medchem exam 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What are the enteral routes of administration
oral, buccal/sublingual, and rectal
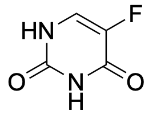
Based on the structure of the chemotherapeutic drug 5-fluorouracil, which mode of absorption is the most likely?
active transport (this can be recognized as a nucleoside analog, which is most likely to be taken up by nucleoside transporters.)
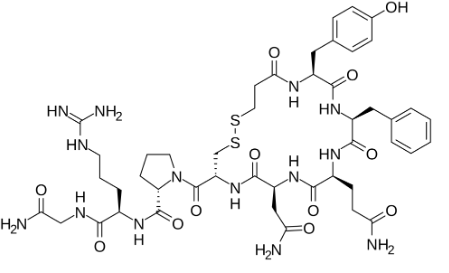
Based on the structure of the antidiuretic hormone desmopressin below, which mode of absorption is the most likely?
paracellular transport
A patient with a genetic polymorphism that results in them being a CYP2D6 "ultra-rapid metabolizer" would likely require ___________ doses of a drug primarily metabolized by CYP2D6 to achieve a therapeutic effect compared to a patient with normal metabolism. (lower or higher)
higher
What are parenteral routes of administration
IV bolus, IV infusion, SubQ, Intradermal, IM, intraarterial, intrathecal, intraperitoneal
What are the “other” forms about administration
transdermal and intranasal
what are the 3 major absorption routes
passive diffusion, carrier-mediated/active transport, paracellular
What are some requirements for paracellular transport
needs good water solubility
can be charged
must be small
where does paracellular transport happen most
GI tract
what types of transport happen in the brain
passive diffusion and active transport. NO PARACELLULAR
how do drugs use active transport enzymes
drugs will mimic endogenous substrates such as amino acids, phosphates and oligiopeptides
explain requirements for drugs taken up by passive diffusion
no energy required
need appropriate lipid solubility to cross membrane (hydrophobic)
lower MW (smaller molecules)
NO CHARGE
how much of a drug needs to pass the membrane to be “effective”
10%
which versions of acids and bases can pass membranes (protonated or deprotonated)
protonated acids, and deprotonated bases. (neutral)
what is the pH of the saliva
6-7.5
what is the pH of the stomach
1-3
what is the pH of the blood
7.4
what is the pH of the sm. and lg. intestine
4-7
what is the pH of urine
4.5-8
what does the pKa value mean?
the pH where 50% of t he drug is ionized and 50% of the drug is unionized
what portion of acid is ionized and unionized when the pH is 1 point higher
90% is unionized and 10% is ionized
what portion of acid is ionized and unionized when the pH is 2 point higher
99% is unionized and 1% is ionized
what portion of acid is ionized and unionized when the pH is 3 point higher
99.9% is unionized and 0.1% is ionized
CP450’s. name the 4 we need to know
CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP3A4
what medications does CYP1A2 metabolize
planar, basic, big molecules
what medications does CYP2D6 metabolize
basic, hydrophilic, HBA or HBD 5-7A away from metabolism site.
what medications does CYP2C9 metabolize
weak acid, lipophilic, 1-2 HBA/HBD 5-8A away from metabolism site,
what medications does CYP3A4 metabolize
high volume, lipophilic, 1-2 HBA or HBD at 5.5-7.5A and 8-10A away from metabolism site.
what are CYP450 inhibitors
drugs that block or slow down the activity of P450 enzymes. examples are ketoconazole and grapefruit juice, which increases the drug level in the blood (which could lead to toxicity) because its not being broken down.
What do CYP450 inducers do
increase the production of CYP450 enzymes, increasing metabolism which lowers the drugs level in the bloodstream making it less effective.
what are the major P450 reactions
aromatic and aliphatic hydroxylation, epoxidation, S-oxidation, alcohol oxidation, aldehyde oxidation, N-oxidation, dealkylations, deamidations, dehalogenations.
3 classes of Phase 1 enzymes
Oxidating
Reducing
Hydrolyzing
What are the oxidating enzymes
CYP450, FAO, MAO, ADH, ALDH
What is FMO
Flavin-containing Monooxygenase
oxidizes @ N, S, and P to form N-oxides, sulfoxides, and phosphites
in the liver, kidney and intestine
in ER membrane of cells
FAD prosthetic group
What is MAO
Monoamine oxidases
liver, intestine
FAD prosthetic group
IN MITOCHONDRIA (M for Mitochondria)
endogenous and xenobiotics
mainly primary amine substrates
What is ADH
Alcohol dehydrogenase
use NAD+ or NADPH
oxidizes xenobiotic alcohols to aldehydes
What is ALDH
Aldehyde dehydrogenase
converts aldehydes into carboxylic acids
also uses NAD+ or NADPH
What are the reducing phase 1 enzymes
CYP reductase
Azo and nitro reductase
carbonyl reductase
what is the most common reducing phase 1 enzyme
carbonyl reductase
what do carbonyl reductases do
turn carbonyls into hydroxyls
What are the phase 1 hydrolyzing enzymes
epoxide hydrolase
esterases
amidases
what do esterases do
cleaves a molecule at the ester bond
what do amidases do?
cleave the molecule at the amide
what are carboxylesterases
a subset of esterases
cleave esters into carboxylic acids
which phase of metabolism effects the drugs hydrophilicity the most
the second phase has the most effect on the water solubility of the drug (larger molecules are added)
what are the 2 main groups of phase 2 enzymes
electrophilic and nucleophilic
what are the phase 2 enzymes
UDP-glucuroryl transferase (UGT), sulfotransferase (SULT or ST), N- and O-methyl transferase, acetyl transferases, amino acids tranferases
what is the nucleophilic phase 2 enzyme
Glutathione S-transferase (GST)
what does UGT do??
adds a sugar molecule to any xenobiotic (makes more polar)
what does SULT/ST do
sulfotransferase
adds sulfate group to xenobiotic
amine or hydroxyl
What is GST
glutathione s-transferases
glutathione added to xenobiotic
what are the 2 groups of phase 3 enzymes
ABC (ATP-binding cassette)
SLC (solute carrier)
what are the common ABC transporters
P-glycoprotein (PGP)
ABCC’s
ABCG2
What are the 3 SLC trasnporters
OATP (organic anion transporter polypeptides)
OAT (organic anion transporter)
OCT (organic cation transpoerter)
which group of phase 3 transporters do efflux
ABC enzymes
which group of phase 3 transporters mainly are used for influx
SLC: primarily uptake molecules into cell (influx)
what are the two ways to excrete the medication
renal and bile excretion
what happens after drugs are metabolized in the liver
they go into the bile in the bile canaliculus, then out into the intestines and feces.
what is enterohepatic cycling
the drug is metabolized in the liver and goes into the bile and gut where certain enzymes reconvert the metabolites into lipophilic versions so they can be reabsorbed into the plasma. this increases duration of action (could be good, could be bad)
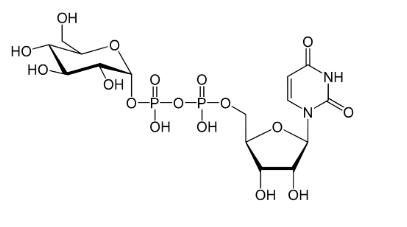
what is this molecule a cofactor for
UGT
what enzyme adds a sugar group to a xenobiotic
UGT
what enzyme adds glutathione to a xenobiotic
GST
where does the xenobiotic bind to GSH after GST is used to attach it
to the Sulfur of cysteine
which enzymes use water to perform hydrolysis during metabolism
esterase’s and amidases
when a prescribed drug is metabolized by CYP3A4 and the patient is also taking an OTC CYP3A4 inhibitor, what is the outcome?
The prescribed medication will not be metabolized as quickly leading to lower therapeutic effect, and levels will increase in the blood, which could cause toxicity.
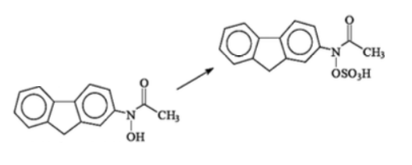
The following reaction is performed by which enzyme?
SULT (or ST)
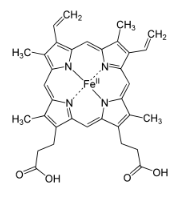
The compound below is a co-substrate or cofactor for which drug metabolism enzyme?
P450’s! The structure is Heme
A person is a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer and they are prescribed a CYP2D6 drug substrate. What is the expected outcome compared to someone who has at least one normally-functioning copy of CYP2D6?
The drug will be more slowly metabolized.
What phase I enzyme shares the following characteristics with P450: monooxygenase, found in the liver, uses O2, forms N-oxides
FMO
Which route of administration is both the safest and easiest for patients?
Oral
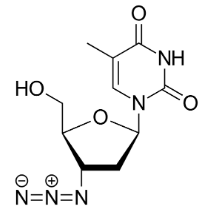
This HIV drug zidovudine looks a lot like what endogenous substance? What transporter would take this molecule?
It is very structurally similar to a nucleotide, causing it to be taking up by an active transporter (probably a SLC)
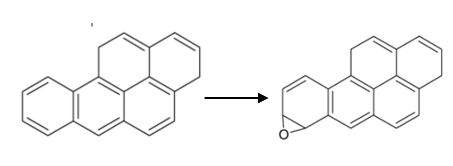
What category of cytochrome P450 metabolic reaction is depicted? Which of the major drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes is most likely to be involved?
expoxidation; CYP1A2
Which is a rapid administration method with variable dose absorption which also has limitations on penetration into the tissue particularly depending on the physical size of the drug particles (not drug molecular weight)?
Inhalation
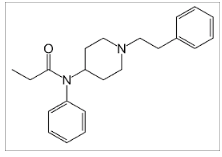
Based on its structure below, you would most likely expect that fentanyl would be most likely absorbed by which route?
passive diffusion. this drug is highly lipophilic and no charge, so it will easily diffuse.
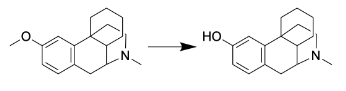
What category of cytochrome P450 metabolic reaction is depicted? Which of the major drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes is most likely to be involved?
O-dealkylation: CYP2D6 (The molecule is basic and relatively hydrophilic)
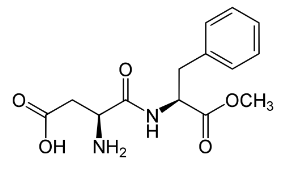
Based on its structure below, you would expect that the artificial sweetener aspartame would be most likely absorbed by which of the following routes?
active transport by a oligopeptide transporter