BOT 121 Final Exam Cal Poly Sean Ryan (Study Questions) (Lecture 9-17)
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Angiosperms
Most popular plant, flowering plant, seeds develop inside fruit
Flower labeling
Know all parts of a flower
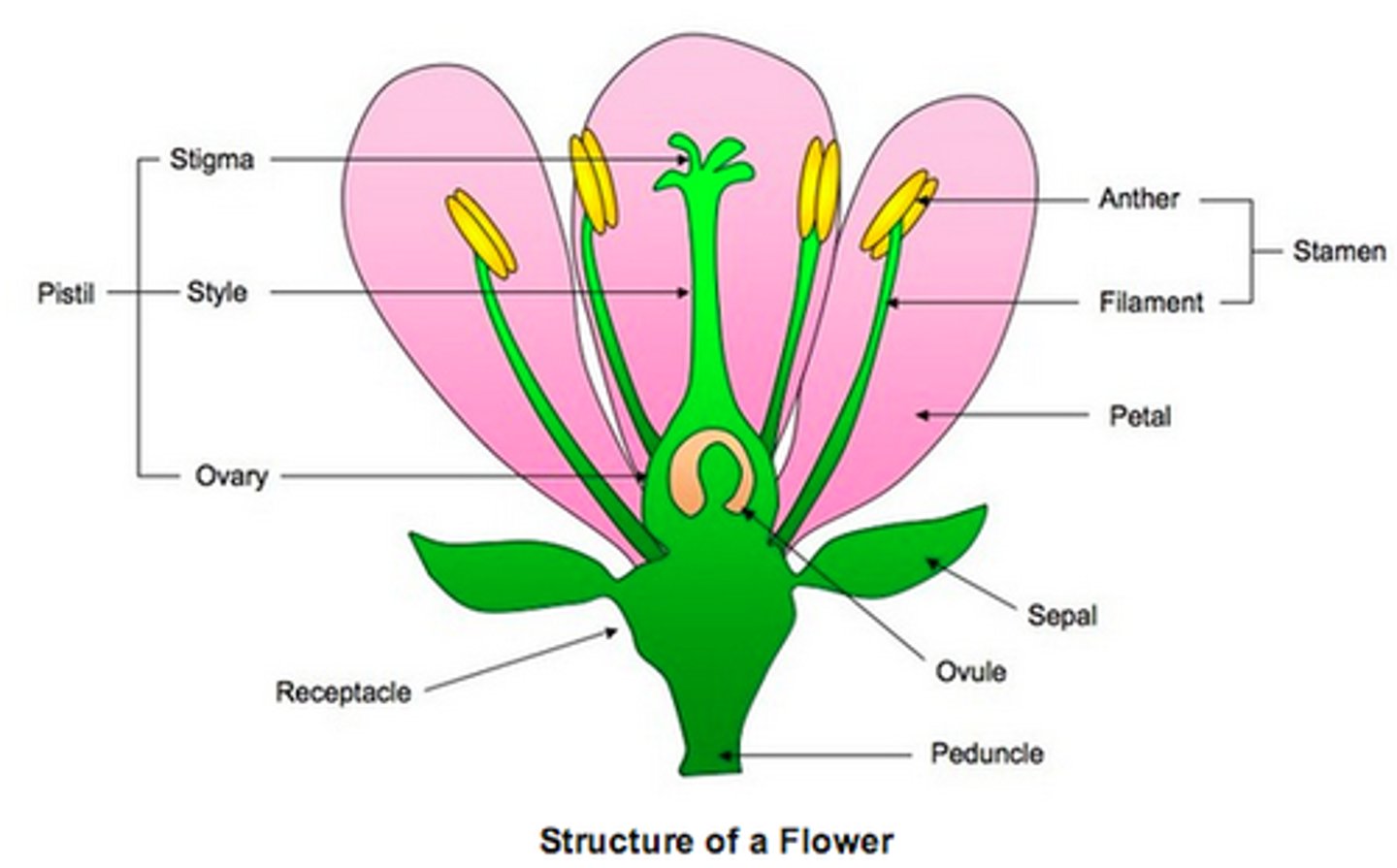
Pedicel
stalk that supports the flower
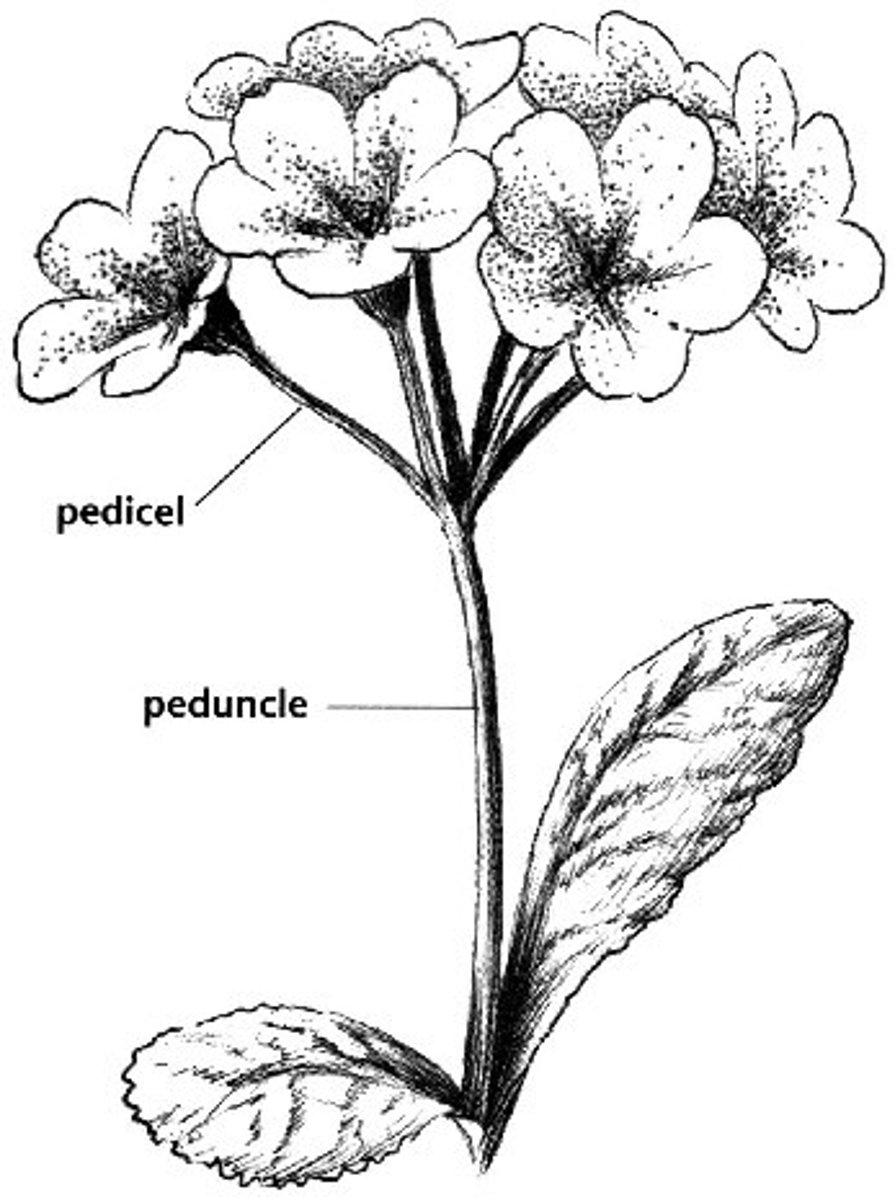
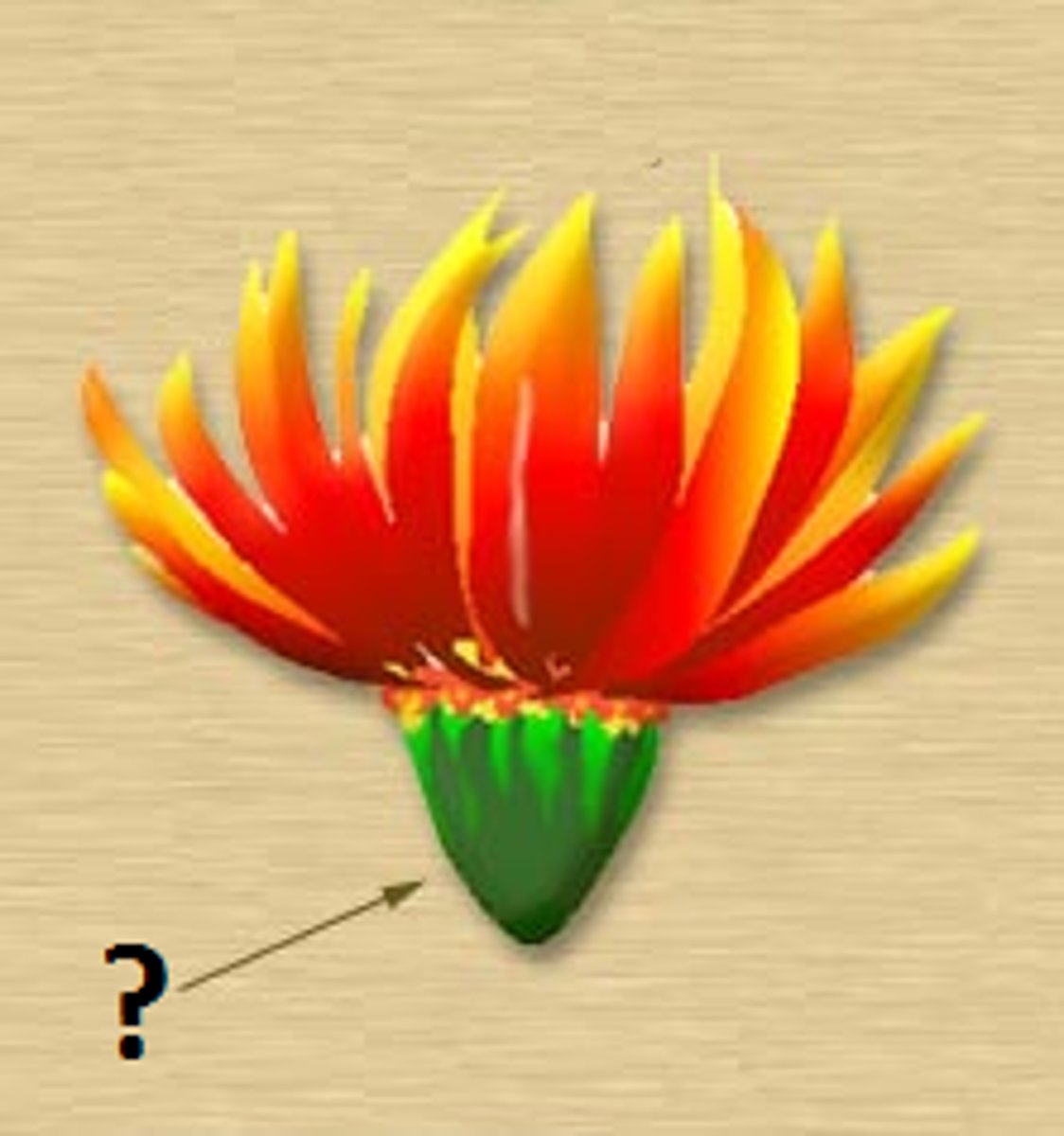
Receptacle
The base of a flower; the part of the stem that is the site of attachment of the floral organs.

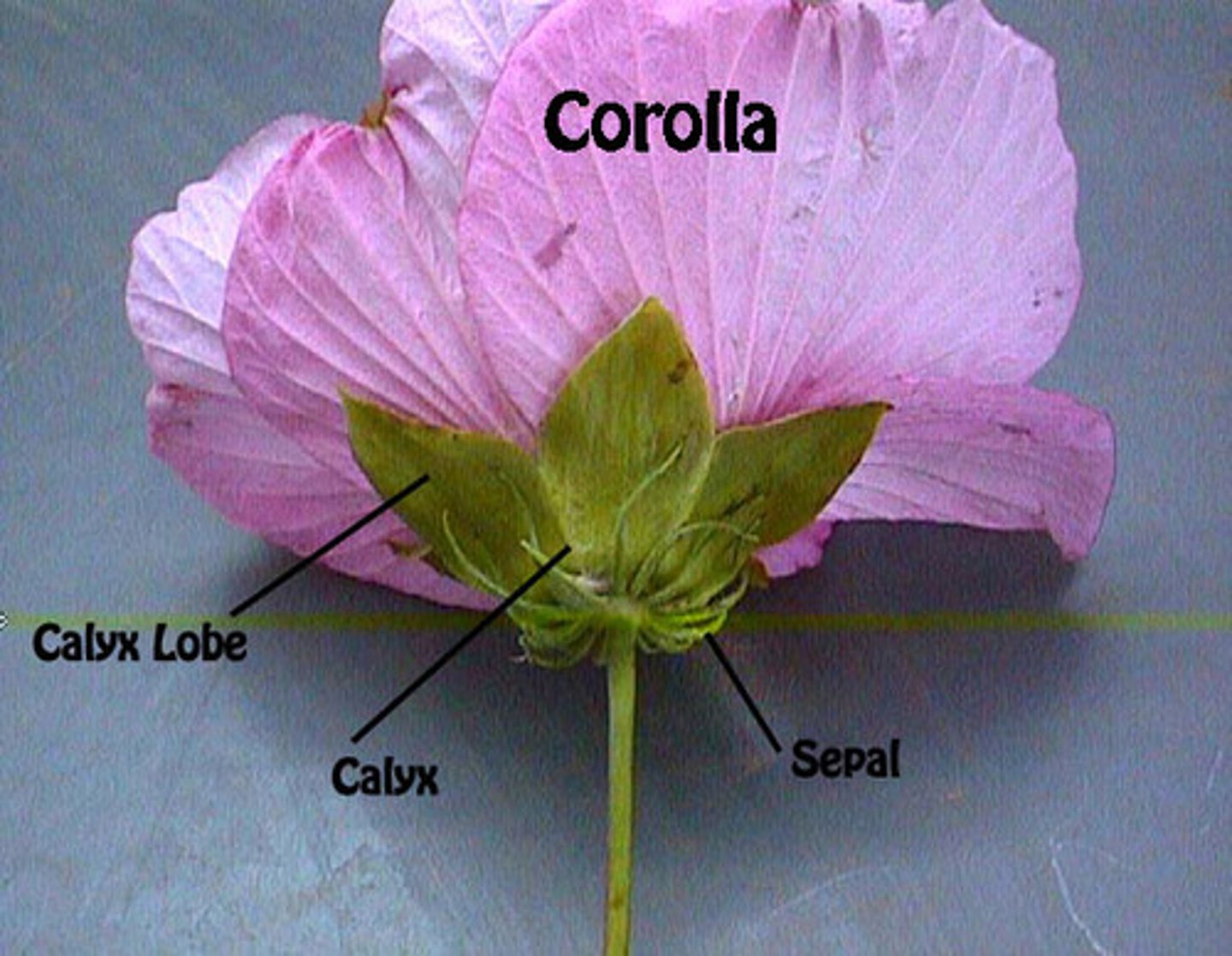
The Calyx is made of many _____
Sepals. (these protect flower in bud, and are often green.
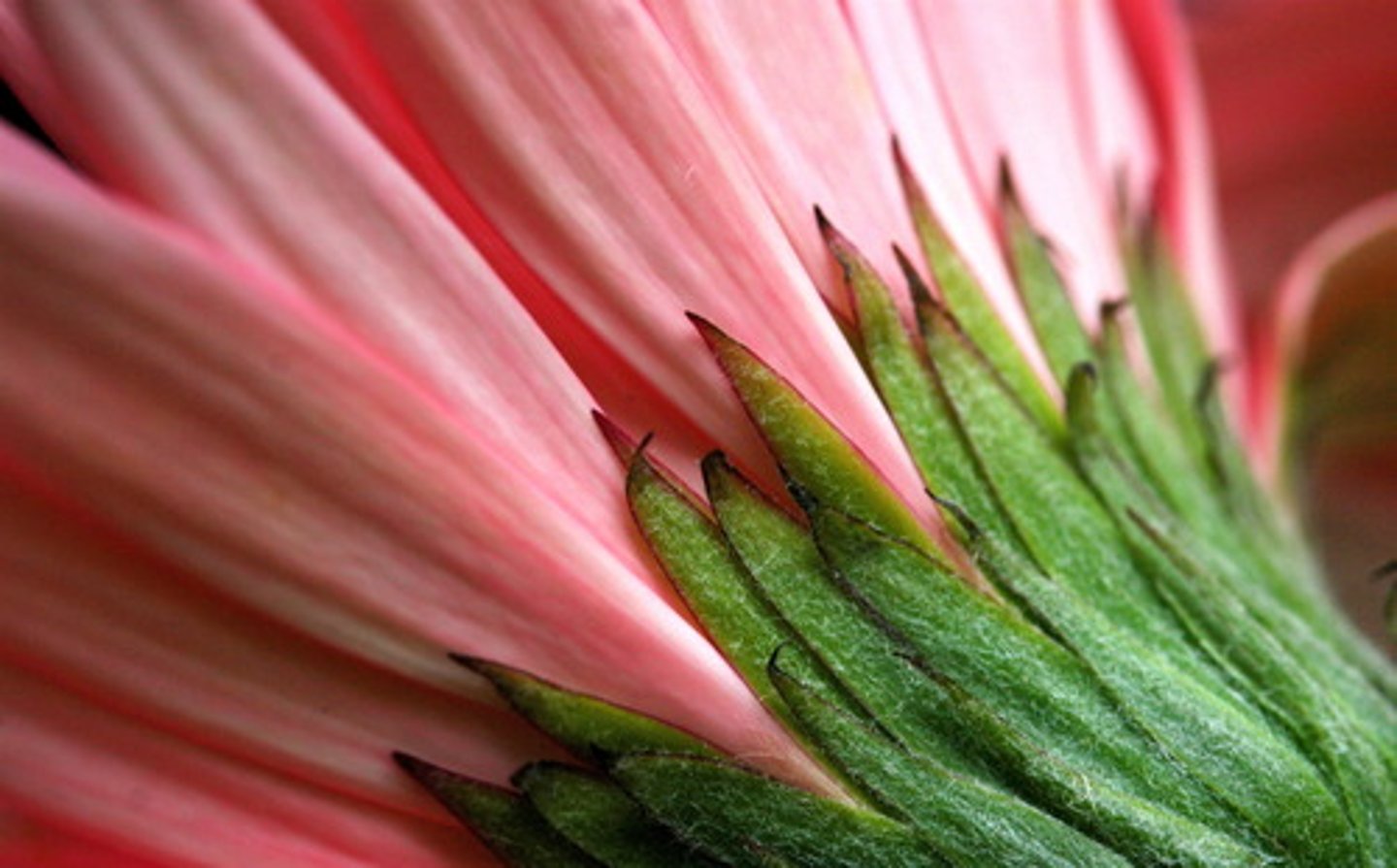

Calyx
all of the sepals of a flower
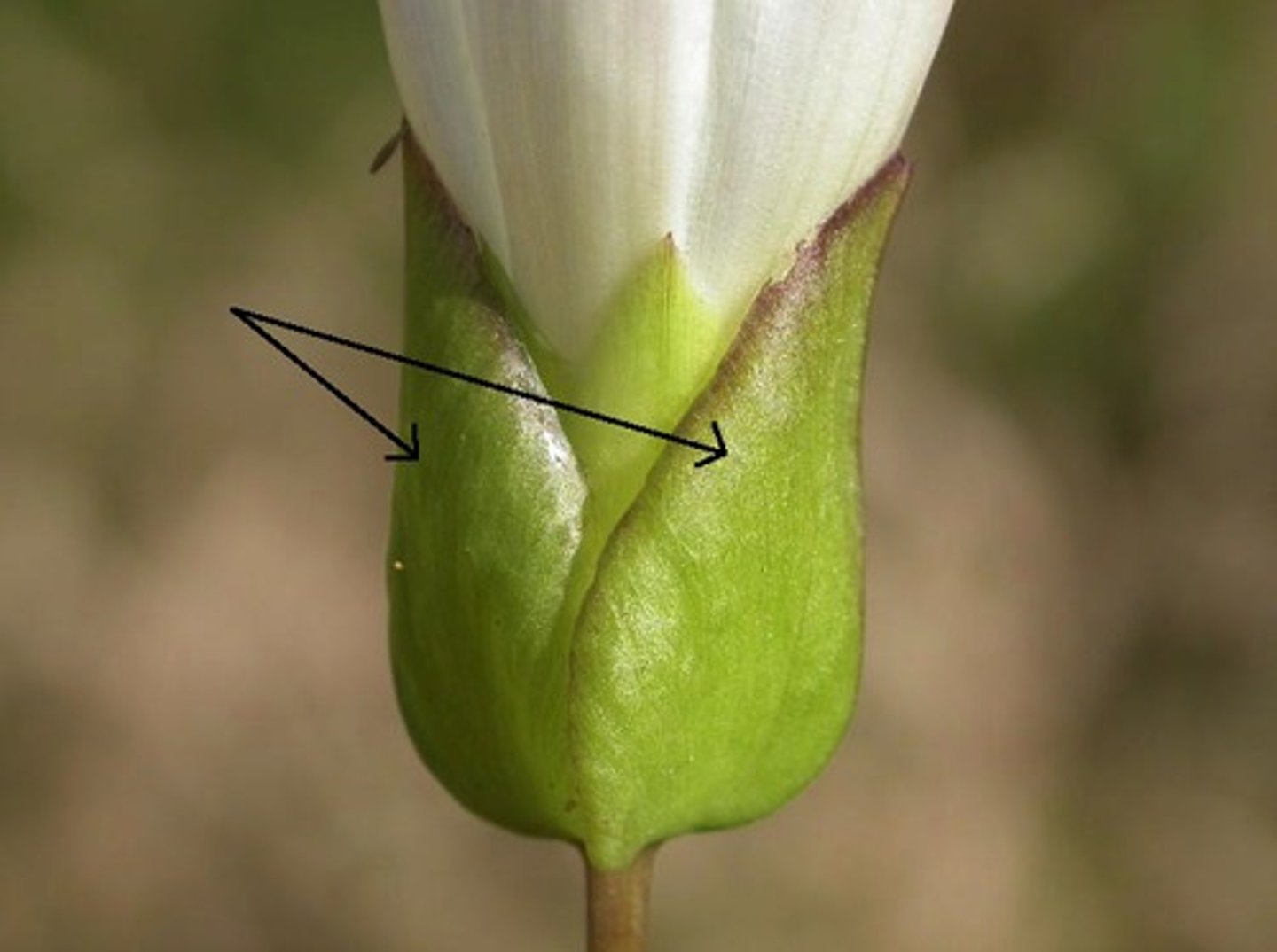
Sepal
A leaflike structure that encloses the bud of a flower.

the corolla is made of _____
Petals (often brightly colored and visually attractive)
Stamens
Male reproductive parts, produce pollen. (Include anther at top and filament as the stem thing)
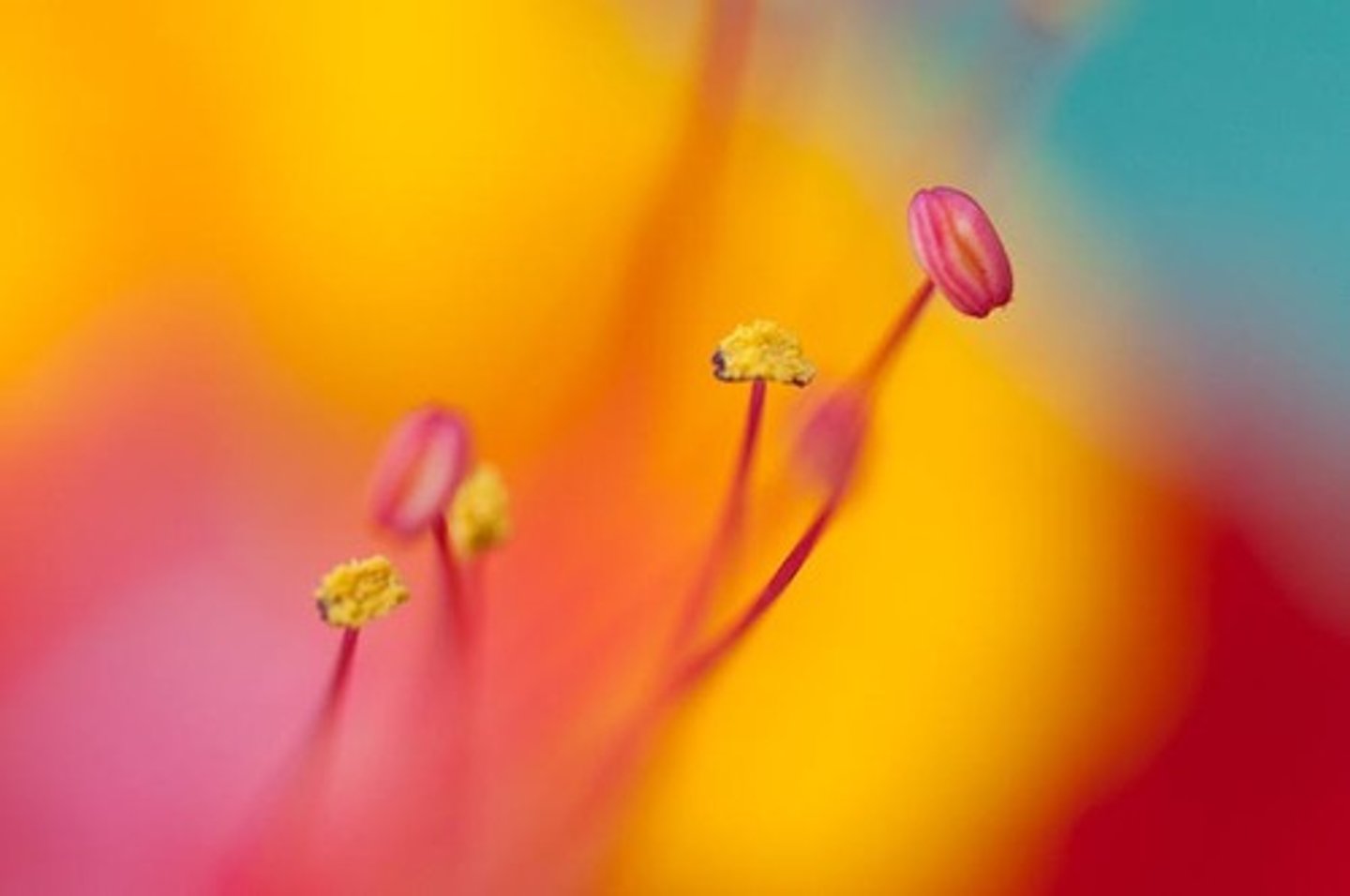

Carpels
The female reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary.

A ____ is made of fused Carpels
Pistil
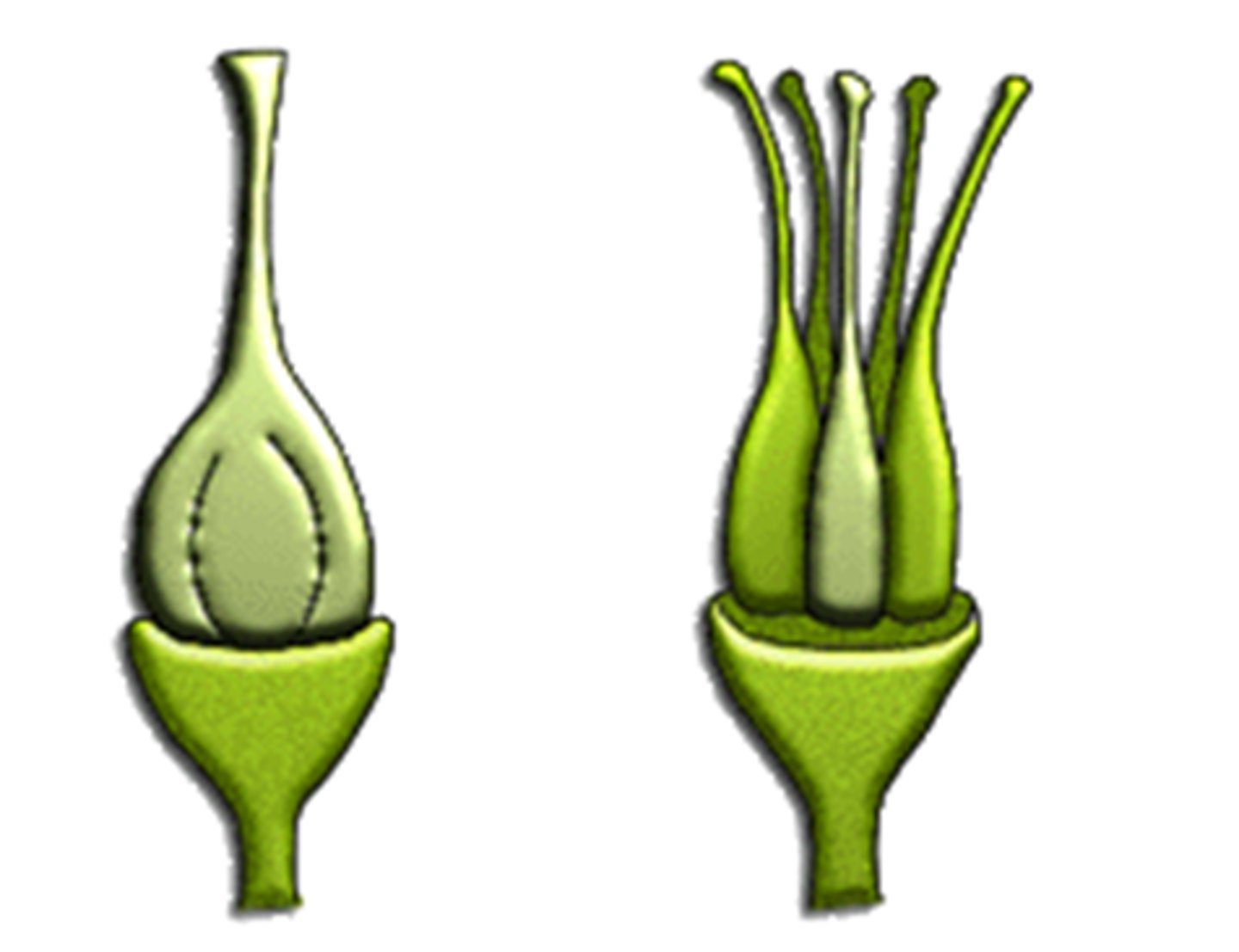
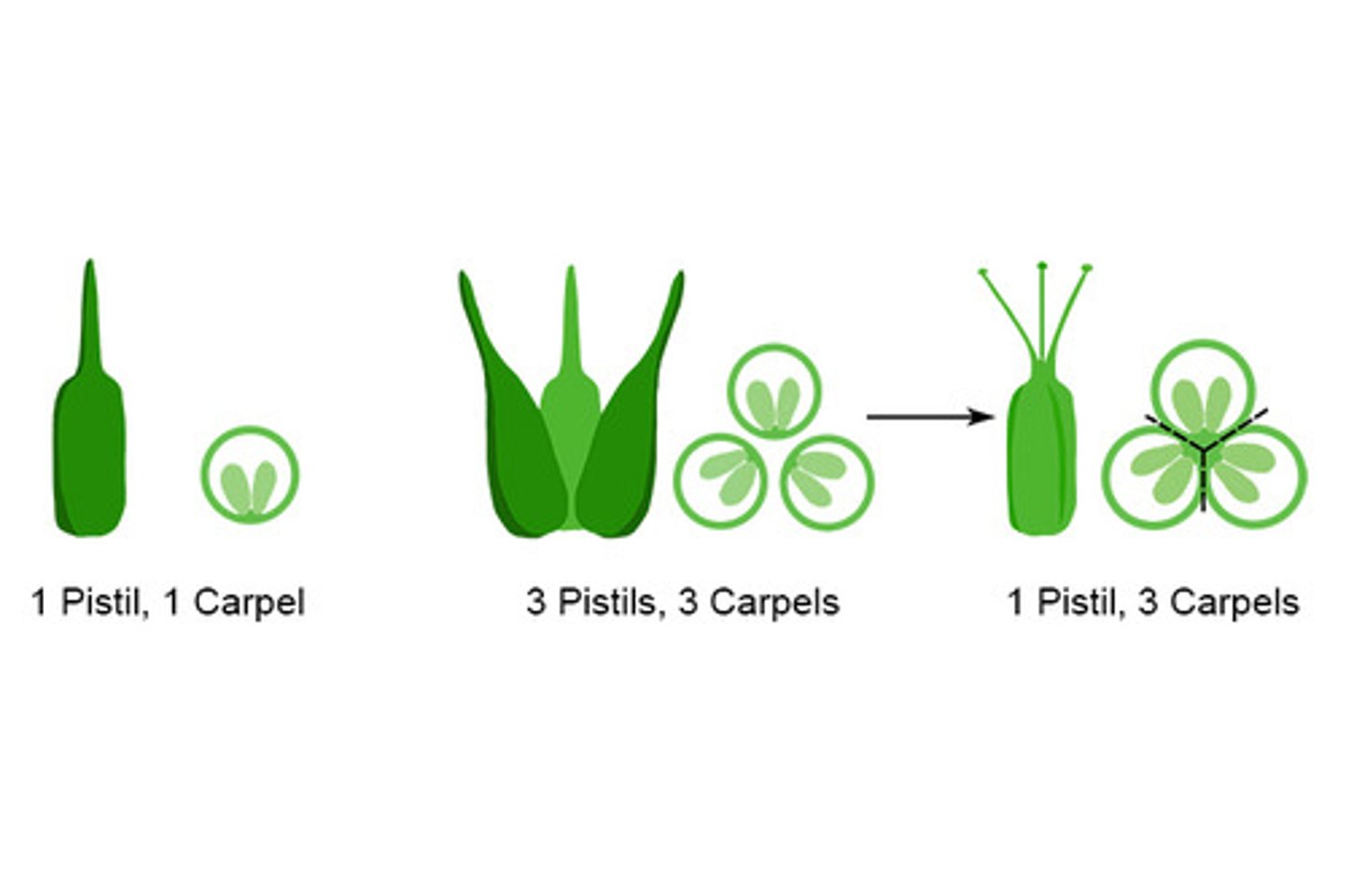
Pistils vs Carpels
Look at picture. Know 1 pistil is like the whole thing and has multiple carpels most of the time. Orange has lots of carpels.
Ovary
Swollen part of a pistil (carpel)
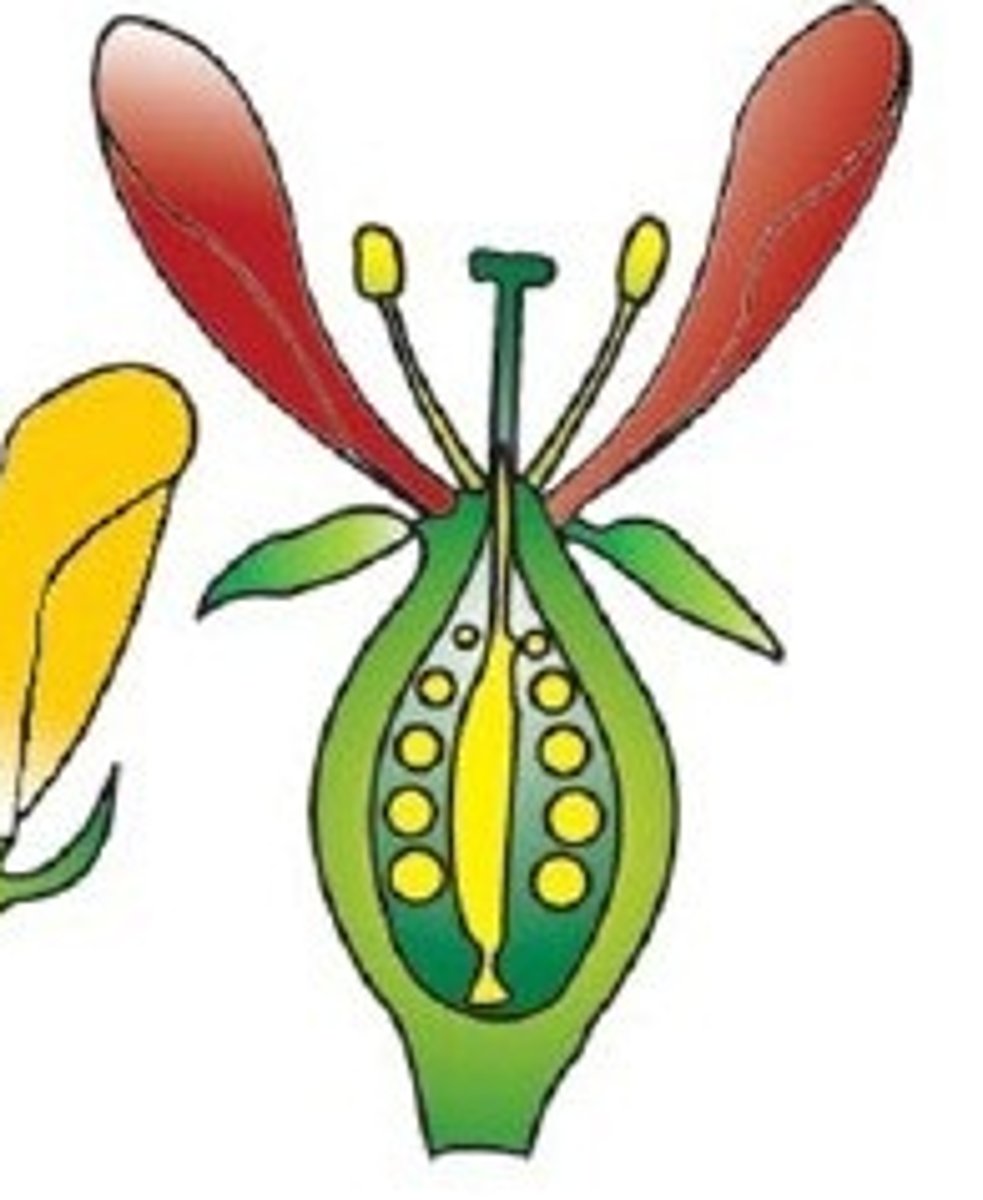
Ovules
Unfertilized seeds

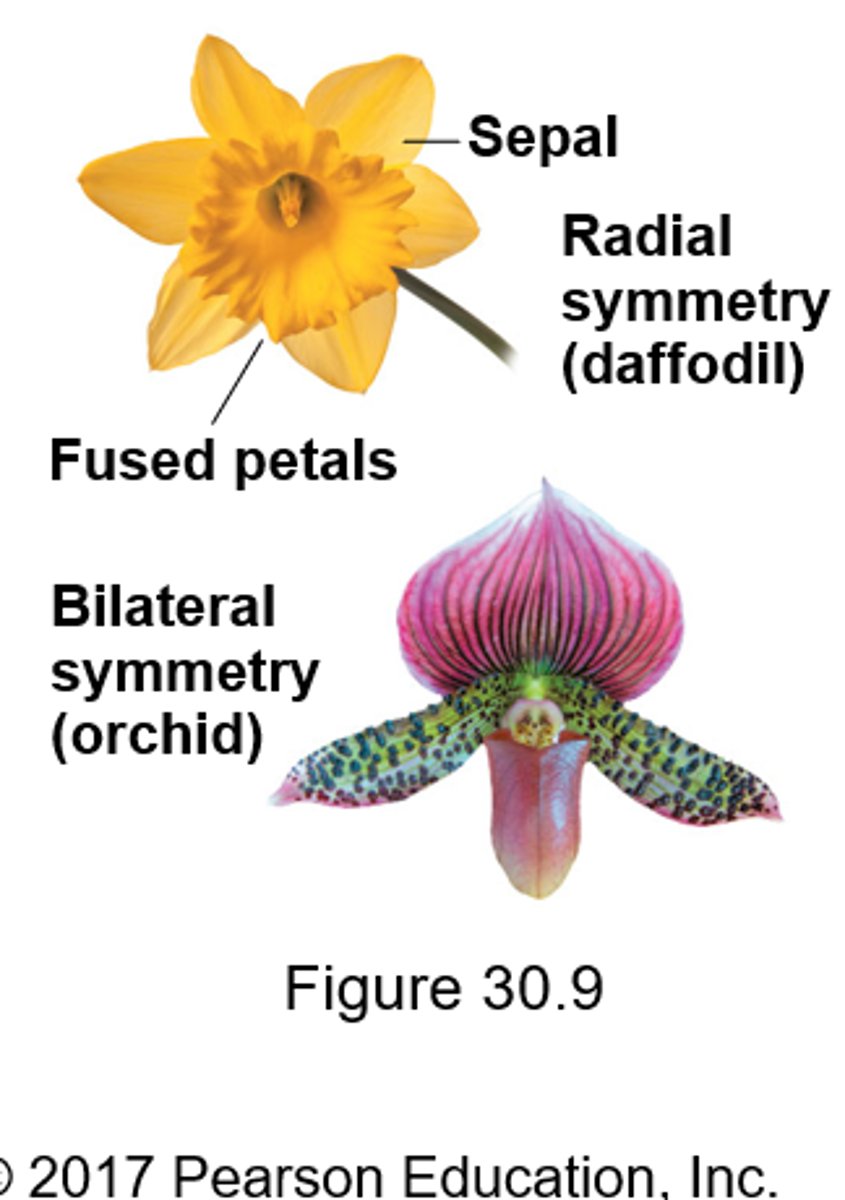
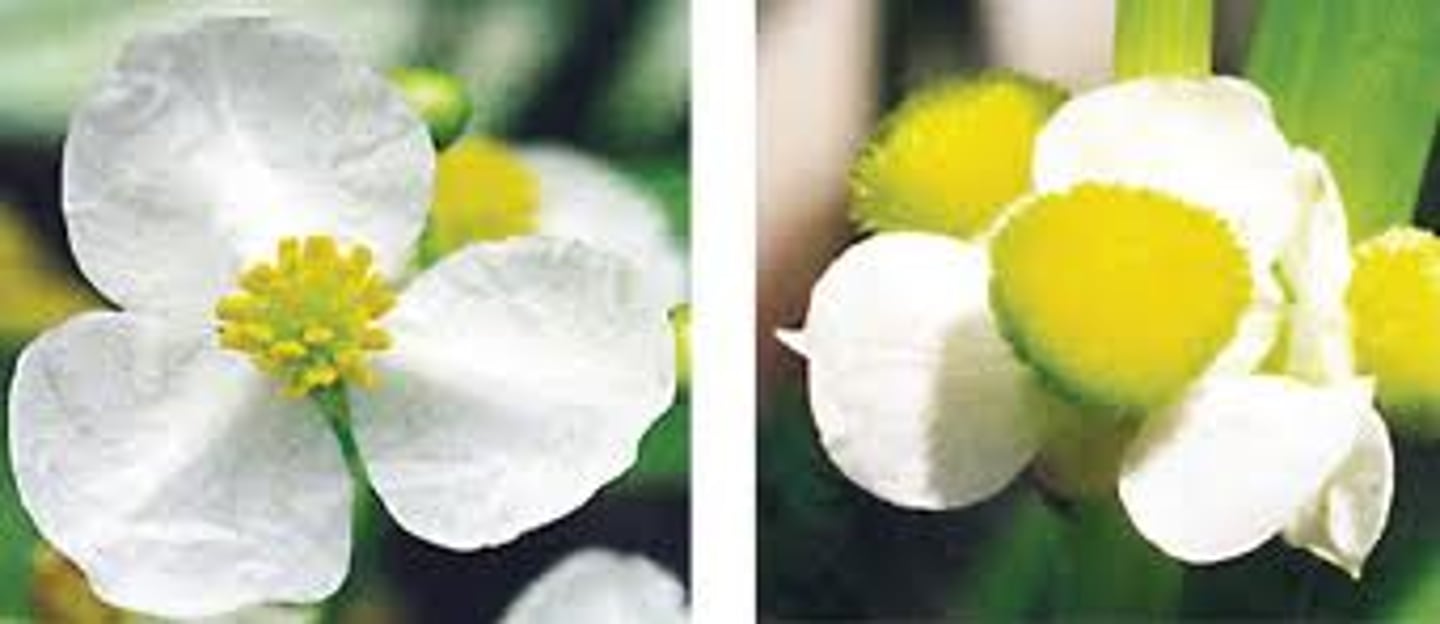
Radial vs Bilateral Symmetry in flowers
Radial - can be split up any way in half
Bilateral - only can be split up one particular way
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from male reproductive structures (like anther) to female reproductive structures in plants (like stigma). Transfer of pollen to the stigma. Pollin adheres to the stigma and grows a pollen tube down the style until it reaches ovule.
Pistillate Flowers
only have pistils, no male parts. ONLY GIRL
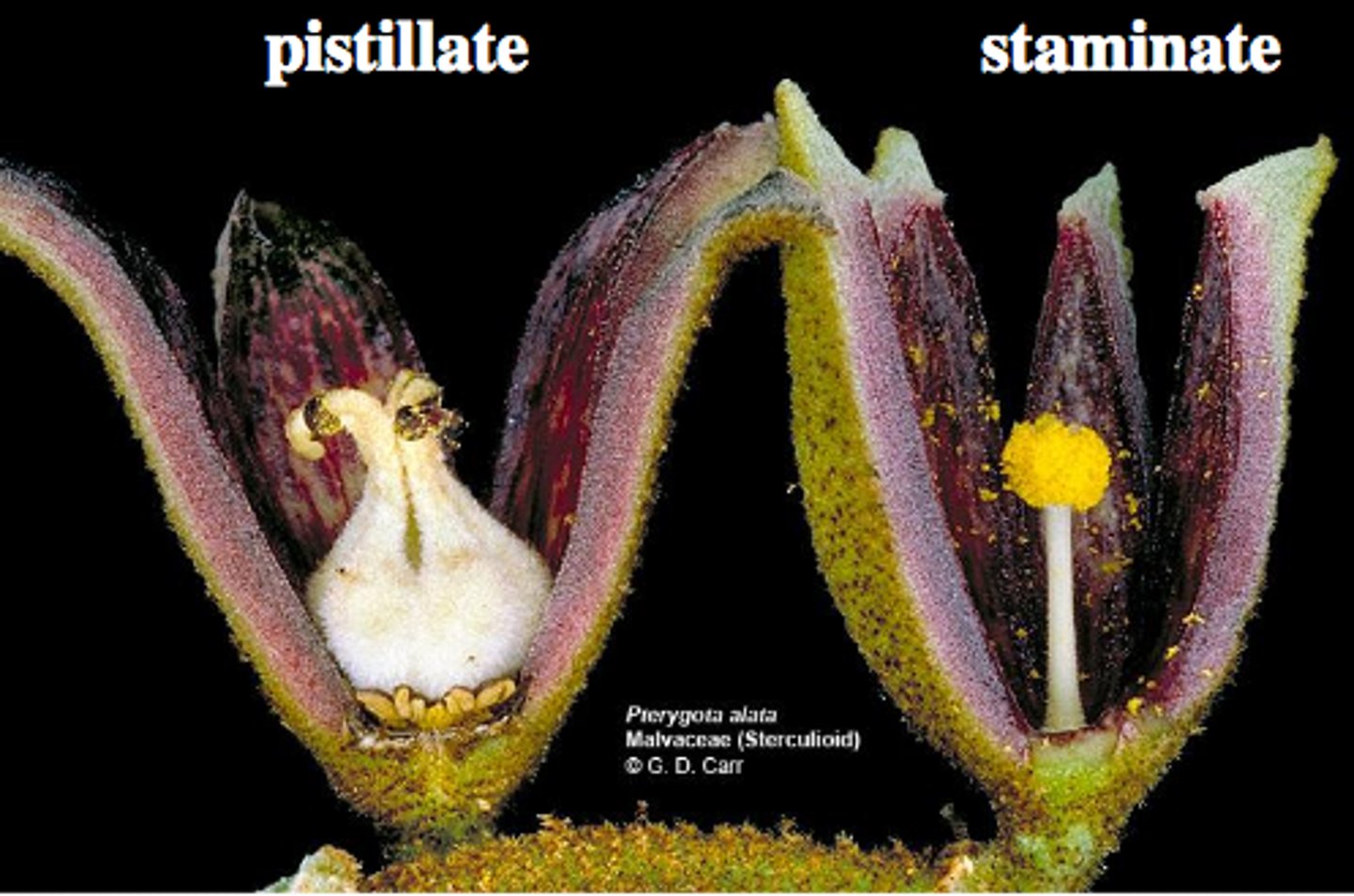
Staminate Flowers
only have stames, no female parts. ONLY BOY

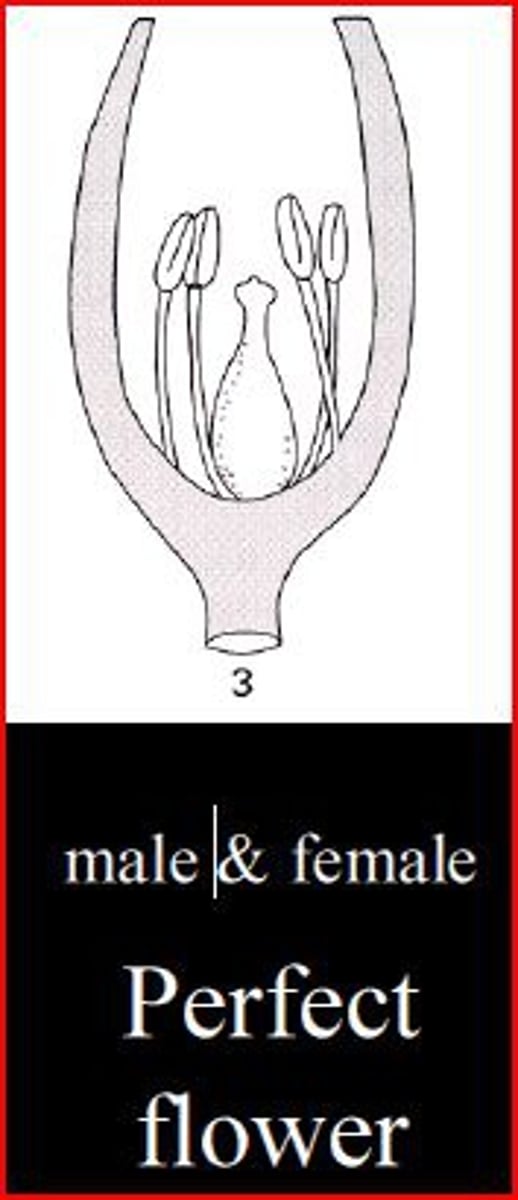
Synoecious
flowers have both stamens and pistils
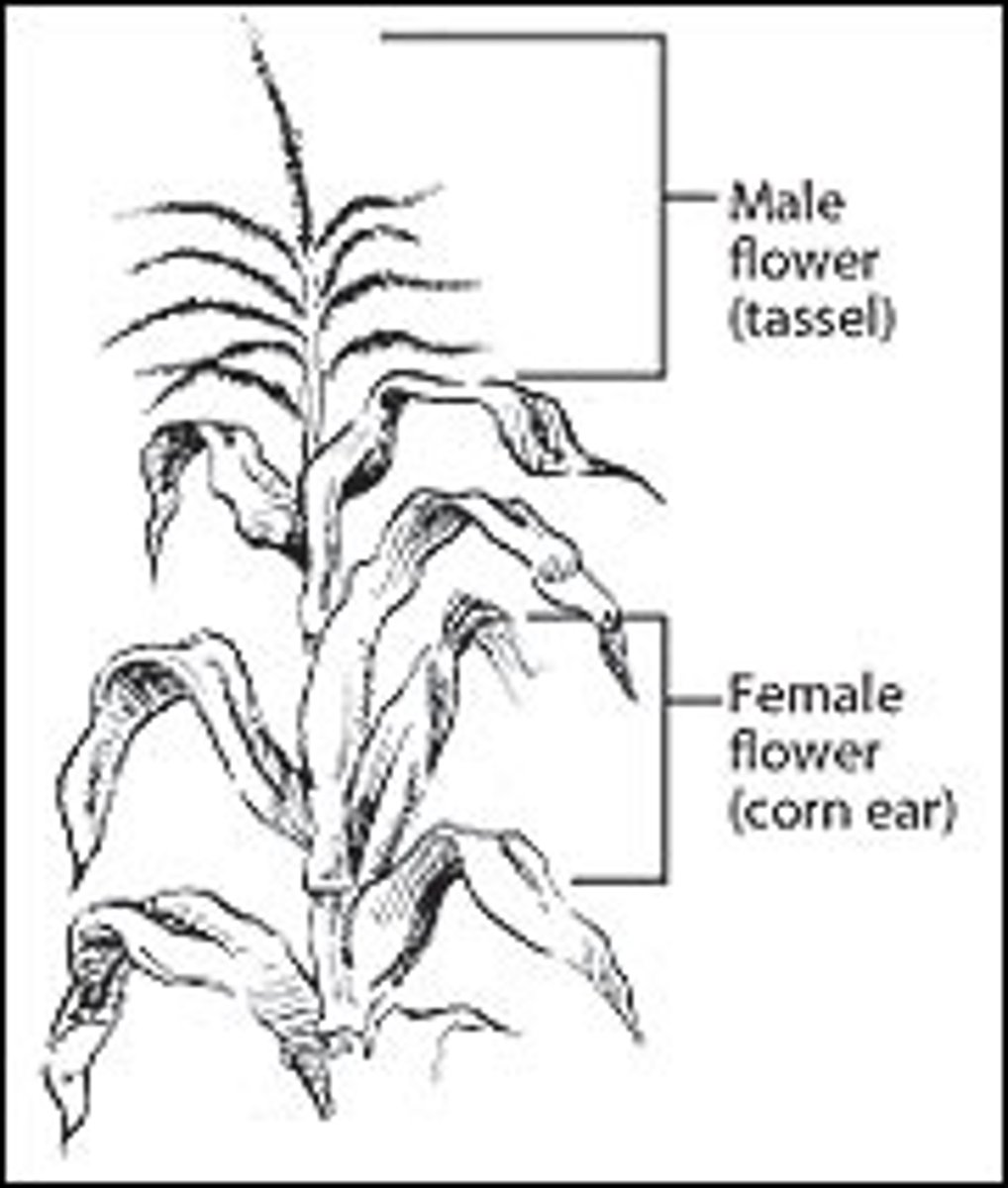
Monoecious
Separate sexed flowers on one individual
Dioecious
Individual plants are one sex or the other. EITHER MALE OR FEMALE

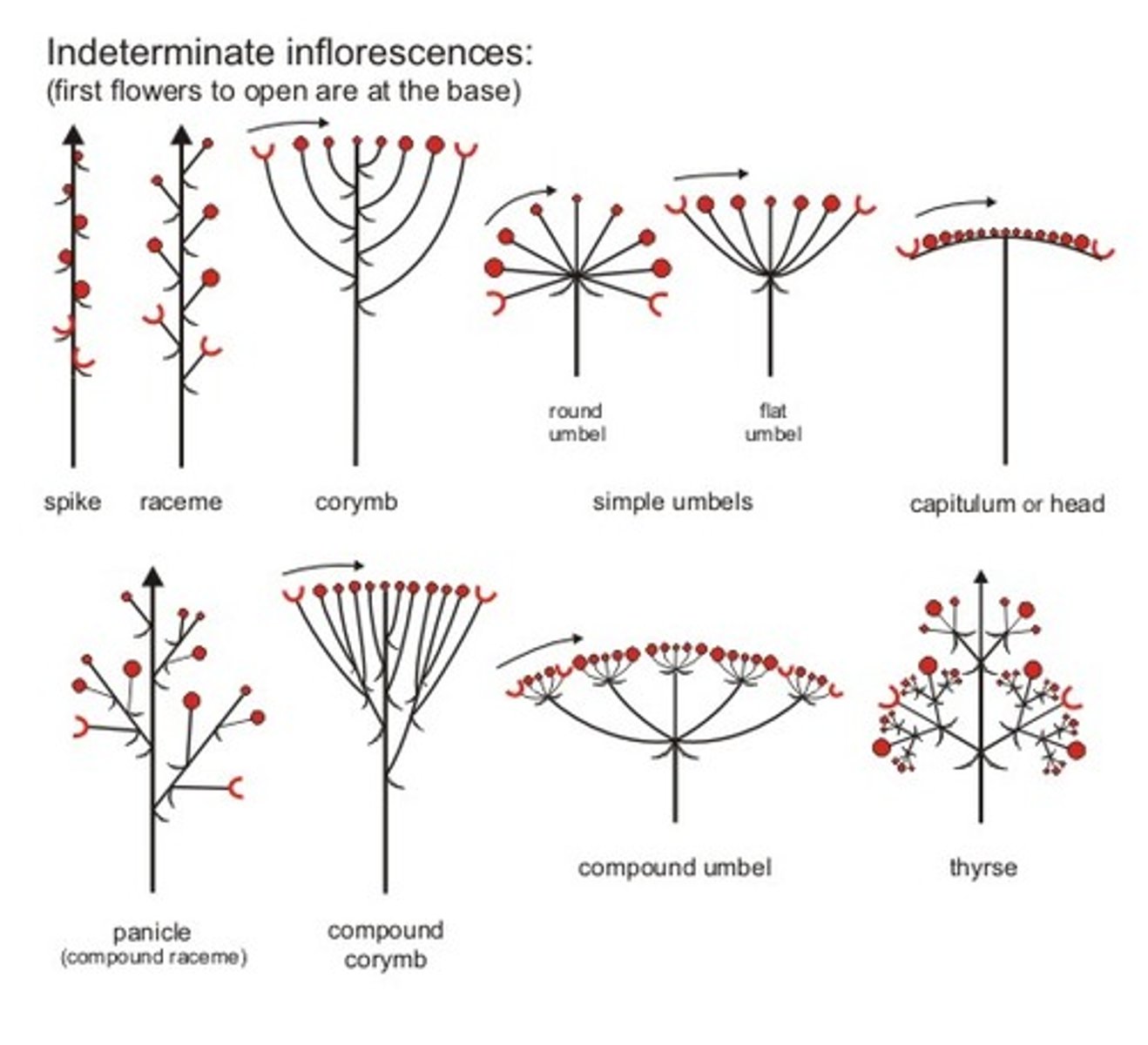
Inflorescence
cluster of flowers in a specific arrangement
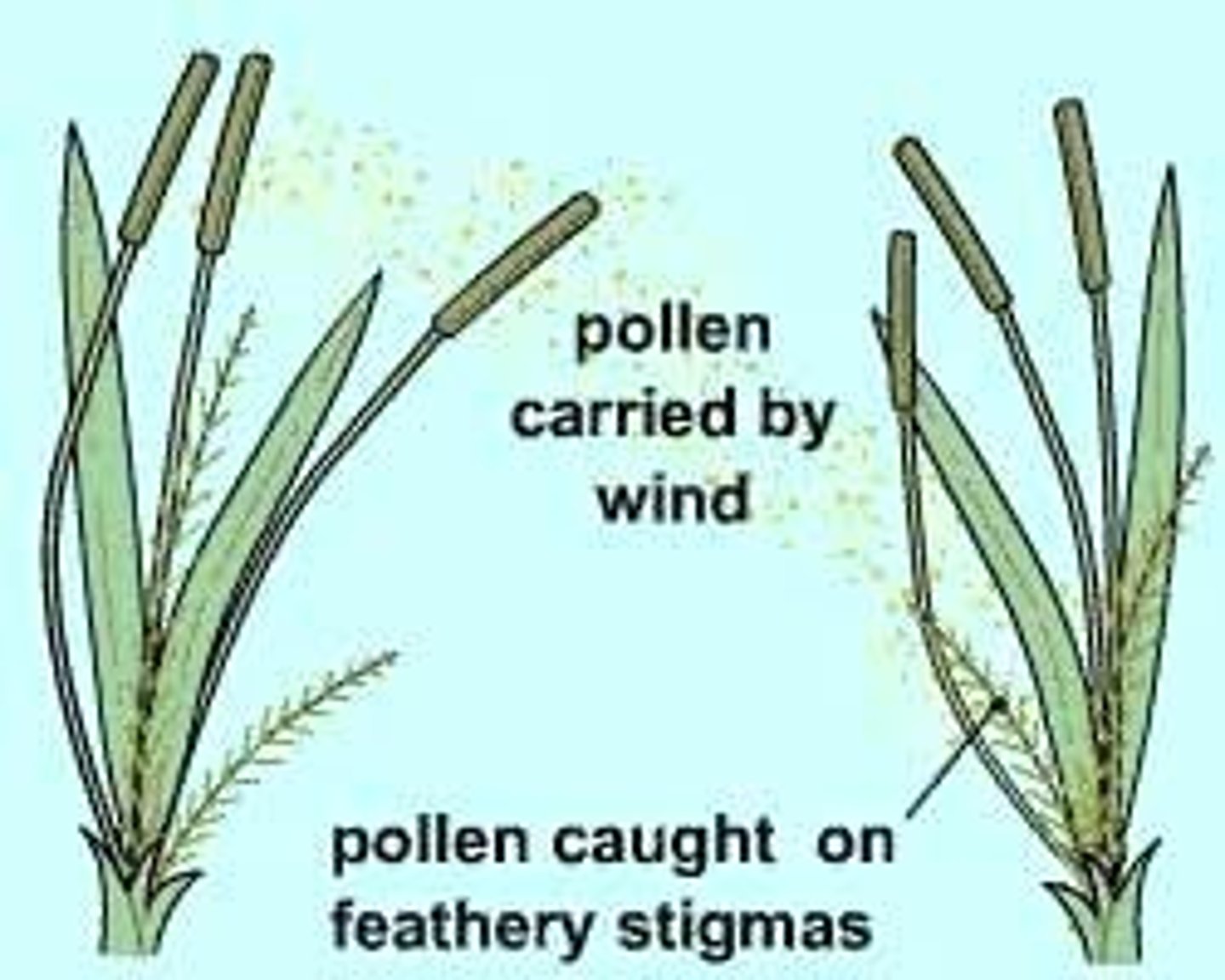
Wind pollination
Flowers produce lots of pollen. These flowers are held out in the open. No nectar. No petals. Very long, not colorful.
Bee pollination
Yellow, blue, purple, white. UV patterns on corolla (on petals) the Nexctar guides the bees. Flat, open, or bilaterally symmetric. "feeding anthers"
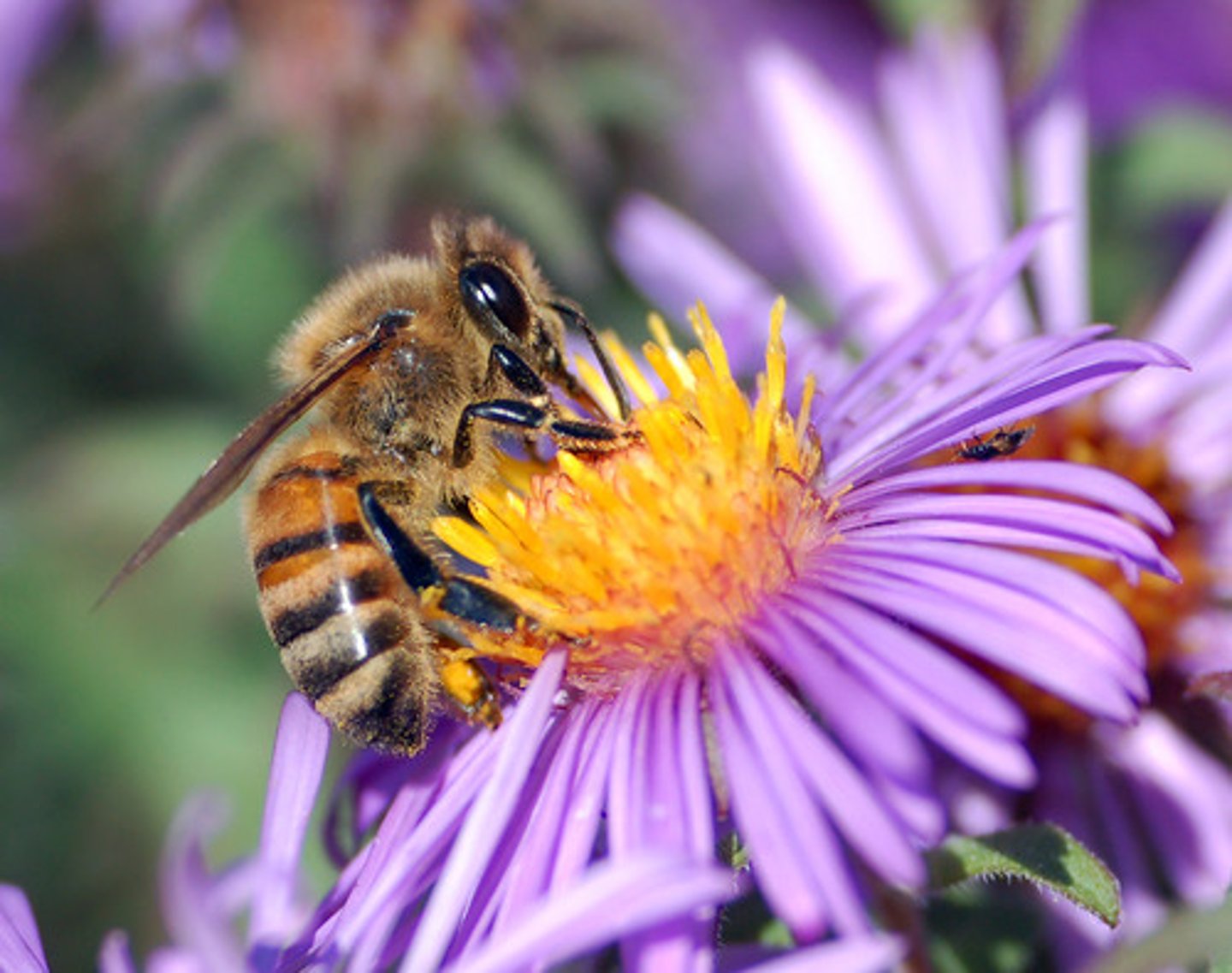

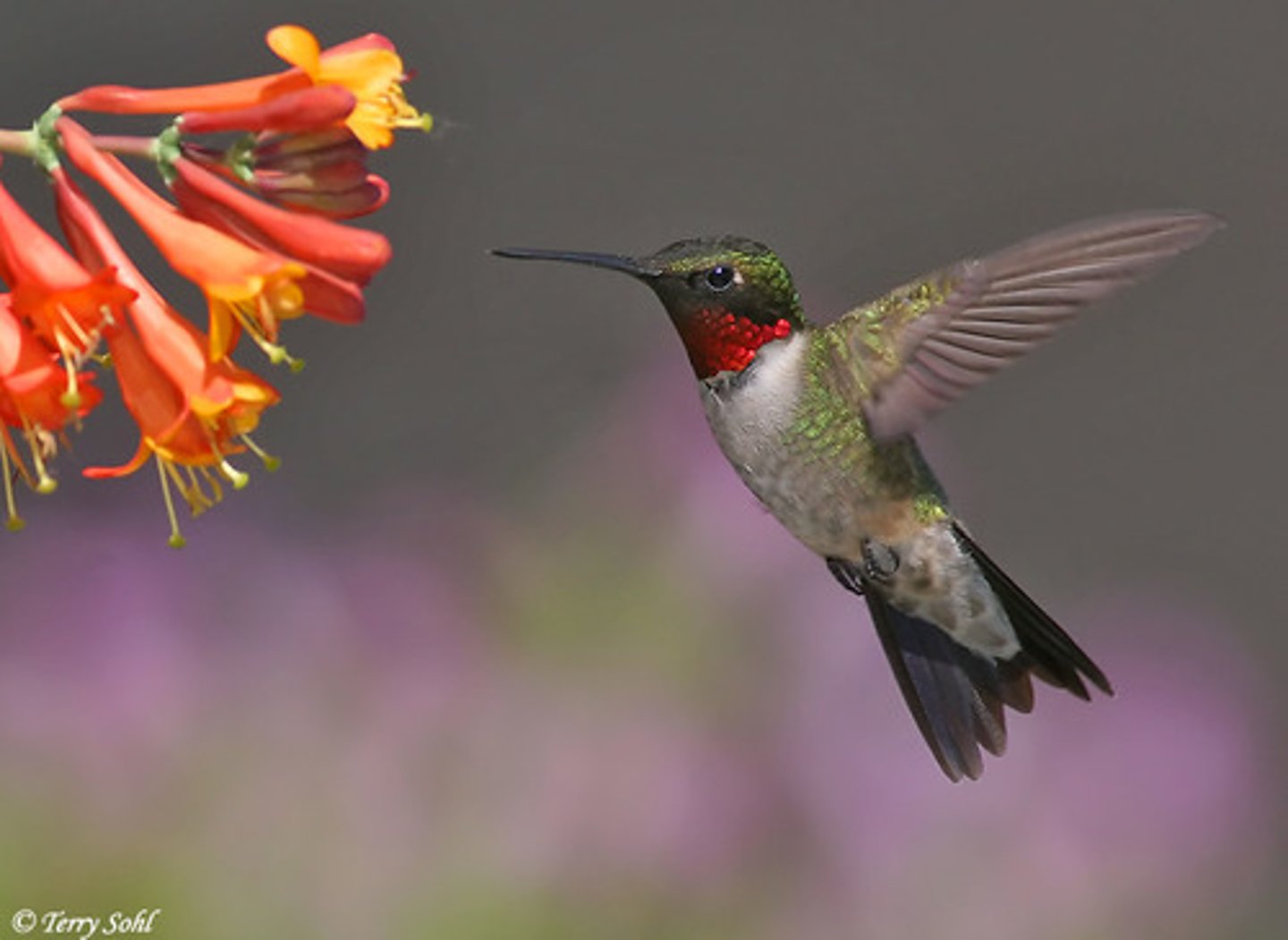
Bird Pollination
Red, orange, purple flowers, long tubular. Produce LOTS of nextar (reward for pollinators). NO scent (many bird have poor sense of smell)

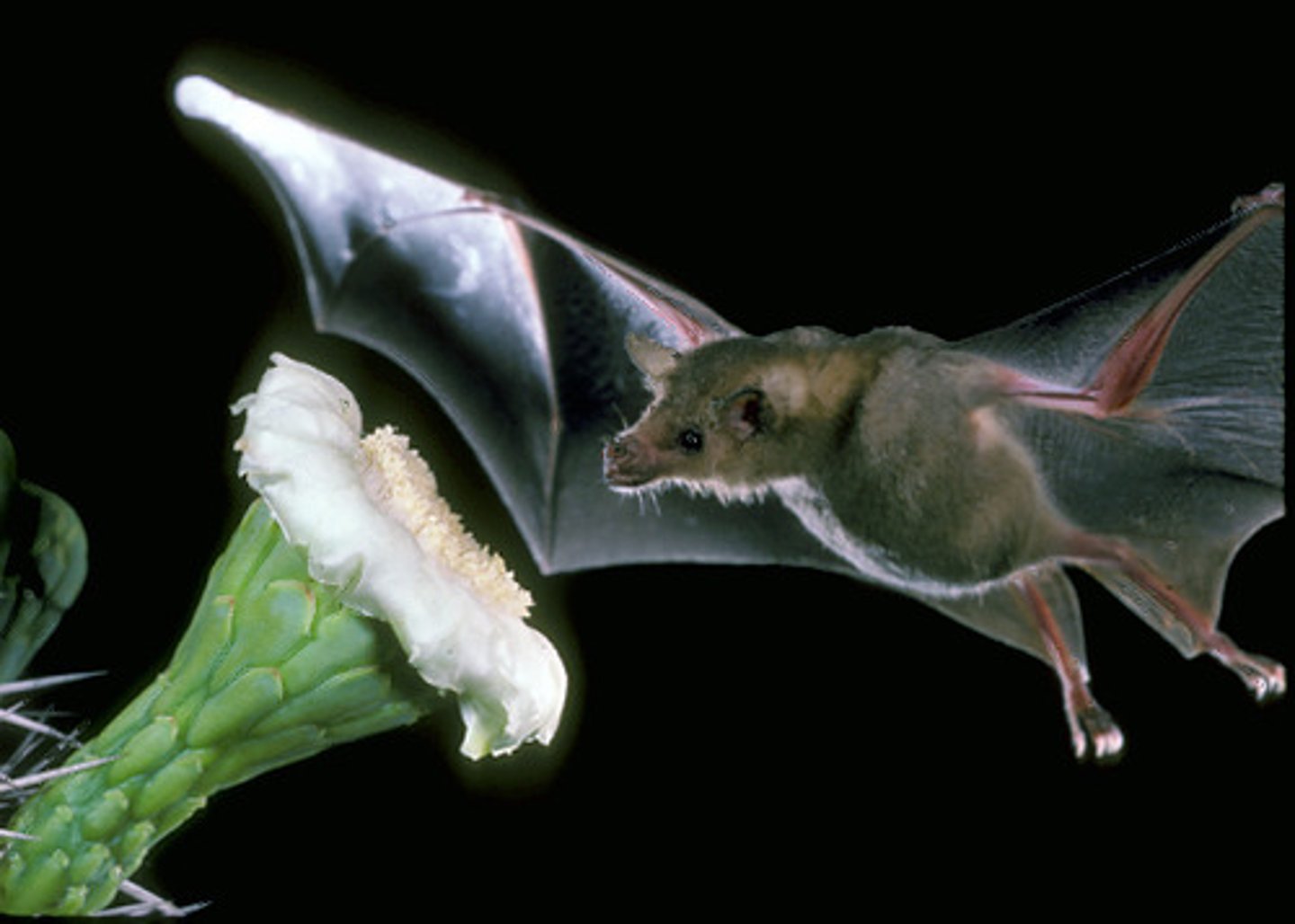
Bat pollination
Flowers open at night (bats are nocturnal) White/light flowers (bats are colorblind) Strong scent, Large, easy access.

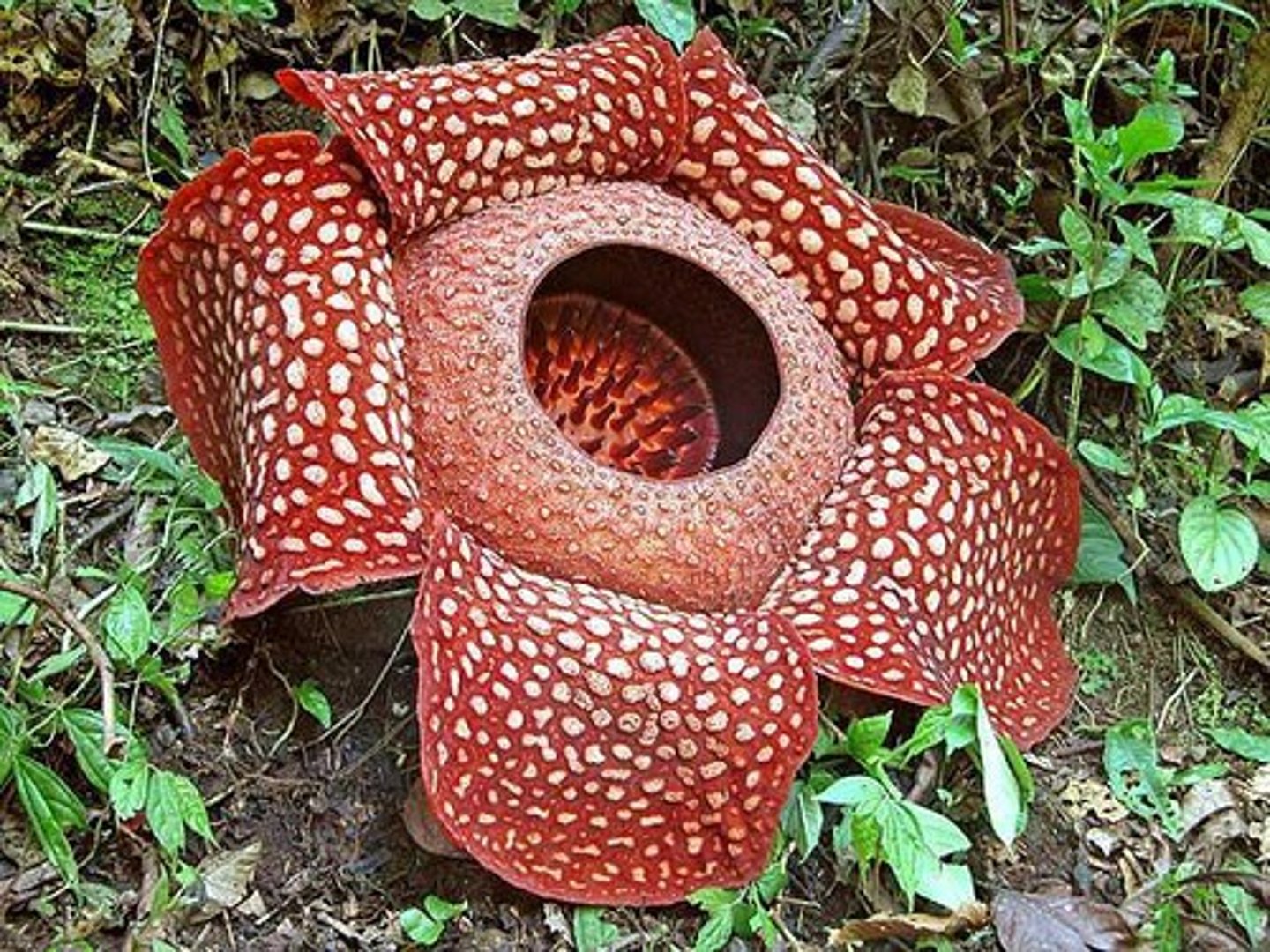
Fly pollination
Look like rotting flesh, Nasty smells, Produce heat

Fertilization Flower
joining of a pollen grain with a flower's immature seed; ovary to swell up and become a fruit; one pollen grain fertilizes one egg
Pericarp
mature ovary wall
Simple Fruits
Develops from a single flower with one carpel or fused
Simple Fruit Types
Dry:
- Dehiscent
- Indehiscent
Fleshy:
- Drupe
- Berry
- Pome
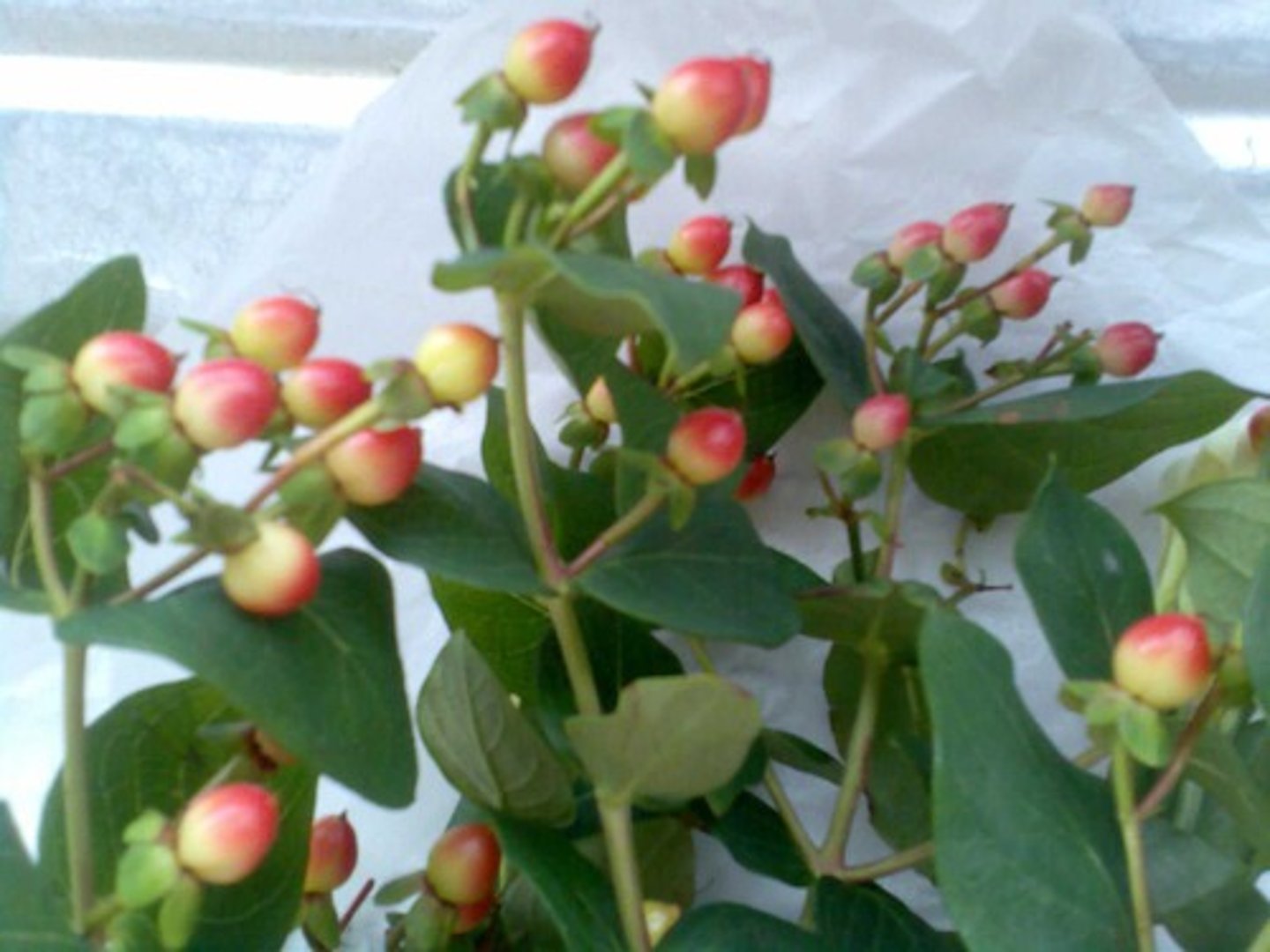
Fleshy Simple Fruit - Berries
Fleshy fruit with one or many seeds inside the ovary.

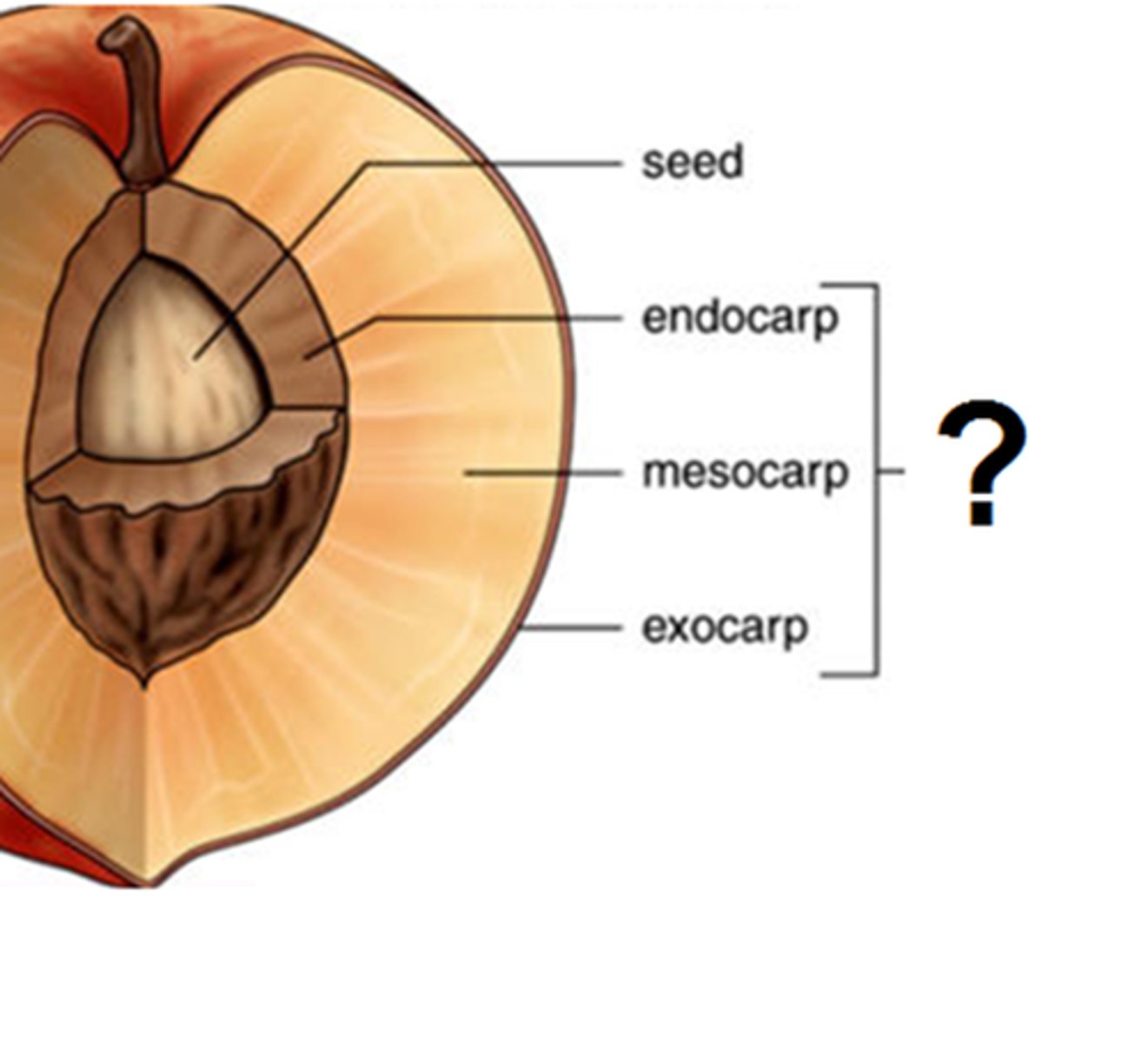
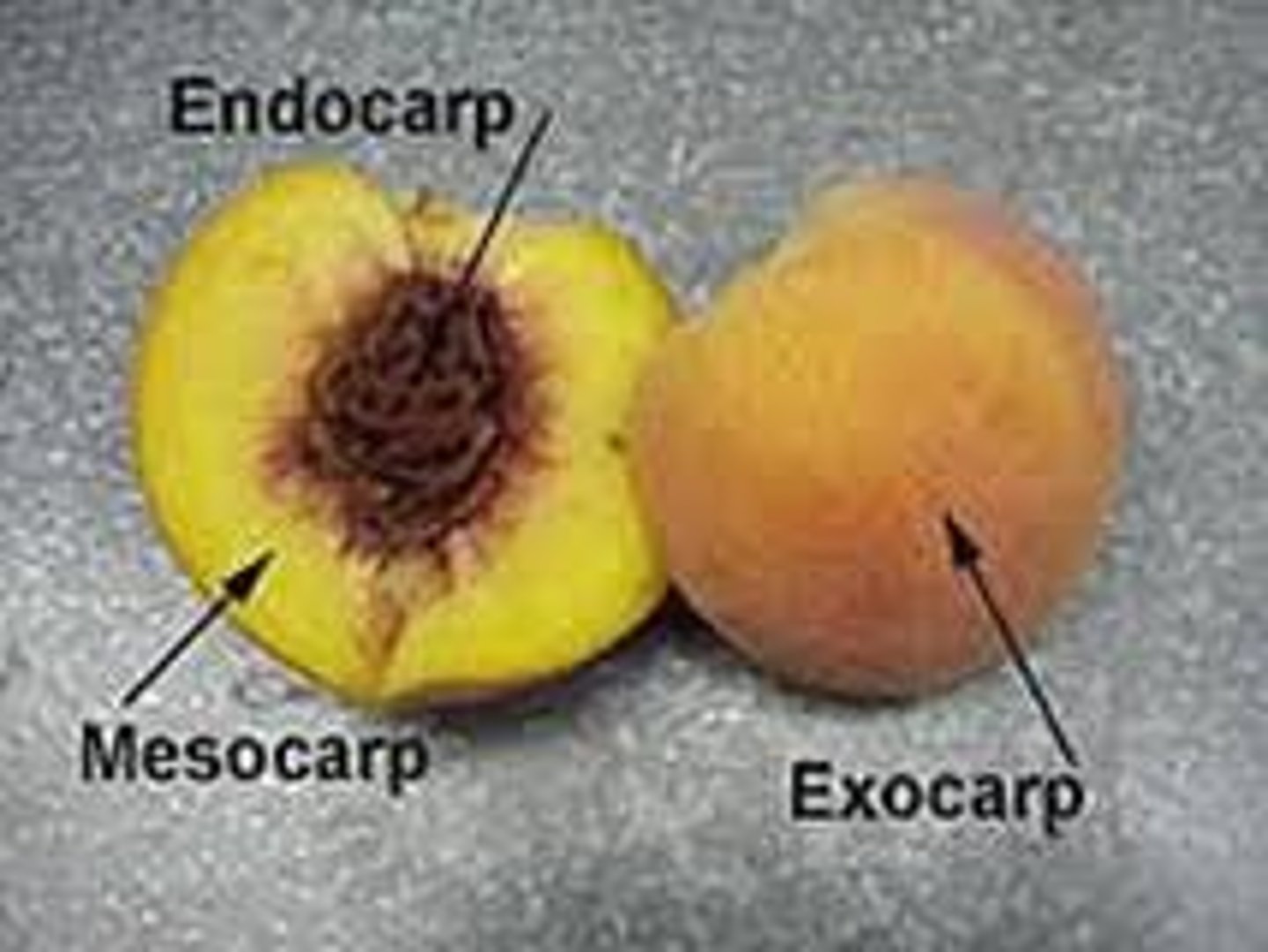
Fleshy Simple Fruit - Drupe
Pericarp is divided into 3 layers.
Endocarp (pit) - is hard, filled with sclereids) to protect single seed
Mesocarp - dry husk outside
exocarp - fleshy skin outside

Fleshy Simple Fruit - Pome
Pericarp is buried within a fleshy receptacle

Simple Dry Fruit - Dehiscent
breaks apart at maturity

Simple Dry Fruit - indehiscent
remains closed at maturity
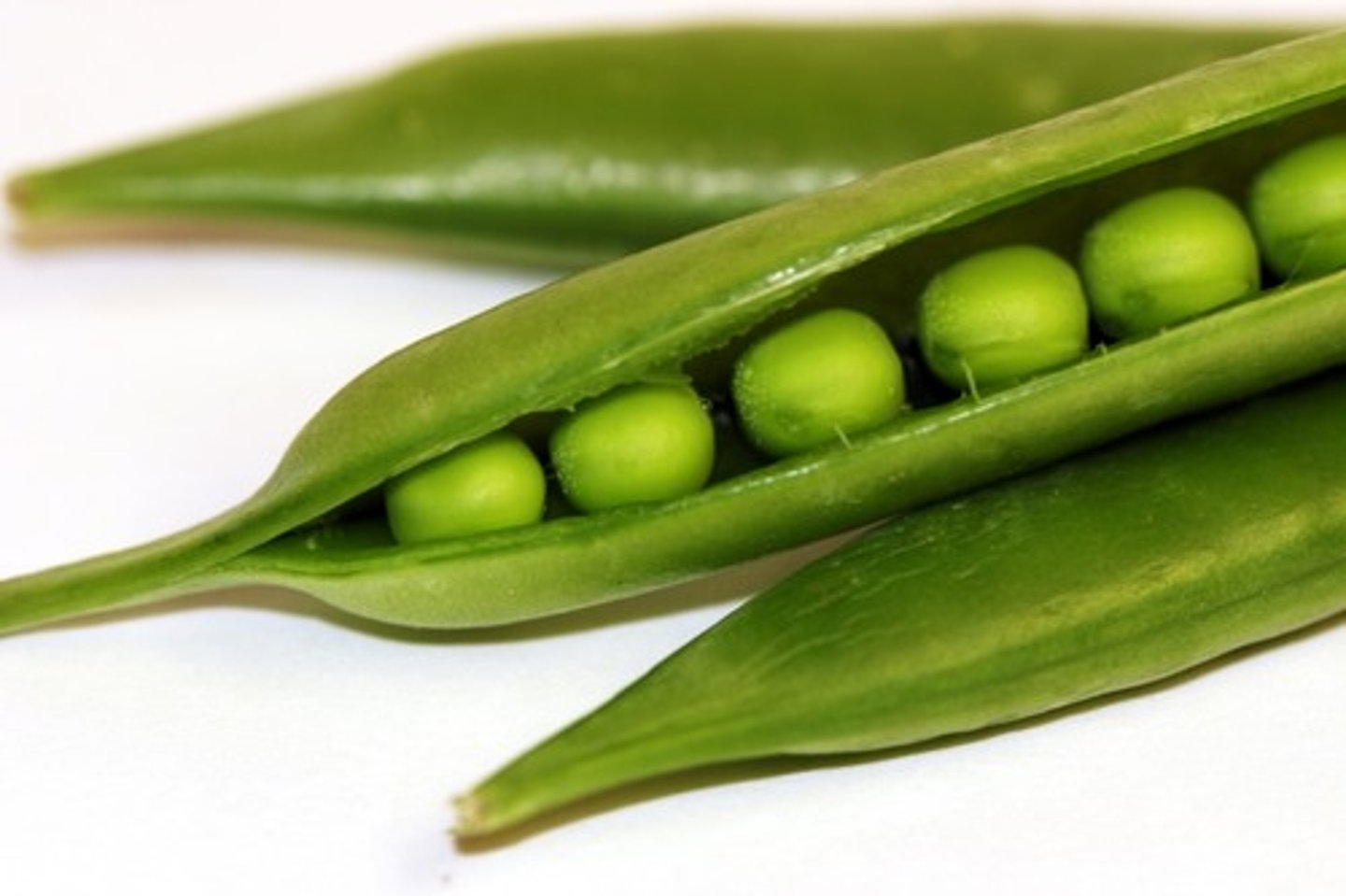
Legume: Pea Pod
Dry dehiscent fruit, Breaks apart at maturity

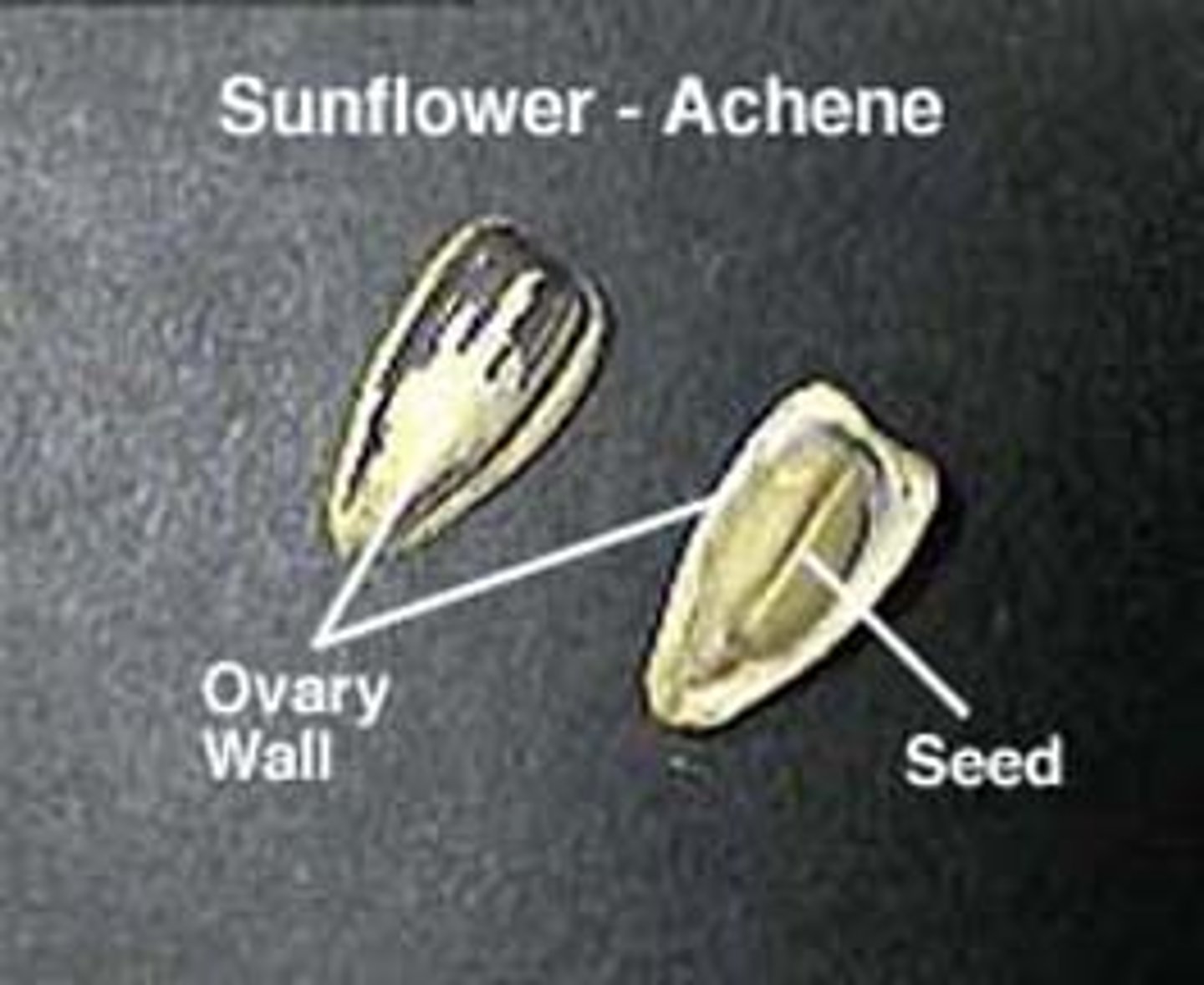
Achene: sunflower "seed"
dry indehiscent fruit, single seed inside
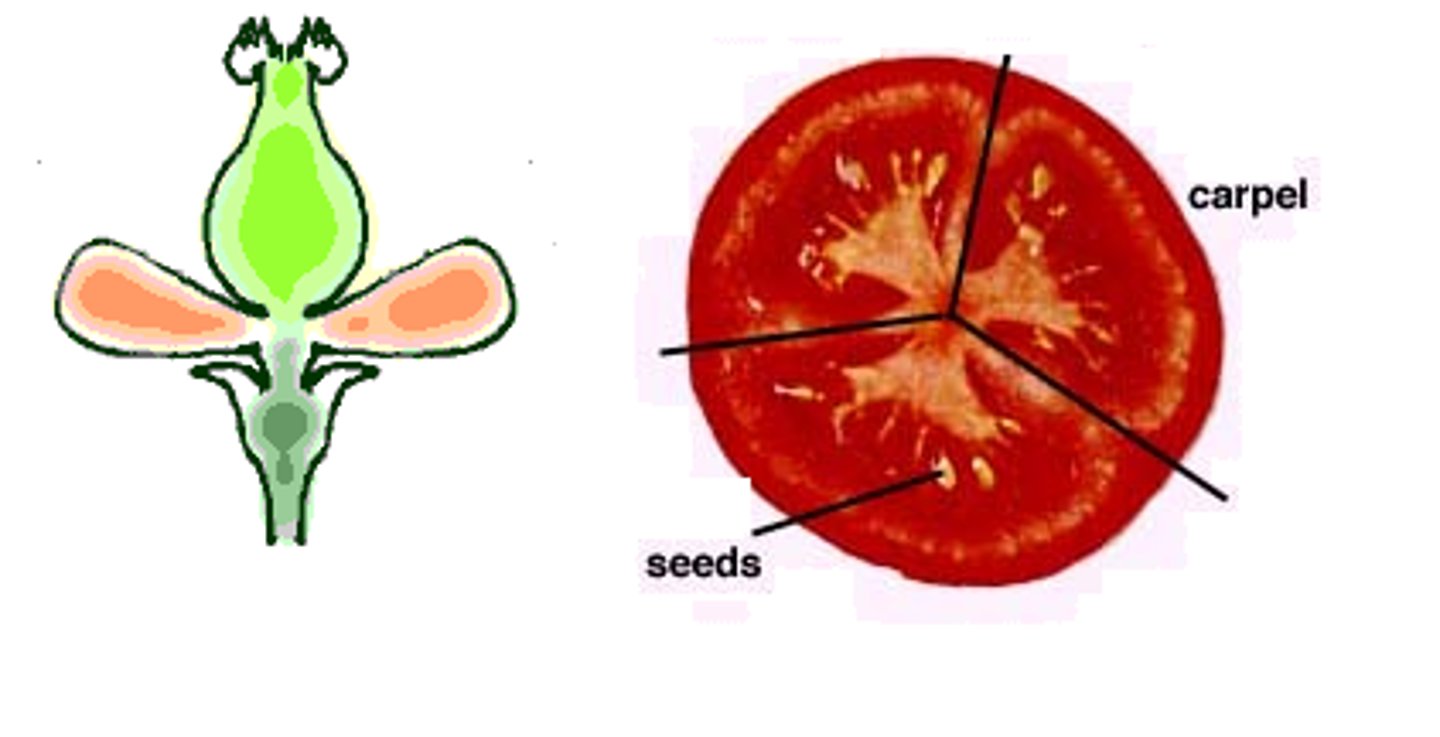
Aggregate Fruit
Develops from a single flower with MANY separate carpels
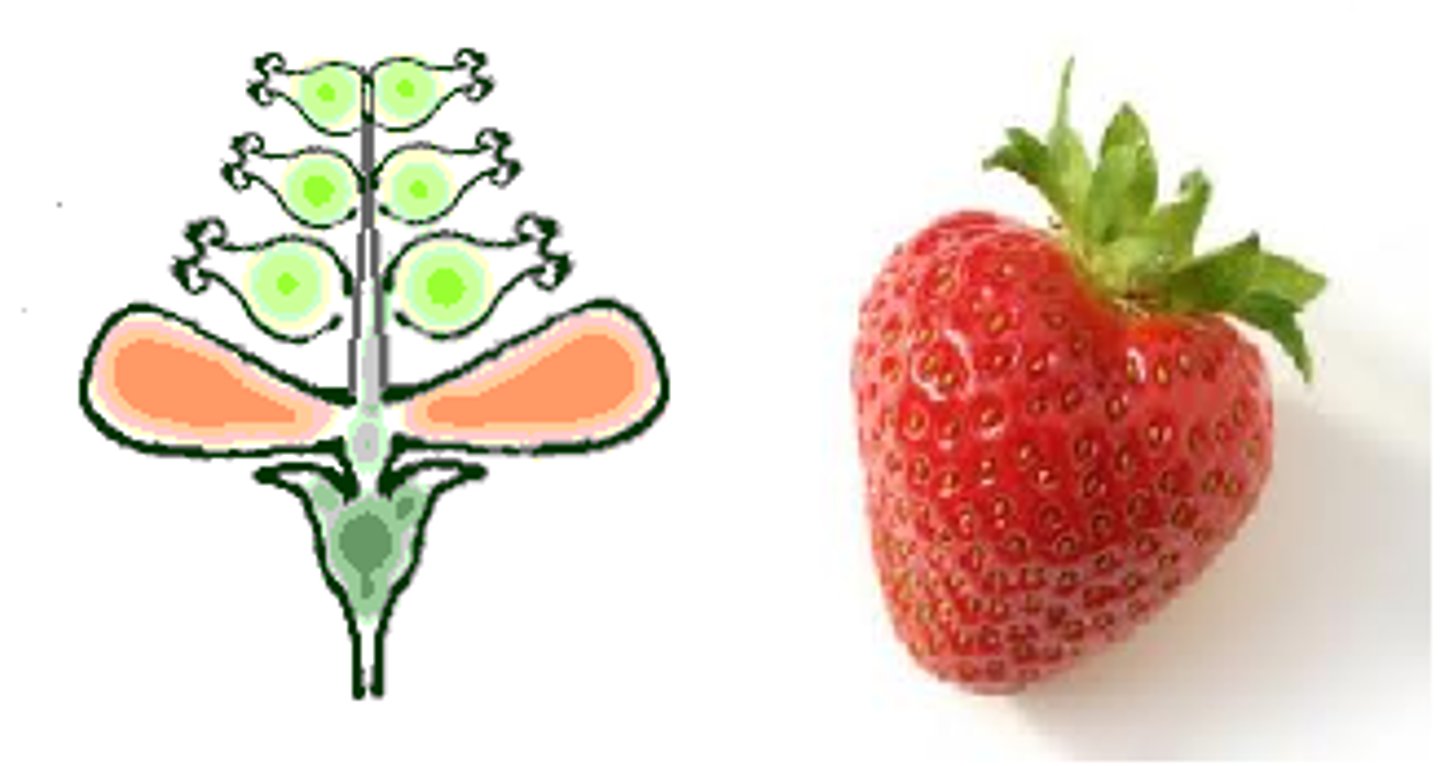
Strawberry
Aggregate of Achenes
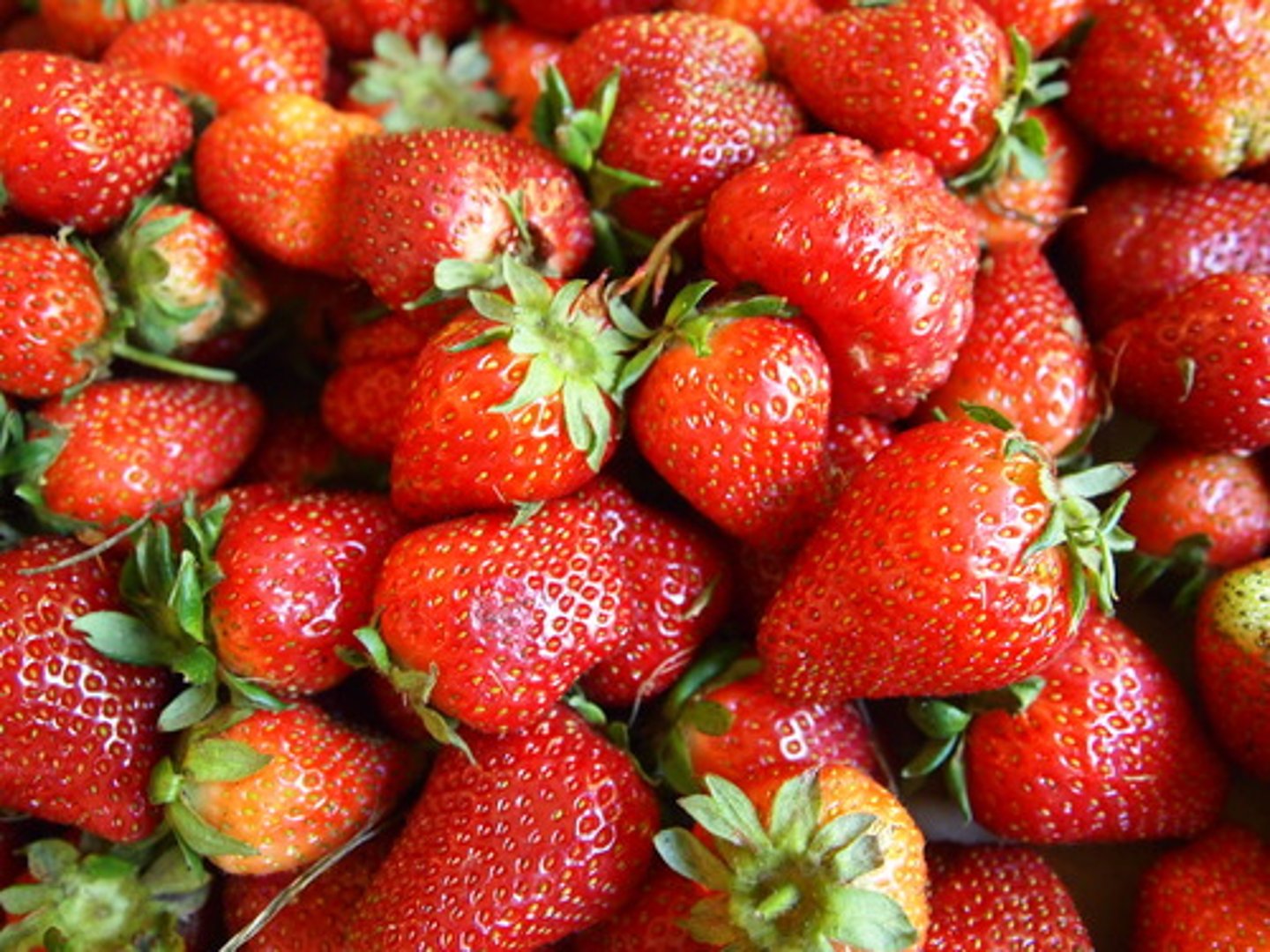

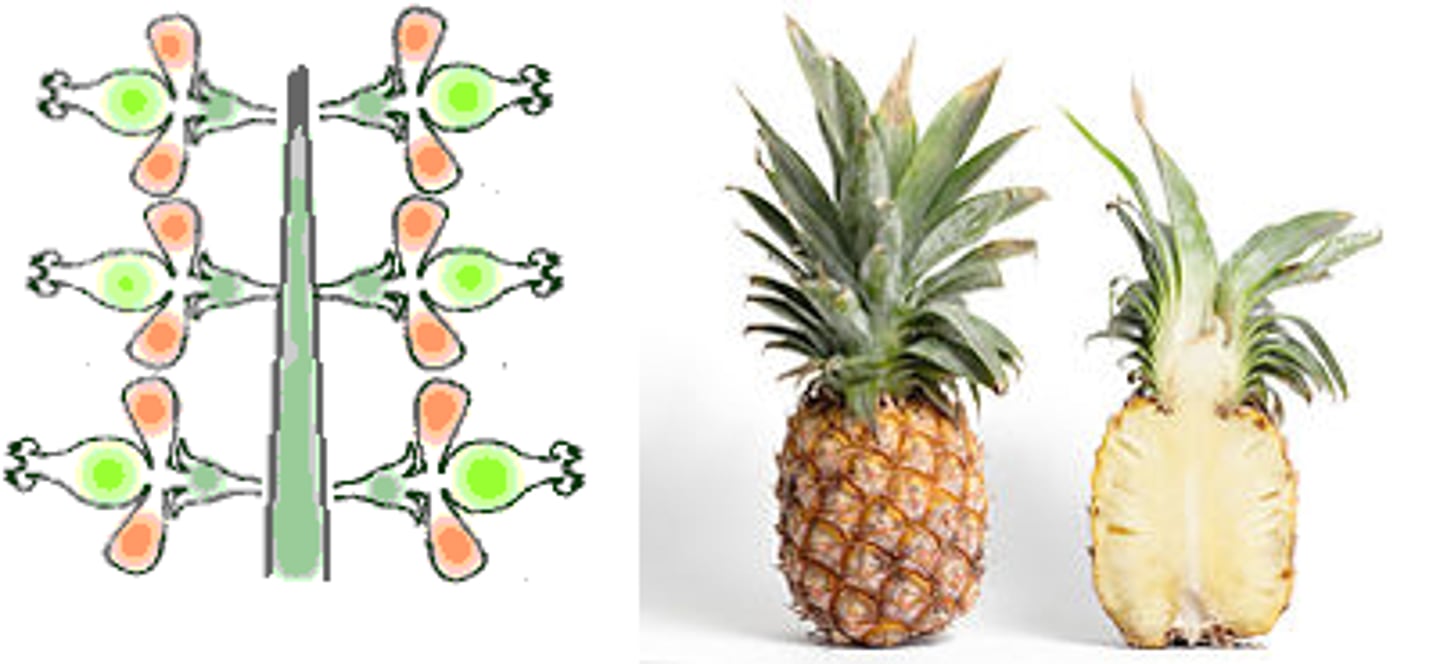
Multiple Fruits
Develops from many FLOWERS with many CARPELS
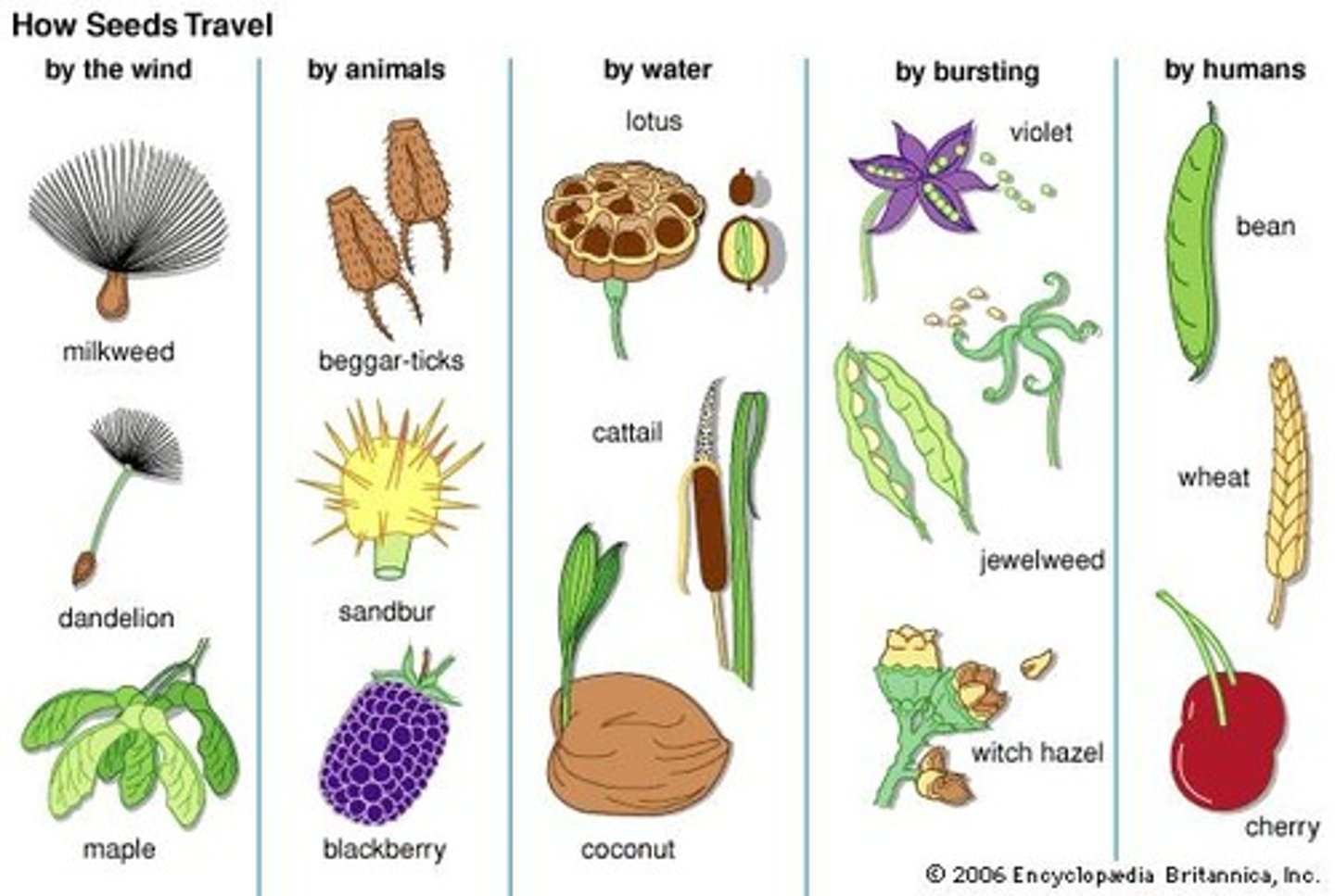
Seed Dispersal
Wind, Water, and Animals
Figs
750-900 species, free standing trees, shrubs, and other things. Tropics, subtropics, and a few species in warm temperate and Mediterranan climates.
Diverse habitats, in rainforest, savannas, riversides, cliff faces.
Fig in Tropical forests
Important, keystone tropical trees.
Year-round fruit produciton
Many birds and mammals (especially bats) thrive on a diet composed almost entirely of figs.
Seeds are dispersed over great distances.

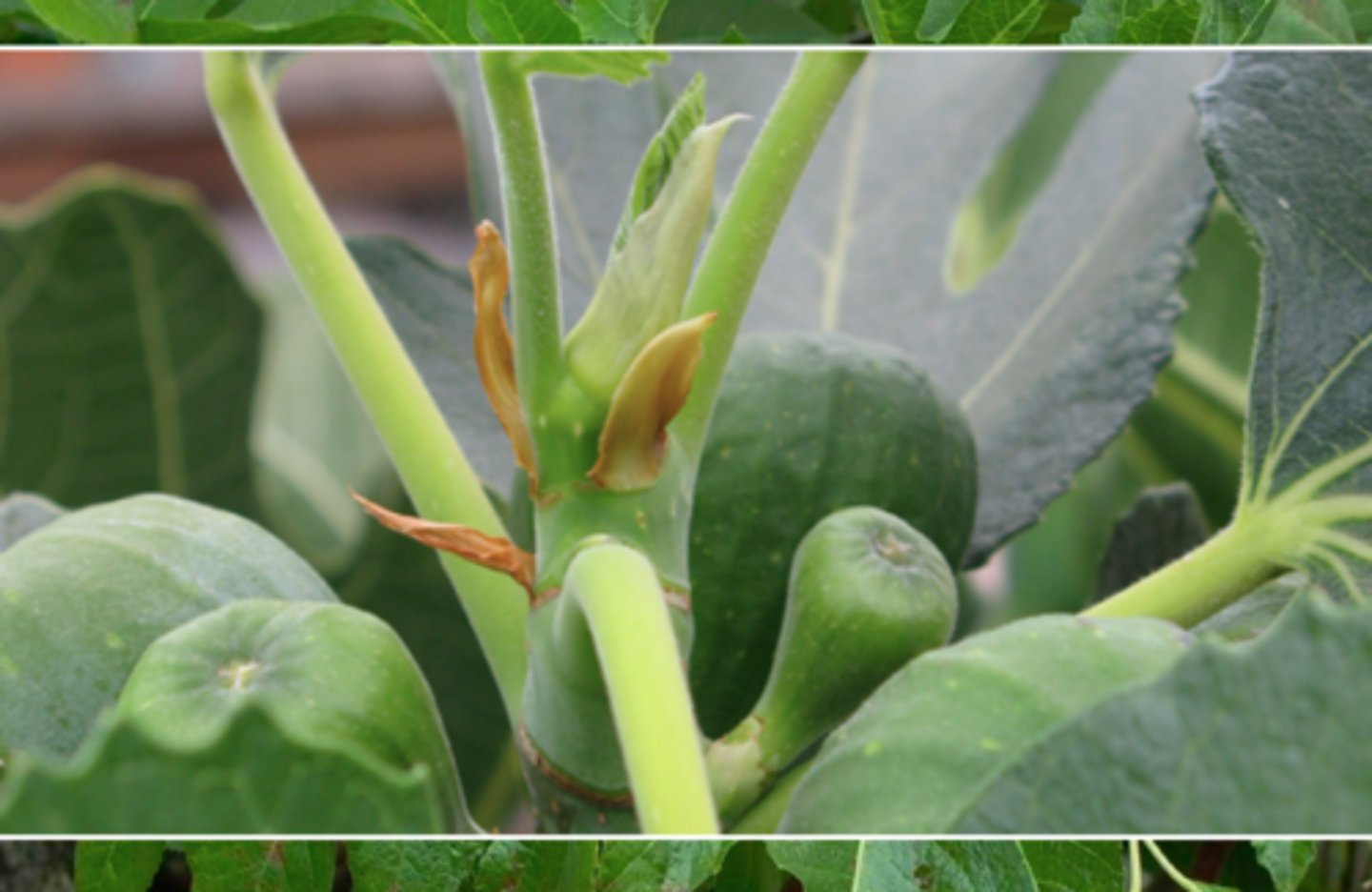
Paired stipules
form ringed scars around each node, in fig trees mostly

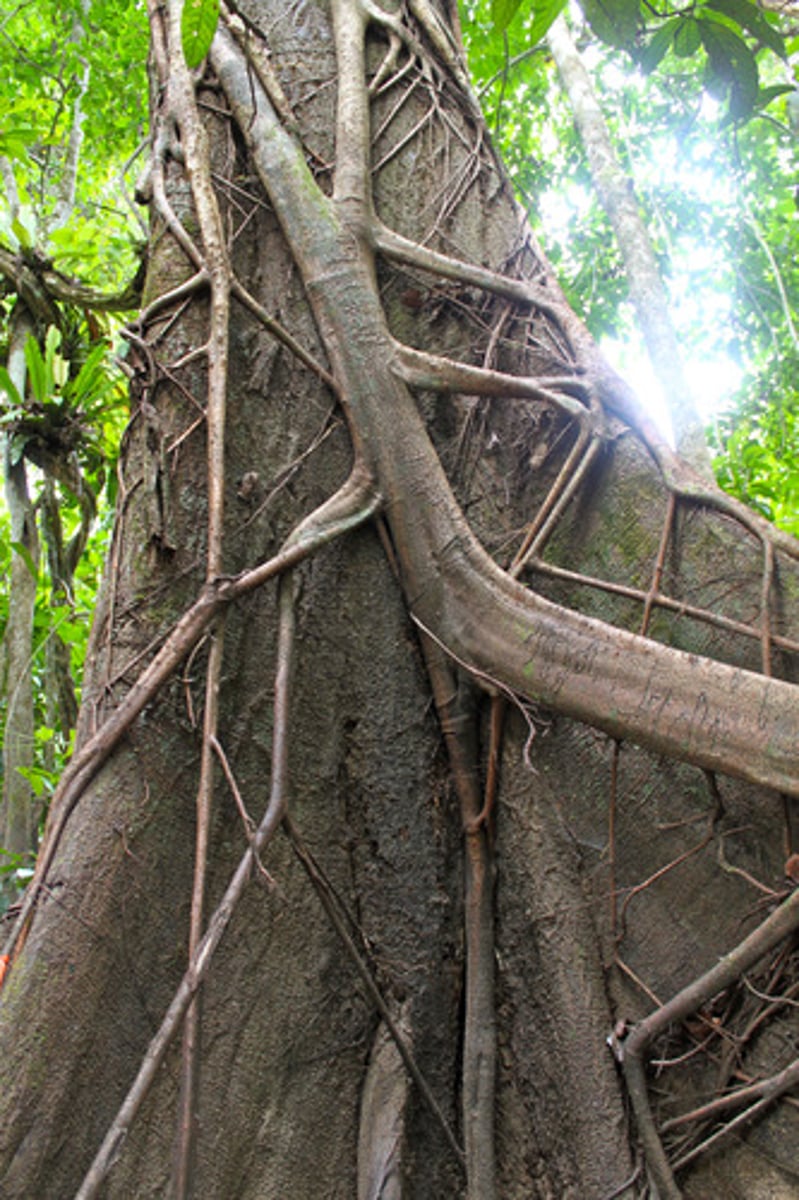
Hemiepiphytic "Strangler Figs"
Some figs begin life as epiphytes (plants that live on other plants)
- Send aerial roots to the ground
- Roots grown downward, around the host trunk

Ficus (fig) Reproduction
Flowers are borne inside a hollow stem (syconium), with a hole at the end (ostiole). Figs are monoecious or dioecious. Female flowers have a single ovule.
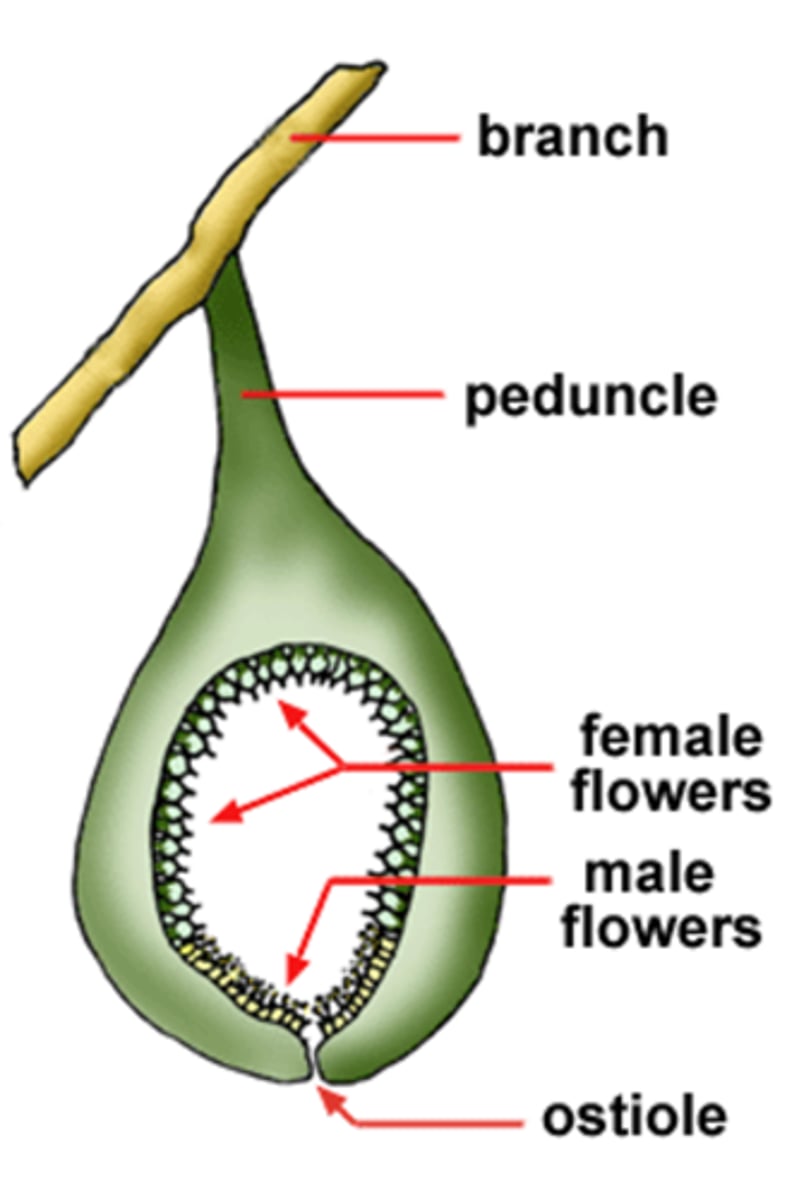
Fig Wasp Pollinators
- Figs are pollinated by small wasps
- Female wasps enter the syconium through the ostiole (wings and antennae are stripped off)
- Female wasps carry pollen from the syconium where she was born
- She pollinates, lays eggs in flowers, then dies
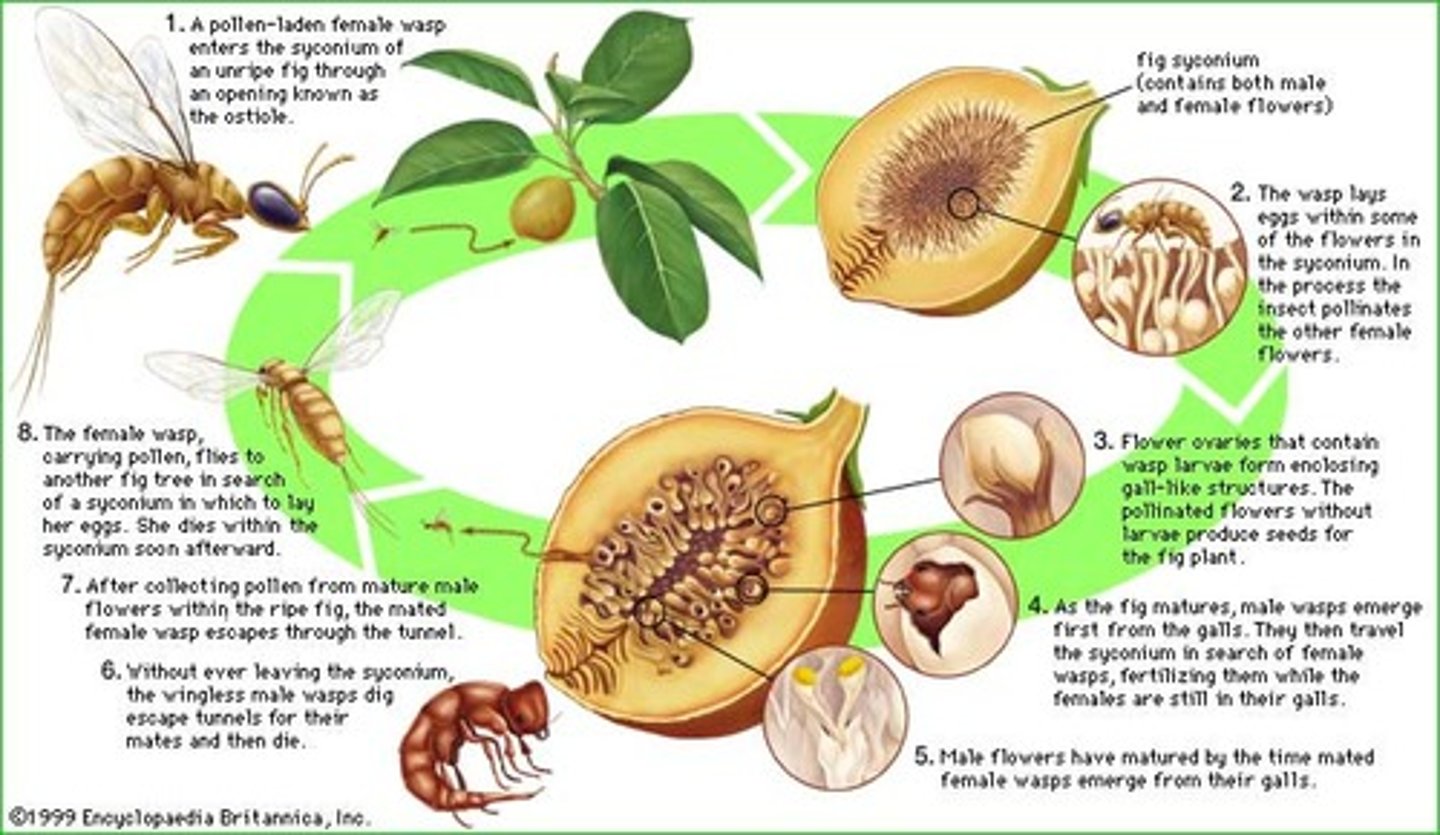
fig Wasp Pollinators part 2
-wingless males emerge from flowers first, mate with femals while theyre in the flowers
- males chew the ostiole wide open, then die
-newly emerged, fertillized femals collect pollen
-exit the syconium and fly to a new one.
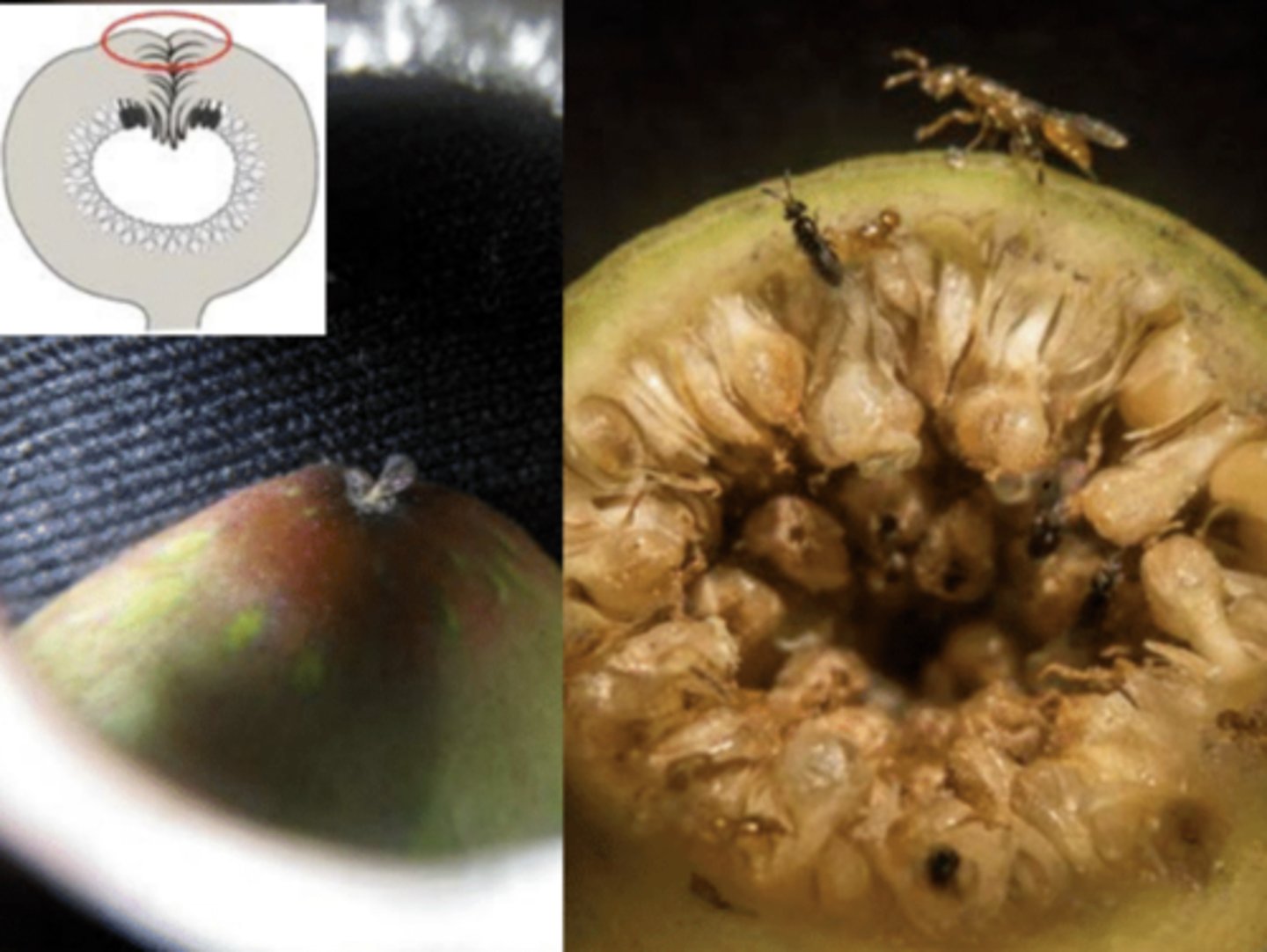

Fig flower diagram
look at image.
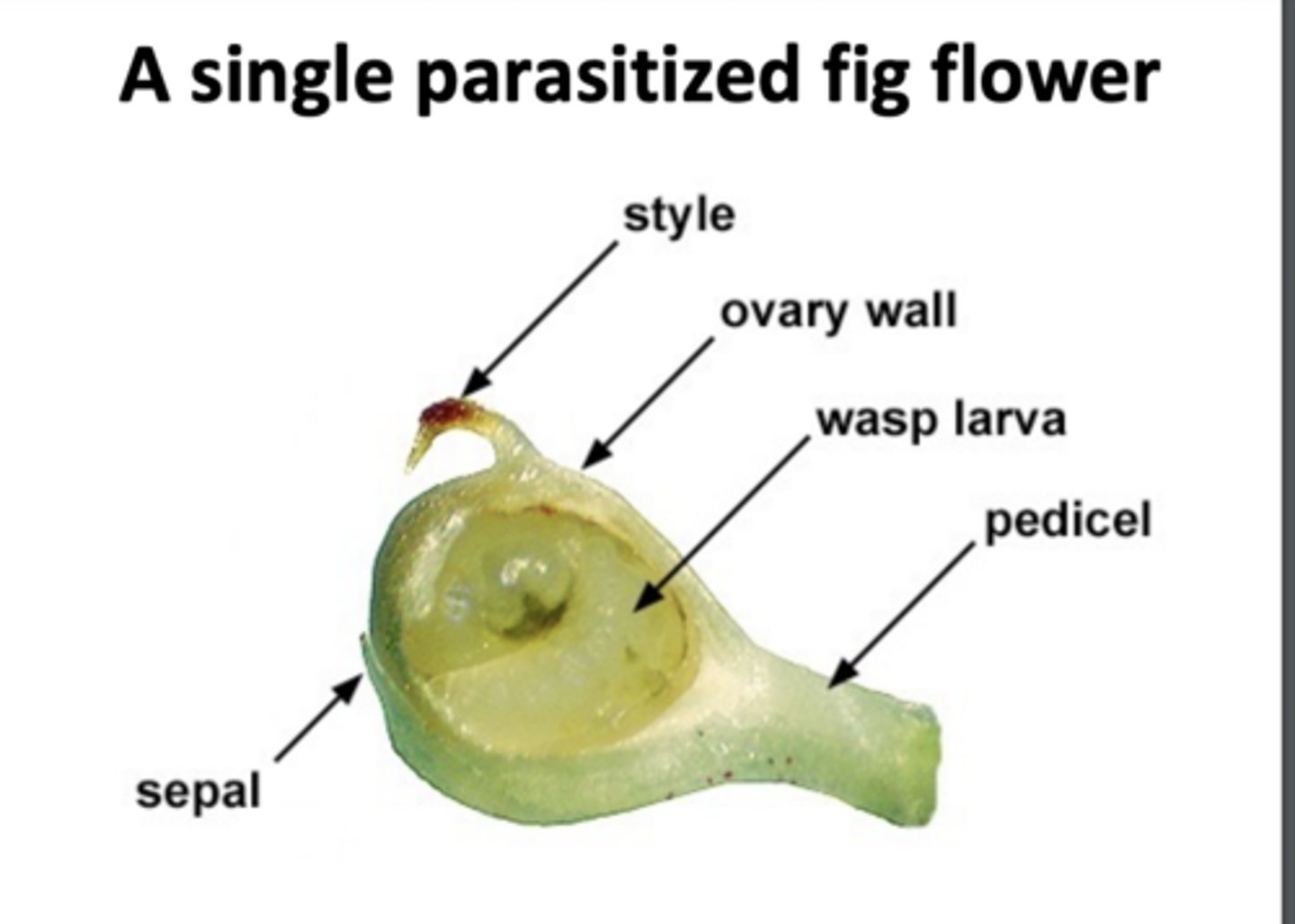
Edible Figs
Black mission fig - fruit ripens without pollination
Calimyrna - variety that needs a wasp to pollinate
Caprifigs - figs with mostly male flowers, few female flowers with wasp larvae (much less appetizing)
Why Have Plant names?
Allow us to communicate about plants that:
- we use for food, clothing, shelter, medicine
- we grow in our gardens, our yards, our orchards
-we encounter in the wild - wildflowers, weeds, forest trees.
Advantages of common names?
-Use begins in childhood
-Used by untrained laymen
-Generally easy to remember
-Usually in the local language
Disavantages of common names?
- Not standard
-vary regionally
-one plant has several common names
- many plants have no common names
-may be misleading
-many different plants share the same common name!!!!
Advantages of Scientific Names?
-standardized by ICBN
-all known plants have a scientici name
- no two speicies share same science name
-unform in all regions and languages
- only 1 correct scientific name
Disadvantages of Scientific Names?
-Often difficult to remember
-written in latin: (sometimes long, hard to spell, hard to pronounce.)
-not used by most people
-may change with new knowlege.
Scientific Names
-species is 2 word latin word (binomial)
-First word is the name of the GENUS (plural=genera) to which the plant is assigned.
-The second word is the specific epithet - oftentimes descriptive
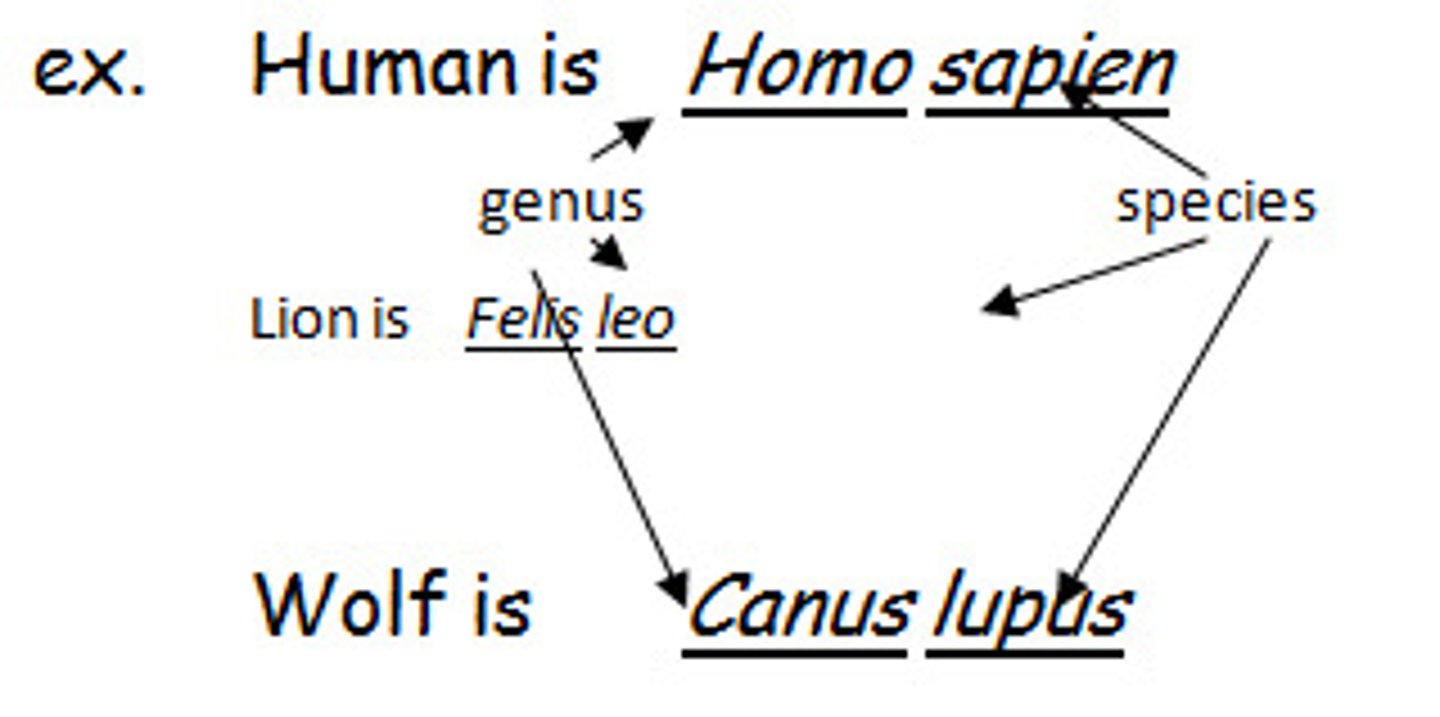
Taxon
taxonimic group of any rank, like species, genus, family.
Genus
group of species with shares ancestry and characteristics

Cultivars
-Cultivated varieties
-Traits maintained by propagation
-King Edward potato
-Cultivar name is in single quotes following the species name

Water is the most abundant resource on the planet, yet most limiting resource for _________
Terrestrial plants

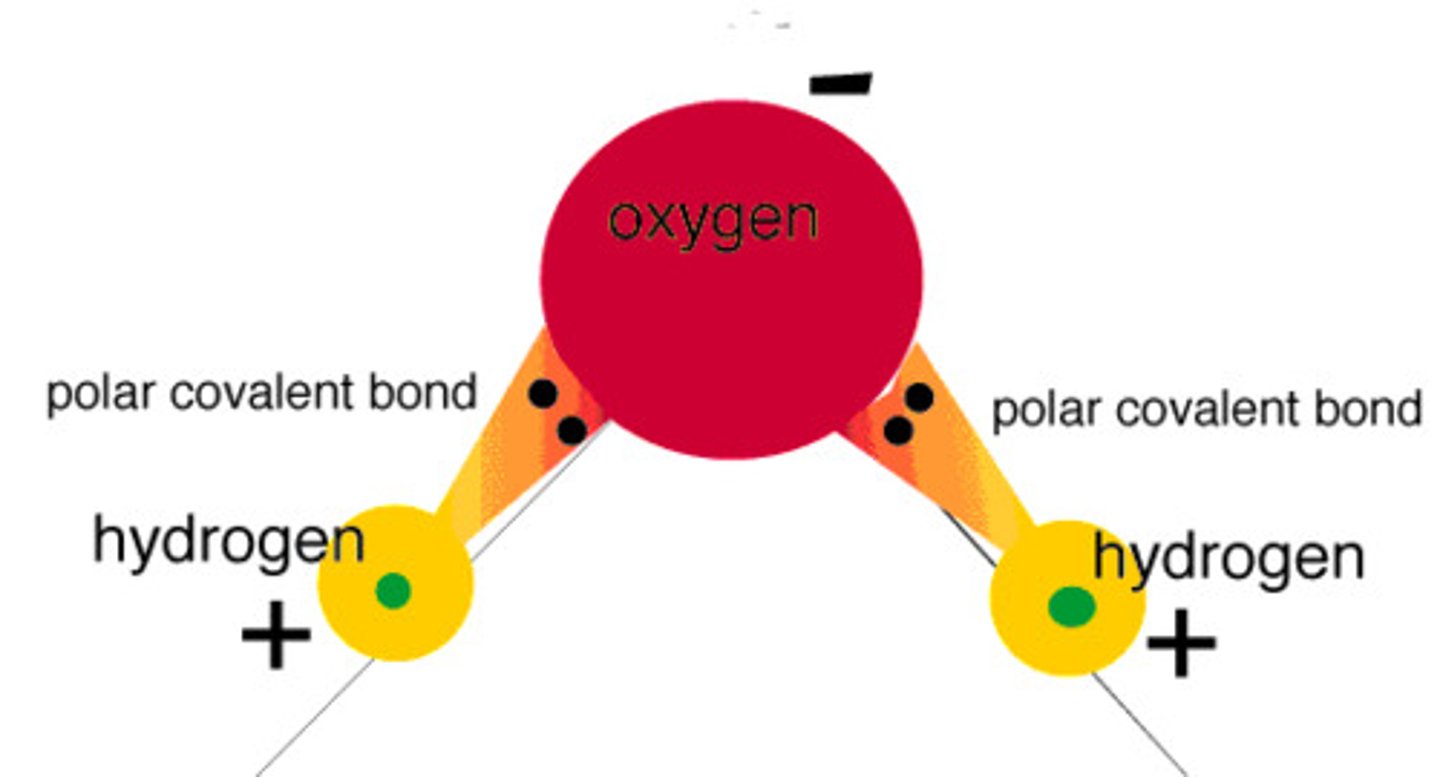
Water is strange molecule!
polar molecule
adhesion - sticks to other molecules
cohesion - water sticks to itself
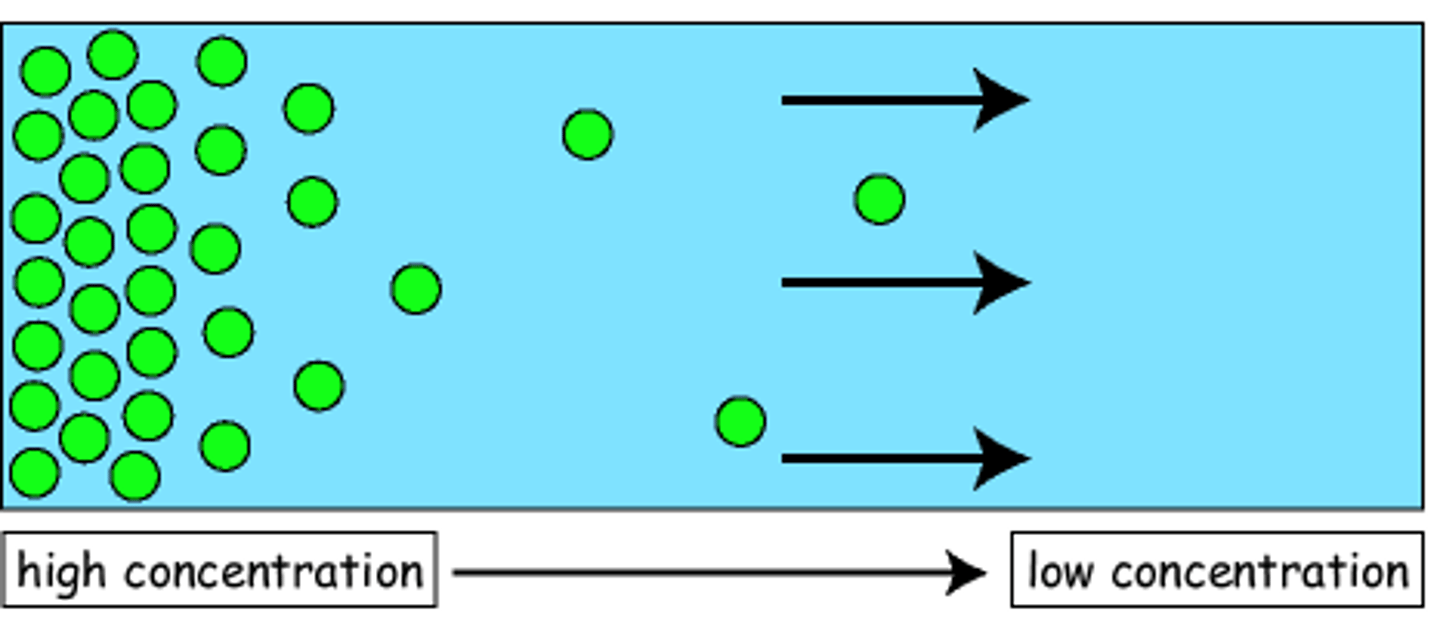
Diffusion
-movement of moledules from areas of high concentration to low concentration
-driven by random movement of molecules
- state of equilibrium reached after some time
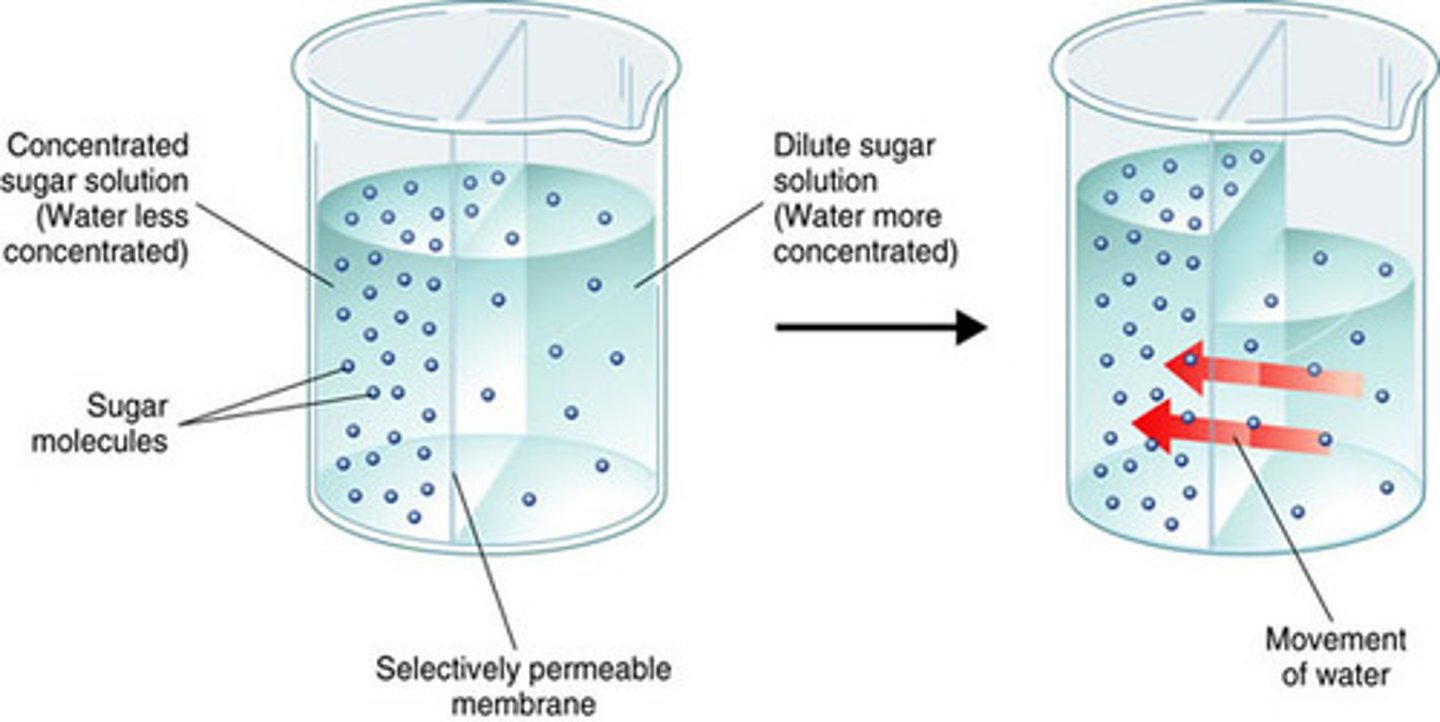
Osmosis
Passive diffusion of water through a differentially permeable membrane
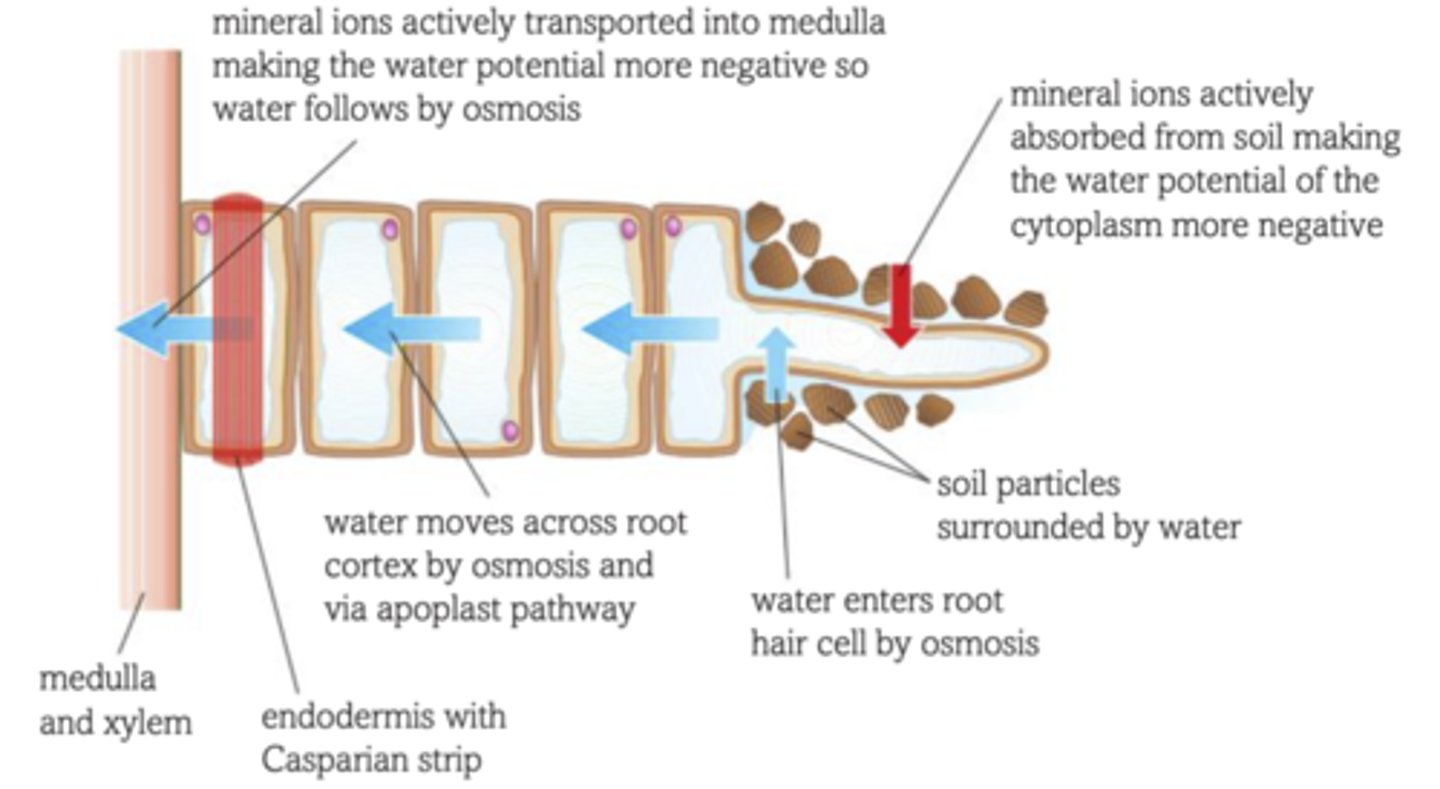
How does water move from roots to xylem?
-Epidermal cells with root hairs absorb water and minerals from surrounding soil by diffusion
-Water diffuses through cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and into the xylem tissue
Turgor Pressure
pressure that is exerted against the cell wall as a result of water entering the cell FRY VERY STIFF REMEMEBR. FULL OF WATER.
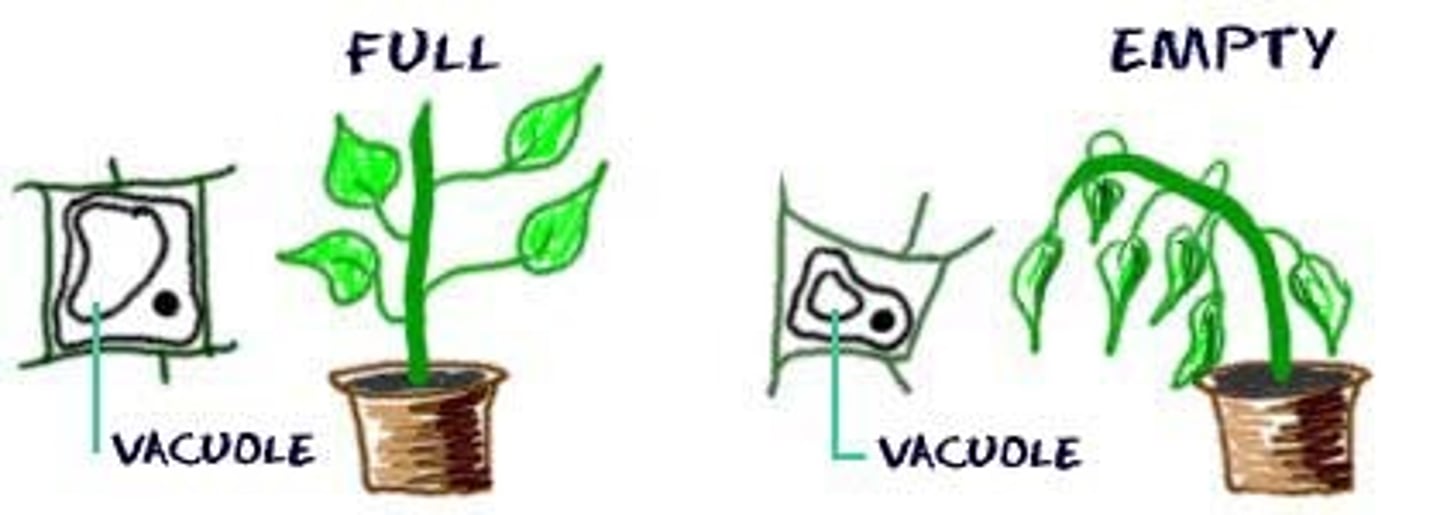
Plasmolysis
cells lose water and become "flaccid", ALL WIGGLY SWIGGLY. LACKING WATER.
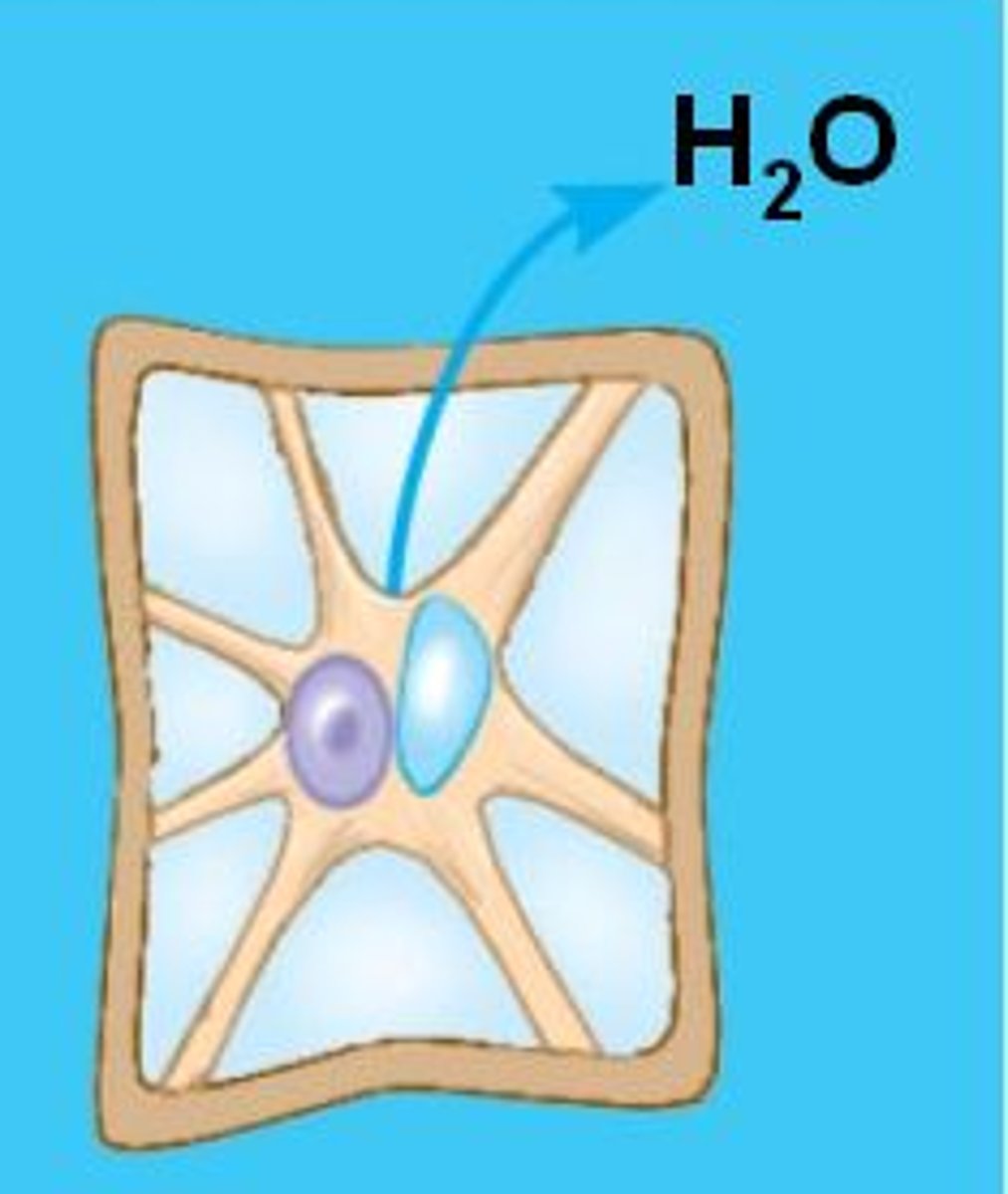
Transpiration
leaves can lose up to 100% of their water for 1 hour. Plants retain less than 15 of the water they absorb.
When does transpiration occur?
when the stomata are open.
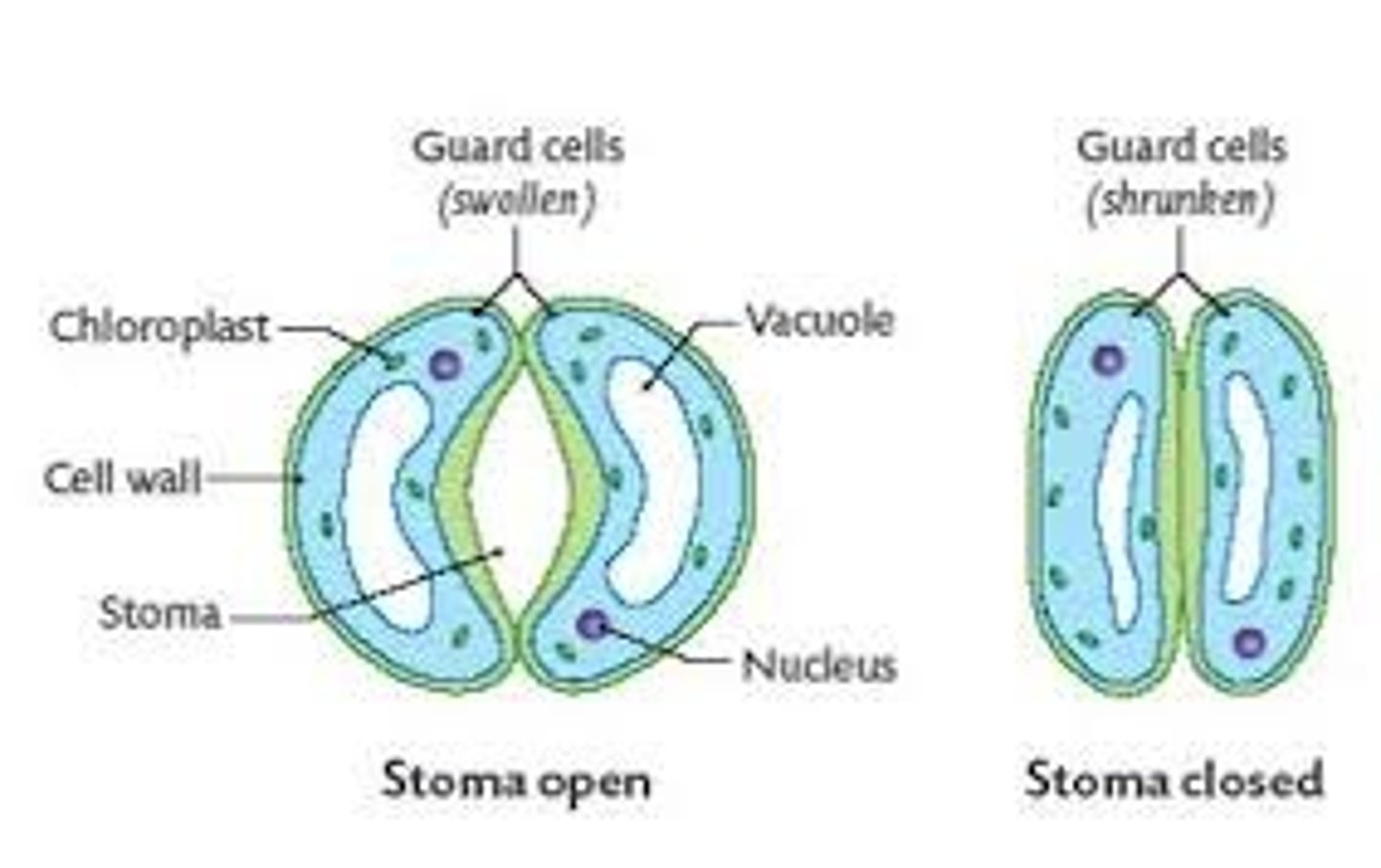
How is transpiration regulated?
by opening and closing the stomata.
-potassium ions pump into guard cells, vacuoles swell with water.
-the different cell wall thickness is the guard cell results in deformation, opening a gap between them - OPEN STOMATE.
-stomata close when K+ ions are pumped out of the guard cells - vacuoles shrink.
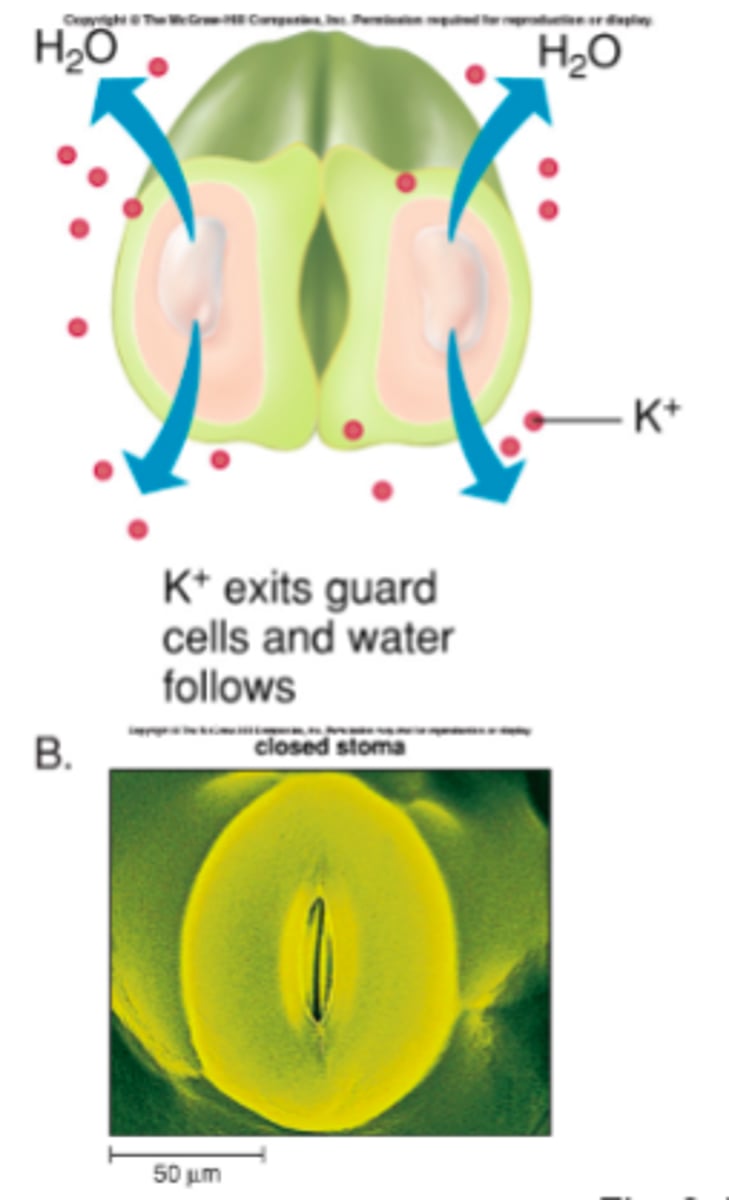
Why do stomata close?
result of:
Darkness
High CO2 in the plant
Low water in cells
High temperature
The Cohesion-Tension Theory
-Transpiration and the cohesion of water causes an upward pull of water from soil to roots to leaves
-The adheasion of water to walls of xylem cells also helps resist gravity.
How tall can a tree grow?
limit due to photosynthetic efficnecy, amount of water, CO2
physiological limit at 425 feet.
Bigger trees grow faster, sequester more carbon as they age.
To fight climate change, protect the really big trees!
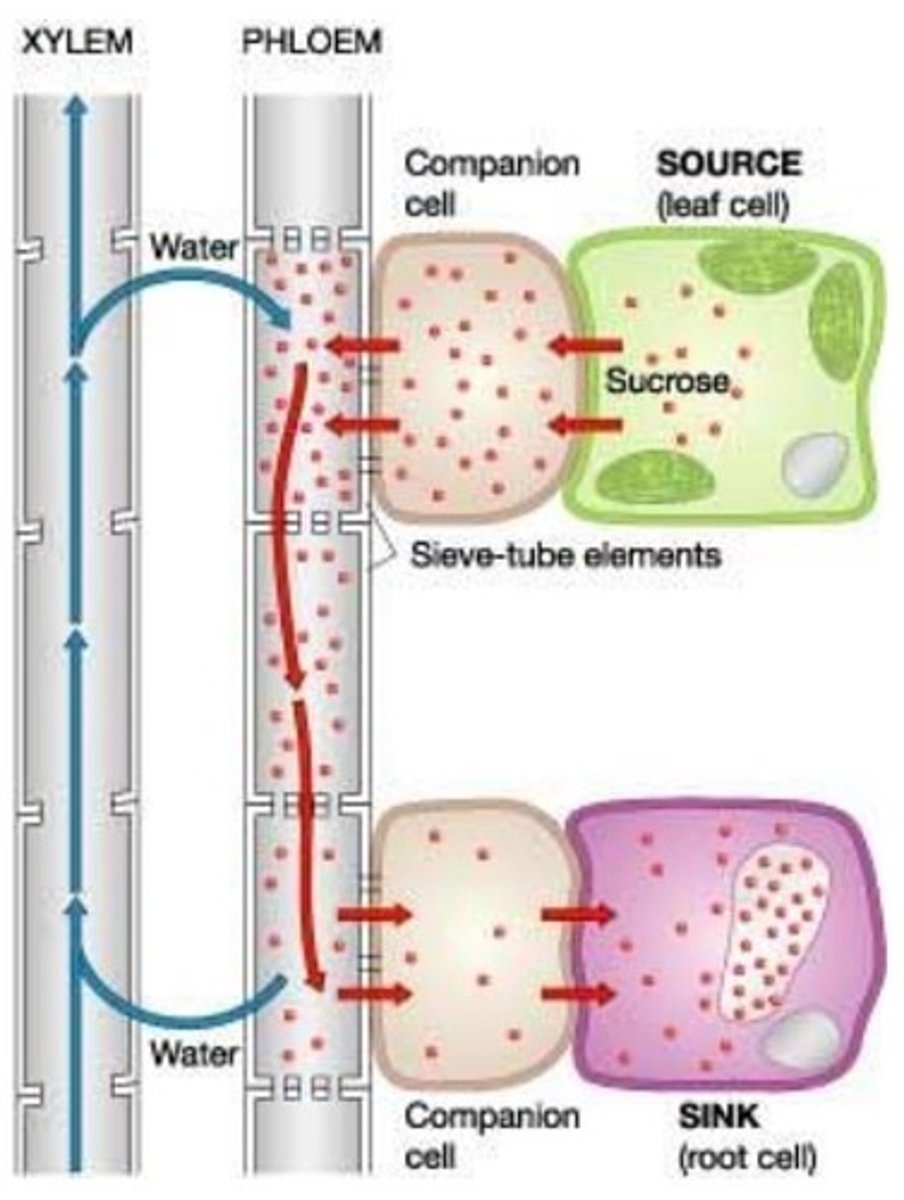
Phloem
Transports sugars and other organic substances.
Composed of different types of cells.
Sieve tube members
Cells in the phloem tissue that lack a nucleus, but are long and cylindrical for conducting sugar water.
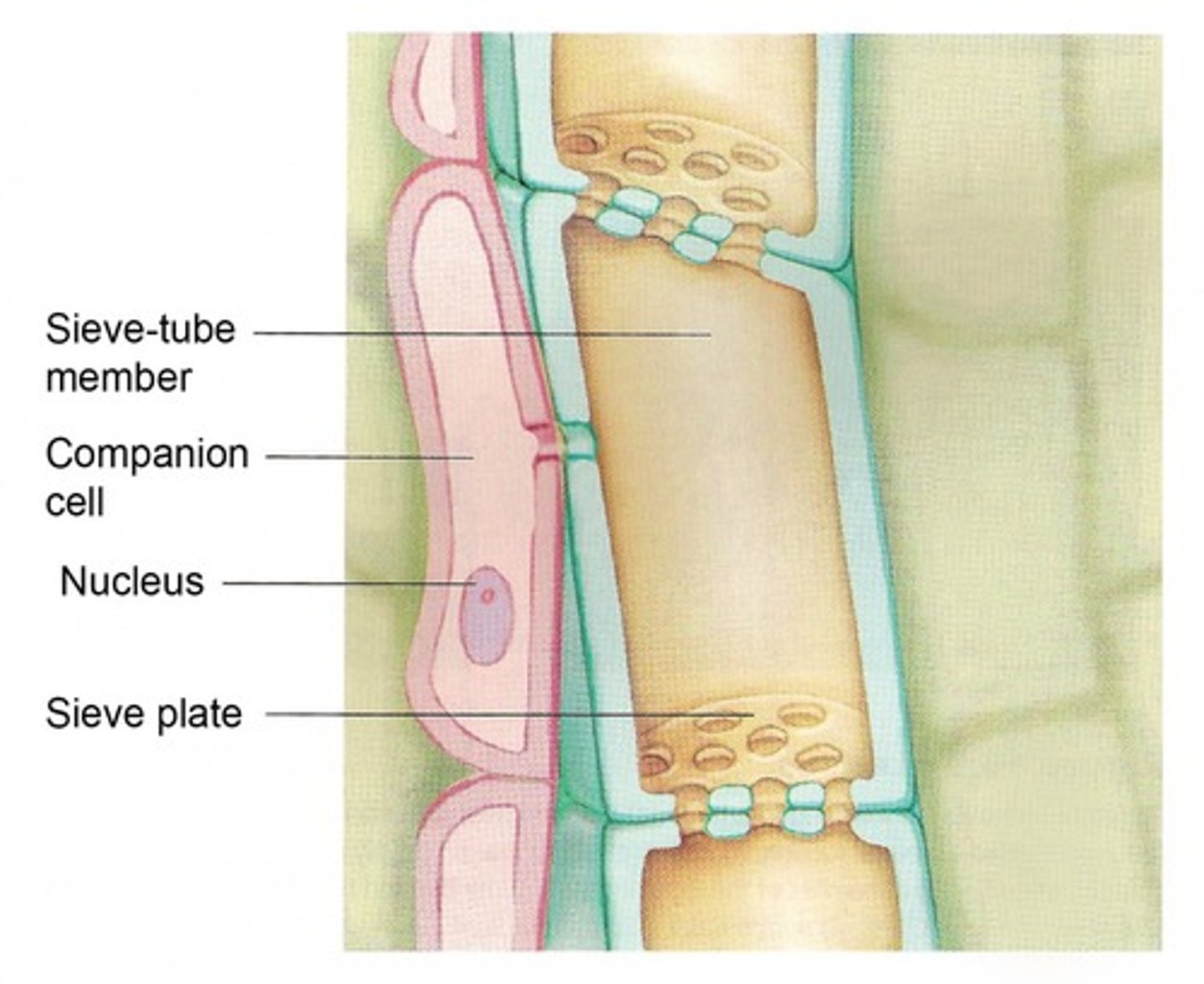
Companion cells
help sieve tube members function
Sugars are transported in the phloem tissue
90% of dry matter in phloem is sugar (mainlu sucrose)
Sucrose is basically table sugar
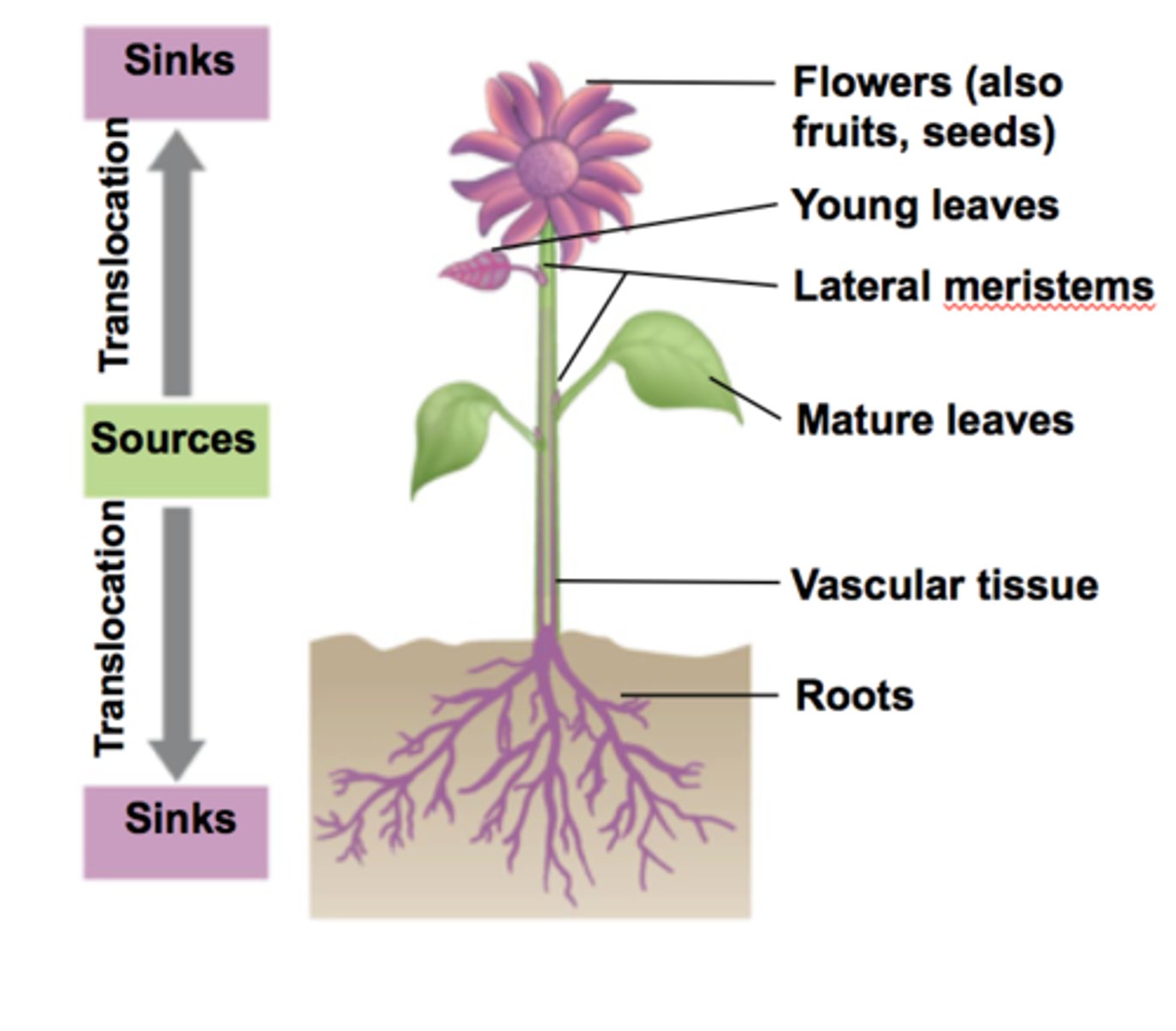
Sugar Sources and Sinks
Stems can be sugar sinks (swollen stems)
roots can be sugar sinks (swollen stems)
Mature leaves are sugar sources
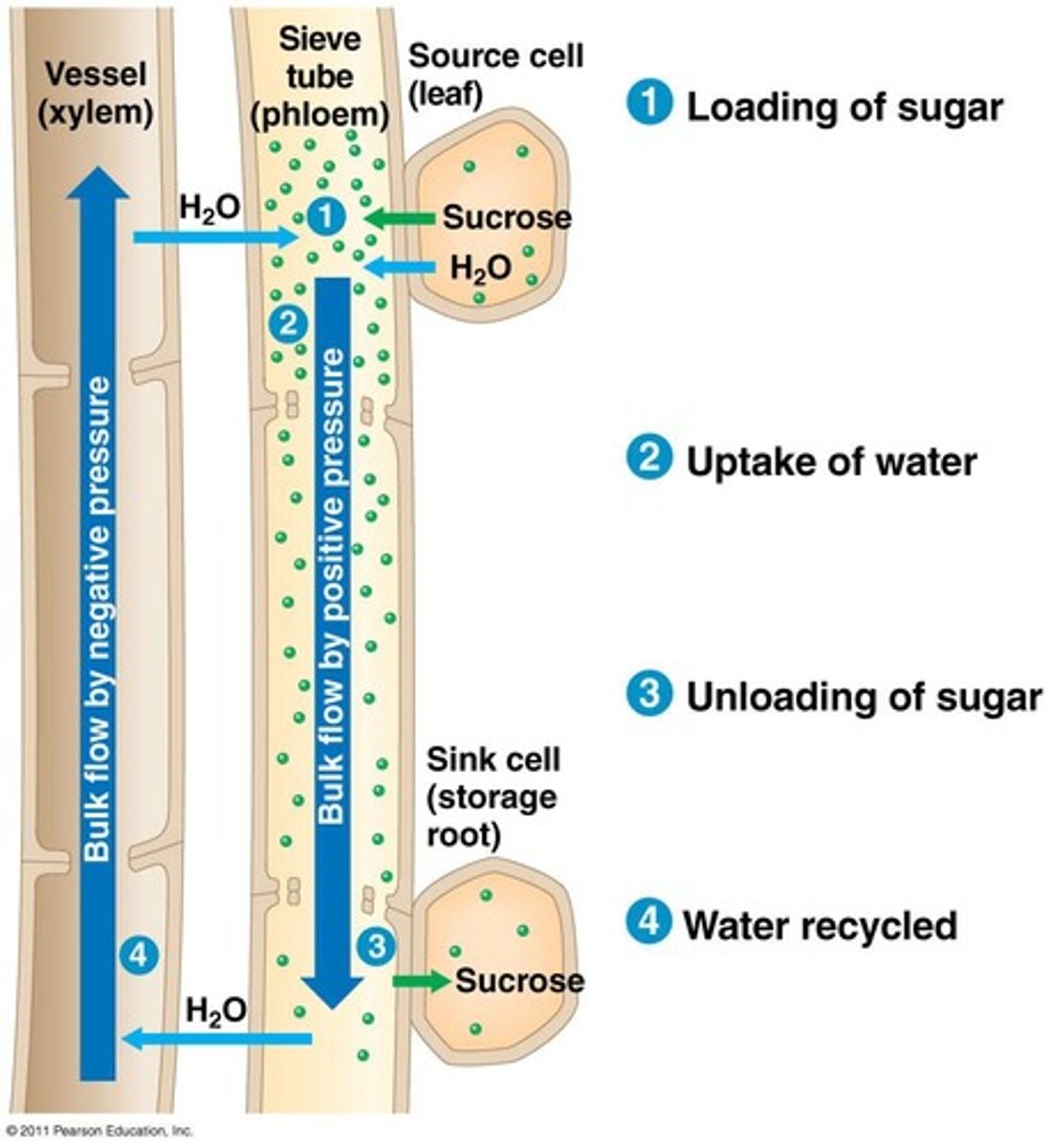
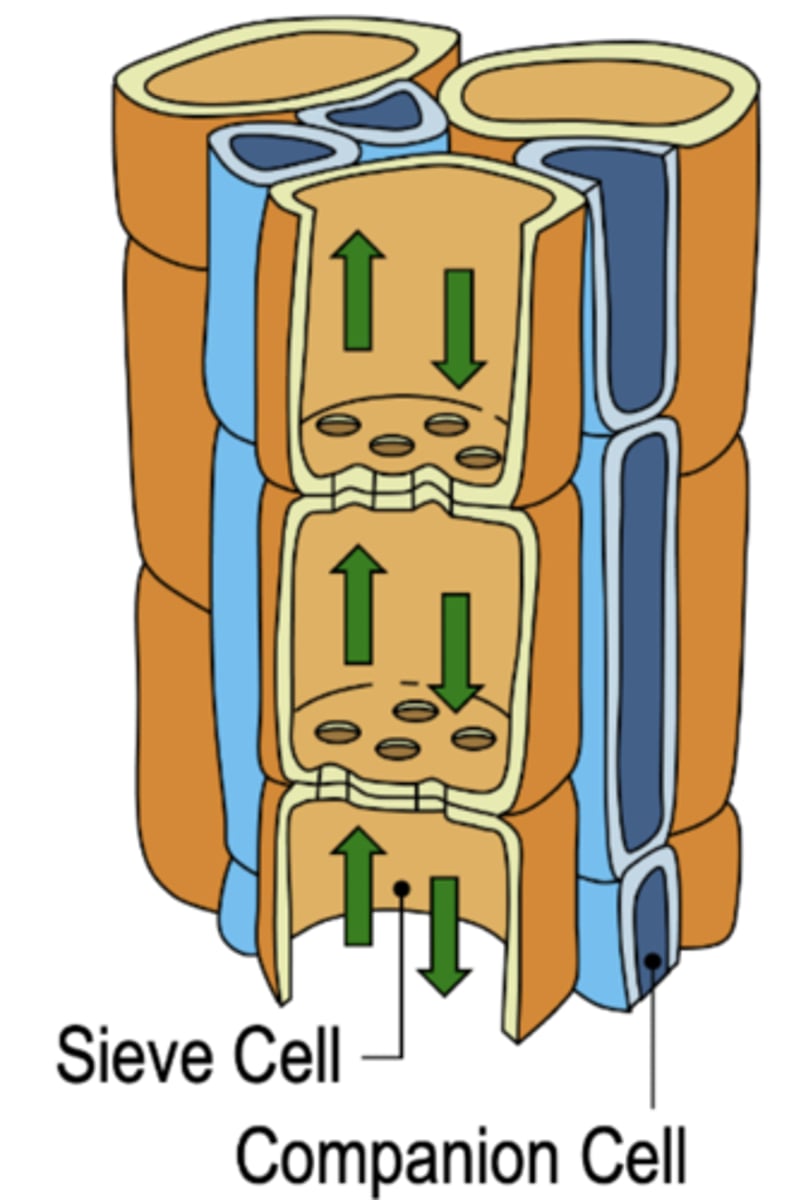
Pressure-Flow/Bulk Flow Hypothesis
1. Sugars are produced in the leaves (photosyntheis)
2. Sugar is transported into companion calls vis ACTIVE TRANSPORT or a POLYMER TRAP MECHANISM
3. Water moves passively into sieve tube member from xylem by OSMOSIS
4. High turgor pressure causes pressure-flow
5. Sugar actively unloaded at sink
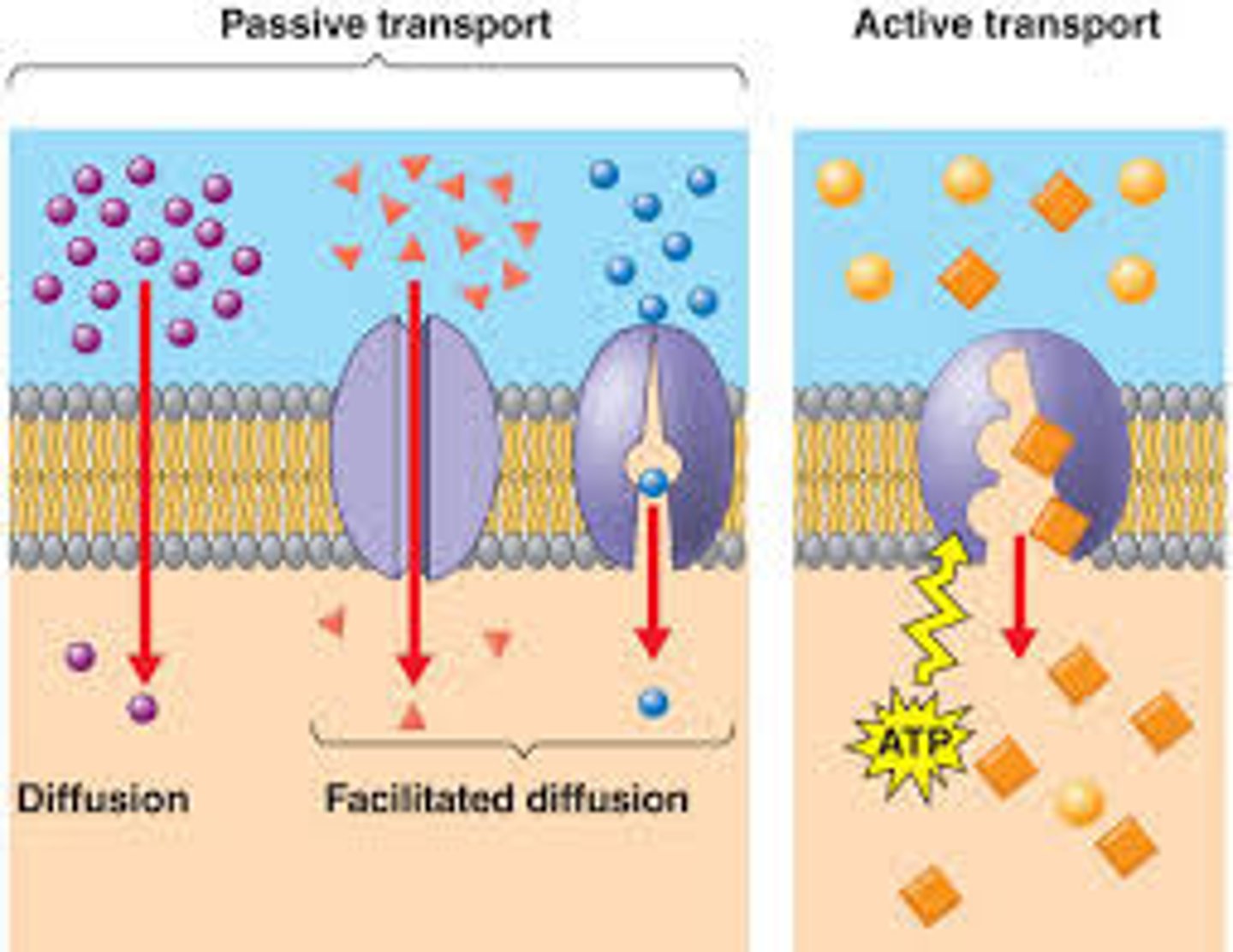
Passive Transport
passive: high to low, no energy, diffusion (osmisis);
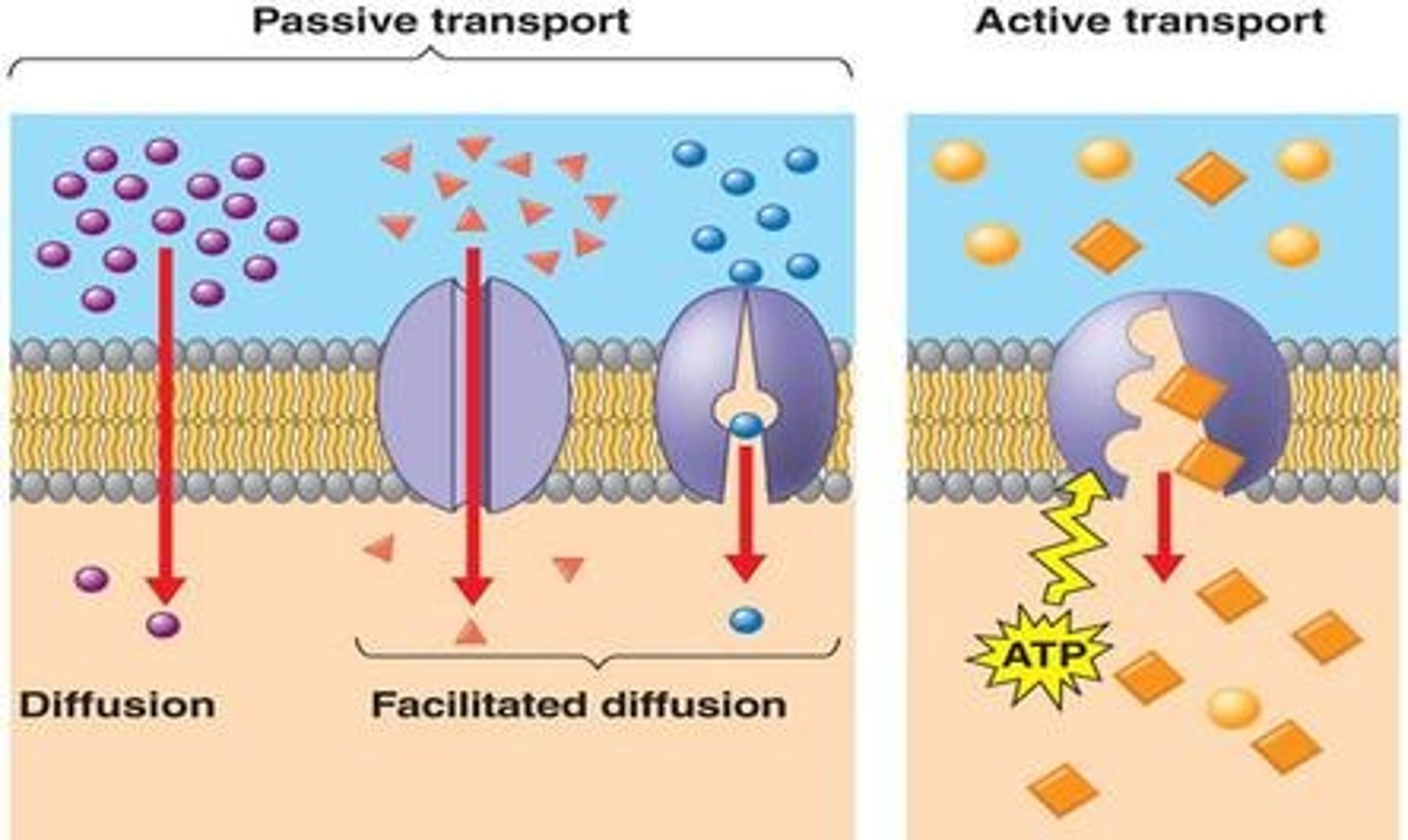
Active Transport
active: low to high, energy, endocytosis, ATP is here!!!!
Active Transport goes against the gradient and requires ATP, while passive does not.
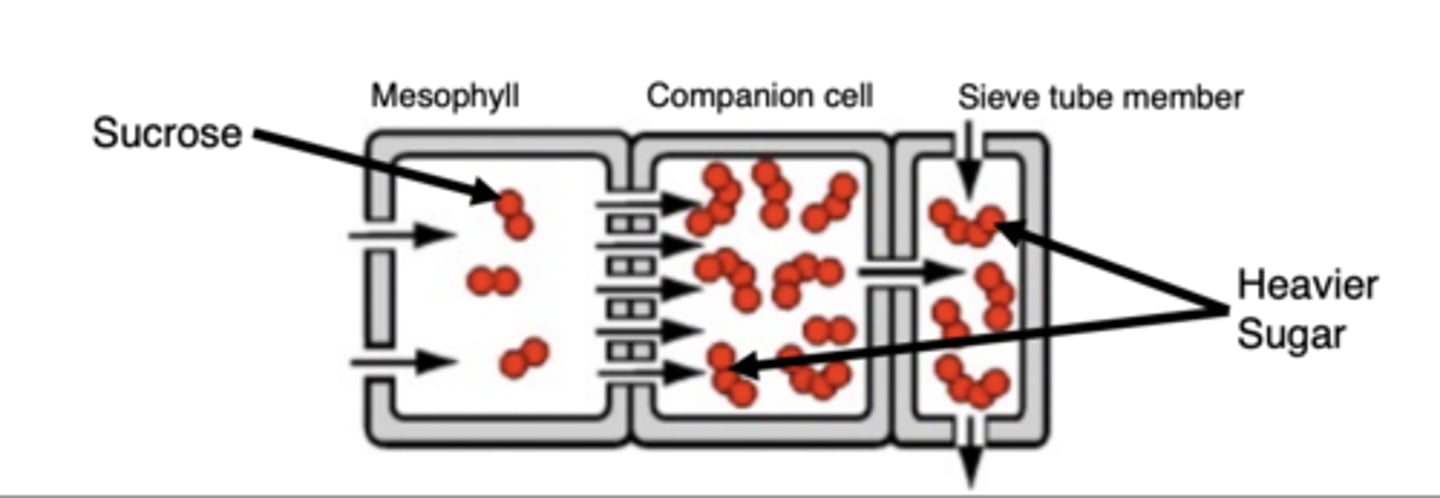
Polymer Trap Mechanism
1. Sucrose accumulates inside leaf mesophyll cells
2. Transported into companion cells via diffusion
3. Sucrose is polymerized into a heavier sugar
4. Heavier sugar is unable to diffuse back into mesophyll, concentration builds up, diffuses into sieve tube members
Translocation: Phloem
-Energetically demanding process
-Minerals, amino acids, hormones
-Materials can go either up or down
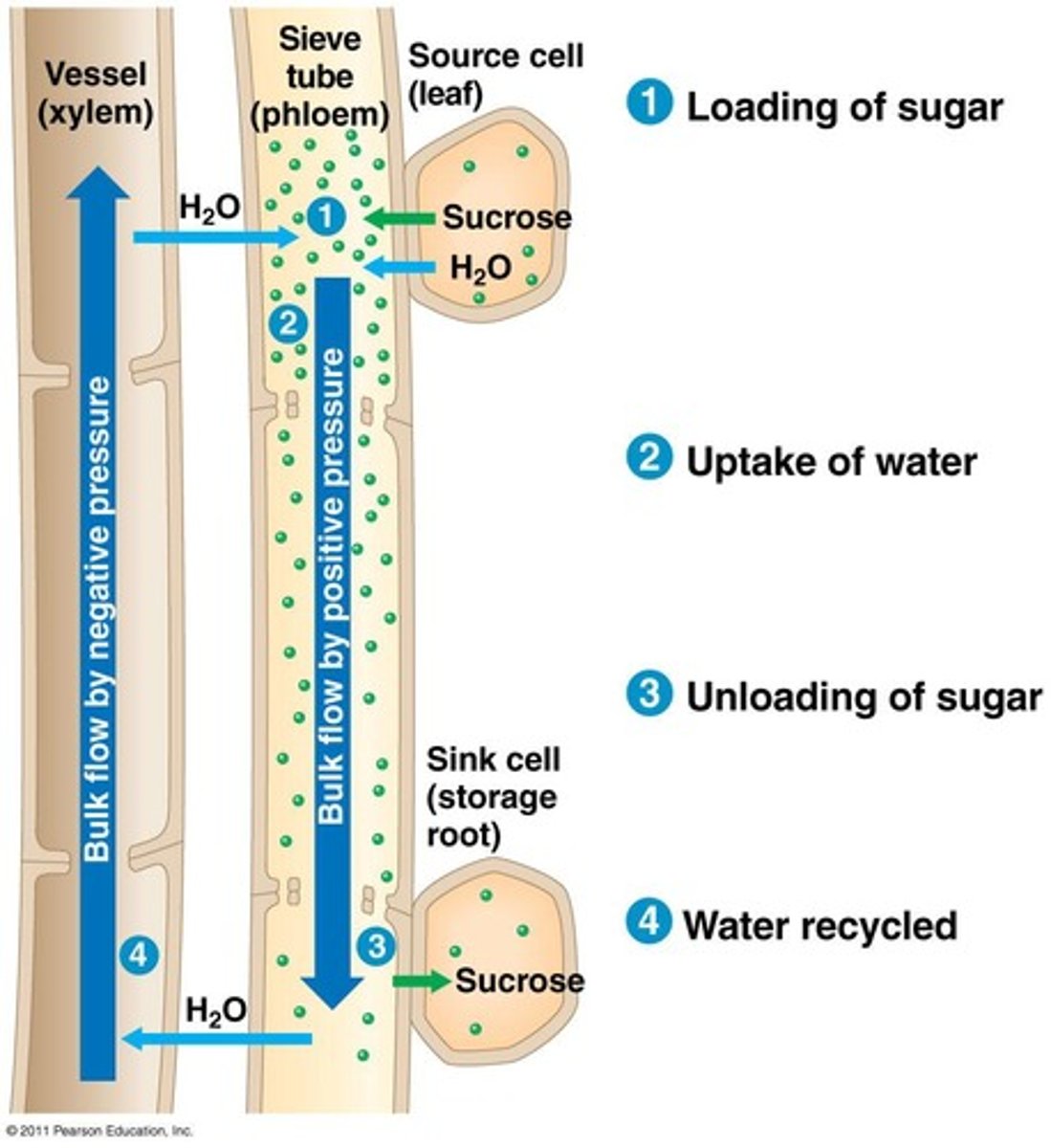
1. What is causing water to rise in the xylem?
cohesion-tension theory
2. What is happening in the leaf?
Photosyntheisis - Creation of sugar
3. Why does water move into the phloem?
1. Active Transport
2. Polymer tract mechanism
4. What causes phloem sap to move in the sieve tube member?
1. Active Transport
2. Plants have energy to transport
5. Name 3 parts of the plant that might be sinks
1. roots, stems, fruits
6. Where are 2 places energy is required?
Phloem sieve tube, active transport (?)
Maple Trees
sugar made during the summer is stored in the stem, roots, and XYLEM
- sugar water throughout the tree prevents freezing.
-sugar moves upward when new leaves are made in the spring
Where does a plant's mass come from?
Carbon Dioxide
Why do cells need energy to perform work and reproduce?
-For sunthesize protiens and complex molecules.
-cellular division (Growth)
-Active transport (movement of substances between cells)
-mentabolism (harnessing stored energy)
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate - Molecule that powers reactions in cells.
-Universal currency of biological energy
-ATP stores potential energy in chemical bonds
NADPH
An electron carrying molecule
NADP+
the electron carrying molecule - but low-energy state - oxidized
Chlorophyll
most important pigment involed in photosyntheisis
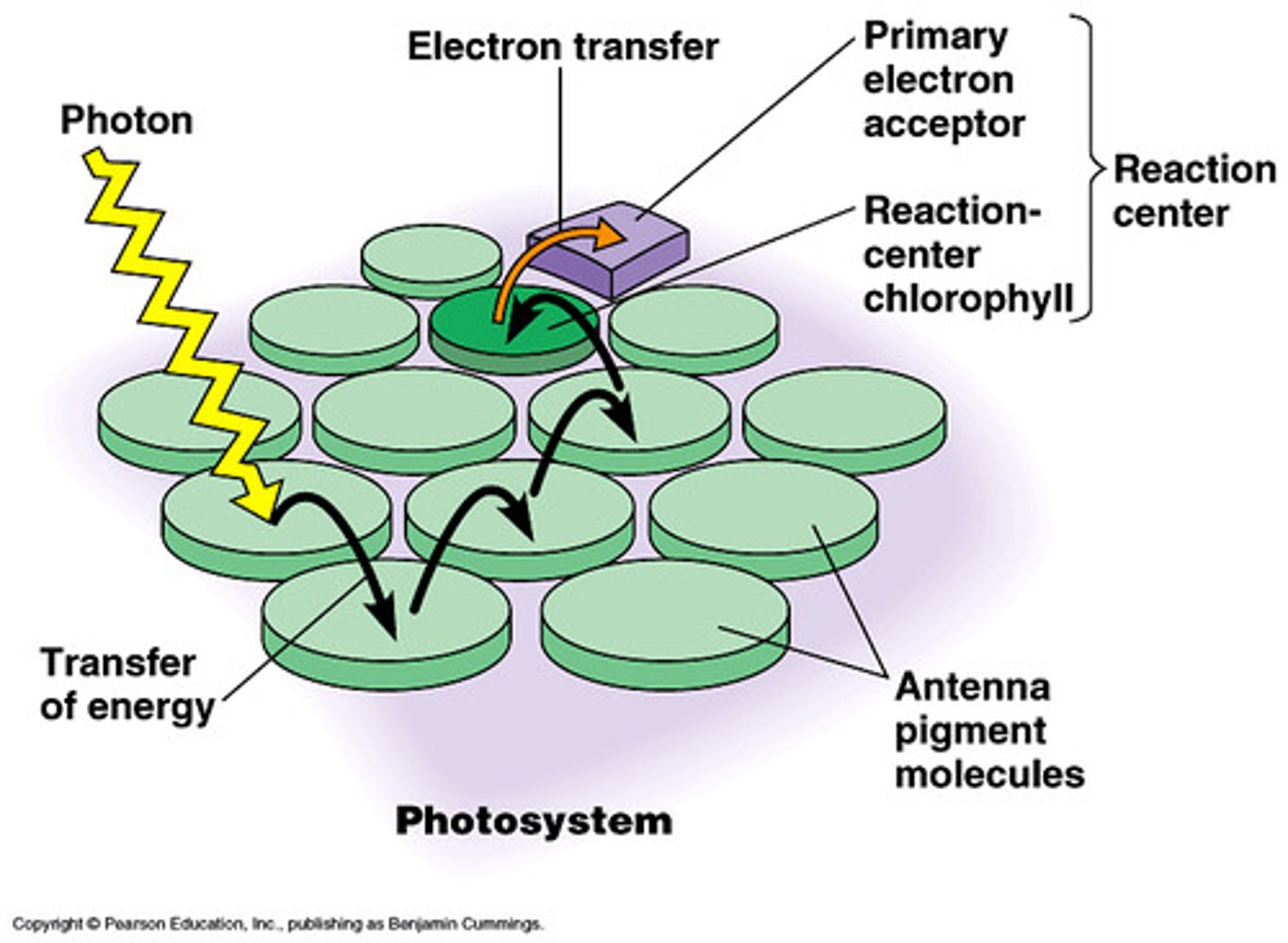
- embedded in thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts
- captures light energy, transfers electrons into photosytems (chemical reaction complexes)
Different pigmens absorb different _________ __ _____ ___
Wavelengths of visible light
Photosystems
Assemblages of chlorophyll and other pigments (carotenoids) closely bound to proteins, enzymes, and election carriers necessary for chemical reactions.
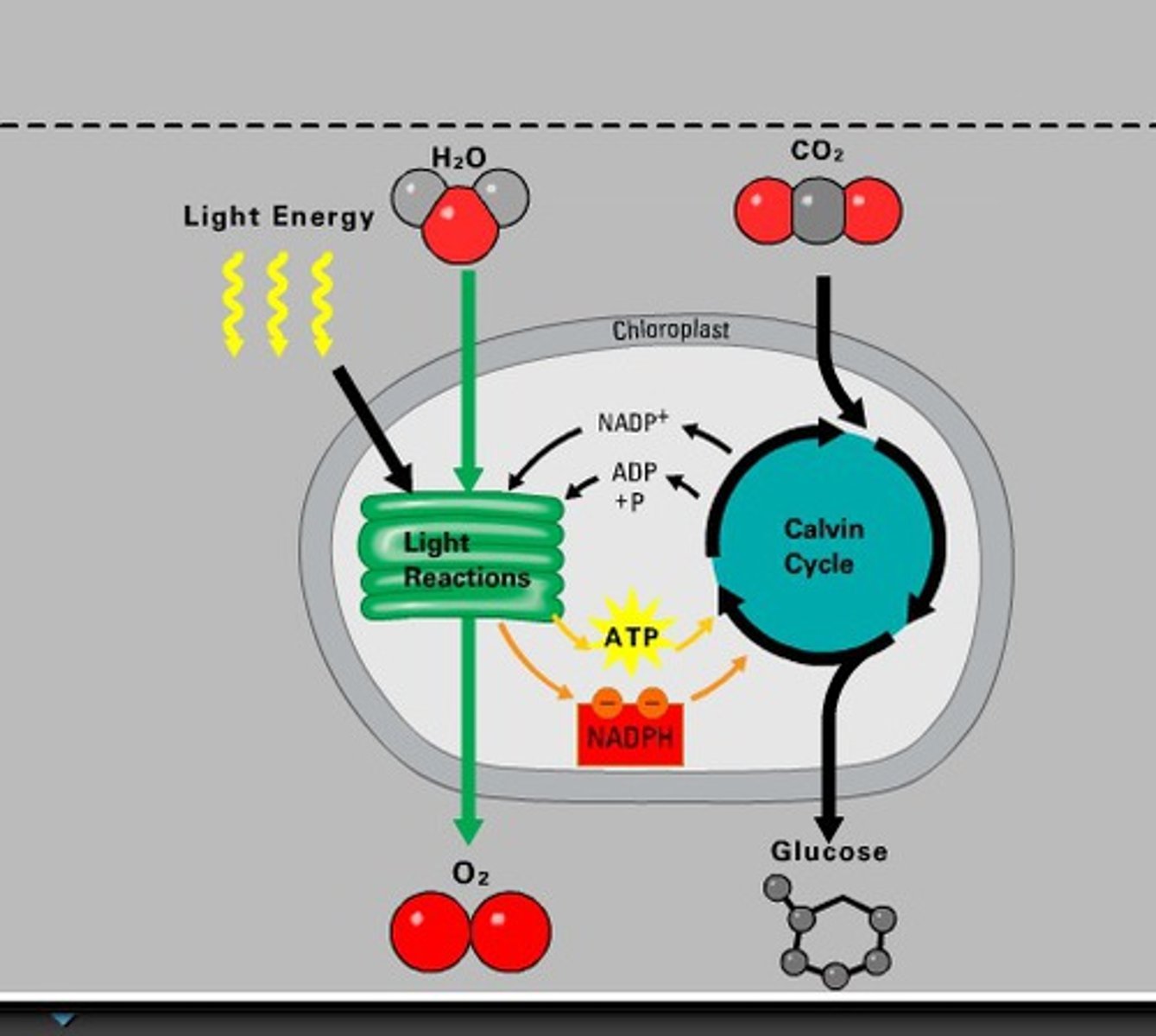
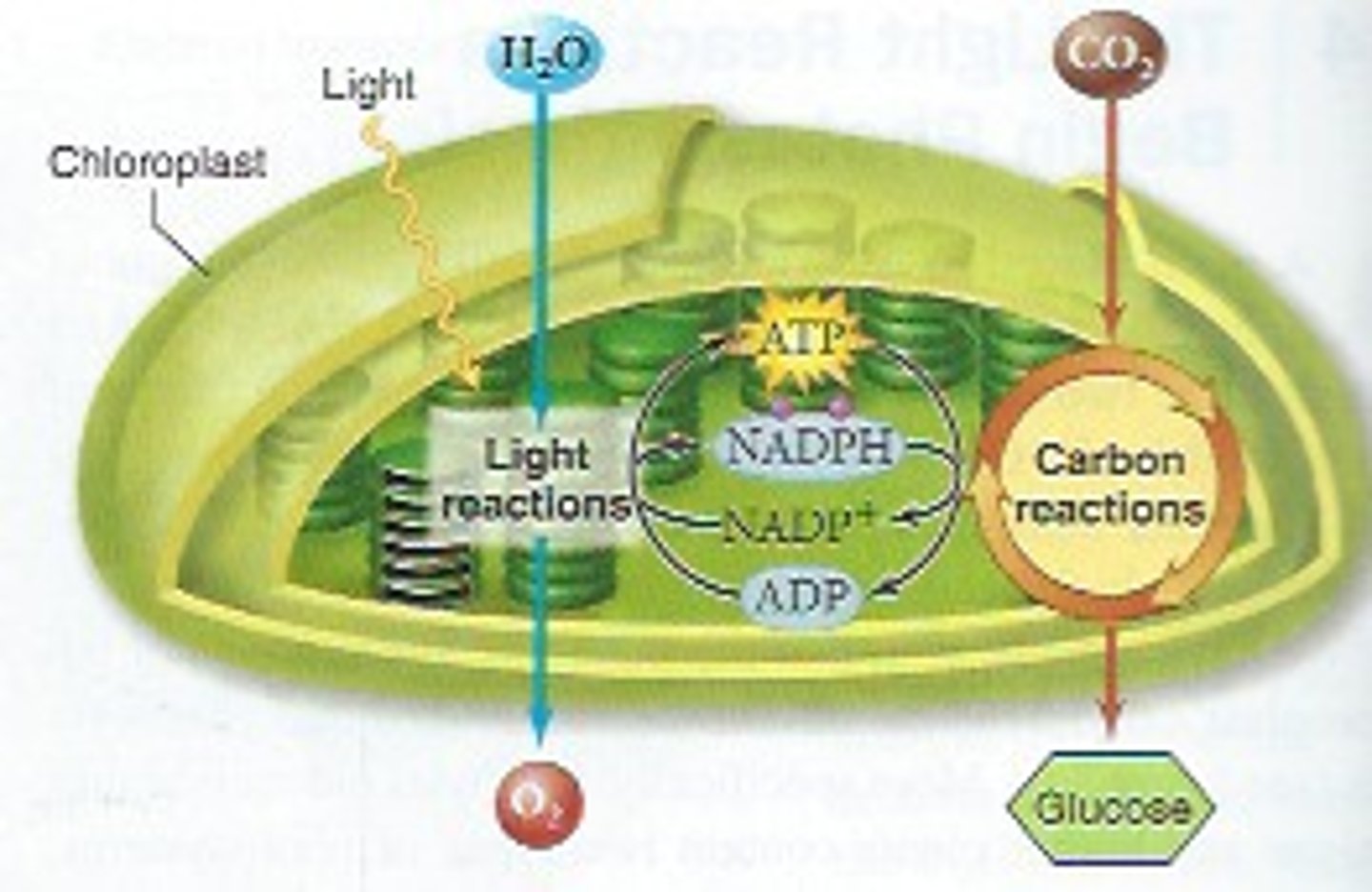
Light Dependent Reactions
happen in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast.
IN:
Water, light, NADP+, ADP
OUT: Oxygen, H+
NADPH, ATP
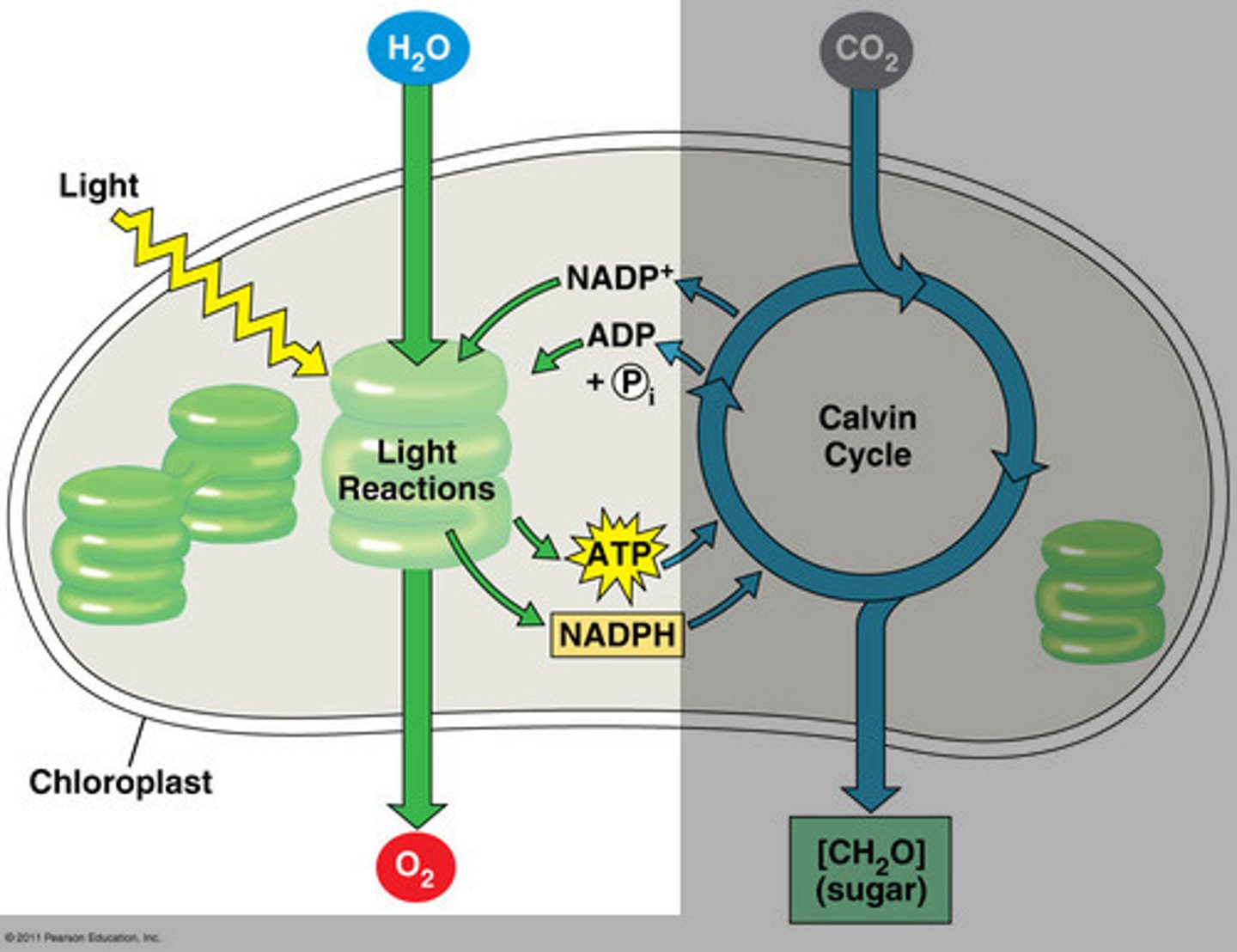
ATP Synthetase uses ____ concentration gradient to synthesize ____
H+, ATP