ECO 2023 Exam 1 FSU Lee
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Scarcity
A situation in which unlimited wants exceed the limited resources available to fulfill those wants
Positive Economics
concerned with "what is," can be tested, and is objective
Normative Economics
concerned with what "should be," can NOT be tested, and is subjective.
Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics
Microeconomics is the study of economics at an individual, group or company level. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, is the study of a national economy as a whole.
Opportunity Cost
The highest valued alternative that must be given up to engage in an activity
Trade Creates Value
participants in markets are able to specialize in the production of goods and services that they have a comparative advantage in making. The values of goods are also subjective.
Private Property Rights
the concept that people have the right and privilege to control their possessions as they wish
Incentives of Private Property Rights
1. Cause owners to bear the opportunity costs of ignoring the wishes of others
2. Provide incentives for good stewardship
3. Create incentives for conservation or environmental quality
4. Hold owners accountable for their actions
5. Can align incentives so as to promote conservation versus extinction
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
A curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two products that can be produced.
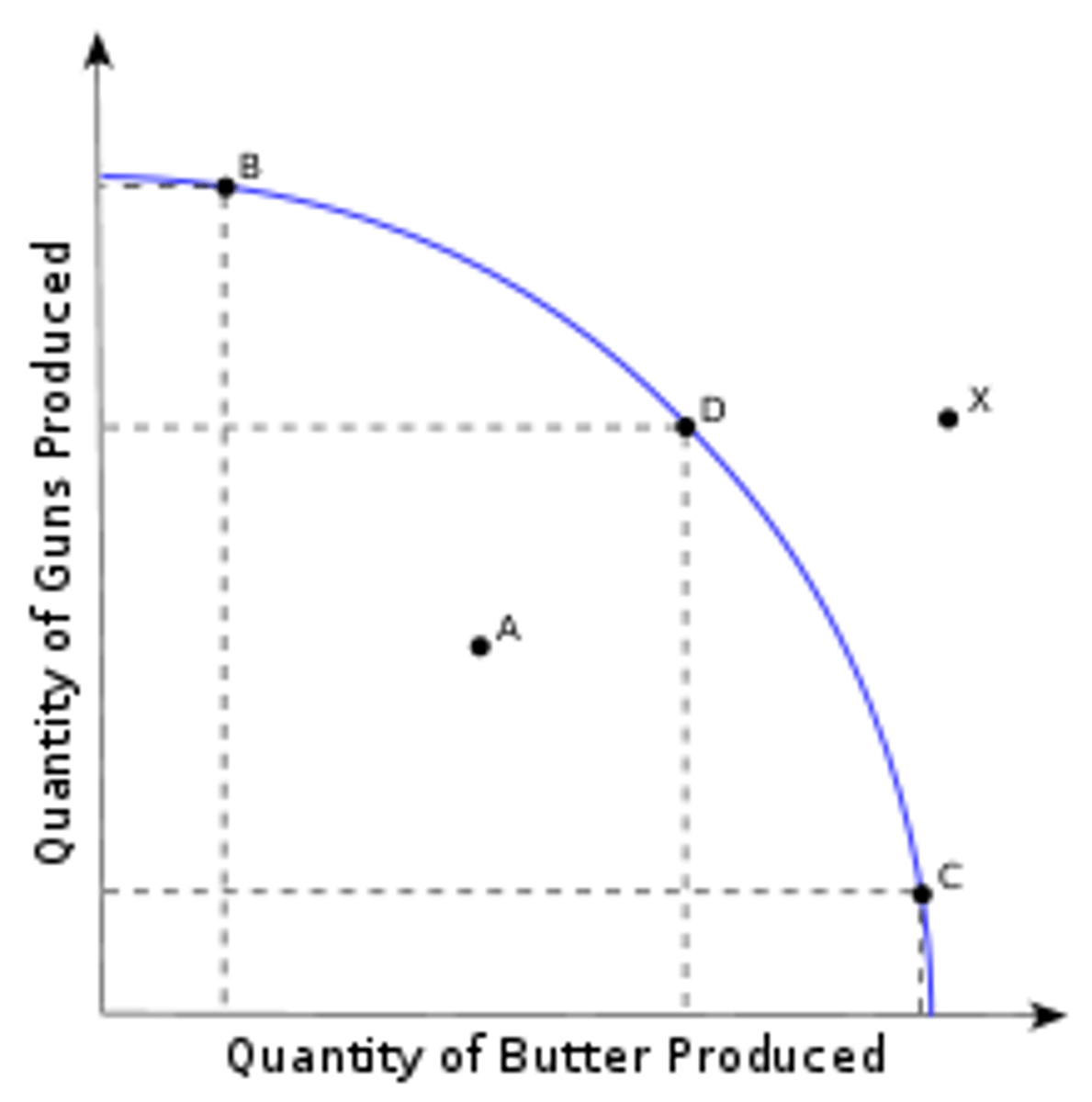
Assumptions of the PPF (Production Possibilities Frontier)
(1) a fixed amount of productive resources
(2) a given amount of technical knowledge, and
(3) full and efficient use of those resources. The slope of the curve indicates the amount of one product that must be given up to produce the other.
What is an efficient point on the PPF?
All points directly on the curve
What is an inefficient point on the PPF?
Points inside the curve
What is an unattainable point on the PPF?
Points outside the curve
Which way does the PPF shift to show expansion?
It shifts outward
How many factors can shift the PPF? What are they?
- There are 4 factors
- 1. an increase in the economy's resource base
-More land, labor, regulation
-changes in unemployment do not effect the PPC
- 2. Advancements in technology
- 3. Improvements in institutions
-ex: strengthen or weakenin property rights
- 4. Increases in effort
-education, training, skills
-Taxation: Tax rates hike dramatically, work goes down and vice versa
Trade
the voluntary exchange of goods and services between two or more parties
How does trade increase output?
1. Specialization and the division of labor
2. Comparative Advantage: the total output of a group of individuals, an entire economy, or a group of nations will be greatest when the output of each good is produced by the person, firm, or nation with the lowest opportunity cost for that good.
3. Gains from mass production methods
4. Gains from innovation
What are the three questions every economist must answer?
1. What good and services should be produced?
2. How should these goods and services be produced?
3. Who consumes these goods and services?
*Memory Cue* WHW
Market Economy
an economy in which the decisions of households and firms interacting in markets allocate economic resources
Centerally planned economy
an economy in which the government decides how economic resources will be allocated
Change in Demand vs. Change in Quantity Demanded
A change in demand is when the WHOLE curve shifts ENTIRELY and a change in quantity demanded is MOVEMENT ALONG the SAME demand curve due to a change in price. Price Doesn't shift the curve.
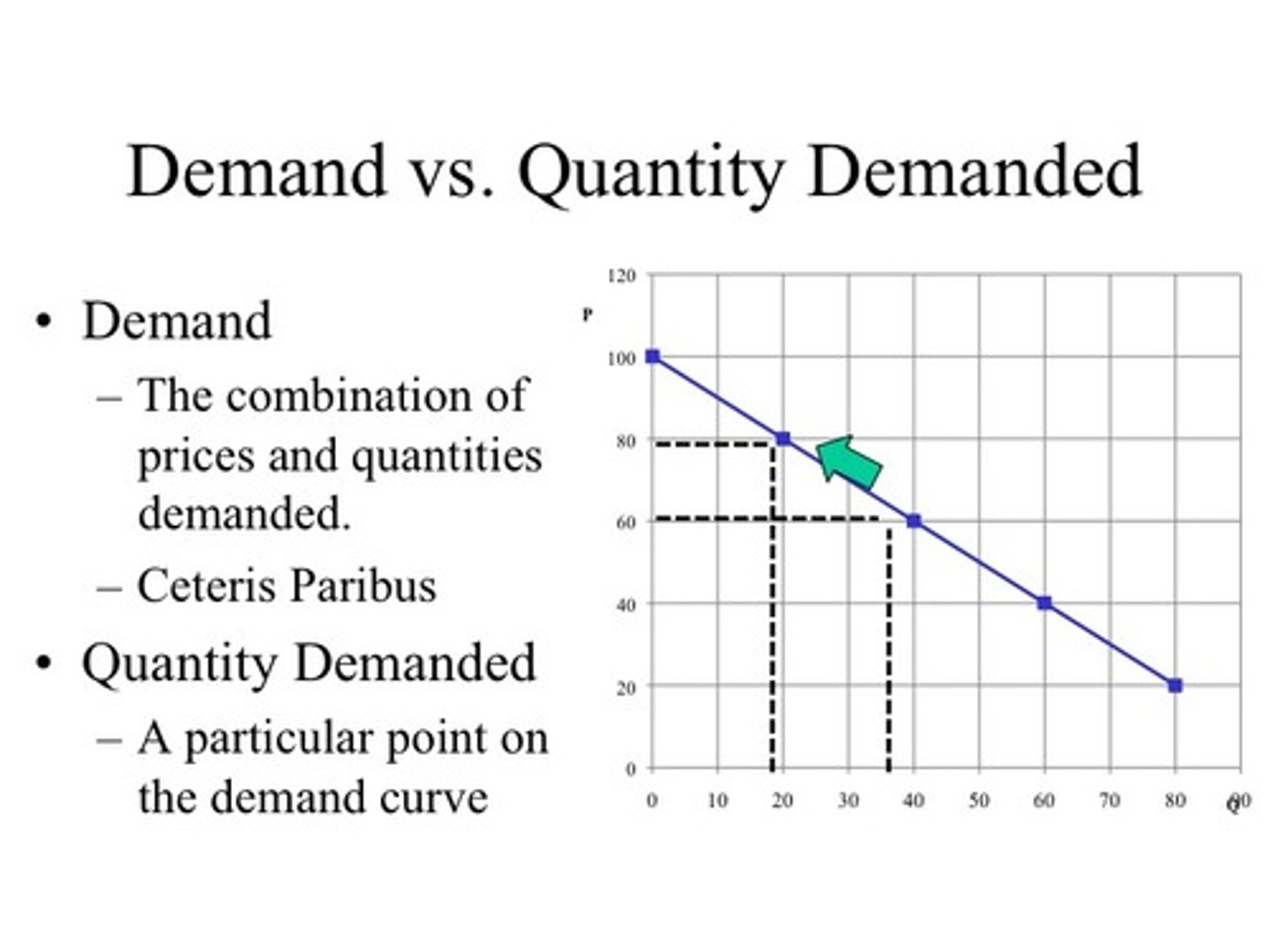
Law of Demand
Ceterus Paribus (all else equal), when the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded will increase; when the price of a product rises, the quantity demanded will decrease
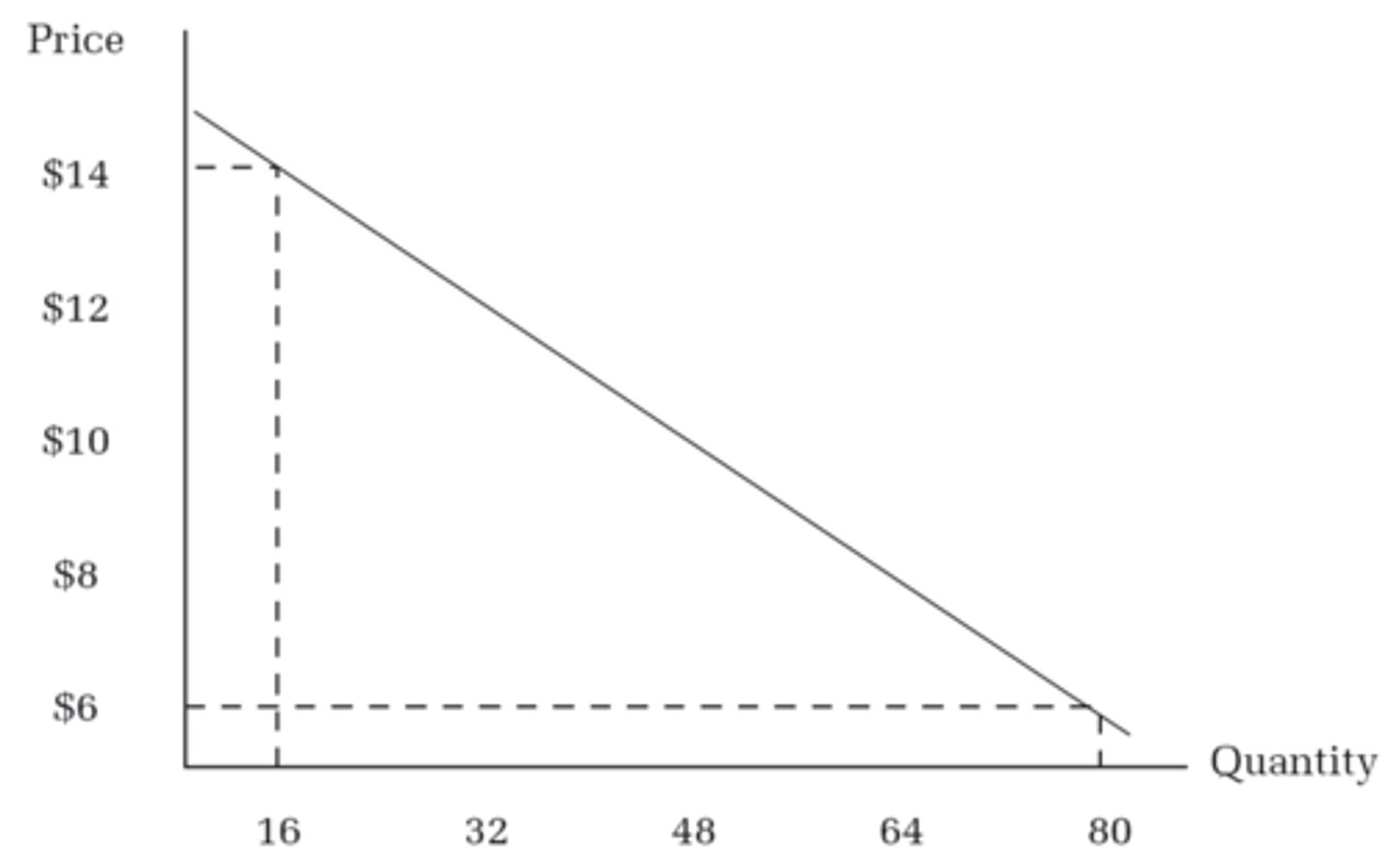
Marginal Benefit
The additional benefit an individual receives from consuming one more unit of a good or service
Demand
Consumer willingness and ability to buy products
Quantity Demanded
the amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase at a given price
Factors Shifting Market Demand
1. Changes in consumer income
2. Changes in the number of consumers in the market
3. Changes in the prices of related goods.
-Either substitute or complement
Substitute Good
Products or services that can be used in place of each other. When the price of one falls, the demand for the other product falls; conversely, when the price of one product rises, the demand for the other product rises.
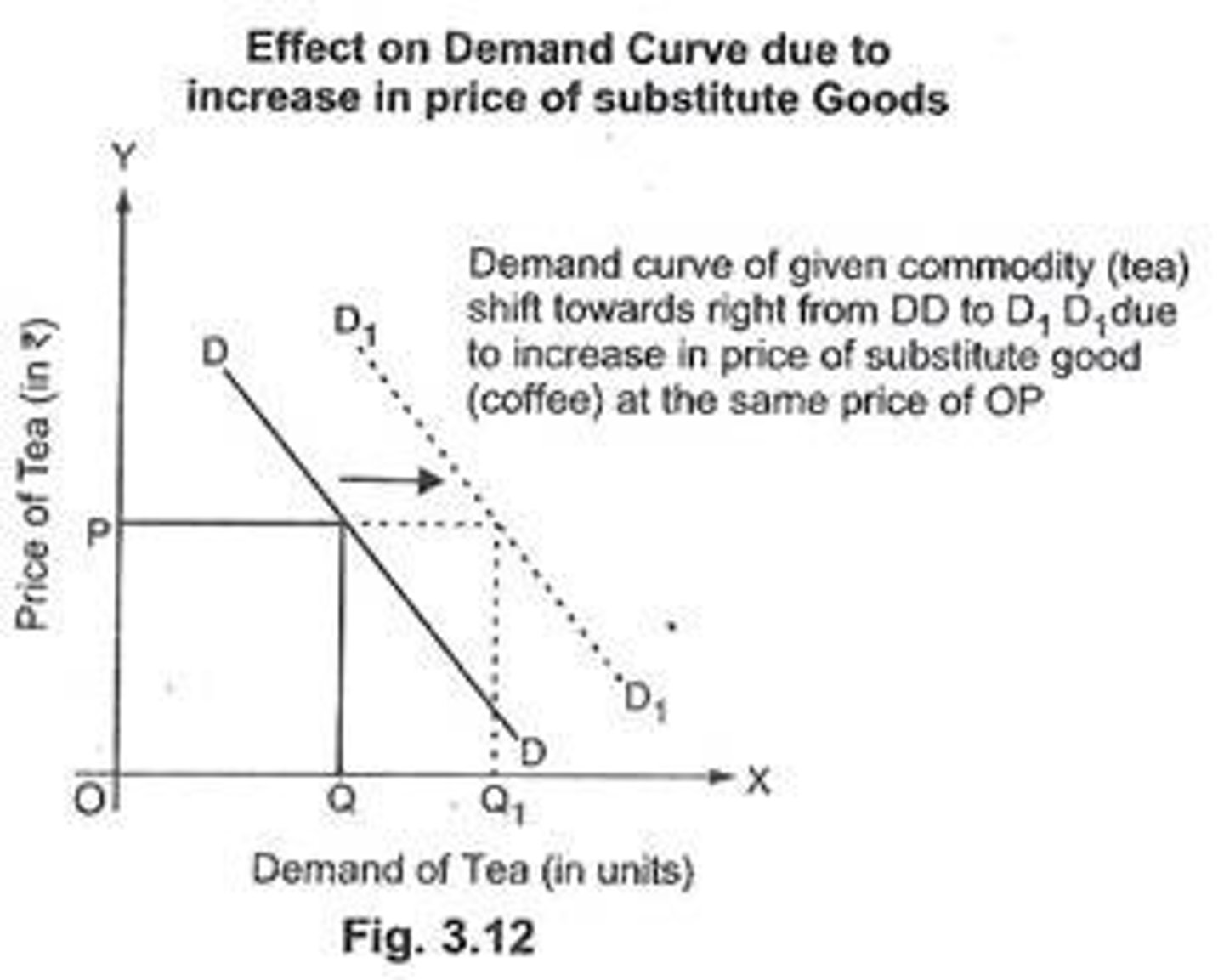
Complement Goods
Products that are usually consumed together (ex: bread and butter, hotdogs and hotdog buns).
A decrease in the price of one will cause in increase in demand for the other

What is the purpose of the Demand Curve?
To show what effect a price change will have on the quantity demanded of a good.
Supply
The amount of goods or services available
Quantity Supplied
the amount of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell
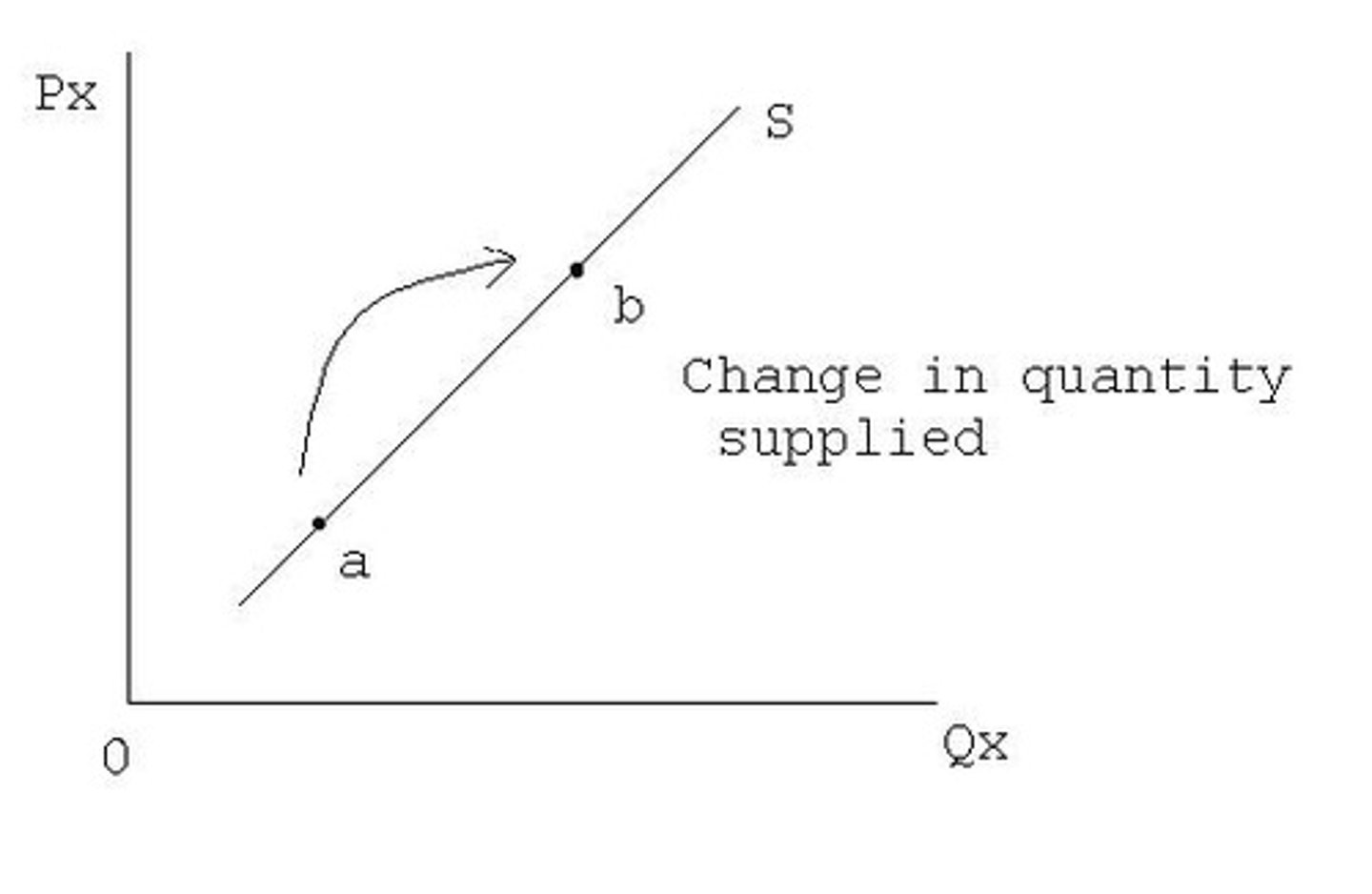
Supply vs. Quantity Supplied
Supply is the curve, but quantity supplied is a point on the curve.
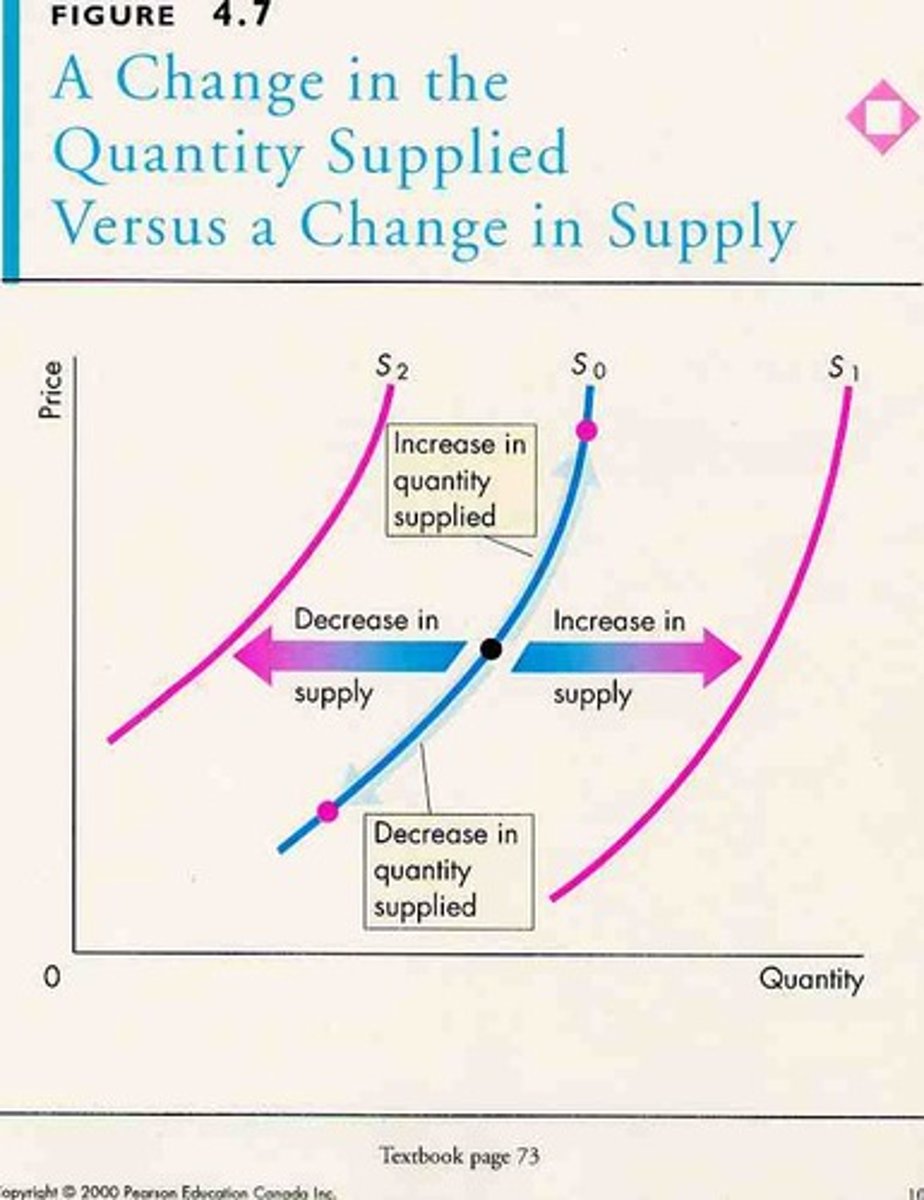
Law of Supply
Ceterus Paribus, when the price of a product falls, the quantity supplied will increase
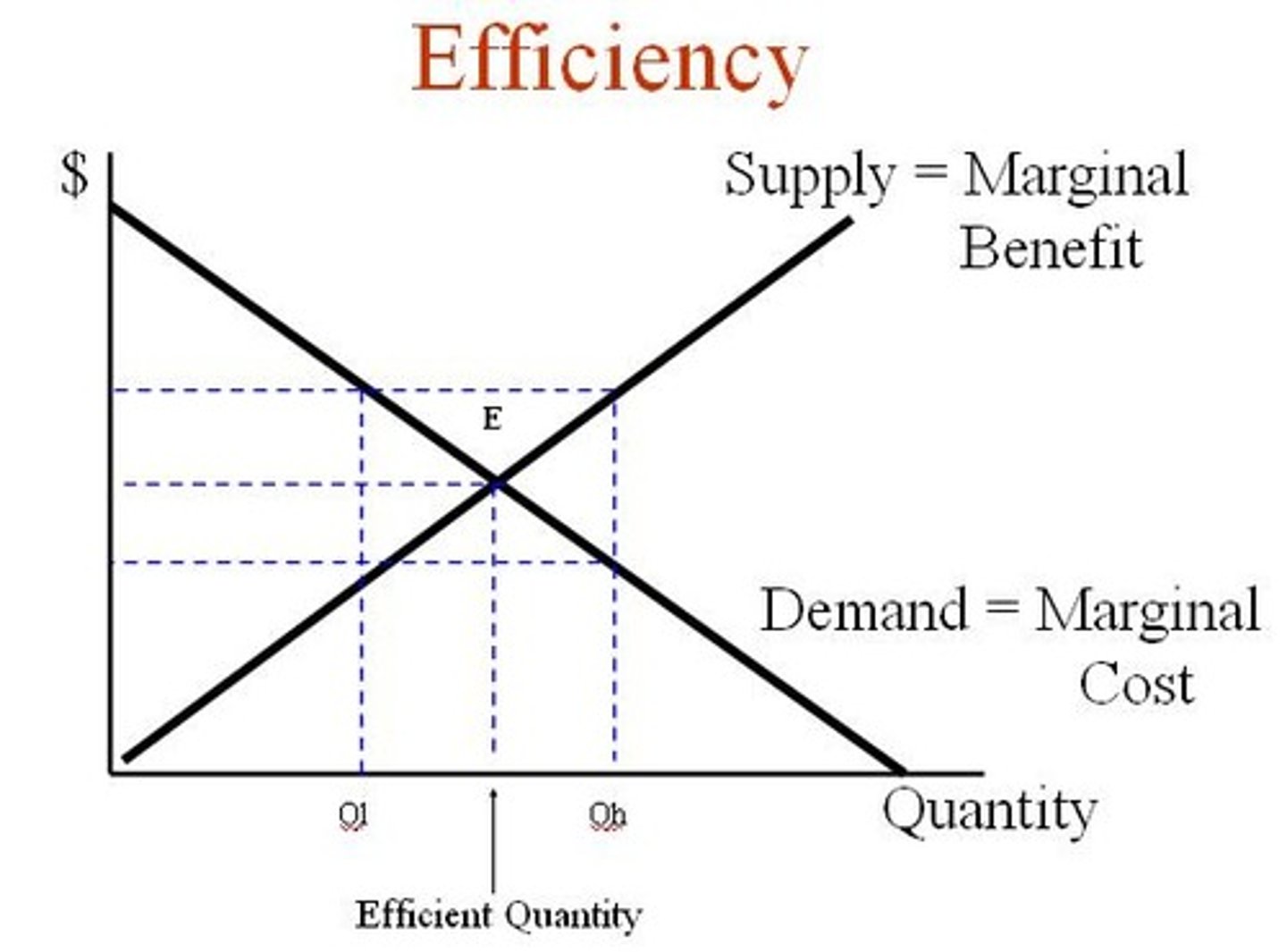
Marginal Cost
The change in total cost required to produce an additional unit of output. (The supply curve)
Factors Shifting Market Supply
1. Changes in the price of inputs (resource prices)
2. Changes in technology
3. Elements of Nature and Political disruptions
4. Changes in taxes or subsidies
5. Changes in the prices of substitutes in production
6. Changes in the number of firms in the market
7. Changes in expectations
Economic Efficiency
A market outcome in which MB=MC (marginal benefit = marginal cost)
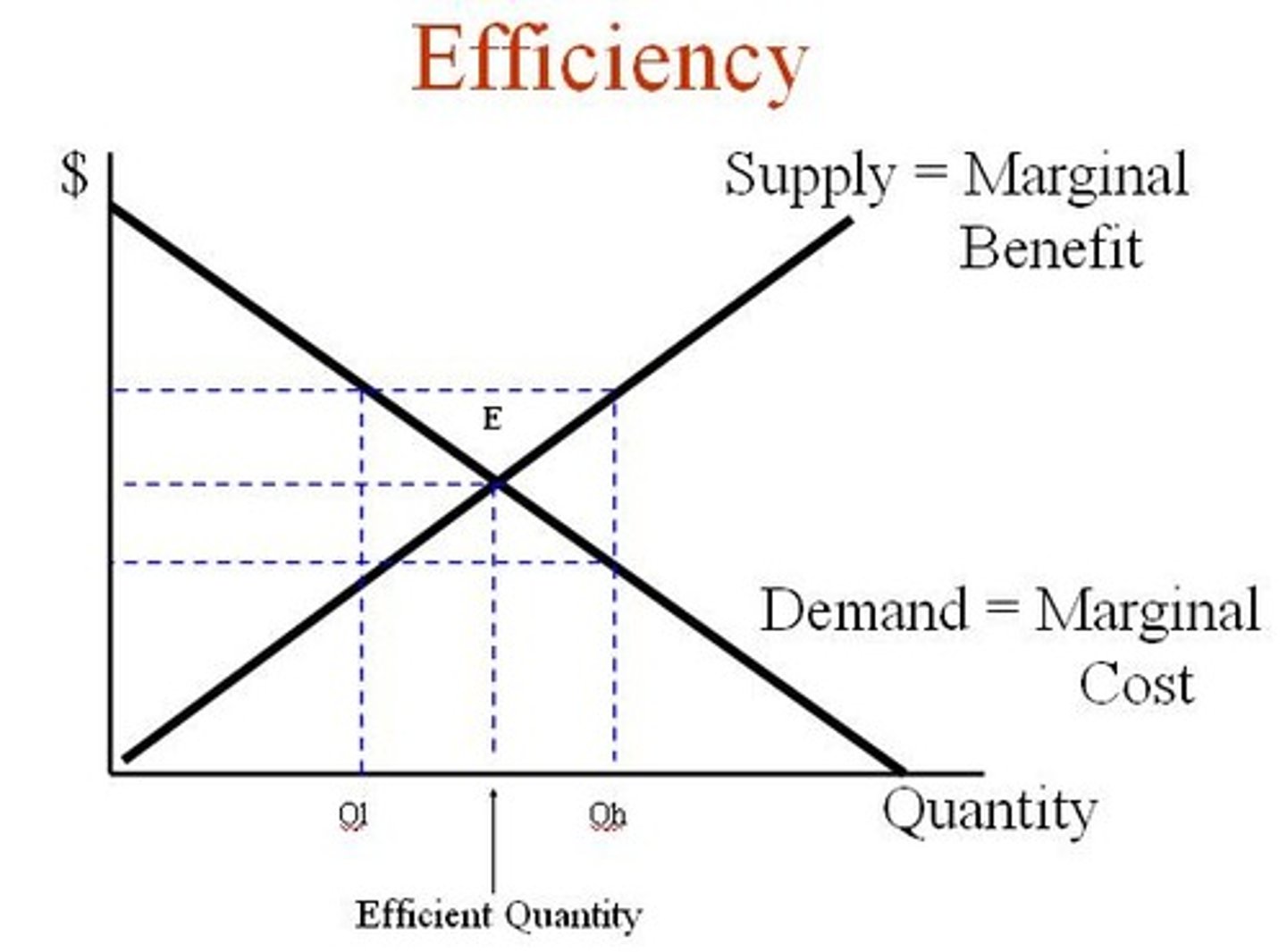
Invisible Hand Principle
For a market to work, individuals must be free to pursue their own self interest
Importance of Entrepreneurs
- job creation
- innovation driver
- opportunities for women/minorities
- helps big business
- significant contributor to GDP
Three Key Economic Ideas
1. People are rational
2. People respond to economic incentives
3. Optimal decisions are made at the margin
Mixed Economy
An economy in which most decisions are made by buyers and sellers in markets, but the government plays a significant role in the allocation of resources
Absolute Advantage
The ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors when using the same amount of resources
Comparative Advantage
The ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than competitors
Product Market
A market for goods
Factor market
A market for factors of production (labor, capital, natural resources, etc.)
Free market
A market with few government restrictions on how a good or service can be produced or sold or on how a factor of production can be employed
What is the invisible hand driven by?
Price