BPK 142: lec 2 (anthropometry and body comp)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the top 3 elements that make up the body?
Oxygen = 65%
Carbon = 18.5%
Hydrogen = 9.5%
What are the 4 types of tissue in the body?
Work together to comprise organs
Nervous
Epithelial
Muscle
Connective
Name the 3 structural components in the body
Distribution of components depends on sex, age, genetics + lifestyle
Muscle
Skeleton (bone)
Fat
What does the two-component model state?
Fat and Fat-free mass in body
FFM = bone, muscle, water, organs + connective tissue
Body mass = FM + FFM
What does the four component model state?
Chemical model
Fat
Protein
Mineral
Water
Anthropometry
Quantitative measurement of body size + proportions
To understand physical variation + body comp
Why assess body composition?
Monitor changes in body comp with growth
Establish optimal ranges for health
Track goals for weight management or strength
Suitable body comp = good health
Eating disorders
Disturbance in eating behavior that jeopardizes physical + psychological health
Essential fat
Required for normal functioning
Structural components of cell membranes
Synthesis of hormones
Transport of fat-soluble vitamins
Storage fat
Stored in adipose (connective) tissue for energy supply
Also stored underneath skin (subcutaneous) in abdominal cavity + around organs
Males vs female fat averages
Females have sex specific fat depots
Breasts, pelvic regions, thigh
Males = taller, heavier + larger muscles with LOWER fat
Storage fat
F= 15%
M= 12%
Essential fat
F= 12%
M= 3%
Is the android (apple) deposition pattern (loco of storage fat) a male or female pattern?
Male pattern
Upper torso + abdomen
Is the gynoid (pear) deposition pattern (loco of storage fat) a male or female pattern?
Female pattern
Thighs, hips, butt
NOTE!!
After menopause females begin depositing more fat in the abdominal area
What BMI indicates obesity for men and women? Are they different?
BMI ≥ 30
Body Fat % ≥ 20% (men) or 30% (women)
Adult obesity in Canada
24% (~6 million adults) are obese
37% (~9 million adults) are overweight
Total number overweight or obese >60%
Overweight percentages are increasing every year
Childhood obesity in Canada
Children now are taller, heavier, fatter and weaker
Obese kids ages 6- 9 have 55% chance of becoming obese as adults
What are the 5 causes of the obesity epidemic?
Caloric intake exceeds caloric expenditure
Eating more calories
Decreased physical activity
Cars, work from home, TV, etc
Increased consumption of calories
Processed food, high sugar, etc
Social environment
Pressure to consume
Biology
Genes don’t cause obesity but can make you more susceptible
How does body composition change with aging?
Changes associated with aging in industrialized society:
Increased fat mass
Decreased muscle mass (sarcopenia)
Decreased bone mass
Slowed down w/ exercise + good diet
Fragility in elderly women is related to failure to obtain an optimal level of bone mass during childhood
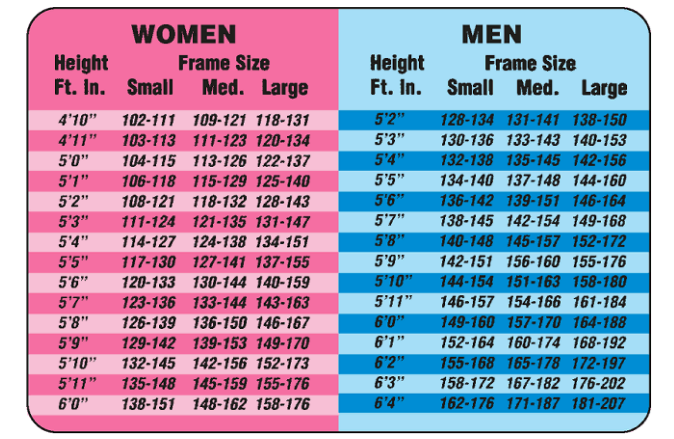
Describe height/weight tables
Desirable weight with regard to the lowest death rates
Predicted from tables developed by insurance actuaries
Height/weight table criticisms?
Do not consider body comp; they estimate health risk
Data comes from white middle class U.S adults 25-59 yrs
NO accepted method for determining frame size

Describe body density and volume measurements
Density = mass/volume
Body density varies with amount of body fat
Fat 0.91 g/mL
Water 1.0 g/mL
Lean tissue 1.10 g/mL and higher
Greater proportion of fat = lower body density
Use underwater weighing or volumetry to measure body volume
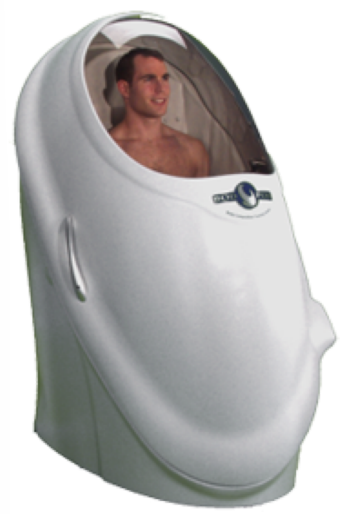
How is the air-displacement plethysmography used for finding body density and volume measurements?
Subject is immersed in a closed air-filled chamber (plethysmograph)
Measure volume of air displaced inside the closed chamber
What is the SIRI equation used for? What does is determine?
Used for body density and volume measurements
To determine % body fat
SIRI equation assumptions?
The human body has two compartments - fat and nonfat
Each of these compartments has densities which are known constants. Assume that:
Fat density = 0.90 g/ml
Nonfat density = 1.10 g/ml
Why is densitometry not used as a universal criterion for prediction of percent fat/ body density?
Hydrostatic weighing was a universal method (gold standard)
Cadaver studies have shown the density of nonfat compartment varies as a function of
Age, sex + race
Nonfat density value of 1.10 g/ml is not universally applicable
Describe weight/height indices (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Used as an indicator of obesity
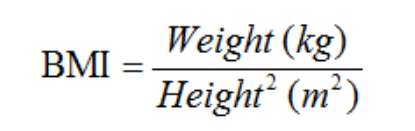
What are the 3 BMI classifications for adults?
BMI less than 18.5 = underweight
BMI of 25.0 to 29.9 = overweight
BMI of 30 or higher = obese
Weight/height indices (BMI) criticisms
BMI does not consider
Body composition
Fat distribution
Amount of visceral fat in dif ethnic groups
Chinese and South Asian people have greater concentration of abdomen (visceral fat) compared to white people
BMI assumed to be closely associated with body fatness and morbidity/mortality
However, overweight does not always mean over-fat
Body builders obese according to BMI
Describe waist circumference
Simple + cheap but effective
Combination of BMI and waist circumference also used (CSEPPATH)
Skinfold measurements
Relationship between fat in depots directly beneath the skin and body density
Skinfold measurements; 2 ways to use
Use sum of a number of skinfolds as an indication of relative fatness among individuals
Compare "before" and "after" in the same individual
Use fat folds in conjunction with equations or tables to predict percent body fat
Skinfold measurement assumptions
Constant densities in a two-compartment model
Proper identification of measurement site and proper measurement technique
Constant compressibility of the skinfold
Fixed adipose tissue patterning
Fixed proportion of internal to external fat
Describe the o-scale system
O Scale developed to combat error of skinfolds
Requires eight skin folds, ten girths, four skinfold-corrected girths and two bone breadths
Provides: Adiposity rating + Proportional weight rating
Describe bioelectrical impedance analysis
Electrical impedance units
Used to measure resistance to flow of electricity in body
Impedance is greater in adipose tissue (14 - 22% water) than in bone and muscle (71 - 75% water)
Higher electrical impedance = fatter the subject
Bioelectrical impedance analysis criticisms
Daily fluctuations in water content from exercise, dehydration, eating and drinking need to be standardized to obtain optimum impedance results
Clients must adhere to strict pretest guidelines
To yield valid estimates of their body composition
Subcutaneous vs visceral fat
Subcutaneous fat = found under skin
Visceral fat = deep within abdominal cavity + surrounds your organs