AP Macro Unit Four: Financial Sectors
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Last updated 5:55 PM on 3/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
Financial Assets
* stocks (ownership of a company)
* bonds (loan to a company)
* money (most LIQUID asset)
* bonds (loan to a company)
* money (most LIQUID asset)
2
New cards
Liquid Assets
Assets that are easily spent
3
New cards
Functions of Money
* medium of exchange (can be used to buy goods/services)
* Unit of Account (standard of value)
* Store of Value (value of work is stored in dollars)
* Unit of Account (standard of value)
* Store of Value (value of work is stored in dollars)
4
New cards
Real vs. Nominal
The Fisher Formula →i = r + π
* i → Nominal Interest Rate
* r → Real Interest Rate
* ***π → Inflation Rate***
* i → Nominal Interest Rate
* r → Real Interest Rate
* ***π → Inflation Rate***
5
New cards
Unexpected Inflation
Borrowers that were HELPED pay a lower real rate of interest
Lenders that helped are HURT b/c they’re paid a lower real rate of interest
\
GDP/Wages → %Change in Nominal = %Change in Real - π
\
\*\* Difference between real and nominal is inflation
\*\* Nominal has inflation, real DOES NOT
Lenders that helped are HURT b/c they’re paid a lower real rate of interest
\
GDP/Wages → %Change in Nominal = %Change in Real - π
\
\*\* Difference between real and nominal is inflation
\*\* Nominal has inflation, real DOES NOT

6
New cards
Measures of Money
M0 (Monetary Base) → bank reserve (not money) and currency (money)
M1 (Money) → Currency and checkable deposits, etc.
M2 (Money and Near Money) → M1 + Savings Deposits, etc.
M1 (Money) → Currency and checkable deposits, etc.
M2 (Money and Near Money) → M1 + Savings Deposits, etc.
7
New cards
Bank Balance Sheets
* Assets ALWAYS equal liabilities in a Bank Balance Sheet
\
Assets include
* Total Reserve (required reserves and excess reserves)
* Loans Given
* The Bank Itself
\
Liabilities include
* Demand Deposits (checkings accounts from people)
* Savings Deposits
* Owner Equity (owed to owners)
* Loans owed to banks
\
Assets include
* Total Reserve (required reserves and excess reserves)
* Loans Given
* The Bank Itself
\
Liabilities include
* Demand Deposits (checkings accounts from people)
* Savings Deposits
* Owner Equity (owed to owners)
* Loans owed to banks
8
New cards
Required Reserves
Percentage of demand deposits **set by the Federal Reserve**
(I think it has to do with the FDIC during FDR’s presidency)
(I think it has to do with the FDIC during FDR’s presidency)

9
New cards
Excess Reserves
Money the bank can loan out
* Total Reserves minus Required equals Excess
* Total Reserves minus Required equals Excess
10
New cards
Money Multiplier
How many dollars worth of new loans, deposits, and money can be created from excess reserves
\
1/Required Reserves
Example: 1/10% = 10
\
\*\* For deposits, include the original deposit (if a deposit or another money)
* Money multiplier tells us the MAXIMUM number of deposits, loans, and new money, BUT numbers are usually much lower due to Leakages
\
1/Required Reserves
Example: 1/10% = 10
\
\*\* For deposits, include the original deposit (if a deposit or another money)
* Money multiplier tells us the MAXIMUM number of deposits, loans, and new money, BUT numbers are usually much lower due to Leakages

11
New cards
Leakages
* banks usually hold excess reserves
* consumers might hold cash, rather than depositing
* consumers might hold cash, rather than depositing
12
New cards
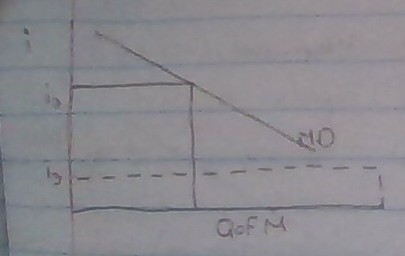
Money Demand
Nominal interest rate is the opportunity cost for holding money
* When the nominal interest rates are high, people demand fewer dollars b/c the opportunity cost of holding your money increases
\
* when Nominal interest rates fall, the demand for money will increase
* When the nominal interest rates are high, people demand fewer dollars b/c the opportunity cost of holding your money increases
\
* when Nominal interest rates fall, the demand for money will increase
13
New cards
Asset Demand for Money
The desire to hold wealth as money, instead of other assets such as stocks or bonds
14
New cards
Transaction Demand for Money (Determinates of Money Demand)
Money is needed in order to buy goods/services
GDP = C + Ig + G + Xn
Price Levels
\
\* if either of the two facets change, the money demand will increase or decrease
GDP = C + Ig + G + Xn
Price Levels
\
\* if either of the two facets change, the money demand will increase or decrease
15
New cards
Money Supply
Determined by the actions of the Federal Reserve
* looks like the long-run aggregate supply in that its vertical
* looks like the long-run aggregate supply in that its vertical
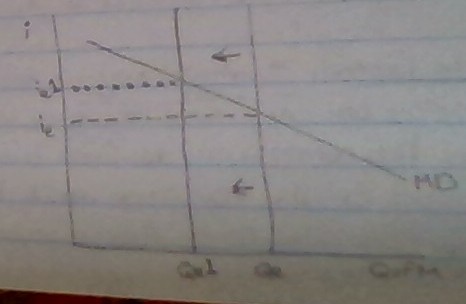
16
New cards
Open Market Operations
The buying/selling of government bonds or stocks
17
New cards
Discount Rate
Interest rate the Federal Reserve charges banks
18
New cards
Reserve Requirements (expounded)
The percentage of checkable deposits (money that cannot be loaned out)
\
\*\* The FED targets the __Federal Funds Rate__
* Federal Funds Rate is the rate at which banks charge each other
\
\*\* The FED targets the __Federal Funds Rate__
* Federal Funds Rate is the rate at which banks charge each other
19
New cards
Monetary Policy is impacted by
Multiplier
20
New cards
Expansionary MONETARY Policy
Buy bonds, lower the discount rate, or lower the reserve requirement
* lower Nominal Interest, more Gross Investment
\*\* Increases in Gross Investment shift AD curves to the right, back to full employment
\
\*\* When in a recessionary gap
* lower Nominal Interest, more Gross Investment
\*\* Increases in Gross Investment shift AD curves to the right, back to full employment
\
\*\* When in a recessionary gap
21
New cards
Contractionary MONETARY Policy
Sell bonds, raise the discount rate, raise the reserve requirements
* Higher Nominal Interest, less Gross Investment
\
\*\* Decreases in Gross Investment shift AD curves to the left, back to full employment
\
\*\* When in an inflationary gap
* Higher Nominal Interest, less Gross Investment
\
\*\* Decreases in Gross Investment shift AD curves to the left, back to full employment
\
\*\* When in an inflationary gap
22
New cards
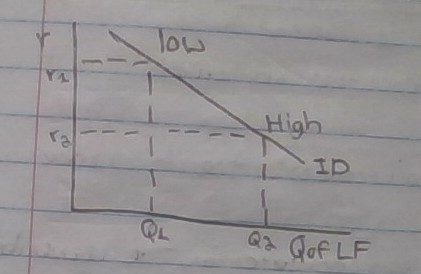
Demand for Loanable Funds
At high interest rates, low quantities of investment will be demanded
\
\*\* Real interest quantity of Loanable Funds Investment Demands - demand by business for Gross Investment
\
\*\* Real interest quantity of Loanable Funds Investment Demands - demand by business for Gross Investment
23
New cards
Shifts in Investment Demand (Loanable Funds Demand Determinates)
Anything that impacts the profit potential of new investments
* changes in economic outlook
* investment tax credits
* changes in economic outlook
* investment tax credits
24
New cards
Savings Supply
Money saved that’s available for loans
* at high interest rates, the quantity of loanable funds will also rise
* at high interest rates, the quantity of loanable funds will also rise
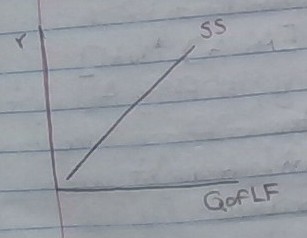
25
New cards
Shifts in Savings Supply
* Disposable income
* Economic outlook
* Foreign investment
* Economic outlook
* Foreign investment
26
New cards
Crowding Out
An increase in the government deficit will increase interest rates and reduce Ig (Investment)
\
\[increase in demand or decrease in supply makes interest rates higher\] → less Gross Investment
\
\*\* Less long-term development
\
\[increase in demand or decrease in supply makes interest rates higher\] → less Gross Investment
\
\*\* Less long-term development
27
New cards
Budget Surplus
Government won’t have to borrow as much money, which decreases interest rates and increases Ig
\
\[decreased demand/increased supply\]
\
\*\* More long-term development
\
\[decreased demand/increased supply\]
\
\*\* More long-term development