital Law and E-Commerce
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Introduction to Digital Law and E-Commerce
Electronic commerce (e-commerce) is the sale of goods and services or the licensing of intellectual property by computer over the internet
Electronic commerce accounts for approximately 15% of the sale, lease, or licensing of goods and services
Federal and state laws that existed before the advent of the information age have been applied to new digital technologies
In addition, federal and state governments have enacted new laws that apply directly to information technology
Email and Text Contracts
Electronic mail (e-mail) and text messaging (texting) two of the most widely used methods of communication
Electronic mail (e-mail) is electronic written communication between individuals and businesses using computers connected to the internet
Text messaging (texting) is composing and sending electronic messages between users of mobile devices
E-mail and text message contracts
Email and text contracts are enforceable so long as they meet the requirements necessary to form a traditional contract
These contracts meet the requirements of the Statute of Frauds which requires certain contracts to be in writing
Use of e-mail communication is somewhat informal
May not have the comprehensive formality of a paper contract that includes the final terms and conditions of the parties’ agreement
The terms of the parties’ agreement may have to be gleaned from several e-mails or texts that have been communicated between the parties
E-Commerce and Web Contracts
Internet sellers, lessors, and licensors use websites to sell and lease goods and services and to license software and other intellectual property
An web contract is a contract entered into by purchasing, leasing, or licensing goods, services, software, or other intellectual property from websites operated by sellers, lessors, and licensors
Assuming the elements to establish a traditional contract are present, web contracts are valid and enforceable
Case 17.1 Web Contract
Case
Hubbert v. Dell Corporation – Appellate Ct. of Illinois, 835 N.E.2d 113 (2005)
Facts
Plaintiffs purchased computers through Dell’s website
Plaintiffs alleged that Dell misrepresented the speed of the microprocessors
Dell’s hidden terms and conditions required arbitration for disputes
Issue
Were the terms and conditions of sale adequately communicated to the plaintiffs?
Decision
The appellate court held that Dell’s terms and conditions of sale, which were accessible by clicking on a blue hyperlink and which included the arbitration clause, were part of the web contract between the plaintiffs and Dell
The appellate court reversed the decision of the trial court and held in favor of Dell
Counteroffers Ineffectual Against an Electronic Agent
In today’s e-commerce, many internet sellers have websites that use electronic agents to sell goods and services
An electronic agent is any computer system that has been established by a seller to accept orders
Web page order systems are examples of electronic agents
Most web pages use electronic ordering systems that do not have the ability to evaluate and accept counteroffers or to make counteroffers
Thus, counteroffers are not effective against these electronic agents
E-SIGN Act
Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (E-SIGN Act) is a federal statute that:
Recognizes electronic contracts as meeting the writing requirement of the statute of frauds
Recognizes and gives electronic signatures the same force and effect as pen inscribed signatures on paper
E-Sign Act protects consumers:
Consumers must consent to receiving electronic records and contracts
Consumers must have access to their electronic records and contracts
Businesses must tell consumers that they have the right to receive hard copy of documents
E-Signatures
The E-SIGN act gives an e-signature the same force and effect as a handwritten, pen-inscribed signature on paper
Provides that a digital signature can be verified in one of three ways:
By something the signatory knows, such as a secret password or pet’s name
By something a person has, such as a smart card, which looks like a credit card and stores personal information
By biometrics, which uses a device that digitally recognizes fingerprints or the retina or iris of the eye
E-Licensing of Software & Info Rights
Much of the cyber-economy is based on electronic contracts and the licensing of computer software and information
E-commerce created problems for forming contracts over the internet, enforcing e-commerce contracts, and providing consumer protection
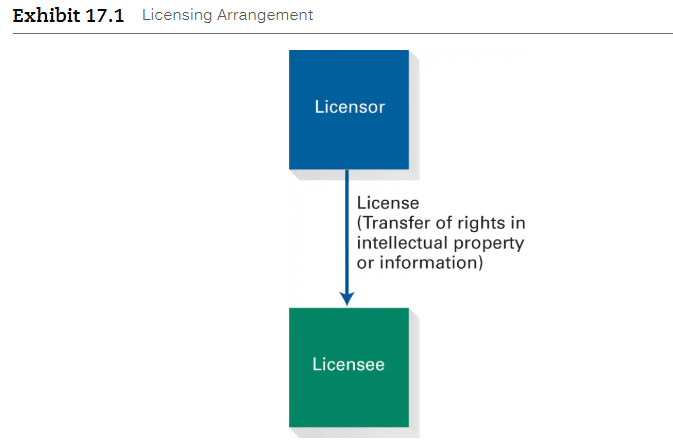
License
A license is a contract that transfers limited rights in intellectual property and informational rights
A license grants the contractual rights expressly described in the license and the right to use information rights within the licensor’s control that are necessary to perform the expressly described rights
A license can grant the licensee the exclusive rights to use the information
A licensor is the owner of intellectual property or informational rights who transfers rights in the property or information to the licensee
A licensee is the party who is granted limited rights in or access to intellectual property or informational rights owned by the licensor
An exclusive license is license in which, for the specified duration of the license, the licensor will not grant to any other person rights to the same information
E-License
An electronic license (e-license) is a contract whereby the owner of software or a digital application grants limited rights to the owner of a computer or digital device to use the software or digital application for a limited period and under specified conditions
E-licensor and e-licensee
Licensing Agreement
A licensing agreement is a detailed and comprehensive written agreement between a licensor and a licensee that sets forth the express terms of their agreement
The parties to a contract for the licensing of information owe a duty to perform the obligations stated in the contract
If a party fails to perform as required, there is a breach of the contract and remedy may be sought
Unfair Business Practices in the Information Age
Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA)
Telephone Robocall Abuse Criminal Enforcement and Deterrence Act (TRACED Act)
Do-Not-Call Registry
Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing Act (CAN-SPAM Act)
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
Communications Decency Act
Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA)
The Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) is a federal statute that curbs abusive telemarketing calls, texts, and faxes
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), an administrative agency, is empowered to enforce the TCPA and to adopt rules and regulations to implement the law
In 2012, the FCC revised its TCPA rules to require telemarketers to (1) obtain prior written consent from consumers before robocalling them, (2) no longer use an “established business relationship” to avoid getting specific consent from consumers, and (3) provide an automated, interactive opt-out mechanism during each robocall so consumers can immediately tell the telemarketer to stop calling
In 2020, the Telephone Robocall Abuse Criminal Enforcement and Deterrence Act (TRACED Act) became effective
The act amends the TCPA by providing additional protections against illegal robocalls, spam calls and texts, and malicious caller ID spoofing
Do-Not-Call Registry
Pursuant to the Do-Not-Call Implementation Act, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) created and administers a National Do-Not-Call Registry
The National Do-Not-Call Registry is a federal registry on which consumers can place their telephone numbers on the registry and free themselves from most unsolicited telemarketing and commercial telephone calls and texts
Both wireless phones and land lines can be registered
The registry applies only to residential phones and not to business phones
The Do-Not-Call Registry also allows consumers to designate specific companies to not call or text them
The act does not limit calls by non-profit organizations, political organizations, and parties conducting surveys
However, the act does apply to telemarketers calling on behalf of these organizations
Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing Act (CAN-SPAM Act)
Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing Act (CAN-SPAM Act) is a federal statute that
Prohibits spammers from using falsified headers in e-mail messages, including the originating domain name and e-mail address;
Prohibits deceptive subject lines that mislead a recipient about the contents or subject matter of the message; and
Requires recipients of spam be given the opportunity to opt out and not have the spammer send e-mail to the recipient’s address
In effect, the CAN-SPAM Act does not necessarily end spam, but instead approves of the business use of spam so long as businesses do not lie
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
Internet service providers (ISPs) are companies that provide consumers and businesses with access to the internet
ISPs provide e-mail accounts, internet access, and storage on the internet to subscribers
Case 17.2 E-Mail Spam
Case
Facebook, Inc. v. Porembski
U.S. Dist. Ct. for the Northern Dist. Of California, 2011
U.S. Dist. Lexis 9668 (2011)
Facts
Defendants spammed Facebook 116,000 users 7.2 million times
Issue
Did the defendants violate the CAN-SPAM Act?
Decision
The U.S. district court held that the defendants had violated the CAN-SPAM Act, awarded Facebook $360 million in damages, and issued a permanent injunction against the defendants
Communications Decency Act
The Communications Decency Act is a federal statute stating that internet service providers are not liable for the content transmitted over their networks by e-mail users and websites
Domain Names
A domain name is a unique name that identifies an individual’s or a company’s website
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the registration and regulation of domain names
Example The domain name for Microsoft Corporation is www.microsoft.com.
Domain names can be registered
Register by filing the appropriate form with a domain name registration service and paying the required fee
Domain Name Extensions
A top-level domain (TLD) is the highest level in the domain name system hierarchy (e.g., .com, .org, .net)
Generic top-level domains (gTLD) are domains that are not restricted to any geographic or country designation (e.g., .name, .pro, .coop)
Specific domain names identify types of business, service, profession, or activity (e.g., .shop, .food, .cocacola, .Microsoft)
Country code top-level domains (CCTLD) are a top-level domain assigned to a country, territory, or sovereign state (e.g., .us, .ca)
Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act
Cybersquatting is a situation that occurs when a party registers a domain name of another party’s trademarked name or a famous person’s name
The Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act: (ACPA) is a federal statute that permits trademark owners and famous persons to recover domain names that use their names where the domain name has been registered by another person or business in bad faith
Two fundamental requirements:
The name must be famous
The domain name was registered in bad faith
In determining bad faith, a court may consider the extent to which the domain name resembles the trademark owner’s name or the famous person’s name, whether goods or services are sold under the name, the holder’s offer to sell or transfer the name, whether the holder has acquired multiple internet domain names of famous companies and persons, and other factors
The act provides for the issuance of cease-and-desist orders and injunctions against the domain name registrant
The court may order the domain name registrant to turn over the domain name to the trademark owner or famous person
The law also provides for monetary penalties
The ACPA gives owners of trademarks and persons with famous names the right to prevent the kidnapping of internet domain names by cyberpirates
Case 17.3b National Arbitration Forum Domain Name
Case
The New York Yankees Baseball Club
National Arbitration Forum, Claim Number FA0609000803277 (2006)
Facts
Defendant owned nyyankees.com
Plaintiff alleged that defendant registered the domain in bad faith and in violation of the ICANN Uniform Domain Dispute Resolution Policy (Policy)?
Issue
Did the defendant violate the Policy?
Decision
The arbitrator held that Moniker violated the ICANN Policy and ordered that the <nyyankees.com> domain name be transferred from Moniker to the Yankees