AP Gov Unit 1 MCQ
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Article I, Section 9 of the United States Constitution lists several powers that are denied to the federal government, such as granting titles of nobility and passing ex post facto laws. This best demonstrates which of the following ideals of democracy?
Responses
A
Natural rights
B
Popular sovereignty
C
Social contract theory
D
Limited government
Answer D
Correct. Limited government is demonstrated in this example because denying powers to the federal government limits it.
As a compromise, the framers agreed on a bicameral legislature, with the House of Representatives directly elected by popular vote within states and the Senate selected by state legislatures. The method chosen for electing members of the House of Representatives conforms most to which of the following democratic ideals?
Responses
A
The social contract is an agreement between citizens and government.
B
Government should be based on the consent of the governed.
C
Policy makers should be the most well-informed and wealthy members of society.
D
State power should be respected in a federal constitution.
Answer B
Correct. The fact that citizens directly elect members of the House of Representatives demonstrates that they have given their approval to the government.
The Declaration of Independence cites specific reasons for separating from British rule, including the British imposing taxes and maintaining a standing army without consent. Which of the following principles or ideas would these grievances be most related to?
Responses
A
Natural rights such as life and liberty
B
The authority to create a centralized military among the colonies
C
The incorporation of checks and balances among the branches of government
D
Concurrent powers allowing the colonies to draft their own laws
Answer A
Correct. The British government was imposing laws considered unfair by the colonies but did not allow the colonists to have legislative representation, which was an infringement on their natural rights
Which of the following describes the social contract theory as advanced by John Locke?
Responses
A
It is an agreement between political actors to maintain their grip on power.
B
It is an agreement in which the government promises to provide a minimum standard of living to citizens.
C
It is an agreement in which the government promises to protect the natural rights of people.
D
It is an agreement between economic elites to maintain a stable economy.
E
It is an agreement in which the government outlines socially acceptable norms of political behavior.
Answer C
“We hold these truths to be self-evident: that all men and women are created equal; that they are endowed by their Creator with certain inalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness; that to secure these rights governments are instituted, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed. Whenever any form of government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the right of those who suffer from it to refuse allegiance to it, and to insist upon the institution of a new government . . .
“. . . Such has been the patient sufferance of the women under this government, and such is now the necessity which constrains them to demand the equal station to which they are entitled. The history of mankind is a history of repeated injuries and usurpations on the part of man toward woman, having in direct object the establishment of an absolute tyranny over her. To prove this, let facts be submitted to a candid world.
“He has never permitted her to exercise her inalienable right to the elective franchise.
“He has compelled her to submit to laws, in the formation of which she had no voice.
“He has withheld from her rights which are given to the most ignorant and degraded men. . . .
“Having deprived her of this first right of a citizen, the elective franchise, thereby leaving her without representation in the halls of legislation, he has oppressed her on all sides.
“He has made her, if married, in the eye of the law, civilly dead.
“He has taken from her all right in property, even to the wages she earns.”
Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Seneca Falls Convention, 1848
The language in the first paragraph of the selection most closely parallels that of which of the following documents?
Responses
A
The Preamble to the United States Constitution
B
The Declaration of Independence
C
The Federalist 10
D
Brutus 1
Answer B
Correct. The passage is from the Declaration of Sentiments, which was authored at the Seneca Falls Convention. It used the Declaration of Independence as a template for the document that promotes women’s rights.
The vice of the groupist theory is that it conceals the most significant aspects of the system. The flaw in the pluralist heaven is that the heavenly chorus sings with a strong upper-class accent. Probably about 90 percent of the people cannot get into the pressure system.
The notion that the pressure system is automatically representative of the whole community is a myth fostered by the universalizing tendency of modern group theories. Pressure politics is a selective process ill designed to serve diffuse interests. The system is skewed, loaded, and unbalanced in favor of a fraction of a minority.
E. E. Schattschneider, The Semisovereign People, 1960
Which of the following best captures the author's argument regarding the forms of democracy?
Responses
A
Pluralist democracy, which seeks to shield elites from popular opinion, functions best when individual citizens do not participate in the process.
B
Participatory democracy, which emphasizes limited participation, marginalizes those who do not have the economic means to participate.
C
Pluralist democracy, though it involves groups at different stages of the process of developing policy, excludes a significant portion of the population.
D
Participatory democracy, which emphasizes expanded participation, creates too much conflict within the system.
Answer C
Which of the following accurately characterizes the main difference between elite theories and pluralist theories of politics in the United States?
Responses
A
Elite theories concentrate on the role of interest groups; pluralist theories emphasize the role of individuals.
B
Elite theories argue that a single minority dominates politics in all policy areas; pluralist theories argue that many minorities compete for power in different policy areas.
C
Elite theories argue that social status is the major source of political power; pluralist theories argue that wealth is the major source.
D
Elite theories emphasize the multiple access points that interest groups have to public officials; pluralist theories stress the limits in the number and effectiveness of such access points.
E
Elite theories view government as efficient; pluralist theories view it as slow and wasteful.
Answer B
“[A] pure democracy… can admit of no cure for the mischiefs of faction. . . . [S]uch democracies have ever been spectacles of turbulence and contention; have ever been found incompatible with personal security or the rights of property; and have in general been as short in their lives as they have been violent in their deaths. . . .
The two great points of difference between a democracy and a republic are: first, the delegation of the government, in the latter, to a small number of citizens elected by the rest; secondly, the greater number of citizens, and greater sphere of country, over which the latter may be extended.
. . . [I]t may well happen that the public voice, pronounced by the representatives of the people, will be more consonant to the public good than if pronounced by the people themselves, convened for the purpose. On the other hand, the effect may be inverted. Men of factious tempers, of local prejudices, or of sinister designs, may, by intrigue, by corruption, or by other means, first obtain the suffrages, and then betray the interests, of the people.”
James Madison, The Federalist 10
Which of the following statements best reflects James Madison’s beliefs about political representation as expressed in the passage?
Responses
A
People would be best served by having a strong leader to make the decisions.
B
People will not truly have a voice in government until they can vote on laws directly.
C
People are best represented by a few politicians chosen to voice their issues.
D
People should elect political representatives who are wealthy enough to avoid corruption.
Answer C
Correct. Madison does admit representatives may harbor local prejudices that would interfere with effective governing, but it is not a sufficient concern to override his argument for the benefits of a representative government.
The framers of the Constitution intended to establish
Responses
A
a representative republic
B
a direct democracy
C
an authoritarian state
D
a socialist democracy
E
a parliamentary republic
Answer A
In The Federalist papers, James Madison argues that political liberty is best protected by
Responses
A
a written constitution
B
a small republic with a parliamentary system
C
a small democracy with a unitary government
D
well-regulated militias controlled by state governments
E
the fragmentation of political power in a large republic
Answer E
The debates between Federalists and Anti-Federalists were primarily about which of the following issues?
Responses
A
The right of the people to rebel
B
The existence of slavery
C
The scope of power of the central government
D
The need to establish a standard currency
E
The representation of large and small states
Answer C
Which of the following is argued by James Madison in The Federalist paper number 10?
Responses
A
A system of republican representation helps to limit the excesses of factionalism.
B
Small republics are better able to ensure individual liberty than are large republics.
C
The presence of a few large factions helps to protect the rights of minorities.
D
Participatory democracy is the surest way to prevent tyranny.
E
The elimination of the causes of factionalism is the best protection against tyranny.
Answer A
According to James Madison, which of the following best controls the effects of faction?
Responses
A
Direct democracy
B
The popular election of state judges
C
A large republic
D
Property requirements for eligibility to work
E
The creation of a merit-based civil service
Answer C
Brutus was an example of an Anti-Federalist because he
Responses
A
believed a centralized government posed a major threat to individual rights
B
argued that a national military force was needed to deal with insurrections
C
argued that the laws passed by the national government were supreme over state laws
D
believed that compromise between the branches of government would ensure a limited government
Answer A
Correct. Anti-Federalists believed that a centralized government would harm individual rights, a view which was espoused by Brutus.
Which of the following features of the United States Constitution would most concern the author of Brutus 1?
Responses
A
The Bill of Rights, which protects individual liberties and states’ rights
B
The reservation of any power not given to the federal government to the states
C
The two-year term for members of the House of Representatives
D
The supremacy clause, which gives the federal government supremacy over states
Answer D
Correct. In Brutus 1, the author argues that these two clauses, in particular, gave the national government nearly unlimited power.
Which of the following is commonly identified as a failure of the Articles of Confederation?
Responses
A
The national government lacked an effective power to raise revenue.
B
The executive branch was granted too much power over the legislature.
C
The federal government had too much control over interstate commerce.
D
The judicial branch was elected and did not consistently adhere to rule of law.
Answer A
Correct. Under the Articles of Confederation, the national government could only request money from the states, which were not compelled to satisfy such requests.
Articles of Confederation | United States Constitution | |
|---|---|---|
A | Protection of individual liberties | No protection of specific individual rights |
B | Powerful executive branch | Federal government supreme over states |
C | Unicameral legislature | Bicameral legislature |
D | Amendment requires unanimity of all states | Amendment requires the president’s approval |
Which of the following is the correct pairing of powers found in the Articles of Confederation and powers found in the Constitution?
Responses
A
B
C
D
Answer C
Correct. Under the Articles of Confederation, legislation was approved by the unicameral Congress of the Confederation. The United States Constitution established a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and House of Representatives.
Of the following, the most significant difference between the Constitution of 1787 and the Articles of Confederation was that the Constitution
Responses
A
made states sovereign over the national government, while the Articles were based on national sovereignty
B
was difficult to amend, while the Articles included an easier process requiring approval by a simple majority of states
C
provided for a presidential system of government, while the Articles provided for a parliamentary system of government
D
created a dominant national executive, while the Articles established a dominant national legislature
E
provided for a strong national government with many powers, while the Articles created a weak central government with few independent powers
Answer E
In the 1780s, proponents of the new Constitution cited Shays’ Rebellion as an example in support of which of the following criticisms of the national government under the Articles of Confederation?
Responses
A
The national government did not provide sufficient protection of individual rights.
B
The lack of a centralized judiciary made enforcement of national laws difficult.
C
States with larger populations were underrepresented in Congress.
D
There was a lack of a national military power to address security concerns.
Answer D
Correct. The inability of the national government to respond militarily to Shays’ Rebellion exposed a critical weakness in the structure of the national government.
While [opponents of the Constitution] admit that the government of the United States is destitute of energy, they contend against conferring upon it those powers which are requisite to supply that energy. They seem still to aim at things repugnant and irreconcilable; at an augmentation of federal authority, without a diminution of State authority; at sovereignty in the Union, and complete independence in the members. . . . This [requires that] a full display of the principal defects of the Confederation [is] necessary, in order to show that the evils we experience do not proceed from minute or partial imperfections, but from fundamental errors in the structure of the building, which cannot be amended otherwise than by an alteration in the first principles and main pillars of the fabric. . . . [T]he United States has an indefinite discretion to [plead for] for men and money; but they have no authority to raise either, by regulations extending to the individual citizens of America. The consequence of this is, that though in theory their resolutions concerning those objects are laws, constitutionally binding on the members of the Union, yet in practice they are mere recommendations which the States observe or disregard at their option.
Alexander Hamilton, The Federalist 15
Which of the following is a difference between the Articles of Confederation and the United States Constitution that is a response to a problem expressed in the passage?
Responses
A
The Articles of Confederation lacked federal executive and judicial branches, whereas the United States Constitution did not.
B
The Articles of Confederation allowed for the federal government to request revenues from states but did not permit it to tax citizens directly, whereas under the United States Constitution the federal government could tax citizens directly.
C
Under the Articles of Confederation, members of the national legislature were paid by the state governments, whereas under the United States Constitution they were paid by the federal government.
D
Under the Articles of Confederation, members of the national legislature were not able to regulate currency, whereas under the United States Constitution the federal government regulates currency.
Answer B
Correct. The author of the passage considers the lack of taxation to be a fundamental problem, so the power to tax was added to Article I, Section 8 to the Constitution in response.


The process shown in the diagram is outlined in which of the following parts of the United States Constitution?
Responses
A
Article I
B
Article II
C
Article V
D
Article VI
Answer C
Correct. Article V details the amendment process shown in the diagram.
At the Constitutional Convention of 1787, delegates from larger states argued that each state’s representation in the legislature should be proportional to its population. Smaller states argued that each state should have equal representation, regardless of population. The disagreement over representation threatened to derail the ratification of the United States Constitution. Which statement accurately describes the compromise that led to both sides reaching agreement?
Responses
A
A bicameral legislature with an upper house selected by the lower house and the lower house representation proportional to each state’s population
B
A bicameral legislature with an upper house representing each state equally and a lower house with representation proportional to each state's population
C
A unicameral legislature with equal representation for every state
D
A unicameral legislature with representation proportional to each state's population.
Answer B
Correct. The Great Compromise, or Connecticut Compromise, provided a dual system of representation; a bicameral legislature with one chamber based on representation by the population and the other chamber based on representation of the states.
In order to appease both Federalists and Anti-Federalists, it was agreed at the Constitutional Convention that a group of delegates would be charged with selecting the president. This would ensure that
Responses
A
the president would be chosen directly by the people to ensure that the process adheres to the principles of democracy
B
the president would be chosen by Congress since Congress has been elected and represents the will of the people
C
a qualified person representative of the people would become president
D
the president would be chosen by the Supreme Court because the Court is charged with making unbiased decisions
Answer C
Correct. The electoral college was a compromise between having the citizens directly elect the president and having Congress elect the president. At the time of the Constitutional Convention, no country had ever had their government leader elected by its citizens. The founders feared that citizens would lack the information to make an informed decision and they feared that if Congress elected the president, it might compromise the independence of the executive. They believed the electors would ensure a qualified and representative person would become president.
The Connecticut (Great) Compromise drafted at the Constitutional Convention of 1787 is significant for which of the following reasons?
Responses
A
It established the presidential system and gave the United States Supreme Court power to serve as the ultimate arbiter of constitutional disputes.
B
It allowed southern states to count each slave as three-fifths of one person for determining representation in the House of Representatives.
C
It provided equality of representation among the states in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.
D
It proposed a Senate with equal representation for each state and a House of Representatives with membership established according to the population of each state.
E
It denied Congress the power to establish tariffs on exported merchandise.
Answer D
Which of the following was a direct outcome of the Three-Fifths Compromise?
Responses
A
The number of senators increased in three-fifths of the states with enslaved populations.
B
Amendments to the United States Constitution required three-fifths of the states to approve.
C
The presidential winner would be determined by three-fifths of the electors in the Electoral College.
D
A formula for calculating a state’s enslaved population for the purposes of representation was enacted.
Answer D
Correct. A formula for calculating a state’s enslaved population resulted in some states increasing their representation.
The term “bicameralism” refers to the
Responses
A
establishment of two legislative chambers that have different structures and rules
B
members of the House of Representatives having two-year terms
C
president having veto power over both chambers of Congress
D
members of the House and Senate having to appease their mutual constituencies
E
checks that Congress has over the federal bureaucracy
Answer A
Legislative checks to the judicial branch | Judicial checks to the legislative branch | |
|---|---|---|
A | Impeaching and removing federal judges | Declaring an entire law unconstitutional |
B | Confirming federal judges | Reviewing laws prior to enactment |
C | Appointing federal judges | Striking down a portion of a law |
D | Establishing the number of Supreme Court justices | Removing the Speaker of the House |
Which of the following is an accurate comparison of the checks held by the legislative and judicial branches?
Responses
A
B
C
D
Answer A
Correct. The legislature can check the judiciary by impeaching and removing judges, and the courts can check the legislature through the power of judicial review, which allows judges to declare a law to be unconstitutional.
One example of constitutional checks and balances is
Responses
A
the president declares war, but Congress appropriates military funds
B
the president nominates cabinet members, and the House holds confirmation hearings
C
the House can impeach federal judges and the president, and the Senate holds the impeachment trial
D
Congress can override United States Supreme Court decisions on the constitutionality of laws
E
presidential vetoes of laws can be overridden by a simple majority vote in both the House and the Senate
Answer C
Constitutional checks and balances, especially applied to the president, are designed to
Responses
A
provide for a balanced budget
B
minimize the threat of tyranny from any one branch of government
C
ensure that the states do not become too powerful
D
ensure efficient government
E
ensure that the federal government is militarily strong
Answer B
Which of the following is an example of checks and balances in action in the United States government?
Responses
A
The House and Senate cannot agree on the same version of a bill to send to the president.
B
The president issues an executive order that freezes federal government hiring.
C
The president vetoes a bill passed by Congress.
D
The voters reject the status quo and elect all new members of Congress.
E
The voters at the state level elect a governor from a party other than the president’s.
Answer C
Which of the following is an accurate description of the decision in United States v. Lopez (1995) ?
Responses
A
The Gun-Free School Zones Act of 1990 was upheld as constitutional because regulating arms is an enumerated power.
B
The Gun-Free School Zones Act of 1990 was upheld as constitutional because any interstate commerce is implied in the commerce clause.
C
The Gun-Free School Zones Act of 1990 was struck down as unconstitutional because it exceeded the commerce clause.
D
The Gun-Free School Zones Act of 1990 was struck down because it exceeded the state’s power to regulate guns.
Answer C
Correct. United States v. Lopez decided that the Gun-Free School Zones Act was unconstitutional because it exceeded the authority of the federal government based on the application of the commerce clause.
Which of the following is an accurate description of the decision in McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) ?
Responses
A
The federal government exceeded its authority in establishing a national bank, and Maryland’s tax was unconstitutional.
B
Maryland was within its authority to tax the federal government, but the Bank of the United States exceeded federal authority.
C
The federal government had the authority to establish a national bank, but it had to pay Maryland’s tax.
D
The federal government had the authority to establish a national bank, and Maryland’s tax was unconstitutional.
Answer D
Correct. In McCulloch v. Maryland, the Supreme Court affirmed that the federal government had certain implied powers not explicitly listed in the Constitution, such as establishing a national bank exempt from punitive state taxes.
Diversity of public policy throughout the United States is primarily a consequence of
Responses
A
federalism
B
separation of powers
C
innovation within bureaucratic agencies
D
decentralization in the Senate
E
lack of party discipline in the House
A
federalism
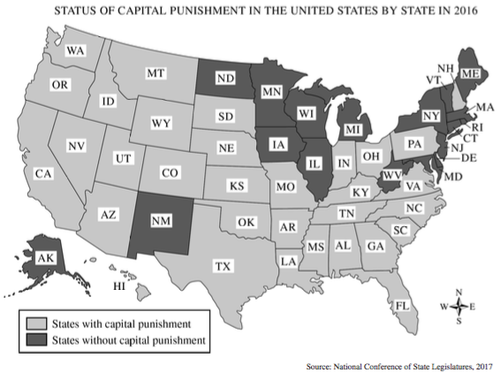
Status of Capital Punishment in the United States by State in 2016

Source: National Conference of State Legislatures, 2017
Which of the following constitutional principles best explains why there is variation among states on the use of capital punishment?
Responses
A
Separation of powers
B
Judicial review
C
Checks and balances
D
Federalism
Answer D
Correct. Federalism is the system of sharing power between the federal and state governments. The concept of federalism accounts for variation between the states on issues such as the use of capital punishment. Most crimes are prosecuted at the state level and each state determines for itself the appropriate punishment for that crime.
The supremacy clause in the Constitution states that
Responses
A
federal law takes precedence over state law when the laws conflict
B
only Congress may declare war
C
the Senate should have a greater role in foreign affairs than does the House of Representatives
D
the federal government has the right to regulate interstate commerce
E
the Supreme Court has the power to overturn decisions of lower courts
A
federal law takes precedence over state law when the laws conflict
The following questions refer to the following clause from the Constitution:
"The Congress shall have power...to make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States, or in any department or officer thereof."
The practical effect of this clause has been to
Responses
A
make the legislature the most powerful branch of the national government
B
allow the national government to extend its powers beyond those enumerated in the Constitution
C
allow the state governments to nullify federal laws within their borders
D
give the President uncontested powers in the area of foreign policy
E
ensure that any powers not delegated by the Constitution to the United States government are reserved to the states and the people
B
allow the national government to extend its powers beyond those enumerated in the Constitution
Which of the following forms of financial aid from the national government gives the states the broadest discretion in the spending of money?
Responses
A
Categorical grants-in-aid
B
Foreign aid
C
Unfunded mandates
D
Block grants
E
Military funding
D
Block grants
The decision in United States v. Lopez (1995) reflected new ideas about federalism at the time that can be best characterized by which of the following?
Responses
A
A consolidation of power in the national government based on national supremacy
B
Acknowledgement of the limitations of national power and a recognition of the reserved power of the states.
C
A delegation of power from the state governments to the federal government, increasing the power of the United States government
D
An increase in cooperative federalism, where power and duties are shared between the federal and state governments
Answer B
Correct. The Lopez decision stated that Congress had exceeded its authority to regulate all guns because the Gun-Free School Zones Act of 1990 did not have a substantial impact on interstate commerce. Powers not delegated to the national government by the U.S. Constitution nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states.
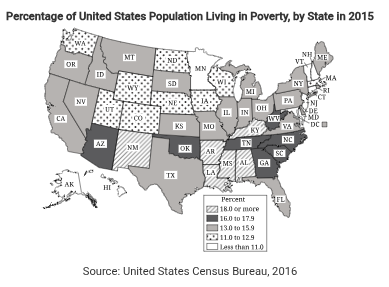
Percentage of United States Population Living in Poverty, by State in 2015

Source: United States Census Bureau, 2016
Which of the following is true based on information on the map?
Responses
A
The number of people living in poverty is lower in Maine (ME) than in New Jersey (NJ).
B
Northern states tend to have higher poverty rates than Southern states.
C
The poverty rate in the United States has increased since the last census was taken.
D
The poverty rate in the United States varies by state and region.
Answer D
Correct. The map shows wide disparity between the poverty rates of different states and regions.
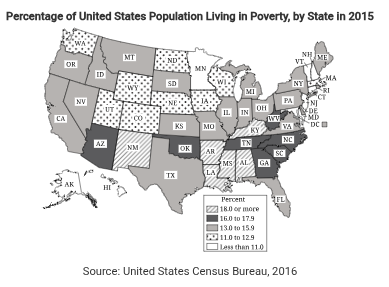
Percentage of United States Population Living in Poverty, by State in 2015

Source: United States Census Bureau, 2016
Which constitutional principle best explains the differences in poverty rates presented in the map?
Responses
A
Checks and balances
B
Federalism
C
Equal protection
D
Enumerated powers
Answer B
Correct. Federalism allows for individual states to create their own policies to address issues such as poverty. Different approaches to the issue can contribute to disparities in the poverty rates between states.

Herblock, Washington Post, 1949A 1949 Herblock Cartoon, © The Herb Block Foundation
Which of the following is the most accurate interpretation of the political cartoon?
Responses
A
State governments have used the Tenth Amendment to override the federal government’s mandates.
B
State governments are unwilling to share their budgetary surpluses with other states.
C
State governments prefer federal funding but do not want federal oversight over how the money is spent.
D
The fiscal irresponsibility of state governments has led to increased federal regulation on their budgetary priorities.
Answer C
Correct. The cartoon suggests that states want federal money, depicted by the money bag offered by Uncle Sam, but do not want federal oversight, depicted by the gesture of rejection given by the “states’ rights” advocate to the paper that says “federal authority” held by Uncle Sam.

Herblock, Washington Post, 1949A 1949 Herblock Cartoon, © The Herb Block Foundation
Which of the following policies would the states most likely prefer according to the political cartoon?
Responses
A
Federal mandates
B
Regulatory preemption
C
Block grants
D
Categorical grants
Answer C
Correct. Block grants provide money to states without great oversight by the federal government, which appeals to states, according to the cartoon.
FEDERAL, STATE, AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT EMPLOYMENT

Source: Cato Institute, 2013
The increasing number of state and local government employees reflects which of the following about the political system in the United States?
Responses
A
There has been a trend toward more liberal state governments since 1970.
B
The addition of new states to the union has weakened the power of the national government.
C
State and local governments provide many necessary public services in a federal system.
D
The shrinking of the national budget has led to a decrease in the number of federal employees.
Answer C
Correct. This is true as the graph depicts an ever-increasing number of state and local personnel from 1950 to 2010.
Which of the following constitutional principles most directly addresses the relationship between the national and state governments?
Responses
A
Checks and balances
B
The Bill of Rights
C
Separation of powers
D
Representation
E
Federalism
E
Federalism