lecture 24, the special sense organs
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
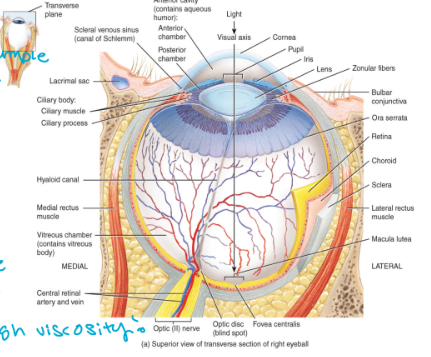
the eyeball has 6 primary components
fibrous tunic
the vascular tunic
the nervous tunic
the lens
the anterior chamber
the posterior segment
eyeball: 1. fibrous tunic
Consists of the sclera (white of the eye), the cornea (transparent portion of the eye)
Both are avascular connective tissue
Also consists of the conjunctiva which covers the anterior surface of the sclera
A vascular mucous membrane
Dilation of blood vessels in this layer results in blood shot eyes
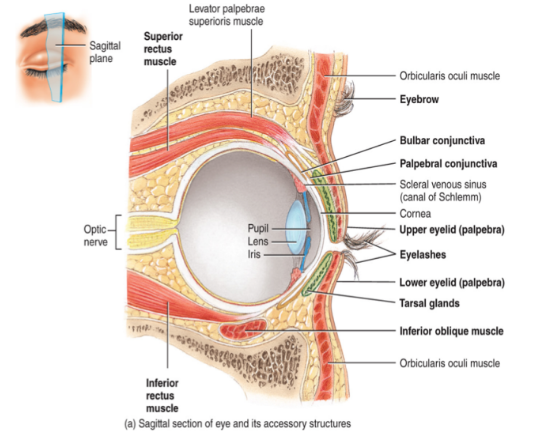
eyeball: 2. the vascular tunic
The iris (the colored part of the eye)
The choroid is highly vascular
Contains melanin which prevents the reflection and the scattering of light
Also contains the ciliary body
Consists of the ciliary muscle and the ciliary processes which control the shape of the lens and secrete aqueous humor
holds eye shape
chamber behind cornea

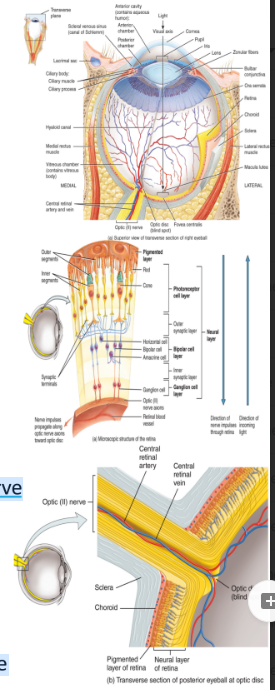
eyeball 3. the nervous tunica
The retina
Sensory portion of the eye
Consists of the outer pigmented layer and an inner neural layer consisting of three layers of neurons
i Photoreceptor neurons:
Rods: for black and white vision
Cones: for colored vision
more rods than cones
ii. Bipolar cells
iii. Ganglion cells:
Axons of these cells form cranial nerve II: the optic nerve
The fovea centralis is where light focuses
The greatest visual acuity is achieved here
The optic disc is the blind spot
This is where the optic nerve and blood vessels exit the eye (bundles of neurons)
eyeball: 4 . the lens
a transparent, avascular layer
cataracts occur when the lens becomes cloudy
can be caused by a number of different things
eyeball: 5. the anterior chamber
located anterior to the lens
contains the aqueous humor
very similar to blood plasma (take a sample)
replaced every 90 minuets (replenish)
drains into a sinus located at the junction between the sclera and the cornea
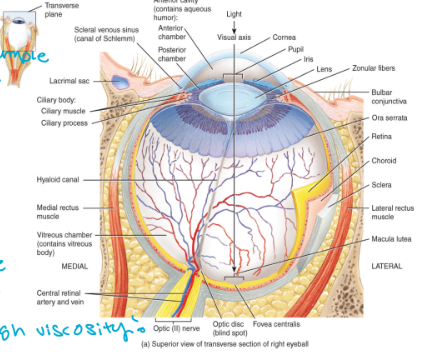
eyeball: 6. posterior segment
located posterior to the lens
contains the gel-like vitreous humor
this humor is not replace
big bubble of the eye
high viscosity
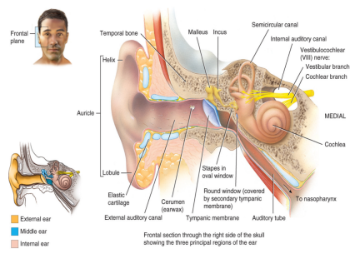
the ear
the external ear
the middle ear
the inner ear
the external ear
consists of the
auditory canal (meatus) (shunt sound in)
tympanic membrane (eardrum) (can rupture)
auricle: elastic cartilage covered in skin (heals poorly)
functions to conduct sound
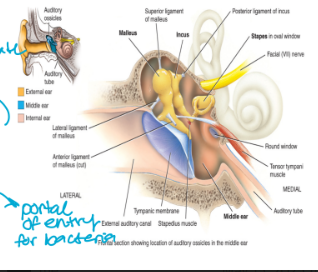
the middle ear
consists of the auditory ossicles
smallest bone in the body
malleus: located against the tympanic membrane of the external ear
incus
stapes: against the oval window of the inner ear
“mis”
also contains the eustachian tube (auditory tube)
connects to the nasopharynx
portal of entry for bacteria
functions to conduct sound
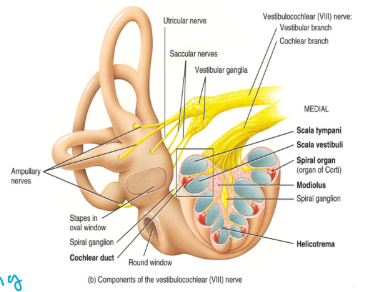
the inner ear
contains the vestibular nerve
also contains the bony (hard) and the membranous (soft) labyrinth
surrounds and protects the ear
a. the bony labyrinth:
contains the
semi-circular canals (not all in same orientation → do different things)
cochlea (“snail shell”
vestibule
lined with periosteum and contains perilymph (inside)
b. the membranous labyrinth:
contains the
semi-circular ducts within the canals: connect with the utricle
cochlear duct within the cochlea
utricle and the saccule within the vestibule
contains endolymph (hairs swish due to this)
the cochlea
this is coiled structure → there are 2.5 coils
there are three channels within each of coils
the scala vestibuli
the scala tympani
both 1 and 2 contain perilymph/are part of the boney labryinth
the scala media: the cochlear duct
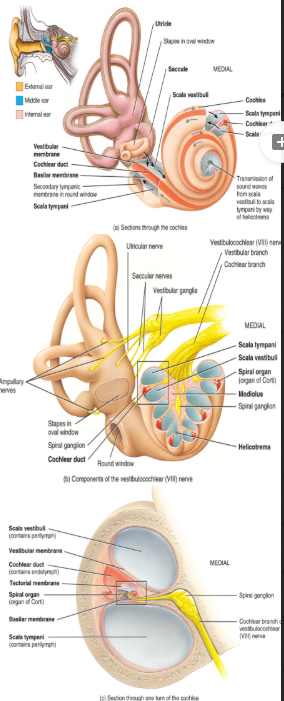
the cochlea: the scala vestibuli
located above the cochlear duct
the cochlea: the scala tympani
located below the cochlear duct
the cochlae: the scala media: the cochlear duct
A continuation of the membranous labyrinth: contains endolymph
The vestibular membrane: separates the cochlear duct from the scala vestibuli
The basilar membrane: separates the cochlear duct from the scala tympani
The tectorial membrane: covers hair cells of the spiral organ
All of the three components contain endolymph
the receptors are the hair cells that synapse with the
neurons → like cilia, extend into the endolymph
functions of the ear include
conduction of sound → the middle and external ear
hearing and equilibrium → the inner ear
the ear directs impulses to the brain via cranial nerve VIII → the vestibulocochlear nerve
branches into positional and hearing