14 - epidemiology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
human health
complete physical, mental, and social well-being
not just absence of disease
public health cycle
surveillance → studies → evaluate interventions
epidemiology
basic science of public health
studies factors which determine presence + absence of diseases + disorders
Ascaris model
direct
no IH
no amplification
Ascaris step 1
adults in SI
Ascaris step 2
unfertilized + fertilized eggs in feces
Ascaris step 3
embryonated eggs with L3 larvae
Ascaris step 4
ingestion of embryonated eggs
Ascaris step 5 + 6
hatched larvar enter circulation + migrate to lungs
Ascaris step 7
larvae coughed up + swallowed
re-enters gastrointestinal tract
matures in SI
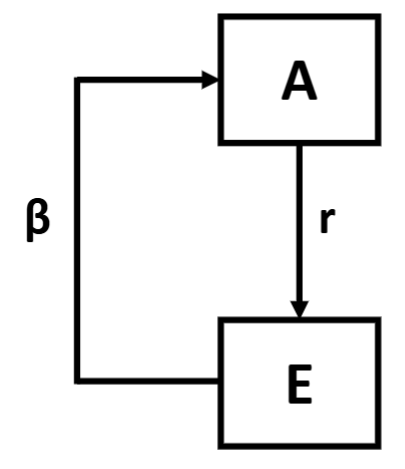
label:
A, E, r, rA and β
A = adults
E = eggs
r = egg prod/ adult
rA = net reproductive rate
β = probability of egg making it to next host
time 0:
A = 10 adults
r = 20 eggs/ adult
rA = ?
β = 0.5
rA = 20 × 10 = 200 eggs
time 1:
rA x β = ?
Total # A in population at end of time 1 = ?
new rA = ?
β = 0.5
rA x β = 200 × 0.5 = 100 adults
Total # A in population at end of time 1 = 10 + 100 = 110
new rA = 20 × 110 = 2200 eggs
time 2:
rA x β = ?
Total # A in population at end of time 2 = ?
rA x β = 2200 × 0.5 = 1100 adults
Total # A in population at end of time 2 = 110 + 1100 = 1210 adults
μ1
probability of adult worm death
μ2
probability of egg death rate
Aμ1
number of adult worms removed from population
Aμ2
number of eggs removed from pop.
model components - parasite reproduction + transmission
rA and β
model components - parasite elimination
Aμ1 and Eμ2
Ascaris control
increase parasitic elimination
decrease parasite transmission
chemo + education
how to increase parasitic elimination
Aμ1: increase μ2 by treating host
Eμ2: increase μ2 by killing eggs in ext env
how to decrease parasite transmission
lower:
contacts
# eggs
# hosts
rA
Ro
basic reproductive ratio
avg # of 2° cases a typical single infected case will cause
pop w/ NO immunty
NO interventions
Ascaris Ro
number of eggs produces by adult that surviveto produce reproductive adults
threshold level of survival is Ro = 1
eradication Ro < 1
Ro of:
smallpox
ascaris
measles
malaria
smallpox = 2
ascaris = 5
measles = 8
malaria = 50
eradication
no longer exists anywhere in world
not rlly realistic
elimination
localized eradication
doesn’t exist in specific location
smallpox eradication
natural exposure → long- lasting immunity
smallpox eradication - vaccine
long-lasting protective immunity
1 dose
easy to administer
efective delivery + education campaign
fear of disease → public acceptance
why are parasites difficult to eradicate?
no vaccine available for any
which parasite is close to being eradicated
dracunculus
not bc of vax, bc of control + other measures
how would parasites become eradicated?
education + control, NOT VACCINE
Enterobius vermicularis types of infection
retroinfection and autoinfection
retroinfection
eggs hatch in perianal area
L1 migrate back to rectum + colon
Enterobius vermicularis step 1
eggs on perianal fold
Enterobius vermicularis step 2
larva in eggs mature w/in 4-6 hrs
embryonated eggs ingested by human
Enterobius vermicularis step 3
larvae hatch in SI
Enterobius vermicularis step 4
adults in lumen of cecum
Enterobius vermicularis step 5
gravid female migrates to perianal region at night to lay eggs
Enterobius vermicularis eggs
flattened side
Enterobius vermicularis adults
alae
female = pinworm
male = curved posterior
Enterobius vermicularis pathology
most asymptomatic
damage w/in intestine + around anus
inflammation + bacterial invasion
sleepless + irritability
Enterobius vermicularis diagnosis
scotch tape test
Enterobius vermicularis treatment
pyrantel, albendazole, mebendazole
how do young children contract Enterobius vermicularis?
sleeping → itch → fingers in mouth
airborne