final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
1
New cards
\
1. Compare and contrast the scopes of practice for each of the nationally recognized EMS certification levels.
1. Compare and contrast the scopes of practice for each of the nationally recognized EMS certification levels.
\
1. EMR: wait for EMT or paramedics to arrive scene, obtain vitals and airway
2. EMT: oxygen therapy, ventilation equipments, limited medication
3. AEMT: advanced airway device, monitor glucose, more medication
4. Paramedic: highest level
1. EMR: wait for EMT or paramedics to arrive scene, obtain vitals and airway
2. EMT: oxygen therapy, ventilation equipments, limited medication
3. AEMT: advanced airway device, monitor glucose, more medication
4. Paramedic: highest level
2
New cards
\
1. Discuss the roles and responsibilities of the EMT and how the EMT can best meet these expectations.
1. Discuss the roles and responsibilities of the EMT and how the EMT can best meet these expectations.
\
1. Proper PCR
2. Do not leave patient
1. Proper PCR
2. Do not leave patient
3
New cards
\
Identify the stages of grief experienced by patients and their families, and explain principles for interacting with these individuals in situations involving death and dying.
Identify the stages of grief experienced by patients and their families, and explain principles for interacting with these individuals in situations involving death and dying.
\
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. depression
5. acceptance
explain the care you are providing, show great respect, keep communicating, allow family members to vent, scream, cry, listen carefully, do not give false assurance, comfort family
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. depression
5. acceptance
explain the care you are providing, show great respect, keep communicating, allow family members to vent, scream, cry, listen carefully, do not give false assurance, comfort family
4
New cards
Compare and contrast the characteristics of acute, delayed, and cumulative stress reactions
acute stress: right after exposure to high stress situation. Nausea, sweat, loss epithet
delayed stress: days or years after incident, PTSD
cumulative stress: “burnout” anxiety
delayed stress: days or years after incident, PTSD
cumulative stress: “burnout” anxiety
5
New cards
Discuss the components of a comprehensive system of critical incident stress management.
CISD: after a day or two, mental counsling
defusing: couple hours after, EMT’s vent out emotion in small groups
defusing: couple hours after, EMT’s vent out emotion in small groups
6
New cards
Describe ways EMTs can protect themselves from exposure to diseases caused by pathogens, as well as from accidental and work-related injuries.
hand washing
eye shields
protective gloves
N-95 masks
\
eye shields
protective gloves
N-95 masks
\
7
New cards
Define key terms introduced in this chapter.
DNR- do not rescue
POLST: patient terminal, only life sustain
POLST: patient terminal, only life sustain
8
New cards
Differentiate between the concepts of scope of practice and standard of care*.*
scope of practice: actions EMT is legal allowed to perform
standard of care: care expected to be provided by EMT
standard of care: care expected to be provided by EMT
9
New cards
Be able to recognize situations in which an EMT would have a duty to act.
Duty to act: legal obligations to provide service
Once you start care tho, you have to finish it
Once you start care tho, you have to finish it
10
New cards
Discuss the actions an EMT should take when a patient refuses care.
false imprisonment: taking patient against his will
make em sign refusal form
make em sign refusal form
11
New cards
List and describe the purpose and typical contents of each section in a PCR.
* chief complaint
* vitals
* demographics
* mechanism of injury
* medical history
* \
* vitals
* demographics
* mechanism of injury
* medical history
* \
12
New cards
Be able to recognize examples of each type of information common to the narrative portion of a PCR.
s/s: signs/ symptoms
NTG: nitroglycerin
PE: physical exam
SOB: shortness of breath
NTG: nitroglycerin
PE: physical exam
SOB: shortness of breath
13
New cards
Discuss how to handle special reporting situations with respect to the PCR and patient documentation.
if you don’t know, look up spelling or just use normal language
14
New cards
Accurately and completely record pertinent patient and EMS call information using the SOAP, CHART, and CHEATED methods.
SOAP
* subjective
* objective
* assesment
* plan
CHART
* chief complaint
* historuy
* assesment
* treatment
* transport
Cheated
* chief complaint
* history
* physical exam
* assessment
* treatment
* evaluation
* disposition
* subjective
* objective
* assesment
* plan
CHART
* chief complaint
* historuy
* assesment
* treatment
* transport
Cheated
* chief complaint
* history
* physical exam
* assessment
* treatment
* evaluation
* disposition
15
New cards
Describe the responsibilities of the Federal Communications Commission
regulates interstate and international communications through cable, radio, television, satellite and wire
16
New cards
Describe the standard rules and expectations for using a transmitter/receiver during radio communications.
* turn to correct frequency
* 2 inches away from microphone
* keep it short
* speak individual digits
* repeat
* \
* 2 inches away from microphone
* keep it short
* speak individual digits
* repeat
* \
17
New cards
Discuss how to provide a concise radio report to medical direction or the receiving facility, and when to update that report while still enroute.
* The patient’s current condition
* The patient’s age and gender
* The patient’s chief complaint
* A brief, pertinent history of what happened
* A description of how you found the patient
* Any major past illnesses
* Vital signs you obtained from the patient
* Pertinent findings of the physical exam
* Any emergency medical care that was given
* The patient’s response to any emergency medical care that was provided
* The patient’s age and gender
* The patient’s chief complaint
* A brief, pertinent history of what happened
* A description of how you found the patient
* Any major past illnesses
* Vital signs you obtained from the patient
* Pertinent findings of the physical exam
* Any emergency medical care that was given
* The patient’s response to any emergency medical care that was provided
18
New cards
Discuss teamwork and communication considerations for lifting and moving patients.
Use commands that are easy for team members to understand. Verbally coordinate each lift from beginning to end
19
New cards
Discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and steps for each of the recommended lifting and moving techniques.
power lift: safe and stable, used by weak rescuers
squat lift: strong legged rescuers,
\
squat lift: strong legged rescuers,
\
20
New cards
positions
supine: lying on back
lateral recumbent position: lying on side
flowers position: 45 degrees
trendelenburg position: feet elevated than head
\
lateral recumbent position: lying on side
flowers position: 45 degrees
trendelenburg position: feet elevated than head
\
21
New cards
cavities
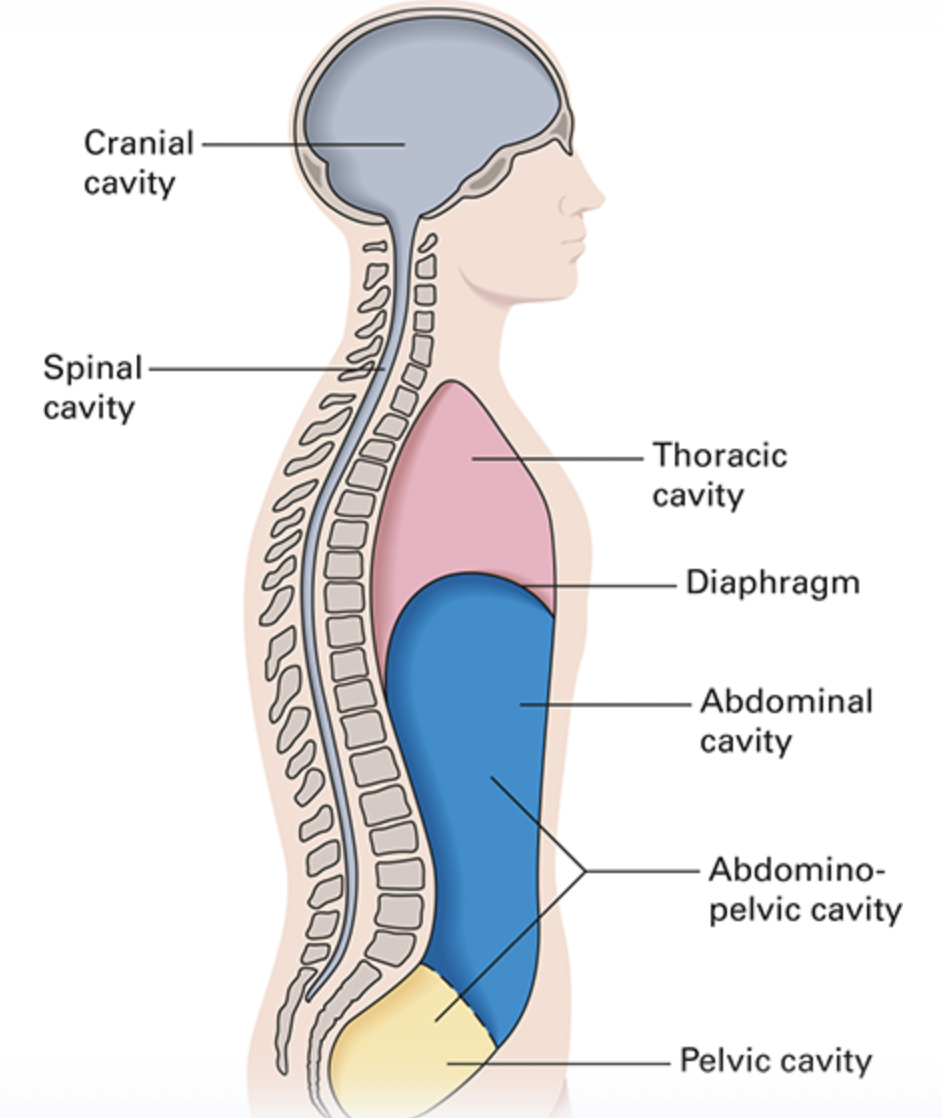
22
New cards
directional terms
anterior: front
superior: towards head
dorsal: back
medial: towards center of body
proximal: near point of reference
plantar: feet
superior: towards head
dorsal: back
medial: towards center of body
proximal: near point of reference
plantar: feet
23
New cards
Identify important anatomic and physiologic differences in children’s respiratory systems as they relate to oxygenation, airway maintenance, and ventilation skills.
* mouth and nose a lot smaller, thus easier to be obstructed by tongue or objects
* chest wall softer so rely more on diaphragm for breathing
* breath more through nose not mouth
* chest wall softer so rely more on diaphragm for breathing
* breath more through nose not mouth
24
New cards
Describe the basic mechanics and physiology of normal ventilation, respiration, and oxygenation.
ventilation: flow of air in and out of lung; diaphragm does most work
respiration: oxygen and CO2 exchanged through alveoli
respiration: oxygen and CO2 exchanged through alveoli
25
New cards
Describe the anatomy and physiology of the heart.
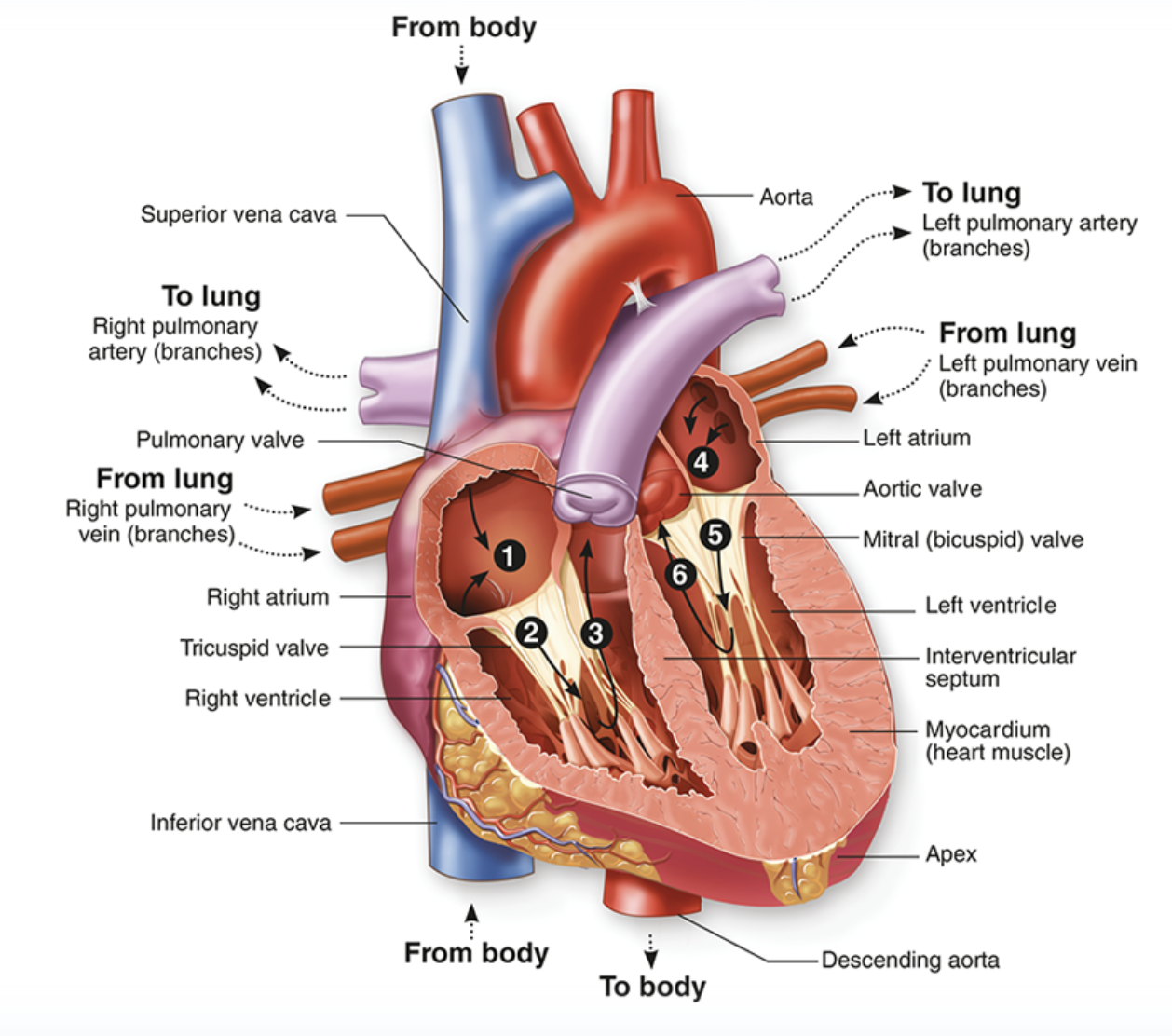
26
New cards
Discuss the anatomy and physiology of the circulatory system, blood, perfusion/capillary exchange, and metabolism.
artery: carries blood away from heart
perfusion: delivery of nutrients to cells
capillary: connects arteriole to venue, exchanges nutrients and waste
perfusion: delivery of nutrients to cells
capillary: connects arteriole to venue, exchanges nutrients and waste
27
New cards
Explain the overall function of the endocrine system, and discuss the locations and general functions of each component that comprises the endocrine system.
made of ductless glands which produce hormones.
28
New cards
explain the importance of understanding basic pathophysiology as it relates to `emergency` patient care
it helps you recognize and treat things faster and at the right order of criticalness
29
New cards
Differentiate between the processes of aerobic and anaerobic cellular metabolism, and outline the consequences of cellular sodium/potassium pump failure.
cellular metabolism: break glucose and gain ATP
if pump fails, cell swells and dies, leading to organ failure
if pump fails, cell swells and dies, leading to organ failure
30
New cards
Explain the concept of perfusion, including components necessary to maintain perfusion.
perfusion: deliver oxygen nutrients, take waste from cells.
* airway
* BP
* \
* airway
* BP
* \
31
New cards
Explain how changes in compliance of the lungs and chest wall and changes in airway resistance affect ventilation.
compliance: ability of chest wall and lung to stretch
airway resistant: ease of airflow to alveoli
decrease of compliance or increase of airway resistant can lead to complications in breathing, less oxygen, hypoxia
airway resistant: ease of airflow to alveoli
decrease of compliance or increase of airway resistant can lead to complications in breathing, less oxygen, hypoxia
32
New cards
Describe and differentiate between tidal volume, alveolar
ventilation, and minute ventilation
ventilation, and minute ventilation
tidal volume: volume of air each breath
alveolar ventilation: volume of air in n out of alveoli 1 min
minute ventilation: volume of air in n out of lung 1 min
alveolar ventilation: volume of air in n out of alveoli 1 min
minute ventilation: volume of air in n out of lung 1 min
33
New cards
Identify and discuss the numeric age range, key physiological and psychosocial developments, and normal \n vital signs for neonates and infants.
neonates: 100-205 heart beat, 30-60 respiratory rate, 67-84BP,
infant: 100-180 heart beat, 20-30 respiratory rate, 70-104 BP, 98-100F
infant: 100-180 heart beat, 20-30 respiratory rate, 70-104 BP, 98-100F
34
New cards
Describe the physiological changes that occur immediately after birth.
lose weight first 2 weeks. immune system don’t exist. reflexes (blinking, sucking, swallowing)
35
New cards
Identify and discuss the numeric age range, key physiological and psychosocial developments, and normal vital signs for school-age children.
6-11 yrs old
75-118 heart beat, 18-25 respiratory rate, 07-115 BP, 98.6F
\
75-118 heart beat, 18-25 respiratory rate, 07-115 BP, 98.6F
\
36
New cards
Identify and discuss the numeric age range, key physiological and psychosocial developments, and normal
vital signs for adolescence
vital signs for adolescence
12-15 yrs old
60-100 beats, 12-20 respiratory rate, 110-131 BP
2-3 year growth spurt, puberty, want to be adults,
60-100 beats, 12-20 respiratory rate, 110-131 BP
2-3 year growth spurt, puberty, want to be adults,
37
New cards
Recognize the progressive assessment findings of mild, moderate, and severe hypoxia in pediatrics and adults
*Signs of Mild to Moderate Hypoxia*
* Tachypnea (increased respiratory rate)
* Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
* Pale, cool, clammy skin (early)
* Tachycardia (increase in heart rate)
* Elevation in blood pressure
* Restlessness and agitation (from hypoxic brain cells)
* Disorientation and confusion (from high carbon dioxide levels in the blood)
* Headache
*Signs of Severe Hypoxia*
* Tachypnea
* Dyspnea
* Cyanosis (bluish gray color to skin, mucous membranes, and nail beds)
* Tachycardia that may lead to dysrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) and eventually bradycardia (slow heart rate)
* Severe confusion
* Loss of coordination
* Sleepy appearance (from high carbon dioxide levels in the brain)
* Head bobbing (head bobs upward with inhalation and downward with exhalation, as if falling asleep while sitting upright) with droopy eyelids (from high carbon dioxide levels in the brain)
* Slow reaction time
* Altered mental status
* Seizure
* Tachypnea (increased respiratory rate)
* Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
* Pale, cool, clammy skin (early)
* Tachycardia (increase in heart rate)
* Elevation in blood pressure
* Restlessness and agitation (from hypoxic brain cells)
* Disorientation and confusion (from high carbon dioxide levels in the blood)
* Headache
*Signs of Severe Hypoxia*
* Tachypnea
* Dyspnea
* Cyanosis (bluish gray color to skin, mucous membranes, and nail beds)
* Tachycardia that may lead to dysrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) and eventually bradycardia (slow heart rate)
* Severe confusion
* Loss of coordination
* Sleepy appearance (from high carbon dioxide levels in the brain)
* Head bobbing (head bobs upward with inhalation and downward with exhalation, as if falling asleep while sitting upright) with droopy eyelids (from high carbon dioxide levels in the brain)
* Slow reaction time
* Altered mental status
* Seizure
38
New cards
39
New cards
Explain the causes and presentation for each abnormal upper airway sound.
snoring: partially obstructed
crowning: muscle around larynx is narrowing airway
gurgling: blood, vomit, in airway, suction it out
stridor: swelling in larynx
crowning: muscle around larynx is narrowing airway
gurgling: blood, vomit, in airway, suction it out
stridor: swelling in larynx
40
New cards
Discuss the procedure for airway assessment and opening of the airway with manual maneuvers and patient positioning.
headtilt, chin lift: use when no spinal injury
jaw thrust: when spinal injury is suspected
place sideways if no spinal injury and patient may throw up
jaw thrust: when spinal injury is suspected
place sideways if no spinal injury and patient may throw up
41
New cards
Discuss the function and performance of fixed and portable suction devices
mounted device: much stronger suction, greater than 300mmHg
portable device: up to 300mmHg pressure,
\
portable device: up to 300mmHg pressure,
\
42
New cards
Explain the difference between rigid and soft suction catheters, how to use both, and special considerations when suctioning patients.
rigid: suction used on mouth of unresponsive patient
soft catheter: suction through nose, measure using nose to ear
soft catheter: suction through nose, measure using nose to ear
43
New cards
Discuss normal and abnormal findings when assessing a patient’s breathing, how to determine oxygen needs, and indications of respiratory distress or failure.
wheezing: inflammation in bronchioles in lung
crackles: fluid surrounding and filling the alveoli
rhonchi: mucus blocking bronchioles
crackles: fluid surrounding and filling the alveoli
rhonchi: mucus blocking bronchioles
44
New cards
Differentiate between normal and abnormal respiratory rates for each age bracket.
elder respiratory rate at rest is usually higher
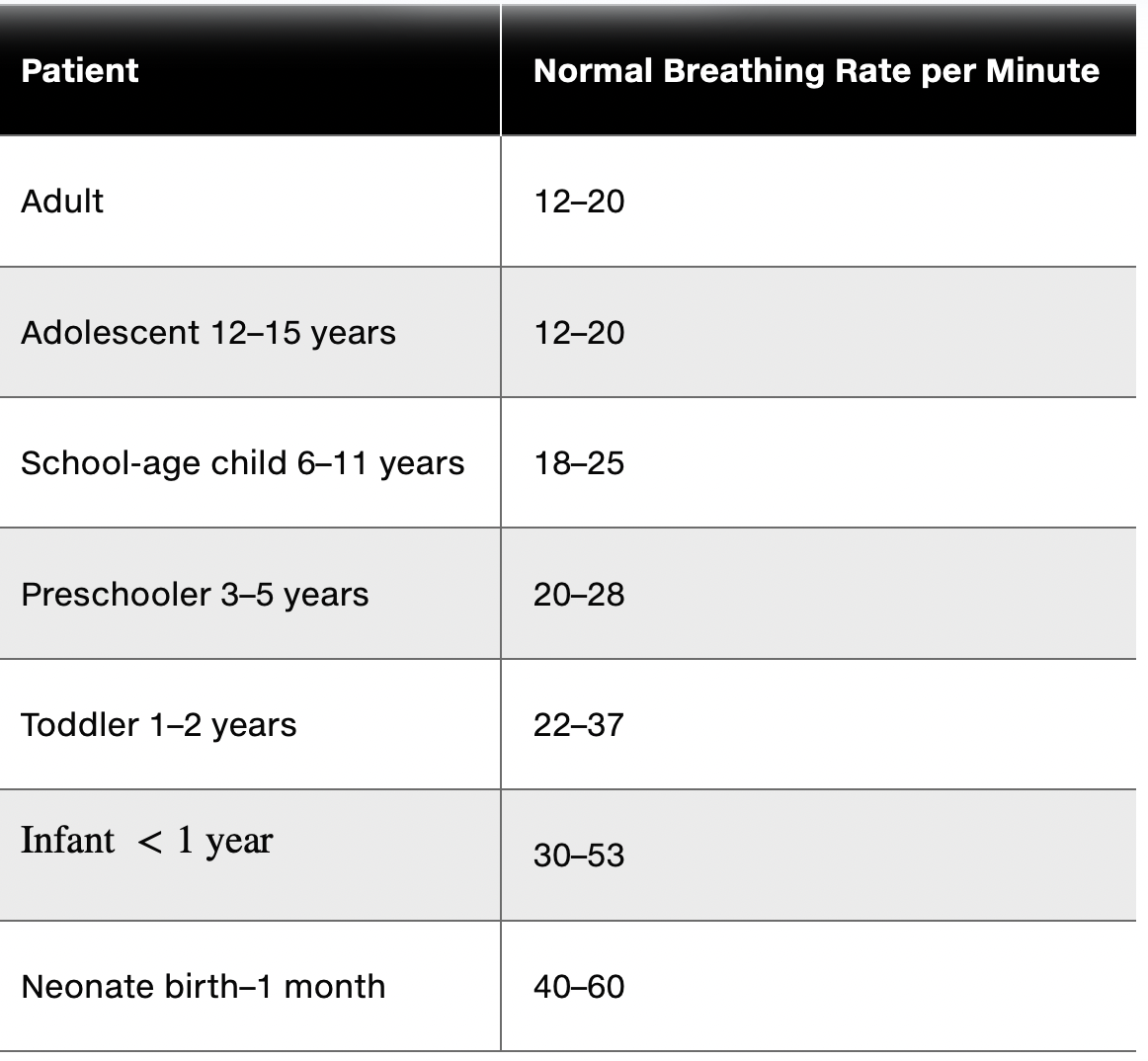
45
New cards
Describe normal and abnormal findings in the assessment of skin color, temperature, condition, capillary refill, and color of the mucous membranes.
white: loss blood
cyanosis (blue): shock
yellow: liver disease
cool: shock
capillary refill: under 2 sec, 3 female, 4 elders
cyanosis (blue): shock
yellow: liver disease
cool: shock
capillary refill: under 2 sec, 3 female, 4 elders
46
New cards
Explain factors that can cause abnormalities to skin color, temperature, condition, capillary refill, and mucous membrane color.
slow capillary refill indicate: shock
dry skin: spinal injury
high fever: infection
dry skin: spinal injury
high fever: infection
47
New cards
When assessing the pupils, recognize normal findings versus abnormal findings, and associate these with potential underlying causes.
dilated pupils: drugs
unequal size: stroke
consensual reflex: reaction to light
contrsticed: nervous system disorder
unequal size: stroke
consensual reflex: reaction to light
contrsticed: nervous system disorder
48
New cards
In relation to blood pressure measurement, explain systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse pressure, and causes of abnormal findings.
kids have lower BP
pulse pressure = systolic - diastolic BP
hypertension: high BP
\
pulse pressure = systolic - diastolic BP
hypertension: high BP
\
49
New cards
Use the mnemonics SAMPLE and OPQRST to ensure a complete prehospital patient history.
SAMPLE
* Signs and symp
* allergies
* medications
* past histories
* last oral intake
* events leading to illness
OPQRST
* onset
* provocation
* quality
* radiation
* severity
* time
* \
* Signs and symp
* allergies
* medications
* past histories
* last oral intake
* events leading to illness
OPQRST
* onset
* provocation
* quality
* radiation
* severity
* time
* \
50
New cards
Explain the purposes and goals of performing a scene size-up on every EMS call.
make sure scene is safe
51
New cards
Identify factors involved in determining the number of patients
call for back up
52
New cards
Explain the importance of developing a systematic patient assessment routine, and list the four main phases of the patient assessment process
scene size up
primary assesment
secondary assesement
reassessment
primary assesment
secondary assesement
reassessment
53
New cards
Review the steps of the scene size-up phase of the patient assessment process.
* ensure safety
* determine mechanism of injury
* establish number of patients
* call for back up as needed
* determine mechanism of injury
* establish number of patients
* call for back up as needed
54
New cards
State the main purpose of the primary assessment, and list the components of the primary assessment phase.
identify and manage immediately life-threatening conditions to the airway, breathing, oxygenation, or circulation. If anything found, musts treat b4 moving onto next
“ABCs”
“ABCs”
55
New cards
Discuss ways to determine if a patient is injured or ill and how to obtain the chief complaint.
“why did you call EMS today?”
56
New cards
Differentiate between patients who do and do not need spinal motion restriction techniques, and discuss proper patient positioning for assessment.
If patient prone, log roll to supine. if spinal suspected, spine motion restriction b4 log roll.
57
New cards
Using the AVPU method, describe how to assess and document the level of responsiveness.
AVPU
* Alert
* response to verbal stimulus
* response to Painful stimulus
* unresponsiveness
* Alert
* response to verbal stimulus
* response to Painful stimulus
* unresponsiveness
58
New cards
Determine airway status in responsive versus unresponsive patients, and identify methods for establishing and maintaining an open airway for each.
If talking or crying without much effort, patent airway may be assumed.
snoring: headtilt
gurgling: suction
crowning: begin ventilation bag valve mask
snoring: headtilt
gurgling: suction
crowning: begin ventilation bag valve mask
59
New cards
Describe how to assess the rate and quality of breathing, and, based upon findings, identify how to manage the ventilatory insufficiency.
bradypnea: rate too slow
tachypnea: rate too fast
apnea: not breathing
\
\
tachypnea: rate too fast
apnea: not breathing
\
\
60
New cards
List the medications in the EMT’s scope of practice that are carried on the ambulance.
* oxygen
* oral glucose
* activated charcoal
* aspirin
* inhaled bronchodilators
* nitroglycerin
* epinephrine
* oral glucose
* activated charcoal
* aspirin
* inhaled bronchodilators
* nitroglycerin
* epinephrine
61
New cards
List the medications in the EMT’s scope of practice that the EMT is permitted to assist the patient to administer.
MDI
SVN
SVN
62
New cards
Explain the roles of off-line and on-line medical direction with regard to medication administration.
online order: medical direction to administer or assist medication
offline: protocols or standing orders
offline: protocols or standing orders
63
New cards
List in order the key steps of medication administration for each of the medications used by the EMT, based on the medication packaging or form.
select correct medication, verify with patient’s prescription, check expiration date, check for contamination, verify route and dosage, document
Five rights
* patient
* medication
* route
* dose
* date
Five rights
* patient
* medication
* route
* dose
* date
64
New cards
65
New cards
Describe the reassessment of a patient after the EMT has administered or assisted the patient in
measure vitals and asses for changes in condition
document
document
66
New cards
Discuss the physiology of adequate perfusion and the pathophysiology of hypoperfusion (shock), including the consequences of cellular hypoxia and death.
Shock: not enough blood flow (hypoperfusion)
not enough oxygen = cell death = organ failure
not enough oxygen = cell death = organ failure
67
New cards
Describe the features, functions, advantages, disadvantages, uses, and precautions related to automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
older than 8 yrs
CPR first, get AED ready
Advantage: fast, efficient, safe
Not useful for trauma arrest
CPR first, get AED ready
Advantage: fast, efficient, safe
Not useful for trauma arrest
68
New cards
Given a series of cardiac arrest scenarios involving infants, children, and adults, discuss appropriate assessment and resuscitative techniques.
30/2 compression to ventilation
asses for 5-10 sec for pulse
lower charge for infants and less than 8 yrs of age
go deeper in children, 2 in for adults, 1 1/2 for baby
asses for 5-10 sec for pulse
lower charge for infants and less than 8 yrs of age
go deeper in children, 2 in for adults, 1 1/2 for baby
69
New cards
Identify assessment and management techniques of a post-cardiac-arrest patient with return of spontaneous circulation.
If tidal volume or respiratory rate is inadequate, continue CPR
do not hyperventilate; adult 10-12 child 12-20
do not hyperventilate; adult 10-12 child 12-20
70
New cards
Define and differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure, and respiratory arrest.
distress: normal rates, difficulty breahting (provide supplmental oxygen)
failure: more extreme distress, not enough oxygen for cells (positive pressure ventilation)
arrest: no tidal volume and breahting (ppv)
failure: more extreme distress, not enough oxygen for cells (positive pressure ventilation)
arrest: no tidal volume and breahting (ppv)
71
New cards
Discuss the pathophysiology, symptomatology, and management goals of a patient suffering from an obstructive pulmonary disease.
airflow limitation and difficulty in exhaling air from the lungs
Symp: wheezing, tripod posture, tachypnea
treatment: Bronchodilation
Symp: wheezing, tripod posture, tachypnea
treatment: Bronchodilation
72
New cards
Discuss the pathophysiology, symptomatology, and management goals of a patient suffering from cardiogenic and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema.
accumulation of fluid in the lungs
cariogenic: heart related
crackles, wheezing, cold clay skin
cariogenic: heart related
crackles, wheezing, cold clay skin
73
New cards
Discuss the pathophysiology, symptomatology, and management goals of a patient suffering from epiglottitis, pertussis, cystic fibrosis, poisonous inhalations, and viral respiratory infections.
epiglottitis: top of neck, can block airway
pertussis: whooping cough
cystic fibrosis: hereditary
pertussis: whooping cough
cystic fibrosis: hereditary
74
New cards
Describe special considerations in the assessment and management of pediatric and geriatric patients with respiratory emergencies.
pediatric: have healthy heart, mostly respiratory issues. Nasal flaring (early sign)
gediatric: place sitting up position, if distress, administer oxygen via nasal cannula
gediatric: place sitting up position, if distress, administer oxygen via nasal cannula
75
New cards
Discuss proper assessment and clinical decision making skills regarding treatment plans for patients when using an assessment-based approach to respiratory distress
tripod: indicate respiratory distress
cyanosis (blue): indicate hypoxia
moist skin: indicate distress
nasal flaring
\
cyanosis (blue): indicate hypoxia
moist skin: indicate distress
nasal flaring
\
76
New cards
Describe the relationships among chest pain or discomfort, heart disease, and cardiac arrest.
chest pain: symptom indicating heart problem
heart disease: heart can’t pump enough blood, narrowed arteris
cardiac arrest: heart not pumping blood at all
heart disease: heart can’t pump enough blood, narrowed arteris
cardiac arrest: heart not pumping blood at all
77
New cards
Explain the pathophysiology, symptomatology, and prehospital management for myocardial ischemia.
heart muscle not receiving adequate oxygenated blood
Symp: crushing chest pressure “dull aching”
treat: oxygen, aspirin, nitroglycerin
Symp: crushing chest pressure “dull aching”
treat: oxygen, aspirin, nitroglycerin
78
New cards
Discuss the current understanding and guidelines for oxygen administration in a patient with an acute coronary syndrome.
Administer supplemental oxygen if the patient is dyspneic, hypoxemic, has obvious signs of heart failure, has an of or the is unknown
79
New cards
Explain the pathophysiology, symptomatology, and prehospital management for cardiogenic shock and hypertensive emergencies.
when one side of ventricle fails to pump out enough blood.
right: low BP Left: high BP
high heart beat
right: low BP Left: high BP
high heart beat
80
New cards
Explain the indications, contraindications, forms, dosage, administration, actions, side effects, and assessment for nitroglycerin.
relieve chest pain
contraindication: hypotensive, allergic
side effect: headache, increased heart rate
dosage: tablet, usually .3mg
\
contraindication: hypotensive, allergic
side effect: headache, increased heart rate
dosage: tablet, usually .3mg
\
81
New cards
Describe the relationship between stroke and transient ischemic attack.
transient ischemic attack resolve on its own; similar symptoms
82
New cards
Describe the way to use the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale, the Los Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen, the Miami Emergency Neurologic Deficit scale, and the Rapid Arterial Occlusion Evaluation (RACE) scale.
determine if it is a stroke
\
\
83
New cards
Identify the assessment-based approach to the assessment and management of a stroke or transient ischemic attack.
if no spinal injury, place lateral recumbent position
\
\
84
New cards
Differentiate the types of generalized seizures: tonic clonic, absence, myoclonic, tonic, atonic, simple, partial seizure with secondary generalization, and febrile seizures.
tonic clonic: loss of consciousness, muscle rigidity
absense: brief loss of consciousness, common in children
myoclonic: jerking of muscle on both sides, children, sleep
atonic: patient drop to ground, loss of muscle strength
partial seizure: one brain hemisphere
\
absense: brief loss of consciousness, common in children
myoclonic: jerking of muscle on both sides, children, sleep
atonic: patient drop to ground, loss of muscle strength
partial seizure: one brain hemisphere
\
85
New cards
Delineate between the care goals for seizure patients who are unresponsive, actively seizing, or in status epilepticus.
if snoring: nasopharyngeal airway
epilepticus: insert oropharyngeal airway to prevent tongue bite
\
epilepticus: insert oropharyngeal airway to prevent tongue bite
\
86
New cards
Discuss the role of insulin and glucagon in glucose regulation and the effects of epinephrine on glucose levels.
Insulin: decreases glucose level
glucagon: increases glucose level
epinephrine: releases stored glucose in liver and stop insulin
glucagon: increases glucose level
epinephrine: releases stored glucose in liver and stop insulin
87
New cards
Discuss the pathophysiology and symptomatology of a hypoglycemic emergency.
hypoglycemia: low glucose level (less than 70mg/dl)
sign: altered mental status,
patio: brain lacks glucose to burn
\
sign: altered mental status,
patio: brain lacks glucose to burn
\
88
New cards
Describe the clinical findings that would be consistent with a mild, moderate, and severe allergic reaction.
mild: runny nose, watery eyes. hives
severe: anaphylactic reaction,
severe: anaphylactic reaction,
89
New cards
Explain the assessment-based approach to assessment and management of an anaphylactic reaction and a biphasic anaphylactic reaction.
administer epinephrine
biphasic: second allergic reaction within 6hrs of first
biphasic: second allergic reaction within 6hrs of first
90
New cards
Describe the pathophysiology, assessment findings, and management principles for a patient who has ingested a poison.
look for container
may administer activated charoal
reassess 5 min
may administer activated charoal
reassess 5 min
91
New cards
Discuss the indications, contraindications, action, side effects, dosage, and administration of activated charcoal
* only through medical direction
* SuperChar
* InstaChar
* Actidose
* Liqui-Char
* contradiction: altered mentalstatus
* dosage 1 gram per 1kg body weight
* side effect: vomit
* SuperChar
* InstaChar
* Actidose
* Liqui-Char
* contradiction: altered mentalstatus
* dosage 1 gram per 1kg body weight
* side effect: vomit
92
New cards
Describe the pathophysiology, assessment findings, and management principles for a patient who has inhaled a poison.
safety first
ABC
was it suicidal attempt? closed or open space? how long exposed
ABC
was it suicidal attempt? closed or open space? how long exposed
93
New cards
Explain the assessment-based approach to acute abdomen, including the incorporation of assessment findings into a field impression and the appropriate prehospital emergency care.
determine trauma or medical or ingestion of medicine
if responsive, collect history OPQRST
if unresponsive, collect physicals, vitals, then history
palpale abd away
pale cool skin, tachycardia, narrow pulse pressure = shock
\
if responsive, collect history OPQRST
if unresponsive, collect physicals, vitals, then history
palpale abd away
pale cool skin, tachycardia, narrow pulse pressure = shock
\
94
New cards
Explain the assessment-based approach to genitourinary/renal emergencies, including the incorporation of assessment findings into a field impression and the appropriate prehospital emergency care.
respect privacy
watch out for shock
watch out for shock
95
New cards
explain the assessment-based approach to cold-related emergencies, including the incorporation of assessment findings into a field impression and the appropriate prehospital emergency care
hypothermia: body mucho cold
warmed humidified supplement oxygen
conduct secondary in warmed ambulance
warmed humidified supplement oxygen
conduct secondary in warmed ambulance
96
New cards
For common terrestrial bites and stings seen by EMS providers, discuss the corresponding pathophysiology, symptomatology, and management principles.
black widow spider: pinprick sensation at bite site. become dull ache within 30min. Severe muscle spasm in shoulder back.
brown recluse spider: bites painlesss at first
scorpion: sharp pain at injection site, drooling, poor coordination, seizure
Fireant: painful vesicles filled w fluid, swelling
toll: can carry fever, stick to head, remove tick rehospital
lower site of injection below heart, apply cold pack, constrict
brown recluse spider: bites painlesss at first
scorpion: sharp pain at injection site, drooling, poor coordination, seizure
Fireant: painful vesicles filled w fluid, swelling
toll: can carry fever, stick to head, remove tick rehospital
lower site of injection below heart, apply cold pack, constrict
97
New cards
List factors that affect the likelihood of survival from submersion incidents.
infants: bathtub
quick rescue, temp of water
quick rescue, temp of water
98
New cards
List actions you should take to protect your own safety when responding to a water emergency.
only jump in water if ur trained and have a partner
\
\
99
New cards
List and discuss psychiatric emergencies encountered prehospitally that commonly result in ==behavioral== changes
phobia: fear of specific event or object
agitated delirium: tolerance of pain, unusually speech, drug
paranoia: mistrust
psychosis: out of touch with reality
\
agitated delirium: tolerance of pain, unusually speech, drug
paranoia: mistrust
psychosis: out of touch with reality
\
100
New cards
Discuss how an assessment-based approach can be used to assess, determine a field impression from assessment findings, and properly manage a psychiatric-emergency patient.
Don’t enter unless you see patient
\
\