Carbon and nitrogen cycle- science
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Carbon cycle:
The element carbon is found in seawater, the atmosphere, roots
Carbon moves from different parts of the cycle
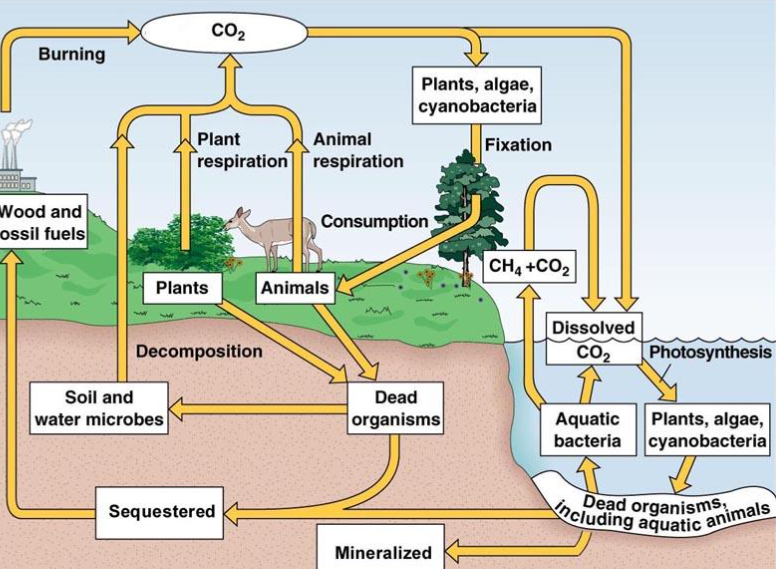
Fixtion (carbon cycle)
photosynthesis by land: taking CO2 into glucose
Consumption (carbon cycle):
Most organisms cannot use CO2 directly
They get it by eating other organisms
Biological molecules are broken down and reused
Cellular respiration (breaking down glucose realeases CO2
Aquatic Ecosystem (carbon cycle) :
CO2 dissolves in water, allowing aquatic producers to photosynthesize
Humain impacts on CO2 (carbon cycle):
Burning fossil fuels (realeasing CO2)
Deforisation
Acid accelerates CO2 realease from limestone
CO2 levels are higher over the years
Nitrogen cycle:
Describes how nitrogen moves between the atmosphere, soil, plants, animals and bacteria
Bacteria is the most important part in the cycle, helping the nitrogen change between states, found in soil
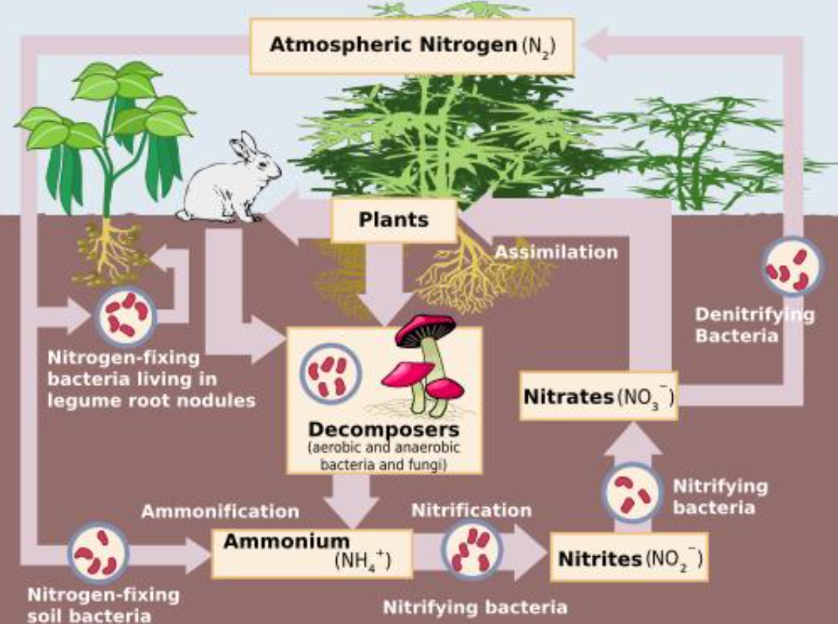
Nitrogen forms:
N2- Atmospheric Nitrogen
NH4-Ammonium, usually by some bacteria and plants
NO2-Nitrite, middle step
NO3-Nitrate, main form absorbed by plants
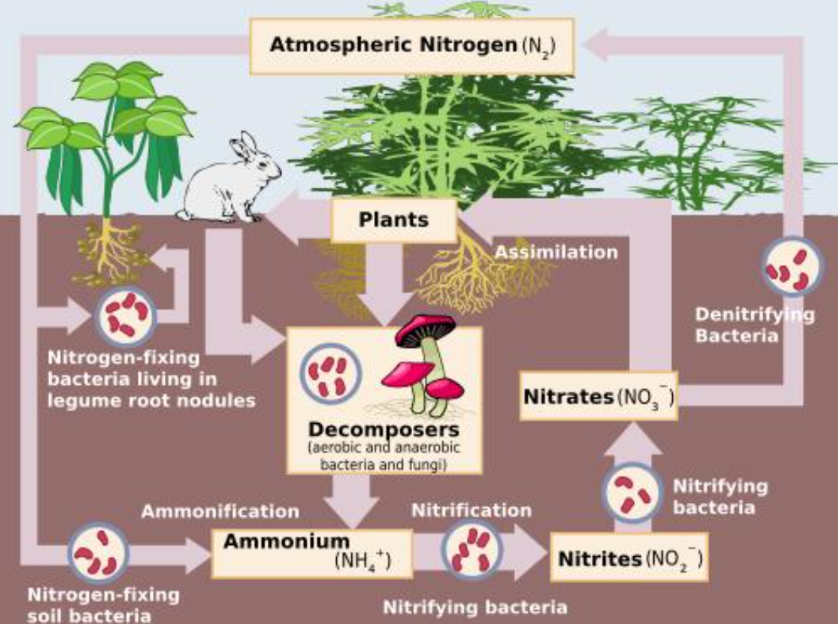
Processes in the nitrogen cycle:
Fixation: Bacteria converts N2→ NH4 (ammonium)
Nitrification: Bacteria that converts NH4→NO2→ NO3
Assimilation: Plants take in NO3 through routs
Ammonification (decomposition): Dead organisms → NH4 by decomposers (fungi, bacteria)
Dentification: Bacteria that converts NO3 back to N2 gas
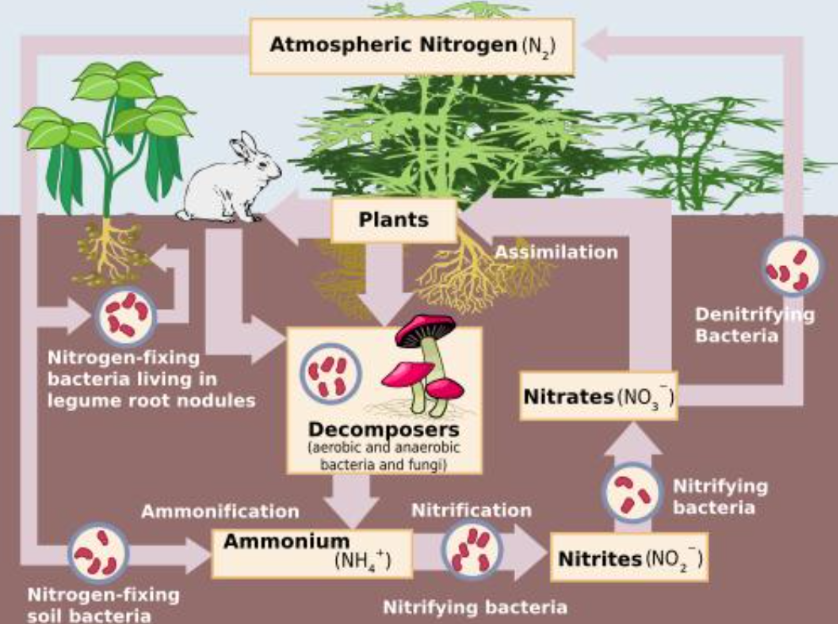
Why nitrogen is important:
Buils amino acids, DNA, proteins
Needed for chlorophyll in plants for photosynthesis
Essential for life on Earth
Human Impact: for nitrogen cycle
Fertilizers add too much nitrogen to soil (clouds can also absorb, with rain bringing it other places)
Release of nitrous oxide gas (from agriculture/industry
Disrupts natural nitrogen balance
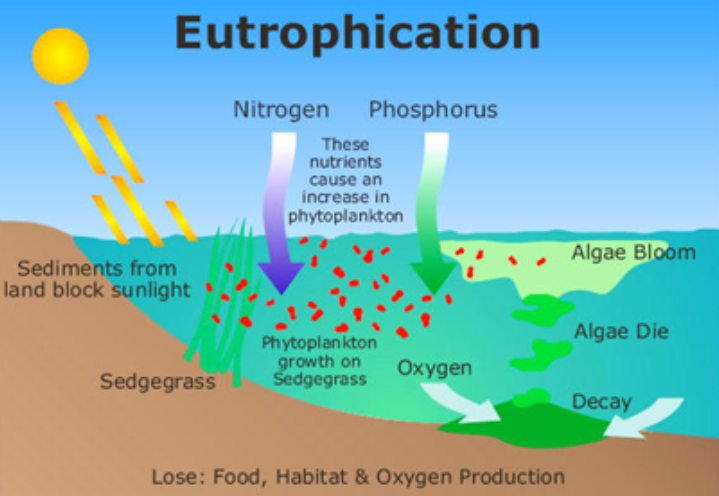
Eutrophication:
caused by leaching of nutrients into watershelds. This leads to a series of effects to the aquatic ecosystem.
nitrogen and phosphorus
Sequestration (carbon cycle):
when carbon from dead organisms trapped underground as fossil fuels
Decomposition ( carbon cycle):
bacteria, fungi breaks down dead plants and animals and returns carbon back into the atmosphere
Minerilization ( carbon cycle):
Dead organisms are transfferered into mineral form fossil form
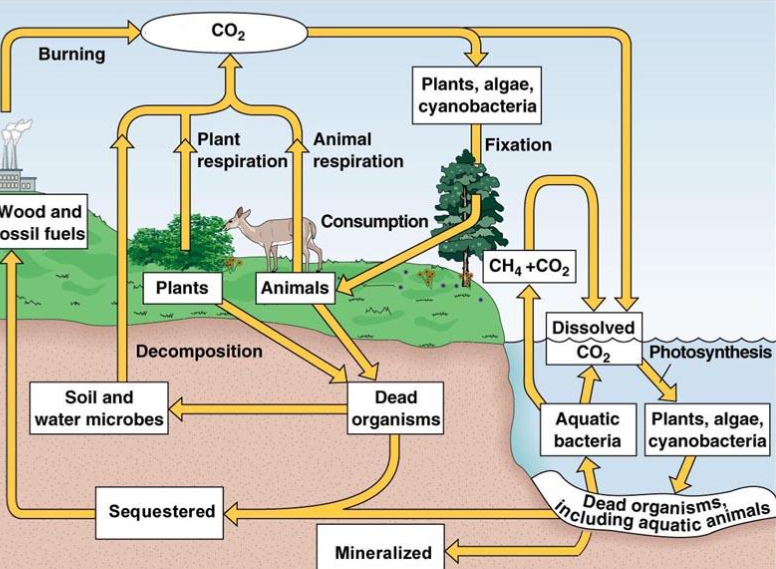
Aquatic carbon cycle:
CO2 dissolves in water (dissoloution)