AP government fall final review!!
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:37 PM on 12/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
Federalist papers #10
James Madison argues that a large republic helps combat against factions (inevitable in a free society.)
2
New cards
Popular sovereignty
All political power resides in the people. The people are independent.
3
New cards
Full faith and credit clause
state laws and court decisions must be honored by outher states.
4
New cards
commerce clause
Gives congress the power to regulate commerce among states, upheld in (Gibbons vs Ogden.)
5
New cards
Federalism
Powers of government are divided between the states and federal government.
6
New cards
Dual federalism
national and state governments are seen as separate entities providing separate services. (weakens the national government.)
7
New cards
Supremacy clause
Establishes the constitution as the “supreme law of the land”, Established in McCullough vs Maryland.
8
New cards
Reserved powers
powers that the constitution does not grant to the national government but does not deny to the states (10th amendment)
9
New cards
Exclusive powers
powers only given to the national government. (Coining money, making treaties, and regulating commerce)
10
New cards
Categorical grants
Grants given to the states for specific purposes, such as building an airport or a school program.
11
New cards
Block grants
money given to the states without strings attached.
12
New cards
Incumbent advantages
well known, more connections, more money.
13
New cards
Linkage institutions
interest groups, political parties, media, and voting all link citizens to the political process.
14
New cards
Realignment
The switching of voter process from one party to another. This can happen during “critical elections”
15
New cards
Interest groups
Primary purpose is to influence public policy, and has a very narrow point of view. They influence through PACS, use of media,and grassroots campaigns.
16
New cards
Pluralism
the idea that having a variety of parties and interest groups will strengthen the system.
17
New cards
Public agenda
the issues that the general public and political leaders agree need attention.
18
New cards
Open primary
a primary in which any voter regardless of party status can vote
19
New cards
closed primary
a primary in which only those with active voter status within the party can vote.
20
New cards
House of representatives
states are given representation based of their population. Speaker of the house is the most powerful figure in the house
21
New cards
Iron triangle
Composed of congress, interest group, and bureaucracy.
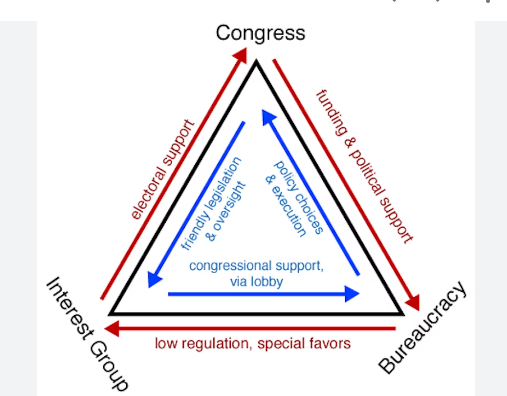
22
New cards
Hard money
Funds that are given directly to a specific candidate. these funds are regulated and disclosed.
23
New cards
soft money
Funds that are NOT directly given to the candidate. these do not have limits.
24
New cards
Citizens united vs. FEC (2010)
supreme court ruled that political spending by corporations and labor unions is a form of free speech and protected under the 1st amendment, removing any bans on “soft money.”
25
New cards
state legislature
The government institution responsible for the drawing of congressional district lines.
26
New cards
Gerrymandering
congressional districts have been drawn in an odd shape to the advantage of the political party in control of state legislature.
27
New cards
Pork barrel spending
Money within spending bills that benefits constituents back home in districts/states.
28
New cards
Treaties
All treaties must be approved by a 2/3 vote of the senate.
29
New cards
senate prestige
terms are longer then the house, and more responsibility therefore more prestige.
30
New cards
Filibuster
used to prevent action on a bill, by talking. (unlimited debate in the senate leads to these.)
31
New cards
cloture
the main way to end a filibuster, by a 3/5ths vote in senate. (60/100)
32
New cards
Congressional committees
divides workload evenly among congress to properly screen bills and allowing members to develop expertise.
33
New cards
standing committees.
Permanent committees that deal with broad areas of public policy. (house rules committee, ect.)
34
New cards
Divided government.
When the House, senate, and presidency are not controlled by the same party.
35
New cards
presidential expressed powers
Command the armed forces, veto acts of congress, grant pardons and reprieves, negotiate treaties, Nominate federal judges, and give the state of the union address.
36
New cards
Rosseau
belived in direct democracy, in which everyone voted.
37
New cards
Hobbes
Most famous for his social contract theory.
38
New cards
Locke
Uses a theory of natural rights to argue that governments have obligations to their citizens.
39
New cards
marburry vs madison
Court case that established the principle of judicial review
40
New cards
Mcullough vs Maryland
Gave the federal government the rights to set up a federal bank and declared that states could not tax the federal government.