Harirfaroosh Cumulative (32 slides)
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Stability issues related to protein formulation: What are examples of chemical instability (6)?
deamidation, oxidation, proteolysis (hydrolysis), disulfide shuffling, racemization, beta elimination
Stability issues related to protein formulation: What are examples of conformational physical instability (2)?
unfolding, misfolding
Stability issues related to protein formulation: What are examples of colloidal physical instability (2)?
aggregation, precipitation
What is the third form of physical instability in addition to conformational and colloidal?
Adsorption
What gauge needles are typically used for insulin injections?
30–32 G needle
The ____ the gauge, the ____ (____) the bore/diameter of the needle
larger, smaller (finer)
Excipients: What is the function of buffers and what are some examples?
Function: pH control, tonicity
Examples: Histidine, phosphate, acetate, citrate, succinate
Excipients: What is the function of salts and what are some examples?
Function: Tonicity, stabilization, viscosity reduction
Examples: Sodium chloride
Excipients: What is the function of sugars, polyols and what are some examples?
Function: Tonicity, stabilization, cryoprotection, lycoprotein, bulking agent, reconstitution improvement
Examples: Sucrose, trehalose, mannitol, sorbitol
Excipients: What is the function of surfactants and what are some examples?
Functions: Adsorption prevention, solubilization, stabilization, reconstitution improvement
Examples: Polysorbate 20, polysorbate 80, poloxamer
Excipients: What is the function of amino acids and what are some examples?
Functions: Stabilization, viscosity reduction, tonicity, pH control, bulking agent
Examples: Arginine, glycine, histidine, lysine, proline
Excipients: What is the function of anti-oxidants and what are some examples?
Functions: Oxidation prevention
Examples: Methionine, sodium edetate
Excipients: What is the function of preservatives and what are some examples?
Function: Bacterial growth prevention
Examples: m-cresol, benzoyl alcohol, phenol
There are 5 challenges in the Characterization of PK and PD of therapeutic proteins: (1) their definition by the production process in ______ rather than a chemically exactly defined _____ and _____
living organisms rather than a chemically exactly defined structure and purity
There are 5 challenges in the Characterization of PK and PD of therapeutic proteins: (2) their structure similarity to __________ or ______ and ________
structural or functional proteins and nutrients
There are 5 challenges in the Characterization of PK and PD of therapeutic proteins: (3) their intimate involvement in physiologic processes on the _________ level, often including ___________________
molecular level, often including regulatory feedback mechanisms
There are 5 challenges in the Characterization of PK and PD of therapeutic proteins: (4) analytical challenges to _______ and ______ them in the presence of many similar molecules
identify and quantify
There are 5 challenges in the Characterization of PK and PD of therapeutic proteins: (5) their __________ weight and ___________ character
their large molecular weight and macromolecule character
What are reasons that the oral administration may lack systemic bioavailability?
high GI enzyme activity, low permeability through GI mucosa
What are suggested approaches to improving the oral bioavailability of protein drugs (3)?
encapsulation into micro- or nanoparticles
amino acid backbone modifications and chemical conjugations
coadministration of protease inhibitors
IV administration of peptides and proteins bypasses ______________
pre-systemic degradation
___ or ____ injections often provide a more desired concentration-time profile compared to _____ or ______ injections
IM or SC; IV bolus or infusion
___ injections allow self-admin by the patient
SC
What are the three types of insulin preparations?
rapid onset and short duration
intermediate onset and duration
prolonged duration
Which insulins are rapid onset and short duration (5)?
Insulin aspart
Insulin lispro
Insulin glulisine
Insulin (Afrezza) (oral inhalation)
Insulin regular
Which insulins are intermediate onset and duration?
isophane insulin (NPH)
Which insulins have a prolonged duration (3)?
Insulin degludec
Insulin detemir
Insulin glargine
Ghrelin stimulates the hypothalamus to release ______ to tell the anterior pituitary to release GH
GHRH
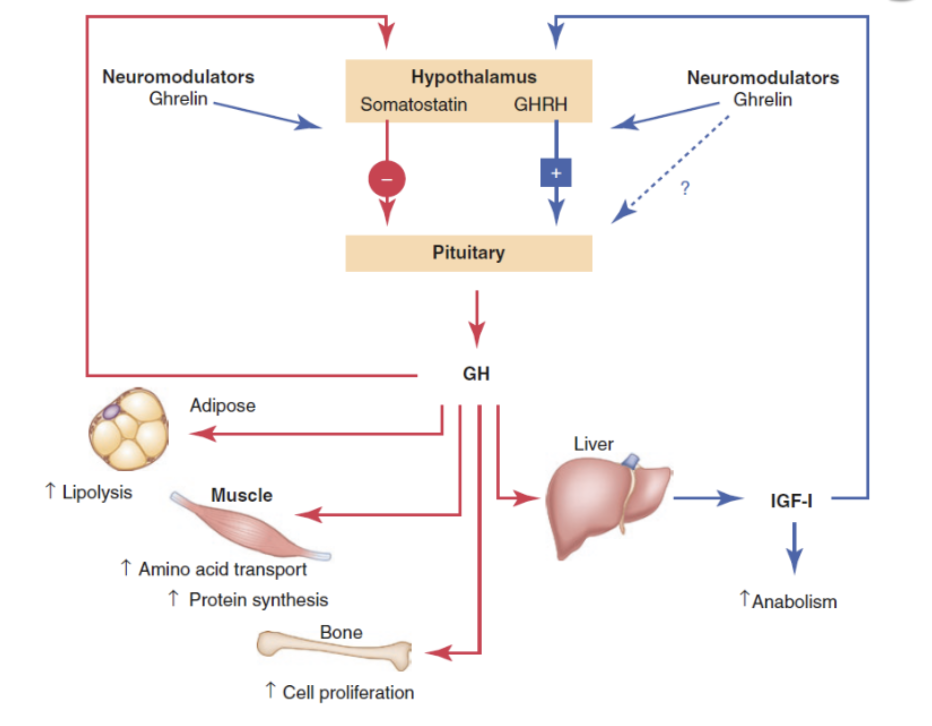
Ghrelin stimulates the hypothalamus to release ______ to stop the anterior pituitary from releasing GH
Somatostatin
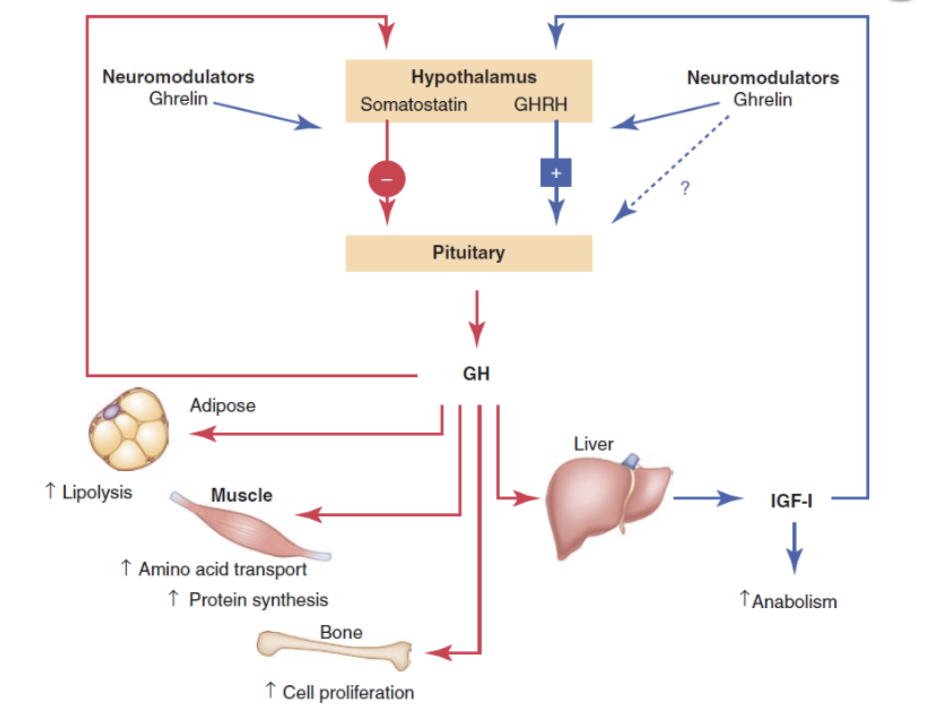
GH from the anterior pituitary will circulated in the body to stimulate to which organs (4)?
adipose tissue, skeletal tissue, bone, liver
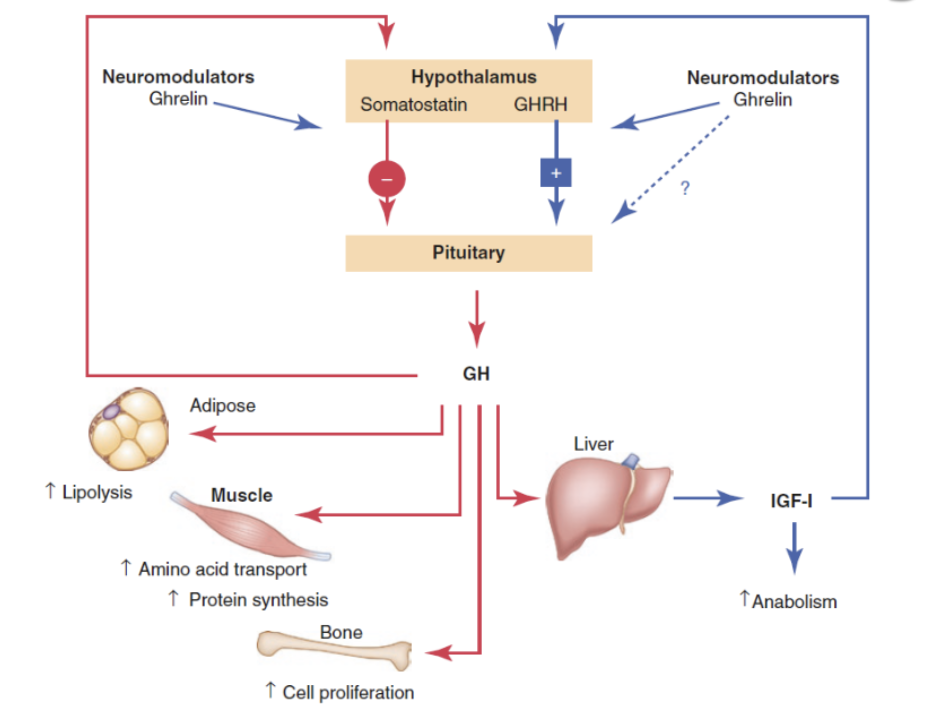
In response to GH, what happens in adipose tissue?
increase lipid breakdown (lipolysis)
In response to GH, what happens in skeletal tissue?
increase amino acid transport and protein synthesis
In response to GH, what happens in bone?
increase cell proliferation
In response to GH, what happens in the liver?
releases IGF-i → increase anabolism and positively stimulates hypothalamus to release GHRH
What are the big differences between somatropin and lonapegsomatropin (2)?
somatropin is mostly active, lonapegsomatropin releases fully active somatropin
somatropin’s half-life is much shorter than lonapegsomatropin’s (2.1-7 hr vs 30.7 ± 12.7 hr)
What are the big similarities between somatropin and lonapegsomatropin (2)?
hepatic and renal metabolism
excreted in urine
where is urofollitropin sourced from?
human urine
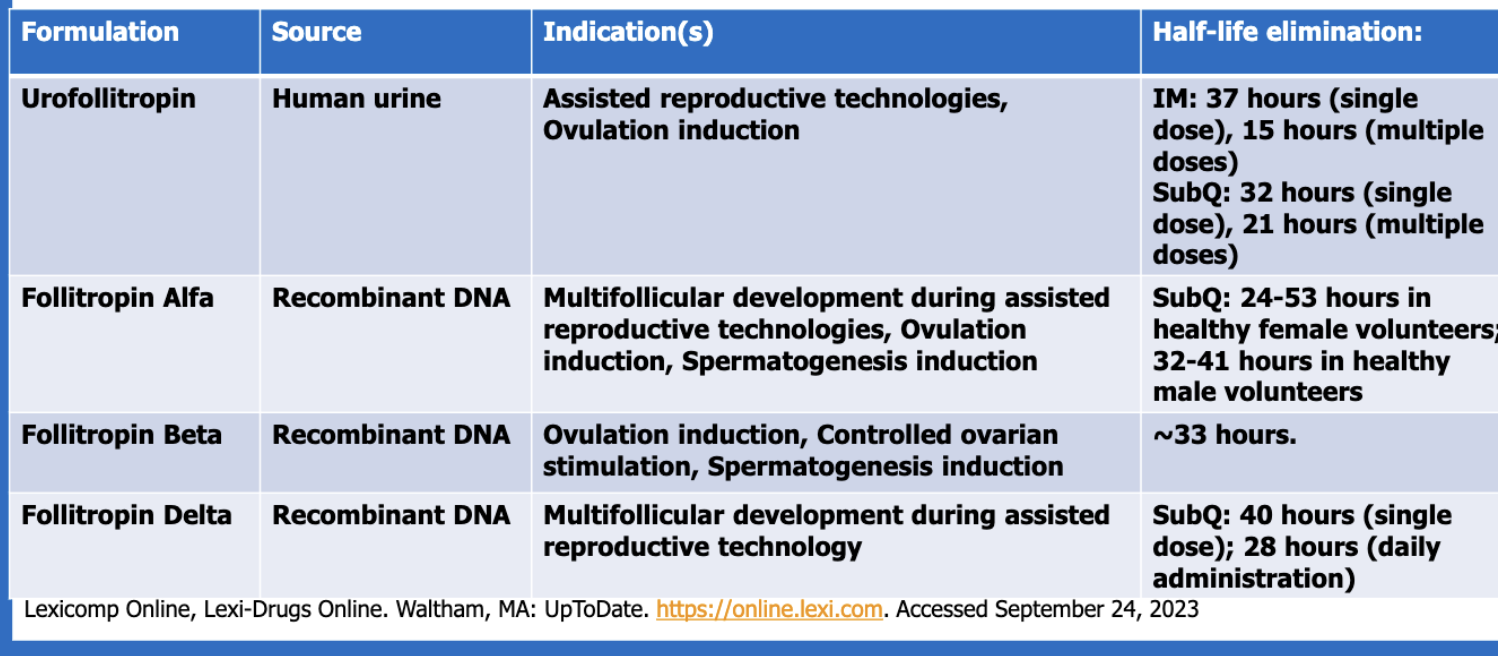
Where is follitropin Alfa, Beta, and Delta sourced from?
recombinant DNA
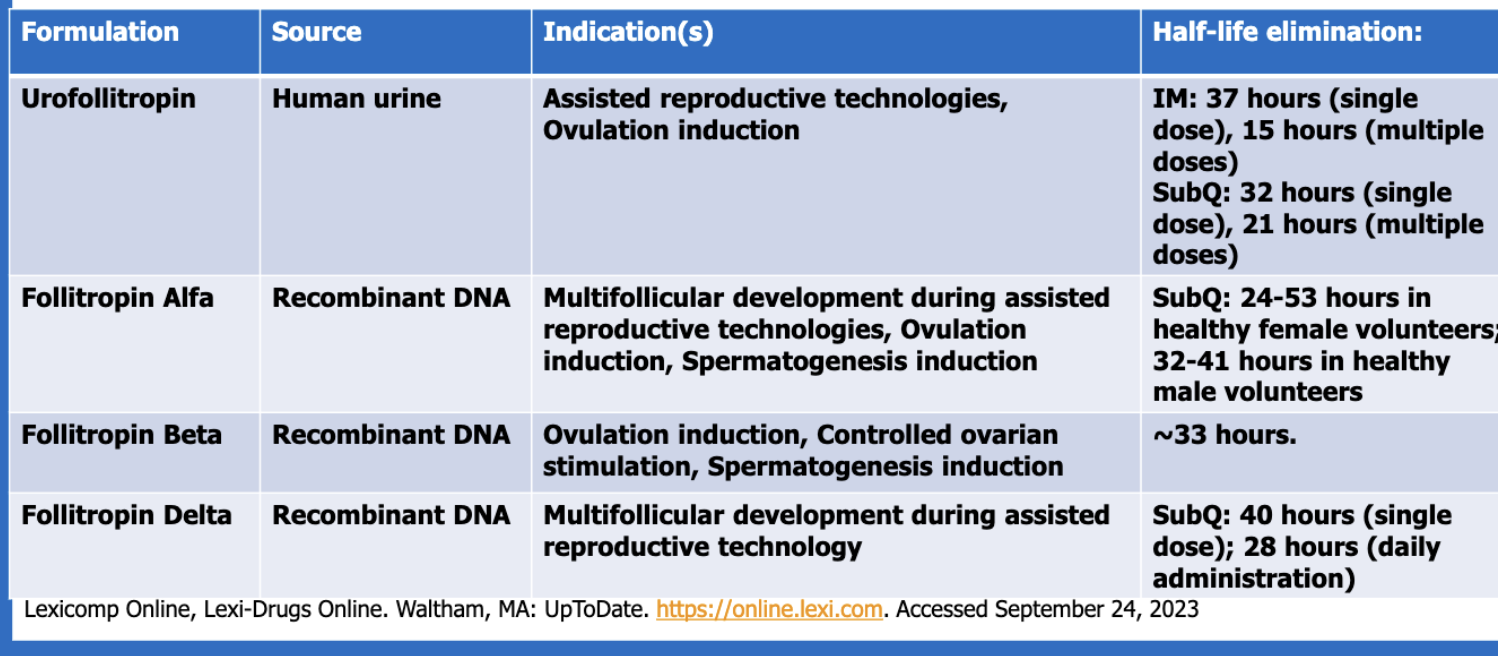
Which drug products are myeloid hematopoietic growth factors (4)?
filgrastim
pegfilgrastim
eflapegrastim
sargramostim
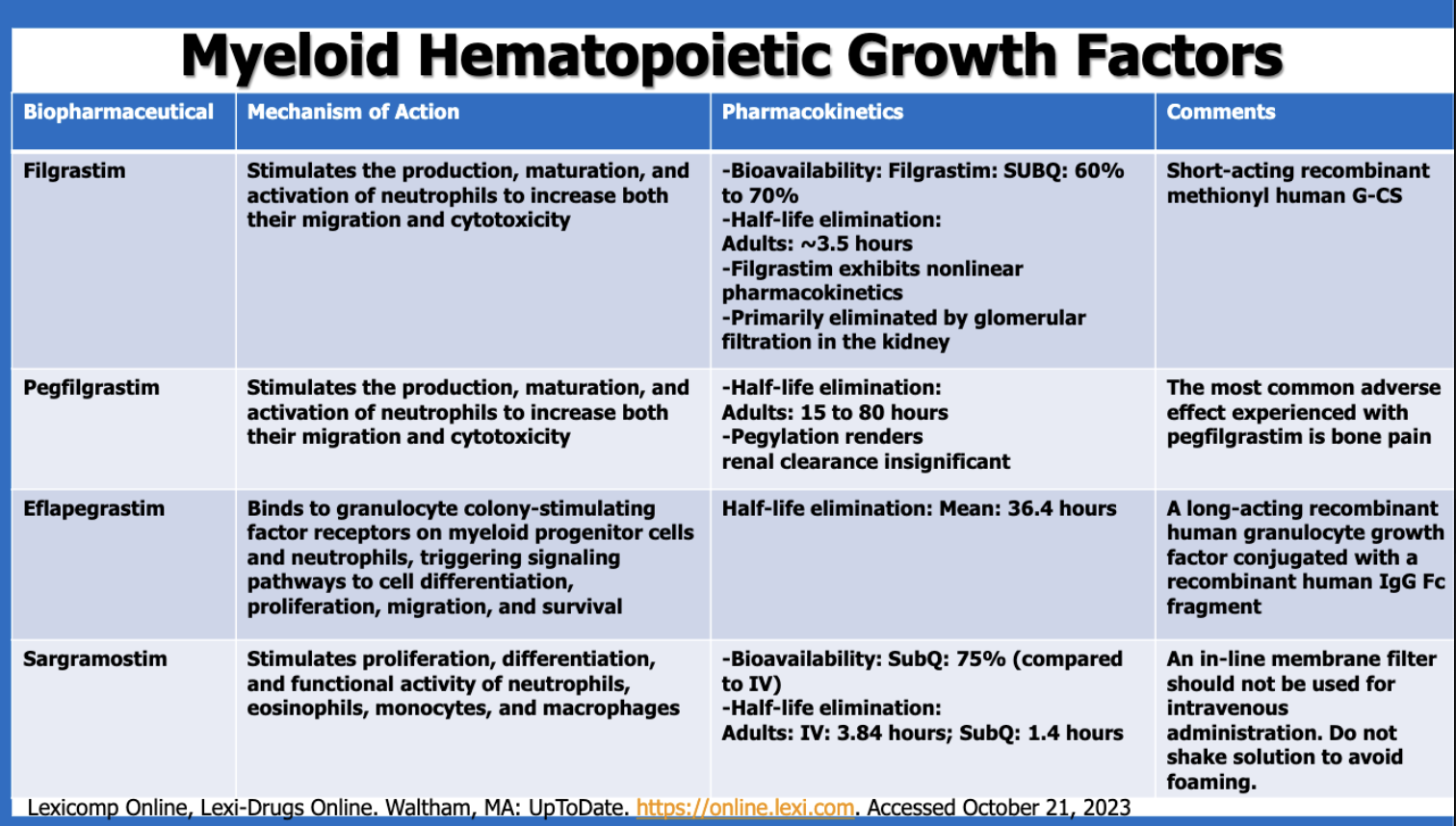
What is a major characteristic with filgrastim’s PK?
exhibits nonlinear PK
short half-life
mostly active (60-70%)
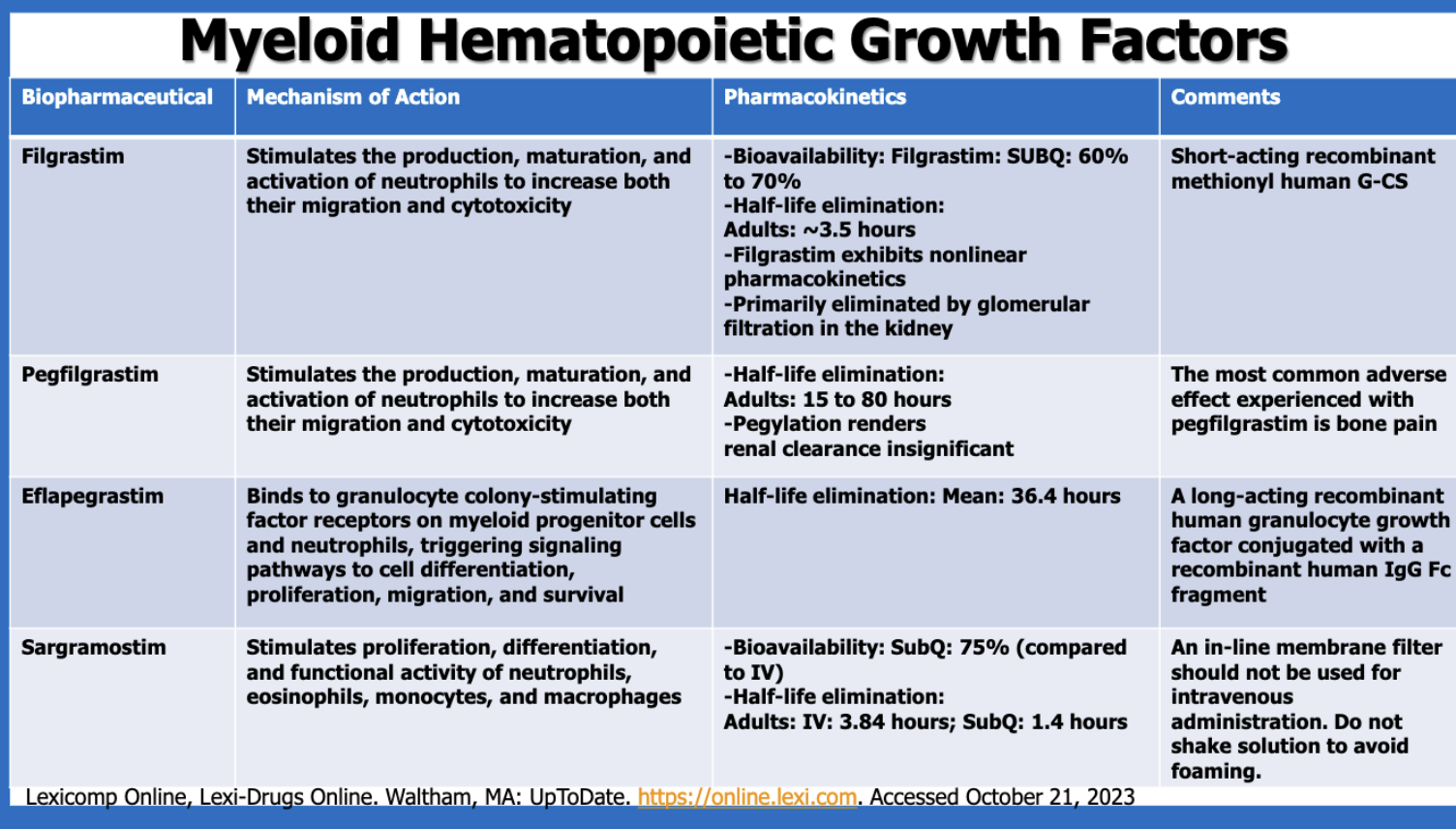
What is the most common side effect of pegfilgrastim?
bone pain
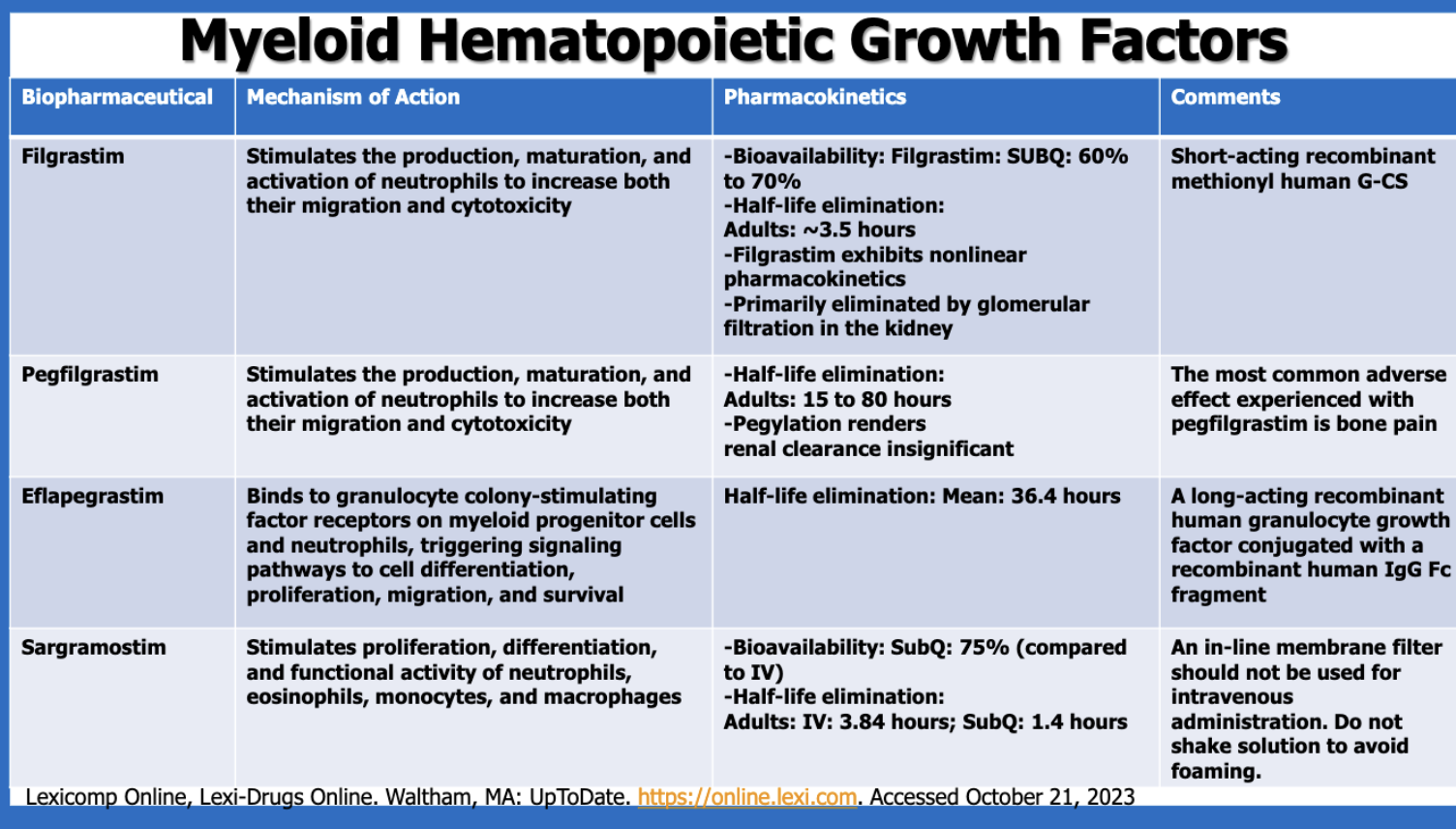
Which of the myeloid hematopoietic growth factors is made with a human IgG Fc fragment?
eflapegrastim
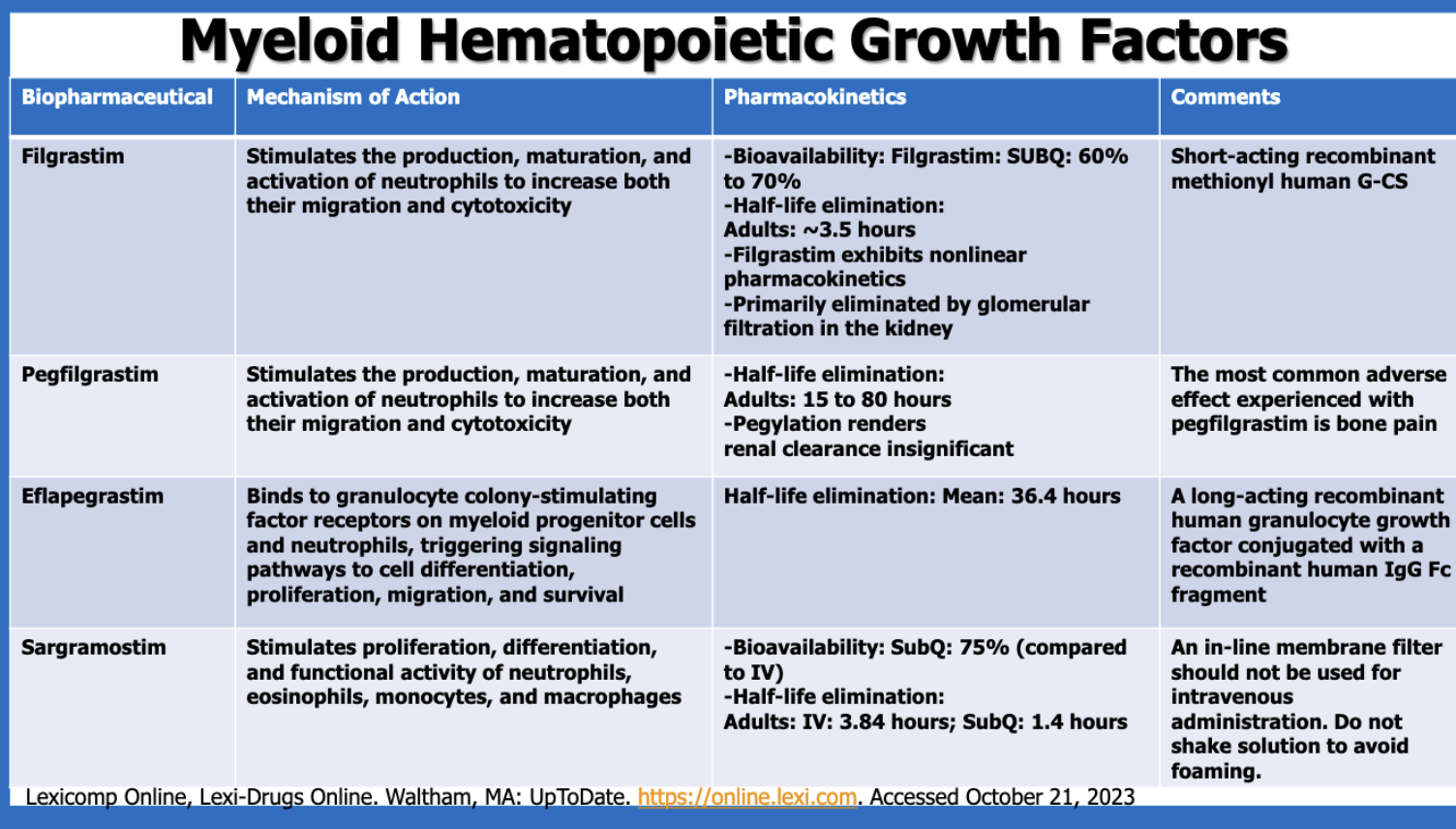
Of the myeloid hematopoietic growth factors, which has the longest half-lives?
pegfilgrastim (?) (pegfilgrastim’s half-life has a range 15 - 80 hours, whereas elfapegrastim has a mean half-life of 36.4 hours)
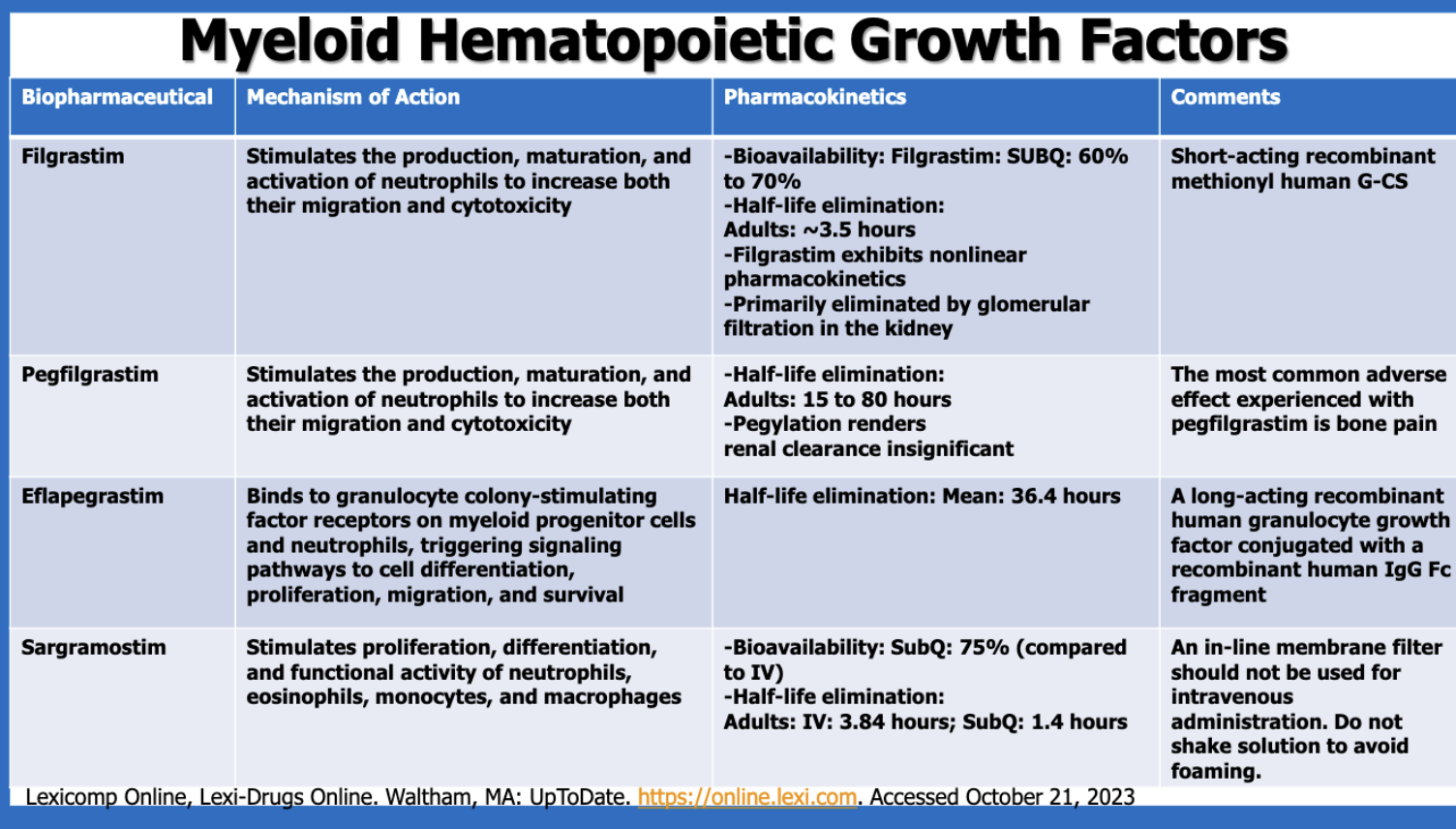
Of the myeloid hematopoietic growth factors, which has the shortest half-lives?
sargramostim SubQ (1.4 hours) (filgrastim’s is 3.5 hrs, sargramostim IV is 3.84 hr)
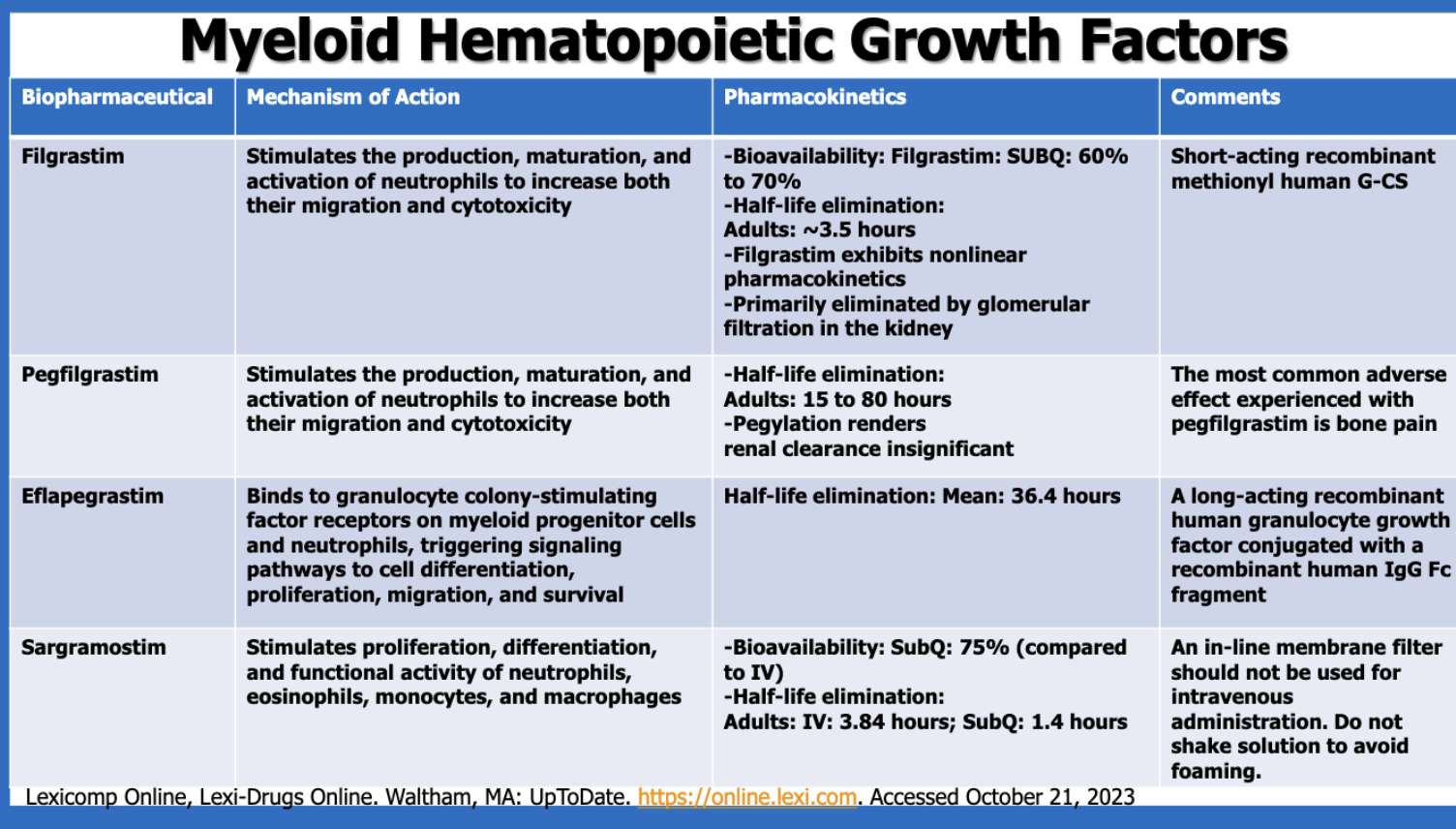
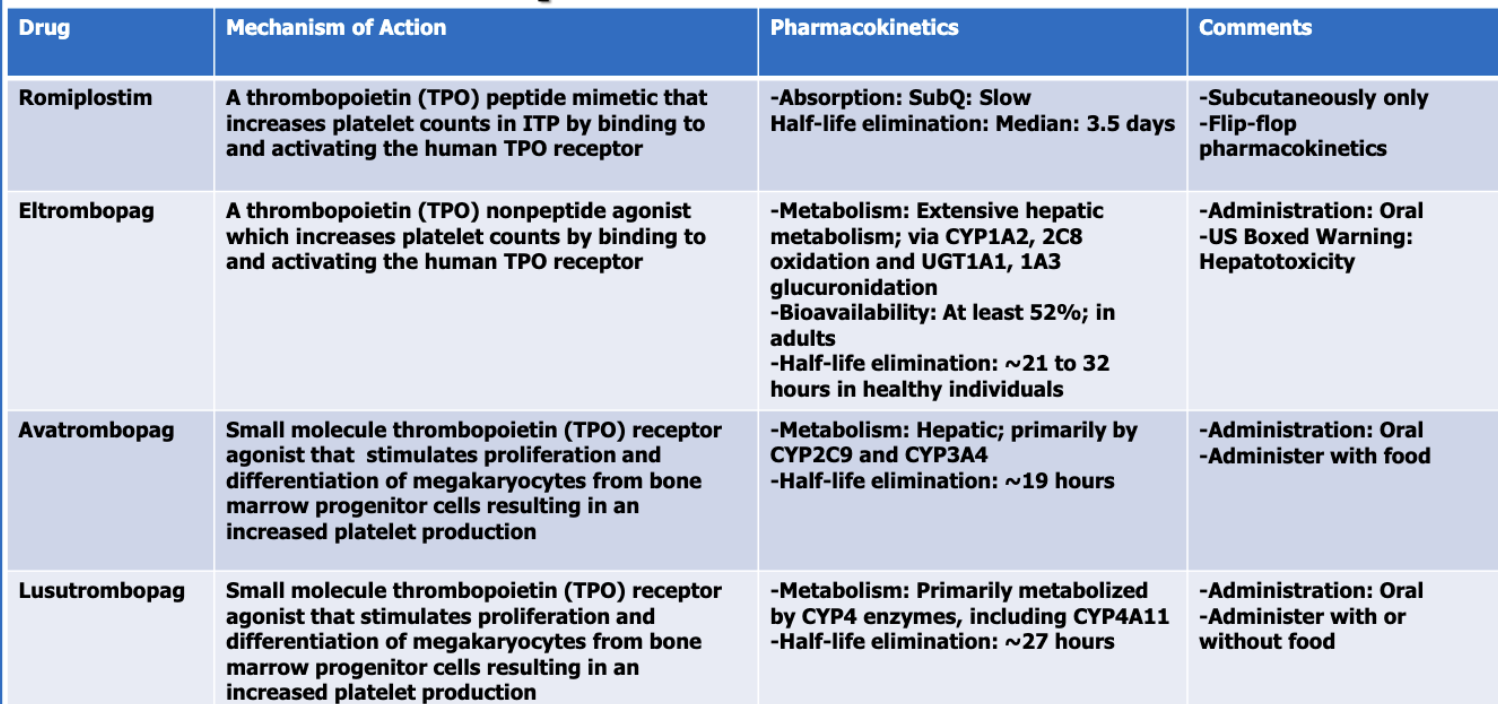
What are the thrombopoietic growth factors (4)?
romiplostim
eltrombopag
avatrombopag
lusutrombopag
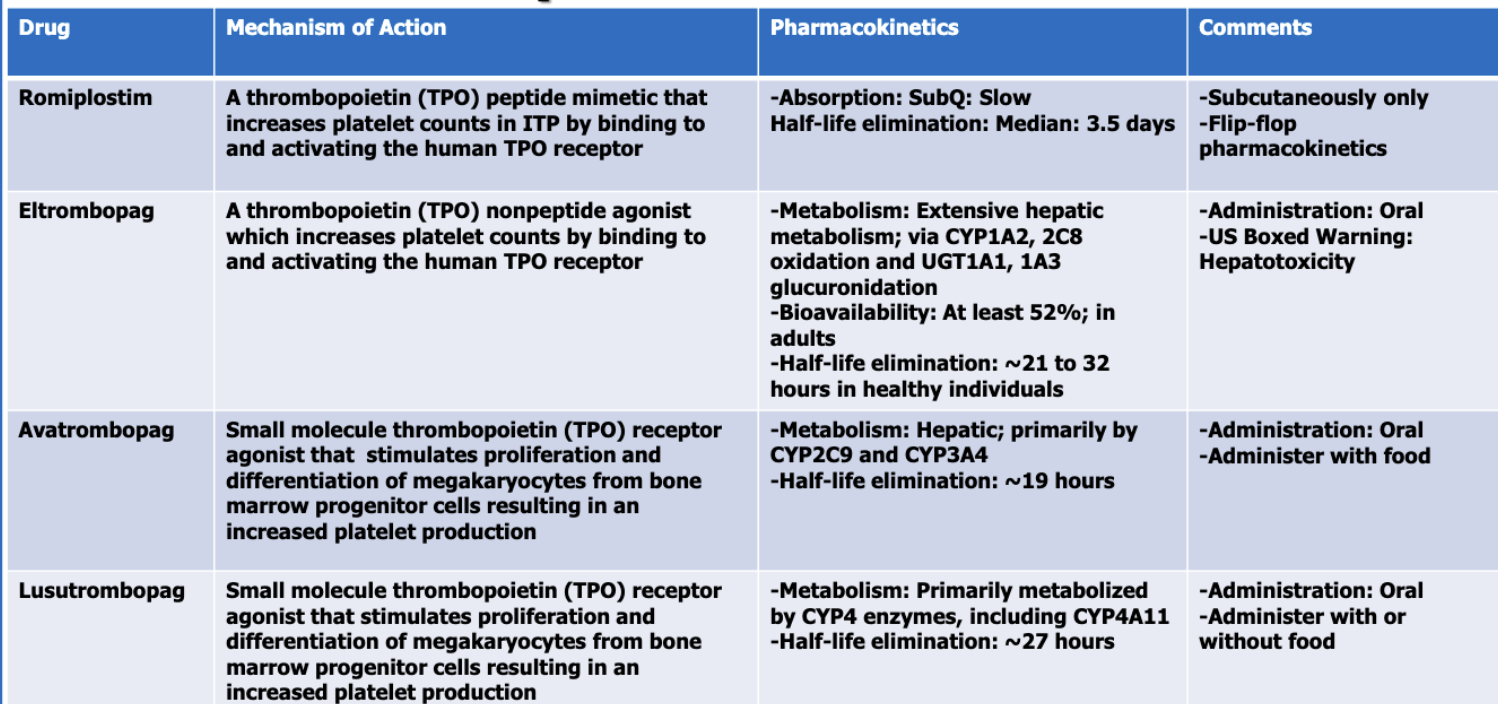
Of the thrombopoietic GFs, which follows flip flop PK?
romiplostim
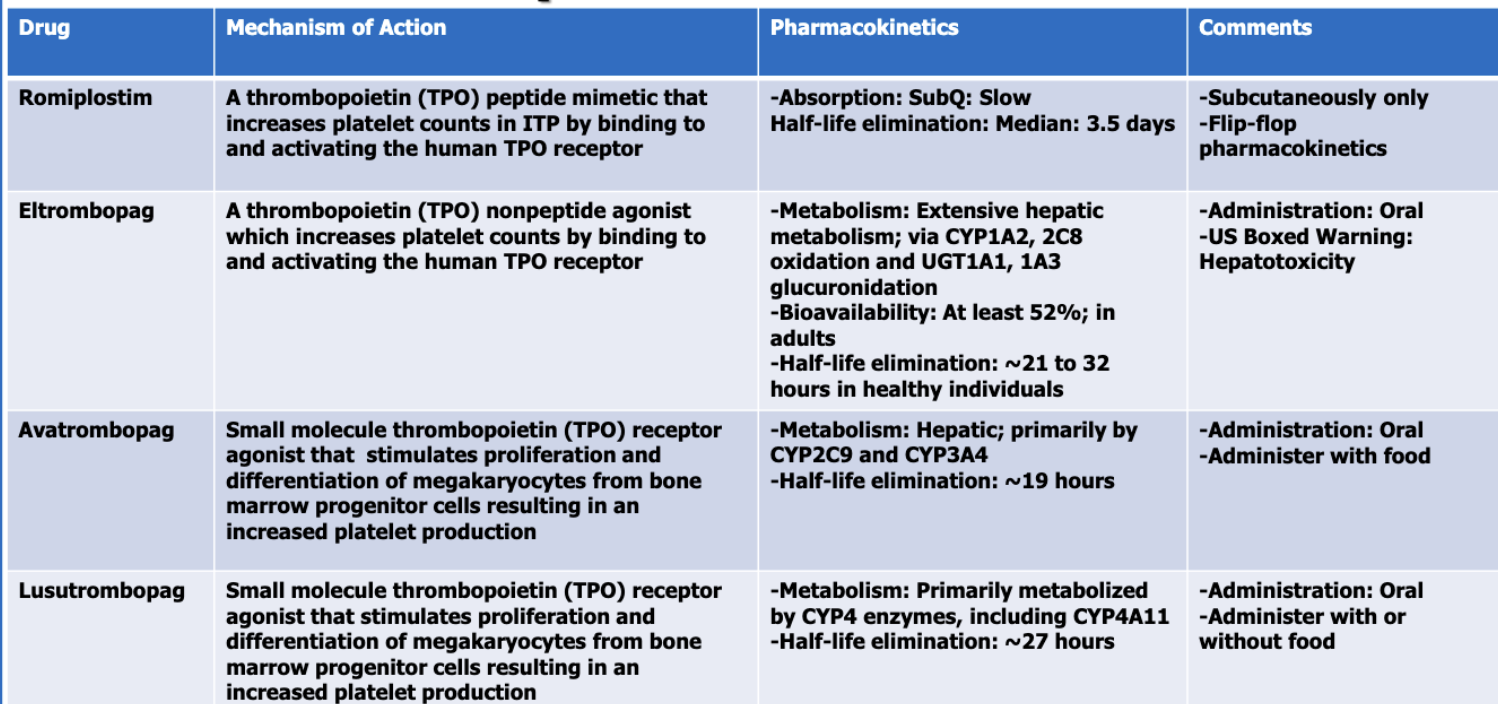
Of the thrombopoietic GFs, which has a BBW for hepatotoxicity?
eltrombopag
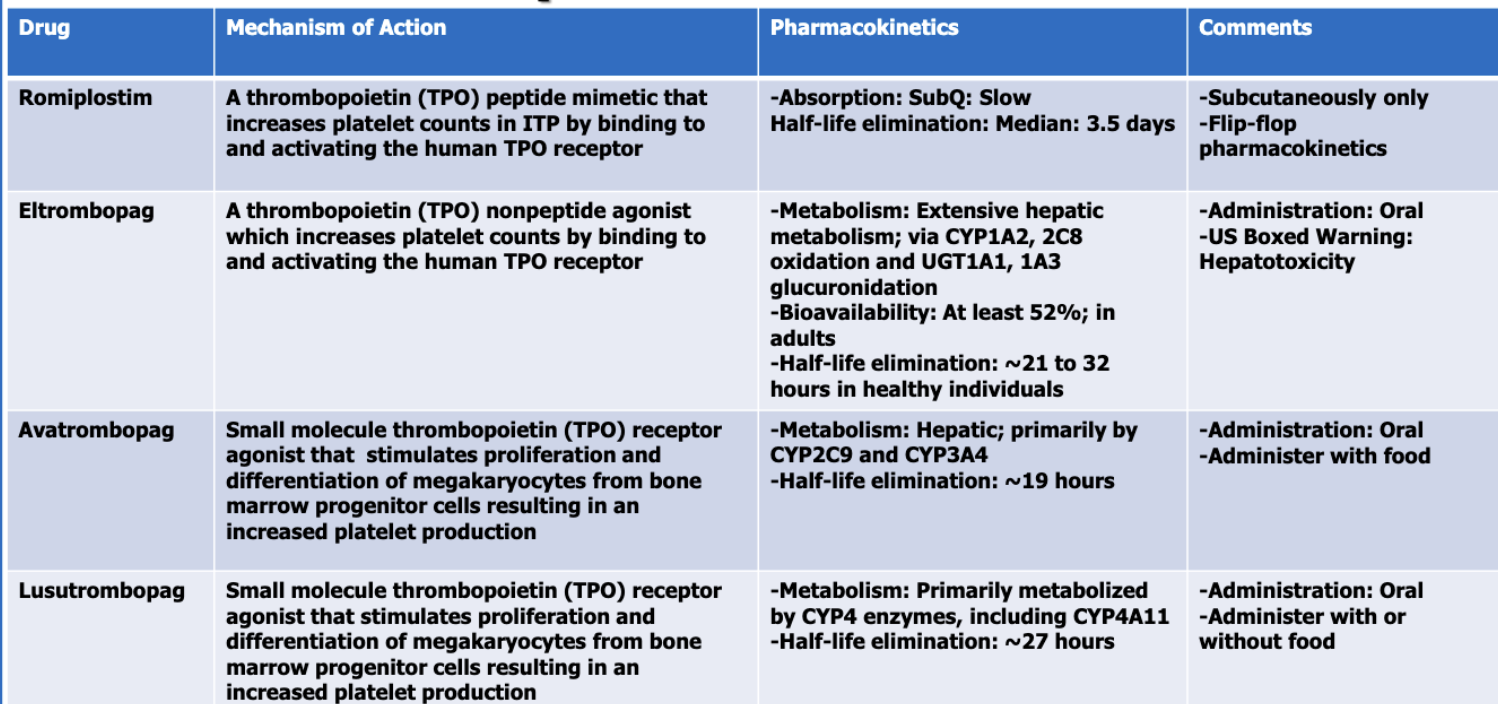
Of the thrombopoietic GFs, which has the longest half-life?
romipiostim
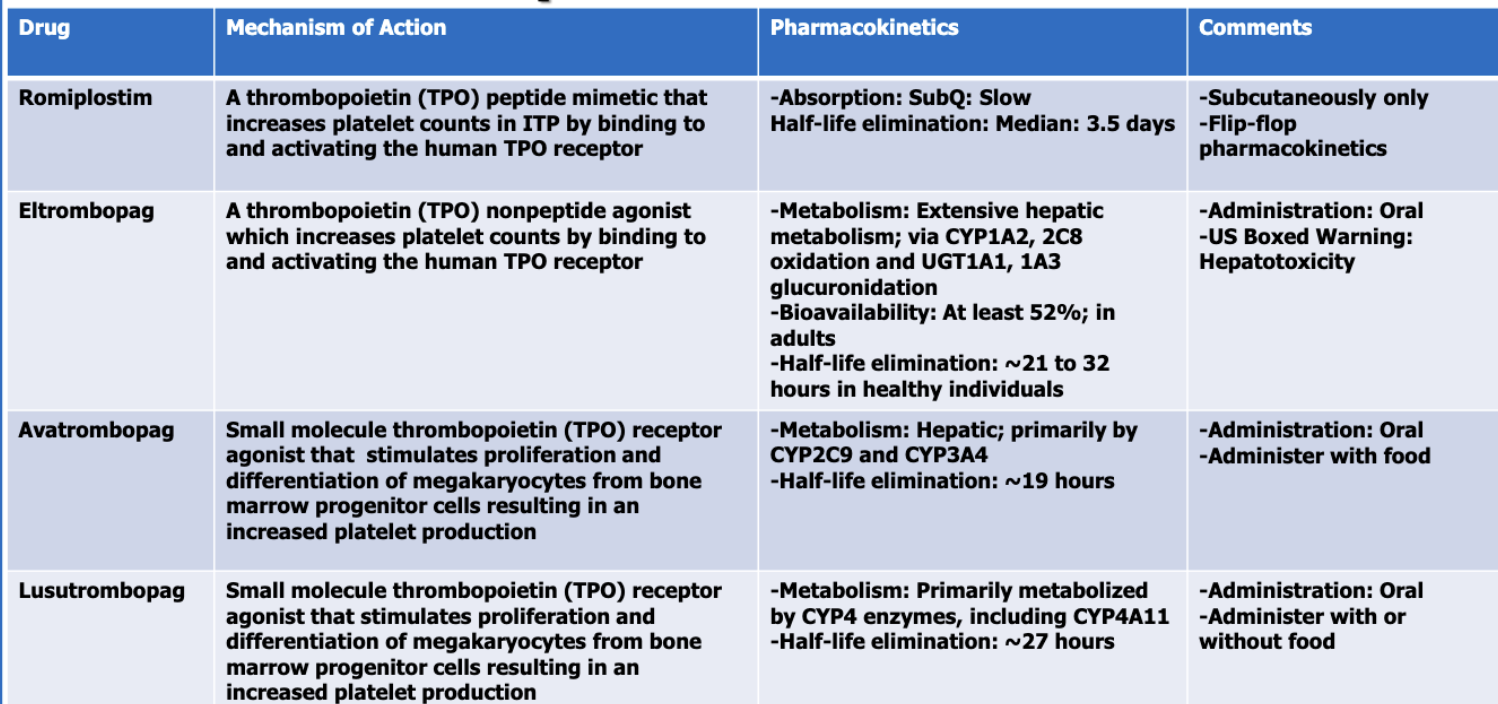
Of the thrombopoietic GFs, which has the shortest half-life?
avatrombopag
What is hemophilia B?
a defect in the gene encoding factor IX
What is hemophilia A?
Factor VIII deficiency
Where are genes encoding factor VIII and factor IX located?
X chromosome
What is the most common bleeding disorder?
von Willebrand’s disease
Which agents are used to lyse an occluding thrombus?
Plasminogen activators

Which enzyme removes an NH2 group from deoxyadenosine to deoxyinosine for purine salvage?
adenosine deaminase (ADA)

Other than be metabolized by ADA, deoxyadensoine can be converted can be converted to deoxyadenosine triphosphate via which ezyme?
deoxyadenosine triphosphate (d-ATP), leading to build up and lymphotoxicity

What are the treatments available for SCID (severe combined immunodeficiency disease)?
Enzyme replacement thearpy,
For SCID what is the drug product for enzyme replacement therapy?
eleapega
What is Gaucher’s disease?
deficient glucocerebrosidase activity leading to the accumulation of certain fatty substances (glucocerebrosides)
What are the treatment options for Gaucher’s disease?
imiglucerase (Cerezym)
velaglucerase alfa (Vpriv)
Both based on B-glucuronidase
Imiglucerase (Cerezym) has a shorter or longer half life than Velagluceraase alfa (Vpriv)?
Imiglucerase (Cerezym) has a shorter half life (3.6 - 10.4 min) than Velagluceraase alfa (Vpriv) (11-12 min)
What is L-asparaginase used for?
L-asparaginase is an oncolytic enzyme used for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia
What is the mechanism of action of L-asparaginase in leukemic cells?
L-asparaginase hydrolyzes L-asparagine to ammonia and L-aspartic acid/aspartate, leading to the depletion of asparagine and tumor growth is inhibited
What are the three different biologics of L-Asparginase?
Asparaginase (Erwinia [Recombinant]) (Rylaze)
Pegaspargase (Oncaspar)
Calaspargase Pegol (Asparlas)
(Rile up On my AS(p))
What is the biologic pegaspargase (Oncaspar) conjugated with?
monomethoxypolyethylene
(M-M-P-E)
Calaspargase Pegol (Asparlas) has a structure of L-asparaginase and monomethoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG) linked via…?
a succinimidyl carbonate linker (mPREG… suck-on-my-dicc)
What is rhDNase I used for?
treatment of cystic fibrosis
What biologic is a form of rhDNase I?
Dornase Alfa (Pulmozyme)
What is the typical concentration of dornase alfa (pulmozyme)?
2500 U/2.5 mL
What are oligonucleotides?
short chains of single stranded or double stranded ribo- or deoxyribonucleotides
What do oligonucleotides bind to?
chromosomal DNA, mRNA, or non-coding RNA (ncRNA)
What do oligonucleotides modulate, and via what process?
gene expression through Watson-Crick base pairing w/ targeted nucleic acids
What micro/macromolecules are included under the umbrella term, oligonucleotides?
antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), small interfering RNA (siRNAs), microRNA (miRNAs), aptamers, and DNAzymes
Oligonucleotides are very ____ molecules
potent
MOA of oligonucleotides
direct binding to non-nucleic acids and interfere with gene expression
What are the translation inhibiting oligonucleotides?
antisense oligonucleotides, ribozyme DNAzyme, small interfering RNA
What is the MOA of antisense oligonucleotides?
binds to mRNA, blocking it from ribosomal RNA for translation
What is the MOA of ribozyme/DNAzyme?
bind to mRNA and break it down
What is the MOA of small interfering RNA?
bind to mRNA and RISC protein recognizes the mRNA outside of the nucleus and breaks it down
What is the BBW with mipomersen (Kynamro)?
risk of hepatotoxicity (for a pt to get it, they need to go through strict program called Kynamro REMS)
How is mipomersen (Kynamro) administered? stored?
SUBQ, refrigerated
What is the indication of nusinersen (Spinraza)?
treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
(SPINraza = SPINal)
What are concerning adverse effects with nusinersen (Spinraza)?
Hematologic effects (coagulation abnormalities and thrombocytopenia) and renal toxicity (potentially fatal glomerulonephritis)
Which biologics are antisense?
mipomersen (Kynamro), nusinersen (Spinraza), and inotersen (Tegsedi)
Which biopharmaceuticals are anti-transthyretin small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) agents?
patisiran (Onpattro), vutrisiran (amvuttra) (both for polyneuropathy of hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis in adults)
What are the concerns with patisiran (Onpattro) and Vutrisiran (Amvuttra)?
reduced vitamin A levels, IV infusion-related (patisiran only)
What is the antilipemic siRNA agent?
Inclisiran (Leqvio)
What are concerns with inclisiran (3)?
UTI like blood in urin, burning/pain, feeling need to pass urine often or right away, fever, lower stomach/pelvic pain
SoB
allergic rxn
What is the aminoevulinate synthase 1-directed siRNA agent?
givosiran (Givlaari)
What are concerns with givosiran (5)?
anaphylaxis
hepatic toxicity
increases in blood homocysteine levels
injection-site rxns
renal toxicity
What is CRISPR/Cas9 made up of?
TWO key molecules: Cas9 enzyme, piece of RNA called guide RNA (gRNA)
Which biologics are the Antisense-Mediated Epson Skipping Oligonucleotides?
Casimersen (Amondys 45), eteplirsen (Exondys 51), Golodirsen (Vyondys 53), and vitolarsen (Viltepso)
(used in transcript repair)
What are the antisense-mediated epson skipping oligonucleotides indicated for?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
What are the specific concerns with casimersen (Amondys 45)?
renal clearance is reduced in non-Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) pts w/ renal impairment
What are the specific concerns with eteplirsen (Exondys 51)?
hypersensitivity reactions
What are the specific concerns with Golodirsen (Vyondys 53)?
hypersensitivity reactions, kidney toxicity, including potentially fatal glomerulonephritis