Unit 4: Cell Division and Variation
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
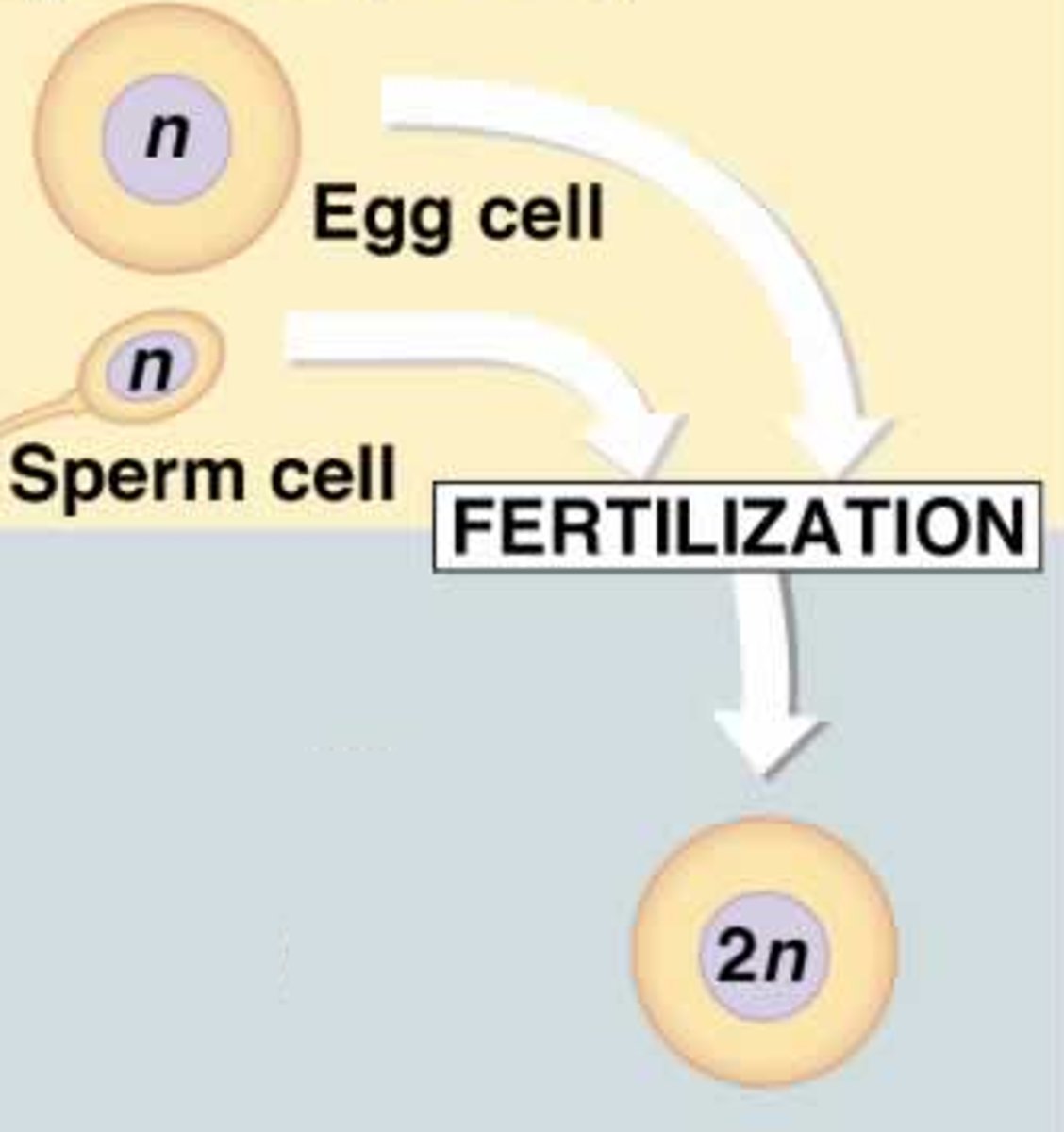
Sexual Reproduction
two parents create a genetically unique offspring, usually by combination of egg and sperm
Asexual Reproduction
offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only; it does not involve the fusion of gametes (sex cells like sperm or egg). Examples include cloning, regeneration, budding, mitosis)
Clone
A cell, group of cells, or organism that is genetically identical to a single ancestor. Can be natural (identical twins) or using technology.

Species
organisms that are genetically similar and can sexually reproduce to make fertile offspring

Variation
any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences or by the effect of environmental factors.

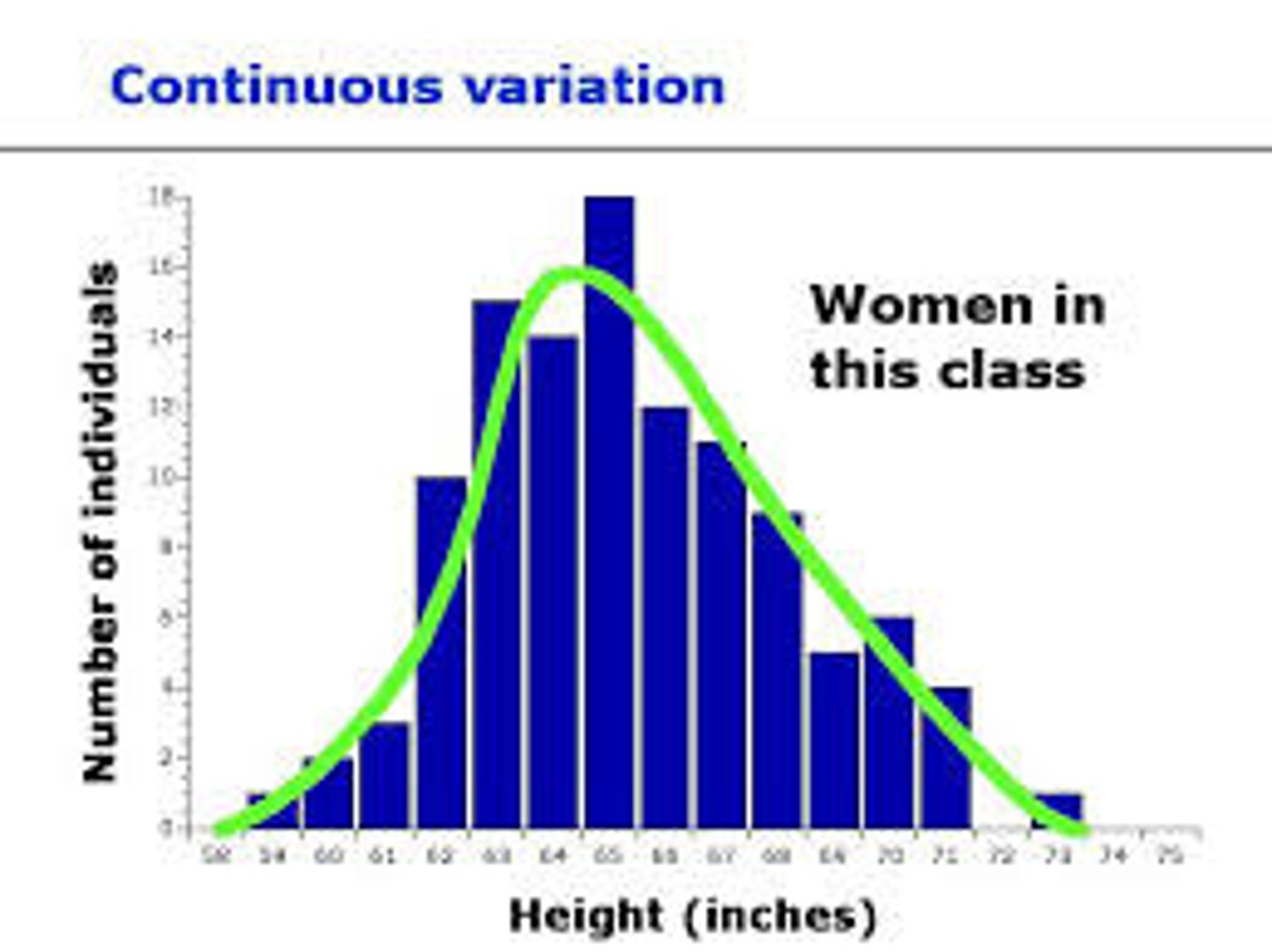
Continuous Variation
natural variations like height where we have a range of natural differences from one extreme to another and everything in between (1.6m, 1.8m, 2.0m, etc)
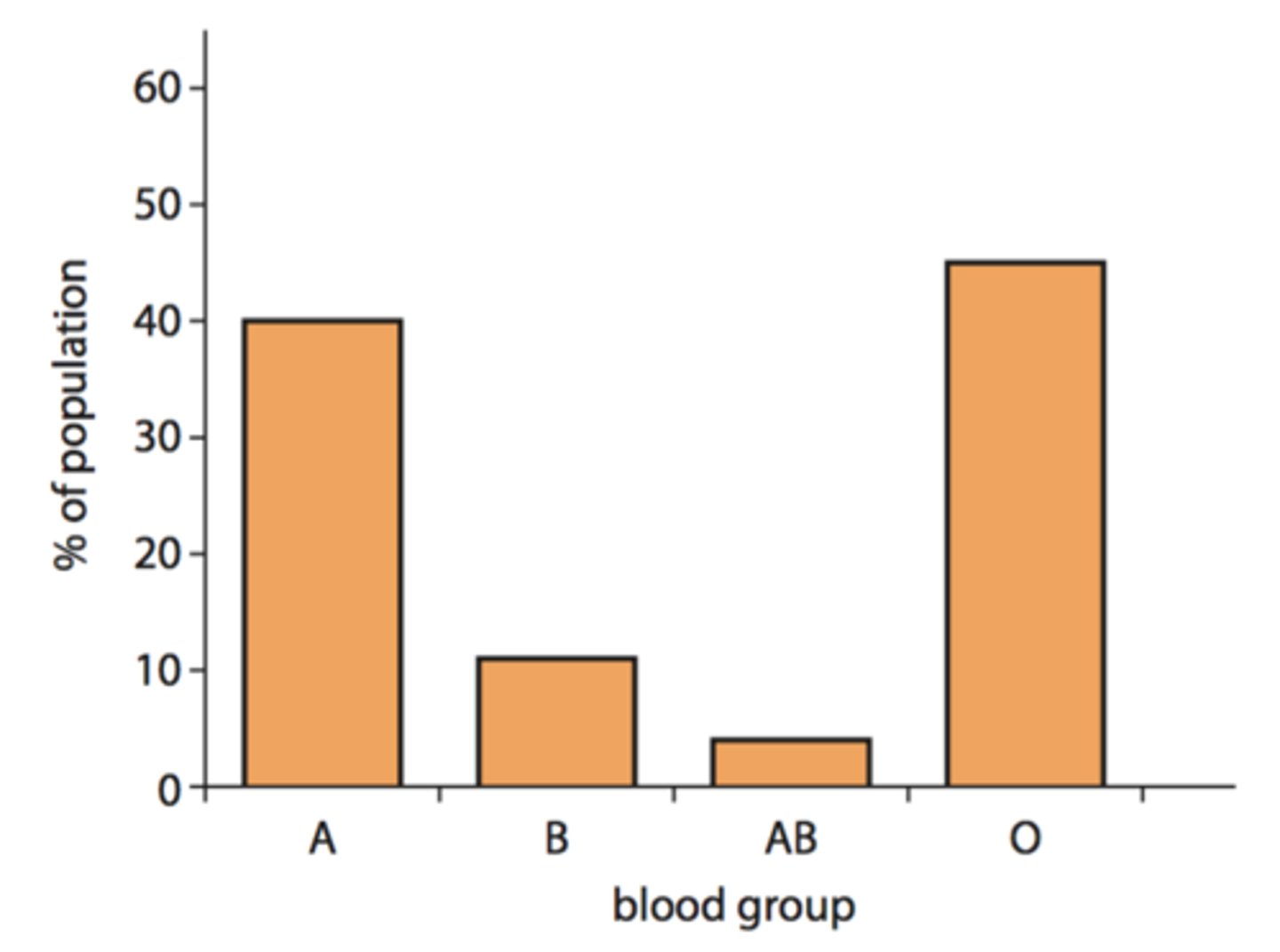
Discontinuous Variation
natural variations that you either have the characteristic or you don't. Blood groups are a good example: you are either one blood group or another - you can't be in between.
Genetic Factor
a trait that is influenced by genetic causes. For example, how you look is partly determined by your genetics.
Environmental Factor
a trait that is influenced by your environment. For example, if you eat too much you will become heavier, and if you eat too little you will become lighter. A plant in the shade of a big tree will grow taller as it tries to reach more light.

Chromosome
a DNA molecule that is coiled up and contains genes.
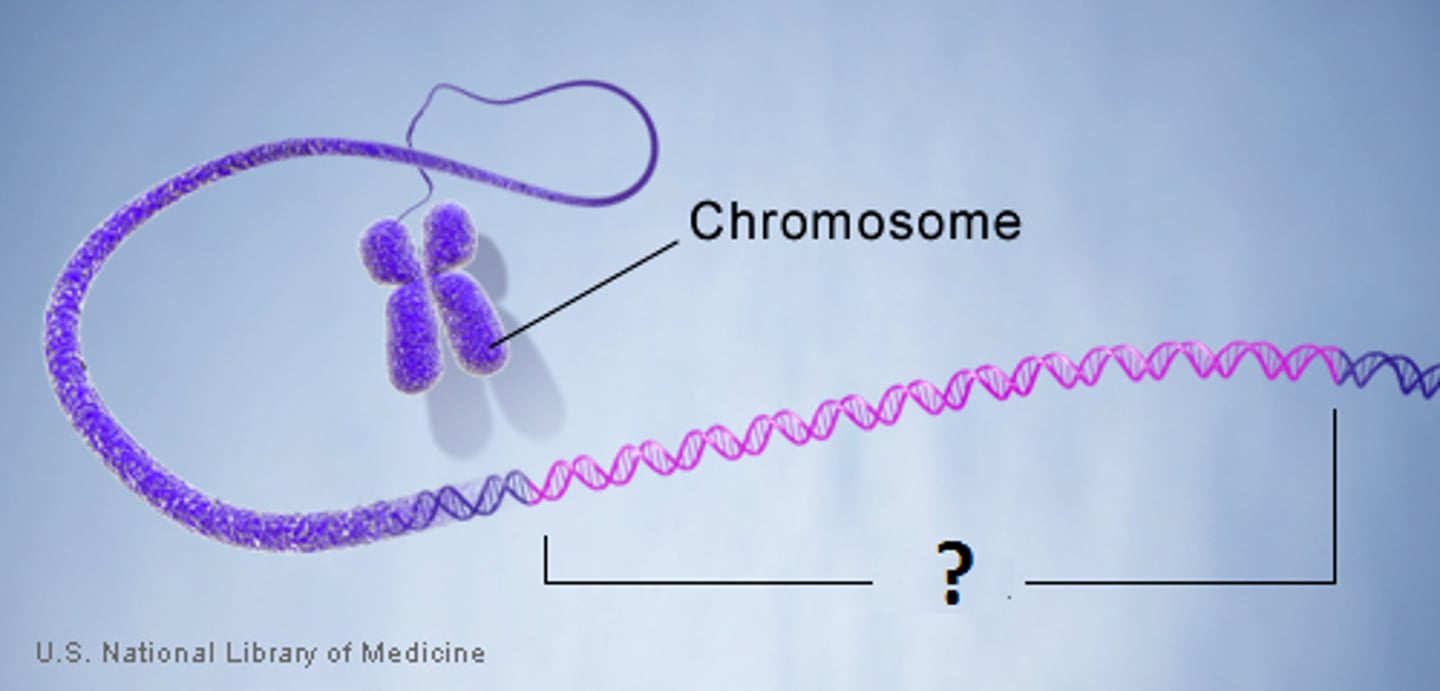
Genes
a section of a DNA molecule that codes for a certain protein.
Diploid
refers to having a full amount of DNA Ex: Somatic cells
Haploid
refers to having half the amount of genetic information Ex: sex cells
Somatic cell
normal body cell with full genetic information and may be sepcialised
Gamete
sex cell Ex: eggs and sperm
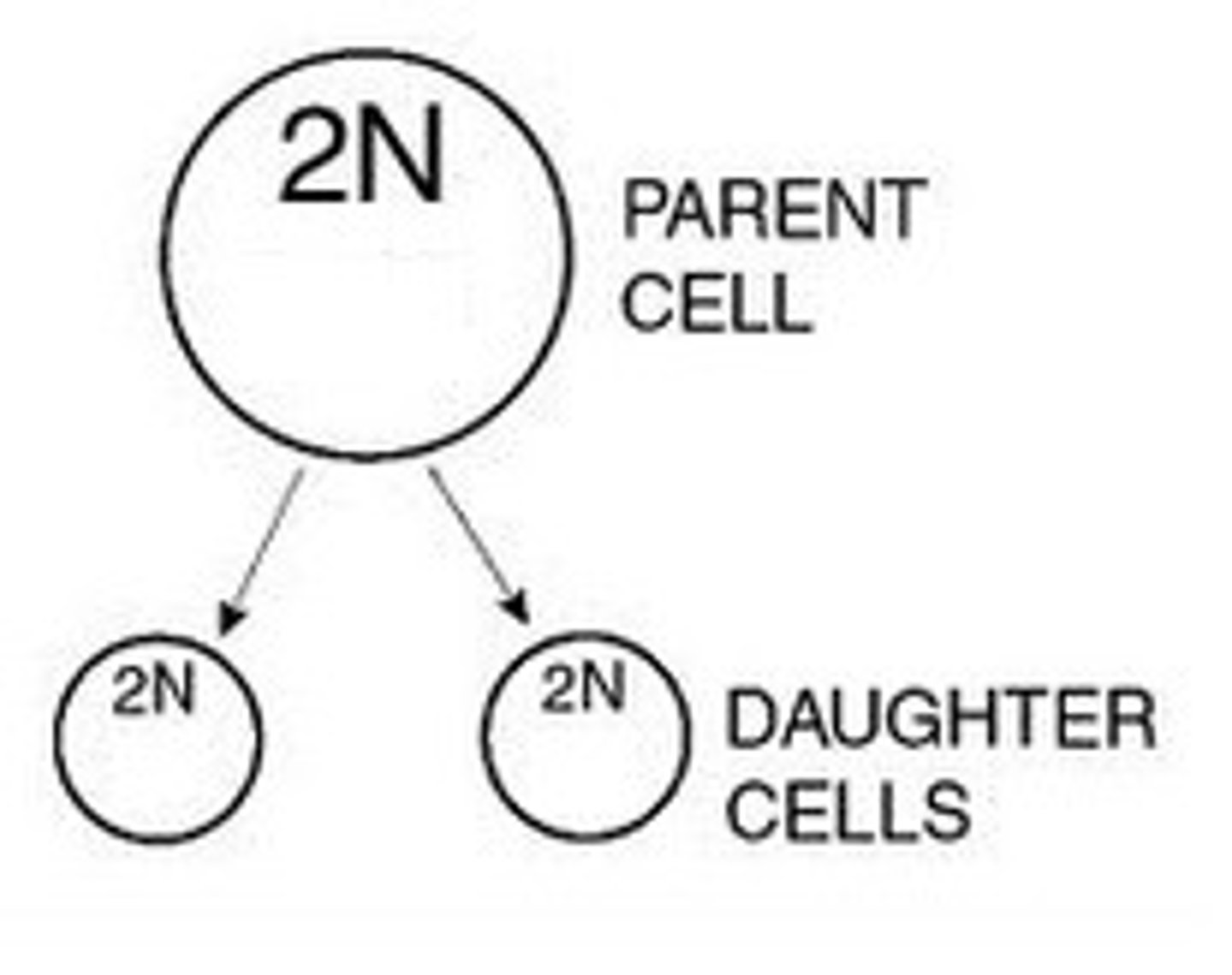
Mitosis
asexual cellular reproduction including prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells
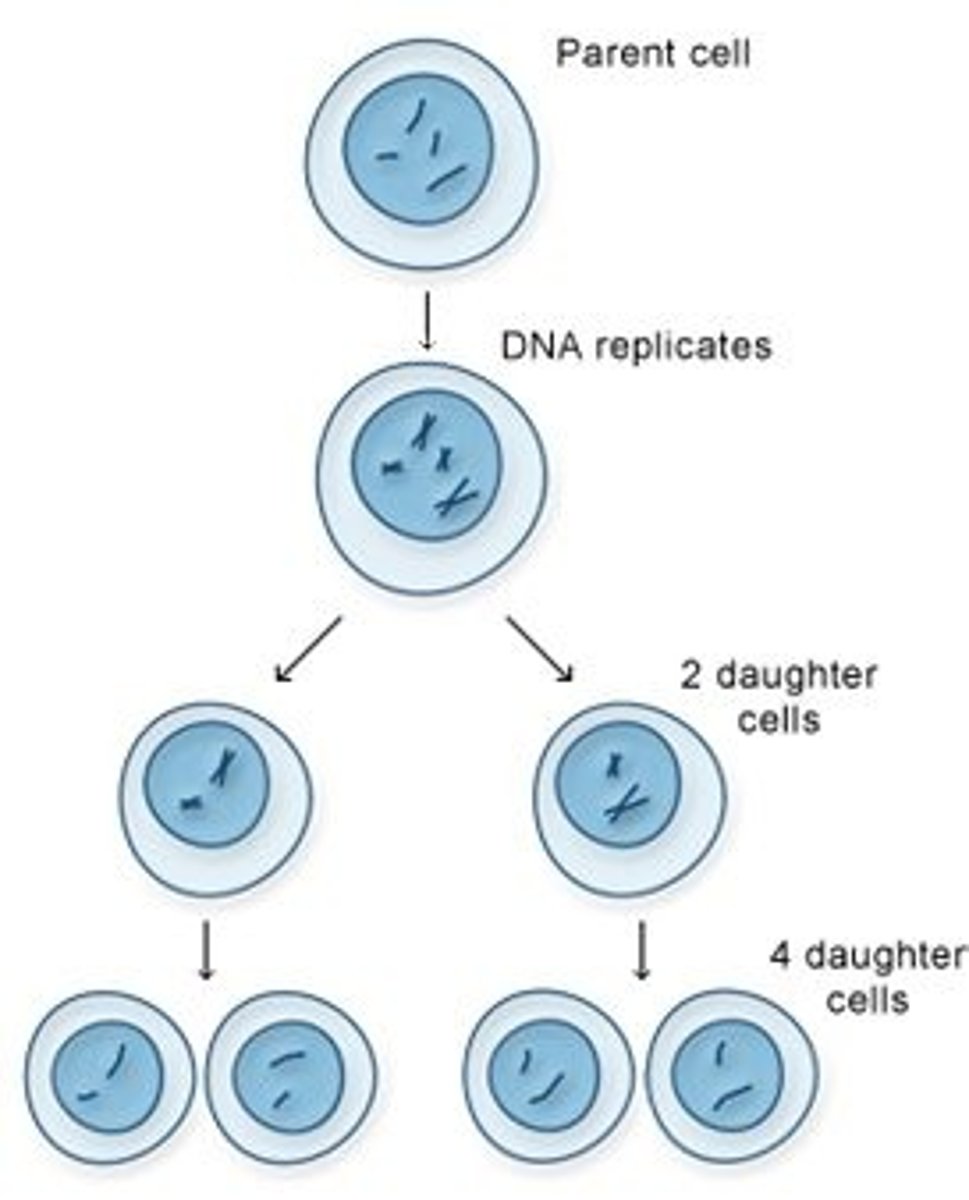
Meiosis
a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four haploid cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction.
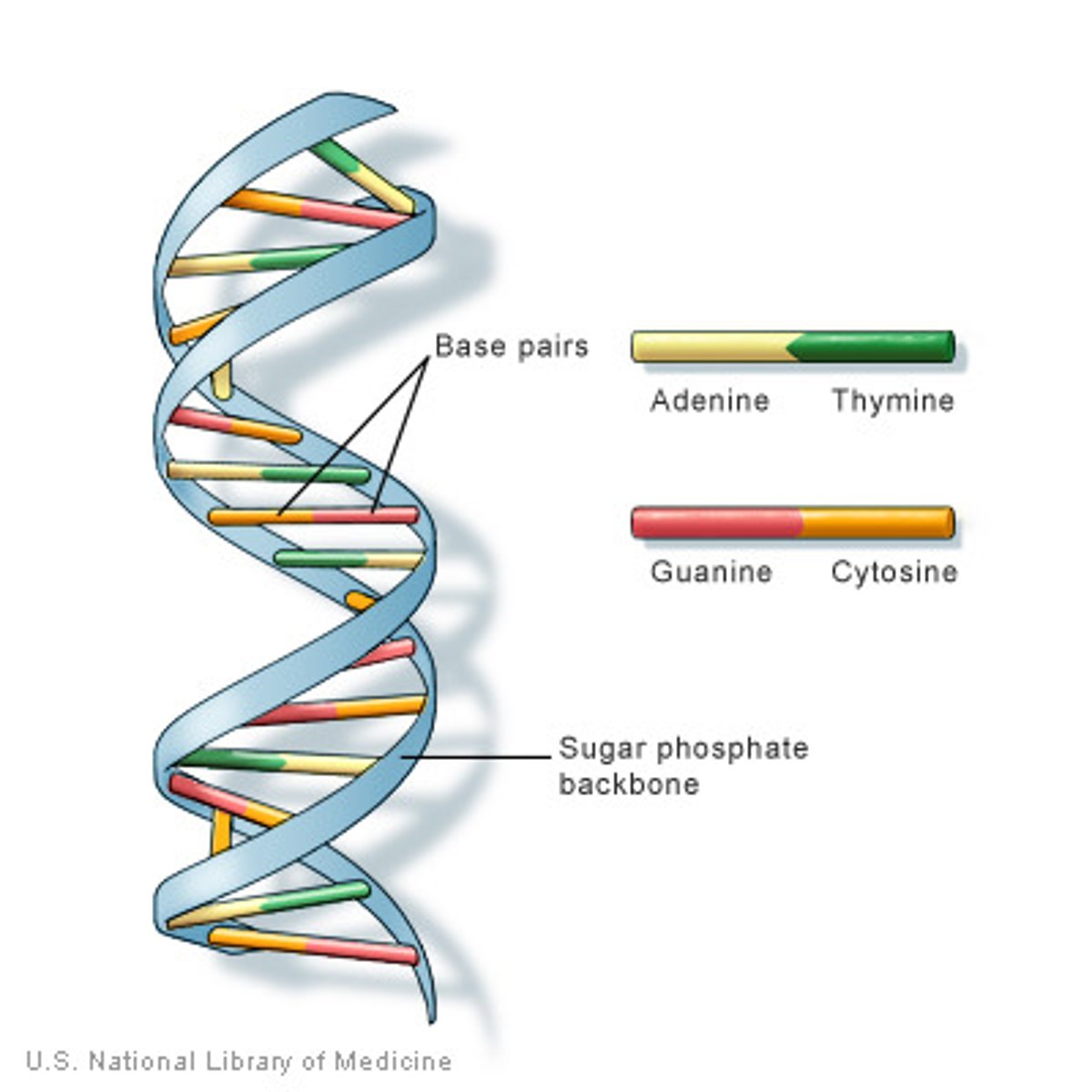
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
a molecule that contains a series of nucleotides to encode genetic information in a double helix structure
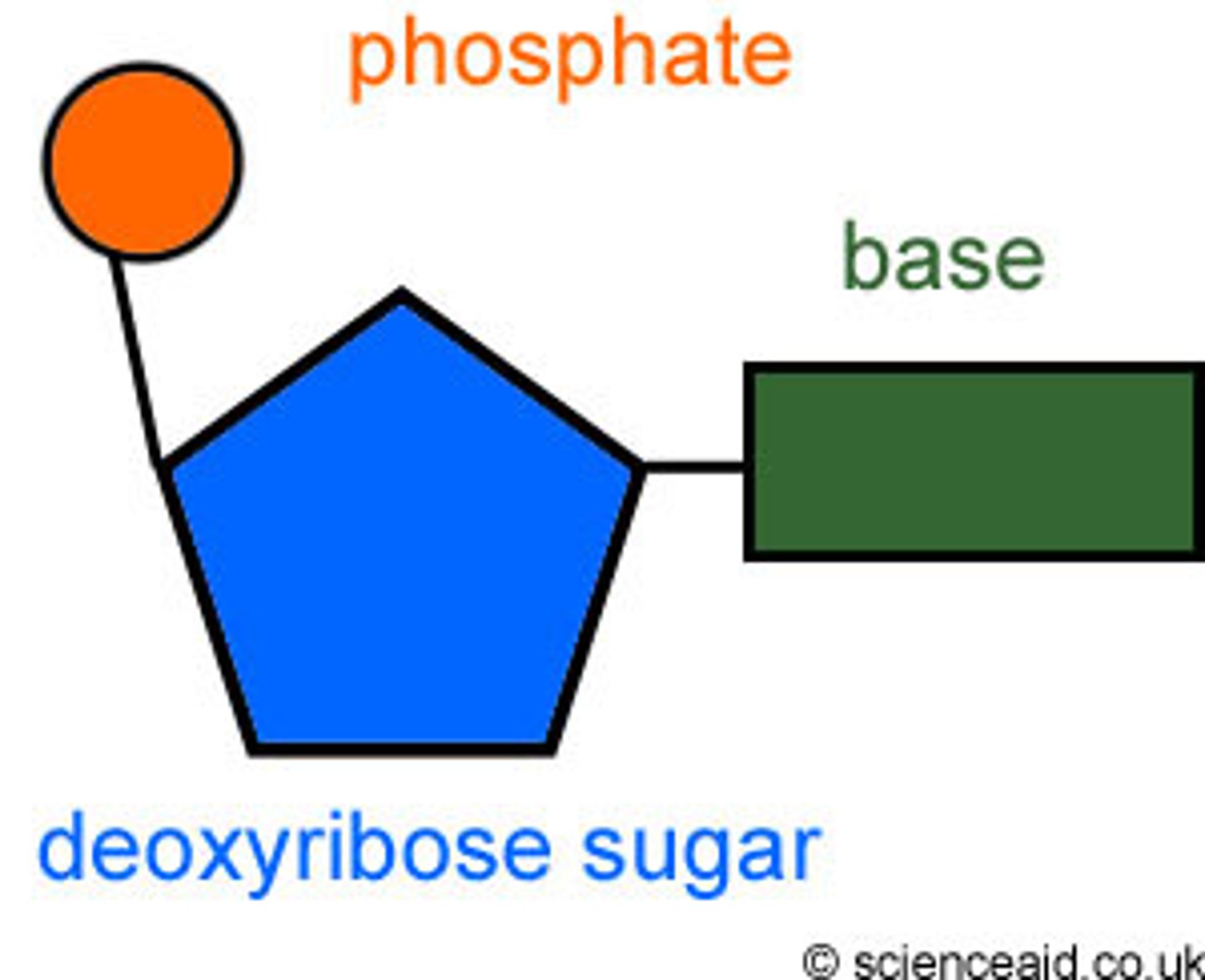
Nucleotide
consists of a phosphate connected to sugar to a base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine)
Polymer
a chemical compound that is a repeating structure of molecules (monomers) to form a larger molecule. DNA is a polymer of nucleotides
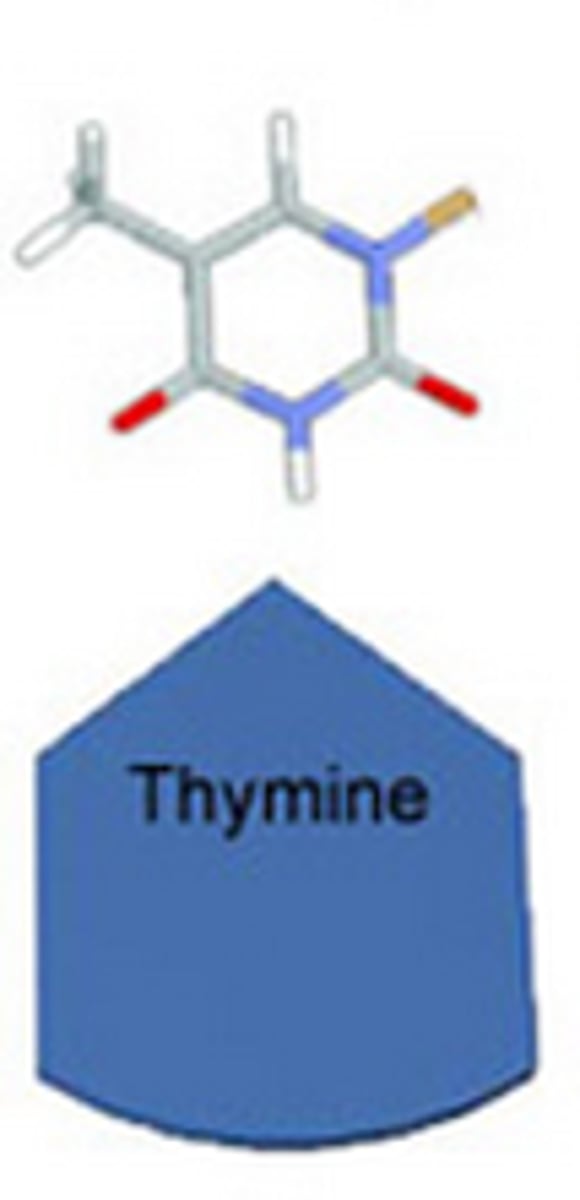
Thymine
one of the bases of DNA that binds with adenine.
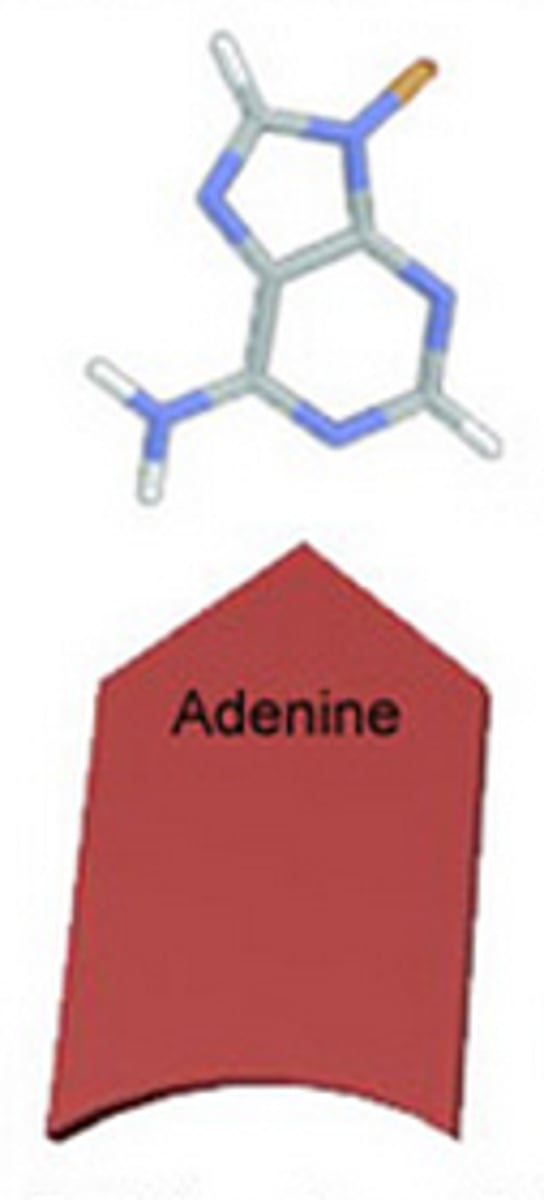
Adenine
one of the bases of DNA that binds with thymine.
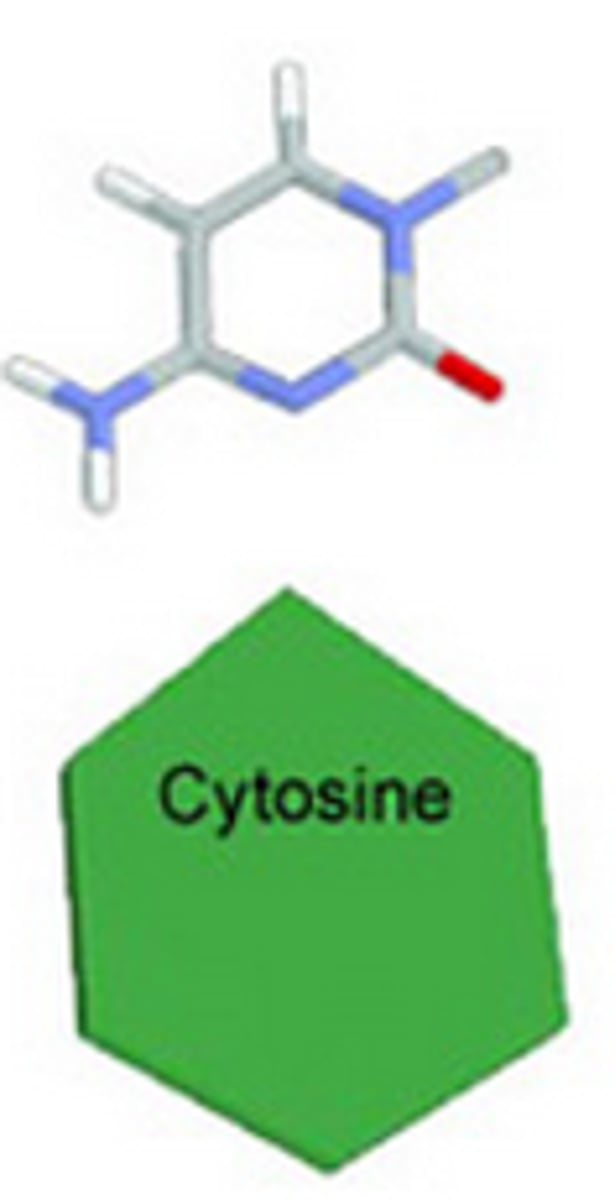
Cytosine
one of the bases of DNA that binds with guanine.
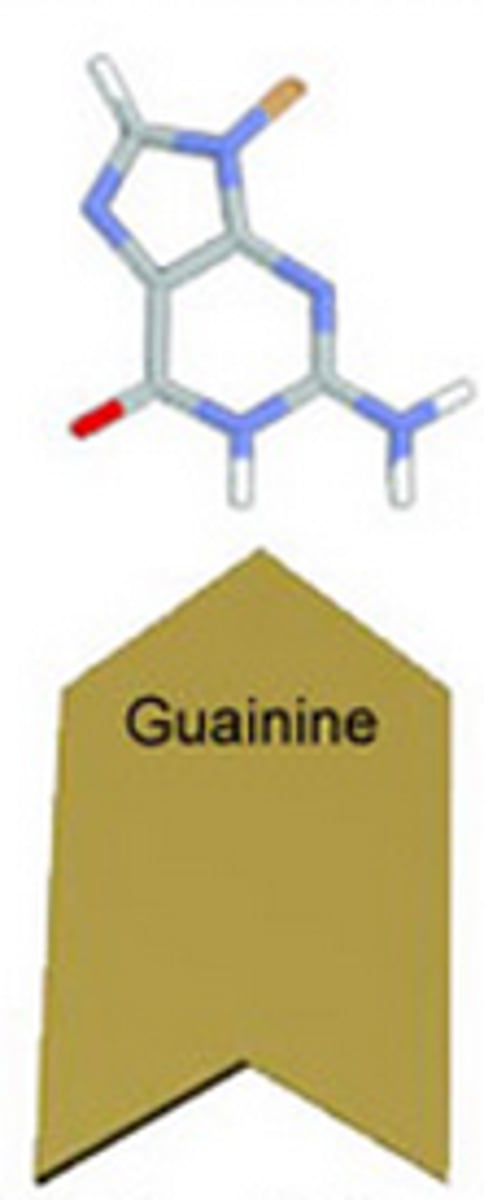
Guanine
one of the bases of DNA that binds with cytosine.
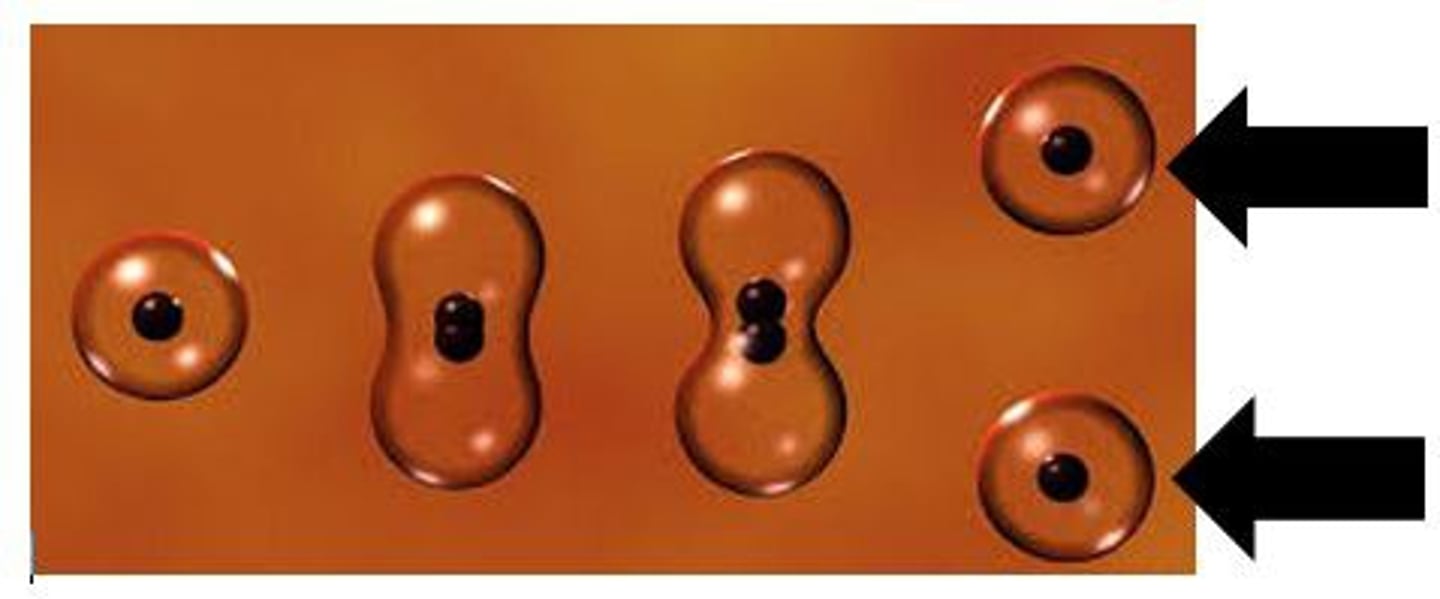
Daughter Cells
cells that result from cell division (mitosis or meiosis)
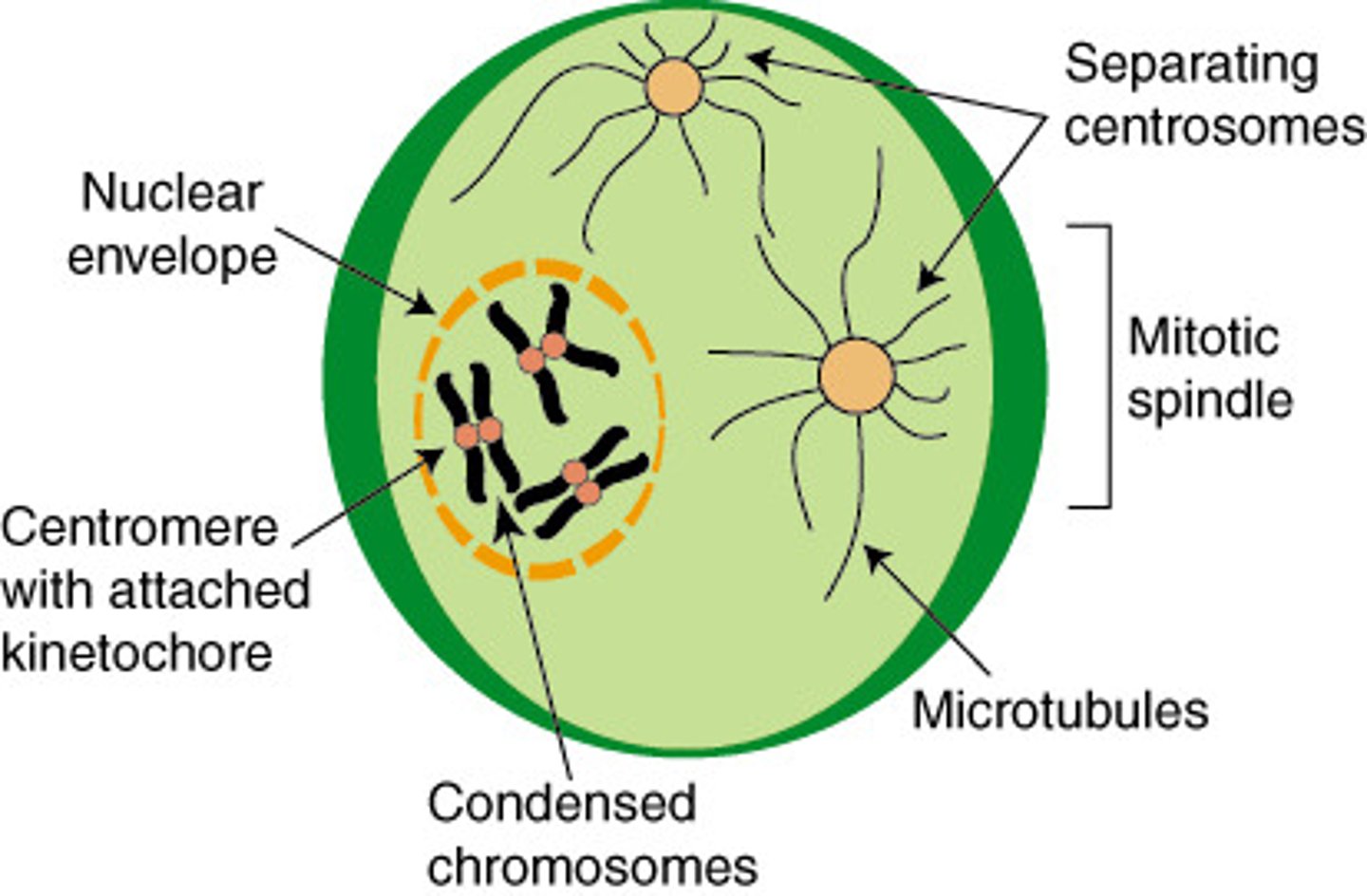
Prophase
the first stage of cell division, before metaphase, during which the chromosomes become visible as paired chromatids and the nuclear envelope disappears.
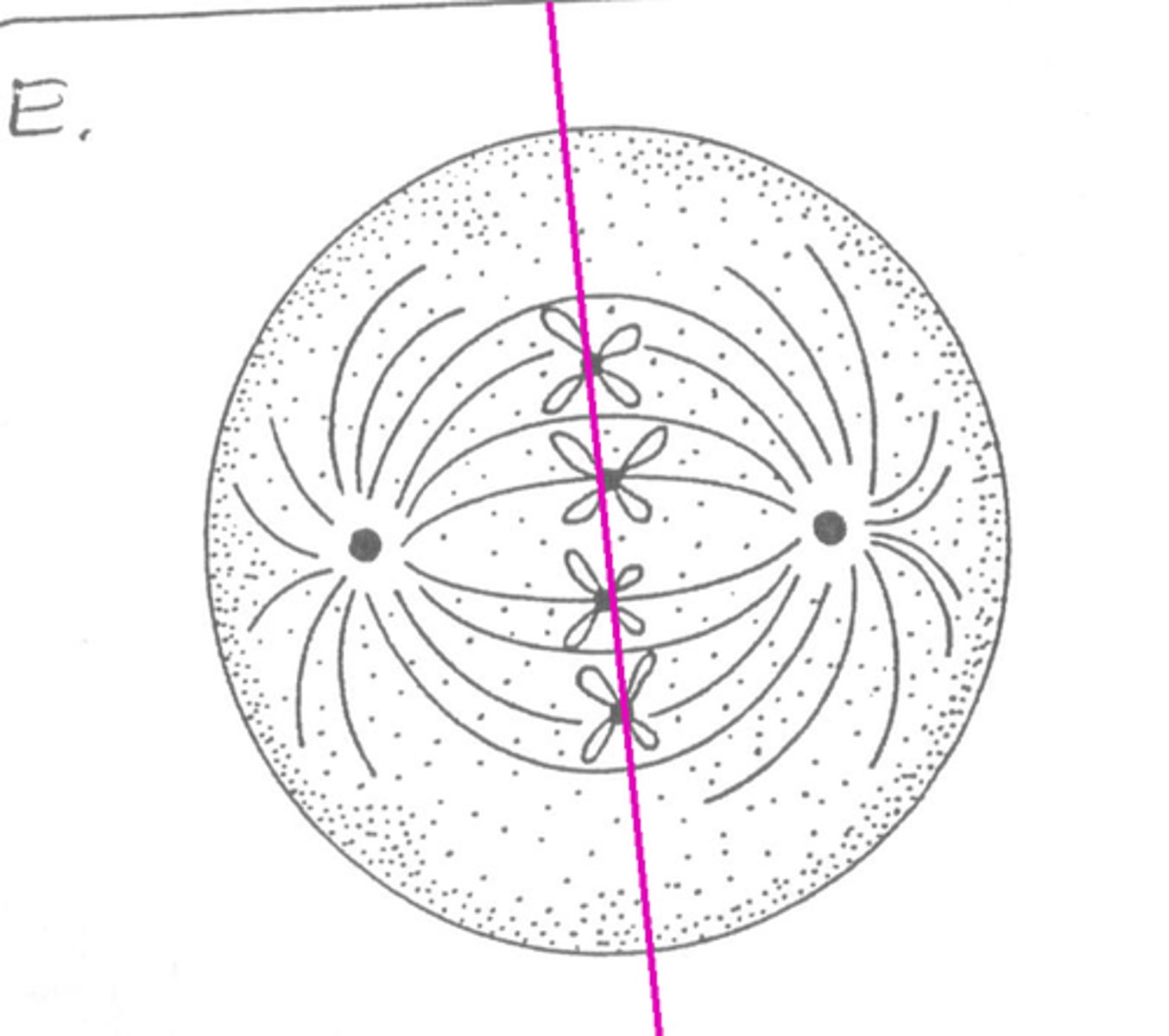
Metaphase
the second stage of cell division, between prophase and anaphase, during which the chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibres and line up
Anaphase
the third stage of cell division, between metaphase and telophase, during which the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle.
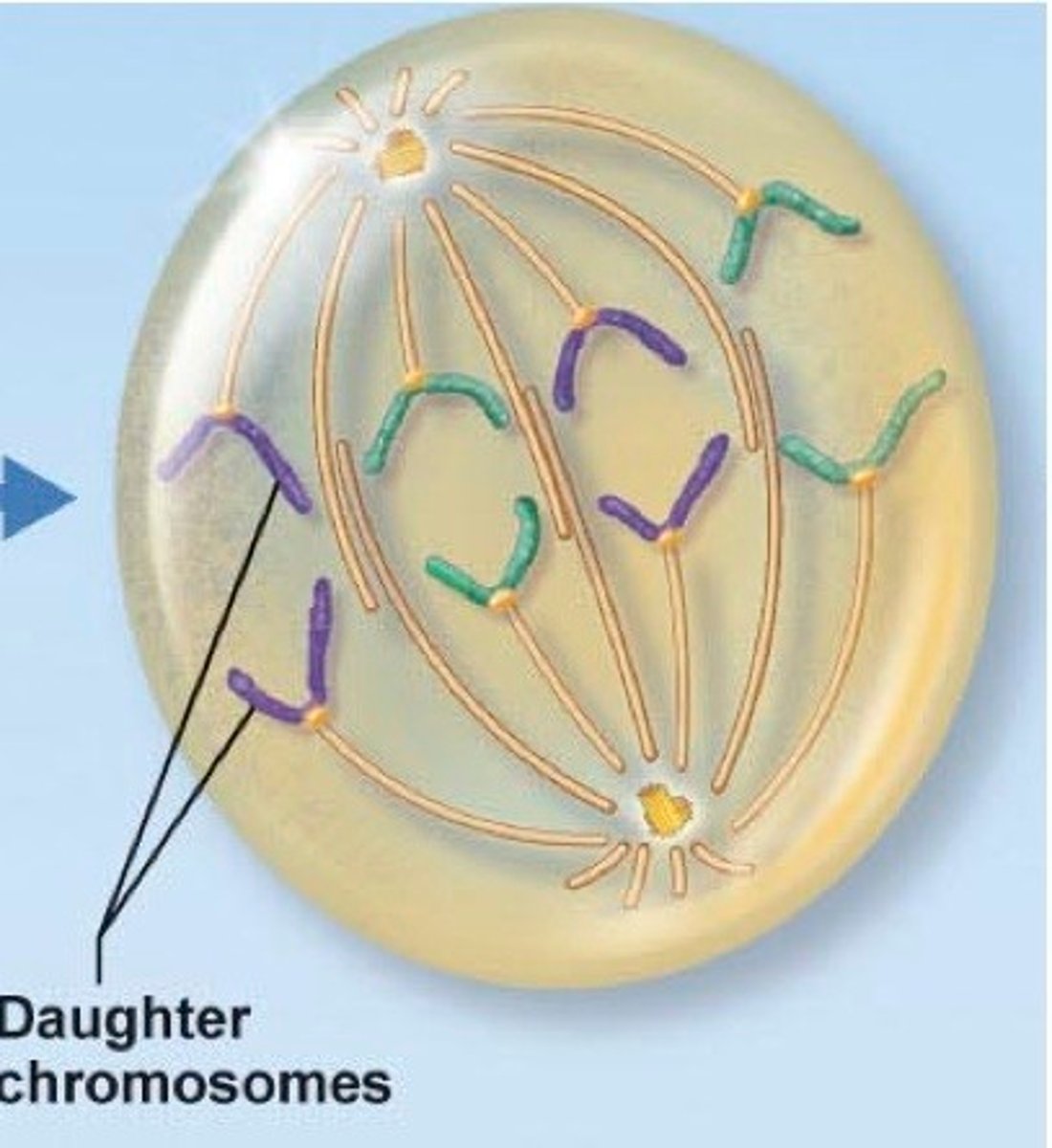
Telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and cytokinesis, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
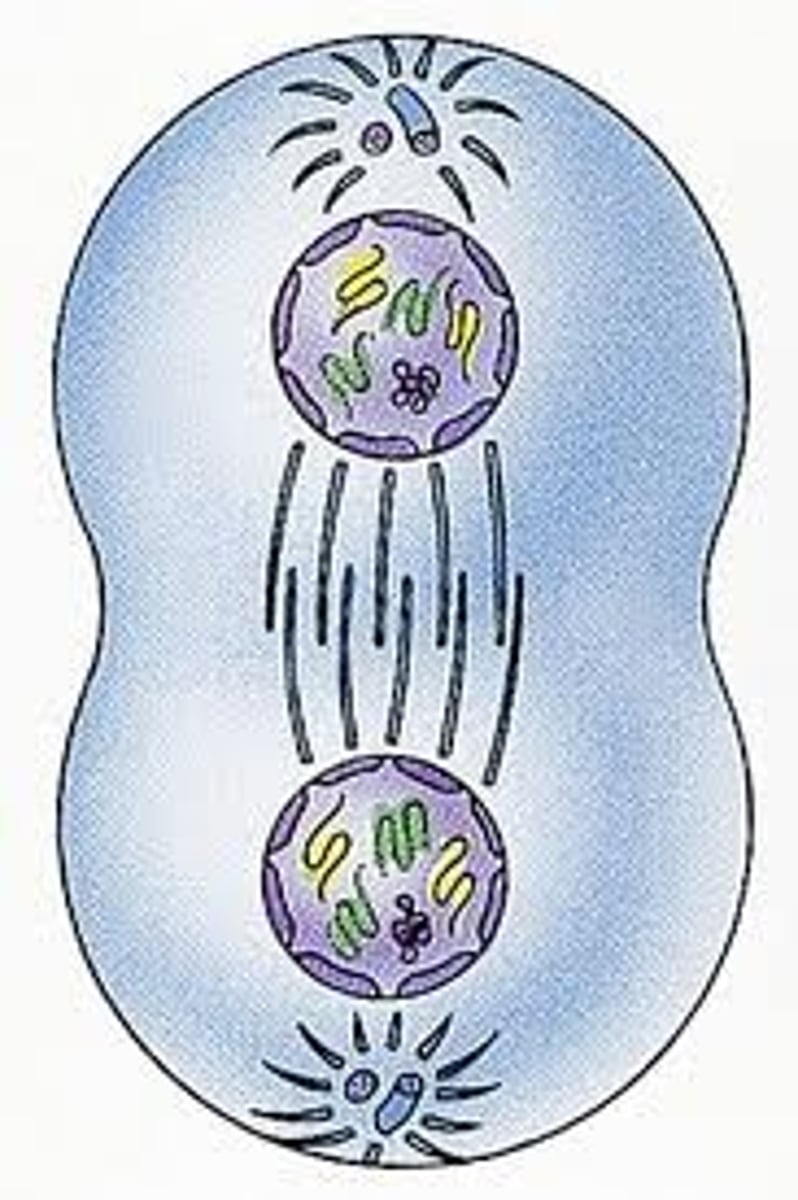
Allele
alternative form(s) of a gene that arise by mutation. An allele can be dominant or recessive.
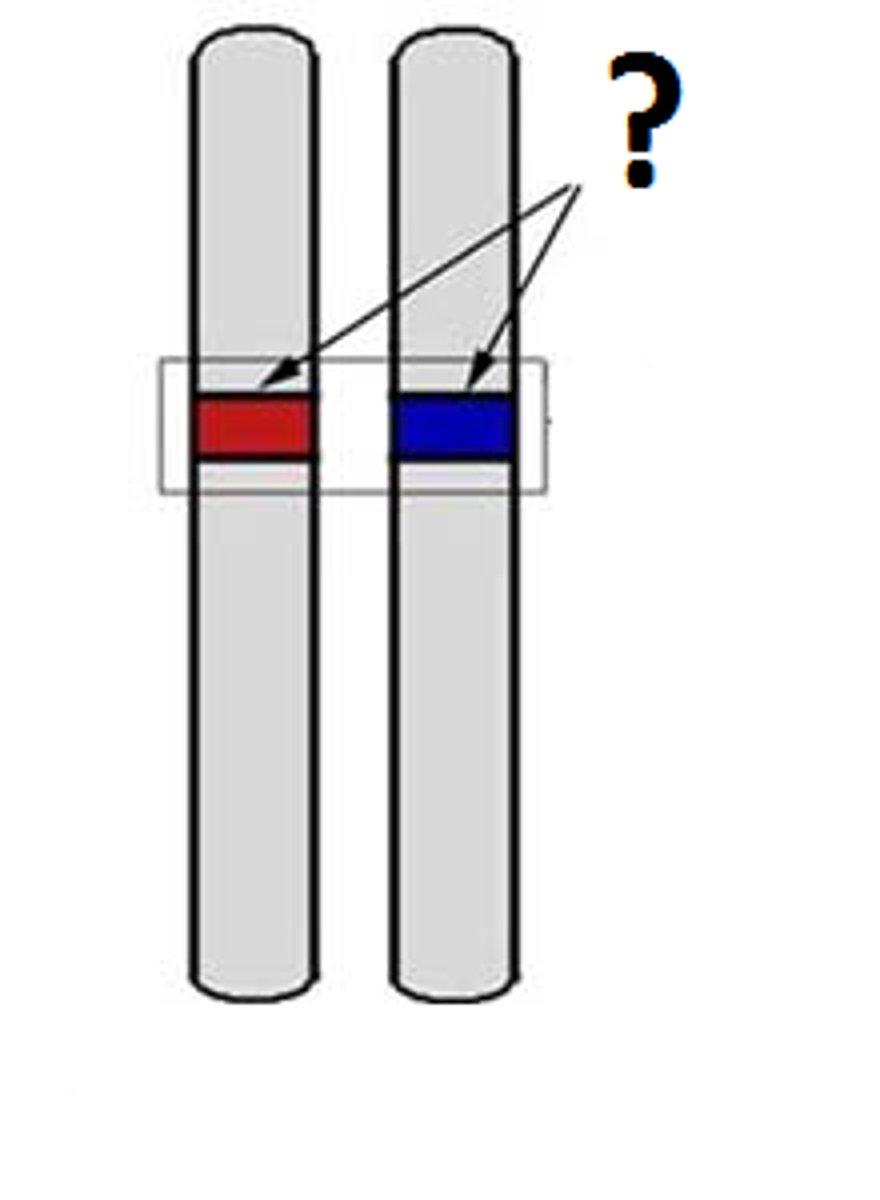
Genotype
The genotype is the genetic code which is responsible for a particular trait.
Phenotype
the set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
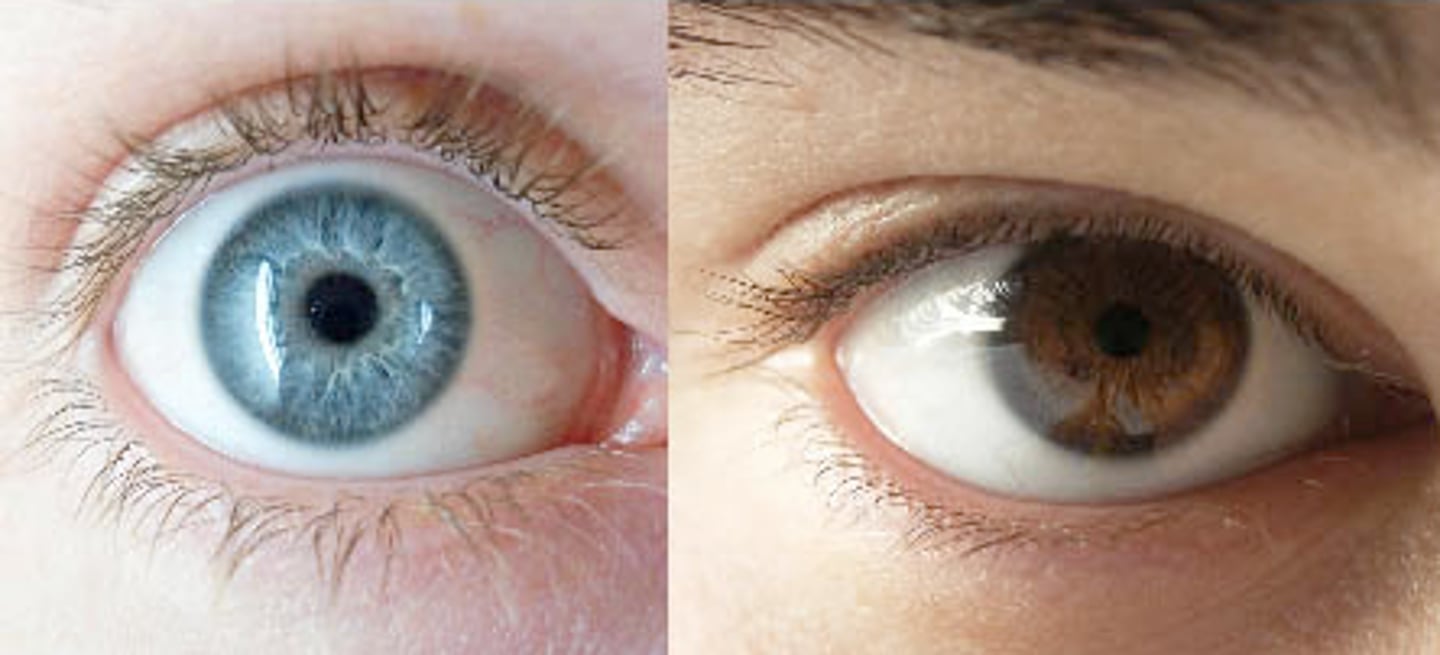
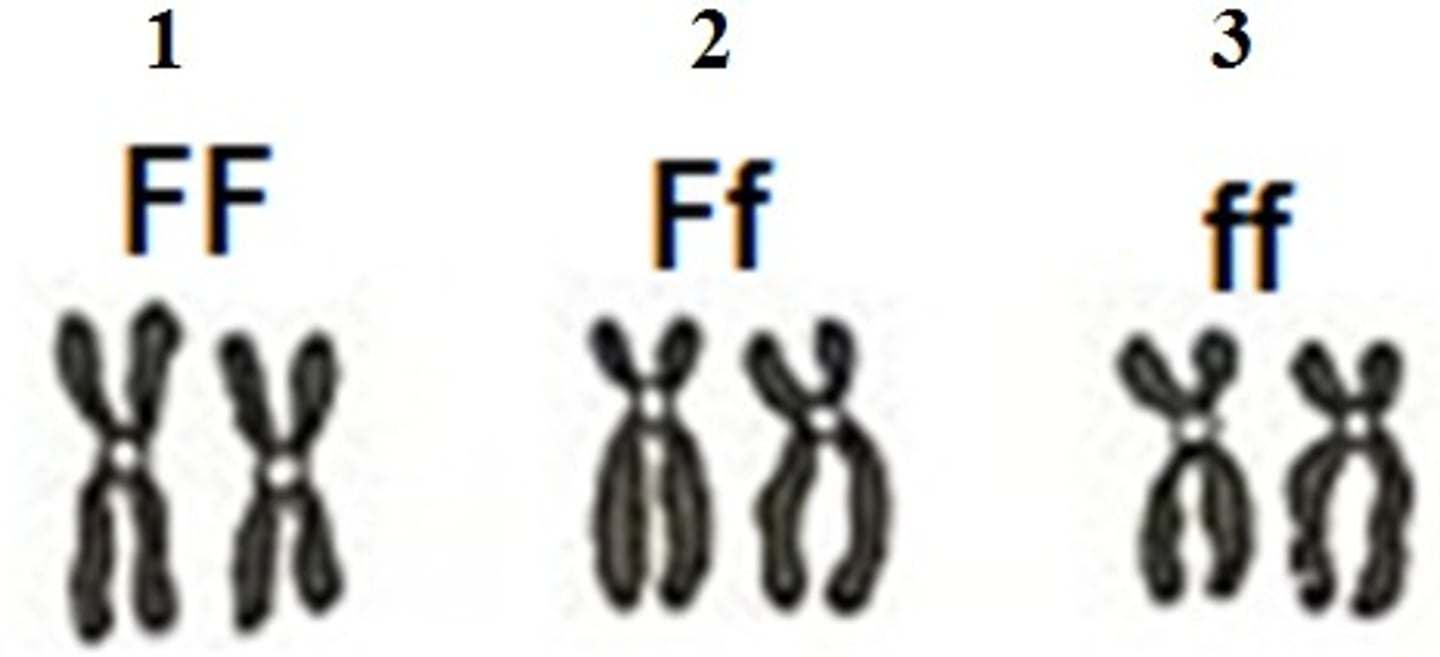
Homozygous
If an organism has two copies of the same allele, for example FF or ff, it is homozygous for that trait.
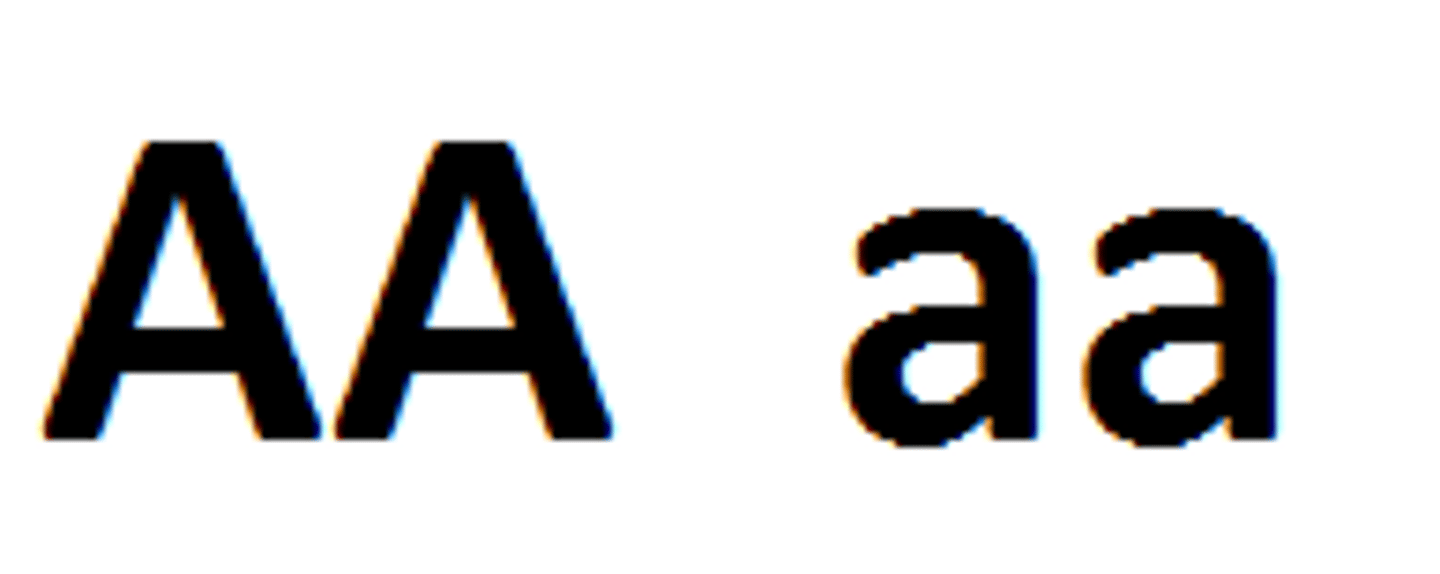
Heterozygous
The genetics term heterozygous refers to a pair of genes where one is dominant and one is recessive. For example, Ff.

Dominant (allele)
an allele that expresses its phenotypic effect even when heterozygous with a recessive allele; thus if A is dominant over a, then AA and Aa have the same phenotype.

Recessive
a recessive allele only shows if the individual has two copies of the recessive allele. For example, the allele for blue eyes is recessive. You need two copies of the allele to have blue eyes.
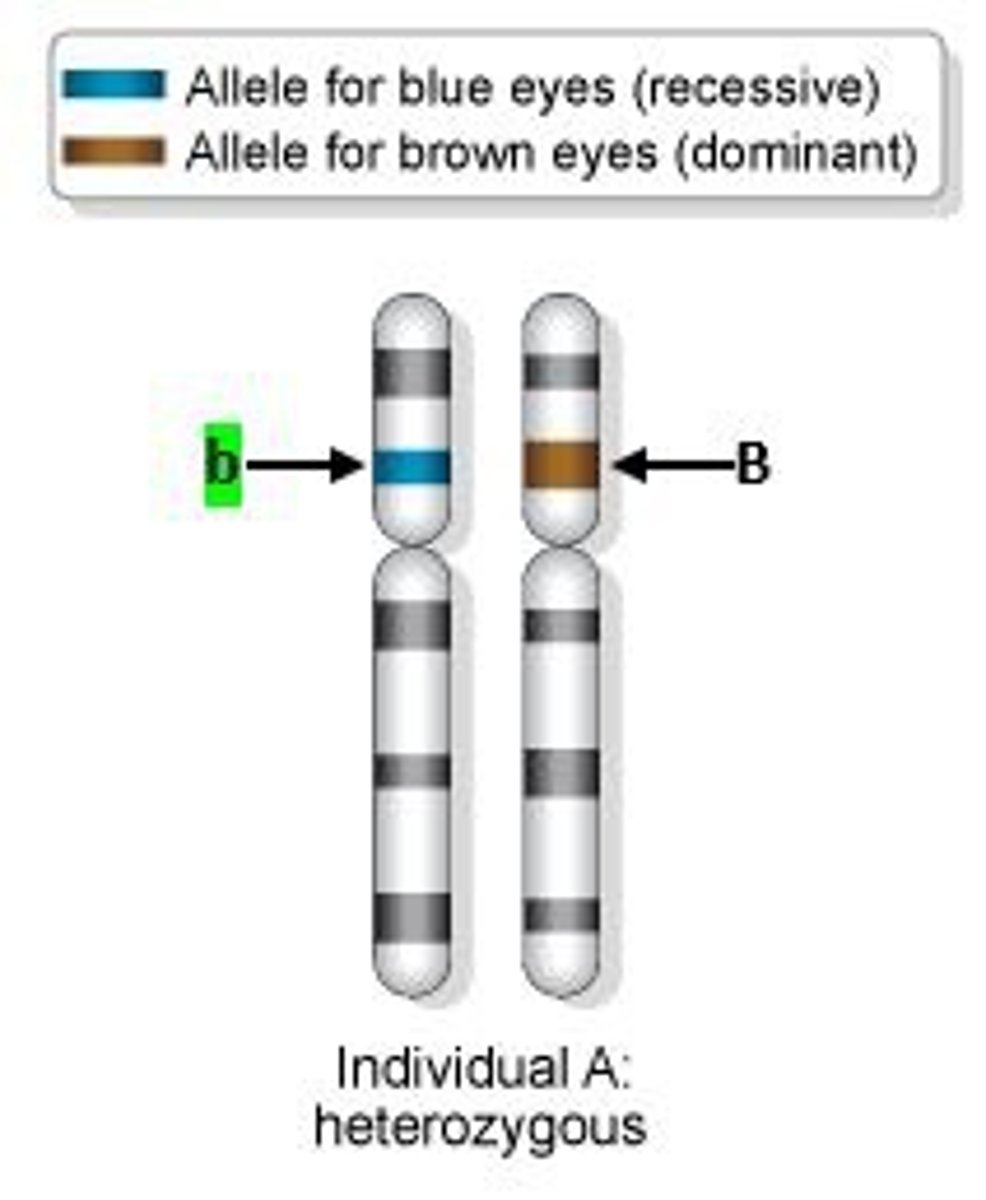
Mutation
a random error that naturally occurs in which DNA sequences are changed and can lead to new traits

Selective Breeding / Artificial Selection
the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together.
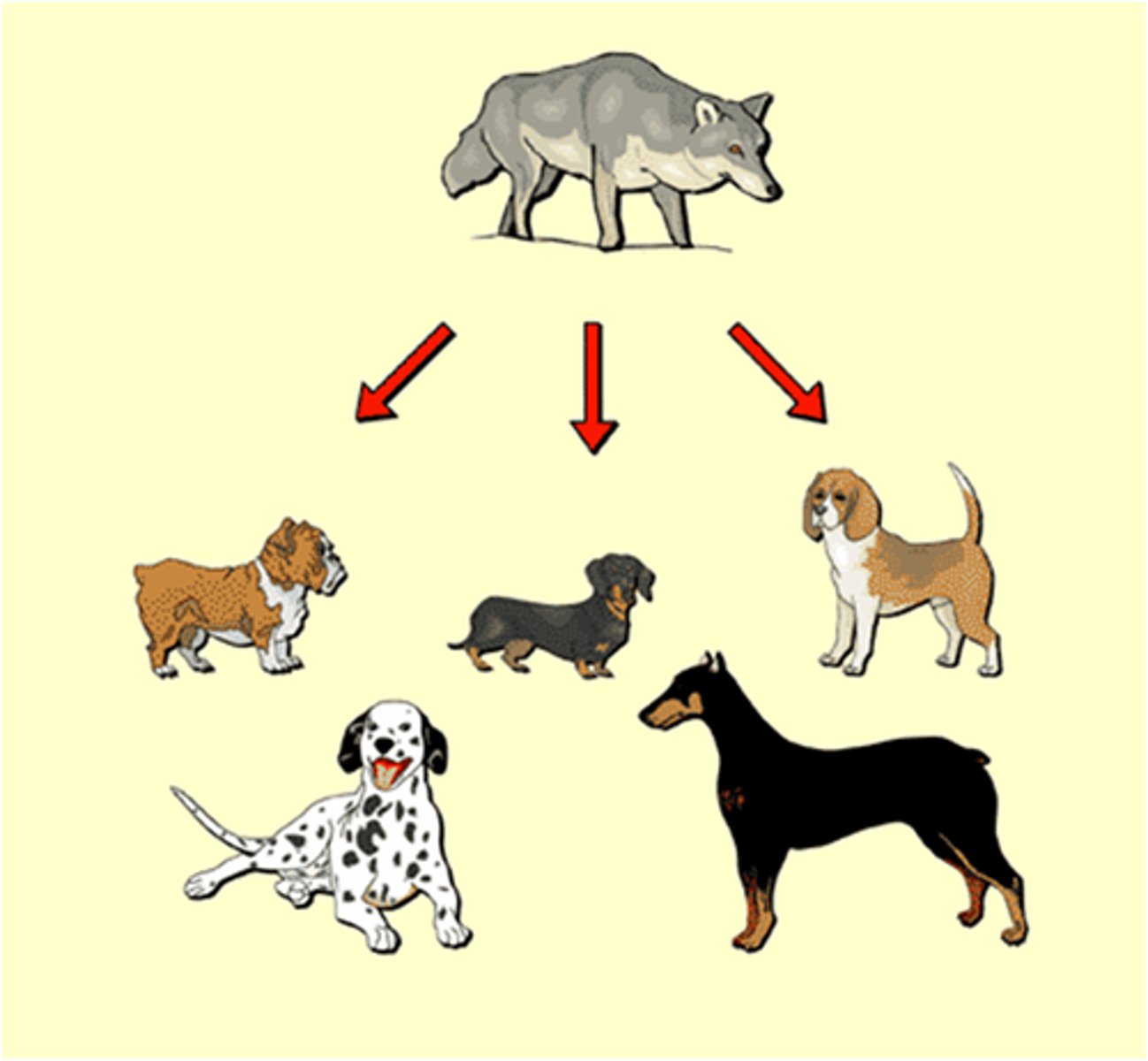
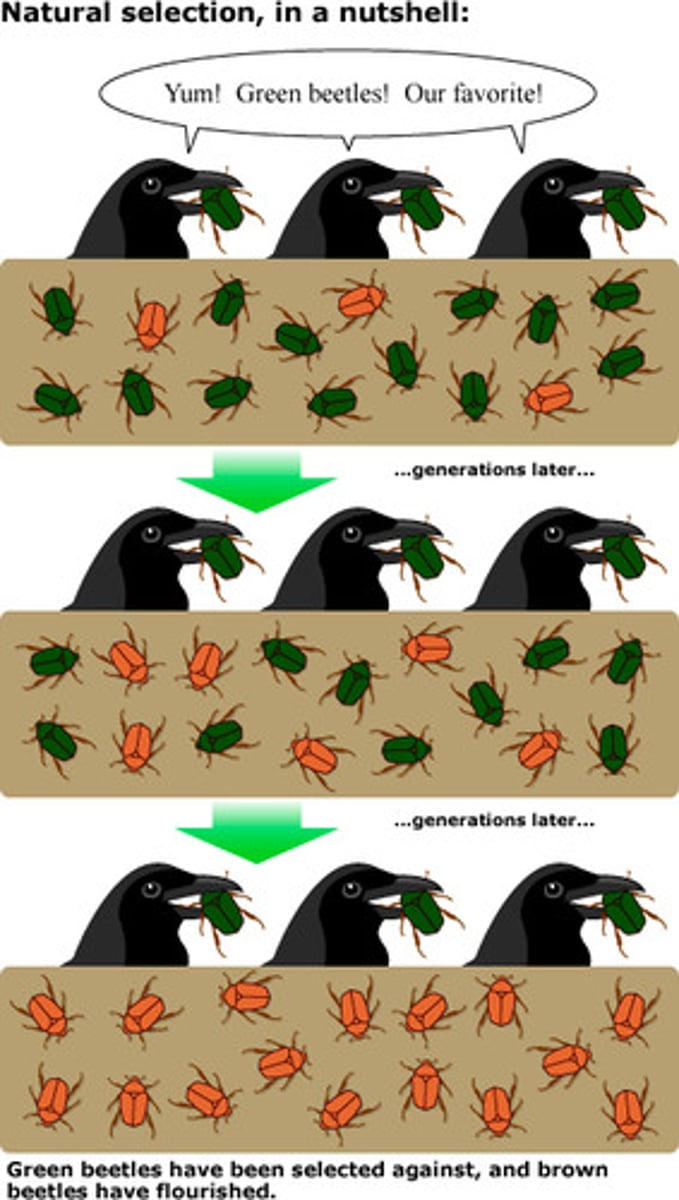
Natural Selection
the process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
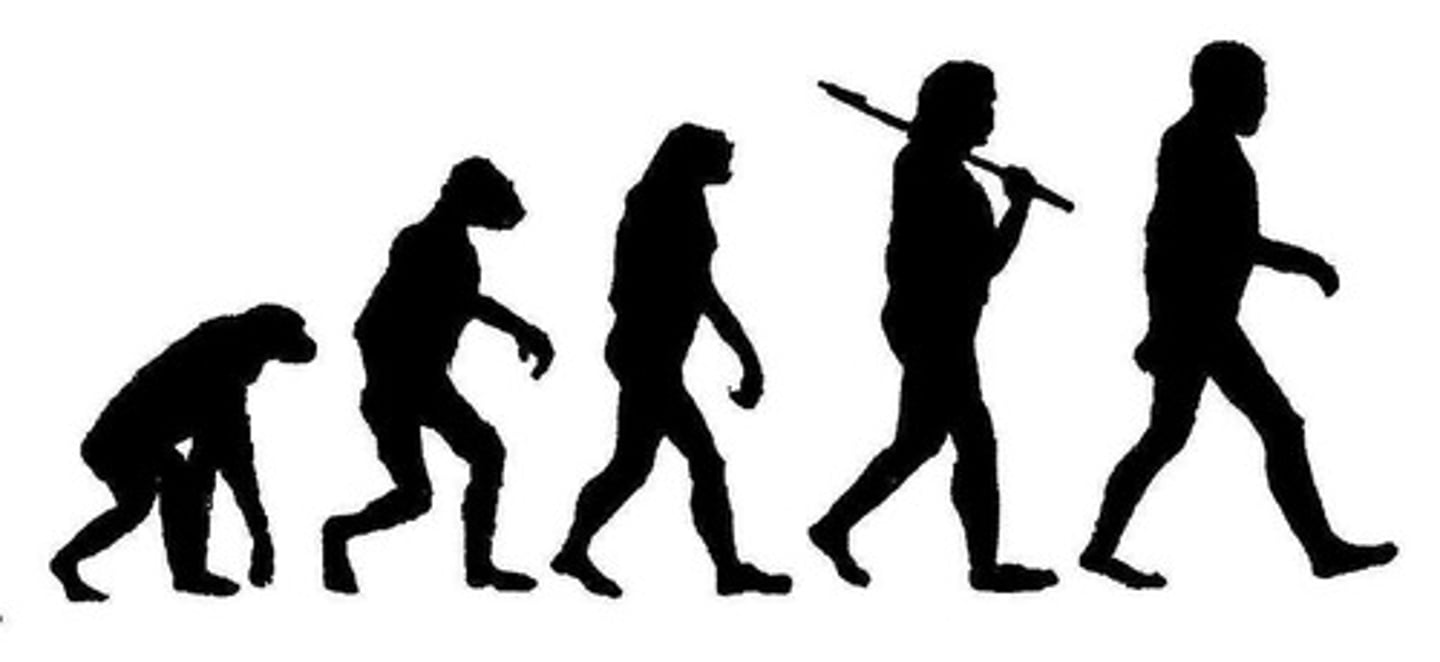
Evolution
the process of gradual development by which different kinds of living organism are believed to have developed from earlier forms during the history of the earth.
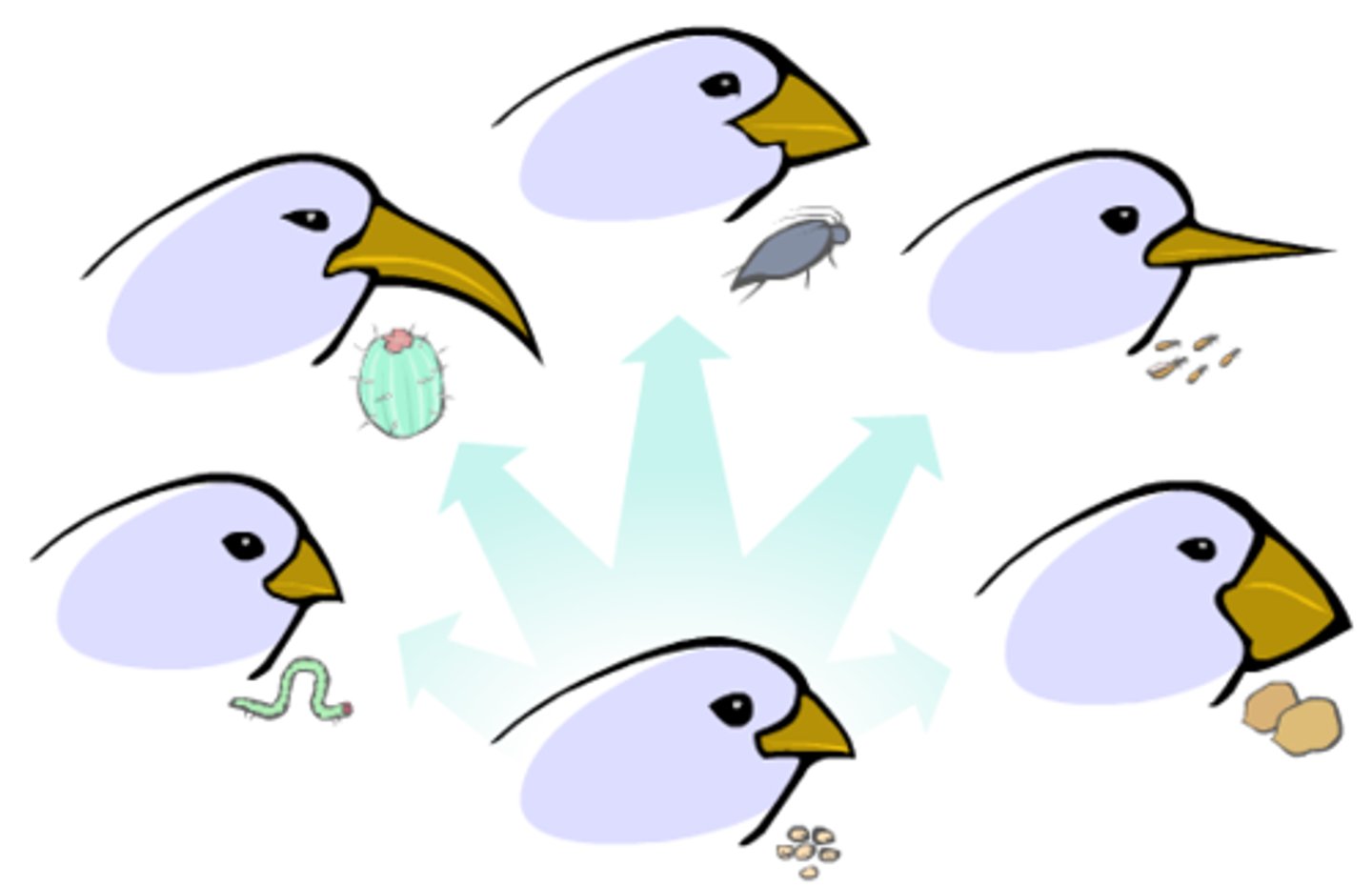
Adaptation
a trait with a current functional role in the life of an organism that is maintained and evolved by means of natural selection.
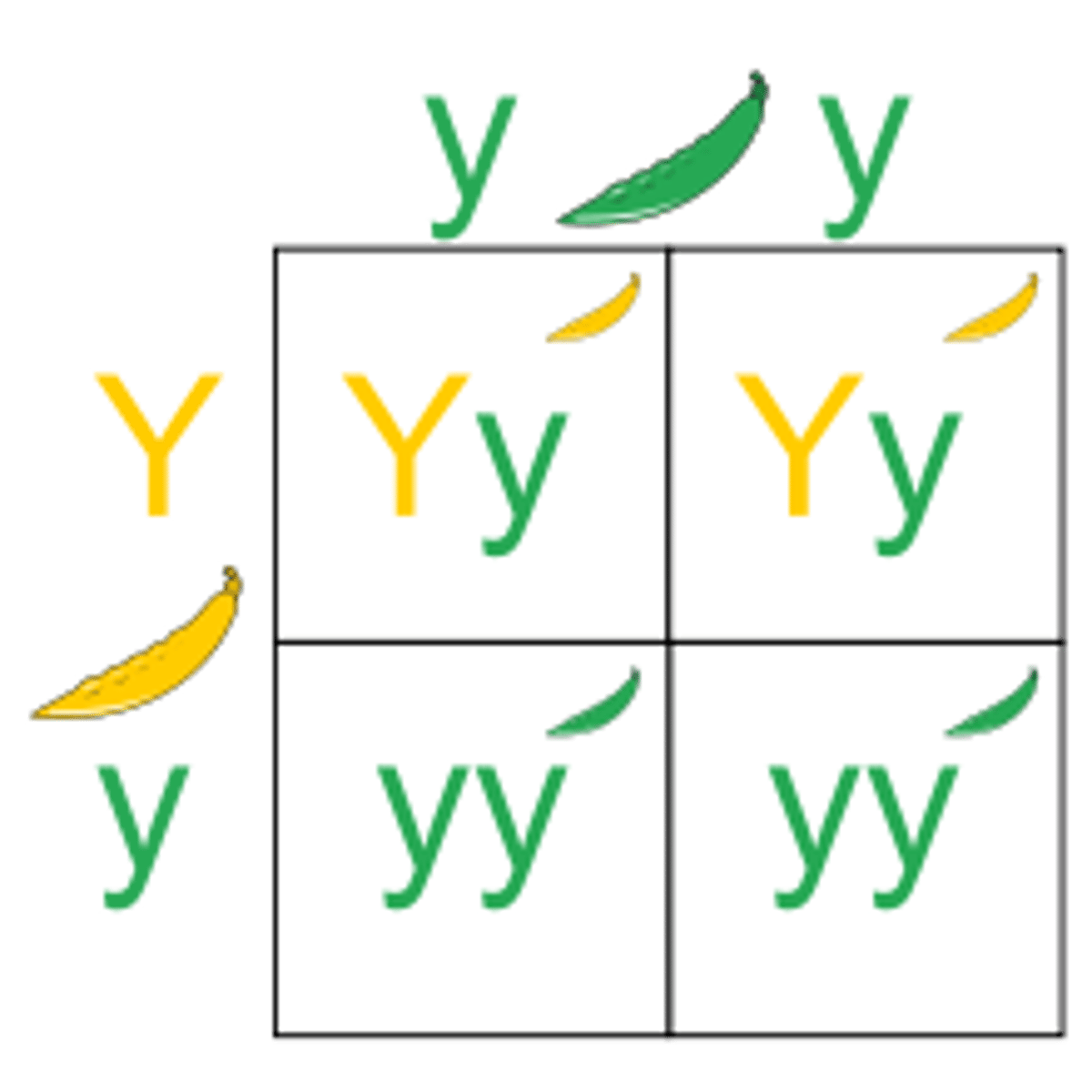
Monogenetic Cross (monogenetic inheritance)
a punnet square to determine possible genetic outcomes based for a single trait.
Sister Chromatids
Genetically identical chromosomes that are held together at the centromere.
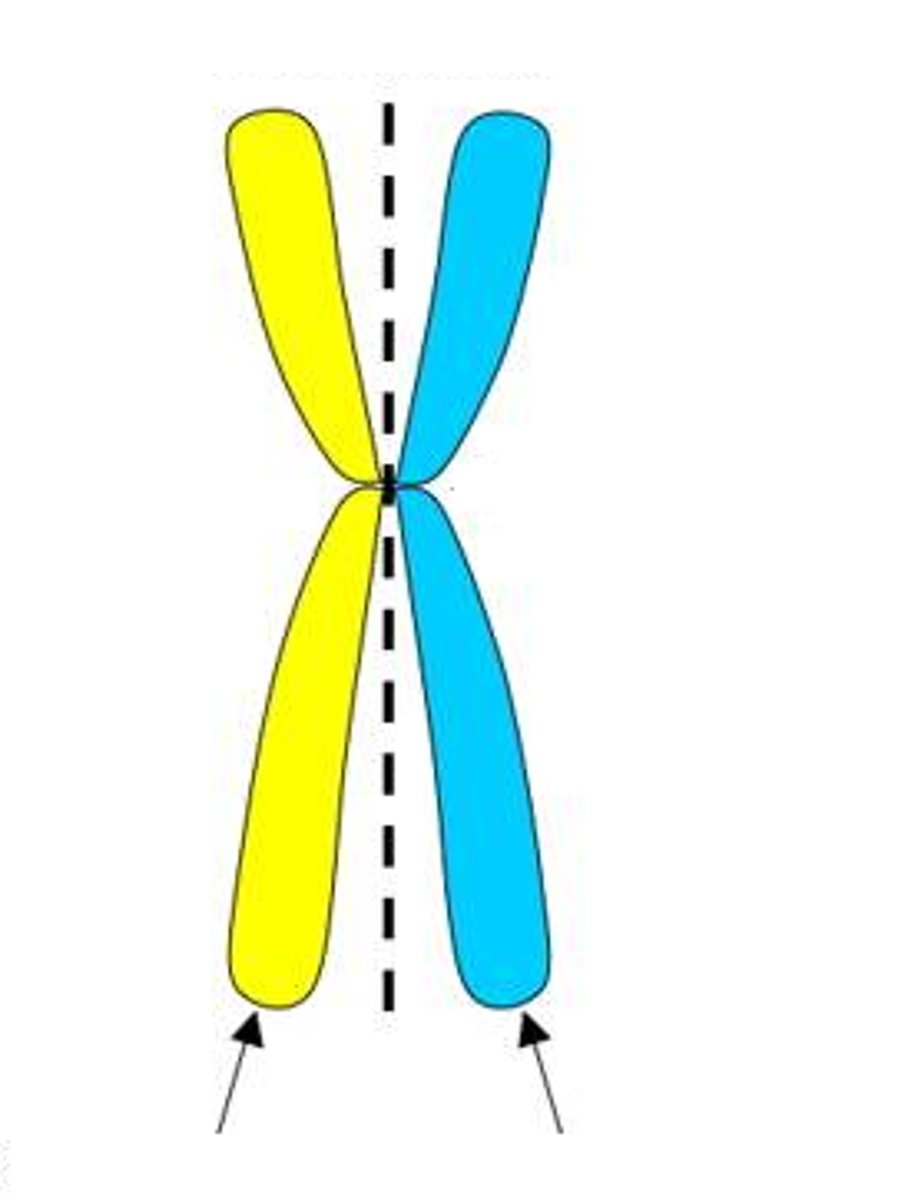
Homologous Chromosomes
Two chromosomes (one from father, one from mother) that code for the same traits, but may have different alleles. They form tetrads during meiosis.
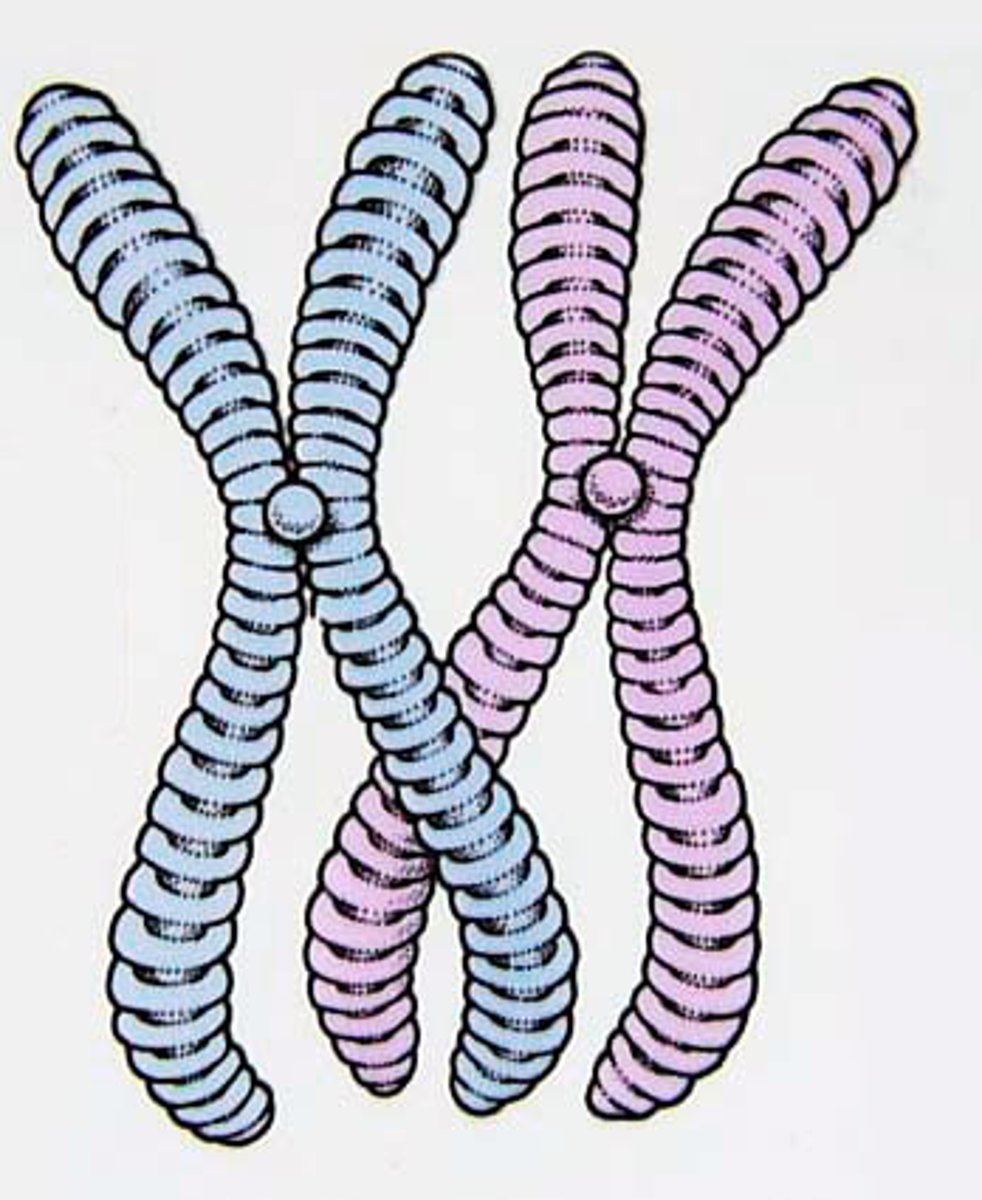
Centrosomes
Contain the centrioles and move to opposite sides of the cell during cell reproduction.
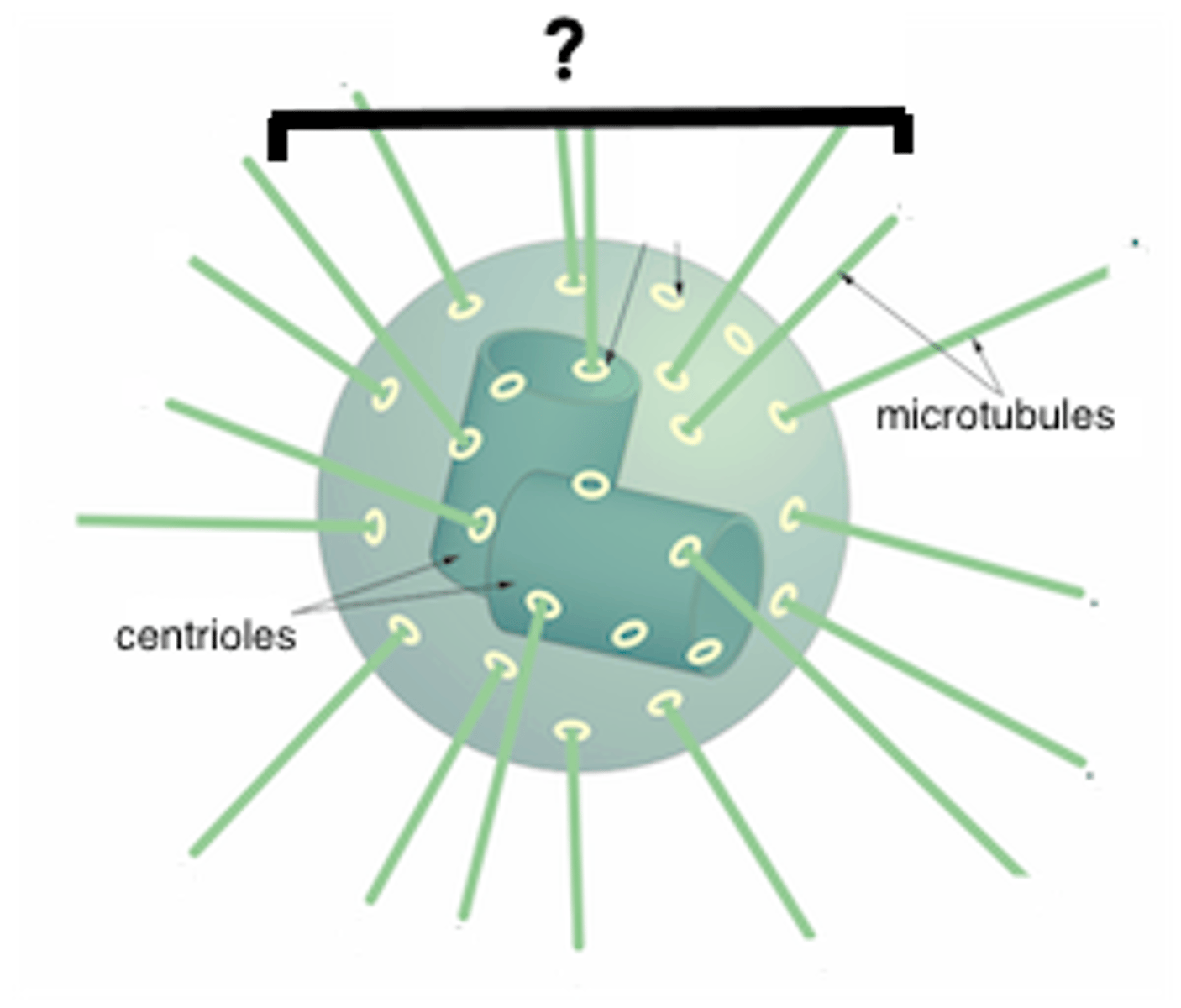
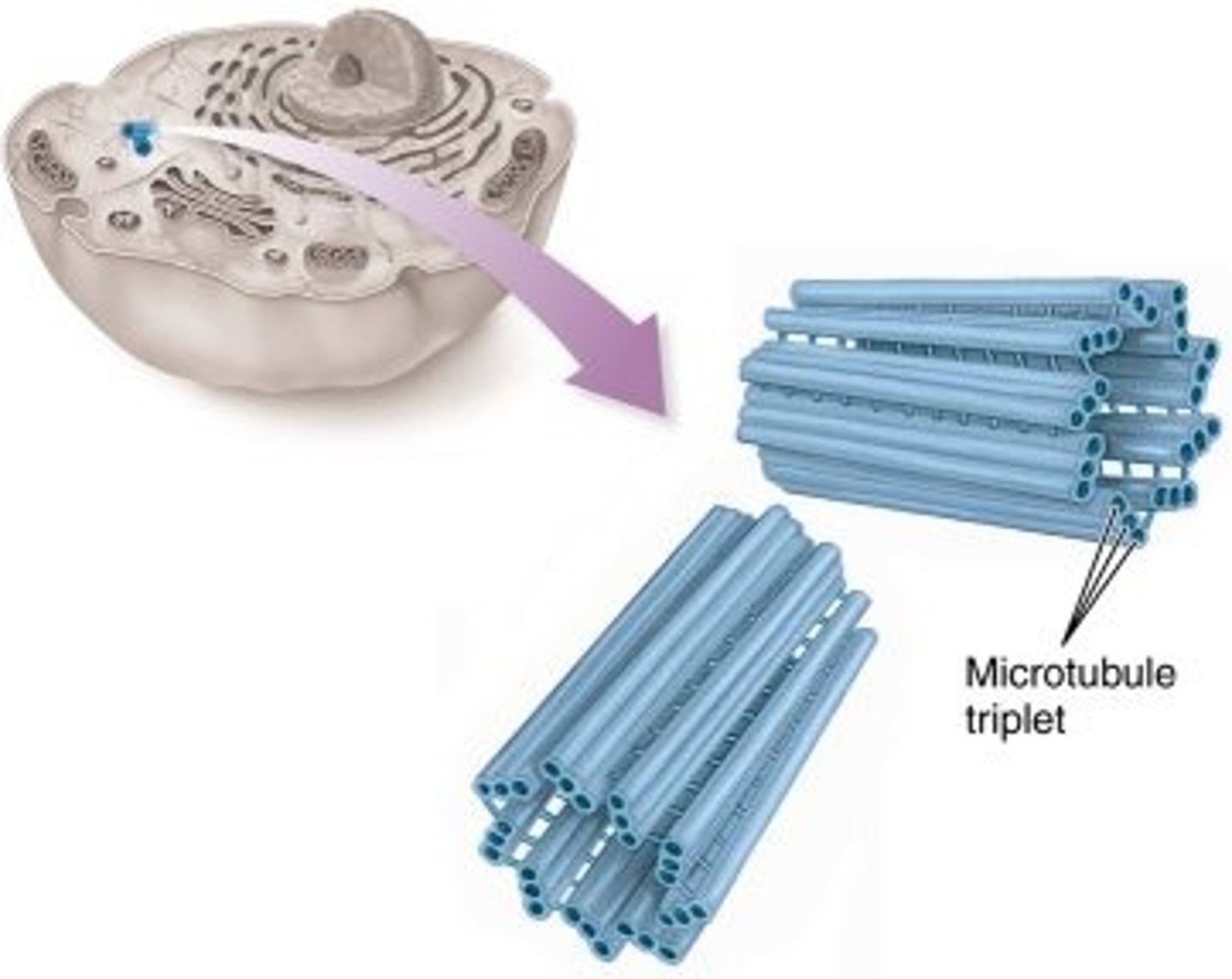
Centrioles
The spindle fibers grow out of these
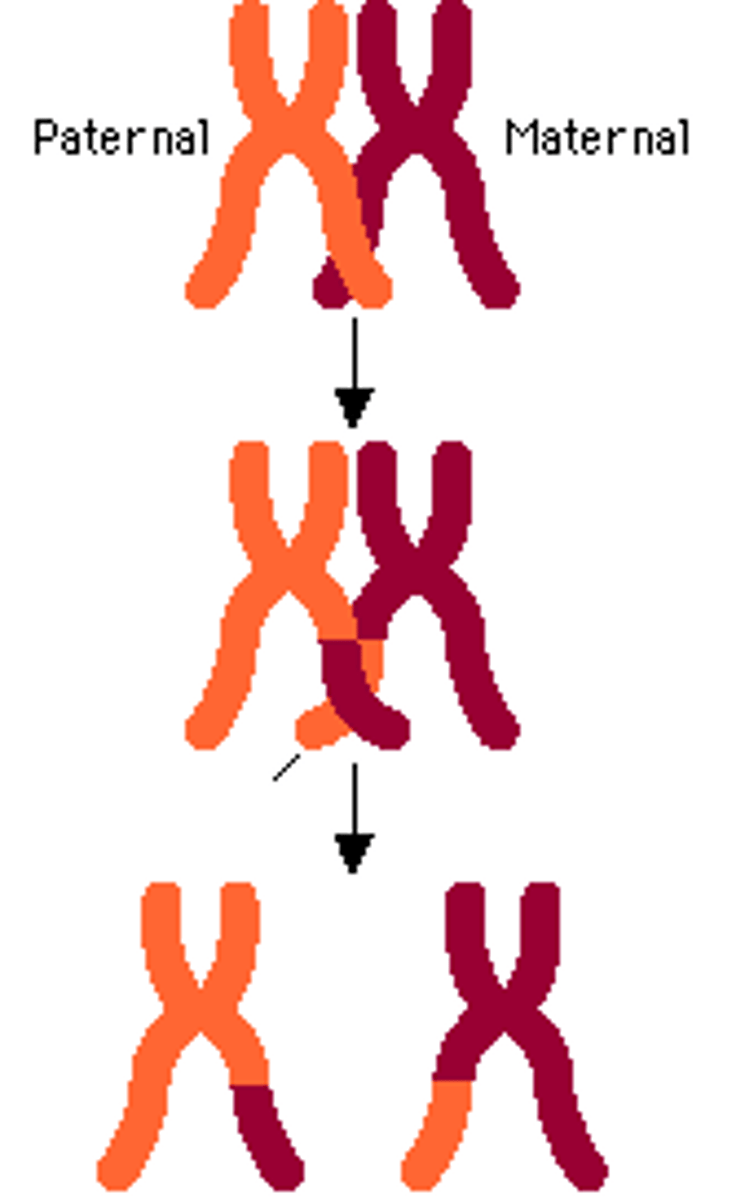
Crossing Over
During prophase I of meiosis when homologous chromosomes exchange sections of DNA at random, leading to genetic variation.
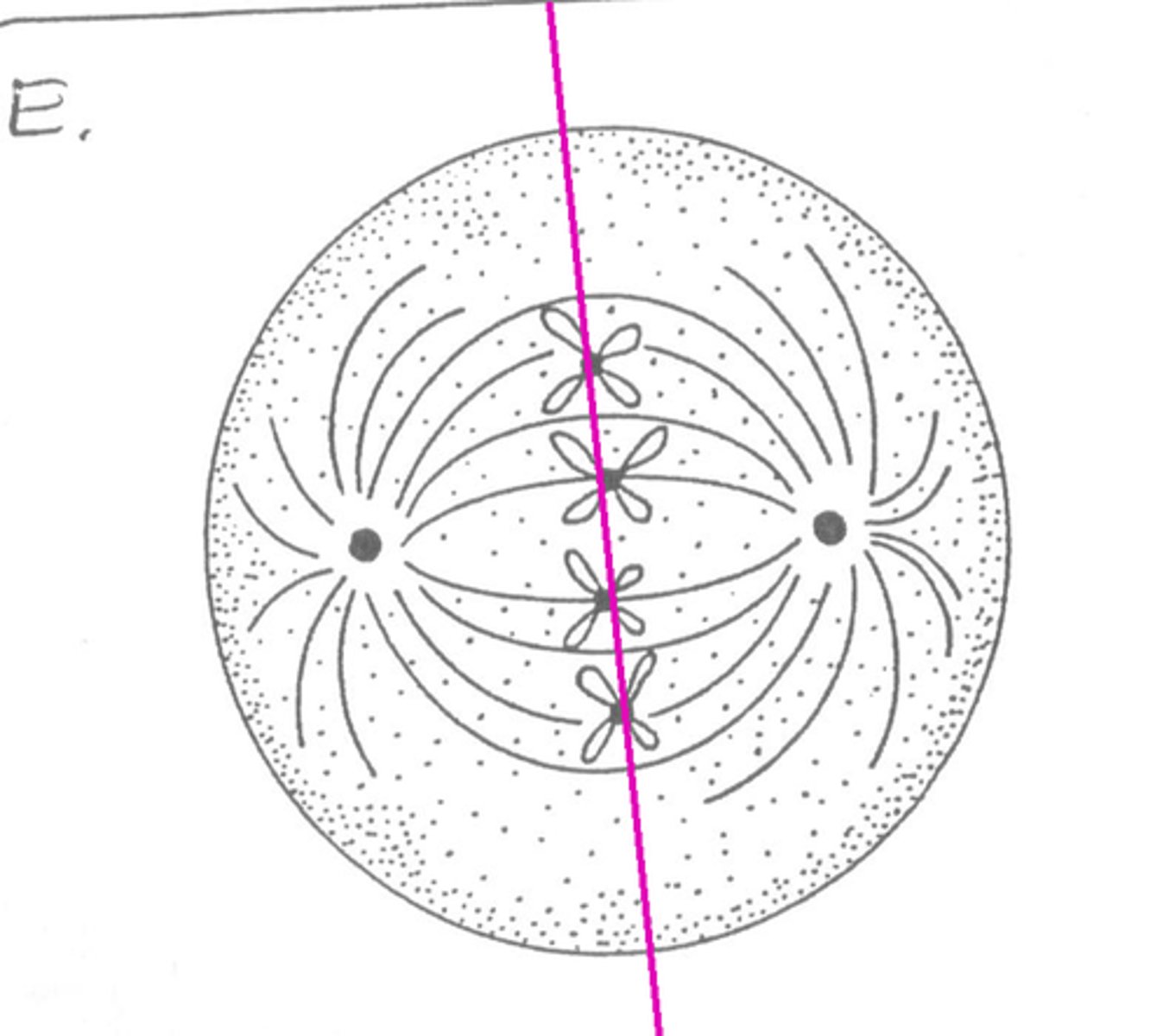
Metaphase Plate
An invisible line that chromosomes line up along during cell reproduction
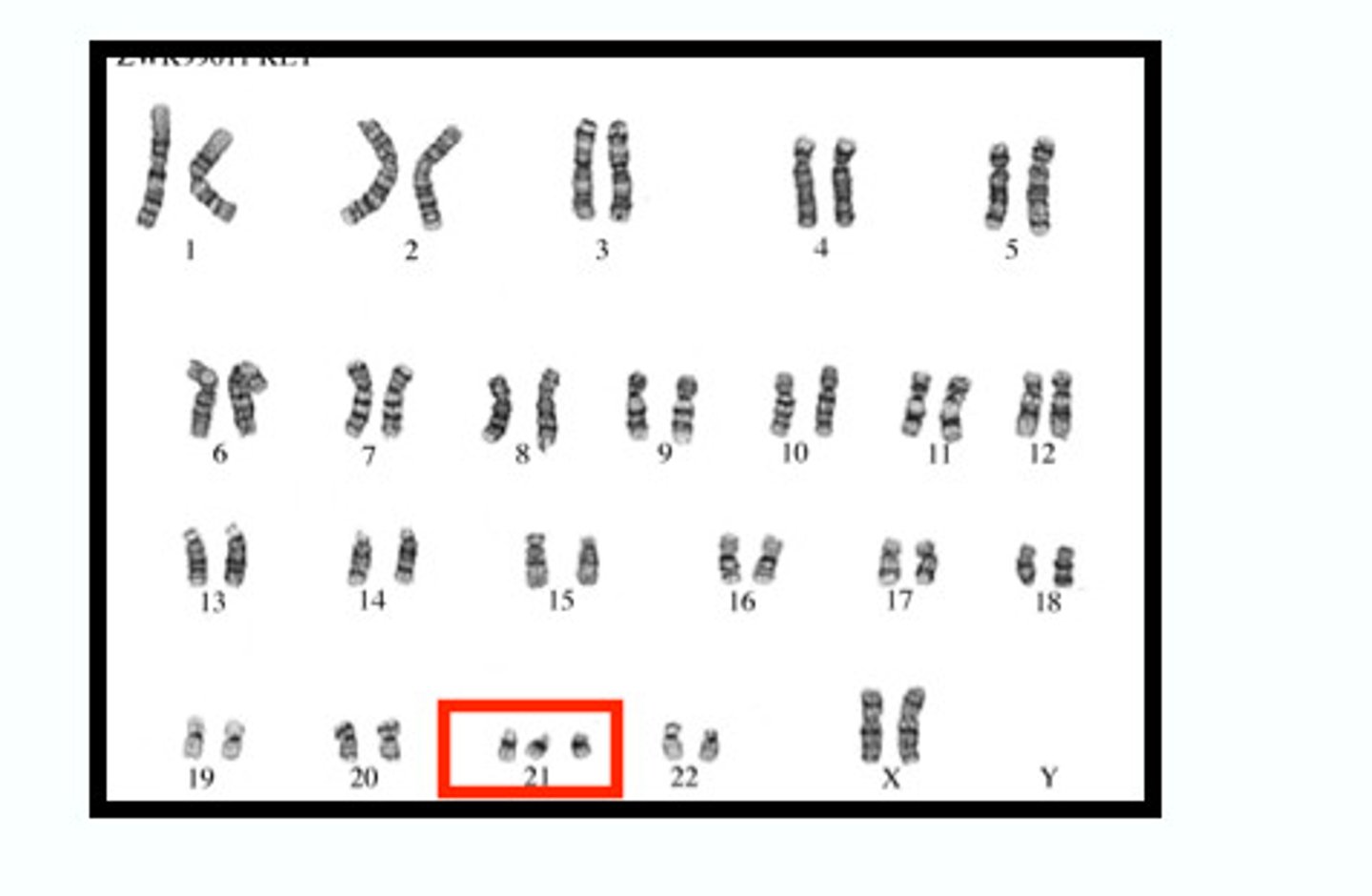
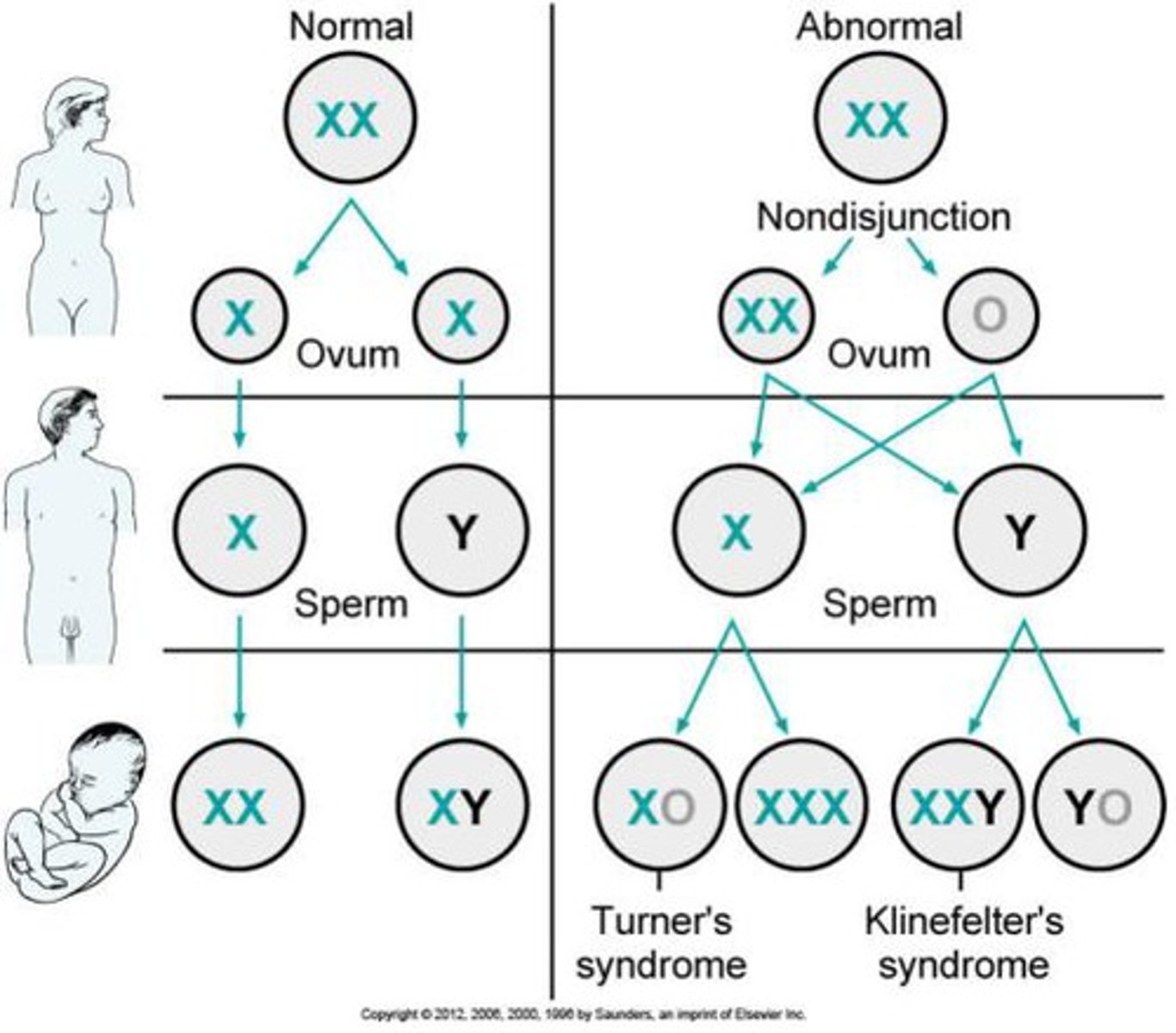
Trisomy disorder
When a karyotype shows that a person has three chromosomes instead of two for one of the pairs Ex: Down's Syndrome
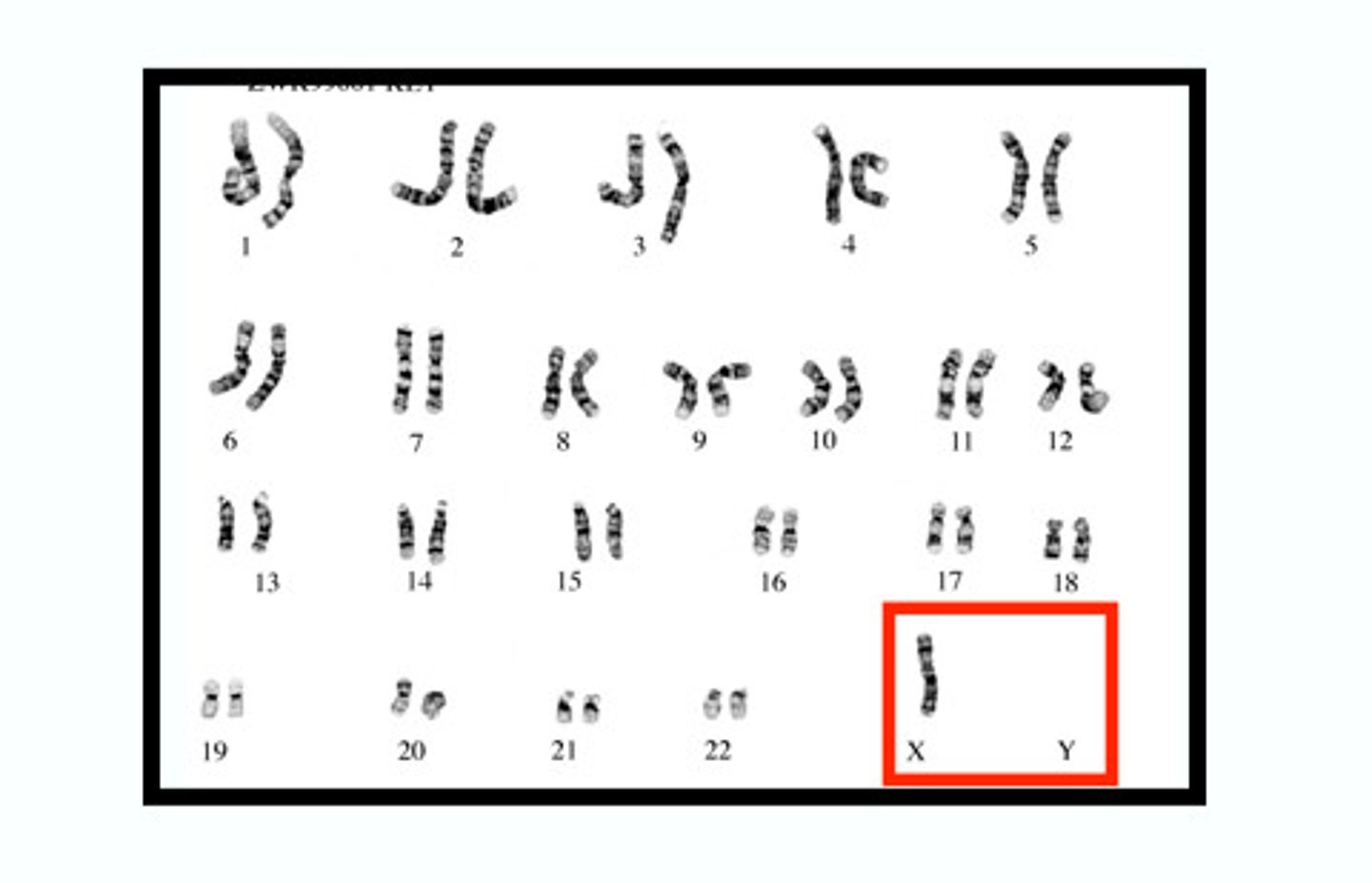
Monosomy disorder
When a karyotype shows that a person has one chromosome instead of two for one of the pairs Ex: Turner Syndrome
Chromosomal Abnormality
When an organism has the incorrect number of chromosomes (ie, a monosomy or trisomy disorder)
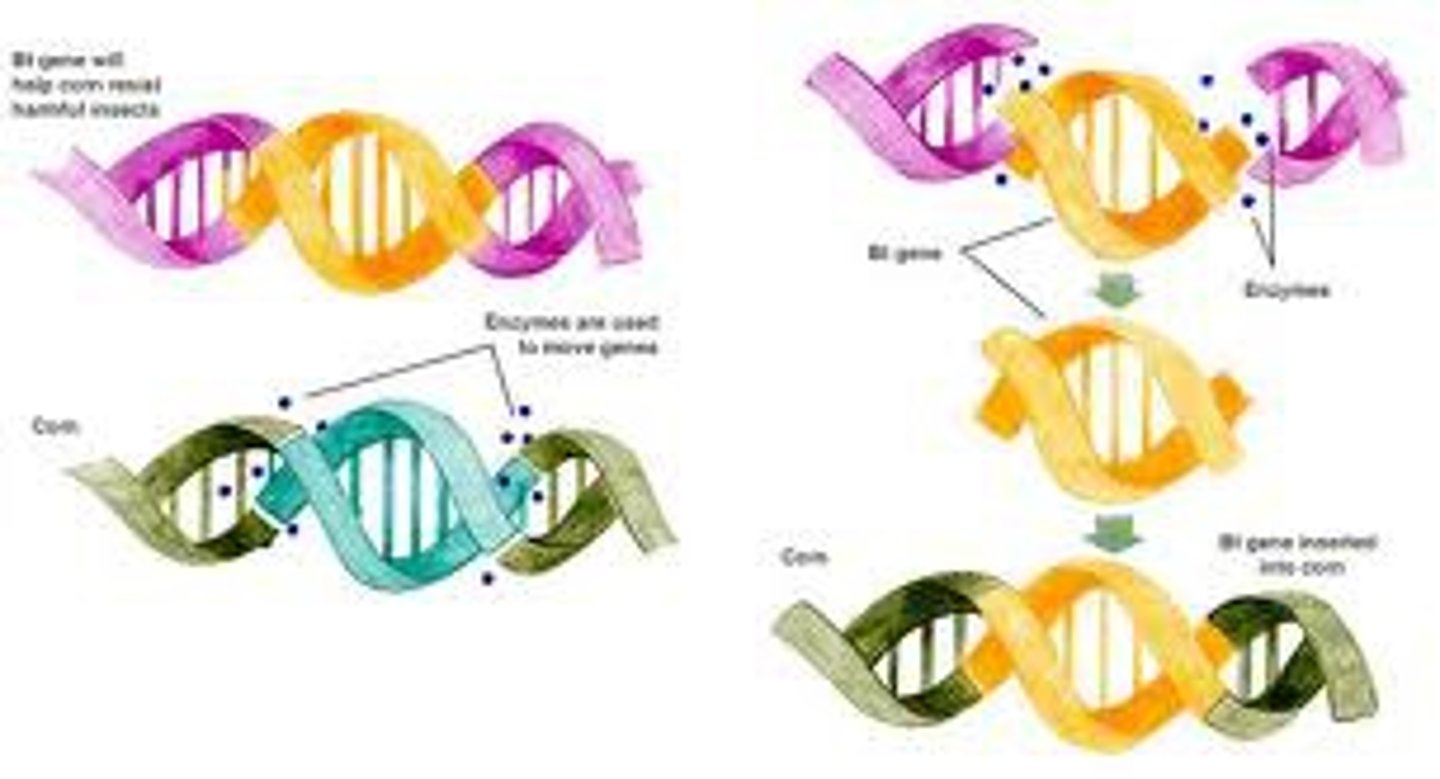
Genetic Engineering
Changing the genetics, in modern times, referring to inserting genes from one species into another.
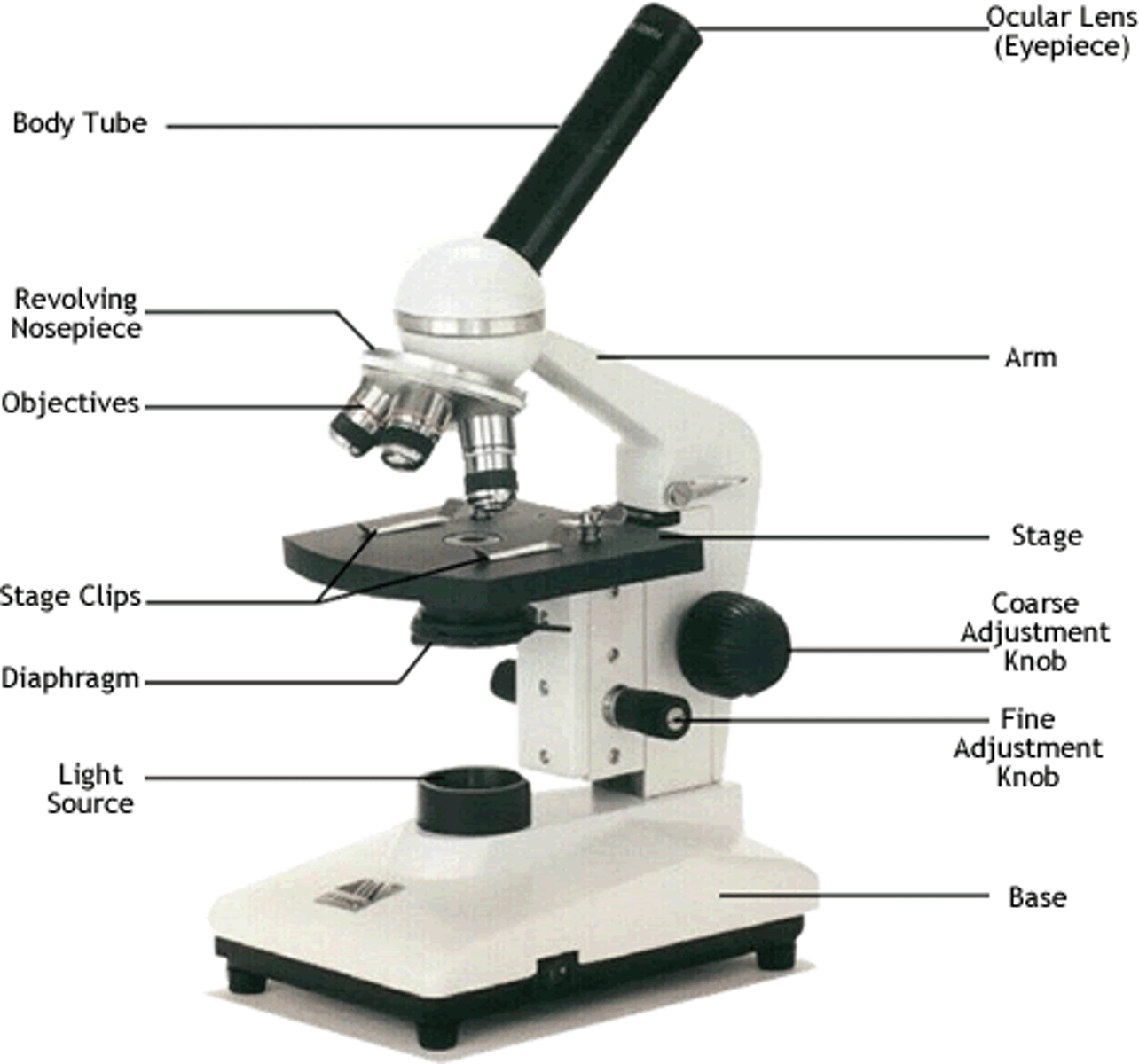
Microscope
A device with lenses used to magnify specimens.
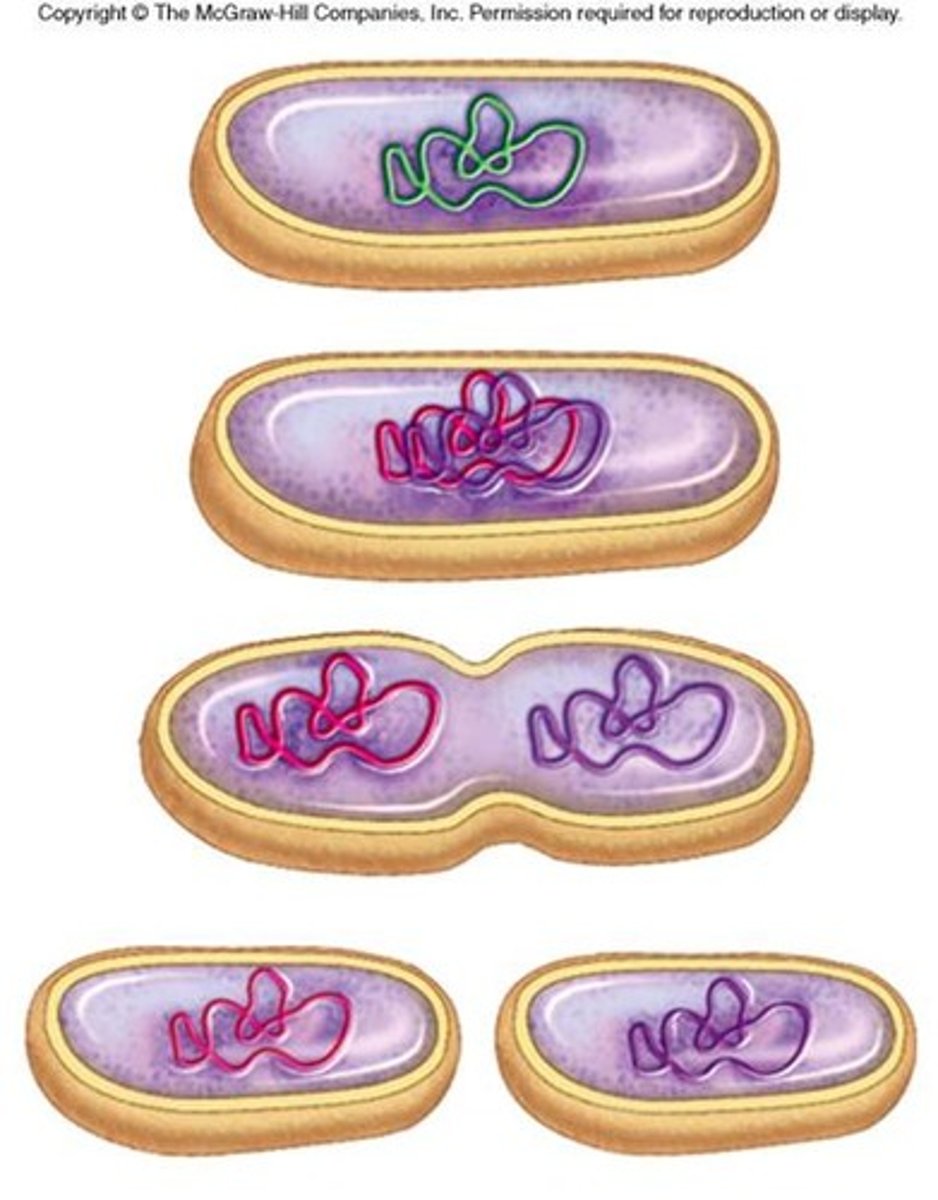
Binary Fission
A method of asexual reproduction usually found in prokaryotes (organisms with no nucleus) that results in two organisms that are often genetically identical.