exam1 human anat 125
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
histology
study of tissue
physiology
study of functions in human body structures
hierarchy of structural organization
Chemical Level
Cellular level
Tissue level
Organ Level
Organ Systems
how many cells in human body?
100 trillion
What are the Groups of Tissue
Muscle
Nervous
Connective
Epitheal
Metric System Units of Measure
Meter, Gram, Liter
Metric Units of Measure in Order Great to Least
Kilo, Hecto, Deka, Deci, Centi, Milli, Micro
Membranes of Ventral Cavity?
Parietal Serosa & Visceral Serosa
Parietal Serosa
Membrane that covers cavity
Viceral Serosa
Membrane that covers organ
Peritoneum
Serosa lining abdominal cavity
Pleura
Serosa lining lungs
Pericardium
Serosa lining heart
Morphology
The study of different cells
Prokaryotic Cell
No nucleus no compartments
Eukaryotic
Many compartments and Yay nucleus
Plasma Membrane
It separates cell from outside and is made of Phospholipids ;join in two layers to creat plasma membrane
osmosis
is the passive transport of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
solution
salute + solvent
concentrated solutiong
>solute (sugar) < solvent (water)
diluted solution
< solute (sugar) > solvent (water)
endocytosis
mechanism by which particles enter cells
Endocytosis Process (Steps)
phagocytosis: engulfs particle in vacuole
pinocytisis: absorbtion of extracellular fluid
receptor mediated endocytosis: binding of external molecules to membrane
Exocytosus
moves substances out of cell
Cytoplasm
Cytosol: jelly like fluid containing organelles in cell
Ribosomes
made of protein and make protein
Central Dogna of Moleulcar Biology
DNA RNA mRNA = Protein!
Peptide Bonds
holds amino acids together so proteins are made
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
has ribosomes attached,, and protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
No ribosomes and it makes enzymes for lipid metabolism
Golgi Apparatus
Packing and ships protein from ER and send to where needed
Where can the Golgi Apparatus Send proteins
exogated (kick out if cell)
Embed in cell membrane
within cell
Mitochondria
Generates energy ATP via respiration (you get this from your mom)
Lysomes
has digestive enzymes that breakdown macromolecules
Peroxisomes
Get rid of reactive chemical bonds (Detoxification)
Centrosomes
sphere structure containing centrioles
Centrioles
cylinder bodies that are located in centrosomes 27 microtubes total
inclusions
temporary structure in some cells (melanin)
Nuclear Envelope
two parallel membrane protects nucleus
nucleolos
little nucleus, ribosome manufacture
Chromatin
DNA + Histones
Purines DNA
A G
Pyrimidines
C T
How many chromosomes do you have?
46! autosomes: 22
Sex chromosome: 1
Mitosis
Cell Division
Genome
set of organisms genes
Homologous Chromosome
Similar chromosomes ex. one eye gene from each parent
Cell Reproduction
A) Cell Replicate
B) Cell Division
Mitosis (PMAT)
Cytokinesis
How to begin Mitosis ?
Replicate parent’s genes first. Then turn them into chromosomes by combining the 4 so they look like X instead of I I.
Prophase
Nuclear Envelope disappears and Mitotic spindle appears! The Chromatin turns into chromosomes for each parent!
Metaphase
Sister chromatids line up on metaplate
-X-X-X-X
Anaphase
sister chromatids break in half and separate to other side of cell
Telephase
Chromosomes go back into chromatin. Nuclear env appears Metiotic spindal disappear
Cytokinesis
Last step of cell division the cells separate! yay complete.
Cancer Cells
disease group of cells have uncontrollable growth and invade different parts of body ; metasis
Tissues
group of cells working for common function
Epitheal
cover and line
Connective Tissue
Support and Bind
Nervous Tissue
communication and control
Muscle Tissue
Movement
Epithelia
Tissue that covers external body (epidermas) lines cavities too
Glands
secretion! hormones sweat allat
Epithelia Functions
Protection
Absorption.
Secretion
Sensory receptors
Simple Epithelia
One layer of cells
Stratified Epithelia
Two or more layers of cell
Squamous
Round cell structure
Cuboidal
Cube shape square
Columbar
Long column like cell
Psuedostratified Epithelium
tall varies in height cells and has cilia
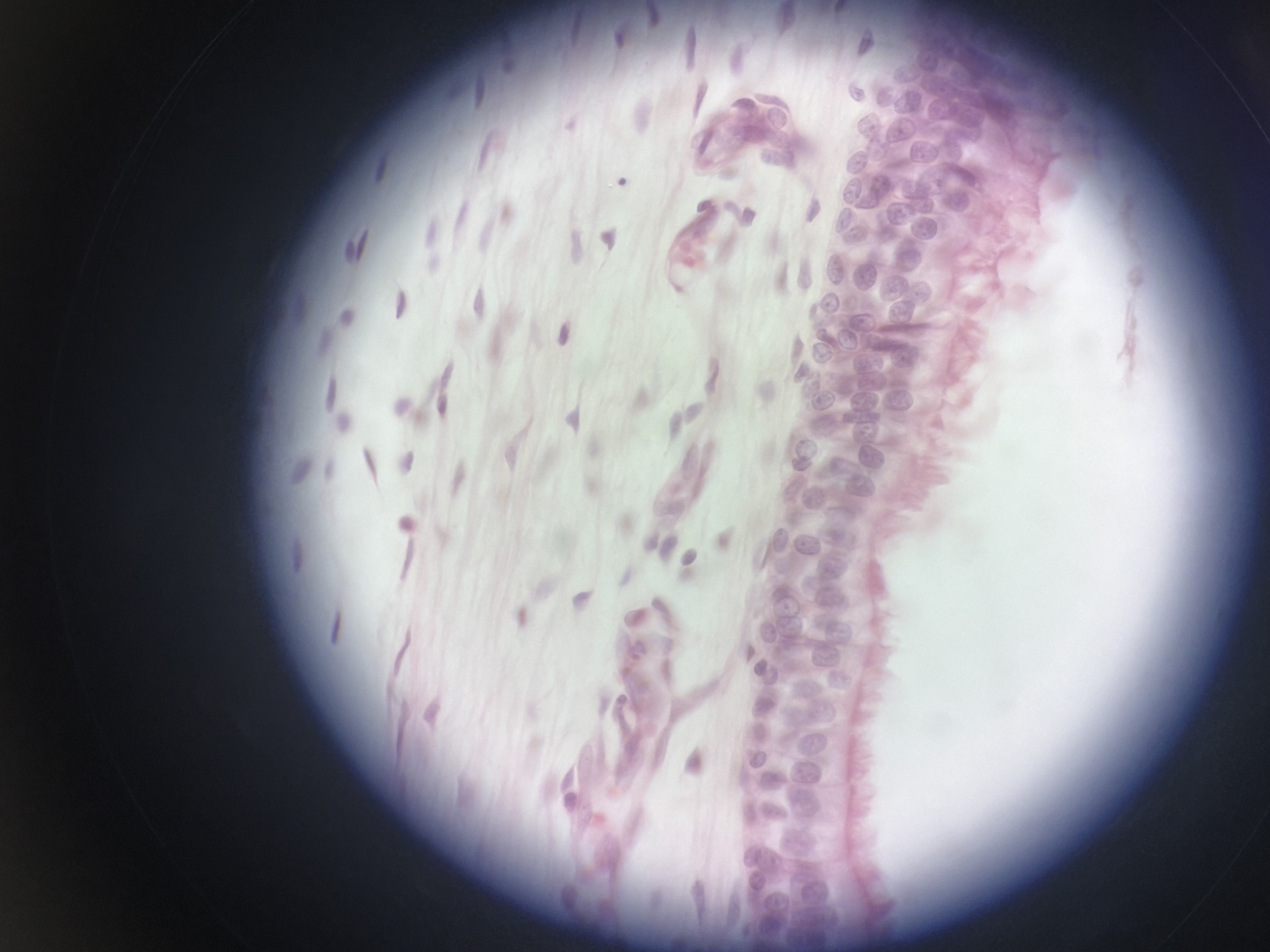
Transitional Epithelium
Stretches,, is found in urinary system
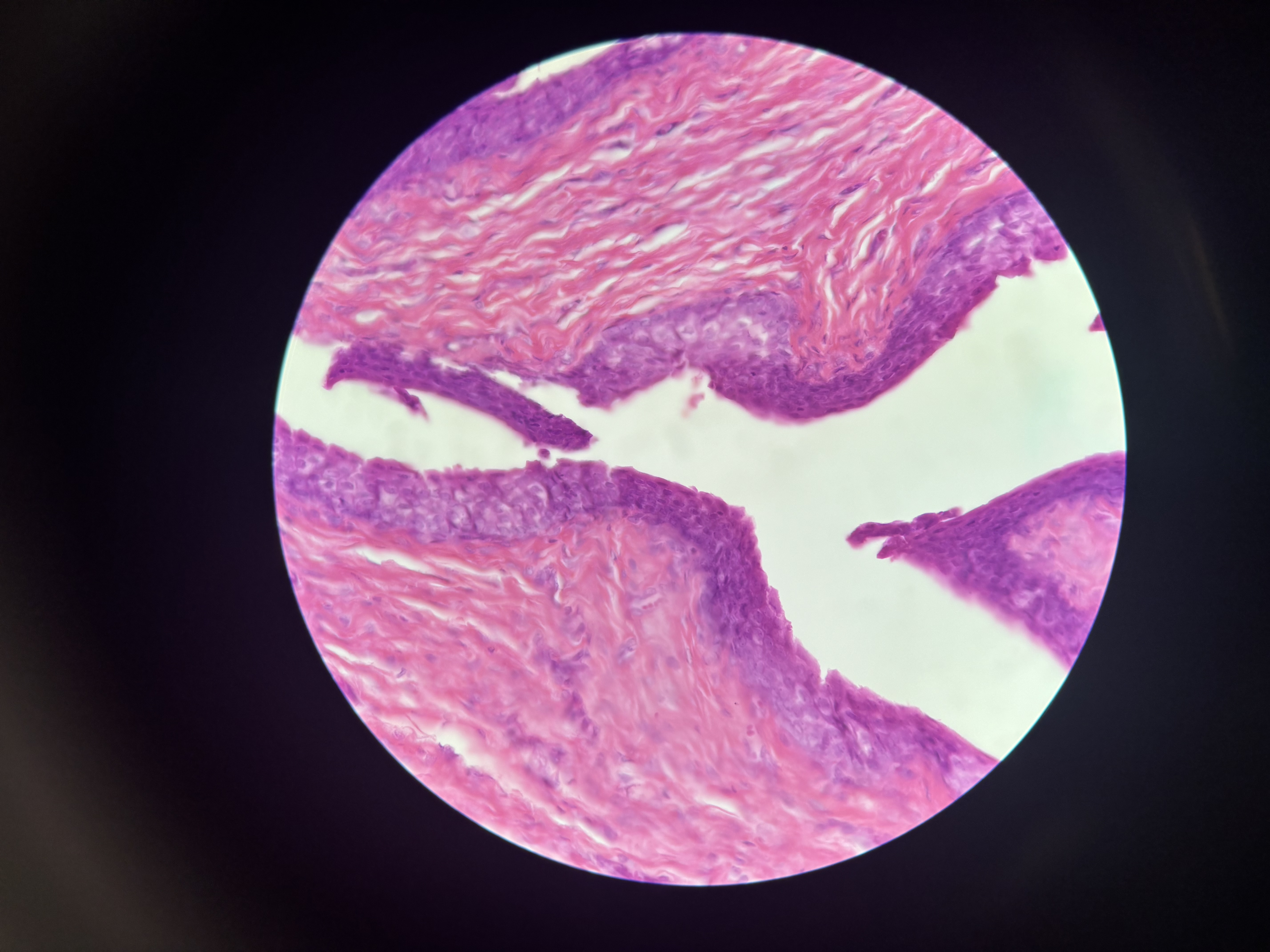
Simple Squamous Epithelium
single layer if cube like cells with disk shaped nuclei
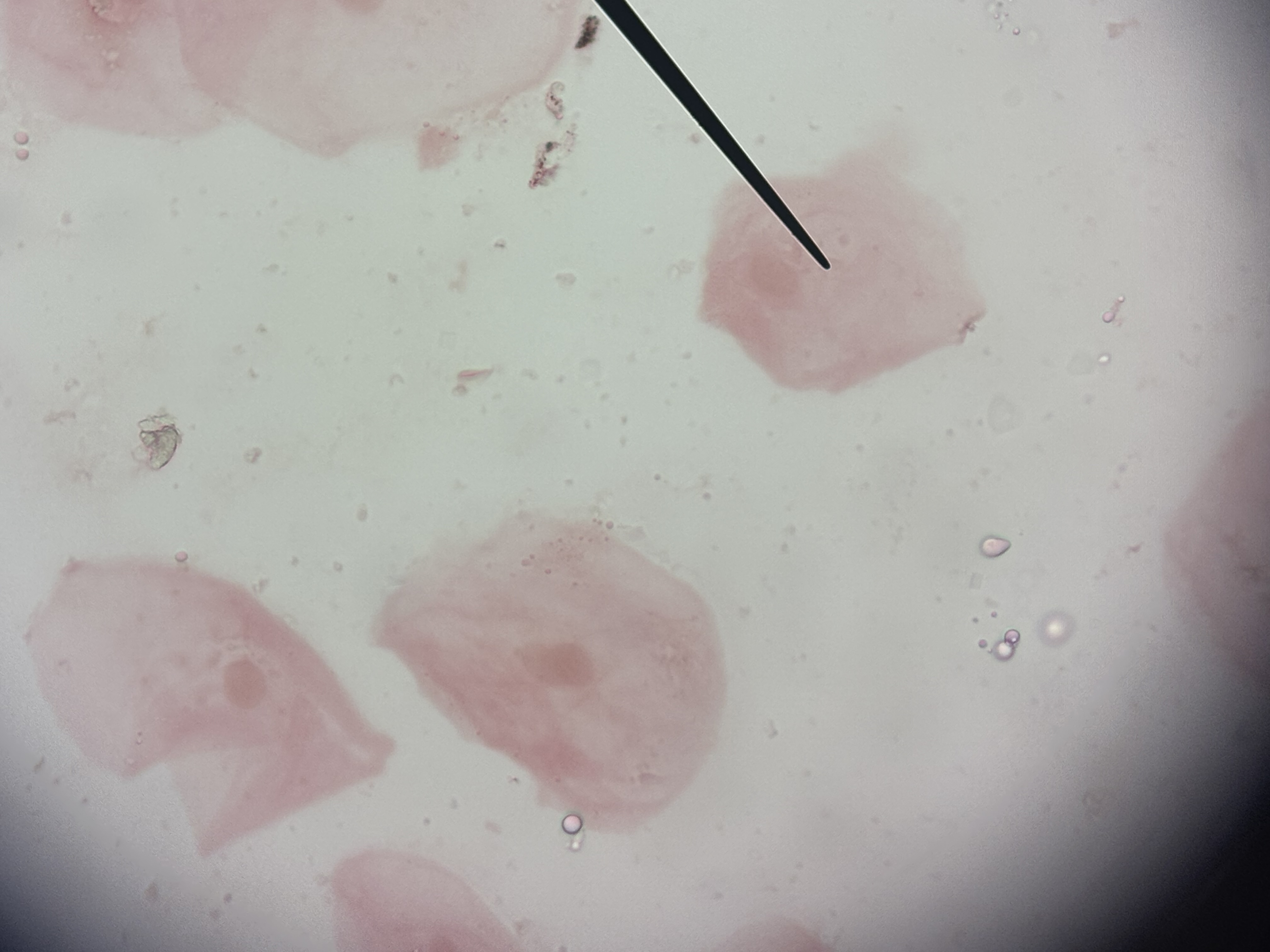
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
single layer cube like cell large nuclei
function: absorption
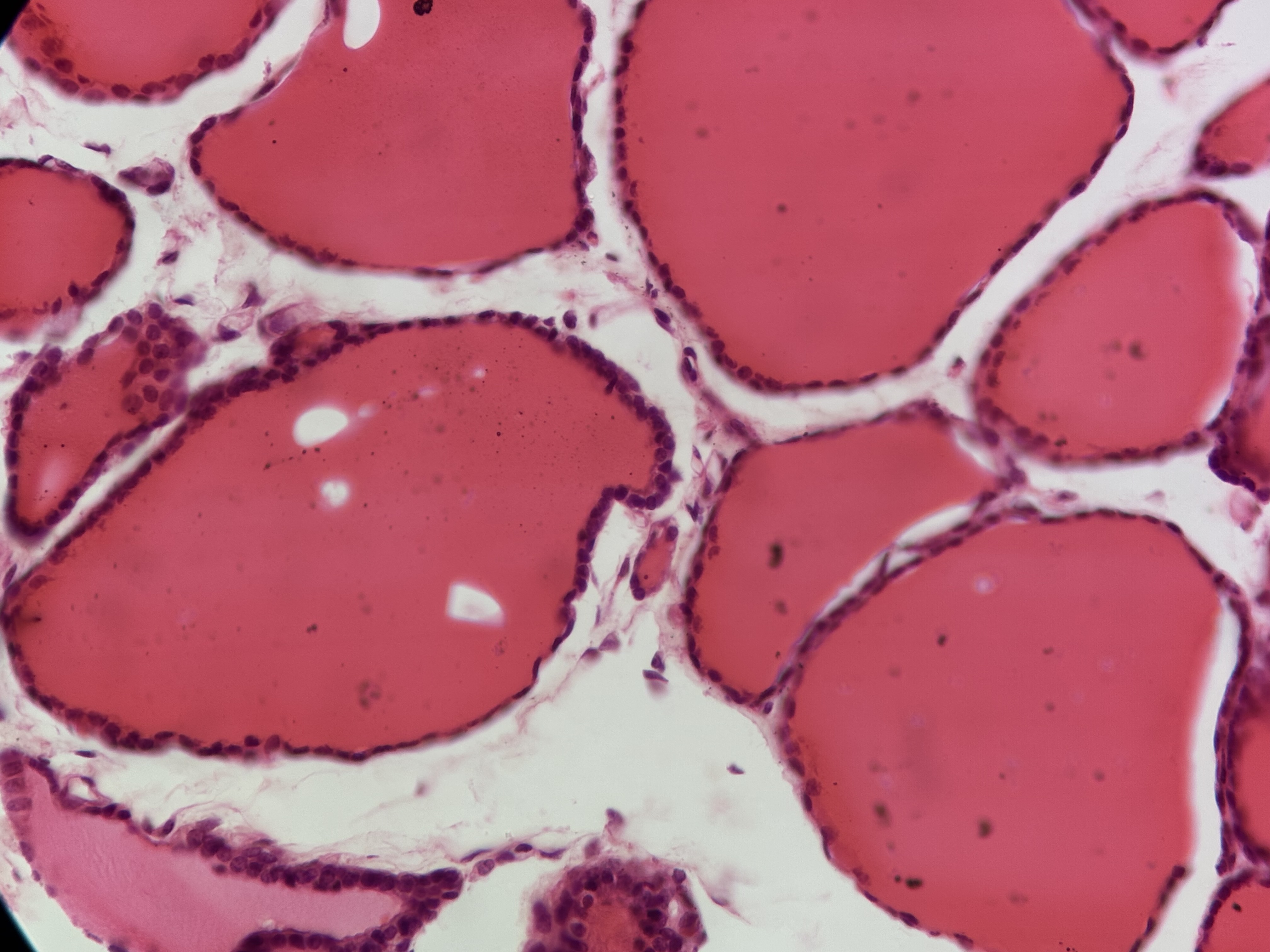
Simple Columnar
single layer of rectangular cells oval nuclei,, some have cillia,, goblet mucus
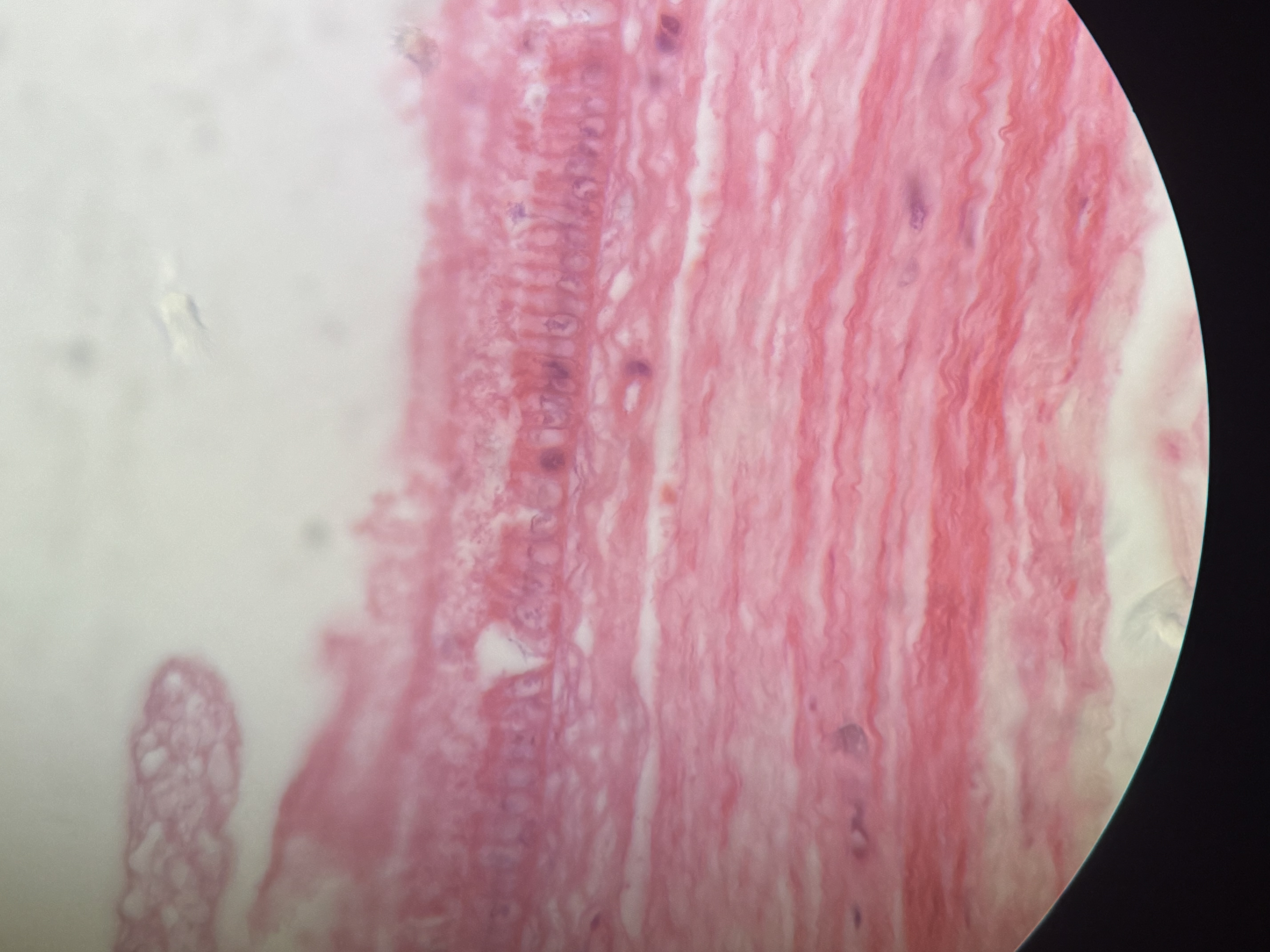
Glands
many epithelial cells that make and secrete
Endocrine Glands
lose surface connection as they develop,, secrete hormones; stay inside
Exocrine Glands
retain ducts, secretion empty through these ducts; goes to surface
Unicellular Gland
scattered through epithelial lining of intestines
Multicellular Exocrine Glands
a) Simple duct
b) compound duct
Simple Duct for Gland
Has only one branch
Compound Duct for Glands
Many branches
Epithelial Surface Features
adhesive proteins
wavy contours to weave cells together
Cell junction
Cell Junction consists of?
tight junction
adheres junction
Desmosomes
Tight Junction Epithelial
closes off space in between on top of cell
Adherens Junction Epithelial
right under the tight junction and helps hold cell together with linker proteins
Desmosomes Junction Epithelial
it is under adherence junction. Main function is binding,, And making sure the inside of the cell is held together.
Pattern of DNA
they go together!
A T
C G
G C
T A
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
poorly vascularized tissue made of fibers of collegen that go in the same direction,, it attaches bones to bone
Dense Irregular CT
tissue that has thick collagen that go different directions
Cartilage
a firm connective tissue that resists compresion and tension,, contains chondrocyte cells
What are the type of Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage, Fibro Cartilage, Elastic Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
supports and cushions ex: ribs
Fribro Cartilage
absorbs shock ex: spine
Elastic
provides flexibility and snaps back into shape ex: throat flap and ear
Bone (Osseous Tissue) Function
support and protect organs, stores calcium, minerals
Bone Marrow
site for blood formaton
Osteoblasts in Blood
secrete collegen fibers and matrix
Osteocytes
are mature bone cells in lacunae
Blood Tissue
the fluid in blood vessels that develop from mesenchyme (nonliving matrix plasma)
3 Types of membranes
Cutaneous Membrane, Mucus Membrane, Serous Membrane
Cutanous Membrane
it is the skin that protects the body